Show filters
Engineering skill and perseverance
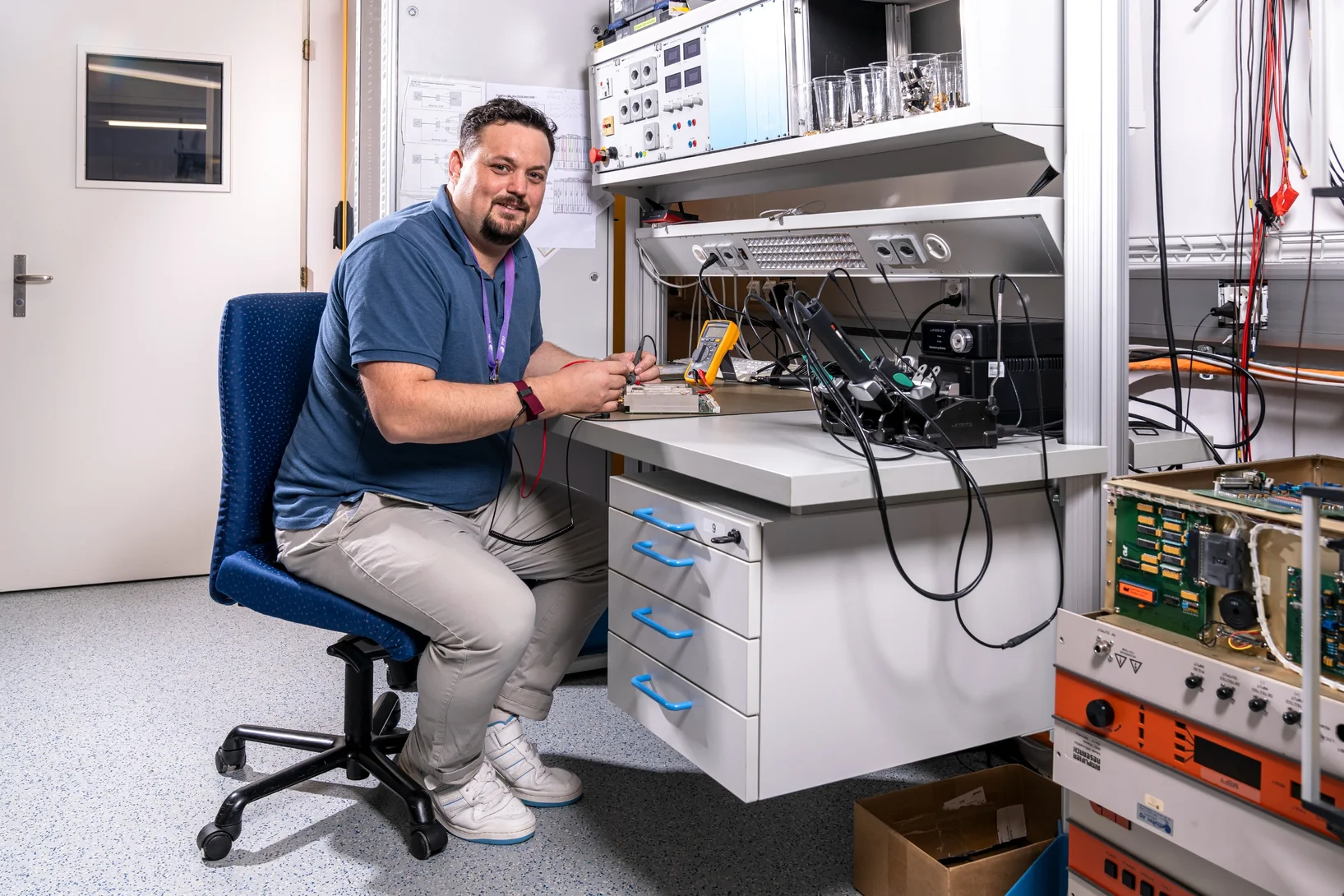
Credit for the on-time completion of the major SLS 2.0 upgrade project is due in part to a team of dedicated electrical engineers.
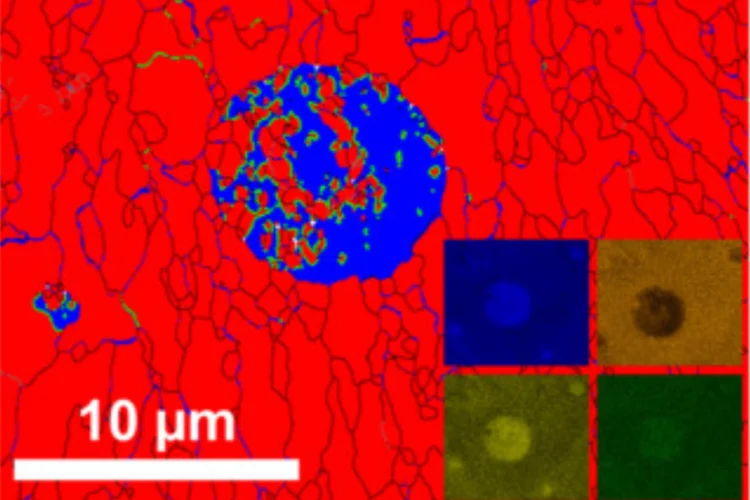
Uncovering Hidden Phases in 3D-Printed Fusion Steels
3D synchrotron X-ray mapping uncovered unexpected internal phase structures in laser-printed steels, showing how processing controls what we cannot see.
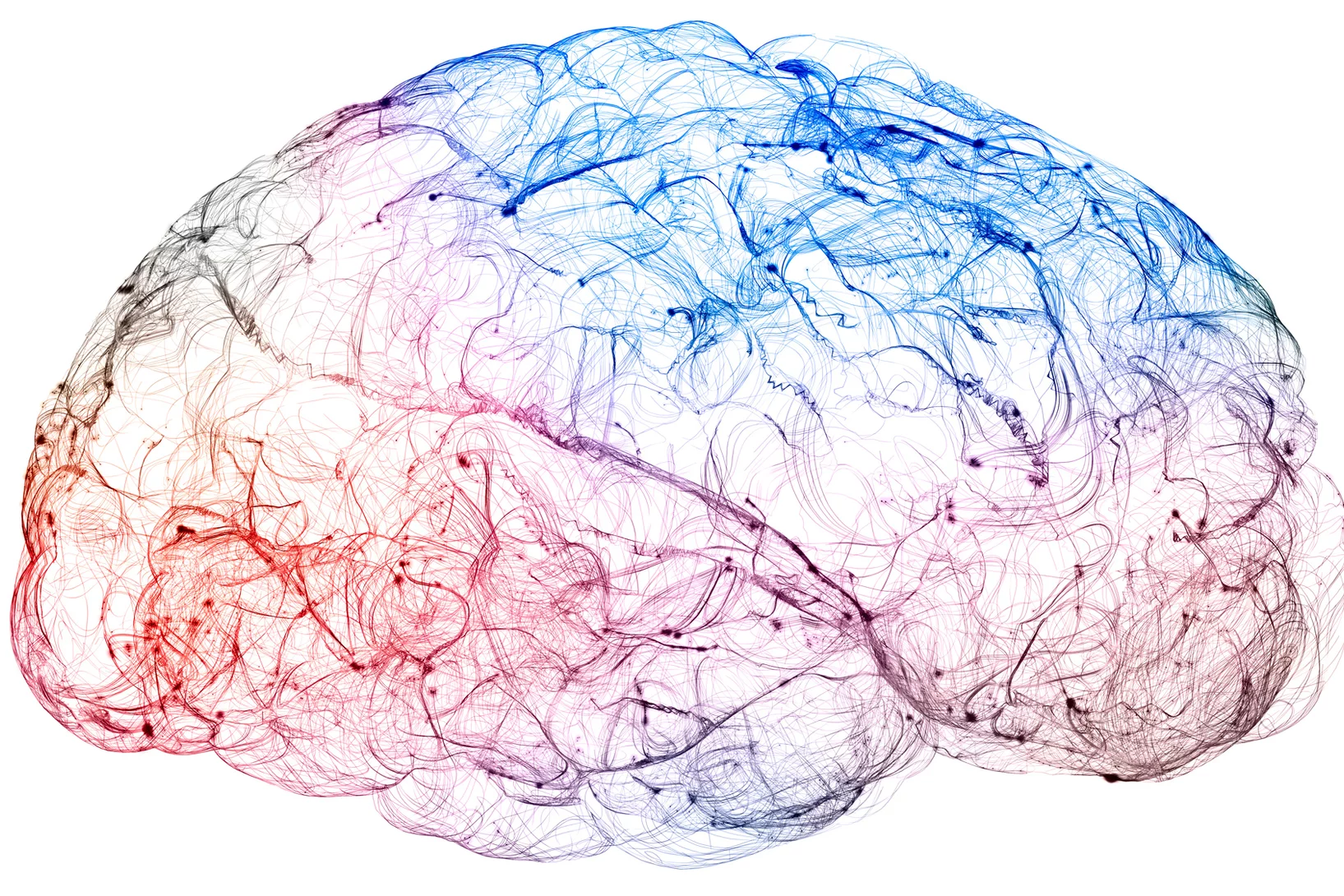
X-rays bring high-resolution brain mapping within reach
A new imaging breakthrough could reveal brain connectivity in 3D detail never before accessible.
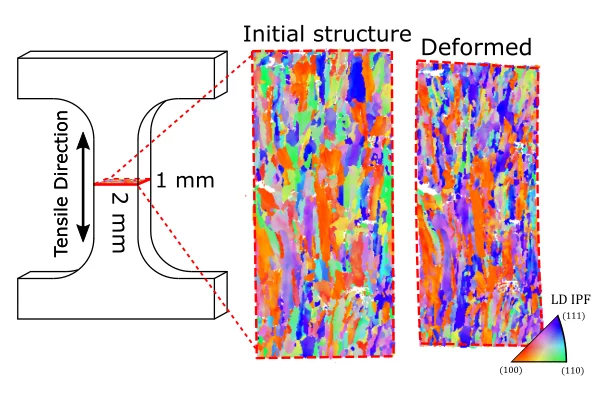
Following Twin-Formation in 3D Printed Steel
Using hard-xray microscopy to study the deformation of 3D printed steel.
How the cheese-pasta principle could help counter Alzheimer's
PSI researchers have discovered cellular mechanisms that could help to mitigate diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
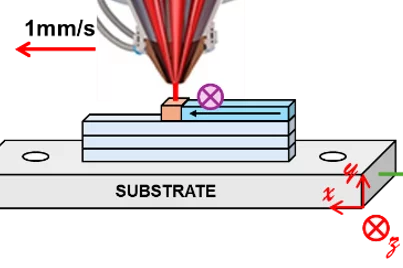
From Melt to Martensite
Real-time synchrotron X-ray diffraction reveals how different phases of steel emerge and evolve under the intense heat of laser powder bed fusion.
Coexistence of Insulatorlike Paramagnon and Metallic Spin-Orbit Exciton Modes in SrIrO3
We probe the spectrum of elementary excitations in SrIrO3 by using heterostructured [(SrIrO3)m / (SrTiO3)l] samples to approach the bulk limit. Our resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) measurements at the Ir L3 edge reveal ...
Big heart, acute senses key to explosive radiation of early fishes
X-rays of a 400-million-year-old fossil illuminate a key moment in our deep evolutionary past.
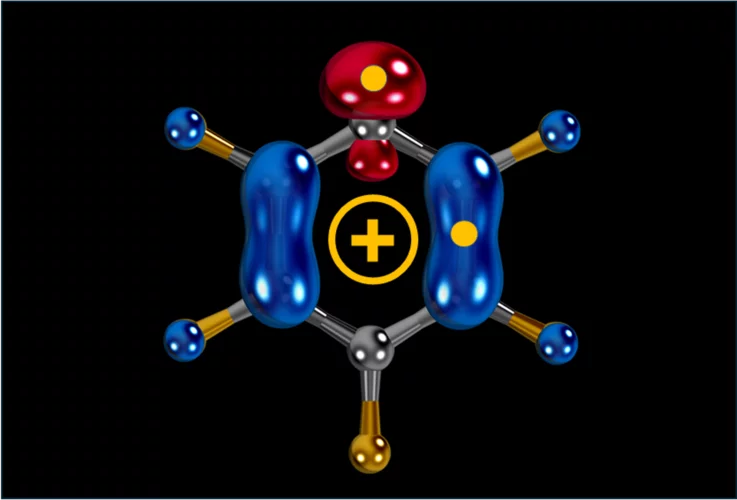
Carbocation, diradical, and superelectrophile in one molecule?
The pentafluorophenyl cation (C₆F₅⁺) breaks these rules with a borderline “crazy” reactivity.
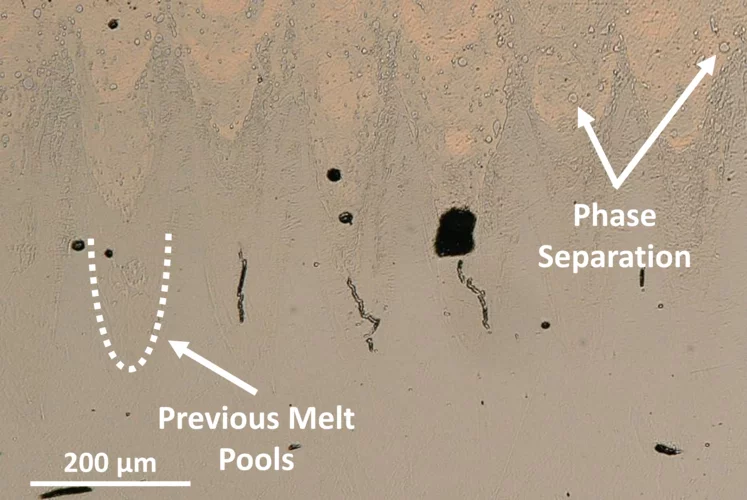
Why Ni-Cu Alloys Fail in 3D Printing
3D printing with nickel–copper alloys holds great promise — but hidden mechanisms can cause them to crack. Our latest study reveals why.
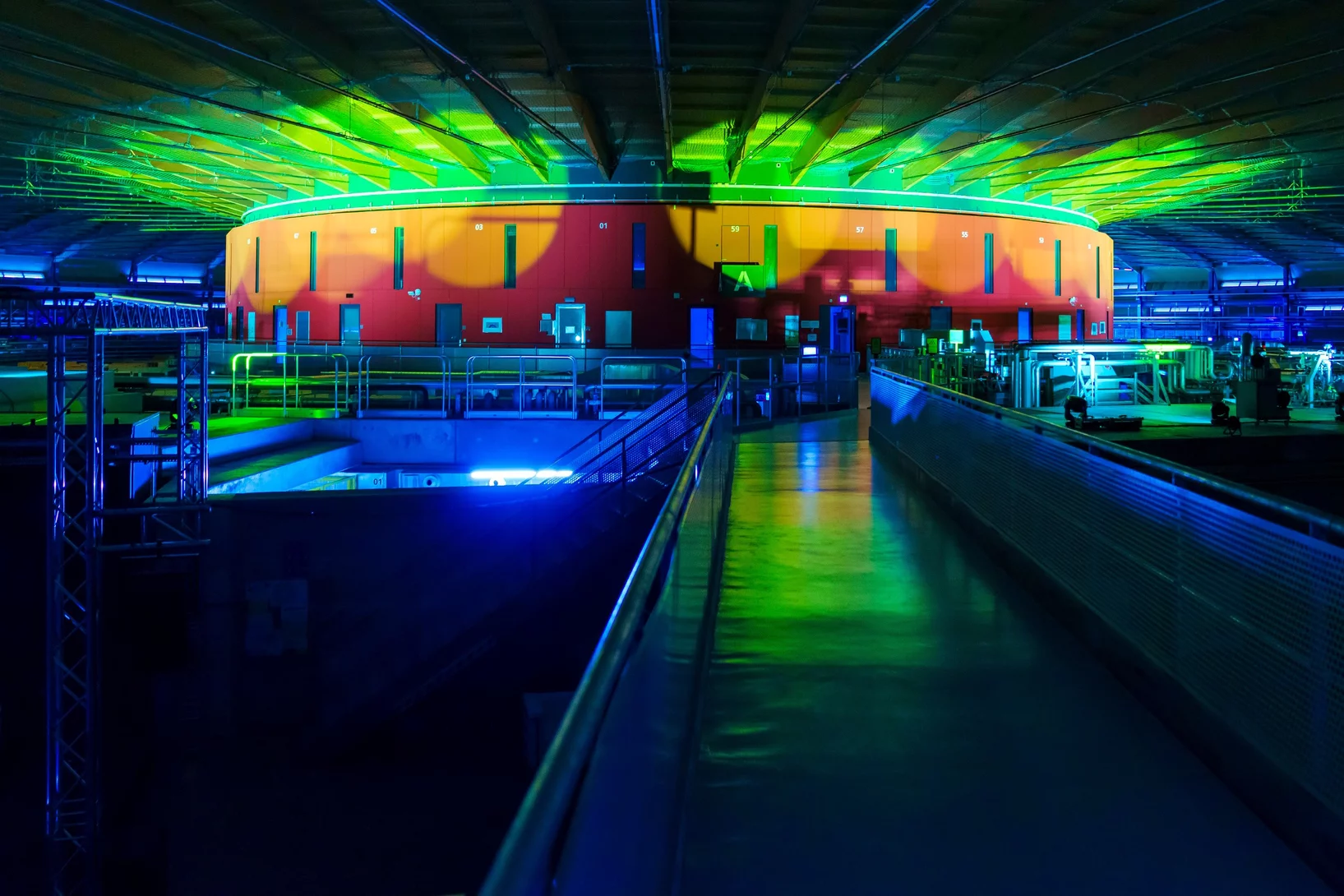
A bright light for Switzerland
The new Swiss Light Source is inaugurated
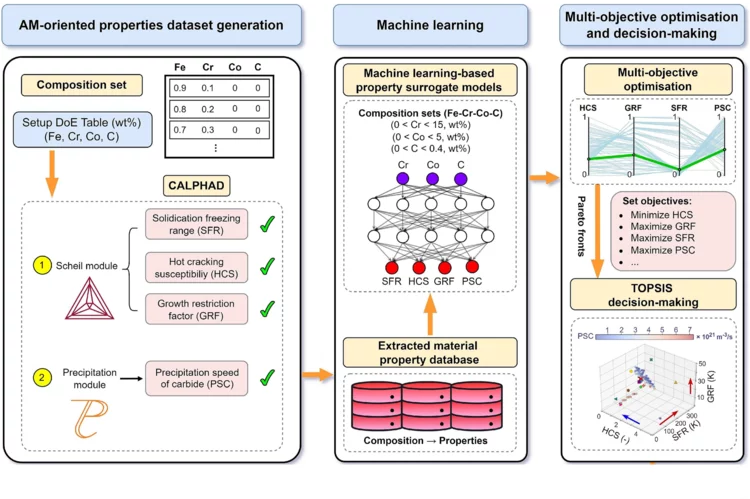
Machine Learning Accelerates Alloy Design for Additive Manufacturing
A new machine learning–designed alloy demonstrates how materials can be tailored for specific performance properties required in additive manufacturing.
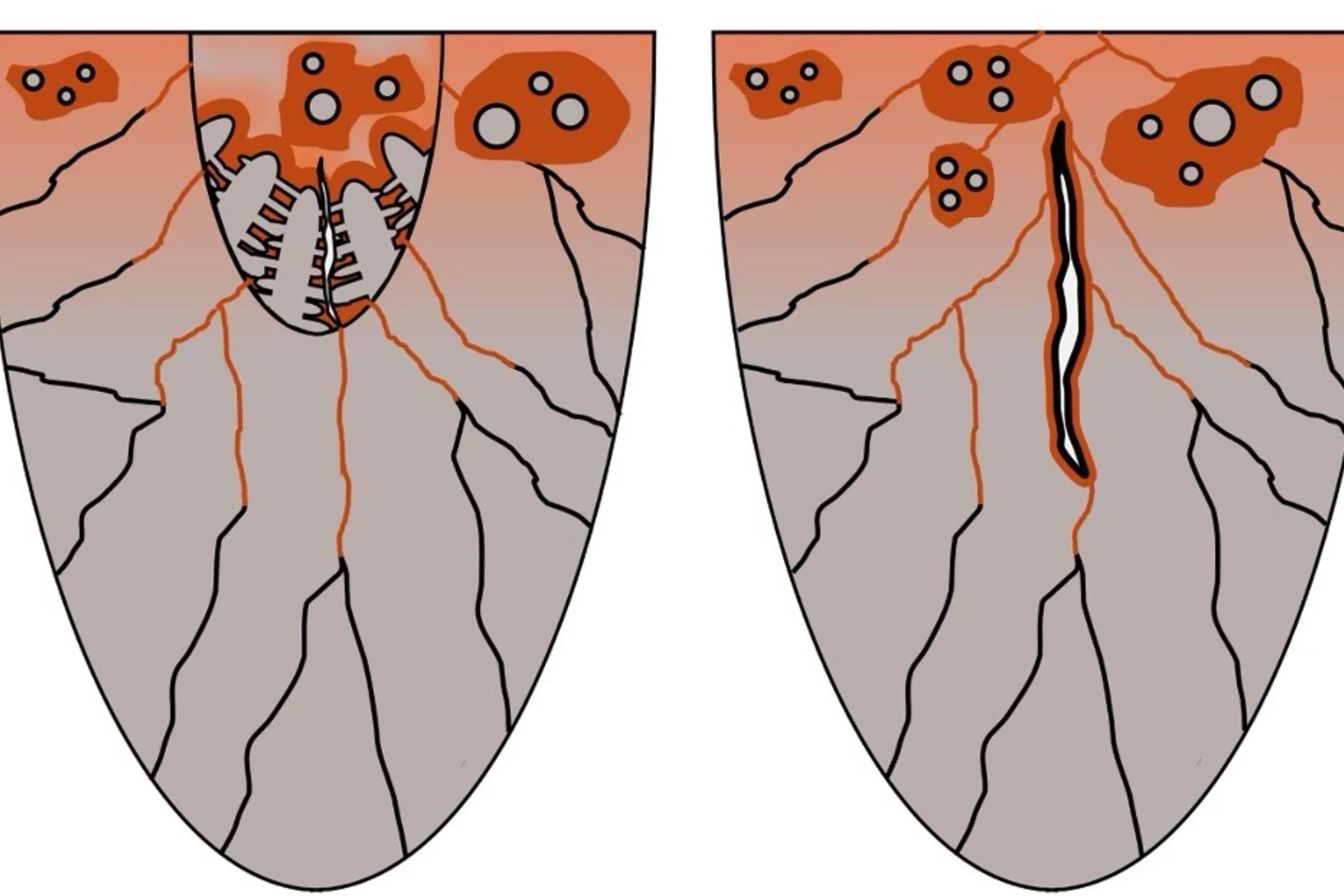
X-rays reveal fossil stealth technology
PSI imaging helps to uncover the hunting strategy of a prehistoric predator.
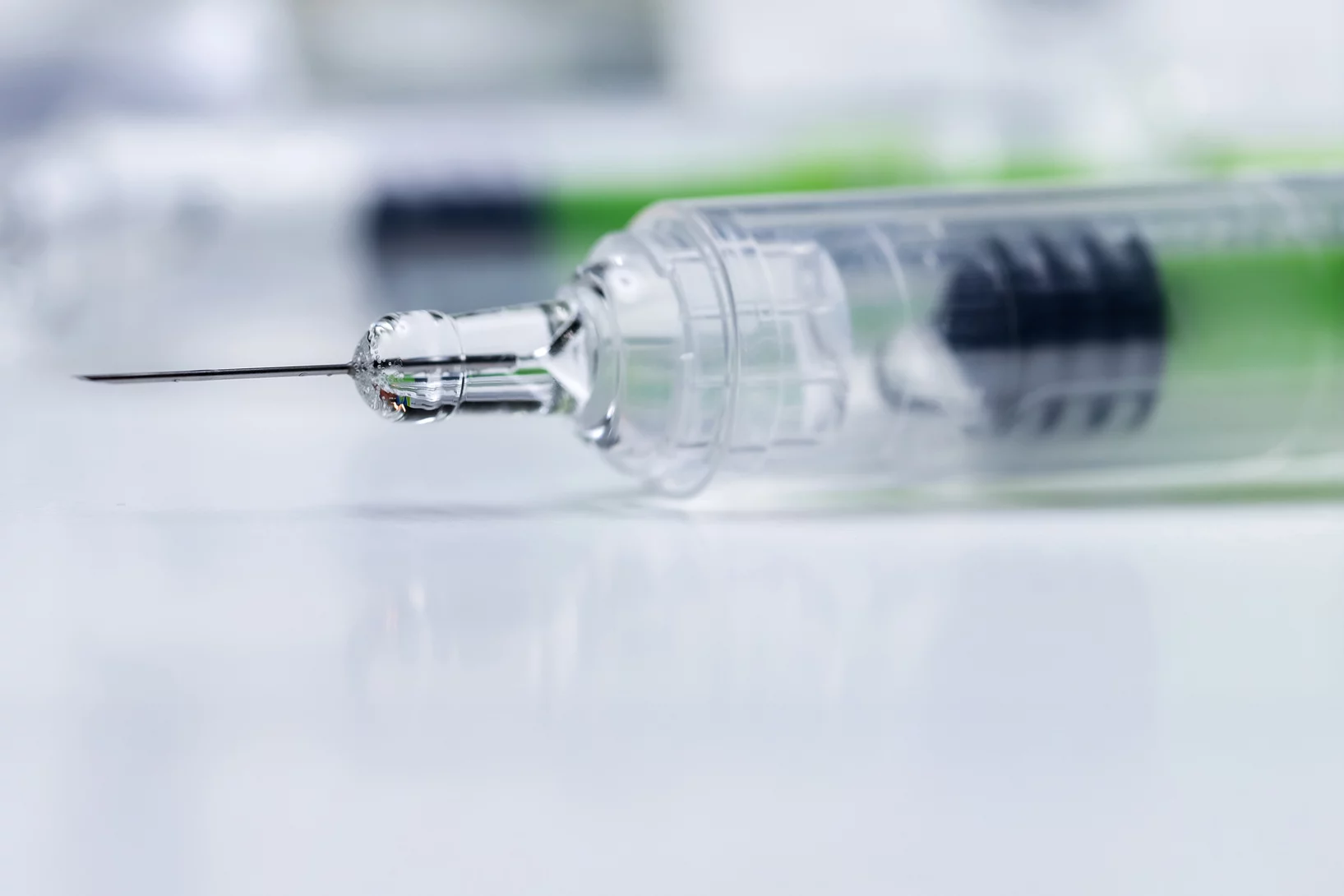
Zinc detected in clogged syringes
With the help of researchers at PSI, ANAXAM has been investigating, on behalf of the pharmaceutical company MSD, whether zinc may contribute to clogging of pre-filled syringes.
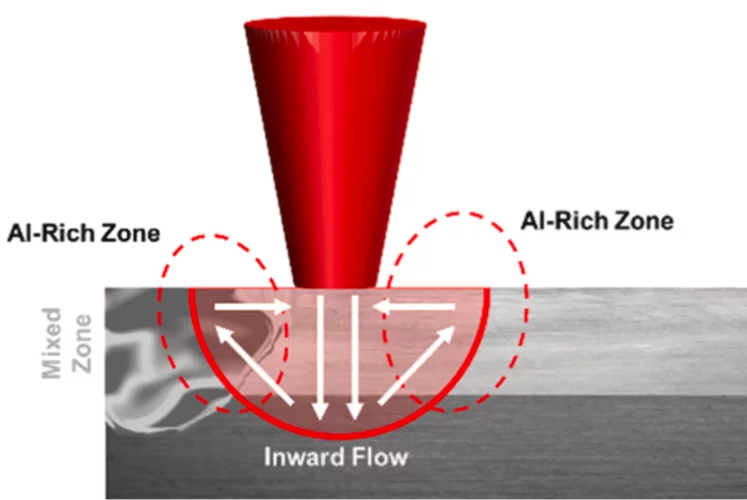
Cracking the Challenge of Steel–Copper Fusion
Why do cracks appear when joining steel and copper? We track the mechanisms in real time to find out.
Attorney for cutting-edge technology
Former PSI doctoral candidate Stephanie Smit now works as a patent attorney for a company that is among the most important in the world. That’s because this company builds machines that are worth a fortune and are highly sought after.
Interfacial Phase Formation in 316L–CuCrZr Hybrids
In-situ X-ray diffraction reveals how phase separation and fluid flow shape microstructure in laser-welded multi-material metal builds.
Phase by Phase: How Stainless Steel and IN625 Solidify Together
Where steel meets superalloy: real-time X-ray snapshots reveal how composition and cooling shape metal during 3D printing
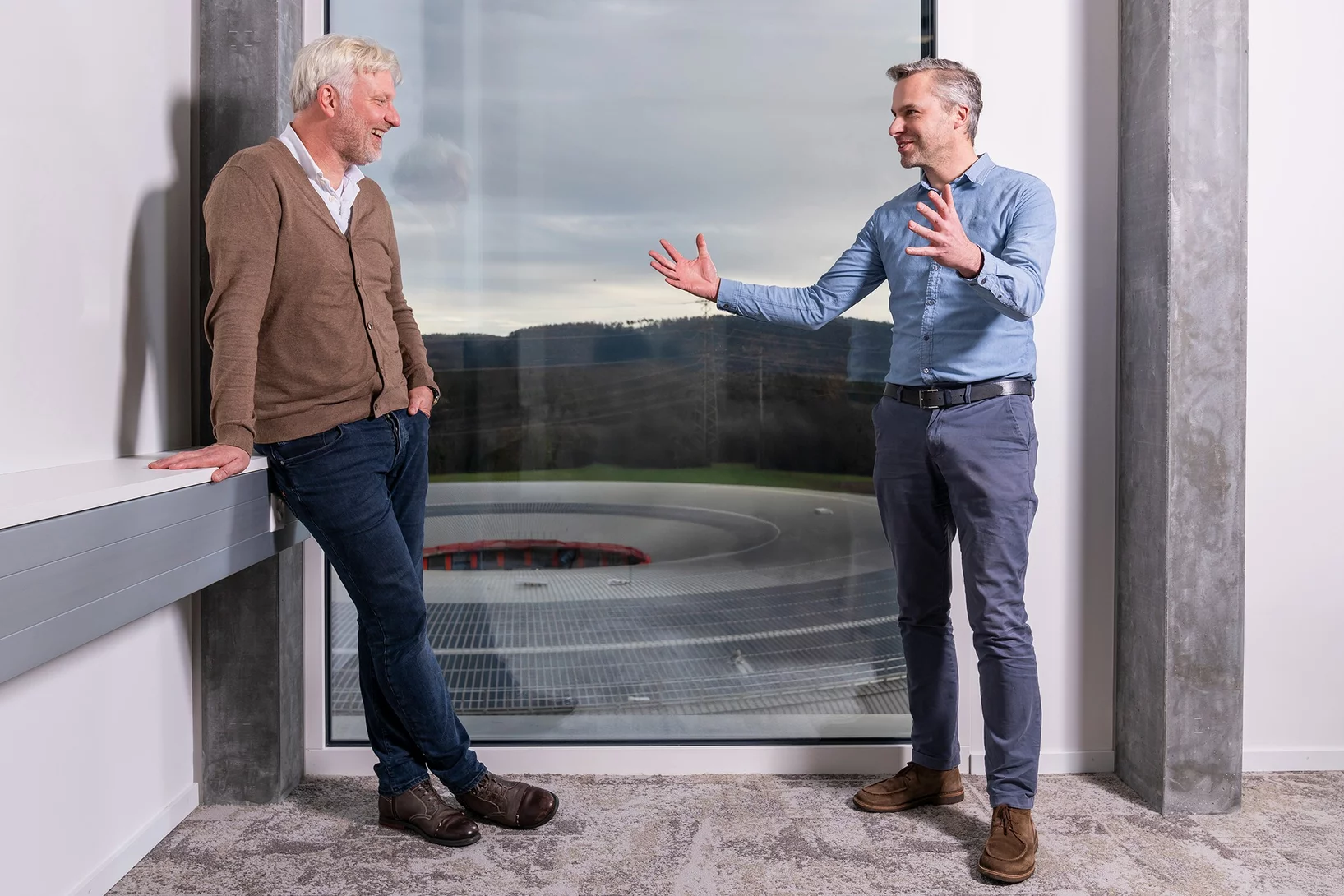
Science meets industry – innovation with an impact
Hans Priem and Cees Maris of VDL ETG explain what advanced manufacturing means in industry and talk about their collaboration with PSI.
Faster, more precise, more reliable – the future of manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing means using state-of-the-art production methods. Researchers at PSI are helping to make techniques such as 3D printing more reliable and to advance the miniaturisation of high-performance chips.
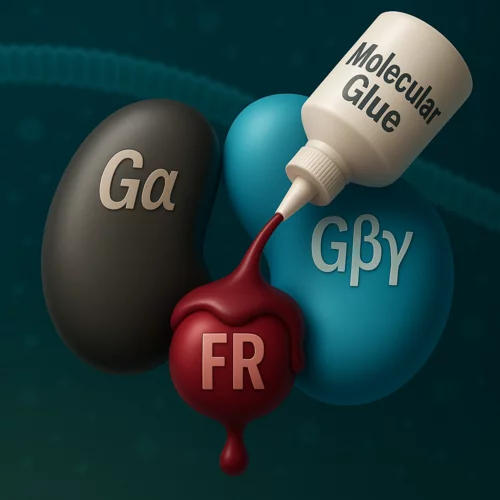
From coral berries to new therapies: uncovering the molecular glue mechanism of natural compounds
Researchers at the Center for Life Sciences and the Center for Scientific Computing, Theory, and Data at the Paul Scherrer Institute have identified the mechanism by which certain natural compounds interfere with cellular signaling. These ‘molecular glues’ have a therapeutic potential for the treatment of specific cancer types. Their latest study on this topic has been published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
Aluminium made visible
PSI researchers have for the first time determined the exact position of the aluminium atoms in zeolites, which make these materials such good catalysts.
Antiferrodistortive and ferroeletric phase transitions in freestanding films of SrTiO3
Epitaxially grown thin films are commonly used to strain engineer electronic properties by the choice of a substrate, and therefore do not match bulk properties (leading to properties that deviate from the bulk material). Free standing ultrathin oxide films are expected to preserve the bulk-like properties due to the absence of substrate influence. However, we show that this expectation is not fulfilled with ultrathin free standing SrTiO3, as they get ferroelectric at 80K.
Water gets in shape for VUV absorption
Nanometre‑thin, free‑flowing liquid sheets now let Swiss Light Source users record pristine VUV absorption spectra of water, and soon any solvent.
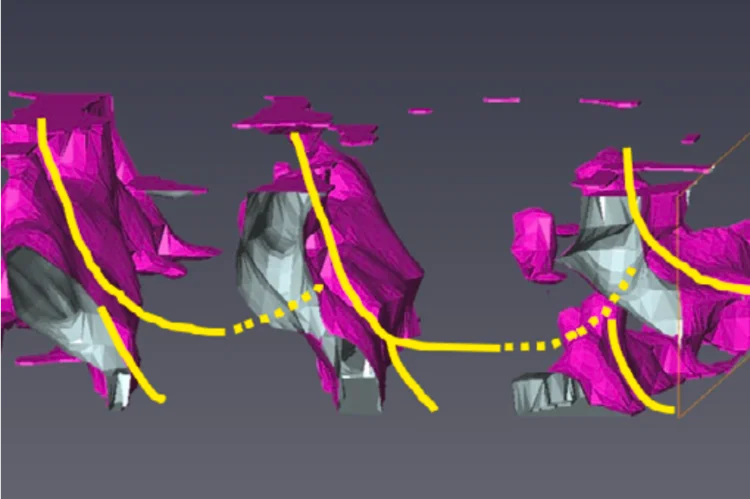
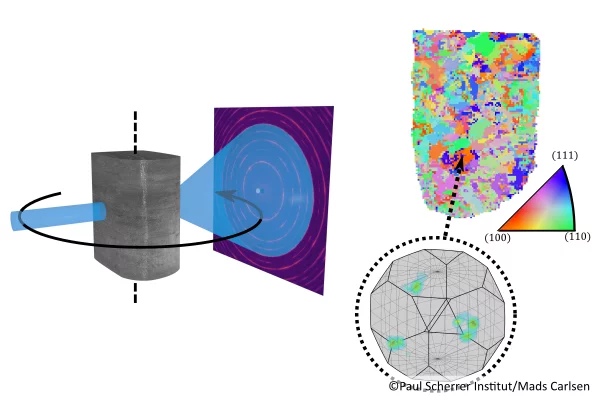
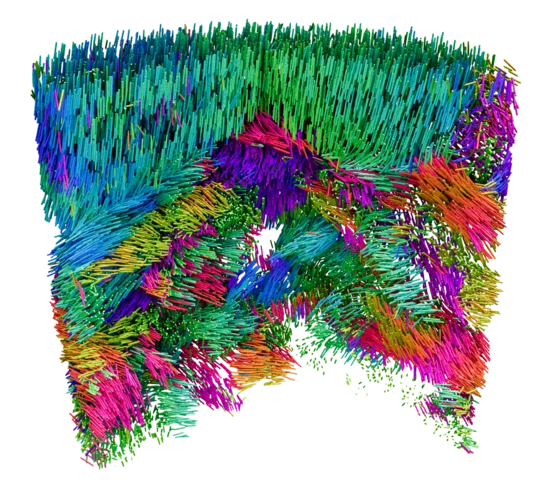
Mapping crystallite orientation in bulk polycrystals
A new experimental technique allows the orientation distribution of small-grained polycrystal materials to me mapped in 3D.
A faster route to green hydrogen
The pH value determines how easily hydrogen can be produced from water when cobalt is used as a catalyst. PSI researchers have now found out why.
PILATUS4 detector arrives at PXIII
On April 4, 2025, a Dectris Pilatus4 2M detector was successfully installed at beamline PXIII. In the coming weeks, this new detector will be used to measure the first macromolecular crystallography (MX) experiments using the SLS 2.0 machine.
SLS 2.0: How to start up a particle accelerator
The electrons are back: after its upgrade, the Swiss Light Source SLS is starting up again, step by step.
Prestigious funding for three research projects at PSI
Concrete, chemical catalysis and the search for new physics – three PSI researchers have each received a grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation for these areas of research.
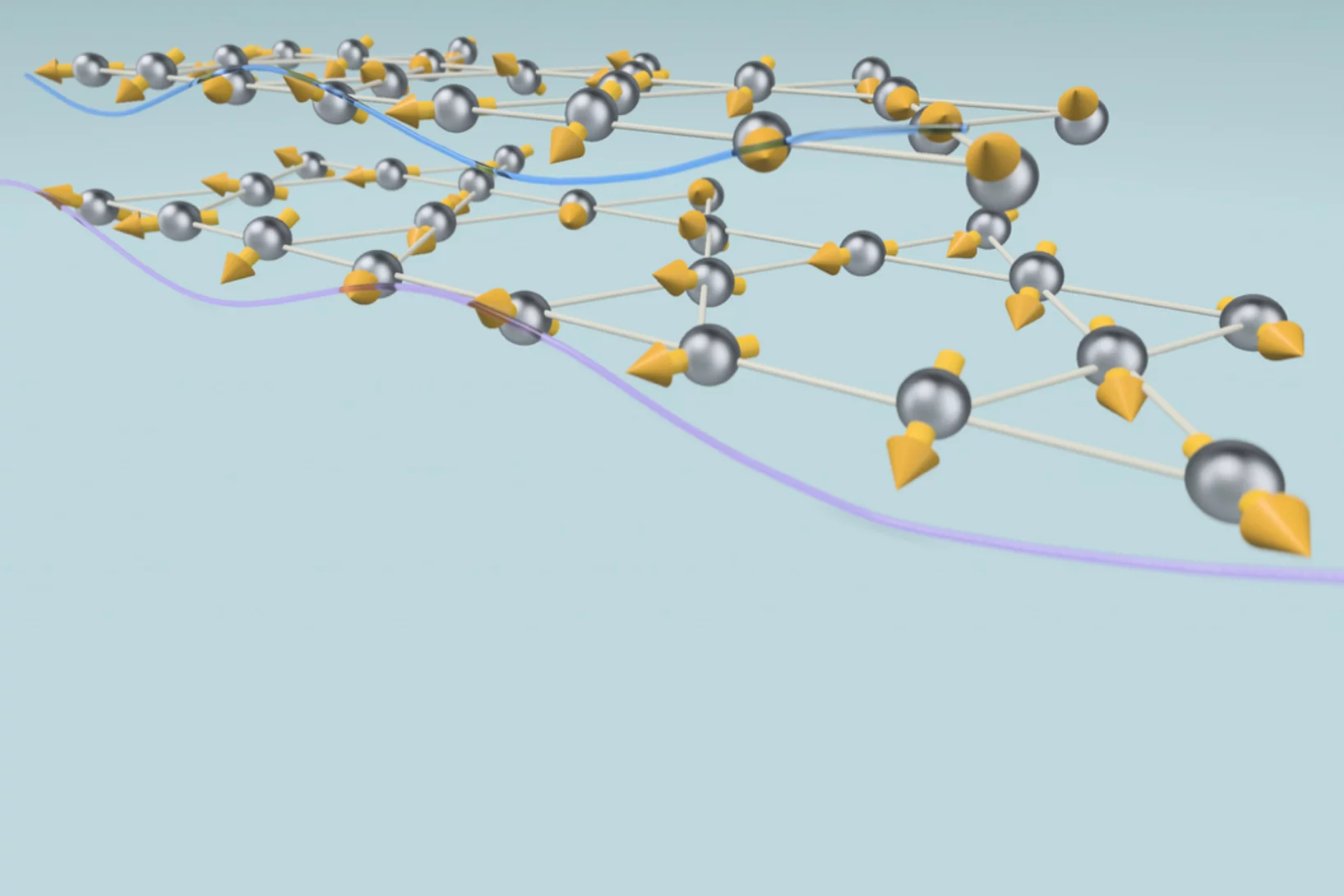
A new dimension of complexity for layered magnetic materials
X-rays reveal magnetic phenomena driven by interactions between the layers of a kagome ferromagnet
Mitigating Cracks in Multi-Material Printing
Integrating metallic powders with thin foils in laser powder bed fusion can reduce interfacial cracks and improve microstructure quality in titanium-aluminum multi-material printing.
The Cables of the SLS
Building services, magnets, IT – many different parties are involved in the SLS upgrade. What connects them all is several hundred kilometres of cables.
Mapping the Nanoscale Architecture of Functional Materials
A new X-ray technique reveals the 3D orientation of ordered material structures at the nanoscale, allowing new insights into material functionality.
Together for Science with Neutrons, Muons and X-rays
Strategic partnership between research facilities in UK and Switzerland will create new capabilities to address global challenges using neutrons, muons and X-rays.
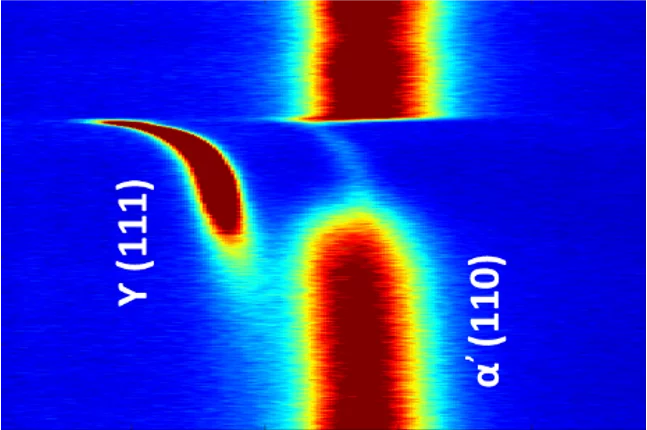
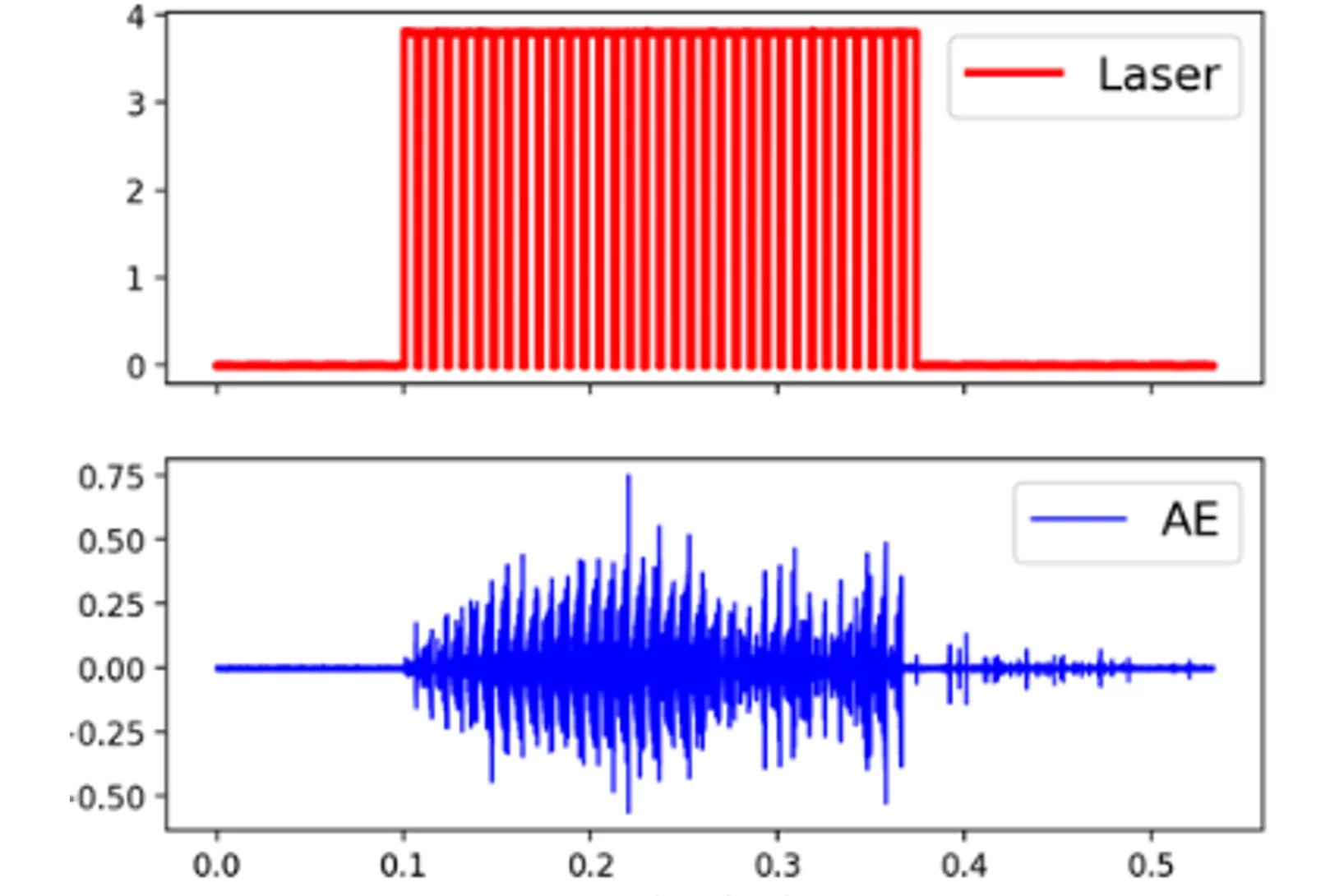
Acoustic emission signature of a martensitic transformation
Acoustic emission monitoring in 3D printing: real-time insights into martensitic phase transformations and crack formation.
Recognition at MNE 2024 Micrograph Contest
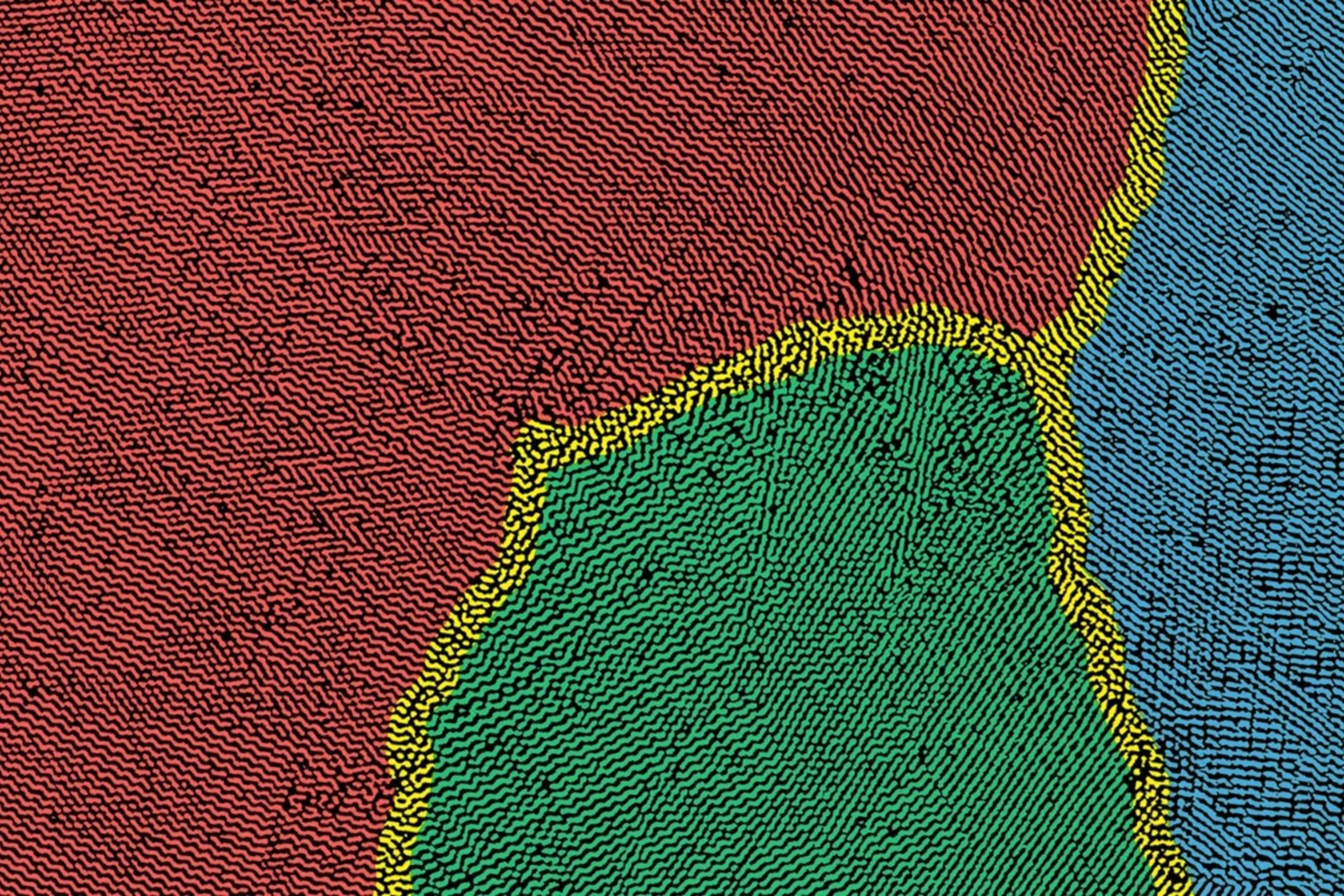
The MNE conference is the flagship event of the International Society for Micro- and Nanotechnology (iMNEs). The research fields covered by the MNE conferences have consistently driven advancements in the development of smaller and smaller structures. To emphasize the significance of micrographs in this field, the conference features a micrograph contest, sponsored and hosted by Zyvex Labs. Entries are judged based on both their technological relevance and artistic merit.
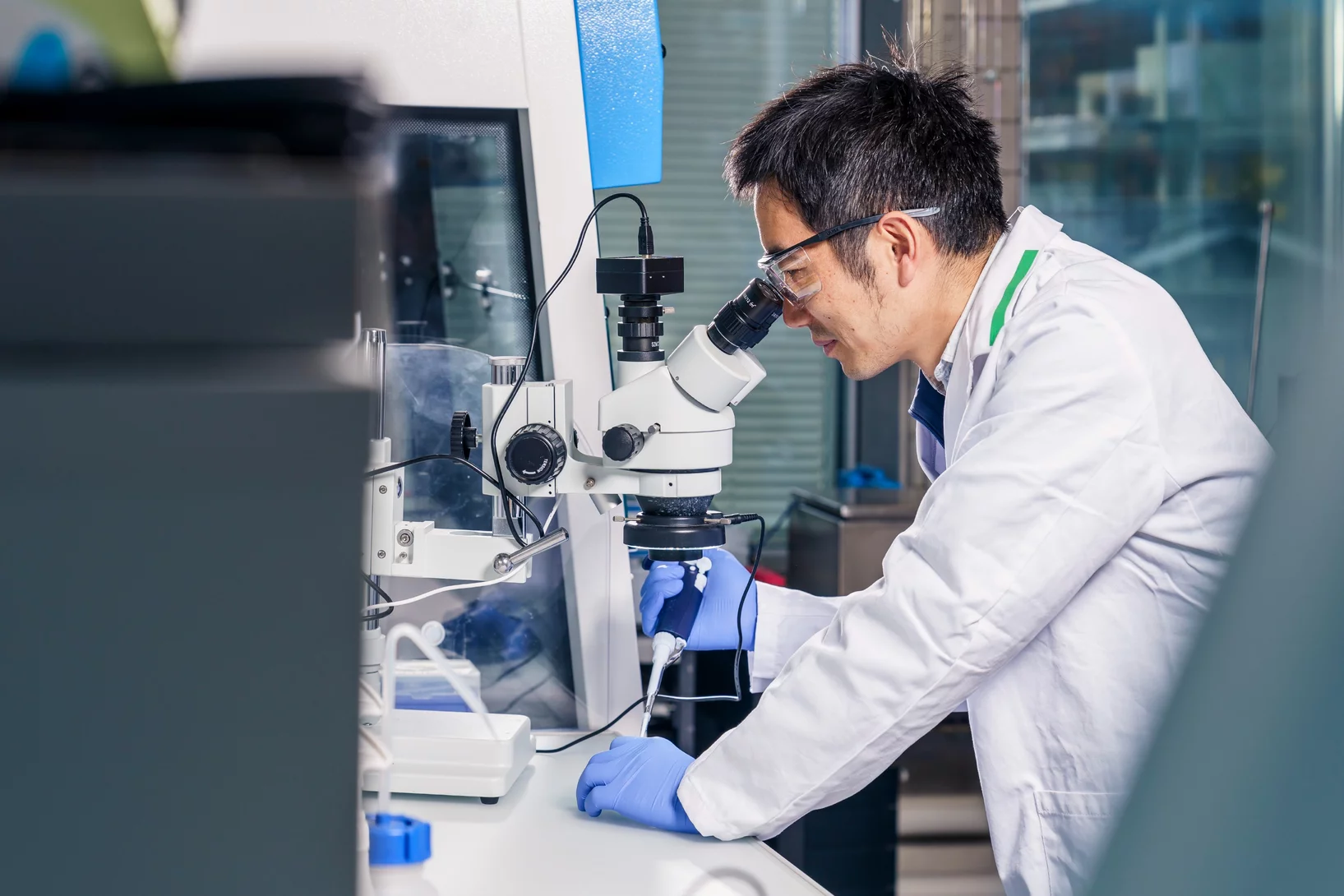
This year, Peng Qi from the X-ray Nano Optics group, LXN, CPS, earned third place and an honorable mention for his two submitted images.
Magnetism in thin layers: One electron makes the difference
An important step towards novel computer memory
Orbitronics: new material property advances energy-efficient tech
Discovery of orbital angular momentum monopoles boosts the emerging field of orbitronics, an energy-efficient alternative to electronics.
Excited About SLS 2.0!
Researchers tell us why they are excited about SLS 2.0 and more brilliant light for science
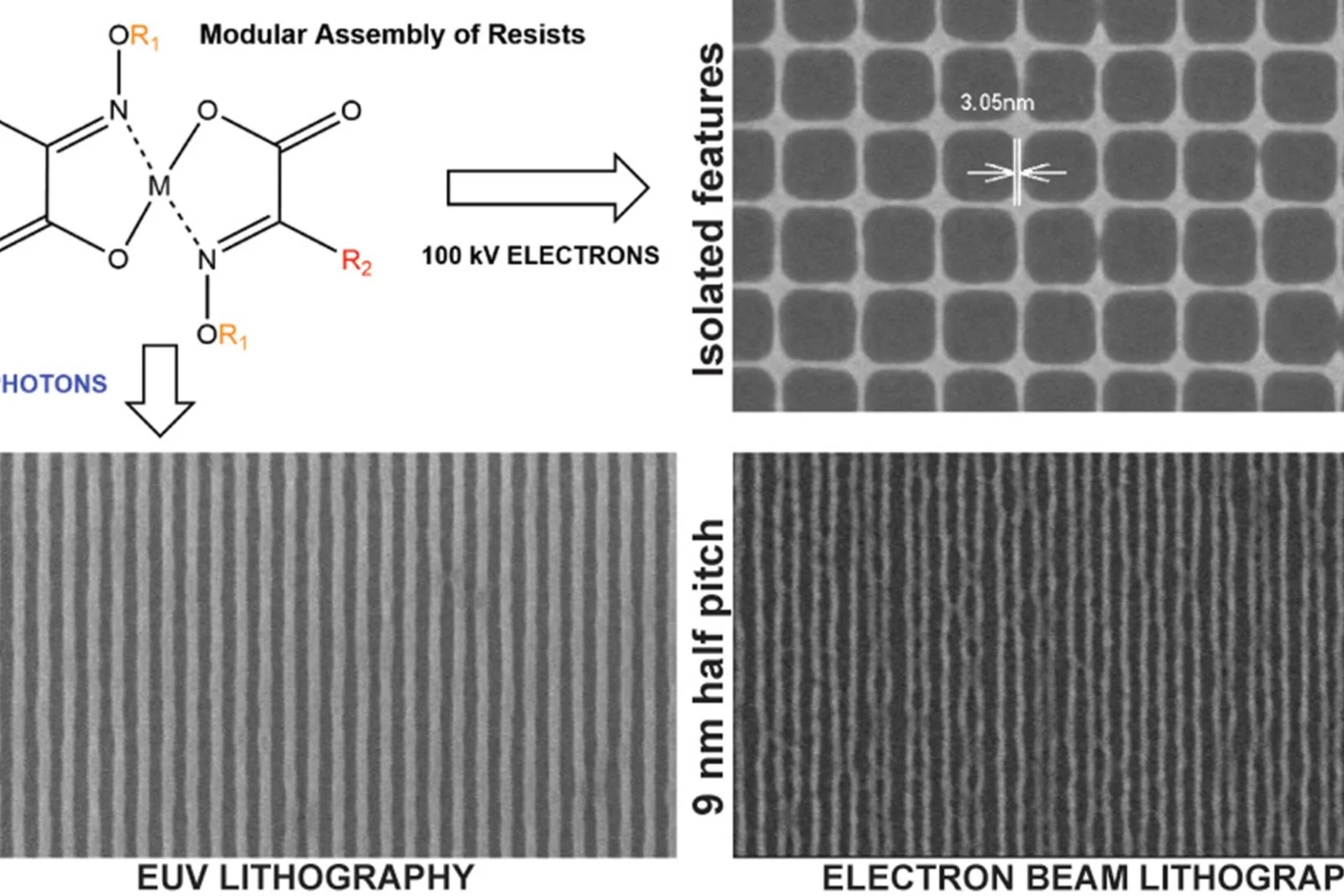
Novel Photoresist Chemistry Enables Lithography Approaching Angstrom-Scale Resolution
Photoresist materials are crucial in the manufacturing of computer chips, where the circuits are initially printed in the photoresist using photolithography. As the demand for smaller and more precise circuitry in computer chips grows, photoresists must resolve features with smaller sizes and higher density. One of the factors determining the ultimate resolution in lithography is the molecular size/mass of the photoresists.
New X-ray world record: Looking inside a microchip with 4 nanometre precision
Researchers at PSI have succeeded in imaging the spatial structure of a computer chip with a record resolution of 4 nanometres using X-rays.
Nanoimaging Reveals Topological Textures in Nanoscale Crystalline Networks
X-ray nano-tomography reveals collective behavior in synthetic self-assembled nanostructures. The new method opens opportunities for the synthesis of photonic and plasmonic materials with improved long-range ordering.
Rescuing music with X-rays
SLS plays the King of the Blues – B.B. King! In collaboration with the Montreux Jazz Digital Project, historic audio tapes are being digitised at PSI.
Making powerful lithium-air batteries suitable for everyday use
Chemical processes in lithium-air batteries revealed using neutron beams and synchrotron light.
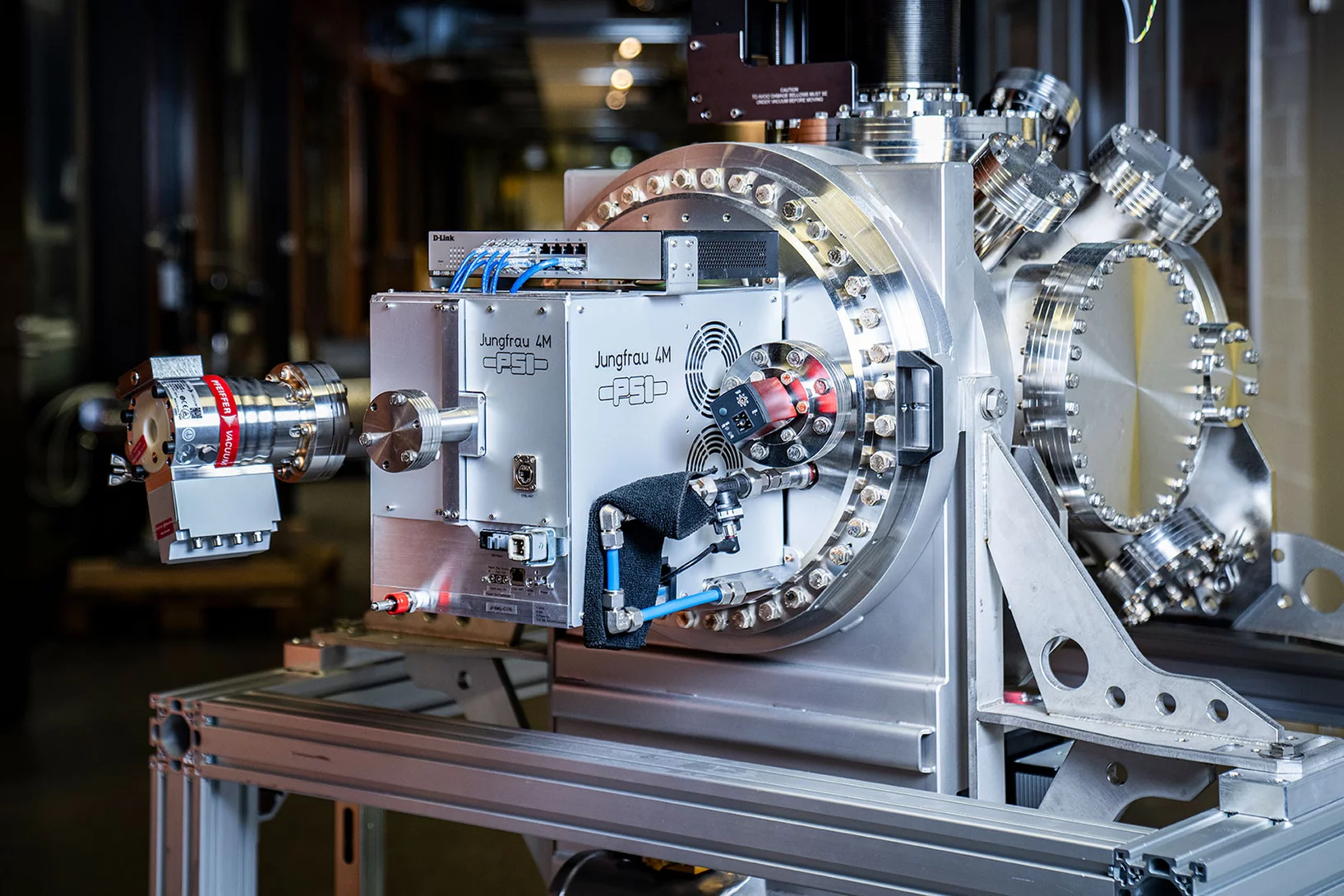
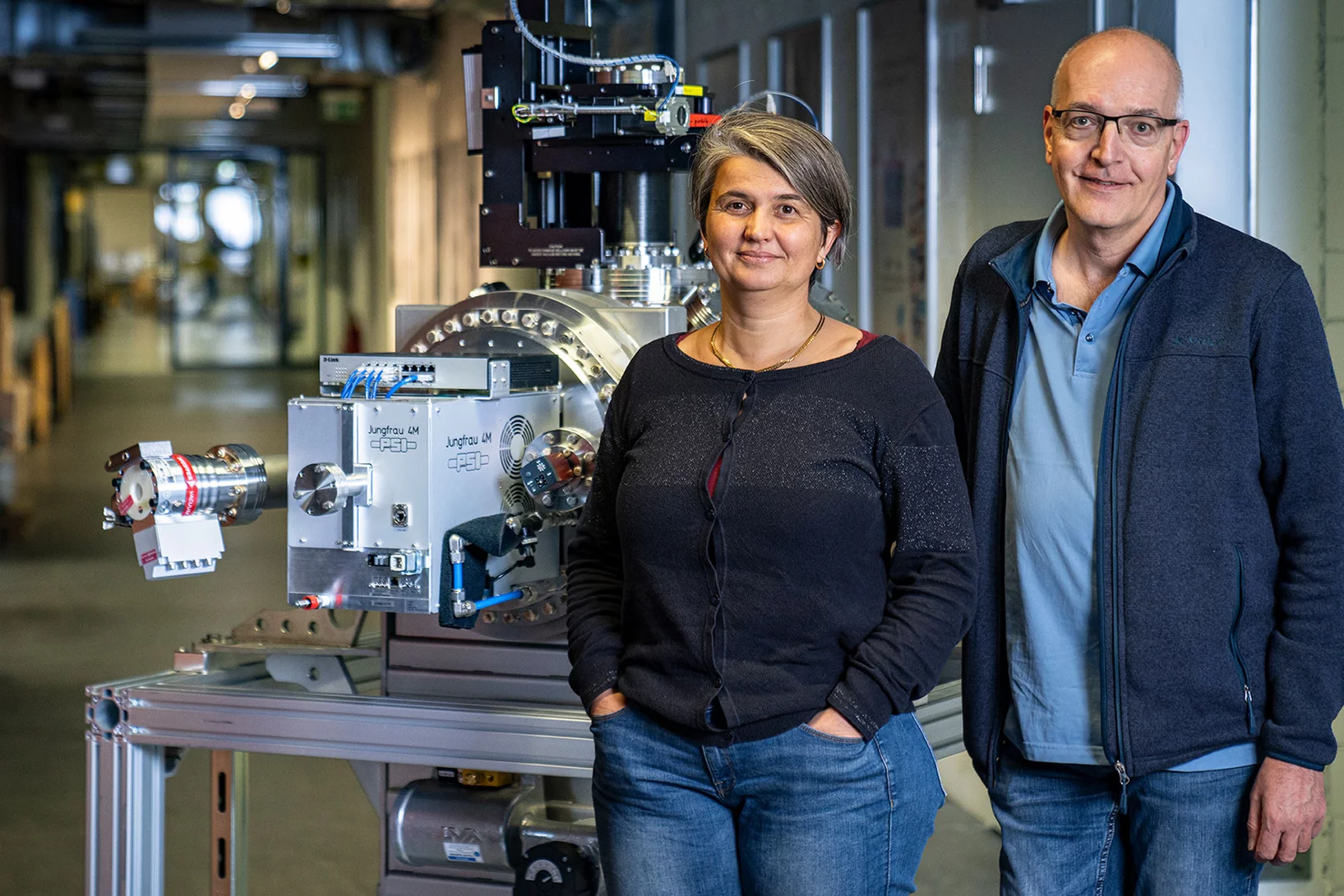
Developing detectors to transform science with light (part 2)
Part II: Why detecting soft X-rays is hard, and how a new breakthrough is set to transform low energy X-ray science.
Cause of clogged hypodermic needles discovered
Researchers at PSI and the ANAXAM technology transfer center have found the cause of clogging in prefilled syringes.
Developing detectors to transform science with light (part 1)
Part I: How the Jungfrau detector went from inception to perfection to ubiquity.
Altermagnetism proves its place on the magnetic family tree
Experiments at the Swiss Light Source SLS prove the existence of a new type of magnetism, with broad implications for technology and research.