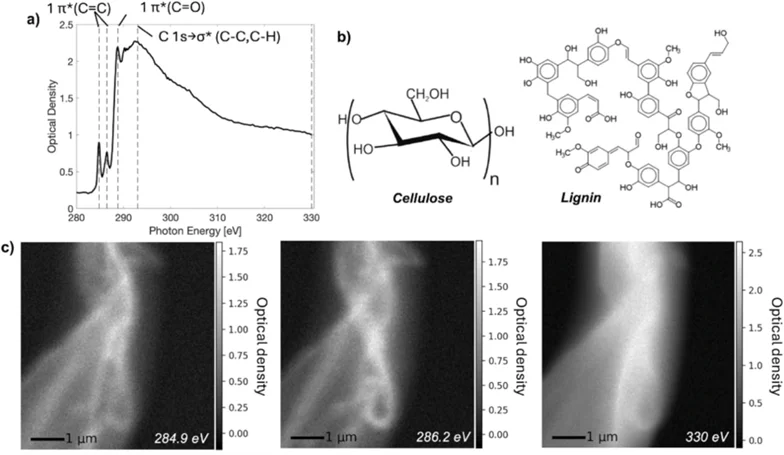
Different approaches for preparing ultrathin samples (~ 100 nm) suitable for scanning transmission X-ray microscopy (STXM) experiments are examined and evaluated, providing guidelines for synchrotron based spectro-microscopy around the carbon K-edge to image lignocellulose-based fibres with chemical contrast.
Soft X-ray spectro-microscopy around the carbon K-edge is showcased as a powerful tool for visualising the chemical composition of lignocellulose-based fibres with high spatial resolution available at the Pollux beamline at SLS. We show that the technique can spatially differentiate variations in lignin composition across a single thermomechanical pulp fibre, highlighting its sensitivity for detecting subtle chemical modifications.
To enable STXM measurements with improved data quality, five different embedding and sectioning strategies, including epoxy embeddings, cryo-embedding with water or sucrose, and elemental sulphur, were systematically evaluated. We examine how each approach affects section quality, spectral quality and sensitivity to radiation dose. Epoxy embeddings resulted in large homogenous sections advantagous for imaging, while embedding strategies without carbon species, such as elemental sulphur or cryo-embedding with water, was better for evaluation of the chemical content in the fibre due to less overlap in the spectral signal from the embedding material.
Finally, measurement strategies for efficient data collection are presented, with an emphasis on reducing the inflicted radiation dose. Together, these results provide practical guidelines for preparing and characterising cellulose fibres using synchrotron-based X-ray spectro-microscopy around the carbon K-edge.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Marianne Liebi
Structure and Mechanics of Advanced Materials Group (SMAM)
Center for Photon Science
Paul Scherrer Institute PSI
+41 56 310 44 38
marianne.liebi@psi.ch
Original publication
Björn, L., Olsson, M., Westman, G. Ziolkowska, A., Avaro, J., Watts, B., Matic, A., Liebi, M.* Sample preparation and measurement strategies for characterisation of lignocellulose fibres using carbon K-edge spectro-microscopy. Cellulose (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-025-06869-1