Show filters
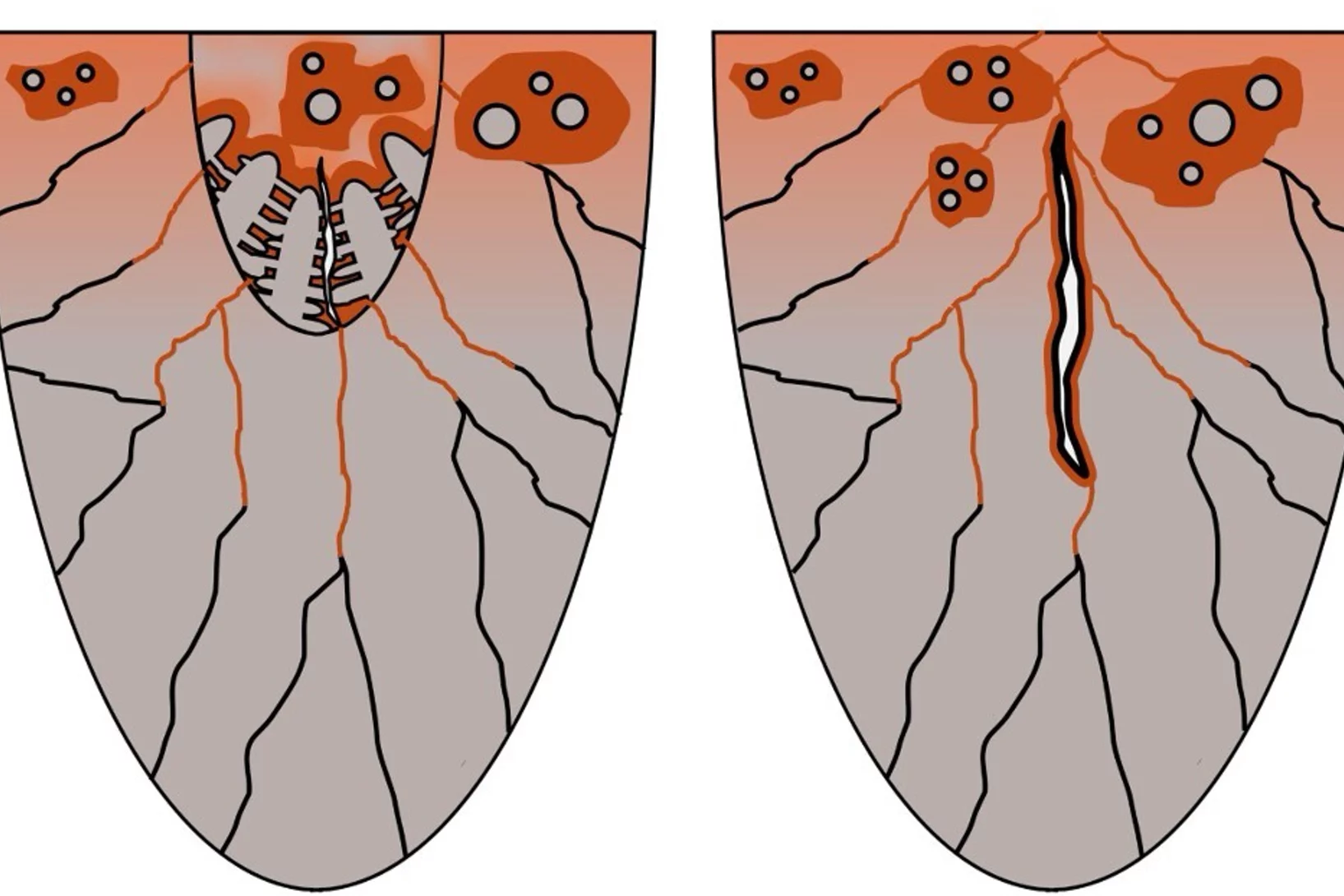
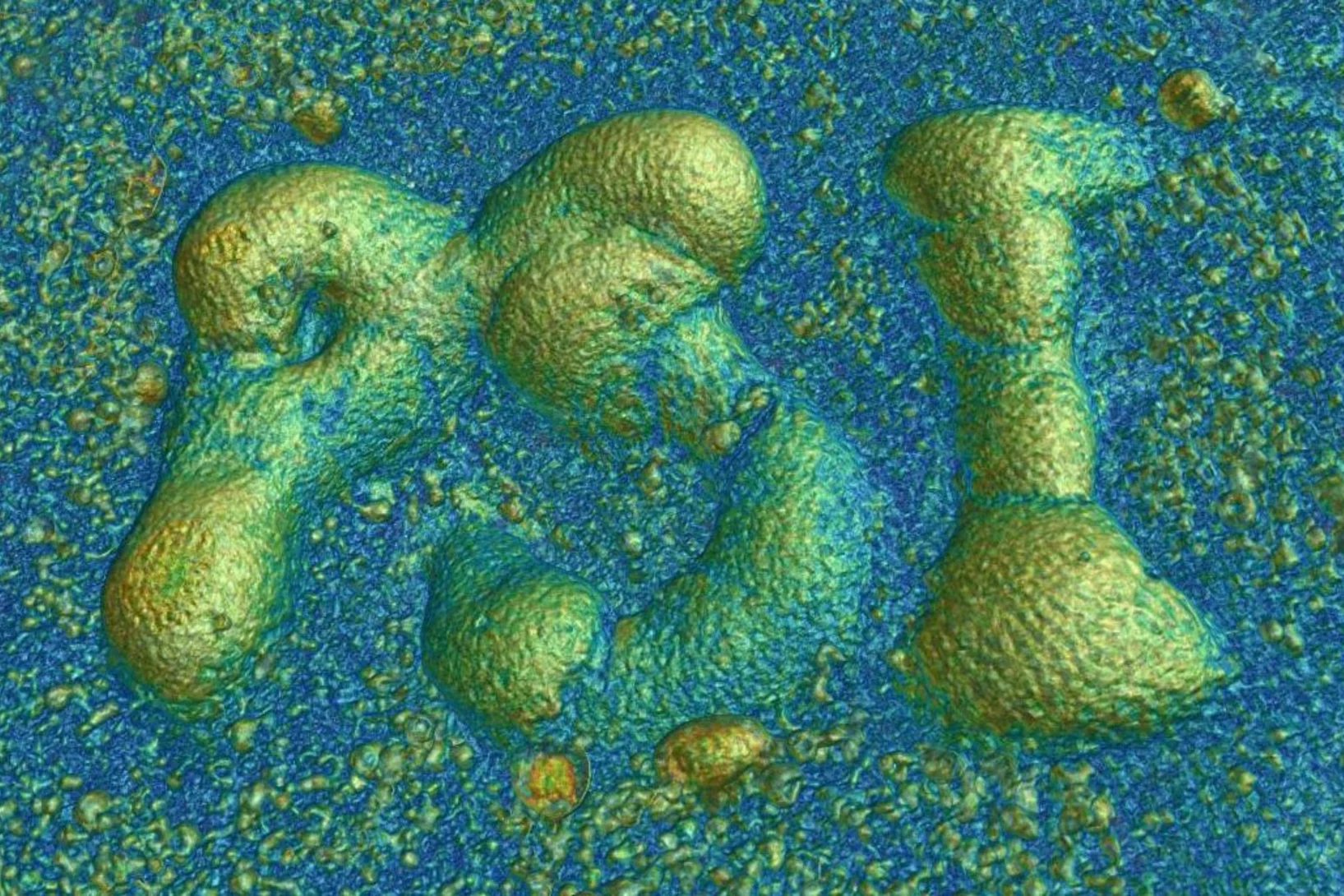
Why Ni-Cu Alloys Fail in 3D Printing
3D printing with nickel–copper alloys holds great promise — but hidden mechanisms can cause them to crack. Our latest study reveals why.
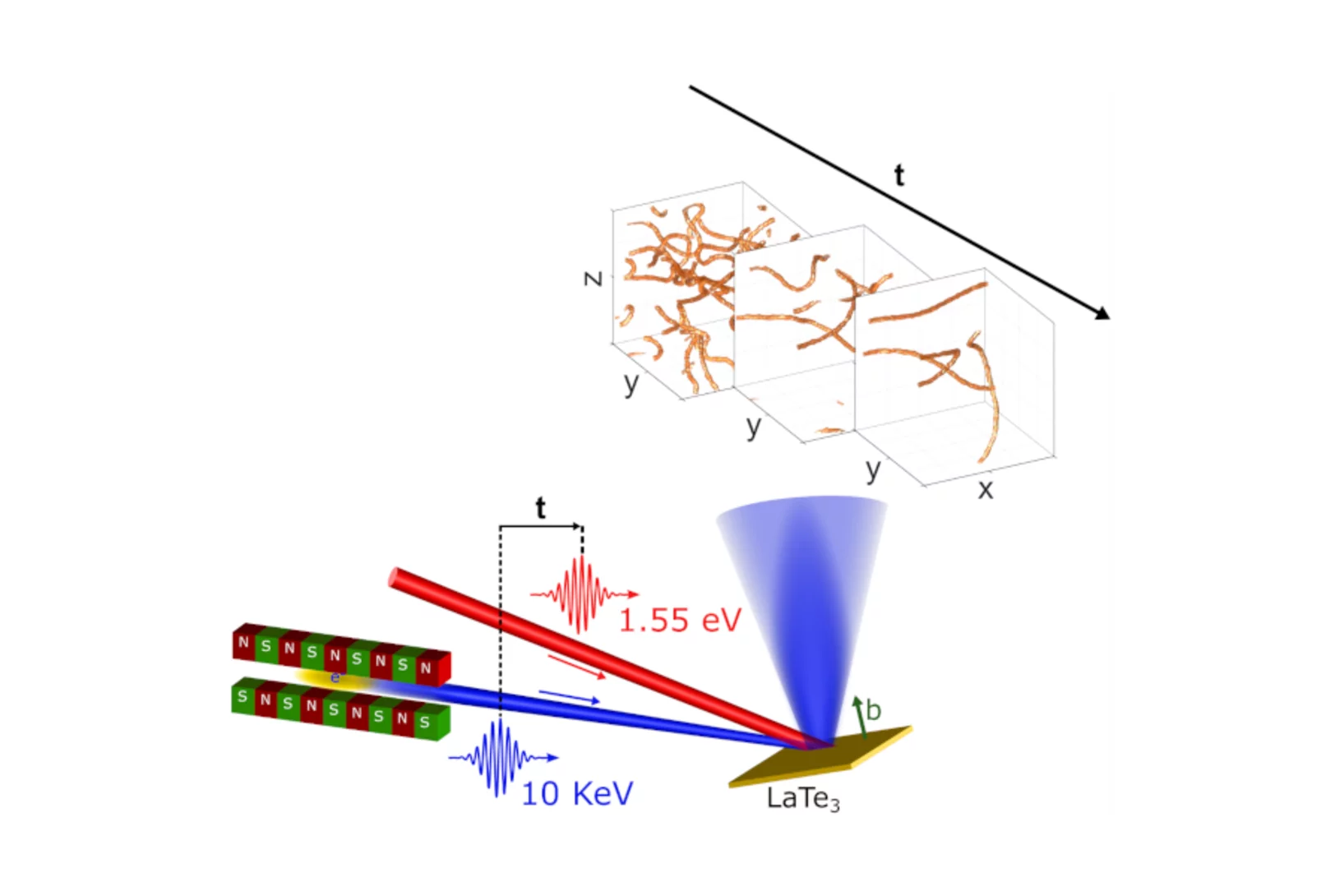
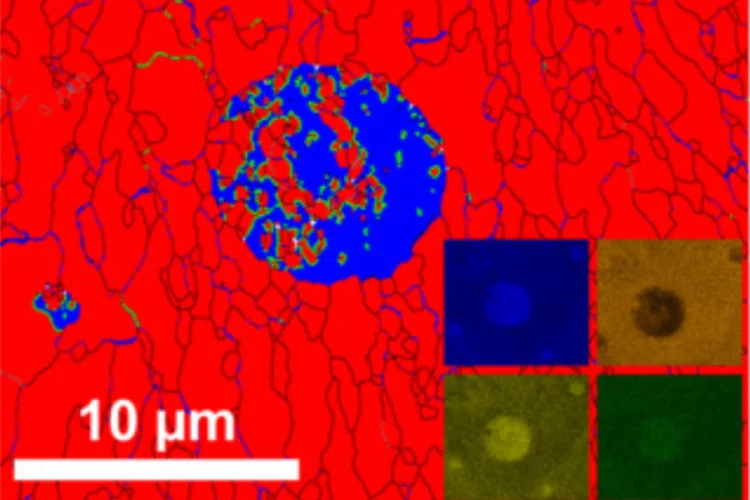
Topological defects determine evolution of charge density wave phase transition
Total scattering signals collected at SwissFEL reveal the role of topological defects when switching properties of a charge density wave material. The defect formation and dynamics after laser excitation reveals new insights into the functionality of quantum materials.
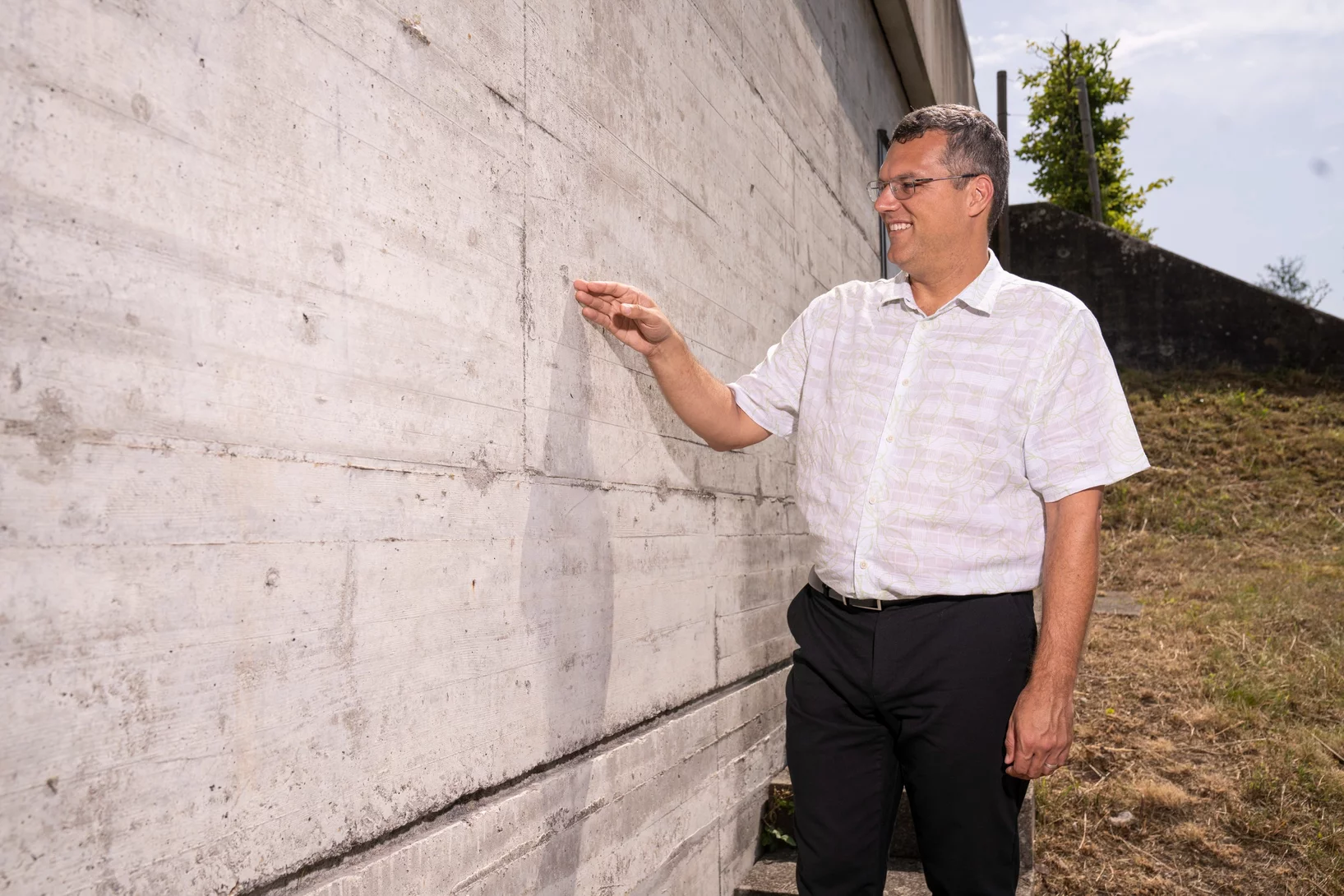
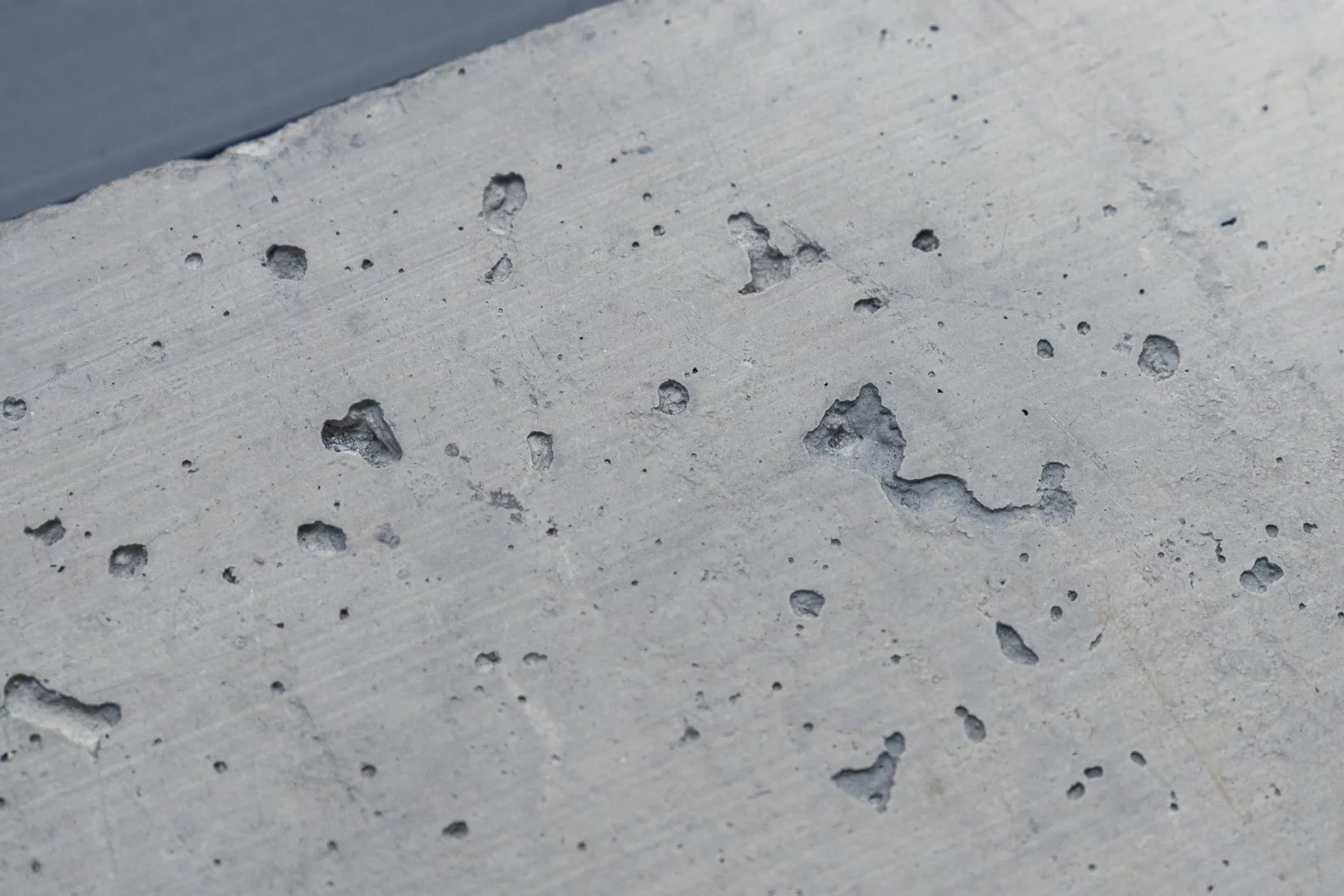
PSI’s cement whisperer
John Provis has dedicated his research career to a building material that is far more exciting than you might think.
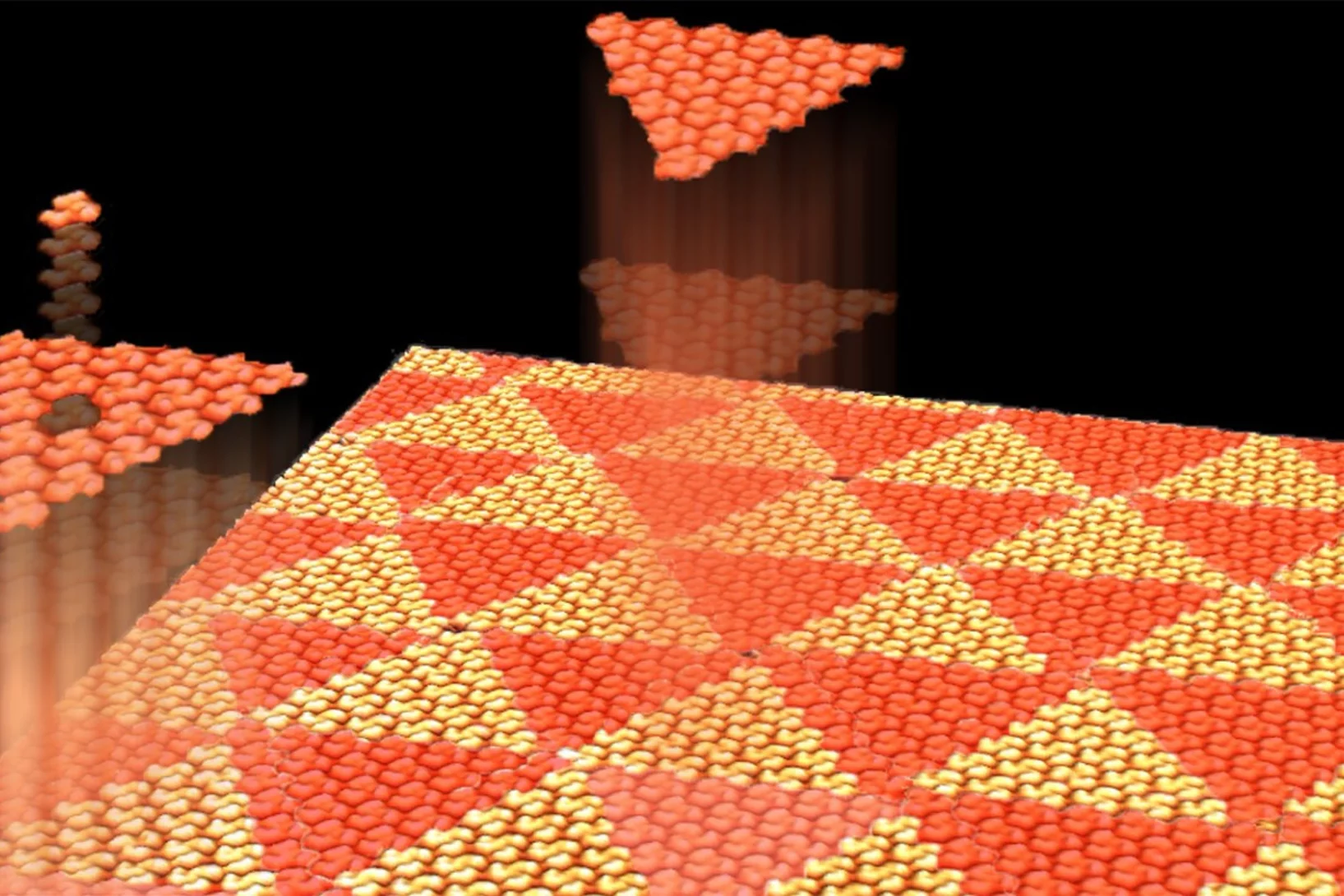
Aperiodic Chiral Tiling by Molecular Self-Assembly
The 2D self-arrangement of a molecule that resembles three-armed spirals leads to a triangular pattern that is effectively aperiodic.
Machine Learning Accelerates Alloy Design for Additive Manufacturing
A new machine learning–designed alloy demonstrates how materials can be tailored for specific performance properties required in additive manufacturing.
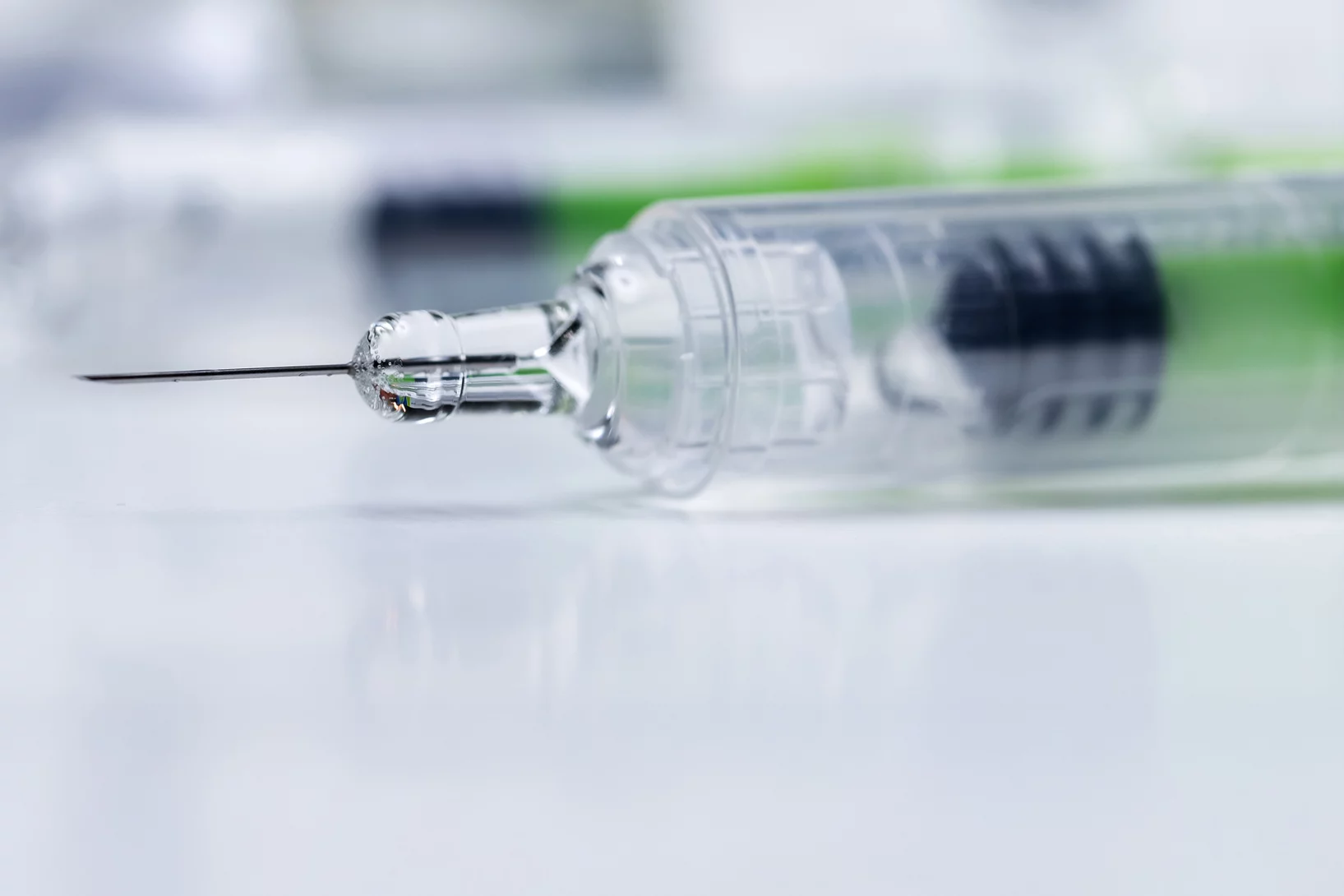
Zinc detected in clogged syringes
With the help of researchers at PSI, ANAXAM has been investigating, on behalf of the pharmaceutical company MSD, whether zinc may contribute to clogging of pre-filled syringes.
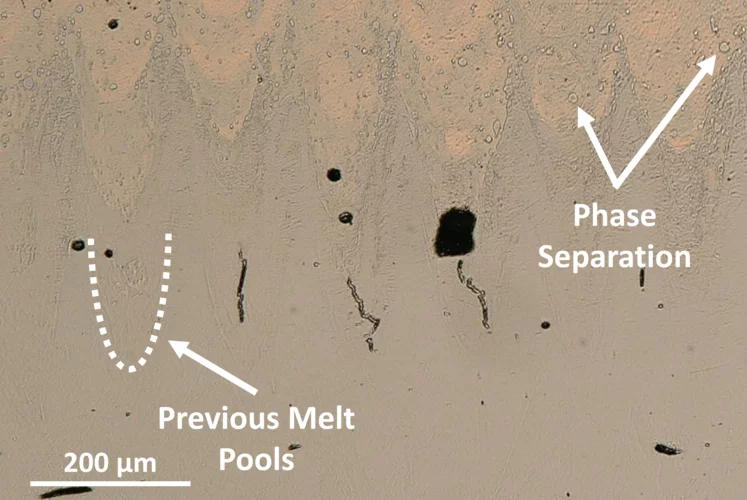
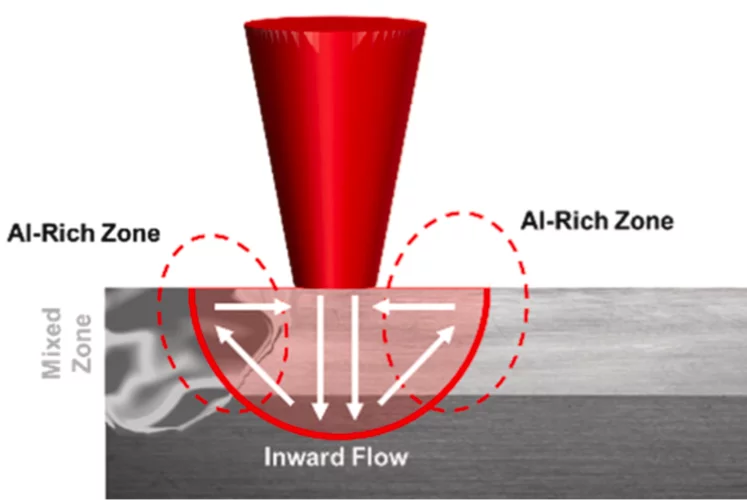
Cracking the Challenge of Steel–Copper Fusion
Why do cracks appear when joining steel and copper? We track the mechanisms in real time to find out.
Interfacial Phase Formation in 316L–CuCrZr Hybrids
In-situ X-ray diffraction reveals how phase separation and fluid flow shape microstructure in laser-welded multi-material metal builds.
Phase by Phase: How Stainless Steel and IN625 Solidify Together
Where steel meets superalloy: real-time X-ray snapshots reveal how composition and cooling shape metal during 3D printing
AI paves the way towards green cement
Researchers at PSI are using artificial intelligence to develop environmentally friendly formulations for cement.
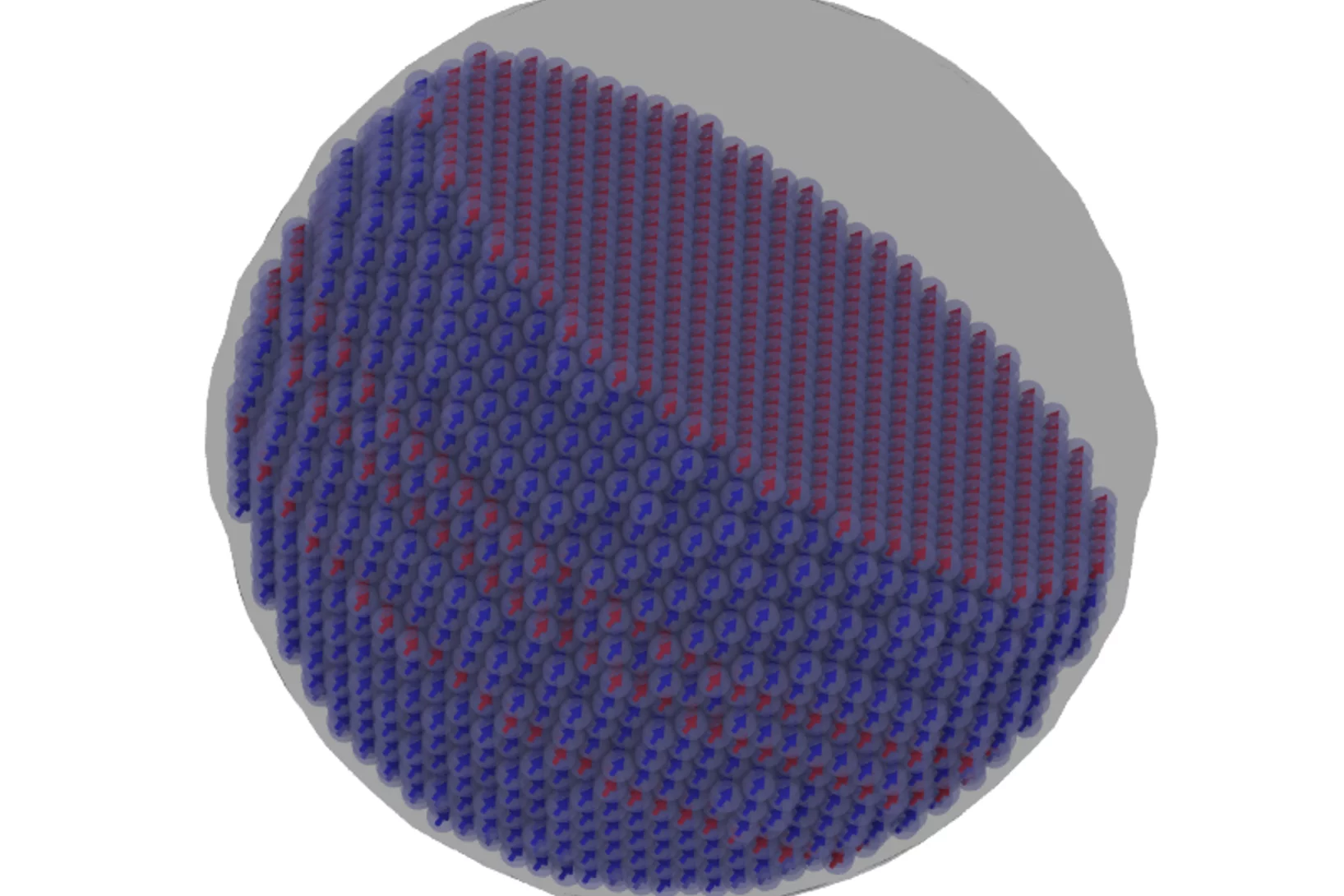
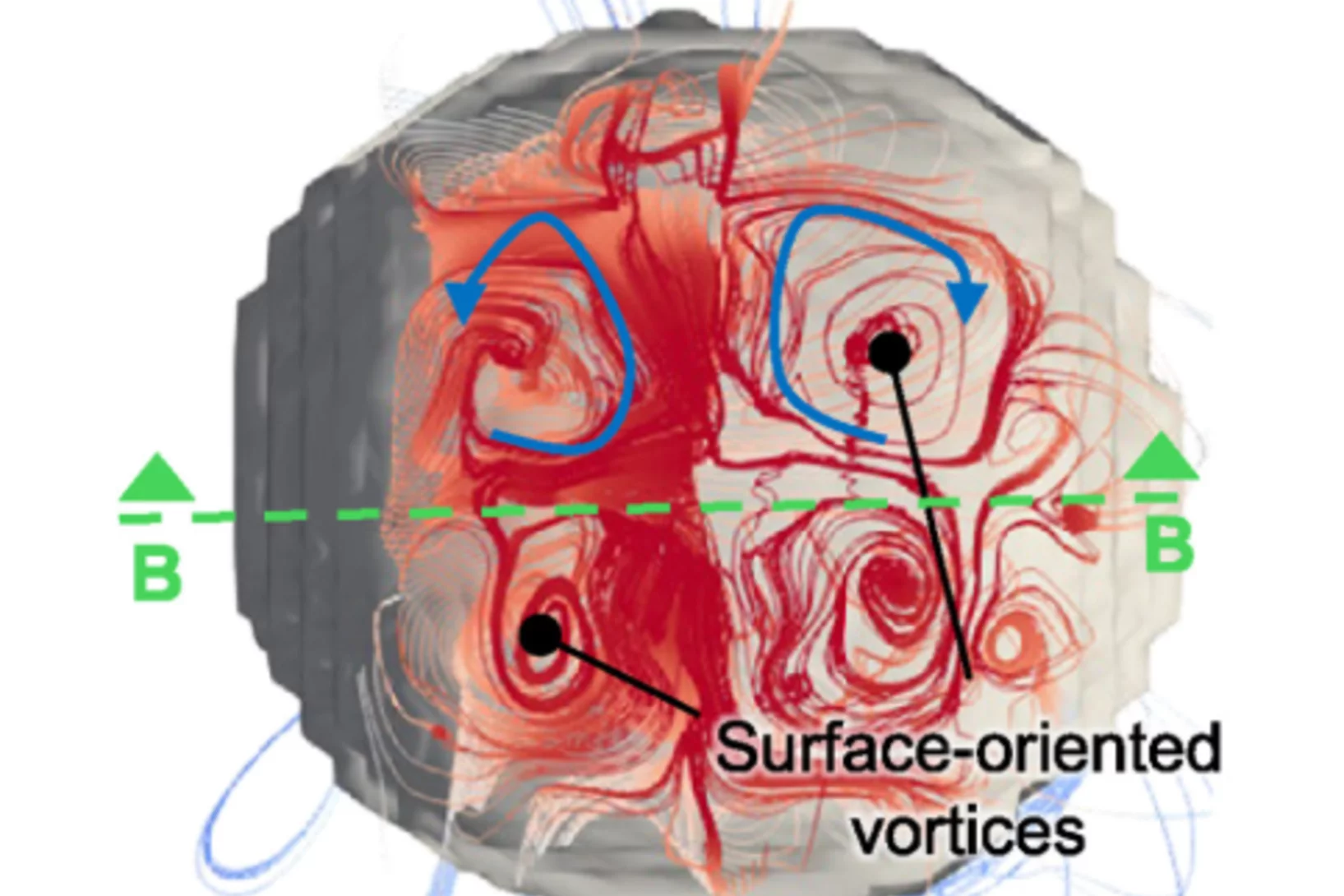
Steering magnetic textures with electric fields
Neutrons reveal a new way to control magnetism at the nanoscale
Stabilising fleeting quantum states with light
X-rays from SwissFEL probe emergent properties of quantum materials
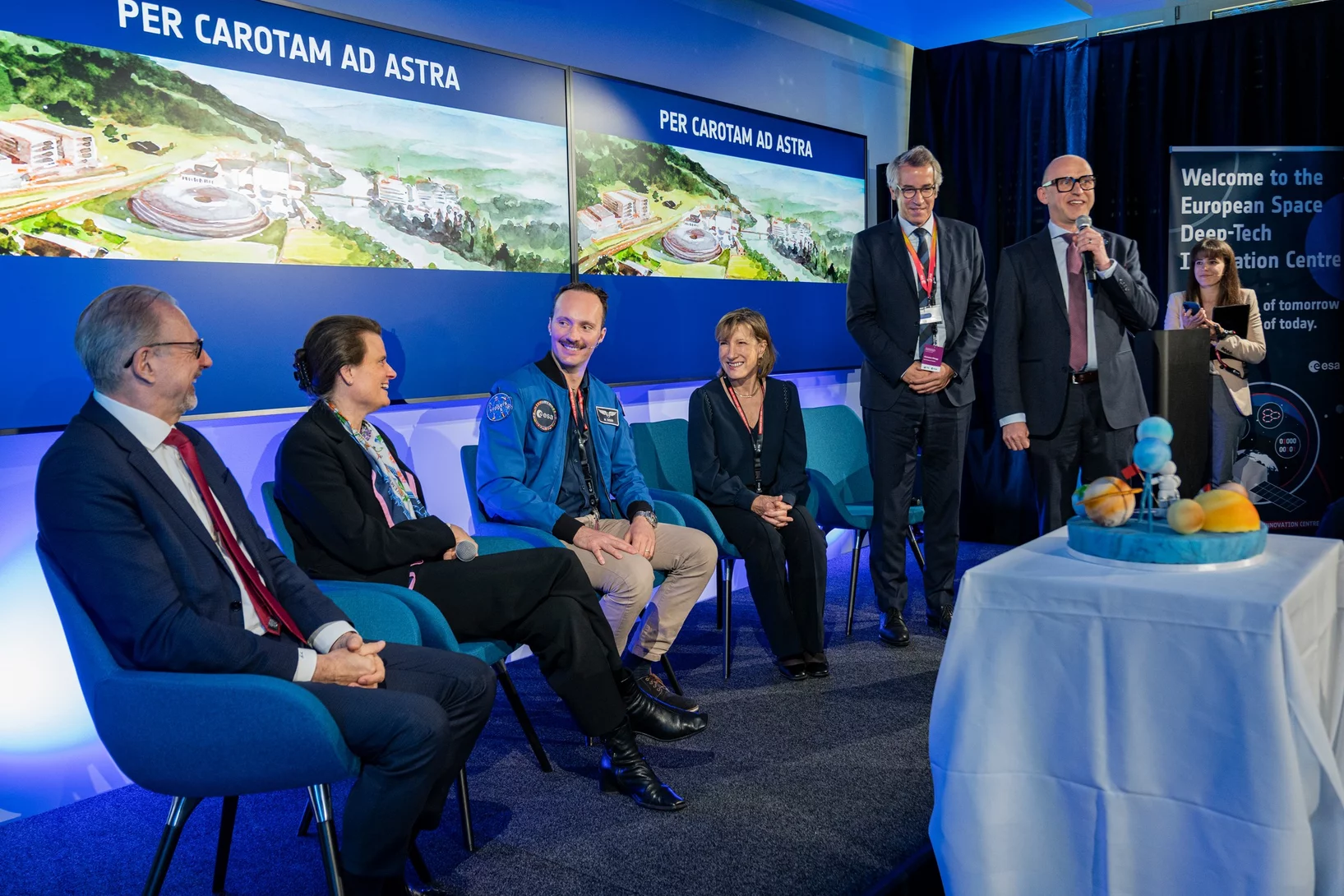
ESA Centre of Excellence opens in Switzerland
The opening ceremony of the “European Space Deep-Tech Innovation Centre” ESDI brought together distinguished guests.
Aluminium made visible
PSI researchers have for the first time determined the exact position of the aluminium atoms in zeolites, which make these materials such good catalysts.
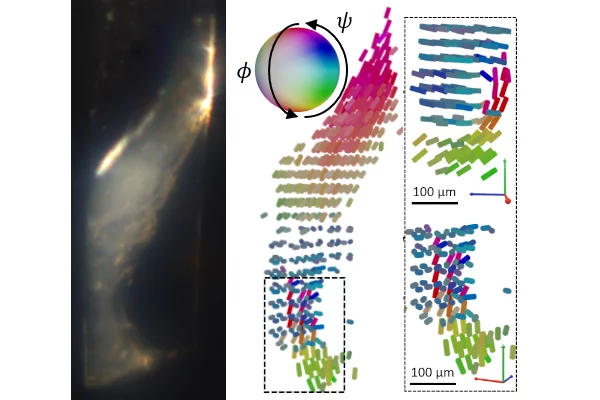
Nanostructure orientation in 3D with visible light by Tomographic Müller-Polarimetric Microscopy
We developed a new method, tomographic Müller-polarimetric microscopy (TMPM), that allows to retrieve at three-dimensional microscopic resolution the nanoscale structural information of the ultrastructure probed with polarized light in a non-destructive manner using a low cost and experimentally simple optical setup.
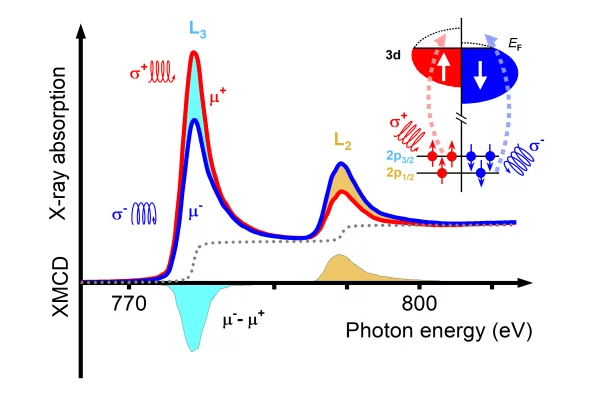
Primer on X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) is a magneto-optical effect that describes the difference in absorption between left and right circularly polarized X-rays by a magnetized material. It has been widely applied to the study of magnetic systems and of magnetic phenomena and its unique capabilities make it a fundamental tool for the study of novel magnetic phenomena and new materials systems.
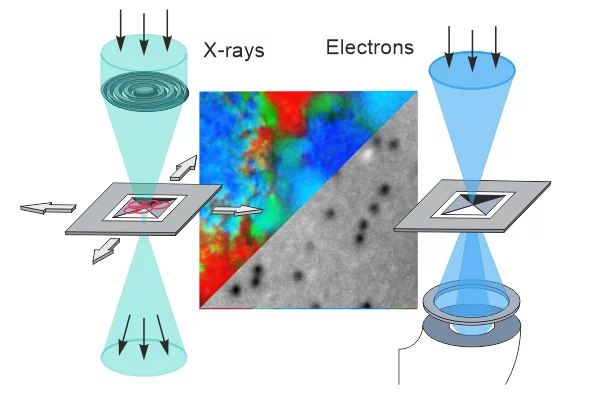
Correlating transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy to bridge atomic- and mesoscales
Transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy have contributed significantly to our understanding of phenomena in fields ranging from biology to materials science. In this review, we present recent developments in combining transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy techniques, including progress in sample environment, and in situ and operando approaches and highlight the unique opportunities offered by fully correlative transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy.
Antiferrodistortive and ferroeletric phase transitions in freestanding films of SrTiO3
Epitaxially grown thin films are commonly used to strain engineer electronic properties by the choice of a substrate, and therefore do not match bulk properties (leading to properties that deviate from the bulk material). Free standing ultrathin oxide films are expected to preserve the bulk-like properties due to the absence of substrate influence. However, we show that this expectation is not fulfilled with ultrathin free standing SrTiO3, as they get ferroelectric at 80K.
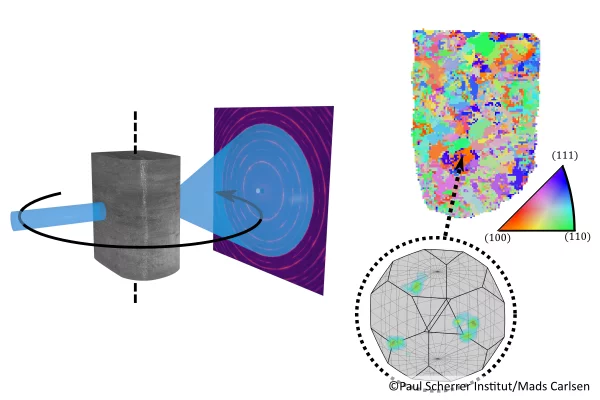
Mapping crystallite orientation in bulk polycrystals
A new experimental technique allows the orientation distribution of small-grained polycrystal materials to me mapped in 3D.
Defect structure controls the thermal magnetic switching rate of nano-sized metallic particles.
Past experiments done at the Paul Scherrer Institut, probed the thermal switching properties of nano-sized metallic magnetic particles
Rethinking 3D Printing for ceramics
Using a powerful combination of in-situ X-ray imaging and high-fidelity simulations, researchers uncover how alumina behaves under laser-based 3D printing—paving the way for more reliable ceramic additive manufacturing.
Prestigious funding for research at PSI
Concrete, chemical catalysis and the search for new physics – three PSI researchers have each received a grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation for these areas of research.
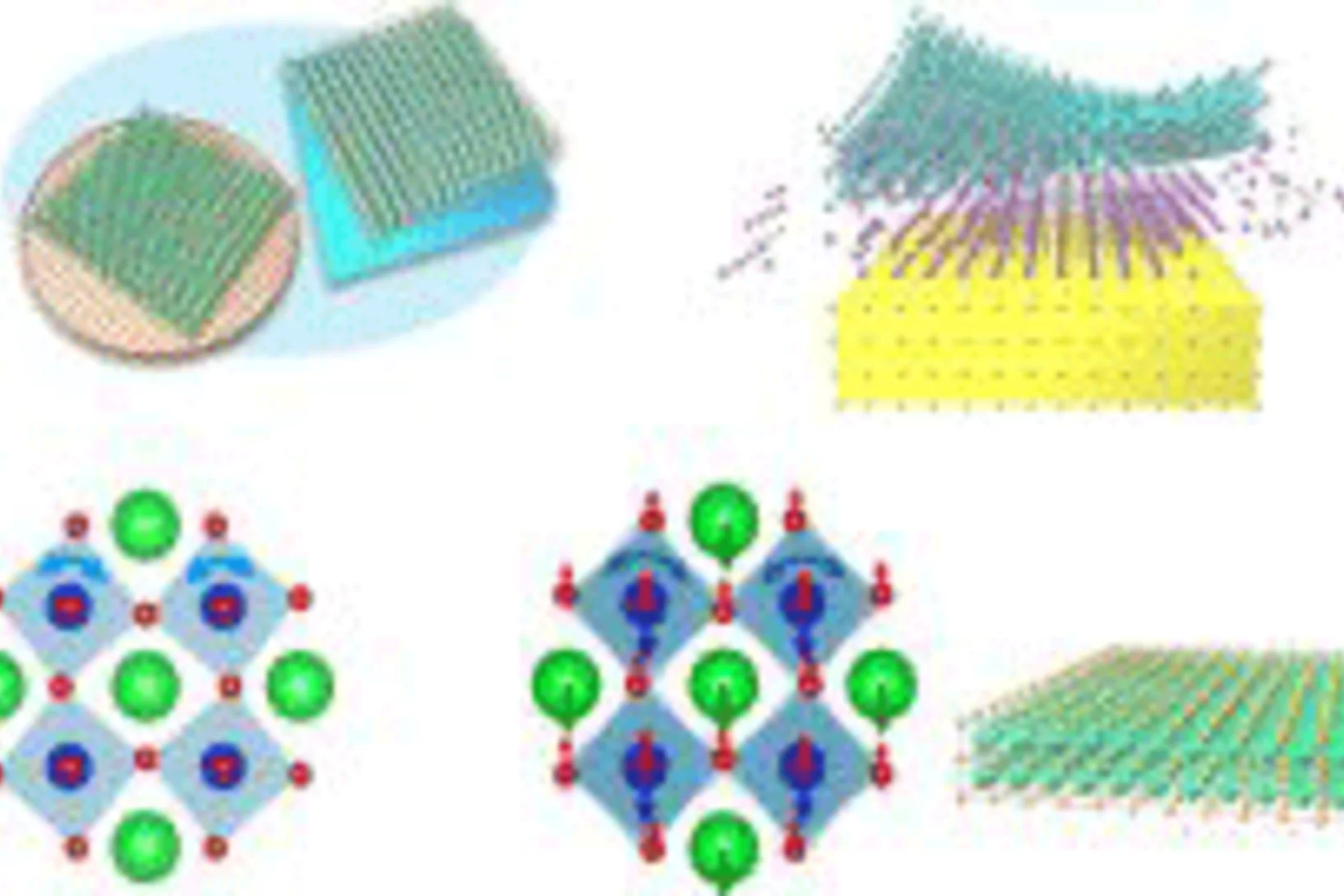
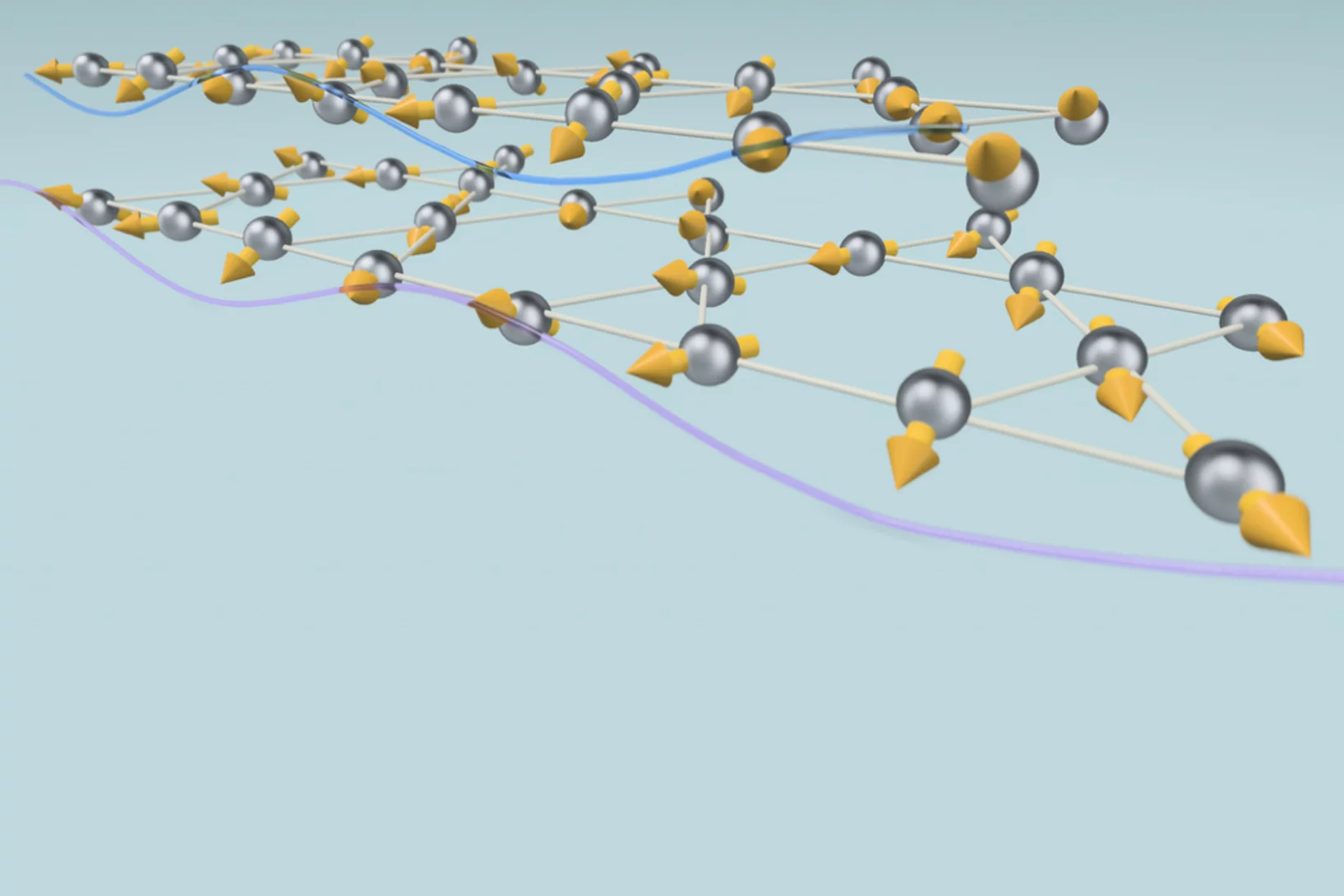
A new dimension of complexity for layered magnetic materials
X-rays reveal magnetic phenomena driven by interactions between the layers of a kagome ferromagnet
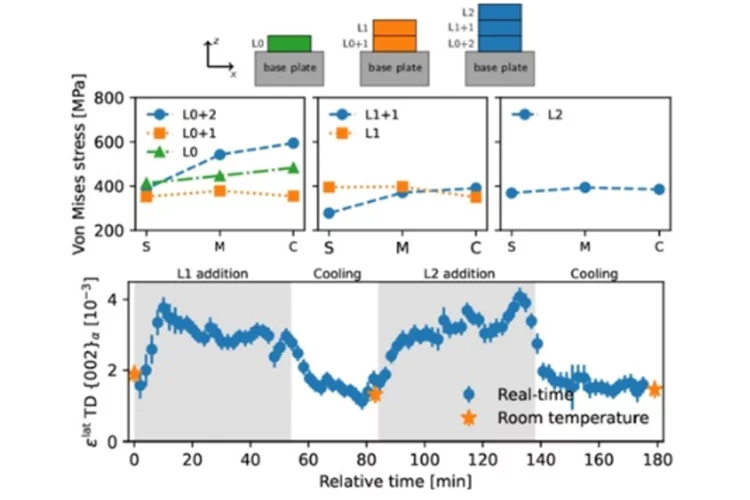
Texture and residual stress evolution during 3D printing
Discover how advanced neutron diffraction sheds light on the evolution of stress and texture in 3D-printed duplex stainless steel.
Mapping the ecosystem of Wannier Functions software
A new review article, just published in Reviews of Modern Physics and highlighted on the journal cover, provides a map to the vast landscape of software codes that allow researchers to calculate Wannier functions, and to use them for materials properties predictions. The authors, from all over Europe and the USA, include two PSI scientists. After providing readers with the theoretical foundations on Wannier functions and their calculation, together with intuitive graphical schematics to explain what Wannier functions are, the authors map the existing Wannier codes and the key applications.
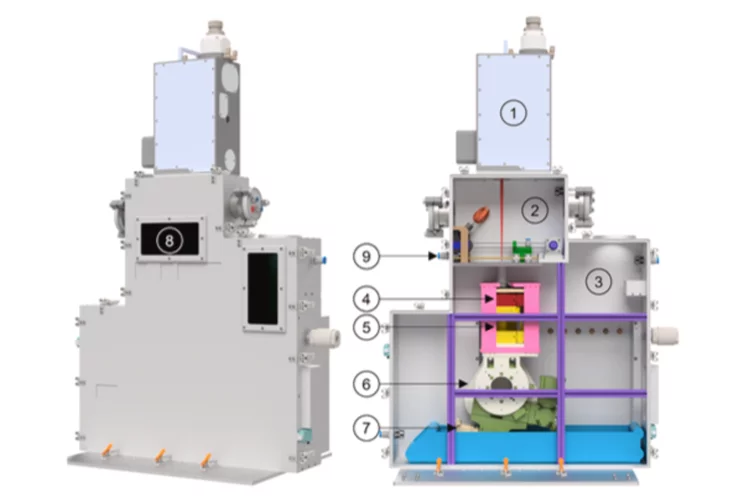
Operando Neutron Characterization During 3D Printing
A new laser powder bed fusion device enables real-time neutron diffraction and imaging, providing detailed insights into structural evolution, defect formation, and temperature mapping during metal additive manufacturing.
Mitigating Cracks in Multi-Material Printing
Integrating metallic powders with thin foils in laser powder bed fusion can reduce interfacial cracks and improve microstructure quality in titanium-aluminum multi-material printing.
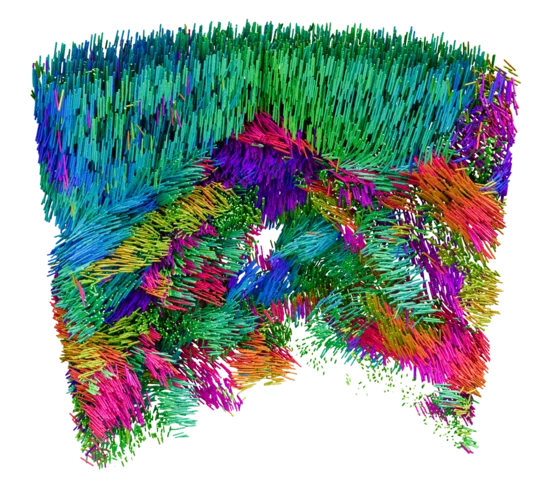
Mapping the Nanoscale Architecture of Functional Materials
A new X-ray technique reveals the 3D orientation of ordered material structures at the nanoscale, allowing new insights into material functionality.
New widgets and extensions expand the OSSCAR platform for educational notebooks in materials science
In a new article published in Computer Physics Communications, the team of the Open Software Services for Classrooms and Research project (OSSCAR) describes how to create custom widgets and extensions that can be used in interactive notebooks to teach computational materials science. The article also introduces two new entries in OSSCAR: a widget to display an interactive periodic table that allows users to group elements into different states, and one to plot and visualize electronic band structures and density of states.
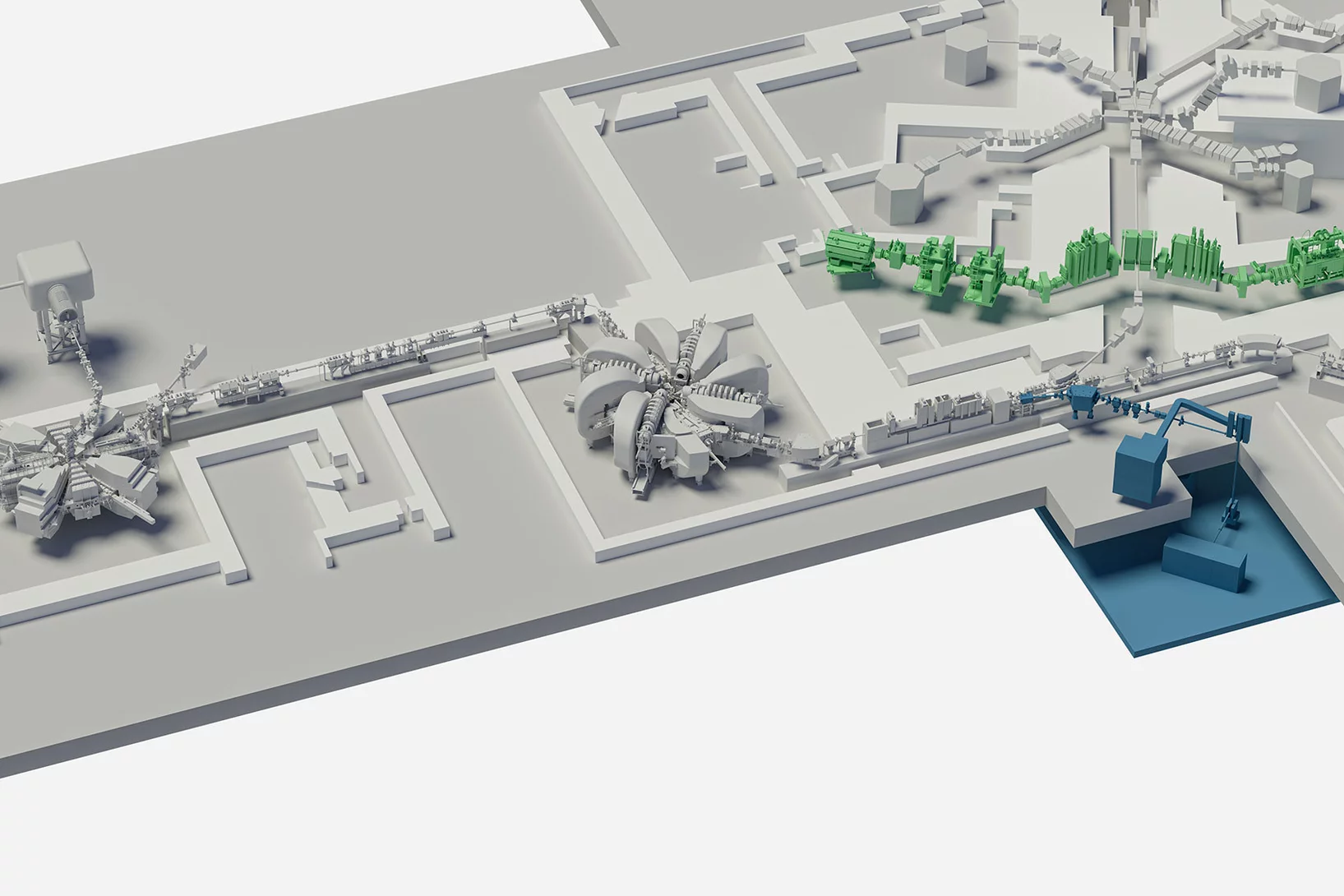
IMPACT for Swiss society
World leader in muons and in production of medical radionuclides: The far-reaching significance of the planned upgrade.
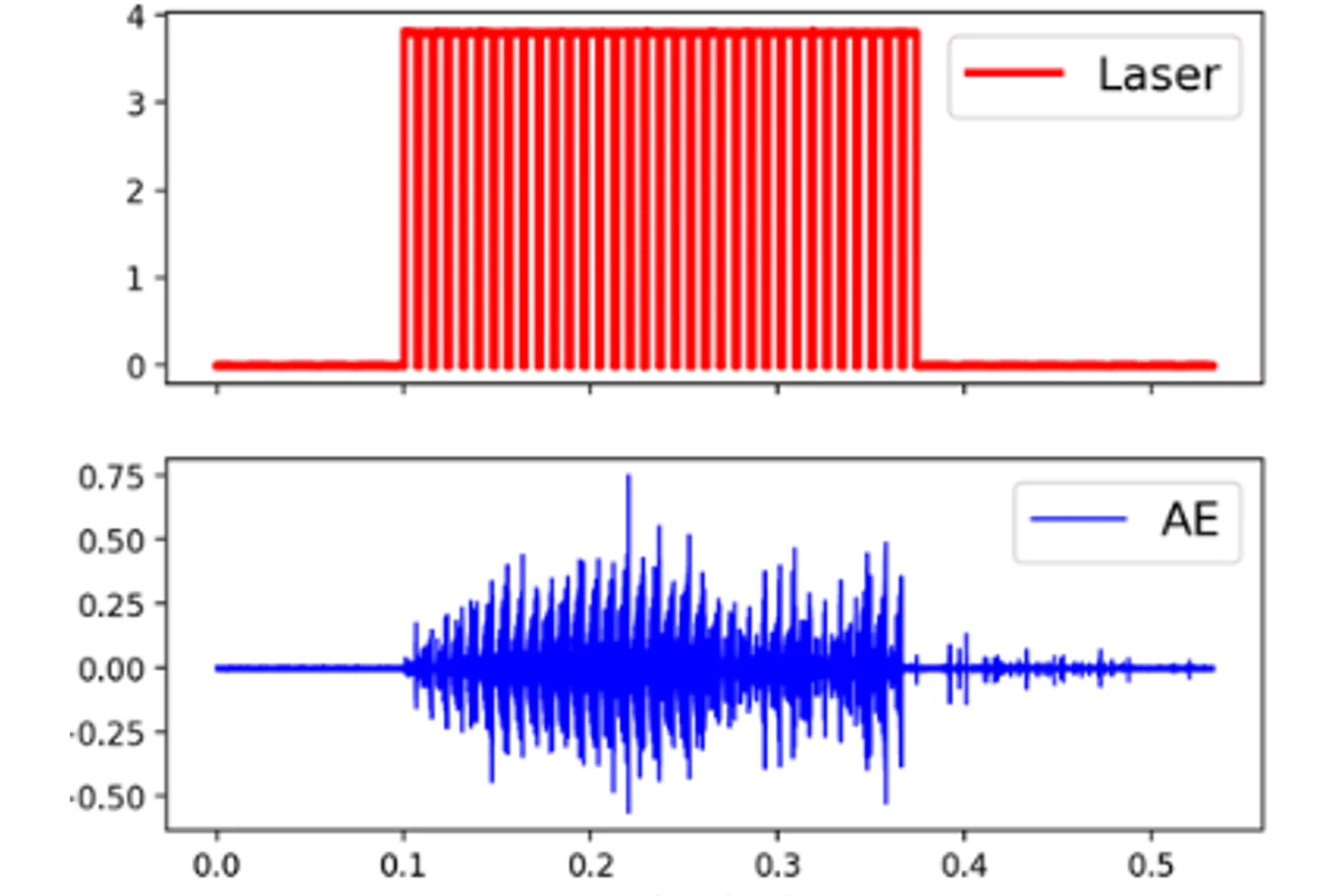
Acoustic emission signature of a martensitic transformation
Acoustic emission monitoring in 3D printing: real-time insights into martensitic phase transformations and crack formation.
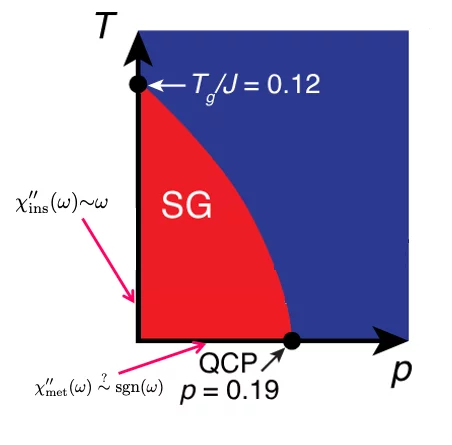
Exact solution of the classical and quantum Heisenberg mean field spin glasses
We solve and elucidate the physics of quantum Heisenberg spins glasses, which governs the local moments in randomly doped, strongly correlated materials.
ESA comes to Switzerland
The signing of a contract between the European Space Agency ESA and PSI marks the start of the European Space Deep-Tech Innovation Centre ESDI.
Magnetism in thin layers: One electron makes the difference
An important step towards novel computer memory
Orbitronics: new material property advances energy-efficient tech
Discovery of orbital angular momentum monopoles boosts the emerging field of orbitronics, an energy-efficient alternative to electronics.
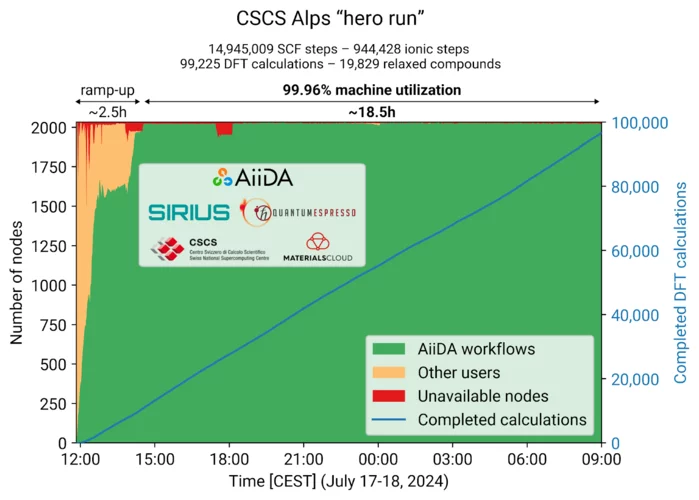
Computational marathon matches the efficiency of the AiiDA platform with the power of Switzerland Alps supercomputer
A group of researchers from the LMS lab at PSI has conducted a "hero run" on the new Swiss supercomputer, occupying it entirely for about 20 hours with calculations managed remotely by the AiiDA software tools. The run demonstrated the efficiency and stability of AiiDA, that could seamlessly fill the entire capacity of an exascale machine, as well as the performance of the Alps supercomputer, that has been just inaugurated. All the results will soon be published on the Materials Cloud.
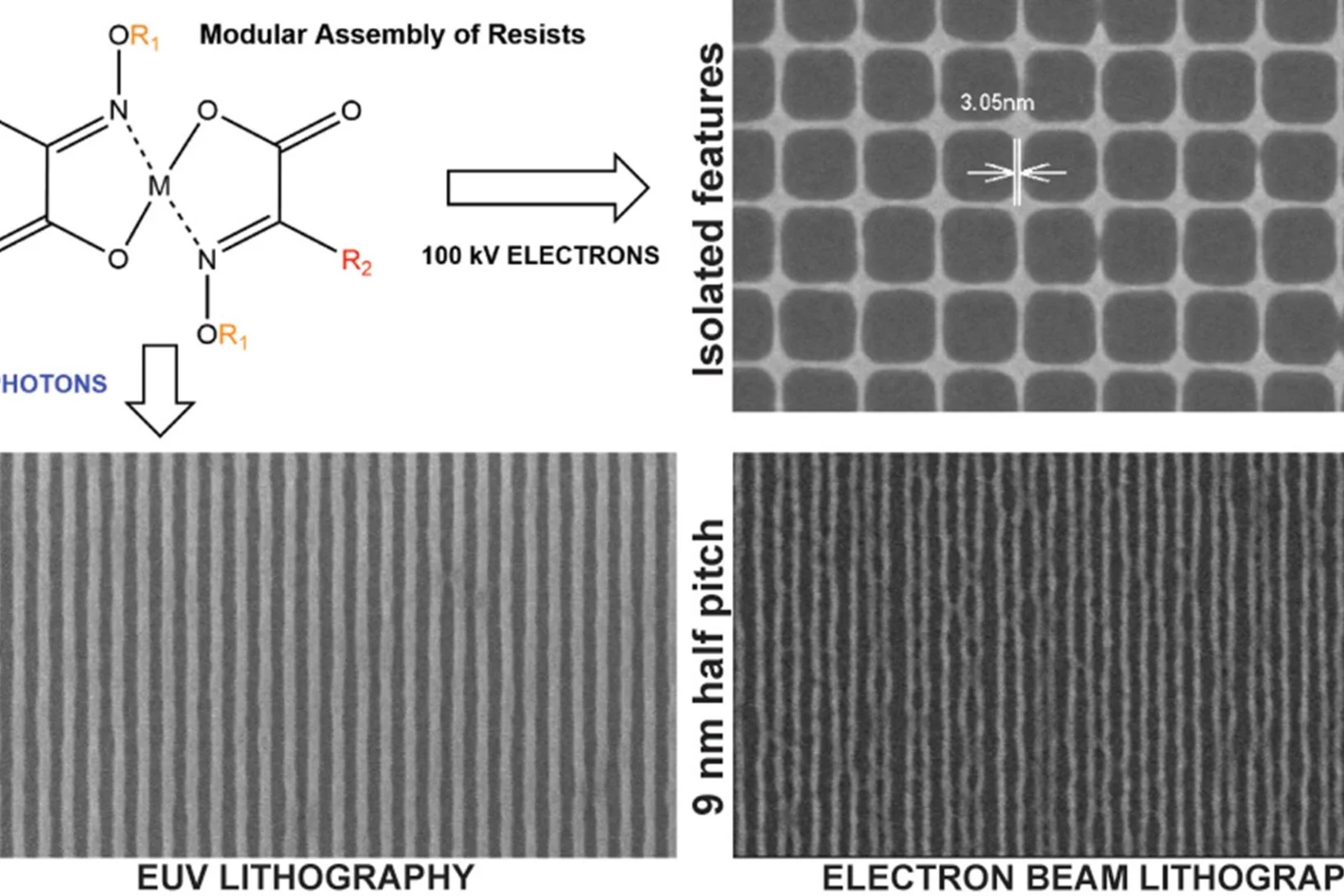
Novel Photoresist Chemistry Enables Lithography Approaching Angstrom-Scale Resolution
Photoresist materials are crucial in the manufacturing of computer chips, where the circuits are initially printed in the photoresist using photolithography. As the demand for smaller and more precise circuitry in computer chips grows, photoresists must resolve features with smaller sizes and higher density. One of the factors determining the ultimate resolution in lithography is the molecular size/mass of the photoresists.
International collaboration lays the foundation for future AI for materials via the OPTIMADE standard
Artificial intelligence (AI) is accelerating the development of new materials. A prerequisite for AI in materials research is large-scale use and exchange of data on materials, which is facilitated by a broad international standard. A major international collaboration including researchers from the LMS laboratory now presents an extended version of the OPTIMADE standard.
Charge fractionalisation observed spectroscopically
Quantum mechanics tells us that the fundamental unit of charge is unbreakable – but exceptions exist.
„IMPACT is very important in terms of international competition“
Daniela Kiselev talks about the upgrade planned at PSI's proton accelerator facility.
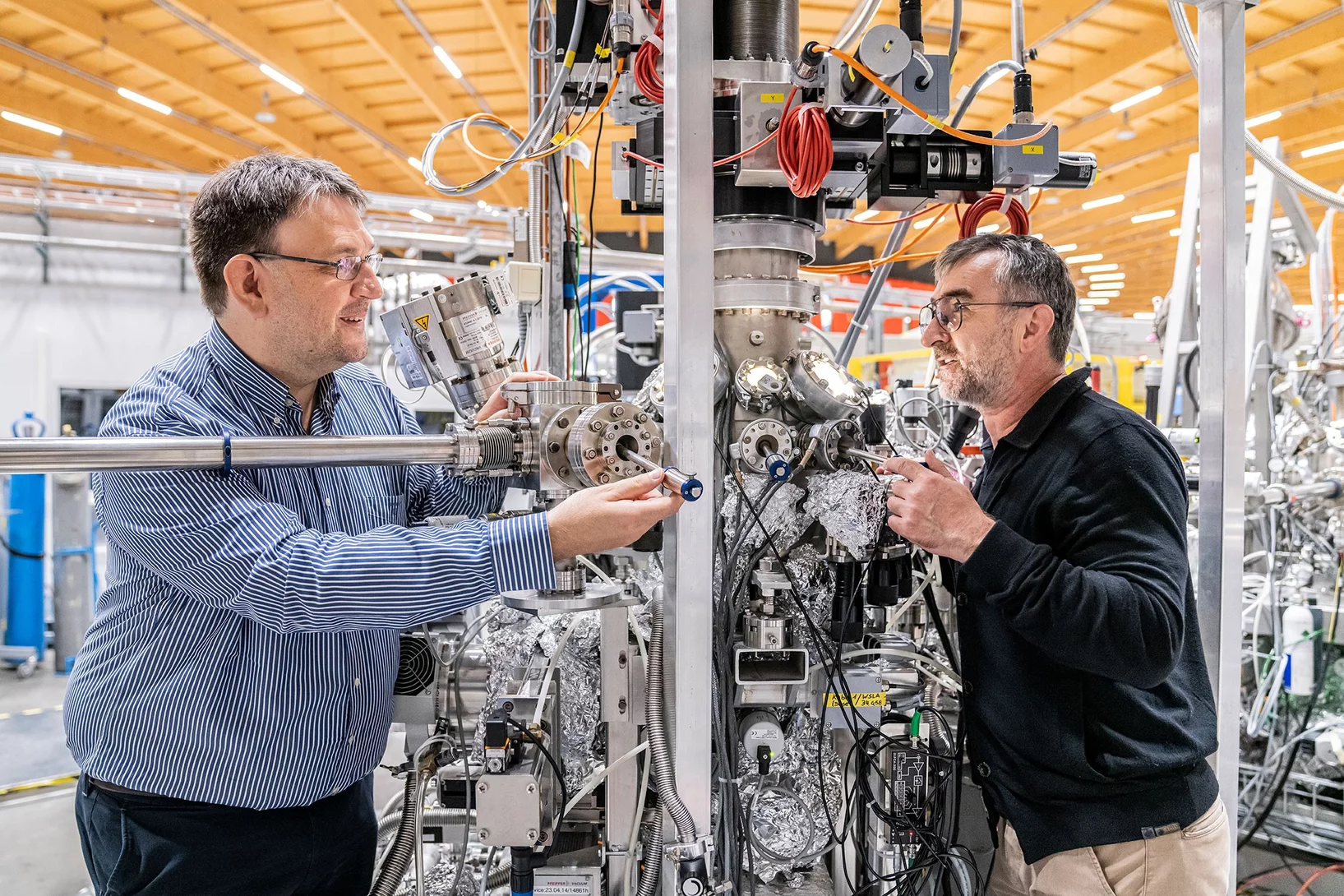
3D insights into an innovative manufacturing process
3D printing for creating complex shapes
PSI researchers use extreme UV light to produce tiny structures for information technology.
Synchrotron light can be used in follow-up after a heart transplant to determine whether the body may be rejecting the new organ.
“A jewel we must treasure”
HIMB is one of the two parts of the upgrade project IMPACT. Klaus Kirch speaks about the plans.
A two-part upgrade for the proton accelerator
A two-part upgrade is planned for HIPA starting in 2025. Preparations are already under way.
New materials for the computer of the future
Researchers are identifying and studying material compounds whose unique properties could lead to the development of novel types of chip.
Of fusion reactors, fuel cells, and tin cans
The technology transfer centre ANAXAM has been facilitating access to the material analytics at PSI.
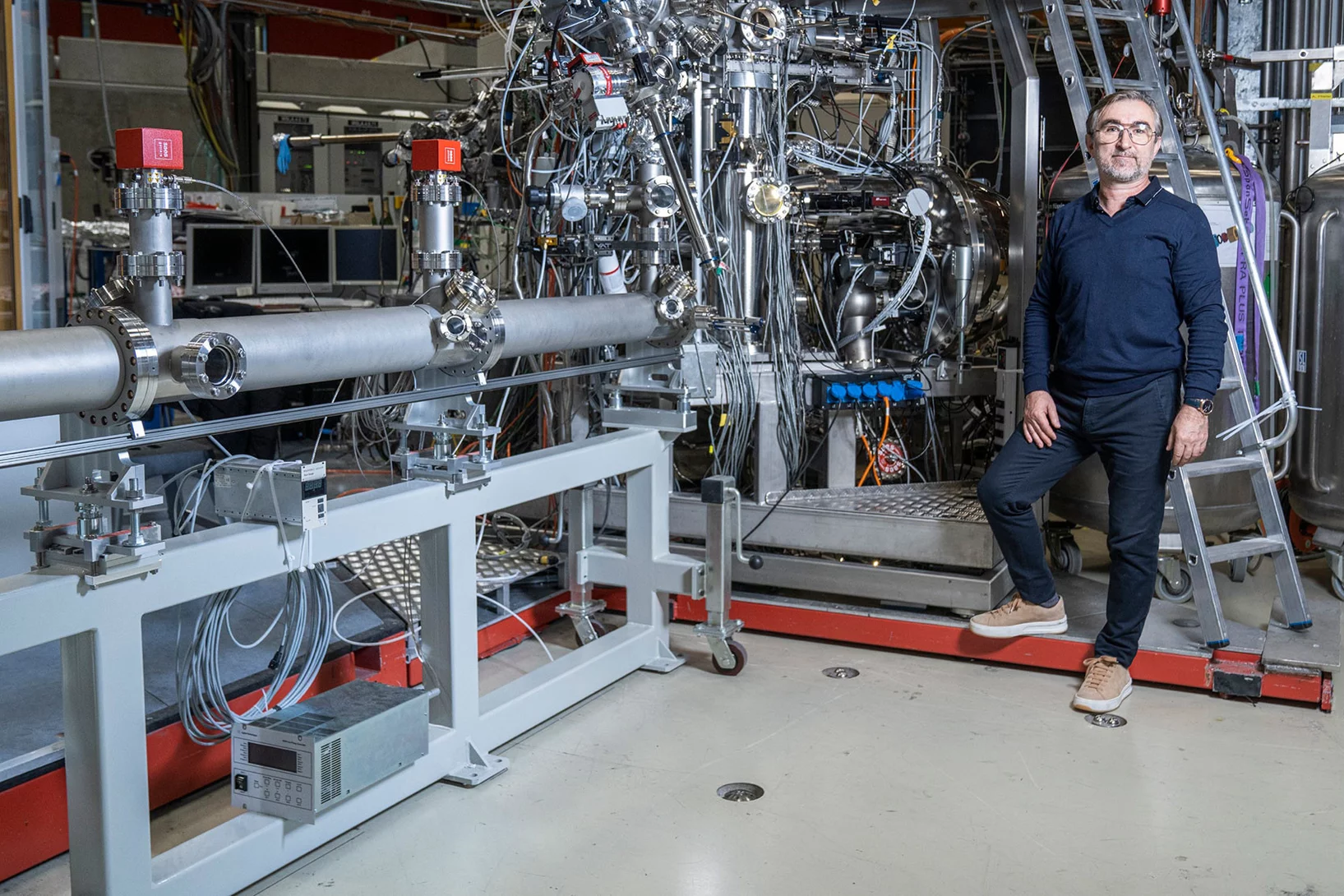
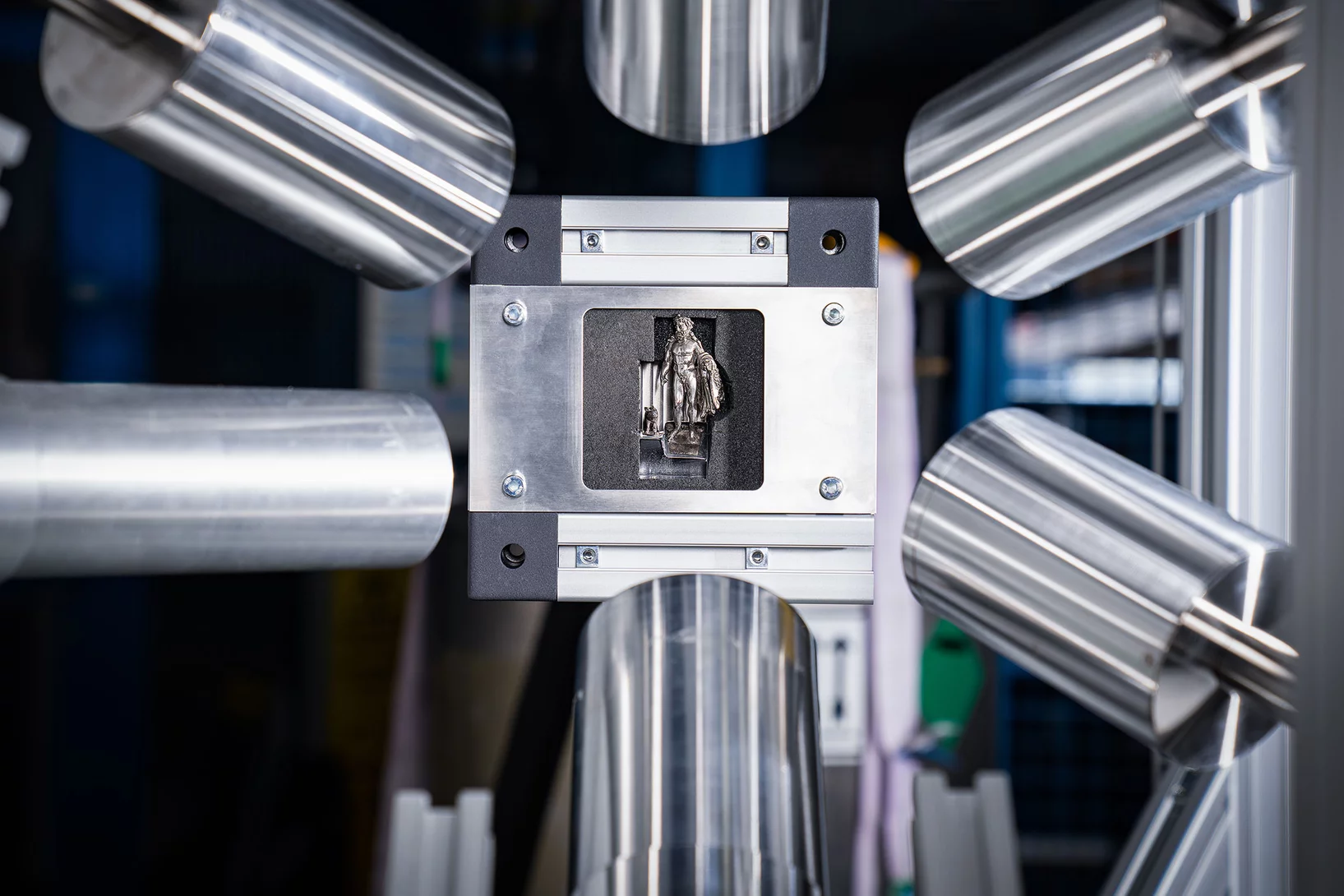
Hercules and batteries, X-rayed
With muons, PSI researchers can examine objects non-destructively. This helps in archaeology and battery development.
“If you’re in a certain position, you should step forward”
Kirsten Moselund heads the new Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Technologies. In this interview she discusses quantum research at PSI and how nanophotonics can assist with this.