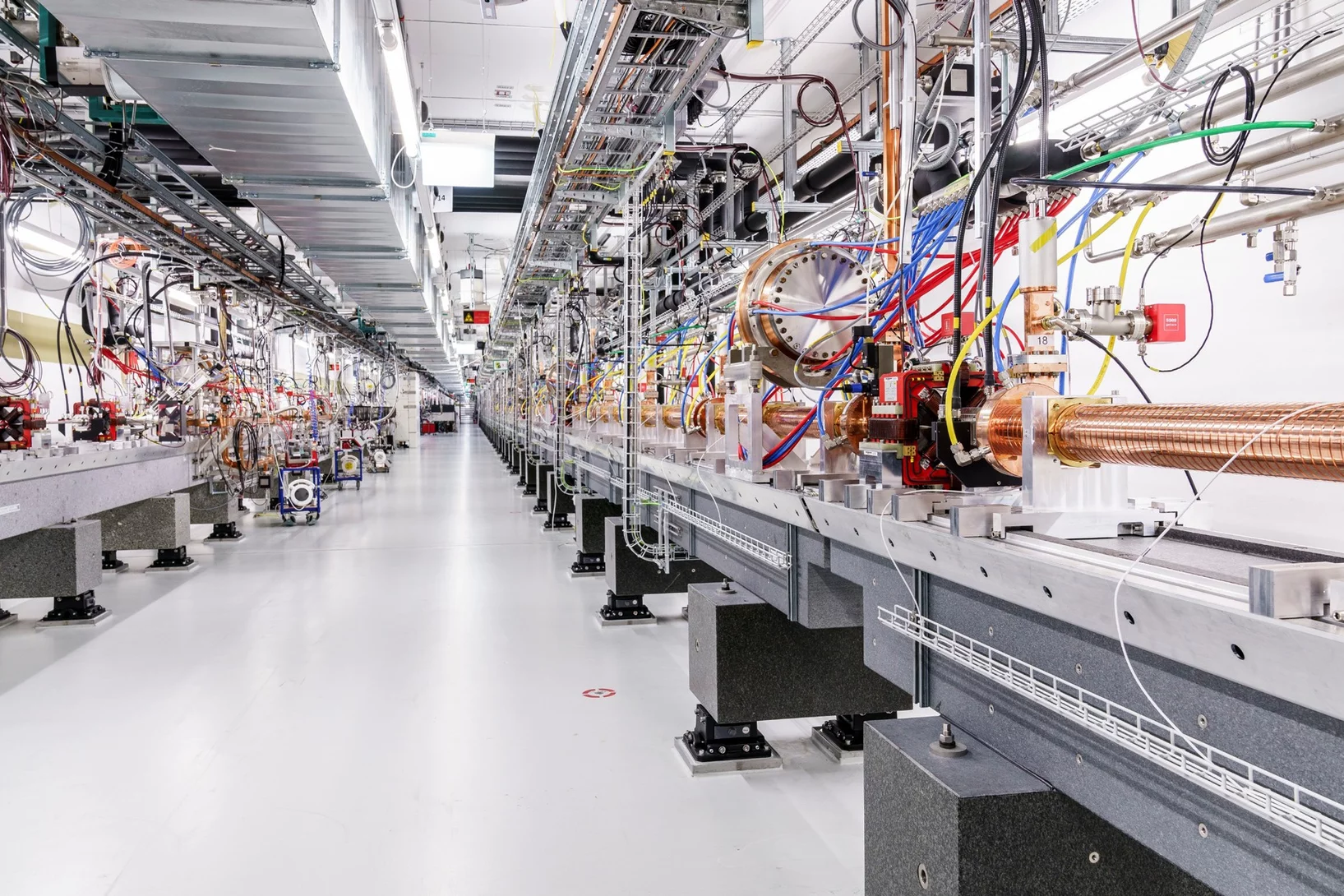
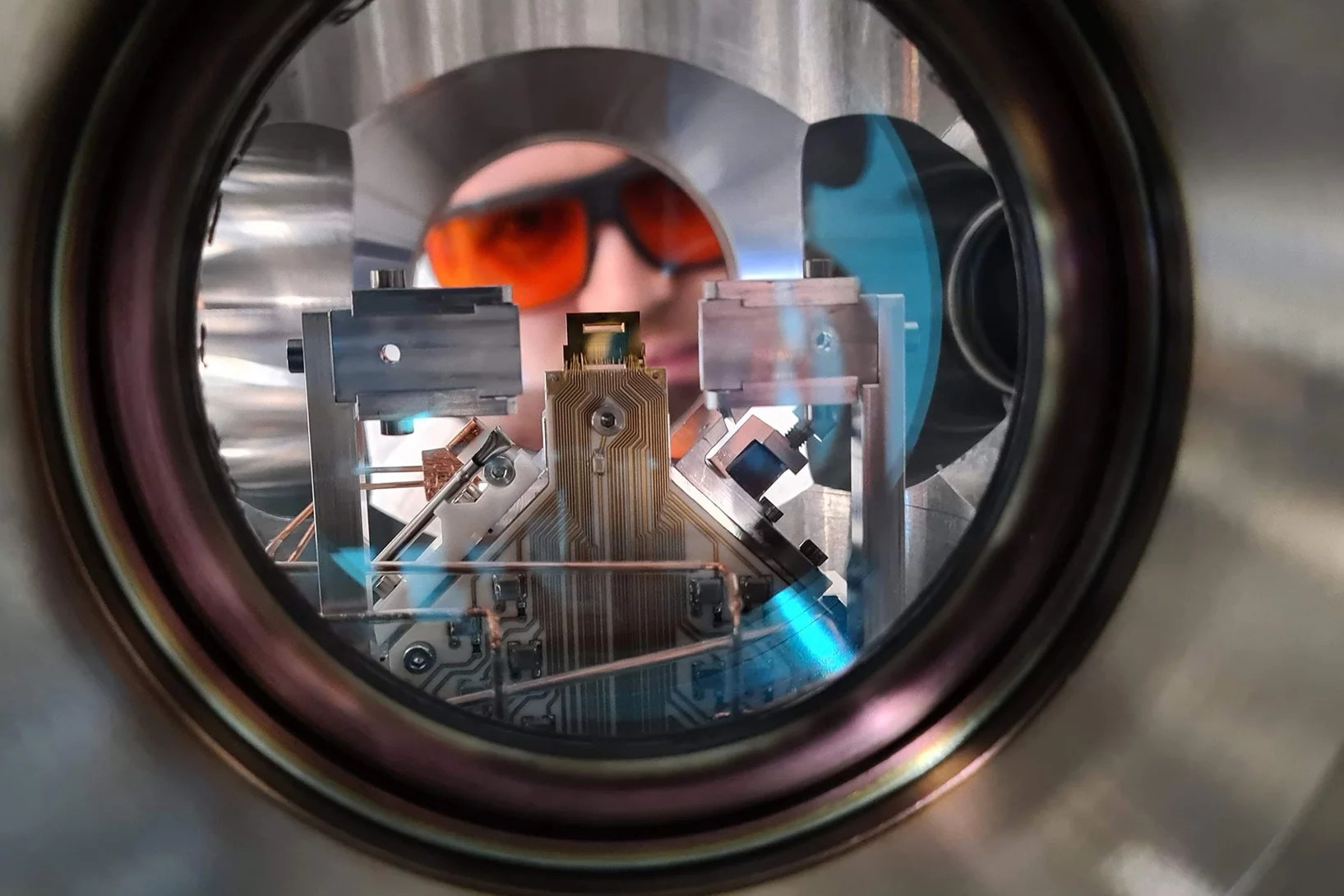
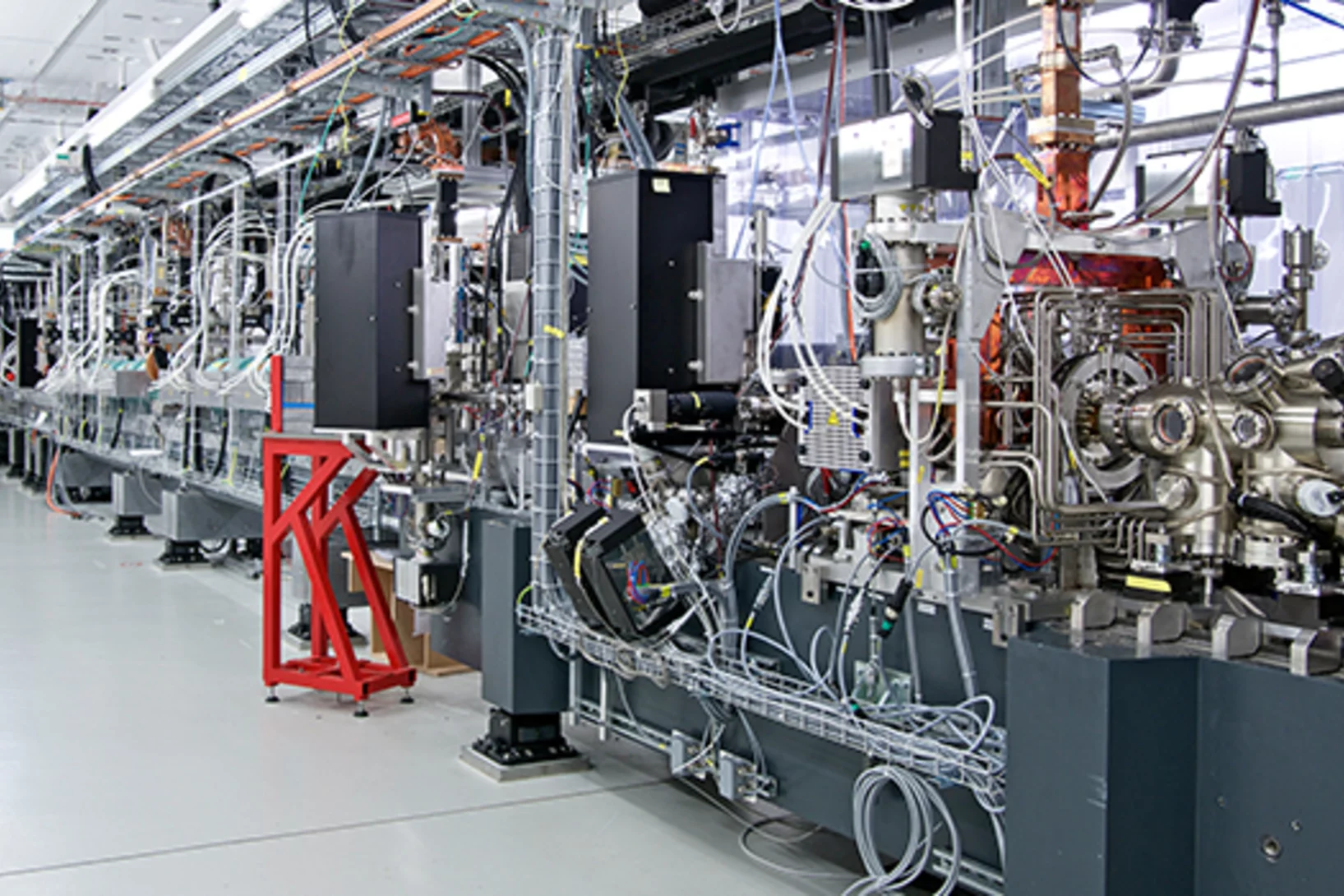
Peering into matter with ultrashort X-ray ripples
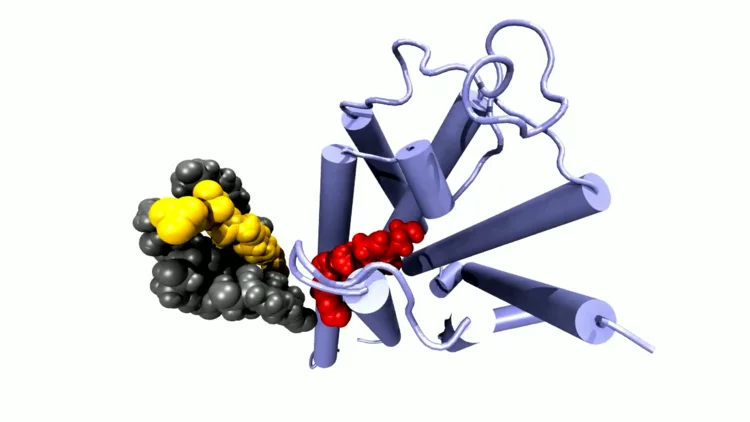
An all-X-ray transient grating experiment allows scientists to study the dynamics of quantum particles at the nanoscale.
Stabilising fleeting quantum states with light
X-rays from SwissFEL probe emergent properties of quantum materials
World record attosecond measurement at SwissFEL
Scientists at SwissFEL can measure X-ray pulses with attosecond time resolution.
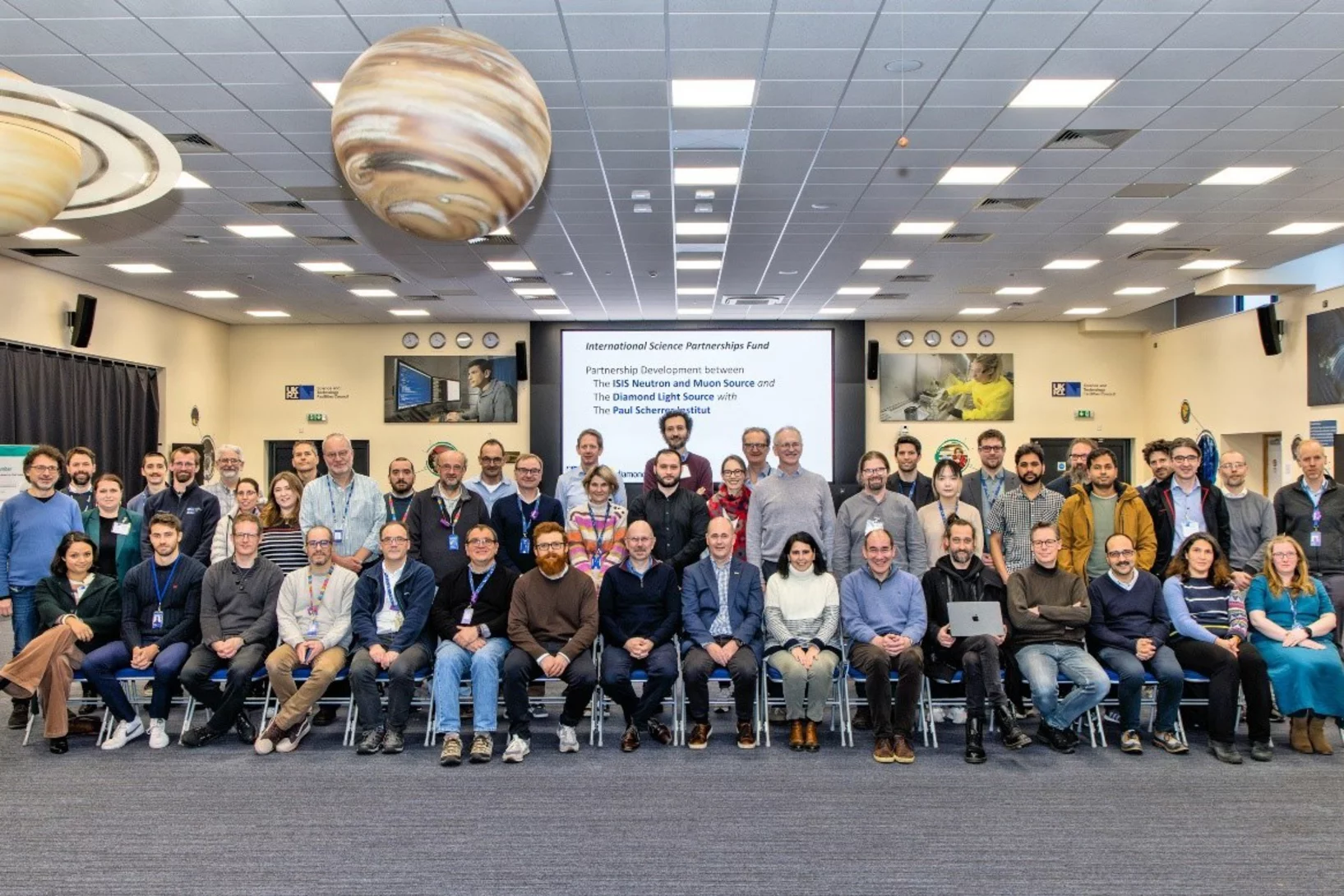
Together for Science with Neutrons, Muons and X-rays
Strategic partnership between research facilities in UK and Switzerland will create new capabilities to address global challenges using neutrons, muons and X-rays.
Neat, precise and brighter than ever
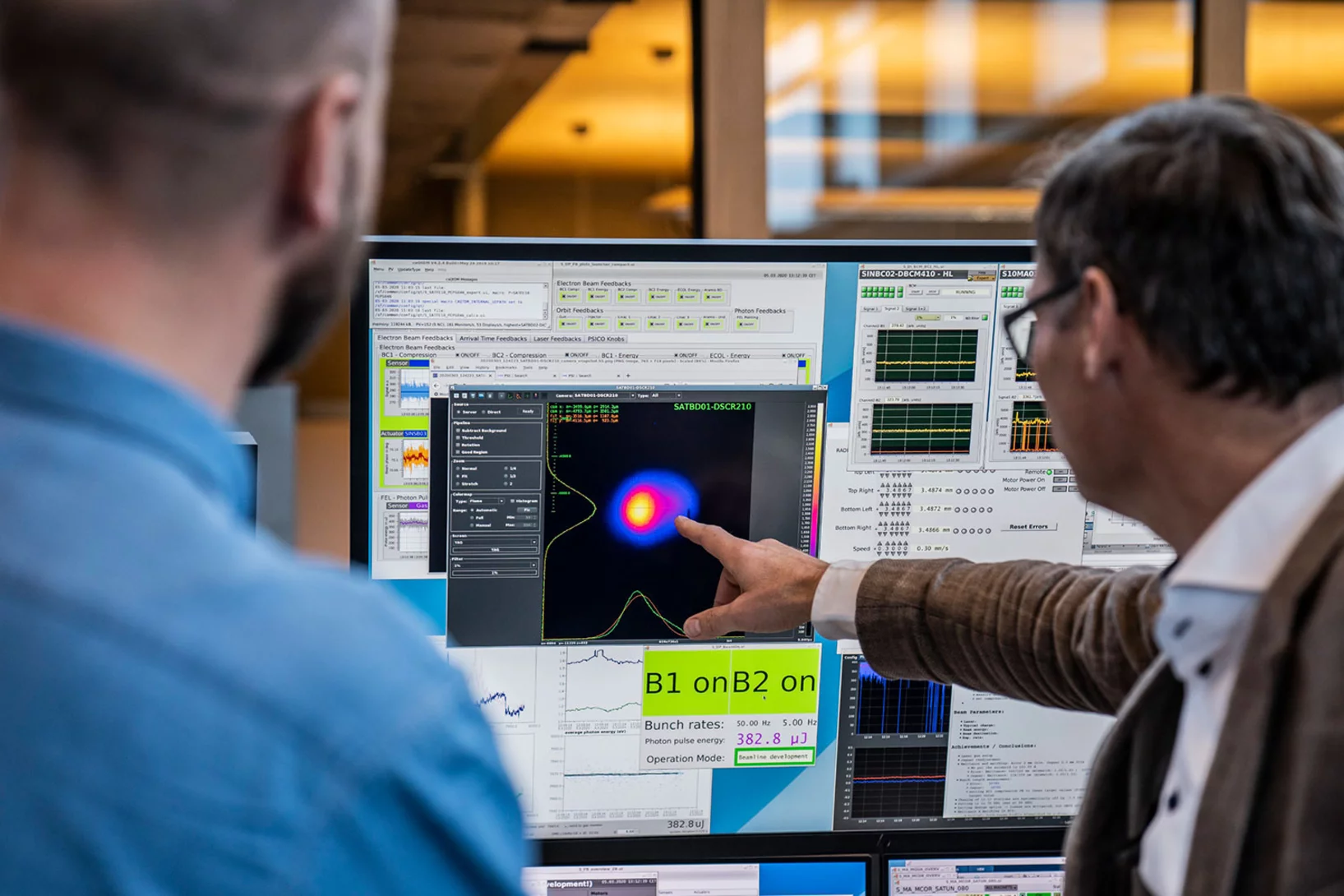
Researchers at SwissFEL succeed in improving the temporal coherence of XFEL pulses
Nobel Prize winner Anne L’Huillier visits SwissFEL
X-ray free-electron lasers could unlock the next frontier in attosecond research
Controlling magnetic waves in a spin liquid
Scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have shown that excitation of a spin liquid with intense THz pulses causes spins to appear and align within less than a picosecond. This induced coherent state causes a magnetic field to form inside the material, which is detected using ultrashort X-ray pulses at the X-ray Free Electron Laser SwissFEL.
Nature’s sunscreen and other SwissFEL stories
From DNA repair to catalysts: how the Alvra experimental station at SwissFEL has developed into a special tool for biology and chemistry research.
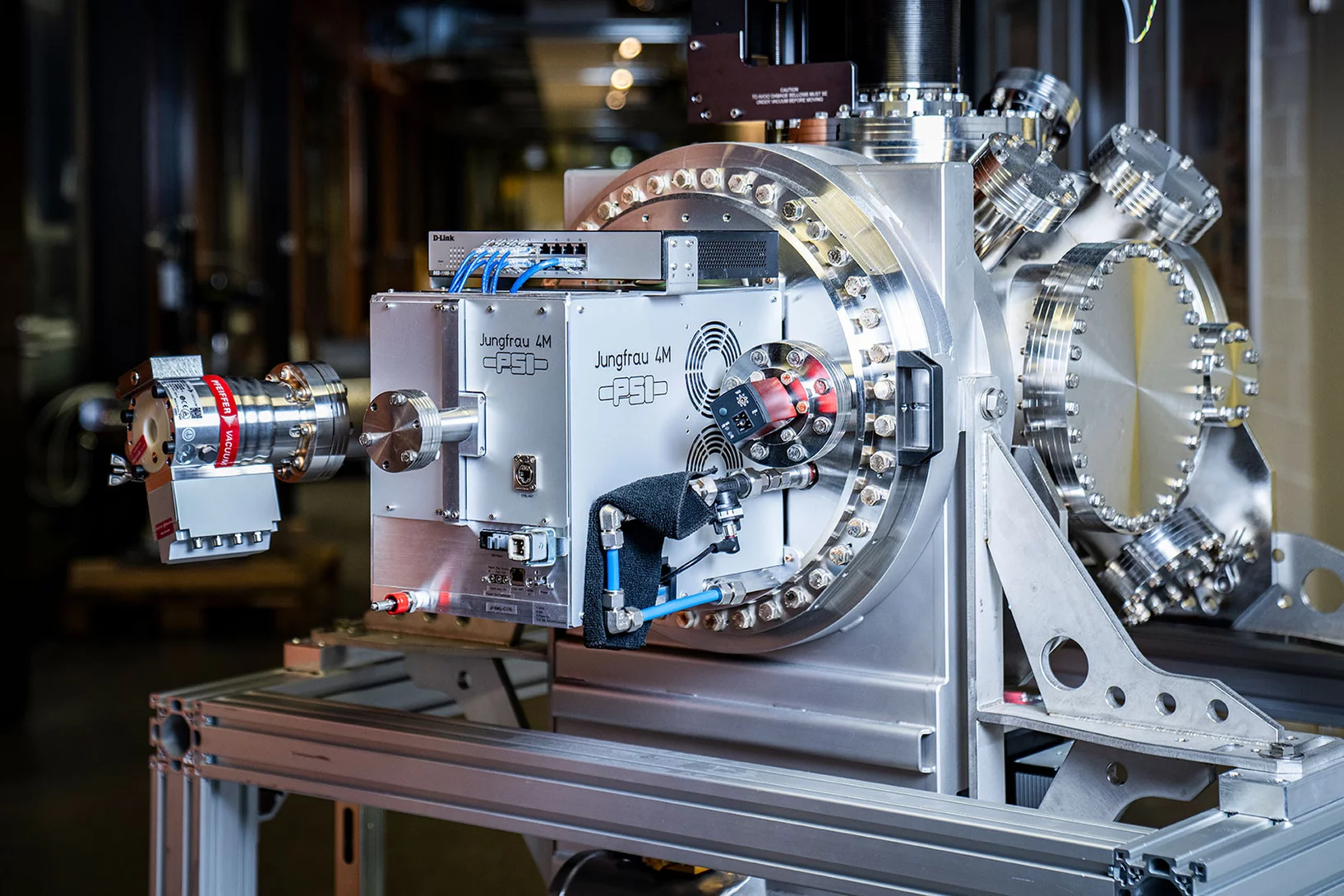
Developing detectors to transform science with light (part 2)
Part II: Why detecting soft X-rays is hard, and how a new breakthrough is set to transform low energy X-ray science.
Developing detectors to transform science with light (part 1)
Part I: How the Jungfrau detector went from inception to perfection to ubiquity.
SwissFEL: a next generation tool for Attosecond Science
The 2023 Nobel Prize in Physics recognises attosecond science’s pioneers. Past and future, this field’s evolution is entwined with SwissFEL.
Repairing genetic damage with sunlight
An international research team at SwissFEL of PSI has discovered how an enzyme repairs DNA damage with the help of sunlight.
The secret life of an electromagnon
SwissFEL sheds light on how lattice and atomic spins jiggle together.
Using quantum computers already today
Analogue quantum computers make ultrafast chemical reactions observable.
Bringing SwissFEL light to industrial users
High throughput experiments will enable new structural biology users to benefit from XFEL light.
An algorithm for sharper protein films
A newly developed algorithm allows measurements performed at X-ray free-electron lasers to be evaluated more efficiently.
How vision begins
PSI scientists have discovered the very first step occurring in the eye when light hits the retina.
Using light to switch drugs on and off
PSI researchers record a molecular film of a cancer drug fitted with a photoswitch. This opens new insights for drug developers.
A piece of PSI history sets off on a long journey
Off to new shores – a high-tech component is on its way from PSI to Australia by sea. In future, it will be deployed at the Australian Synchrotron in Melbourne.
Ultrafast control of quantum materials
Using light to fundamentally change the properties of solids
First light at Furka: The experiments can begin
The path to experiments that are unique in the world is now open.
No rose-coloured glasses here
Light is essential for life, and for researchers it is also a wonderful tool to better understand the structure of materials.
Growth in the data sciences
Another site for the Swiss Data Science Center will be established at PSI. This expansion is expected to give a further boost to the data sciences in Switzerland.
Uniquely sharp X-ray view
A new PSI method allows quantum-physical research on materials with the aid of X-ray lasers.
Compact and high-performance, like a Swiss Army knife
The X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL really is as high-performance and versatile as planned.
Watching receptor proteins changing shape
In our bodies, G protein-coupled receptors mediate countless processes. PSI researcher Ramon Guixà talks about how he brings those receptor molecules to life on the computer screen.
Milestone for the second beamline of SwissFEL
At the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, the second beamline is currently being put into operation. With Athos, researchers want to understand how catalysts work or how biomolecules cause hereditary diseases.
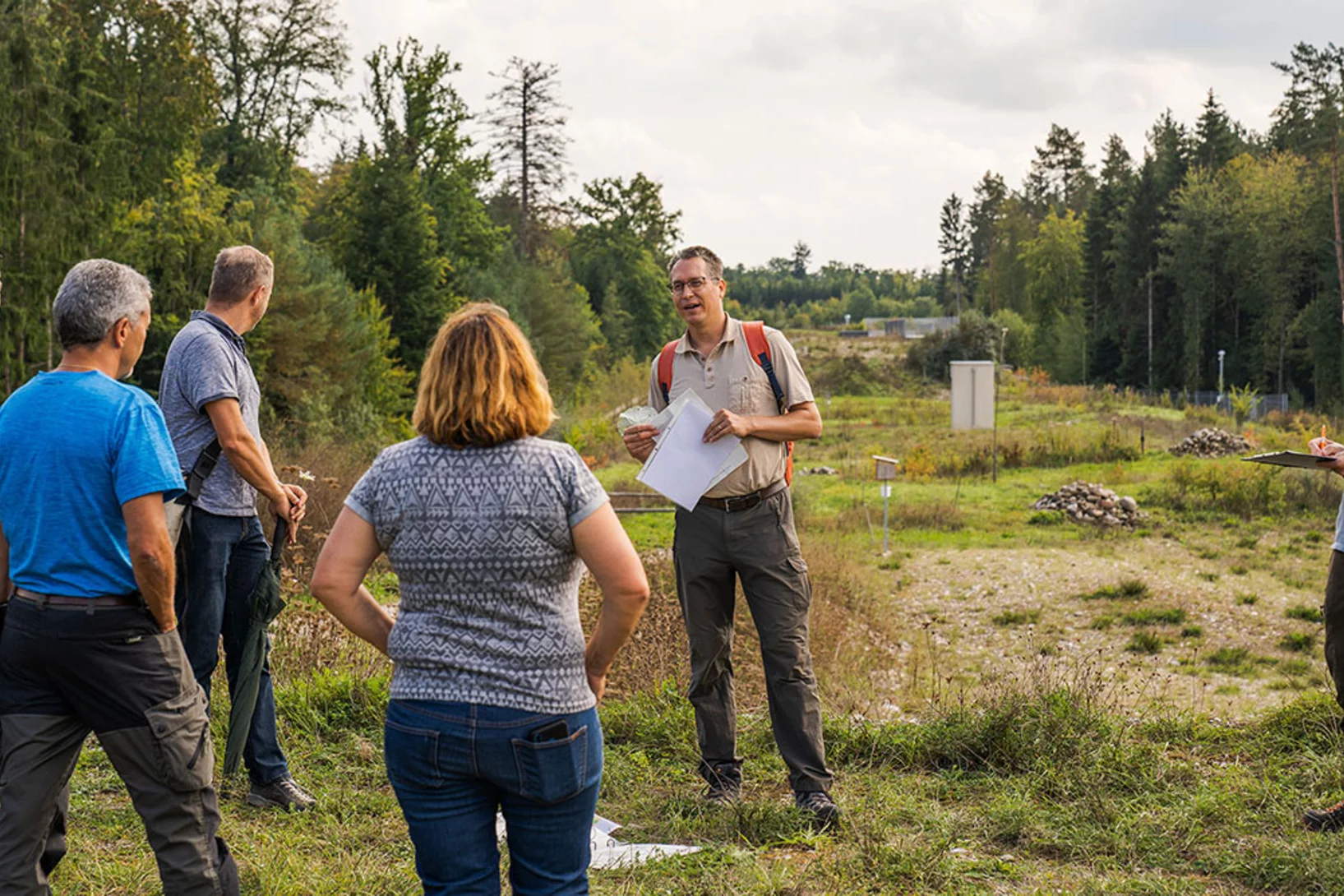
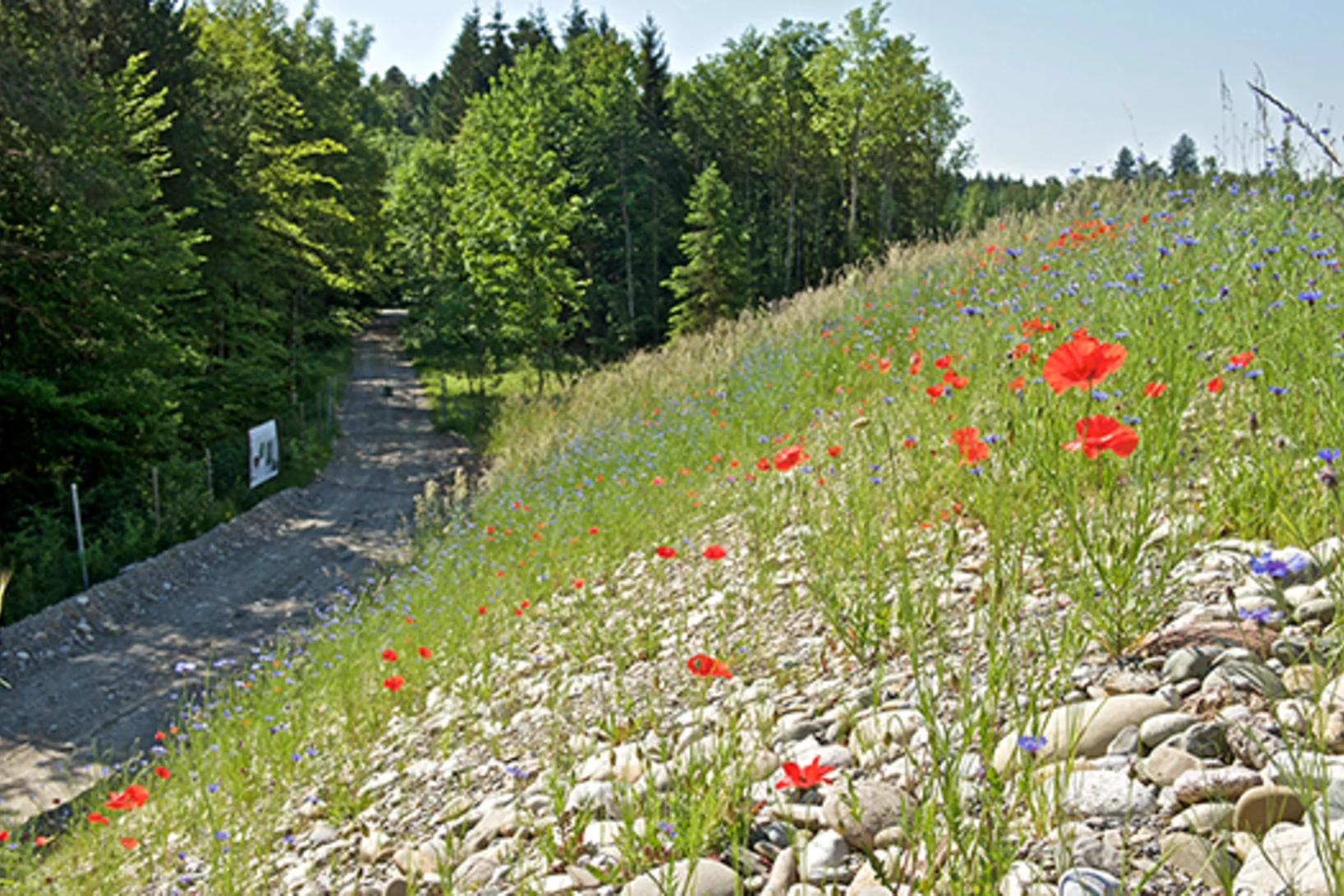
SwissFEL: a perfect habitat for the black mortar bee
For the construction of the SwissFEL facility in 2013, around five hectares of forest were cleared and transformed into a new habitat for flora and fauna. Biologists and forest engineers have now assessed the results of the renaturization project and are excited about the progress to date.
Elucidating the mechanism of a light-driven sodium pump
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded for the first time in recording a light-driven sodium pump from bacterial cells in action. The findings promise progress in developing new methods in neurobiology. The researchers used the new X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL for their investigations.
In search of the lighting material of the future
At the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, researchers have gained insights into a promising material for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). This new understanding at the atomic level will help to develop new lighting materials that have higher light output and also are cost-efficient to manufacture.
Athos is making great strides
The new beamline at PSI's X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL will soon be ready for action. In December, Athos delivered laser light for the first time − even sooner than expected, to the delight of the researchers responsible for its construction.
Research and tinkering – SwissFEL in 2019
The newest large research facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute, SwissFEL, has been completed. In January 2019 it began regular operation. Henrik Lemke, head of the SwissFEL Bernina research group, gives an interim report.
Molecular energy machine as a movie star
Using the Swiss Light Source SLS, PSI researchers have recorded a molecular energy machine in action and thus revealed how energy production at cell membranes works. For this purpose, they developed a new investigative method that could make the analysis of cellular processes significantly more effective than before.
This time, it's all bio: SwissFEL makes protein structures visible
For the development of new medicinal agents, accurate knowledge of proteins is crucial. In a pilot experiment, researchers have now, for the first time, used the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL of PSI for the examination of protein crystals.
Fast-moving plot
How do dye-sensitised solar cells work, and what's behind the brilliant new mobile phone displays? The ultrashort X-ray pulses at SwissFEL reveal the chemical reactions that take place inside these devices and could help to make them even more efficient and cost-effective.
Movie directors with extra roles
Data storage devices based on novel materials are expected to make it possible to record information in a smaller space, at higher speed, and with greater energy efficiency than ever before. Movies shot with the X-ray laser show what happens inside potential new storage media, as well as how the processes by which the material switches between two states can be optimised.
Biological light sensor filmed in action
Using X-ray laser technology, a team led by researchers of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI has recorded one of the fastest processes in biology. In doing so, they produced a molecular movie that reveals how the light sensor retinal is activated in a protein molecule. Such reactions occur in numerous organisms. The movie shows for the first time how a protein efficiently controls the reaction of the embedded light sensor.
Hollywood in the Würenlingen woods
With the X-ray laser SwissFEL, researchers at PSI want to produce movies of biomolecules in action. This can reveal how our eyes function or how new drugs work.
Light for biomolecules and super-fast processes
The 16th of May is the International Day of Light. The research carried out with light at PSI enables advances in biology and pharmacology and also promotes the development of new materials for data storage and new technologies for personalised medicine.
First experiment at SwissFEL carried out successfully
The years of careful planning and construction have paid off: At the newest large-scale research facility of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI – the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL – the first experiment has been carried out successfully. With that, two goals have been achieved: First, a new scientific result is already expected. Second, the interaction of the many individual components of the highly complex facility is being optimised.
Research experience from California benefits Swiss X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL
An X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) is capable of visualizing extremely fast structural and electronic processes. Pilot experiments will take place at the PSI's Swiss Free-Electron Laser (SwissFEL) from the end of 2017 on. Two current publications in Science and Nature Communications demonstrate the kind of outstanding scientific work that is enabled by such facilities. The work was carried out at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) in California. Two of the leading authors behind these studies have now relocated to the PSI in order to share their expertise as SwissFEL expands its capabilities.
To the limits of the feasible
The company Daetwyler made the undulators for the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, to a precision of one-tenth of the width of a hair.
Second beamline for SwissFEL
This year the first pilot experiments are starting at the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL. The X-ray light generated by SwissFEL will enable a broad spectrum of experiments. Beginning in 2020, a second beamline will provide for a still greater variety.
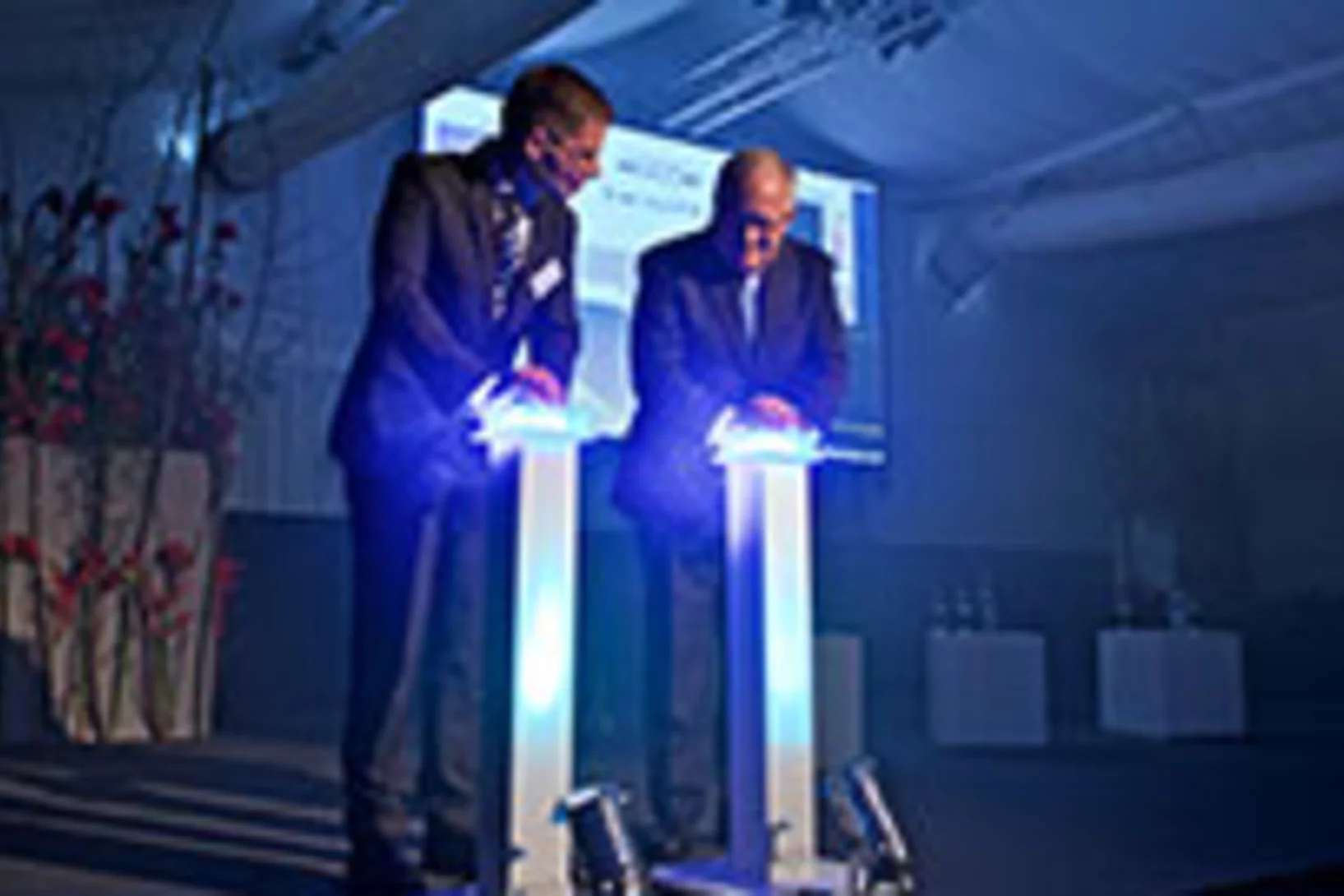
SwissFEL inauguration
Today, on 5 December 2016, the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI held an inauguration ceremony for its new large-scale research facility SwissFEL, with Johann N. Schneider-Ammann, President of the Swiss Confederation, in attendance.
SwissFEL in the home stretch: The first electrons are here
SwissFEL building, 24 August 2016: In the control room above the beam tunnel of the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL, the atmosphere is intense and focussed. Marco Pedrozzi’s team has big plans for this late August afternoon. The last adjustments have been made — it’s time to press the big button and start up the electron source. The goal: SwissFEL should generate its first electrons. A report.
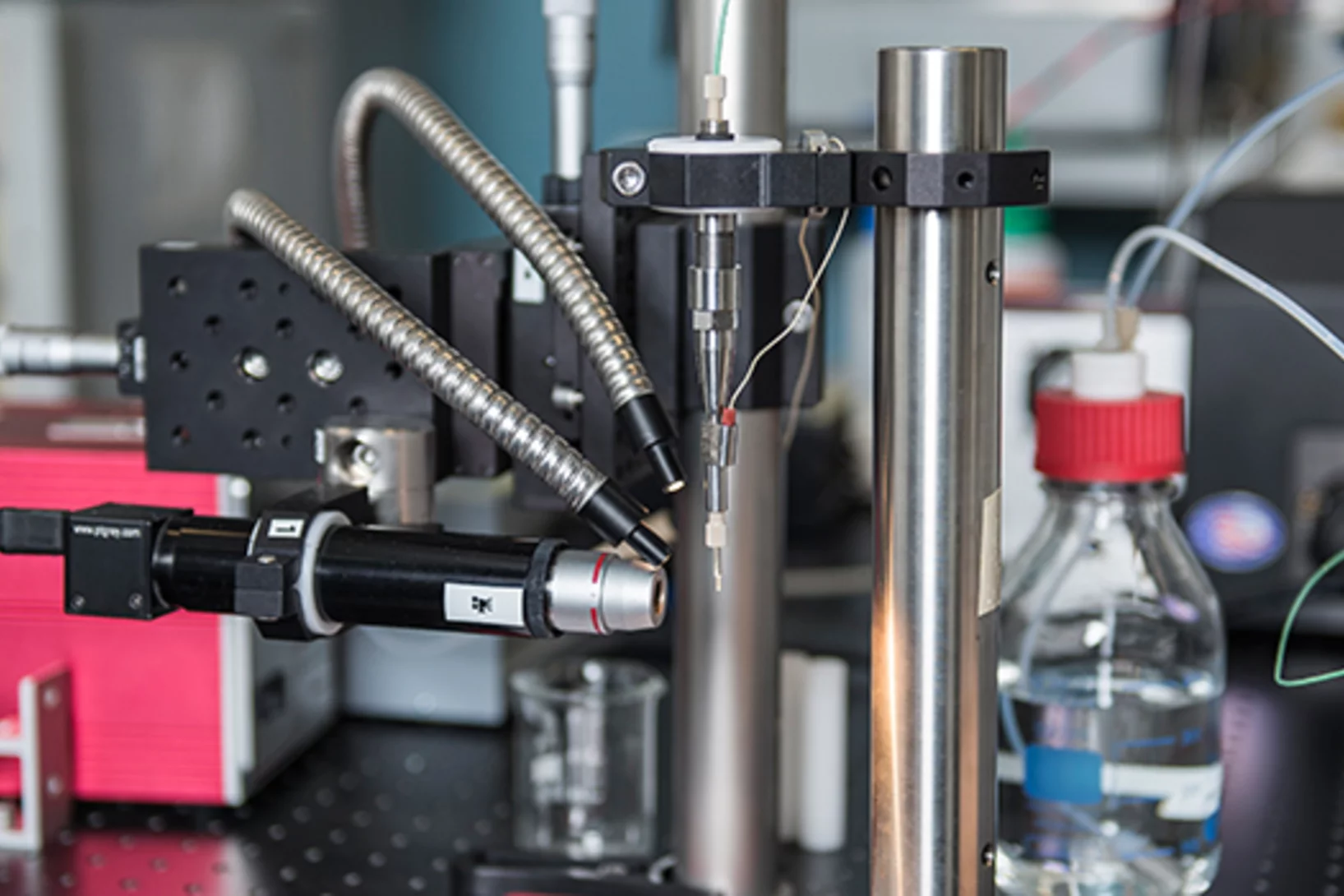
Catching proteins in the act
Proteins are indispensable building blocks of life. They play a vital role in many biological processes. Researchers have now been able to show how the ultrafast processes by which proteins do their work can be studied with free-electron X-ray lasers such as SwissFEL at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI. Free-electron X-ray lasers generate extremely short and intense pulses of X-ray light. Currently there are just two such facilities in operation, worldwide. The results were published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Cooperation with nature
With SwissFEL, a new landscape takes shapeBarely completed, the building housing the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL has disappeared again beneath a mound of earth. Since then, planting and landscaping have been under way on and around this major research facility of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI. Its special location, in a forest, demands that SwissFEL be integrated in an environmentally appropriate way. So the facility is, from the outside, nearly invisible. And rare animals and plants have gained new living space.
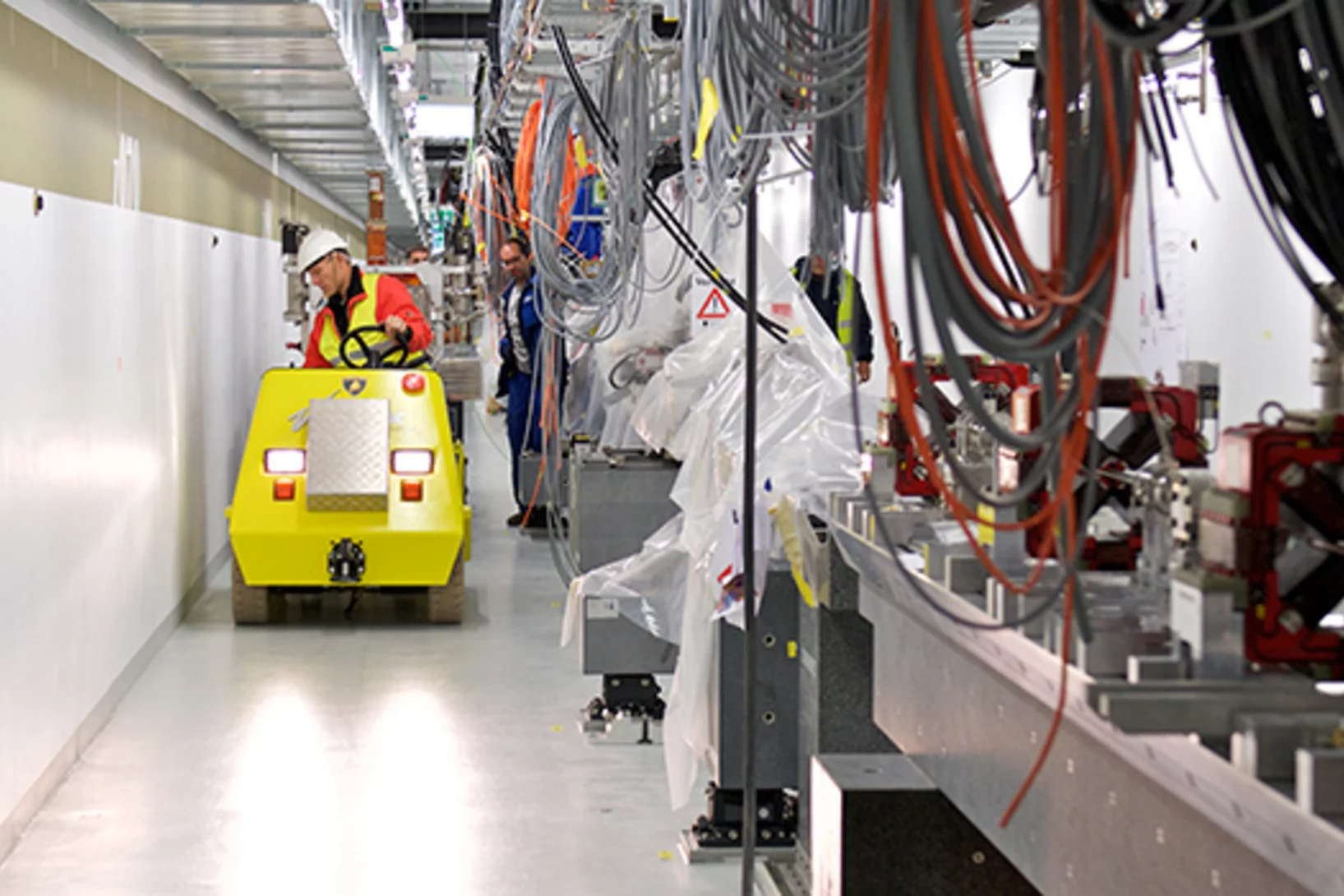
To the beam tunnel
Since the autumn of 2015, the SwissFEL beam tunnel has been filling up with the machine components for the new PSI large research facility. Piece by piece, the pre-assembled components are being brought to their final destination.