The PSI Center for Neutron and Muon Sciences uses neutrons and muons to explore and understand matter and materials.
Recent News & Scientific Highlights
Room-Temperature Magnetic Skyrmions and Intrinsic Anomalous Hall Effect in a Nodal-Line Kagomé Ferromagnet MnRhP
Topological magnetic semimetals with kagomé lattices have attracted significant attention due to their nontrivial electronic band structures and pronounced electromagnetic responses. The search for kagomé-lattice topological semimetals exhibiting magnetic ordering above room temperature is essential ...
Muon Knight Shift as a Precise Probe of the Superconducting Symmetry of Sr2RuO4
Muon spin rotation (𝜇SR) measurements of internal magnetic field shifts, known as the muon Knight shift, are used for determining pairing symmetries in superconductors. While this technique has been especially effective for 𝑓-electron-based heavy-fermion superconductors, it remains challenging ...
Low-frequency electrochemical pulsing to manage flooding and salt precipitation in zero-gap CO2-to-ethylene electrolyzers
The electrochemical conversion of CO2 to ethylene offers a promising approach to expand manufacturing of commodity chemicals and fuels. Specifically, ethylene is a critical precursor for polyethylene a $240B industry. Expanding productivity ...
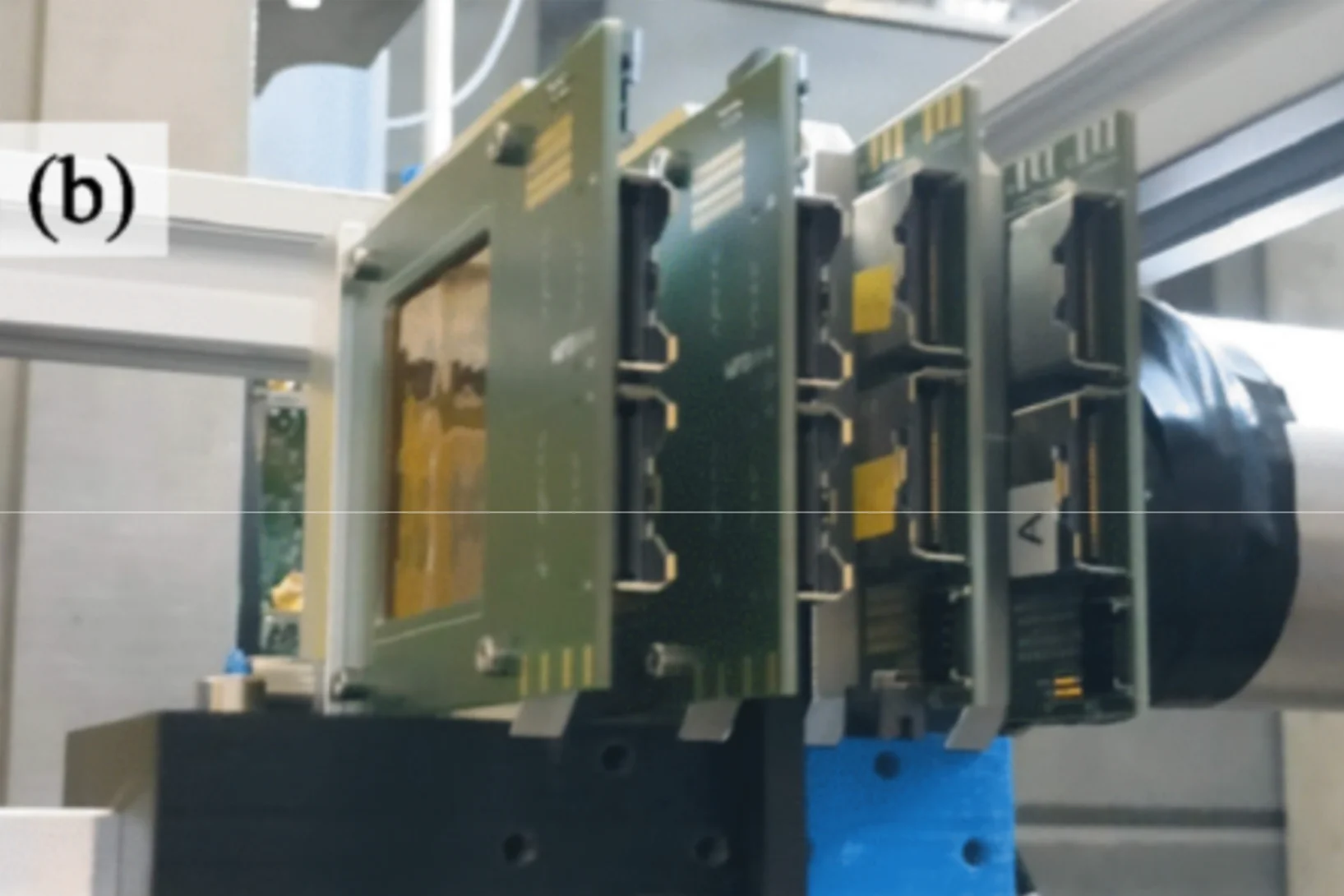
Advanced muon-spin spectroscopy with high lateral resolution using Si-pixel detectors
Muon-spin spectroscopy at continuous sources has stagnated at a stopped muon rate of ∼40kHz for the last few decades. The major limiting factor is the requirement of a single muon in the sample during the typical 10µsdata gate window. To overcome this limit ...
Michel Kenzelmann named as New Chair of the PSI Research Committee
Michel Kenzelmann has been named as new chair of the PSI research committee (FoKo). from 1 March 2026 he will succeed Marco Stampanoni who chaired the committee since 2018.
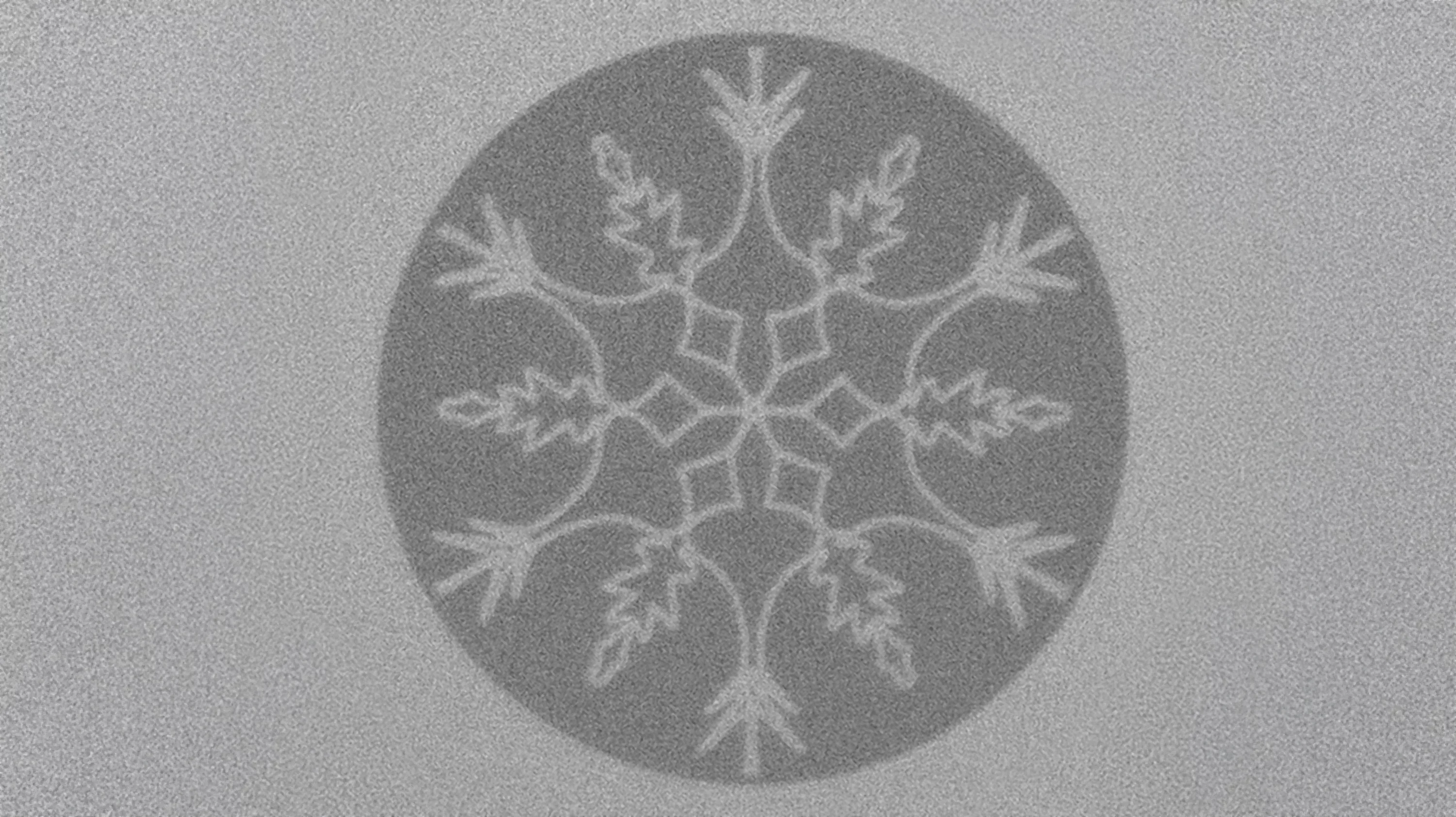
Realizing Blume-Capel Degrees of Freedom with Toroidal Moments in a Ruby Artificial Spin Ice
Realizing exotic Hamiltonians beyond the Ising model is a key pursuit in experimental statistical physics. Onesuch example is the Blume-Capel model, a three-state spin model, whose phase diagram features a tricritical point where second-order and first-order transition lines converge, leading to a coexistence of paramagnetic, ferromagnetic, and disordered phases. Here, we realize ...
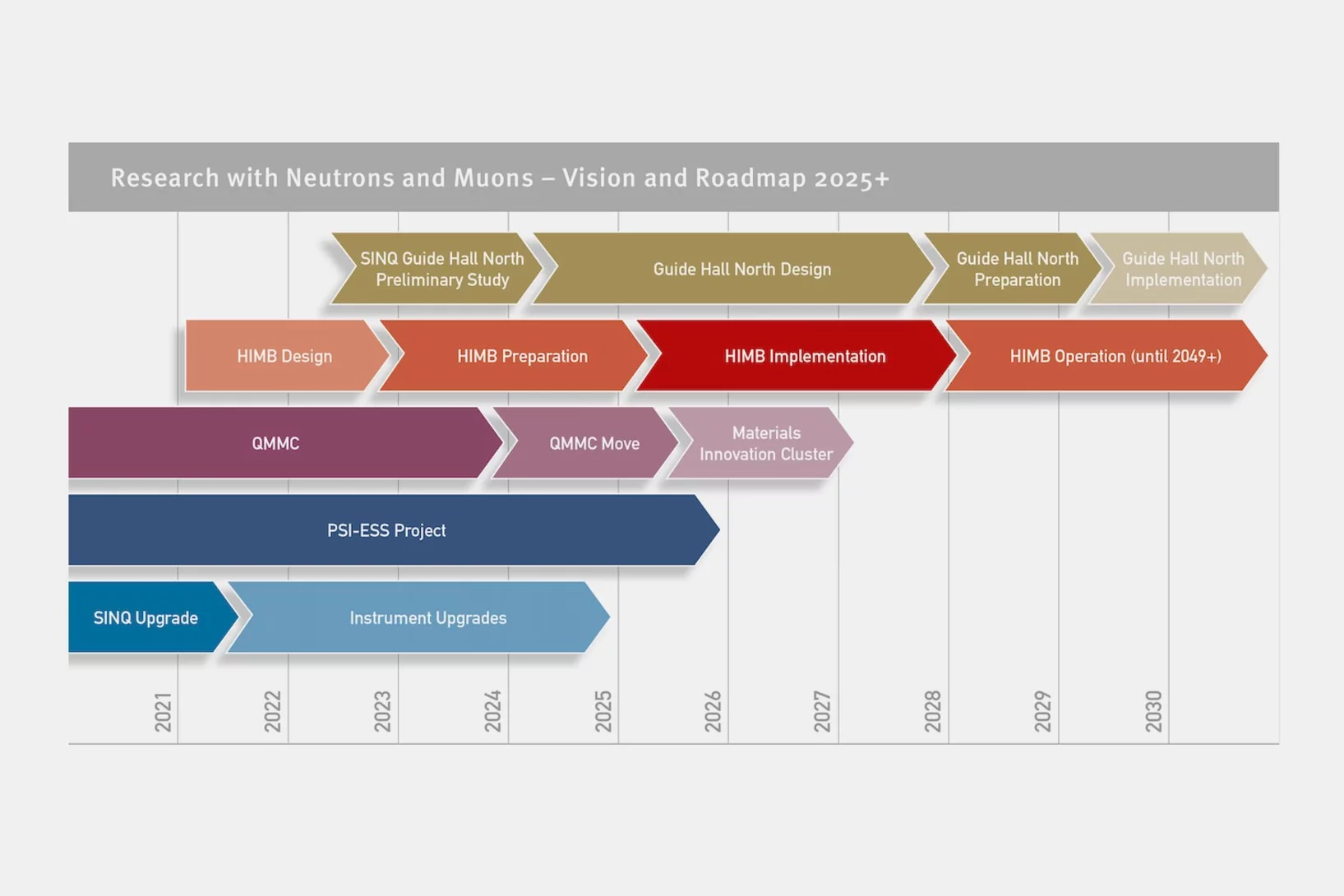
Our Facilities
Latest CNM publications
-
Mandok L, Isenring P, Augustin H, Berger N, Köppel M, Krieger JA, et al.
Advanced muon-spin spectroscopy with high lateral resolution using Si-pixel detectors
Physical Review Research. 2026; 8: 013092 (6 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1103/f4jb-39yn
DORA PSI -
Boraley X, Christianson AD, Lass J, Balz C, Bartkowiak M, Niedermayer C, et al.
Magnetic field dependence of the spin fluctuations in CeCu5.8Ag0.2
Physical Review B. 2026; 113(4): 045154 (7 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1103/bjgt-p16s
DORA PSI -
Melčák M, Durďáková T‐M, Číhal P, Šercl J, Lee J, Boillat P, et al.
Interfacial behavior of methane in methane/p‐xylene/water systems: first principles inspected using neutron imaging and molecular dynamics simulations
Advanced Materials Interfaces. 2026: e00786 (10 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202500786
DORA PSI -
Aplin KL, Tabbett JD, Houghton IMP
Energy spectra from ionising radiation in the troposphere and stratosphere measured with a super-miniaturised scintillator detector
Radiation Measurements. 2026; 191: 107581 (8 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2025.107581
DORA PSI