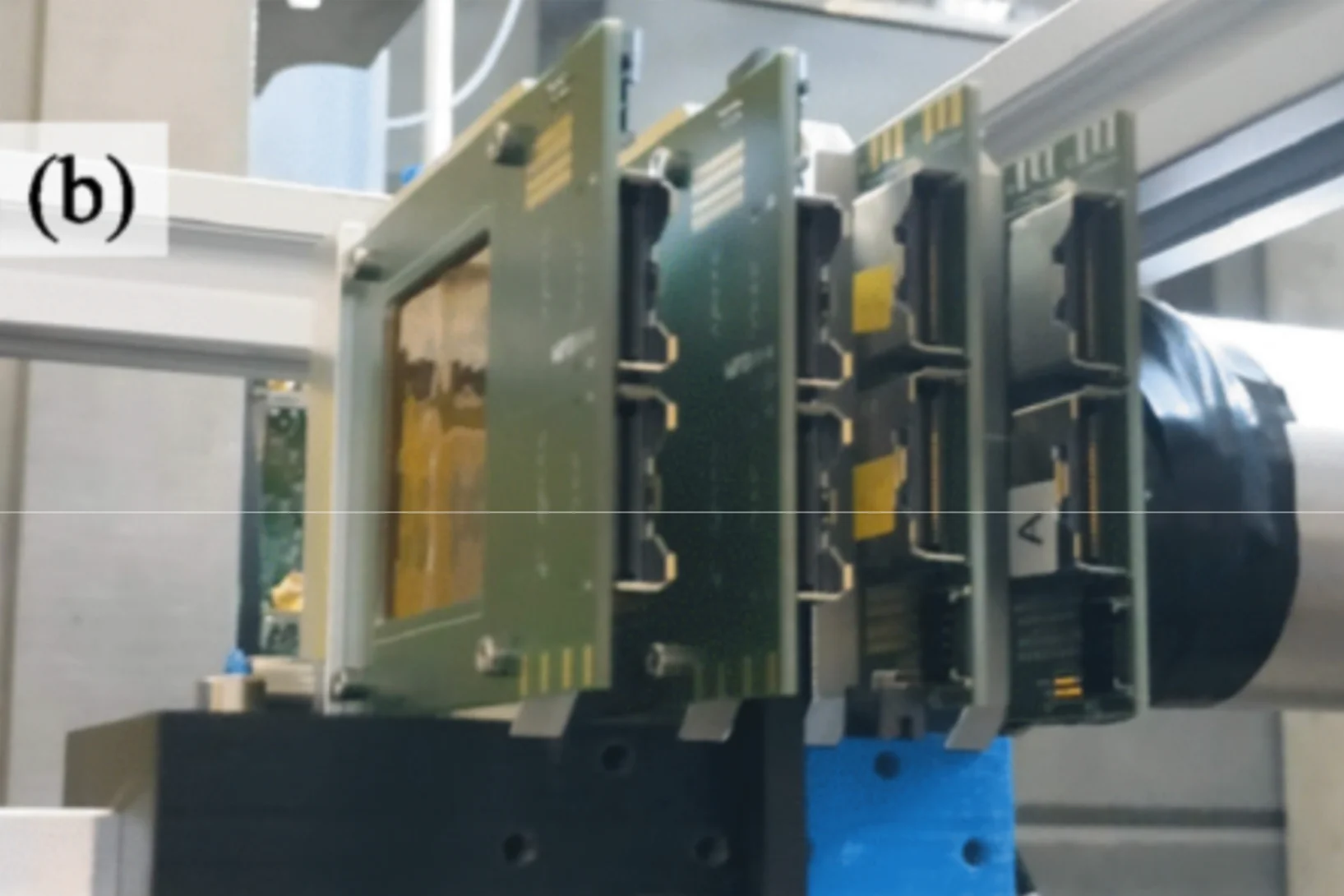
The PSI Laboratory for Muon Spin Spectroscopy uses the fundamental particles from the Swiss Muon Source SµS to investigate matter and materials.
Call for Proposals
Next Deadline: Call 2/2026 June 01, 2026.
- The 1st call (1/2026) for the year 2026 is closed.
- Note: Allocation period for call 1/2026: June 2026 - September 2026.
- Note: Allocation period for call 2/2026: October 2026 - December 2026.
- Experiment schedules
The technique "µSR" - Muon Spin Rotation, Relaxation or Resonance
A research tool using muons as sensitive local magnetic probes in matter.
Worldwide unique instruments:
The Low-Energy Muon (LEM) beam and µSR Spectrometer for the study of thin films, layers and surfaces;
the high-field instrument (HAL-9500) equipped with specially designed detectors to perform studies in fields up to 9.5 Tesla and at very low temperatures;
and the combination of very-high pressures (up to 2.8 GPa) combined with sub-Kelvin temperatures (GPD).
Lab News & Scientific Highlights
Muon Knight Shift as a Precise Probe of the Superconducting Symmetry of Sr2RuO4
Muon spin rotation (𝜇SR) measurements of internal magnetic field shifts, known as the muon Knight shift, are used for determining pairing symmetries in superconductors. While this technique has been especially effective for 𝑓-electron-based heavy-fermion superconductors, it remains challenging ...
Soutien important pour la recherche sur les muons
Le PSI se voit confier un Pôle de recherche national: le projet «Muoniverse» va développer encore davantage la recherche aux lignes de faisceaux de particules élémentaires appelées muons. Et ce à l’installation de faisceaux de muons la plus performante au monde.
Advanced muon-spin spectroscopy with high lateral resolution using Si-pixel detectors
Muon-spin spectroscopy at continuous sources has stagnated at a stopped muon rate of ∼40kHz for the last few decades. The major limiting factor is the requirement of a single muon in the sample during the typical 10µsdata gate window. To overcome this limit ...