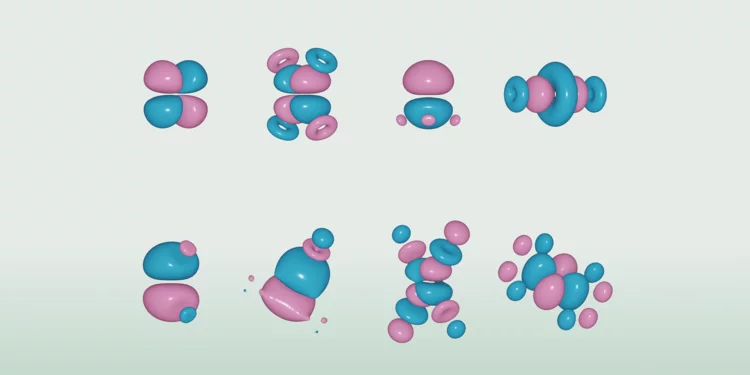Show filters
«Nous mettons tout en œuvre pour y parvenir»
Le PSI multiplie par 100 l’intensité de ses faisceaux de muons, ouvrant la voie à de toutes nouvelles possibilités pour la physique et la science des matériaux.
ISS @SLS 2.0
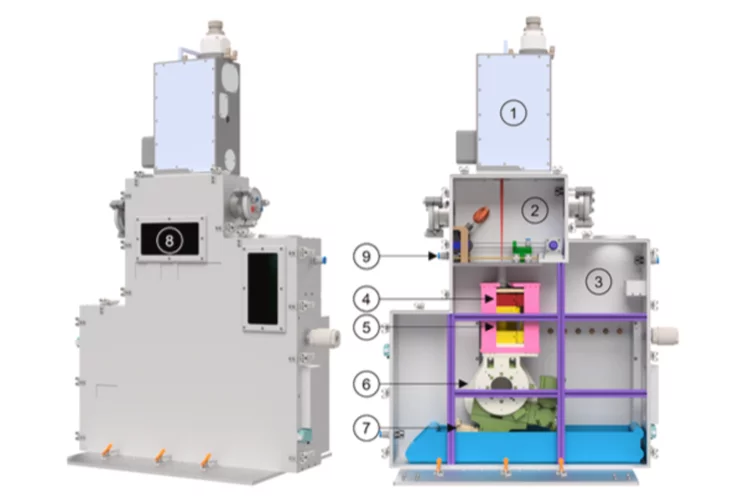
ISS received the first light on 10.07.2025. After that, the endstation has been reconnected and aligned. During the shutdown period, the ScientaOmicron R4000 HiPP-2 analyser has undergone maintenance and upgrade. It features now a new detector (new MCP and 70 Hz camera) and ethernet communication.
First in-house and pilot users have measured in November and December 2025. A first official call for proposals will open in February 2026 (deadline March 16th 2026, beamtime periods scheduled from September to December 2026). Please contact Dr. Luca Artiglia for more information.
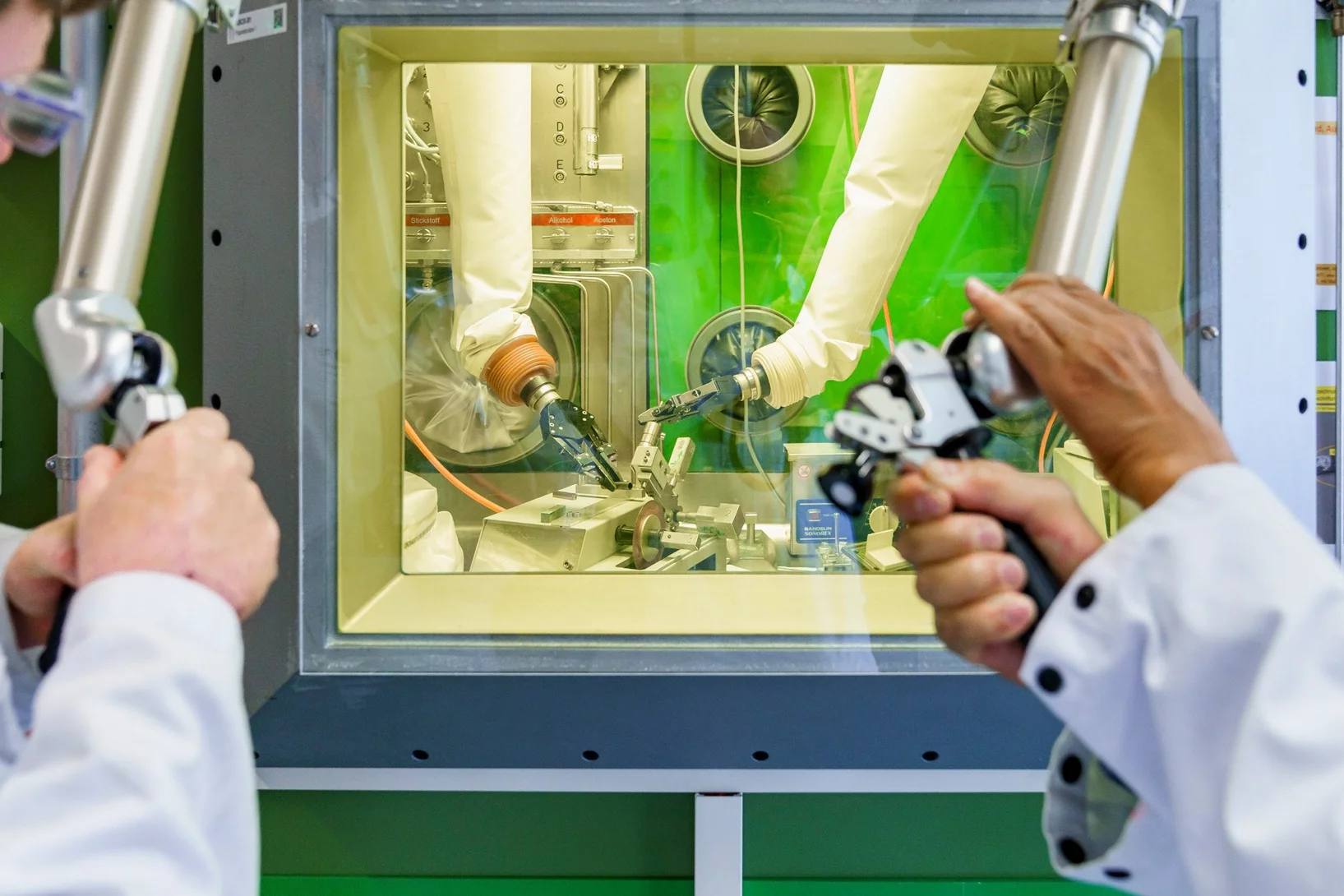
Un nouveau procédé pour des batteries tout solide stables et de longue durée
Des scientifiques du PSI ont développé un nouveau procédé qui rend les batteries tout solide plus résistantes et allonge leur durée de vie.
Chiral phonons in polar LiNbO3
Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering reveals that lattice vibrations can be chiral in a polar material, with phonons having opposite handedness depending on their direction in momentum space.
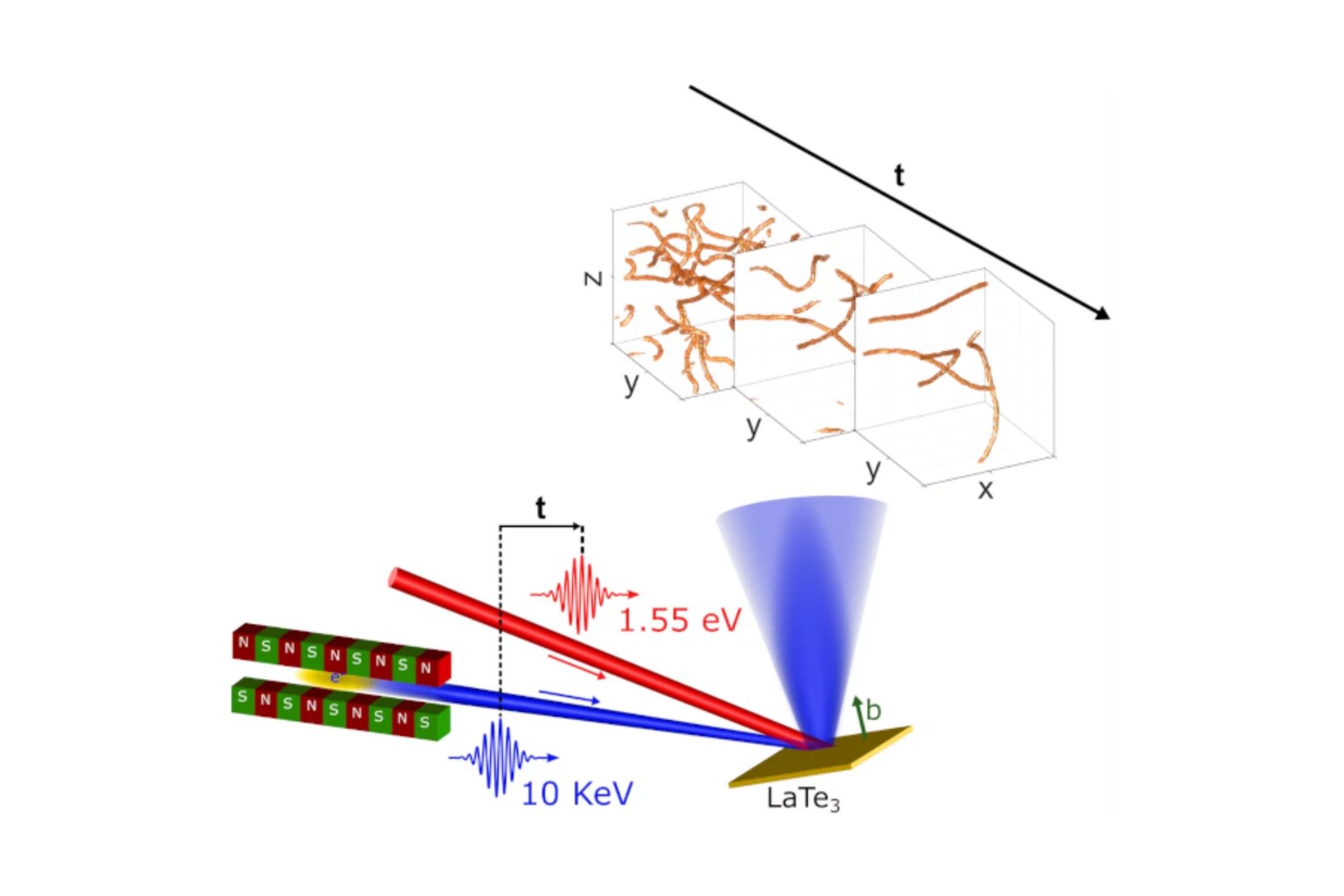
Uncovering Hidden Phases in 3D-Printed Fusion Steels
3D synchrotron X-ray mapping uncovered unexpected internal phase structures in laser-printed steels, showing how processing controls what we cannot see.
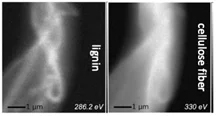
Preparing cellulose sample for soft-Xray spectro-microscopy
Different sample preparation techniques for ultrathin samples to be measured at the carbon-K-edge for chemical contrast are presented.
Un laser dessine des paysages magnétiques sur mesure
Des scientifiques du PSI ont découvert une méthode étonnamment rapide et bon marché pour modifier localement des matériaux magnétiques.
Two-dimensional gradients in magnetic properties created with direct-write laser annealing
Across the fields of magnetism, microelectronics, optics, and others, engineered local variations in material properties can yield groundbreaking functionalities that play a crucial role in enabling future technologies. One-dimensional lateral gradients in material properties give rise to a plethora of new effects in thin-film magnetic systems. However, extending such gradient-induced behaviors to two dimensions has been challenging to realize experimentally. Here, we demonstrate the creation of two-dimensional complex patterns with continuous variations in magnetic anisotropy, interlayer exchange coupling, and ferrimagnetic compensation at the mesoscopic scale in numerous application-relevant magnetic materials. We exploit our engineered gradients in material properties to demonstrate novel magnetic functionalities, including the creation of a spin wave band pass filter and an architecture for passively resetting the position of a magnetic domain wall. Our results highlight the exciting new physics and device applications enabled by two-dimensional gradients in thin film properties.
Predicting component lifetimes in nuclear facilities
For 30 years, experiments have been providing unique insight into how metals and ceramics degrade under high-energy proton bombardment.
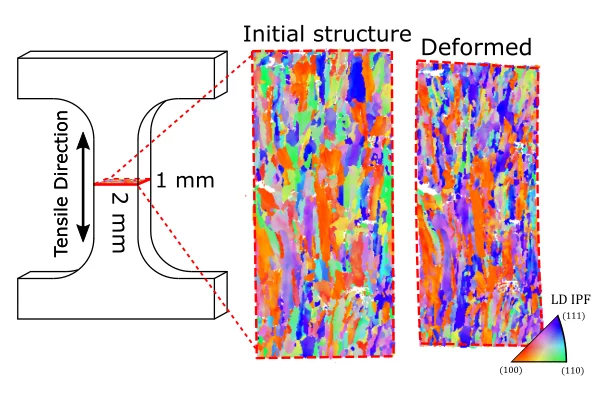
Following Twin-Formation in 3D Printed Steel
Using hard-xray microscopy to study the deformation of 3D printed steel.
From Melt to Martensite
Real-time synchrotron X-ray diffraction reveals how different phases of steel emerge and evolve under the intense heat of laser powder bed fusion.
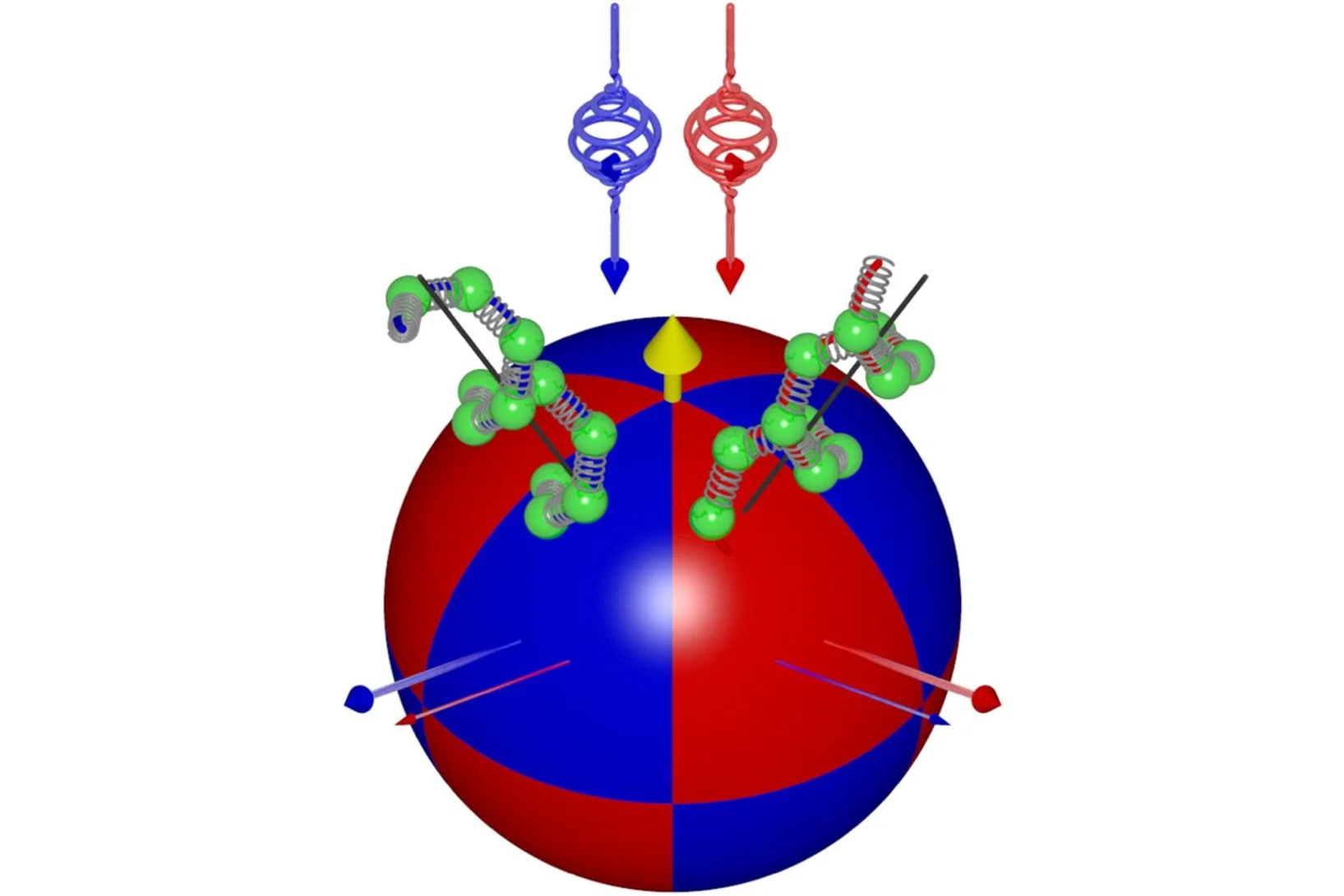
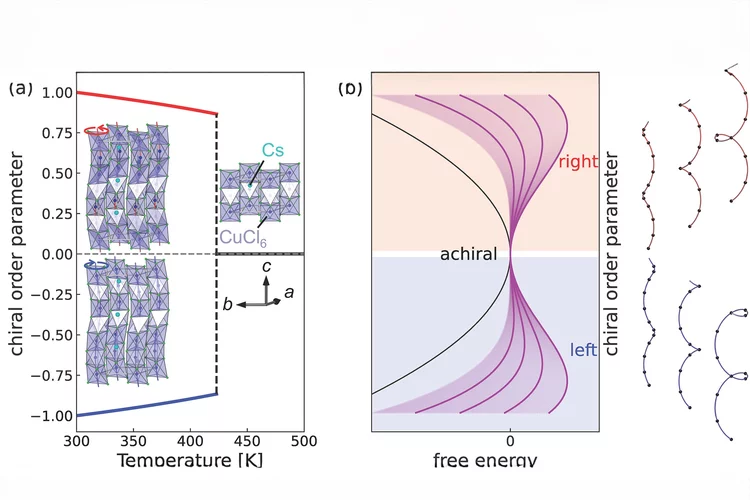
Tuning chirality amplitude at ultrafast timescales in chiral CsCuCl3
We quantify “how chiral” a crystal is, and demonstrate its tunability at ultrafast timescales. This achievement does open up a new direction in chirality-related condensed matter physics and on emergent phenomena, which have both attracted significant attention recently.
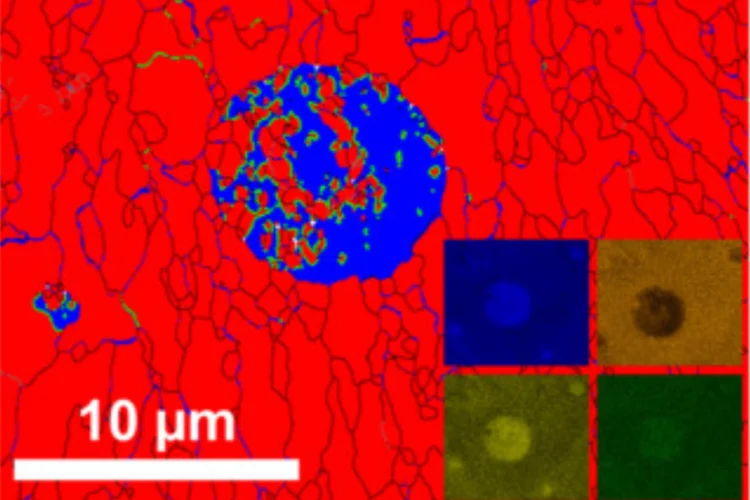
Why Ni-Cu Alloys Fail in 3D Printing
3D printing with nickel–copper alloys holds great promise — but hidden mechanisms can cause them to crack. Our latest study reveals why.
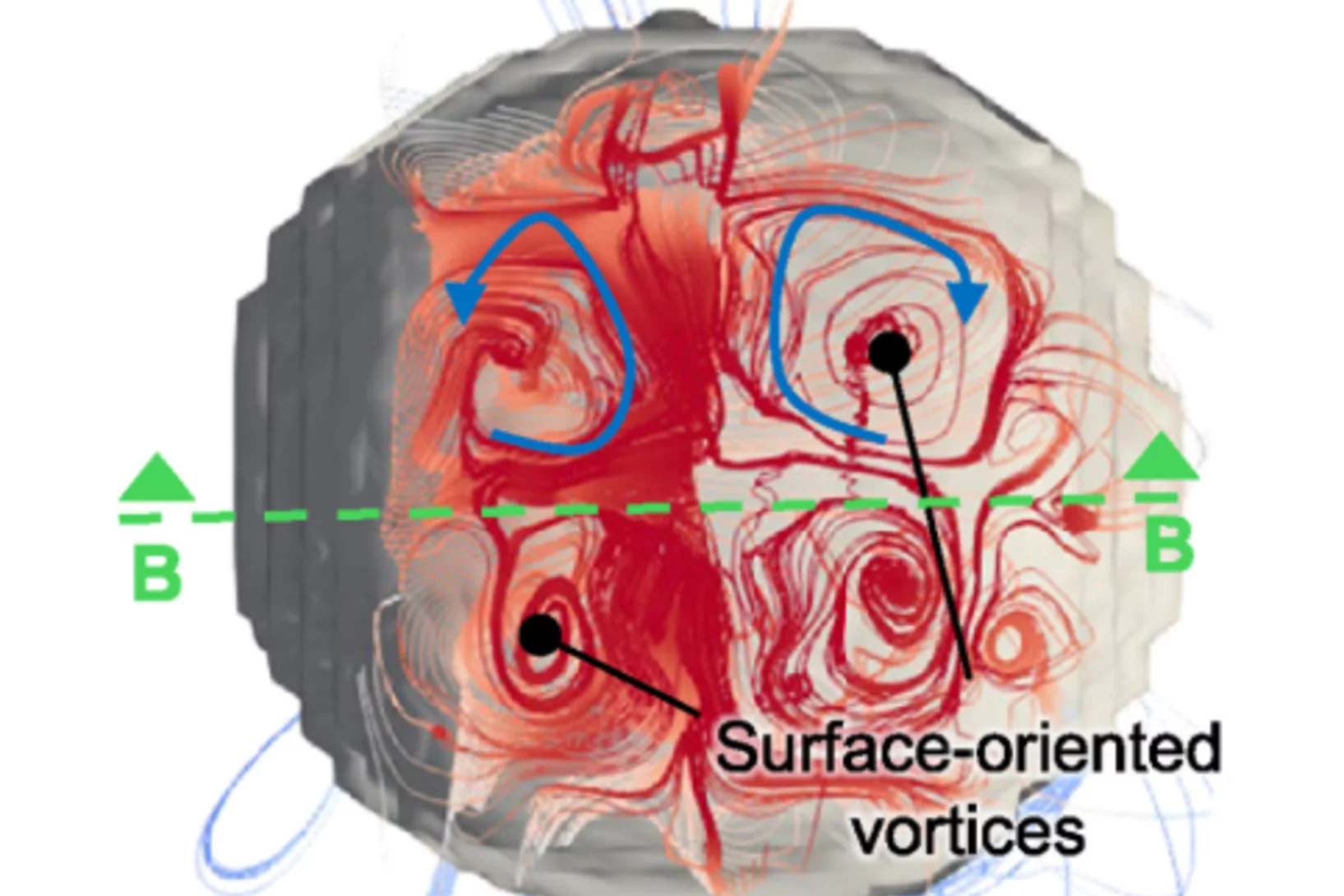
Topological defects determine evolution of charge density wave phase transition
Total scattering signals collected at SwissFEL reveal the role of topological defects when switching properties of a charge density wave material. The defect formation and dynamics after laser excitation reveals new insights into the functionality of quantum materials.
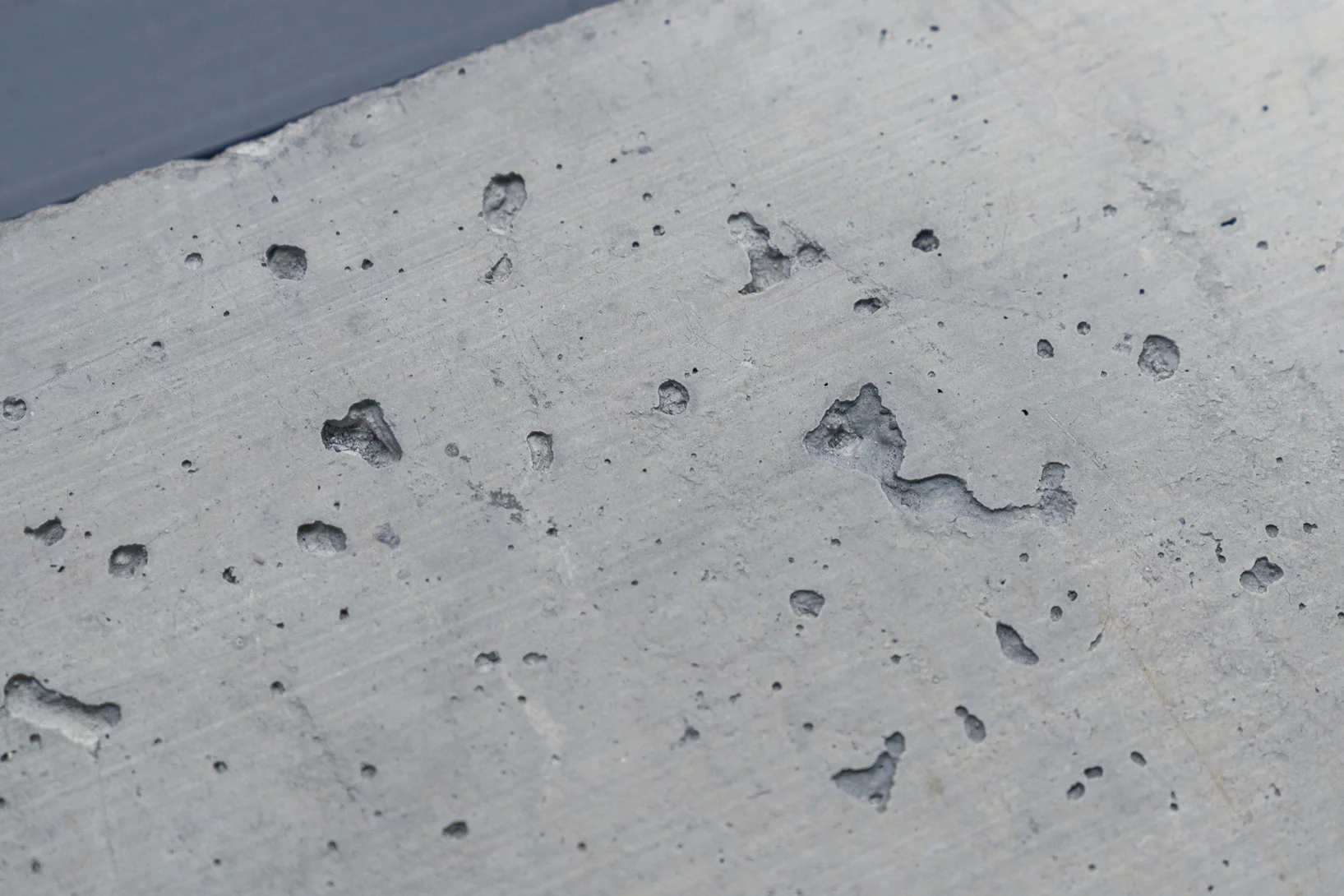
Au PSI, un homme qui murmure à l’oreille du ciment
John Provis a dédié sa vie de chercheur à un matériau de construction qui s’avère plus passionnant qu’il n’en a l’air.
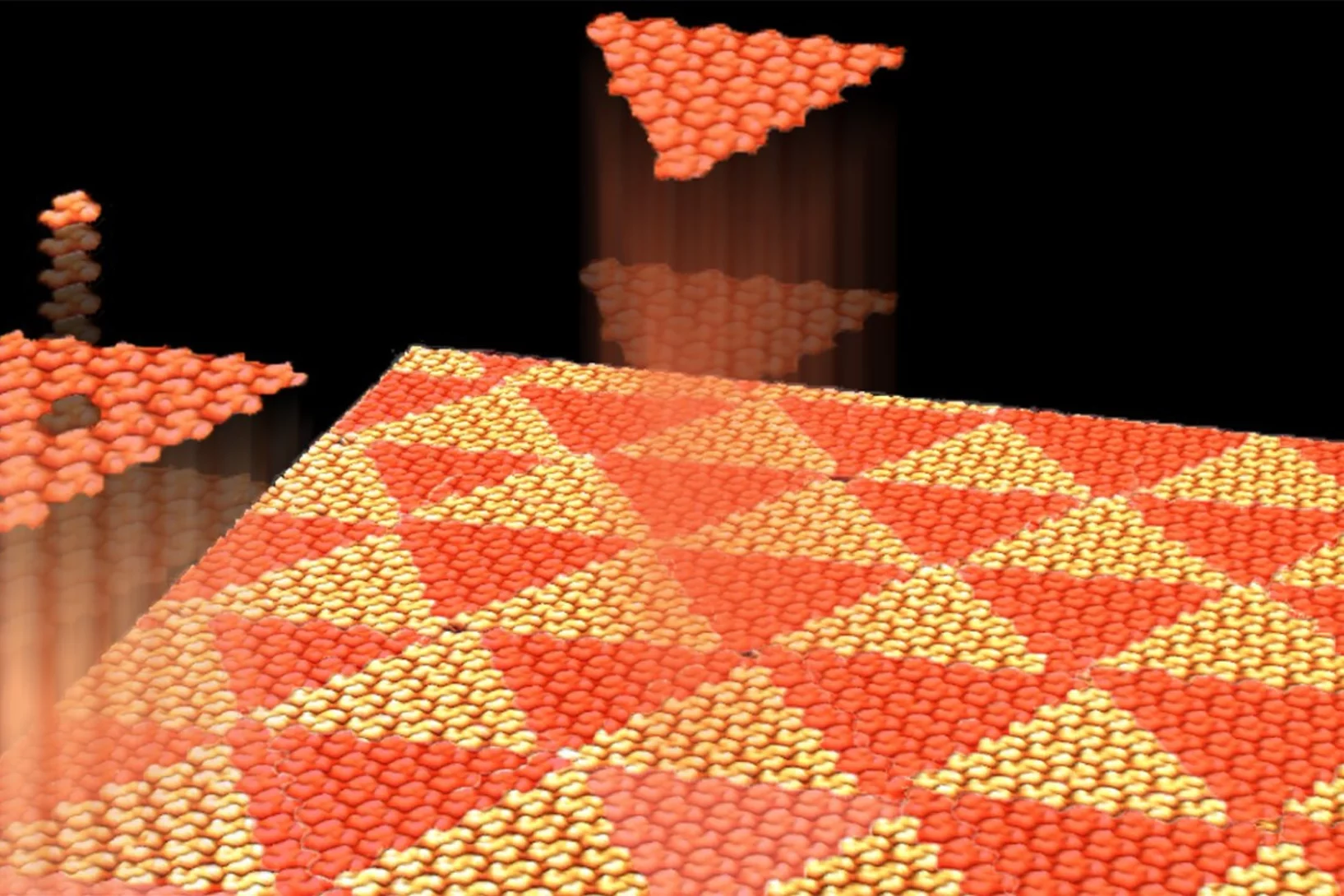
Aperiodic Chiral Tiling by Molecular Self-Assembly
The 2D self-arrangement of a molecule that resembles three-armed spirals leads to a triangular pattern that is effectively aperiodic.
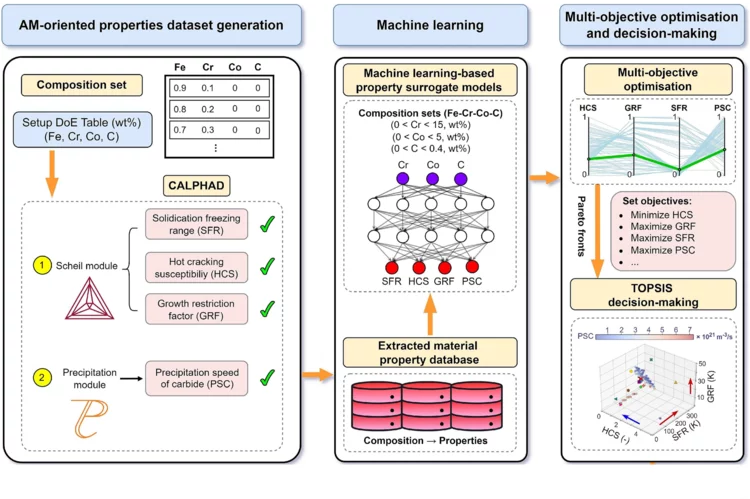
Machine Learning Accelerates Alloy Design for Additive Manufacturing
A new machine learning–designed alloy demonstrates how materials can be tailored for specific performance properties required in additive manufacturing.
Du zinc détecté dans des seringues obstruées
Pour l'entreprise pharmaceutique MSD, ANAXAM a étudié, avec l'aide de scientifiques du PSI, si le zinc pouvait contribuer à l'obstruction des seringues préremplies.
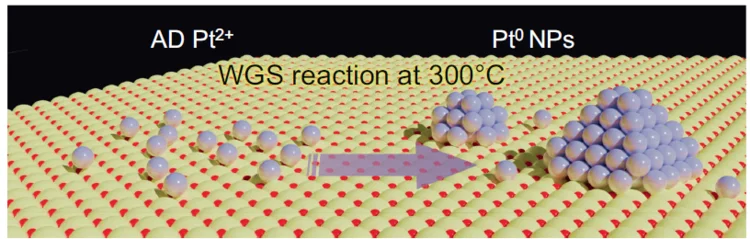
In situ characterization of structure-activity relationships on actual catalysts for water gas shift
By combining in situ XPS measurements carried out at ISS with theoretical calculations, reactivity/kinetics tests and high resolution electron microscopy, it was demonstrated that the reactivity of a Pt/CeO2 towards the low temperature water gas shift reaction is boosted on small platinum clusters originated by sintering of atomically dispersed species. A comprehensive model allowed to determine the most active sites, which are corner sites at the perimeter between platinum and ceria.
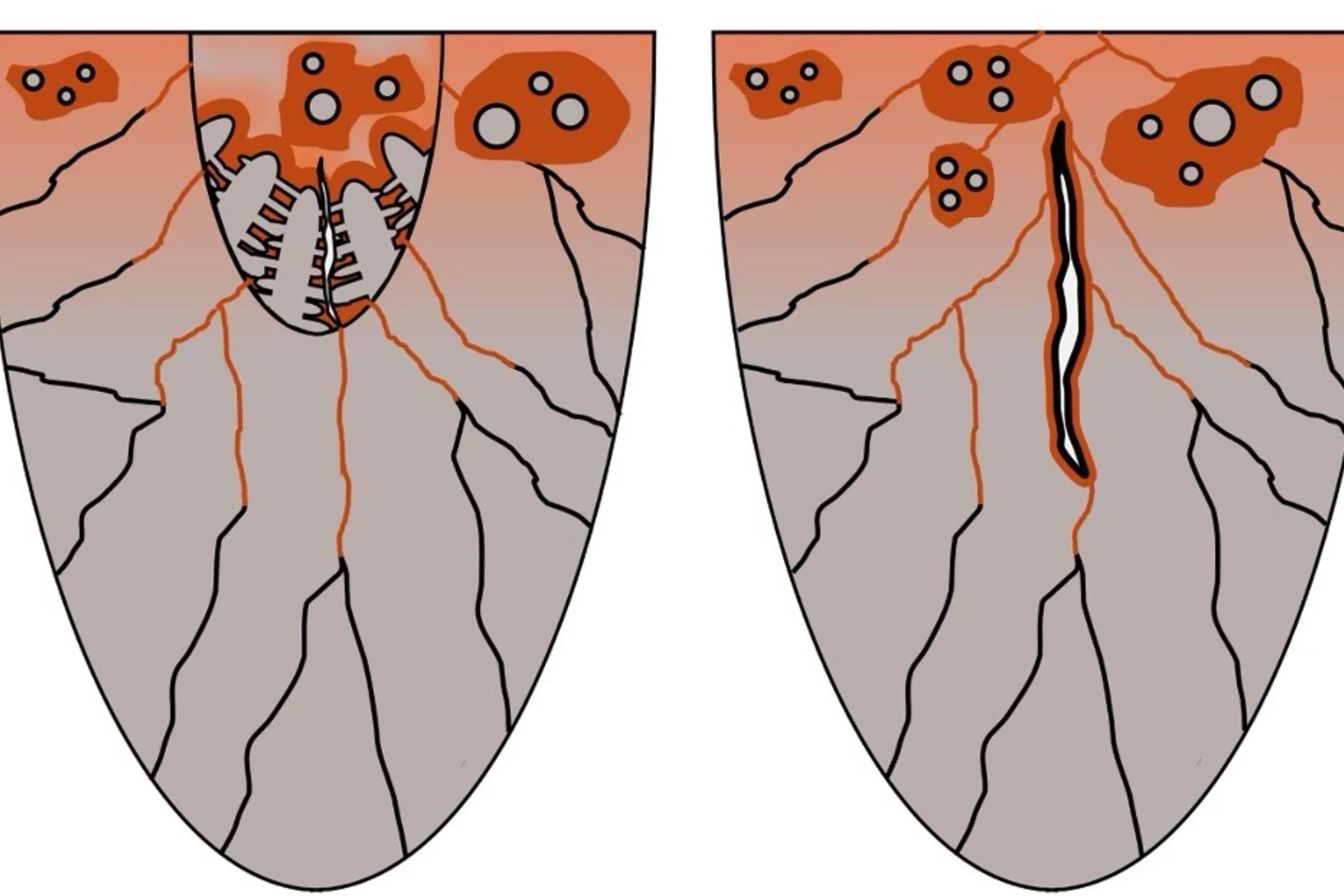
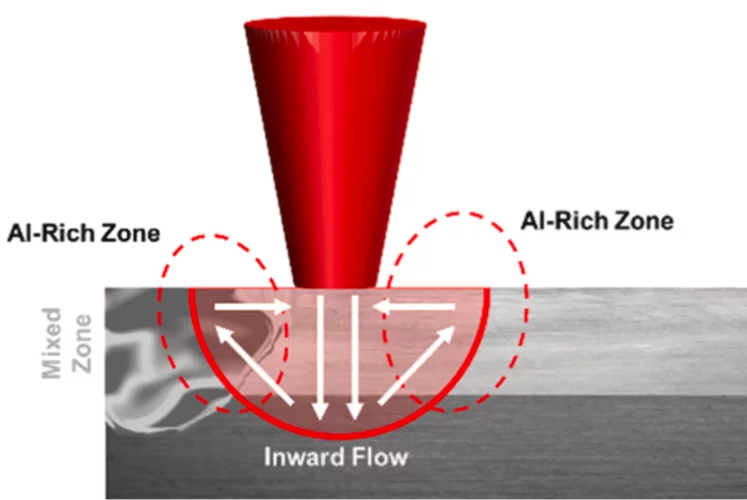
Cracking the Challenge of Steel–Copper Fusion
Why do cracks appear when joining steel and copper? We track the mechanisms in real time to find out.
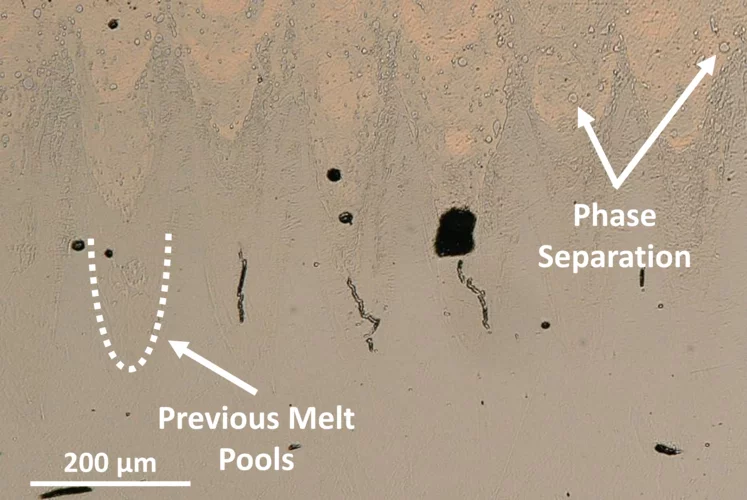
Interfacial Phase Formation in 316L–CuCrZr Hybrids
In-situ X-ray diffraction reveals how phase separation and fluid flow shape microstructure in laser-welded multi-material metal builds.
Phase by Phase: How Stainless Steel and IN625 Solidify Together
Where steel meets superalloy: real-time X-ray snapshots reveal how composition and cooling shape metal during 3D printing
Avec l’IA vers du ciment vert
Des scientifiques au PSI exploitent l’intelligence artificielle pour développer des formules de ciment qui ménagent l’environnement.
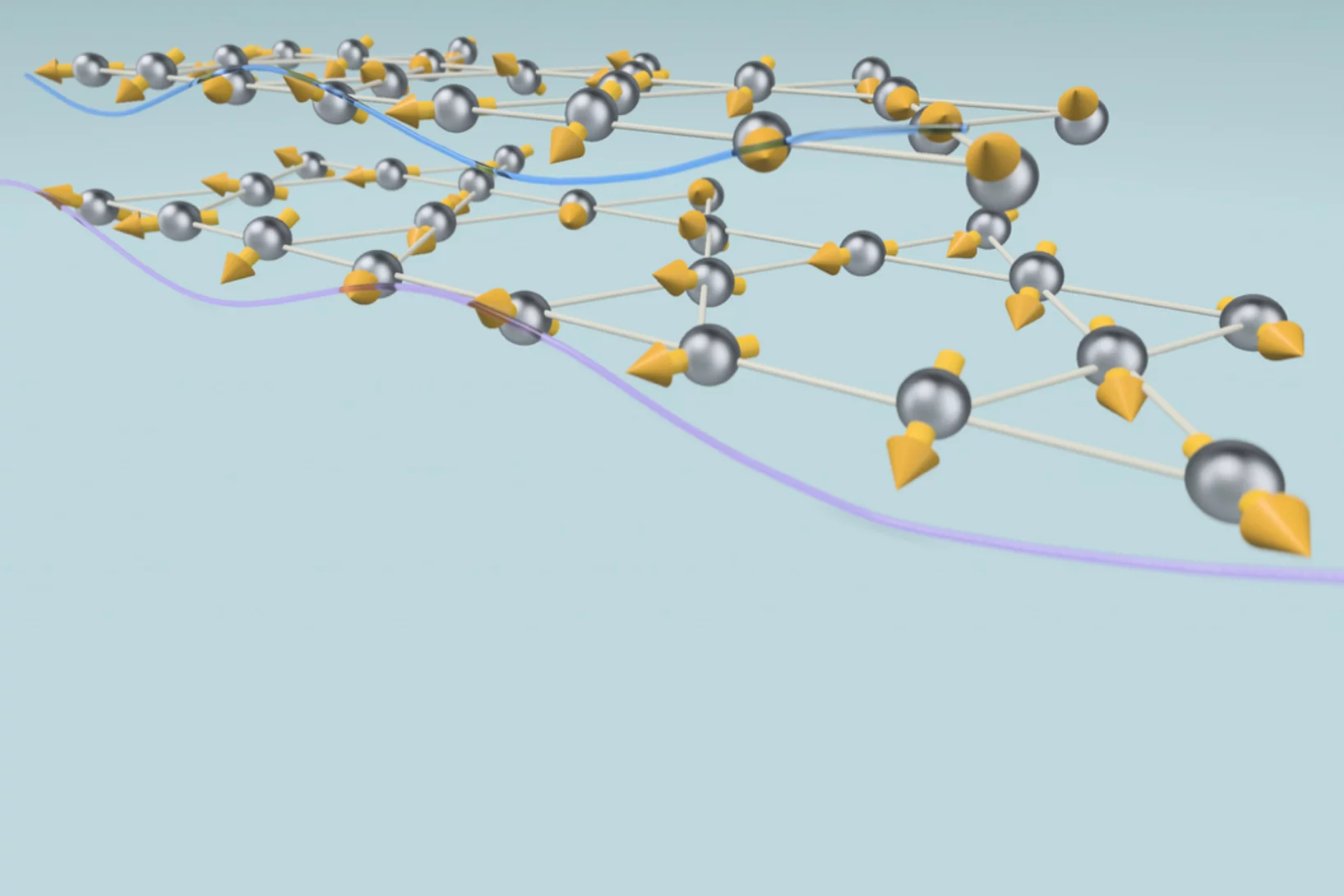
Steering magnetic textures with electric fields
Neutrons reveal a new way to control magnetism at the nanoscale
Stabilising fleeting quantum states with light
X-rays from SwissFEL probe emergent properties of quantum materials
Inauguration du centre d’excellence de l’ESA en Suisse
L’inauguration solennelle du Centre européen d’innovation en deep tech spatiale (ESDI) a réuni des invités de haut vol.
L’aluminium devient visible
Des scientifiques du PSI ont réussi une première: déterminer précisément la position des atomes d’aluminium dans des zéolithes, qui font de ces matériaux des catalyseurs si performants.
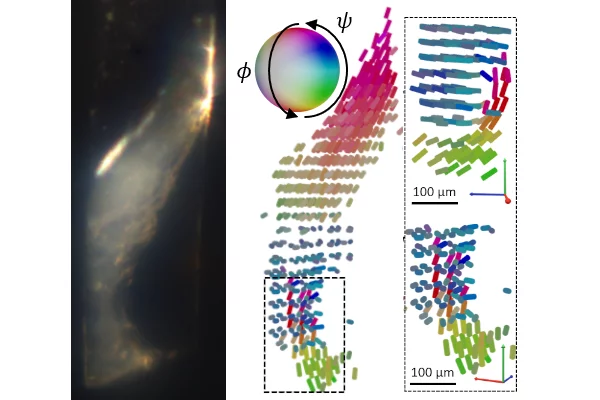
Nanostructure orientation in 3D with visible light by Tomographic Müller-Polarimetric Microscopy
We developed a new method, tomographic Müller-polarimetric microscopy (TMPM), that allows to retrieve at three-dimensional microscopic resolution the nanoscale structural information of the ultrastructure probed with polarized light in a non-destructive manner using a low cost and experimentally simple optical setup.
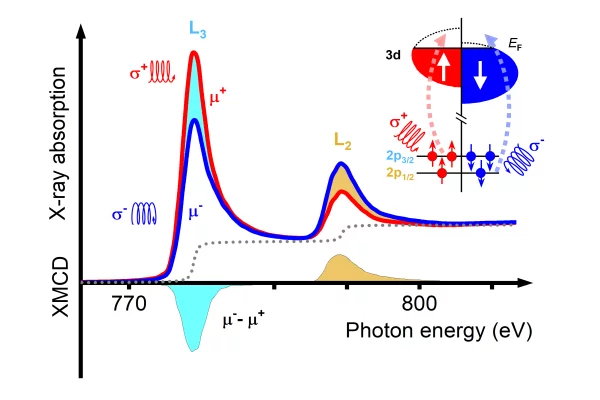
Primer on X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) is a magneto-optical effect that describes the difference in absorption between left and right circularly polarized X-rays by a magnetized material. It has been widely applied to the study of magnetic systems and of magnetic phenomena and its unique capabilities make it a fundamental tool for the study of novel magnetic phenomena and new materials systems.
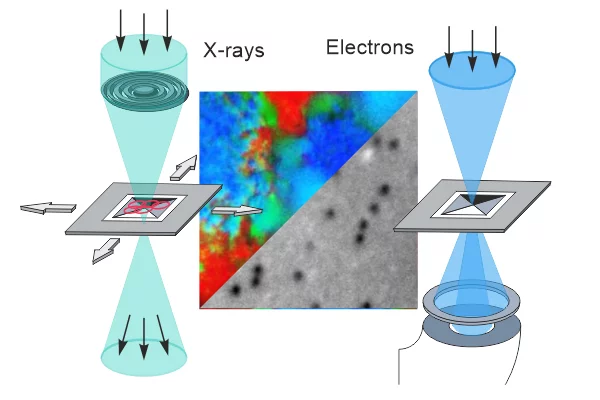
Correlating transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy to bridge atomic- and mesoscales
Transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy have contributed significantly to our understanding of phenomena in fields ranging from biology to materials science. In this review, we present recent developments in combining transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy techniques, including progress in sample environment, and in situ and operando approaches and highlight the unique opportunities offered by fully correlative transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy.
Antiferrodistortive and ferroeletric phase transitions in freestanding films of SrTiO3
Epitaxially grown thin films are commonly used to strain engineer electronic properties by the choice of a substrate, and therefore do not match bulk properties (leading to properties that deviate from the bulk material). Free standing ultrathin oxide films are expected to preserve the bulk-like properties due to the absence of substrate influence. However, we show that this expectation is not fulfilled with ultrathin free standing SrTiO3, as they get ferroelectric at 80K.
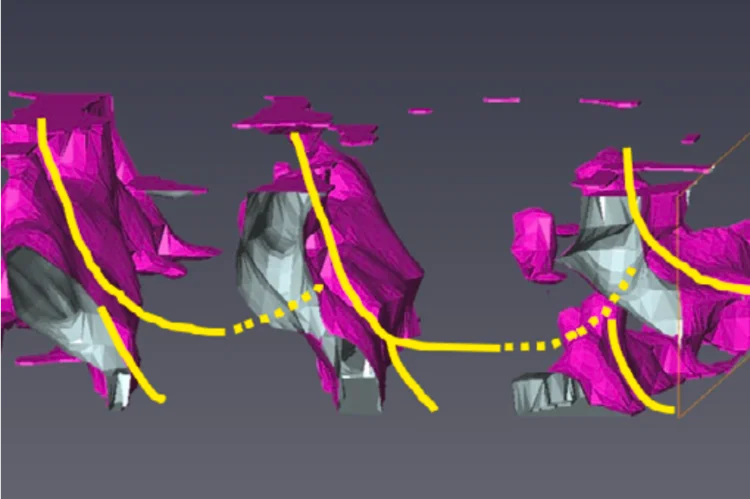
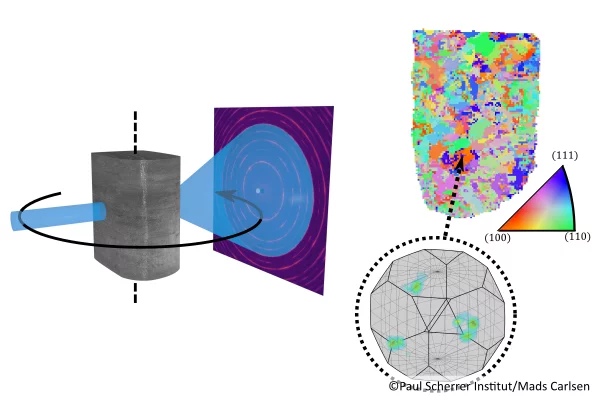
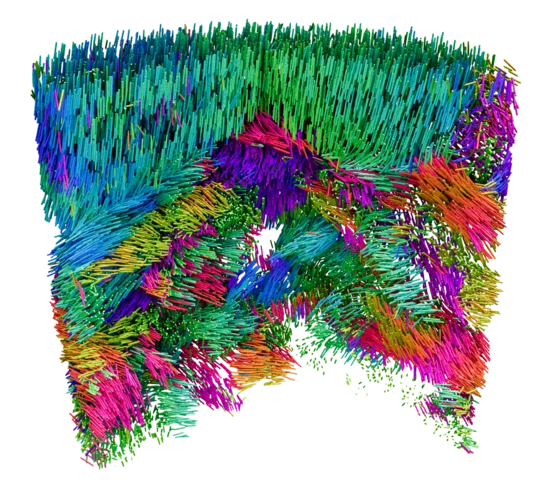
Mapping crystallite orientation in bulk polycrystals
A new experimental technique allows the orientation distribution of small-grained polycrystal materials to me mapped in 3D.
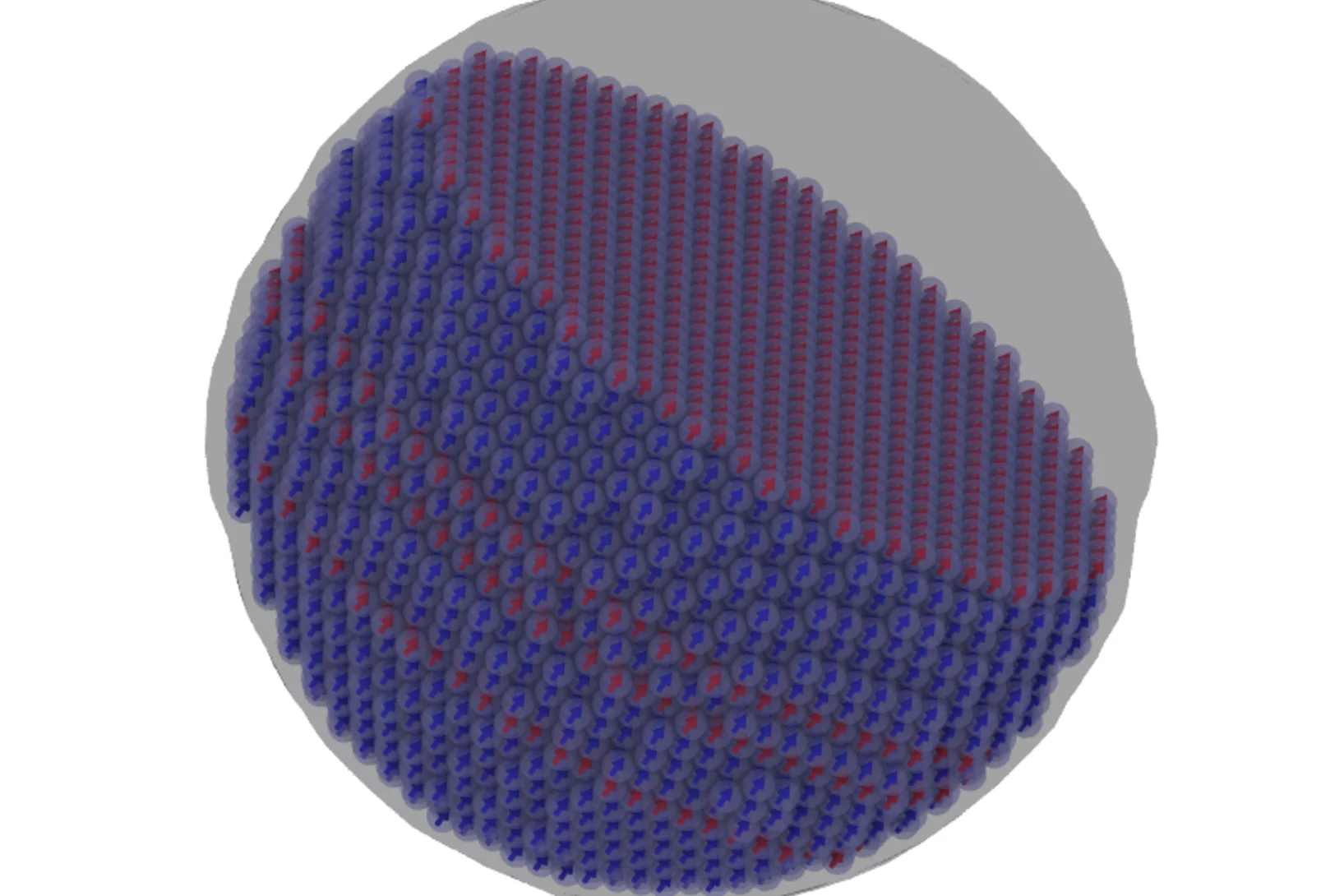
Defect structure controls the thermal magnetic switching rate of nano-sized metallic particles.
Past experiments done at the Paul Scherrer Institut, probed the thermal switching properties of nano-sized metallic magnetic particles
Rethinking 3D Printing for ceramics
Using a powerful combination of in-situ X-ray imaging and high-fidelity simulations, researchers uncover how alumina behaves under laser-based 3D printing—paving the way for more reliable ceramic additive manufacturing.
Subvention prestigieuse pour trois projets de recherche au PSI
Béton, catalyse chimique et quête d’une nouvelle physique: trois chercheurs du PSI ont reçu chacun un grant du Fonds national pour ces thèmes de recherche
A new dimension of complexity for layered magnetic materials
X-rays reveal magnetic phenomena driven by interactions between the layers of a kagome ferromagnet
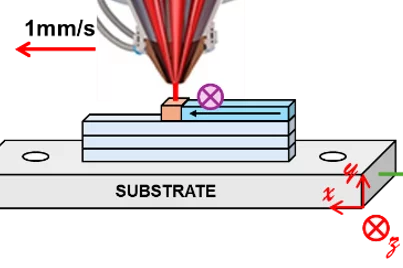
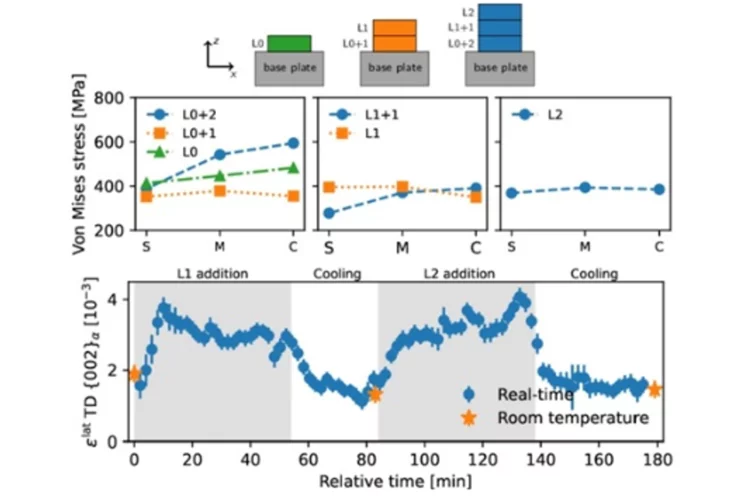
Texture and residual stress evolution during 3D printing
Discover how advanced neutron diffraction sheds light on the evolution of stress and texture in 3D-printed duplex stainless steel.
Mapping the ecosystem of Wannier Functions software
A new review article, just published in Reviews of Modern Physics and highlighted on the journal cover, provides a map to the vast landscape of software codes that allow researchers to calculate Wannier functions, and to use them for materials properties predictions. The authors, from all over Europe and the USA, include two PSI scientists. After providing readers with the theoretical foundations on Wannier functions and their calculation, together with intuitive graphical schematics to explain what Wannier functions are, the authors map the existing Wannier codes and the key applications.
Operando Neutron Characterization During 3D Printing
A new laser powder bed fusion device enables real-time neutron diffraction and imaging, providing detailed insights into structural evolution, defect formation, and temperature mapping during metal additive manufacturing.
Mitigating Cracks in Multi-Material Printing
Integrating metallic powders with thin foils in laser powder bed fusion can reduce interfacial cracks and improve microstructure quality in titanium-aluminum multi-material printing.
Mapping the Nanoscale Architecture of Functional Materials
A new X-ray technique reveals the 3D orientation of ordered material structures at the nanoscale, allowing new insights into material functionality.
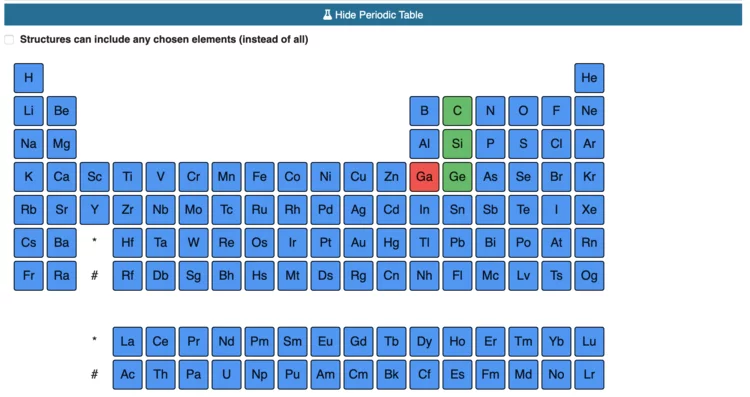
New widgets and extensions expand the OSSCAR platform for educational notebooks in materials science
In a new article published in Computer Physics Communications, the team of the Open Software Services for Classrooms and Research project (OSSCAR) describes how to create custom widgets and extensions that can be used in interactive notebooks to teach computational materials science. The article also introduces two new entries in OSSCAR: a widget to display an interactive periodic table that allows users to group elements into different states, and one to plot and visualize electronic band structures and density of states.
IMPACT: pour la société suisse
Pour être à la pointe, au niveau mondial, dans le domaine des muons et de la production de radionucléides médicaux: l'importance de la mise à niveau prévue.
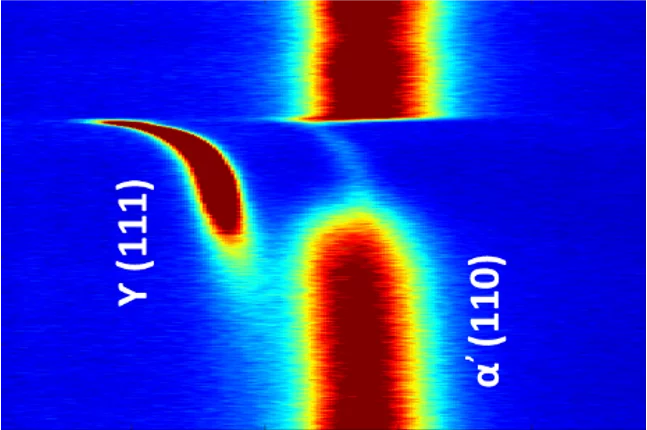
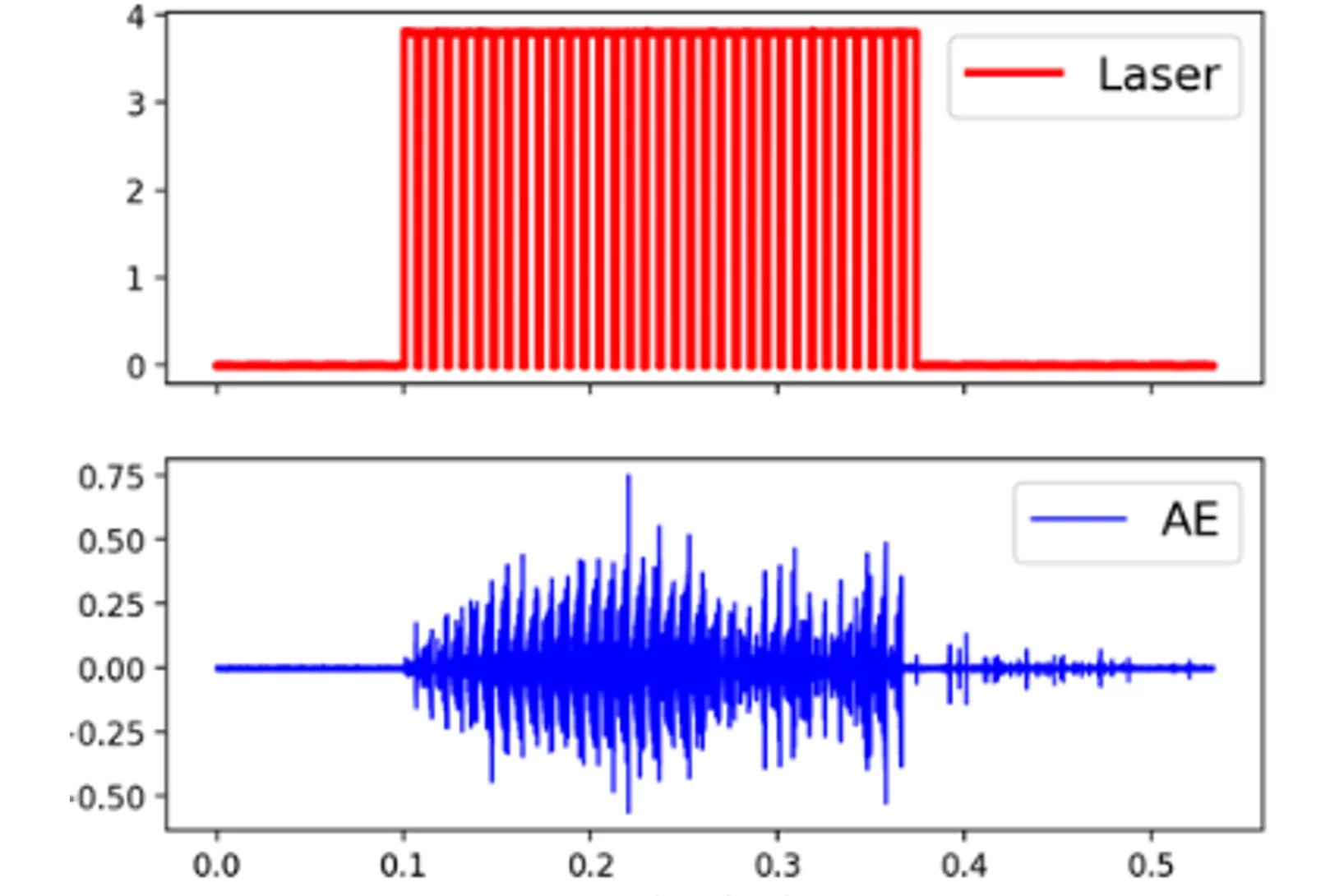
Acoustic emission signature of a martensitic transformation
Acoustic emission monitoring in 3D printing: real-time insights into martensitic phase transformations and crack formation.
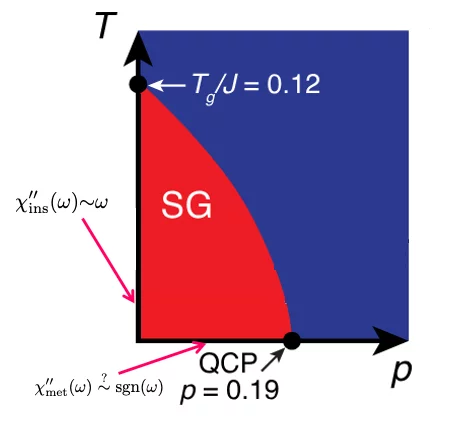
Exact solution of the classical and quantum Heisenberg mean field spin glasses
We solve and elucidate the physics of quantum Heisenberg spins glasses, which governs the local moments in randomly doped, strongly correlated materials.
L’ESA débarque en Suisse
La signature d’un contrat entre l’Agence spatiale européenne (ESA) et le PSI marque le lancement de l’European Space Deep-Tech Innovation Centre ESDI.
Magnétisme en couches minces: un électron fait la différence
Une étape importante vers des mémoires informatiques novatrices
Orbitronics: new material property advances energy-efficient tech
Discovery of orbital angular momentum monopoles boosts the emerging field of orbitronics, an energy-efficient alternative to electronics.