The PSI Laboratory for Nonlinear Optics develops and operates state-of-the-art laser systems for the operation of and for experiments at the X-ray large research facilities of PSI.
Lab News & Scientific Highlights
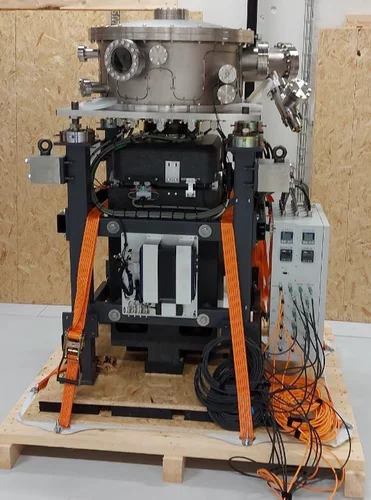
New Monochromators for SLS 2.0
The brand-new monochromators that have been built by XDS Oxford for the hard X-ray beamlines at SLS 2.0 have now arrived. They were unpacked beginning of the week, and are currently being tested in our new lab space at Park Innovaare. These advanced instruments will play a crucial role in enhancing the beamline performance, ensuring superior precision and efficiency in the upcoming experiments.
High-resolution ptychographic imaging at a seeded free-electron laser source using OAM beams
Electromagnetic waves possessing orbital angular momentum (OAM) are powerful tools for applications in optical communications, quantum technologies, and optical tweezers. Now, a consortium of collaborators in France, Italy, Slovenia, Spain, Switzerland, Sweden, and the US reports on using such beams in the extreme ultraviolet region for ptychographic imaging in the cover page article of Optica 11, Issue 3. By controlling the topological charge, the researchers achieve an improvement of 30% in image resolution.
SwissFEL: a next generation tool for Attosecond Science
The 2023 Nobel Prize in Physics recognises attosecond science’s pioneers. Past and future, this field’s evolution is entwined with SwissFEL.