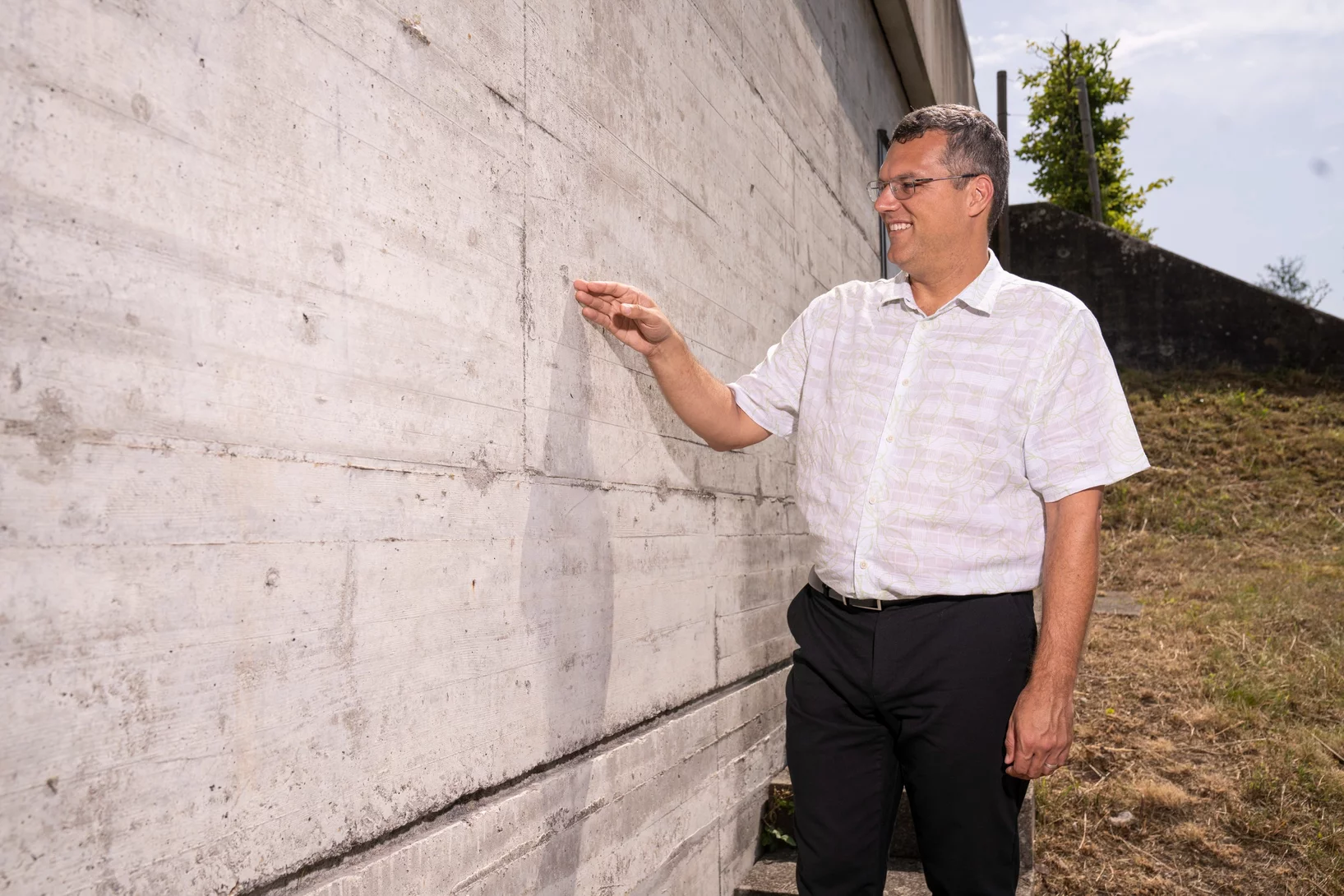
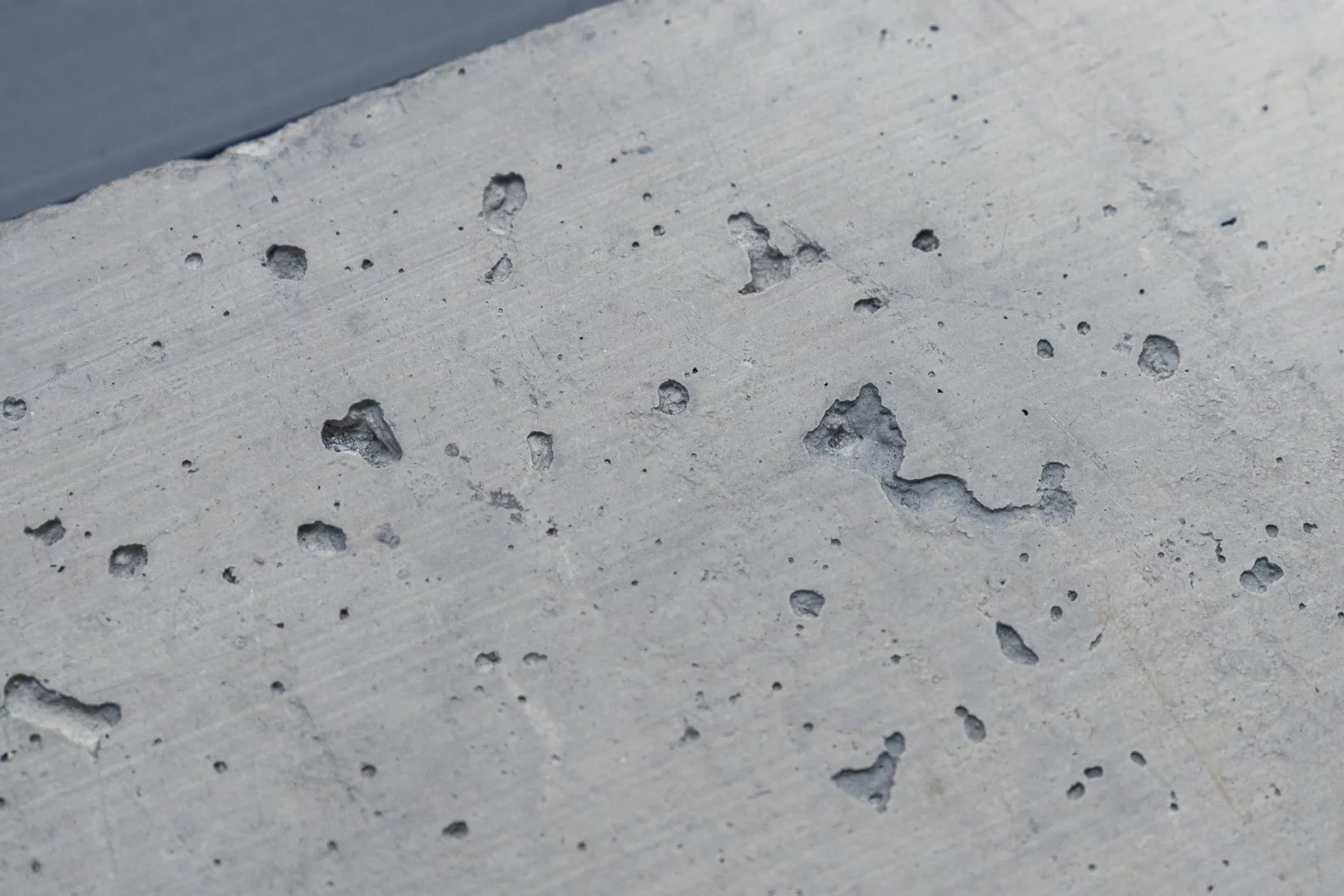
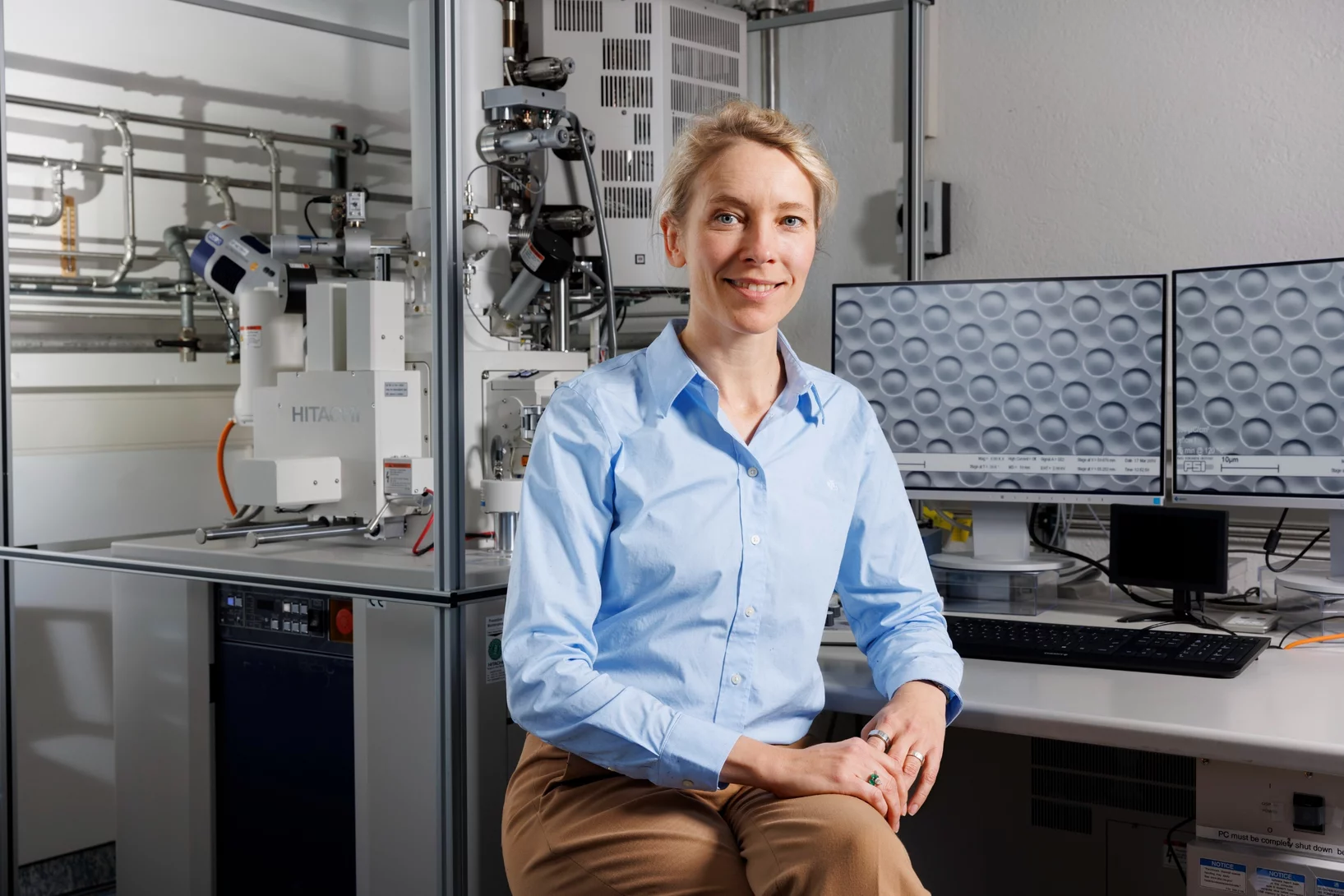
Au PSI, un homme qui murmure à l’oreille du ciment
John Provis a dédié sa vie de chercheur à un matériau de construction qui s’avère plus passionnant qu’il n’en a l’air.
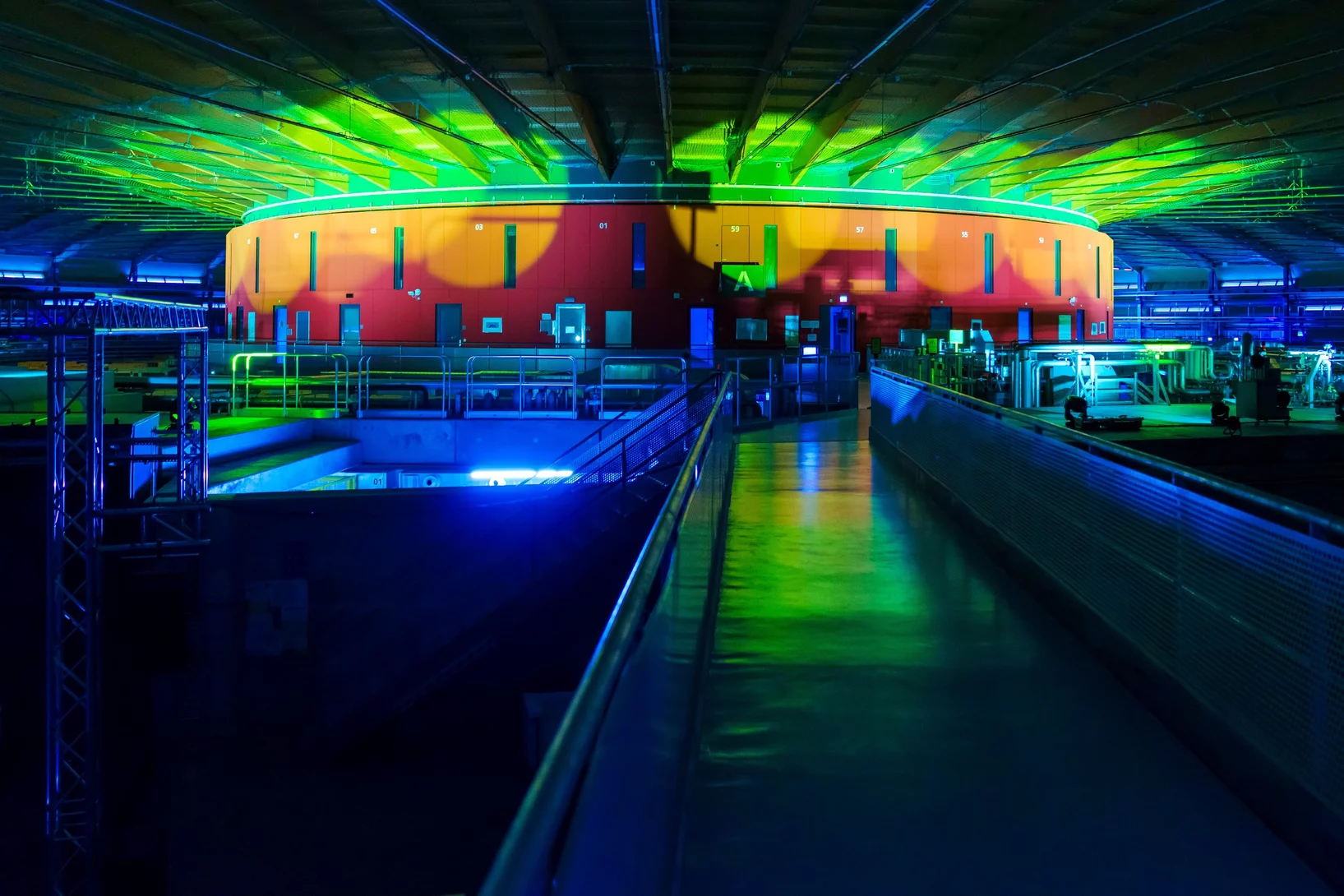
Une brillante lumière pour la Suisse
La nouvelle Source de Lumière Suisse a été inaugurée.
The Quantum Revolution: What's Next?
A century on from the birth of quantum mechanics, 2025 marks the UNESCO International Year of Quantum Science and Technology. What does the future hold? Our experts share their opinions.
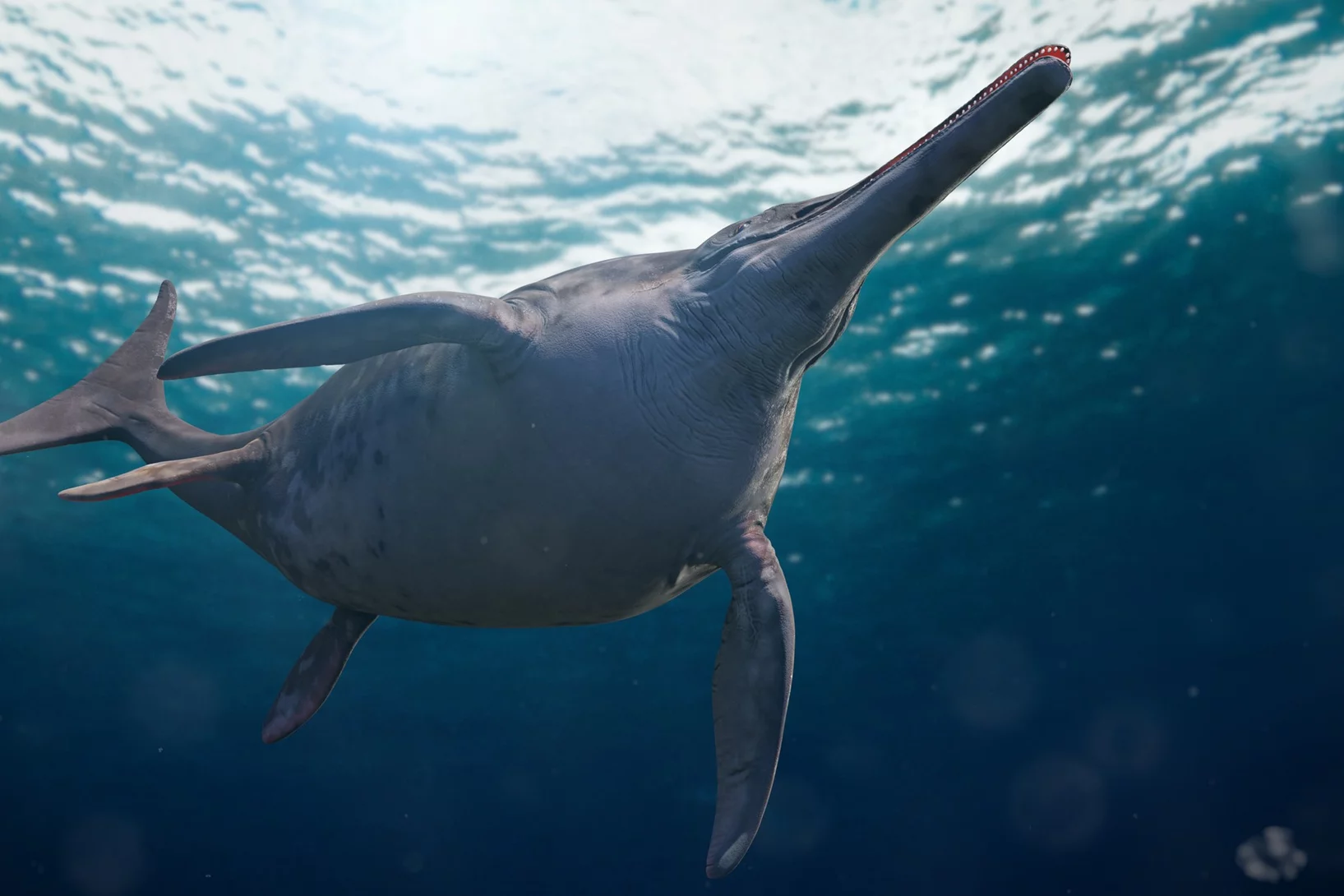
Un fossile maître du camouflage aux rayons X
Le procédé d’imagerie du PSI aide à décoder la stratégie de chasse d’un prédateur préhistorique.
De nouvelles perspectives sur une maladie rare
Des scientifiques du PSI décryptent la manière dont certains défauts génétiques endommagent les cils vibratiles humains de différentes façons. C’est une étape vers l’amélioration du diagnostic d’une maladie encore mal comprise à ce jour: la dyskinésie ciliaire primitive.
Du zinc détecté dans des seringues obstruées
Pour l'entreprise pharmaceutique MSD, ANAXAM a étudié, avec l'aide de scientifiques du PSI, si le zinc pouvait contribuer à l'obstruction des seringues préremplies.
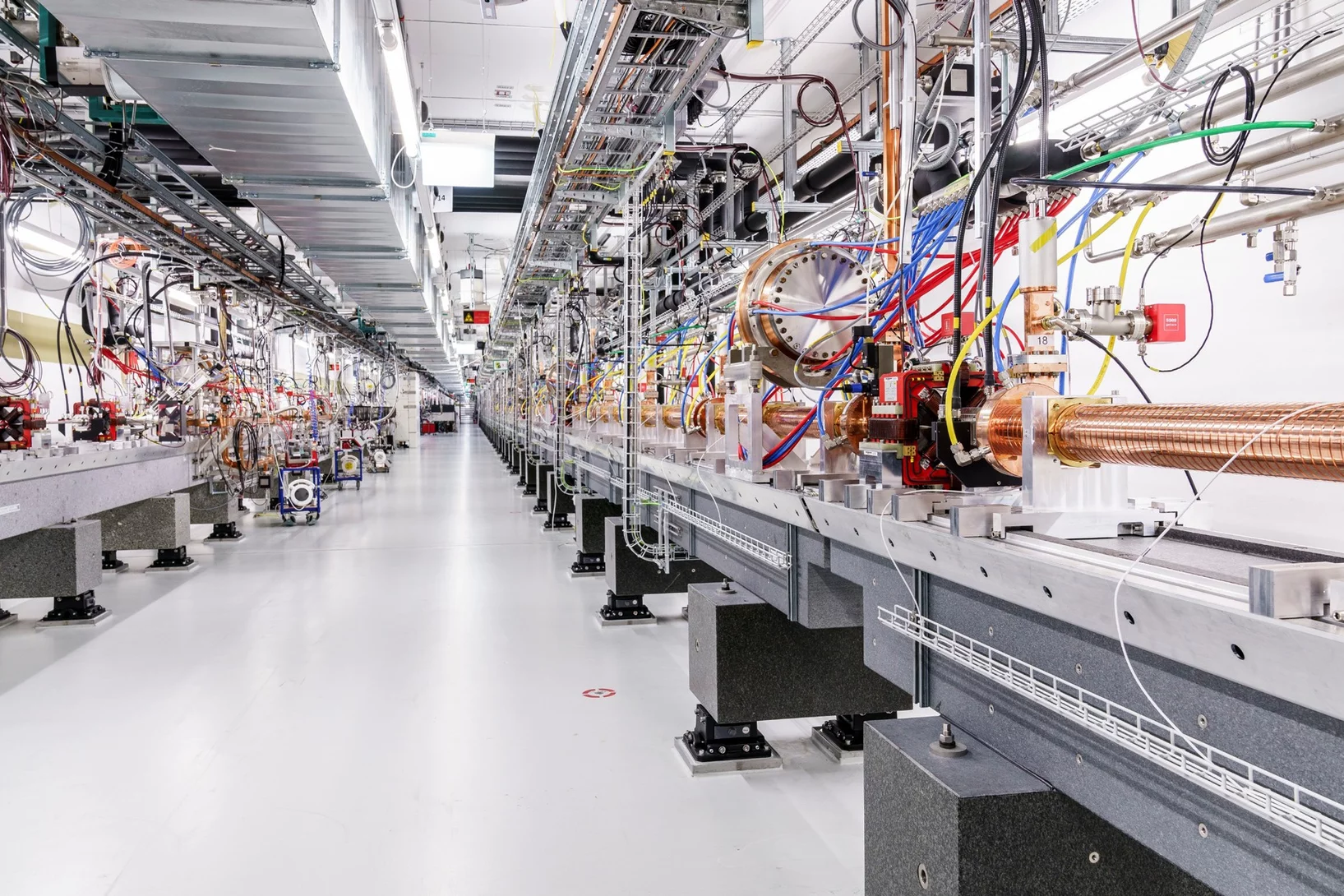
Peering into matter with ultrashort X-ray ripples
An all-X-ray transient grating experiment allows scientists to study the dynamics of quantum particles at the nanoscale.
Conseil en technologie de pointe
Stephanie Smit, ancienne doctorante au PSI, travaille comme ingénieur-conseil en propriété industrielle pour une société qui compte parmi les plus importantes au monde. Celle-ci construit en effet des machines qui valent une fortune et sont très recherchées.
La recherche du PSI dans le musée le plus visité de Suisse
Rendre la recherche énergétique tangible: Le Musée des transports a créé une plate-forme pour encourager le dialogue politique et social autour des thématiques énergétiques.
Avec l’IA vers du ciment vert
Des scientifiques au PSI exploitent l’intelligence artificielle pour développer des formules de ciment qui ménagent l’environnement.
Financement prestigieux pour des réseaux photoniques
Kirsten Moselund, chercheuse au PSI, s’est vu attribuer une importante subvention de recherche par le Conseil européen de la recherche (CER).
Steering magnetic textures with electric fields
Neutrons reveal a new way to control magnetism at the nanoscale
Stabilising fleeting quantum states with light
X-rays from SwissFEL probe emergent properties of quantum materials
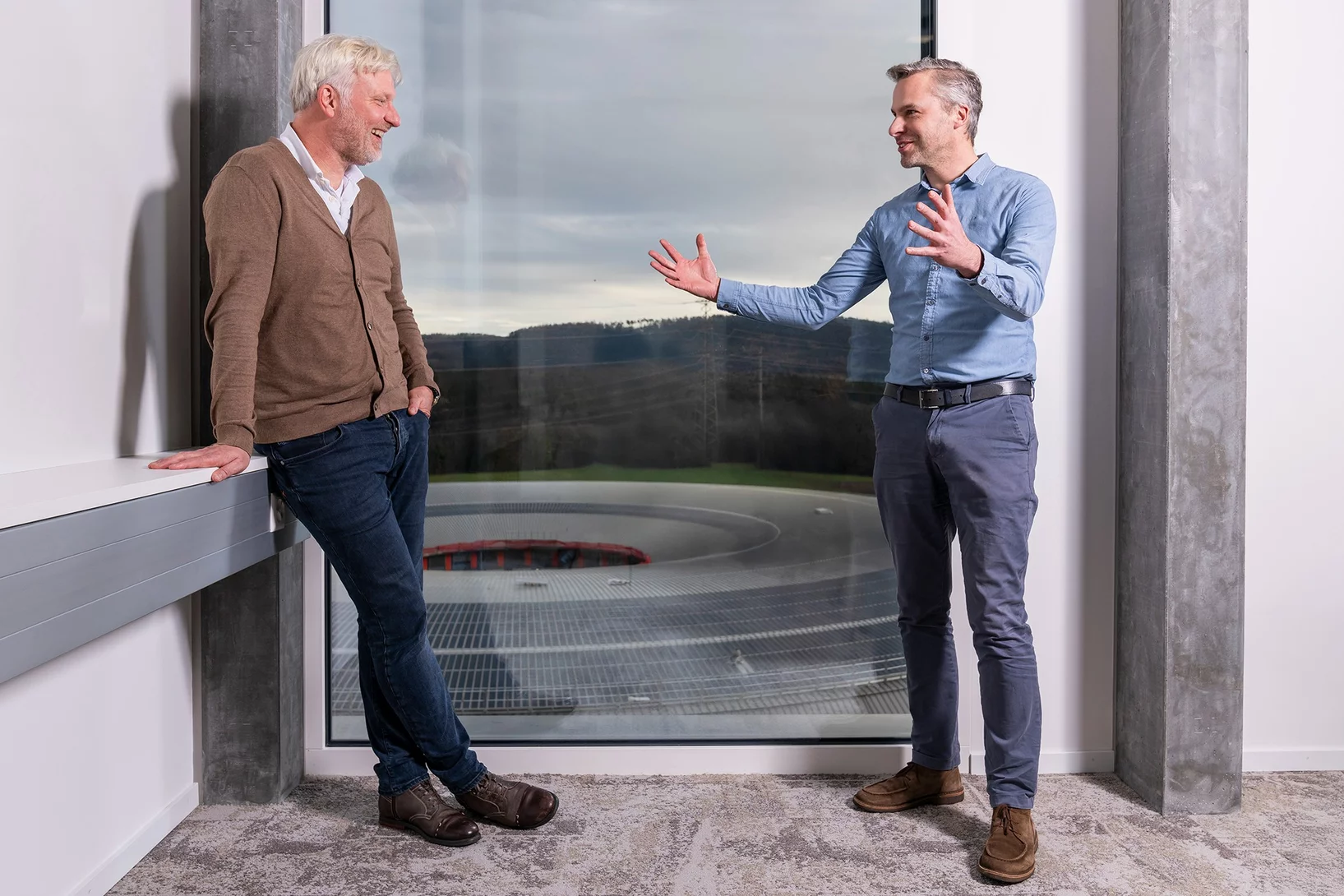
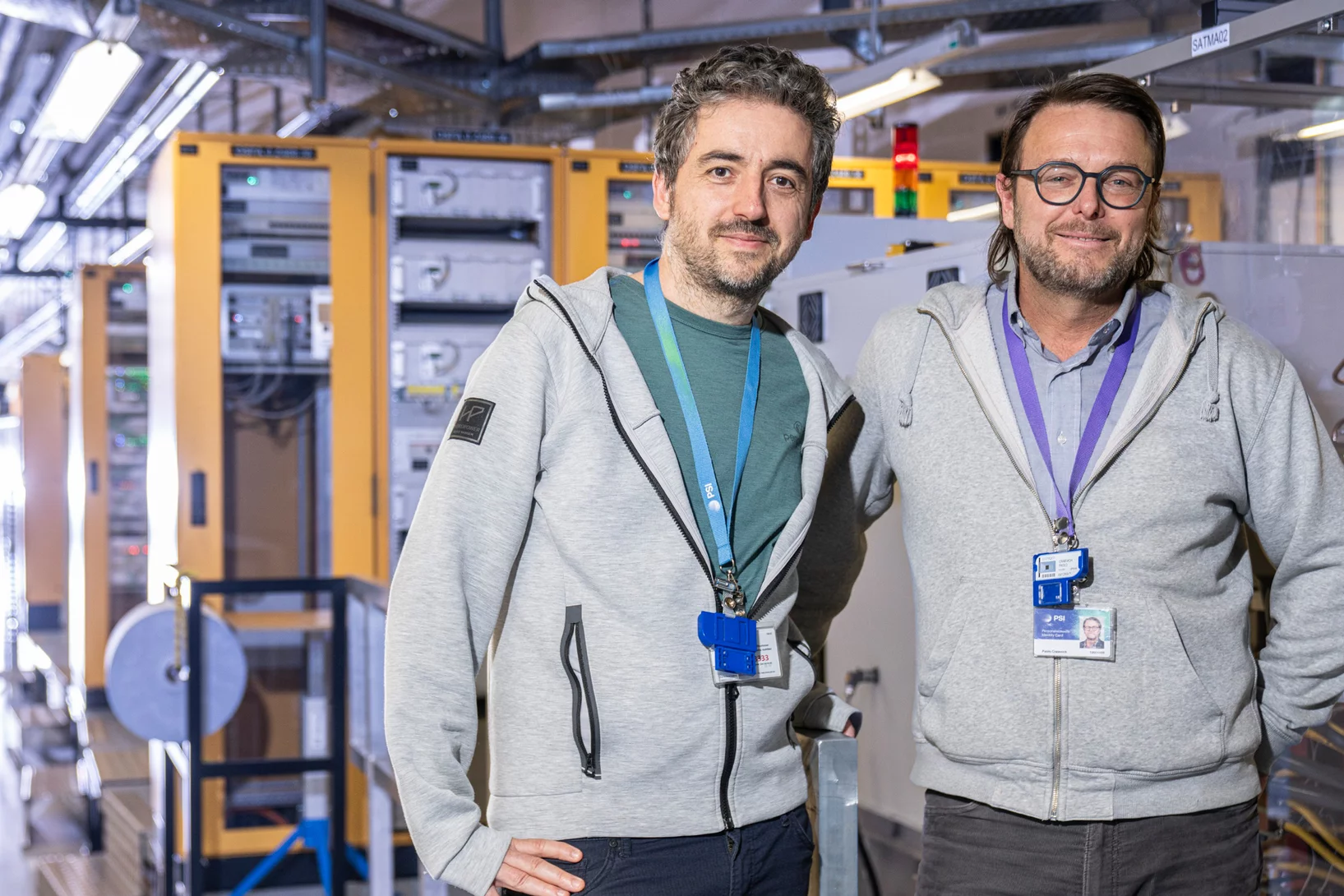
Quand la science rencontre l’industrie, l’innovation a de l’impact
Hans Priem et Cees Maris de l’entreprise VDL ETG nous expliquent ce que signifie la fabrication avancée dans l’industrie et évoquent la collaboration avec le PSI.
Du terbium contre le lymphome
Des expériences de laboratoires prometteuses menées au PSI montrent qu’une thérapie par radionucléide avec l’élément radioactif terbium-161 pourrait s’avérer efficace contre le lymphome.
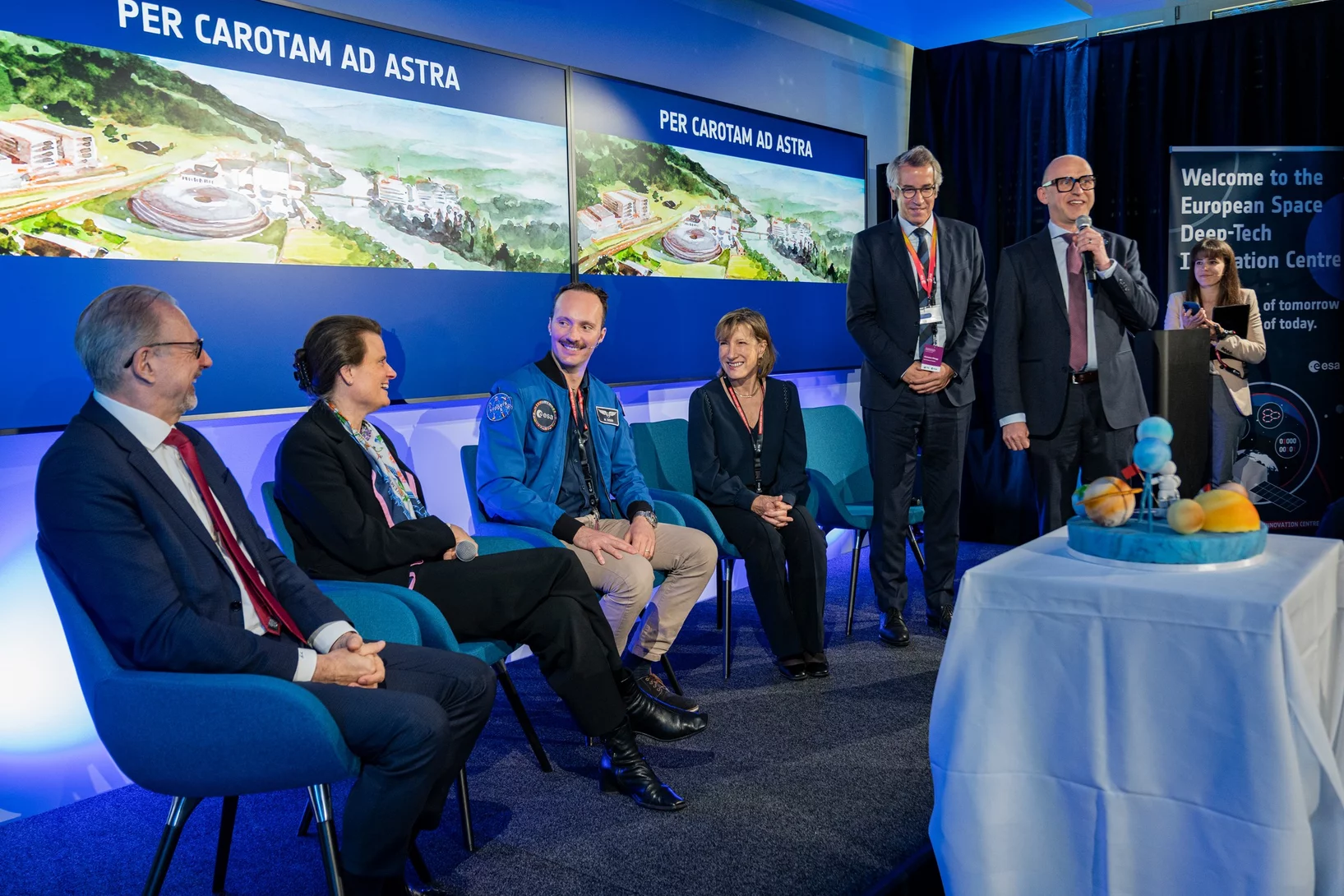
Inauguration du centre d’excellence de l’ESA en Suisse
L’inauguration solennelle du Centre européen d’innovation en deep tech spatiale (ESDI) a réuni des invités de haut vol.
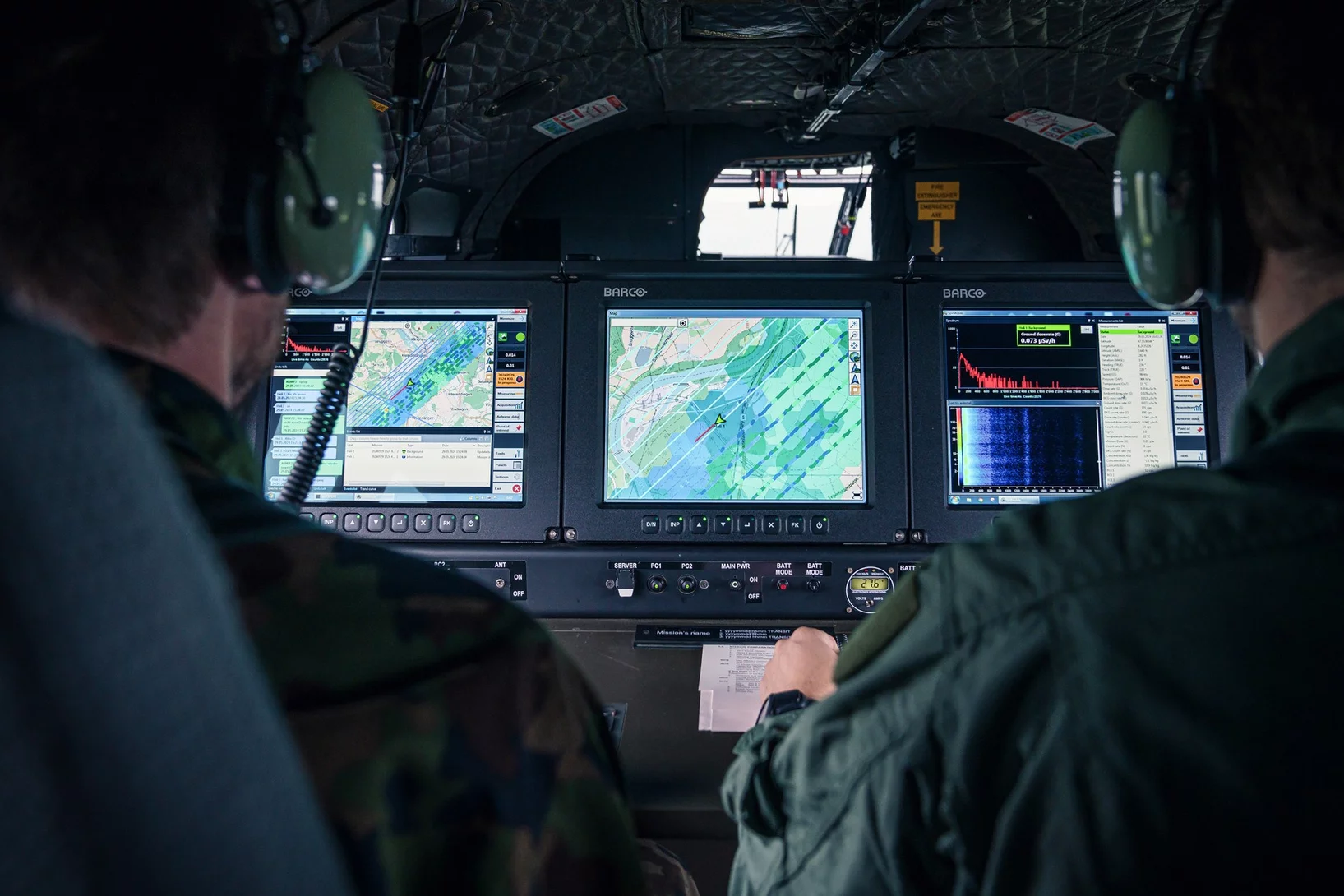
Décrypter les radiations
Les radiations vues du ciel: un détecteur sensible et un algorithme intelligent rendent visible le rayonnement radioactif.
Nouveaux jalons en physique nucléaire
Des scientifiques du PSI mesurent le rayon du noyau de l’hélium-3 muonique avec une précision inégalée à ce jour et mettent à l’épreuve les théories de la physique atomique.
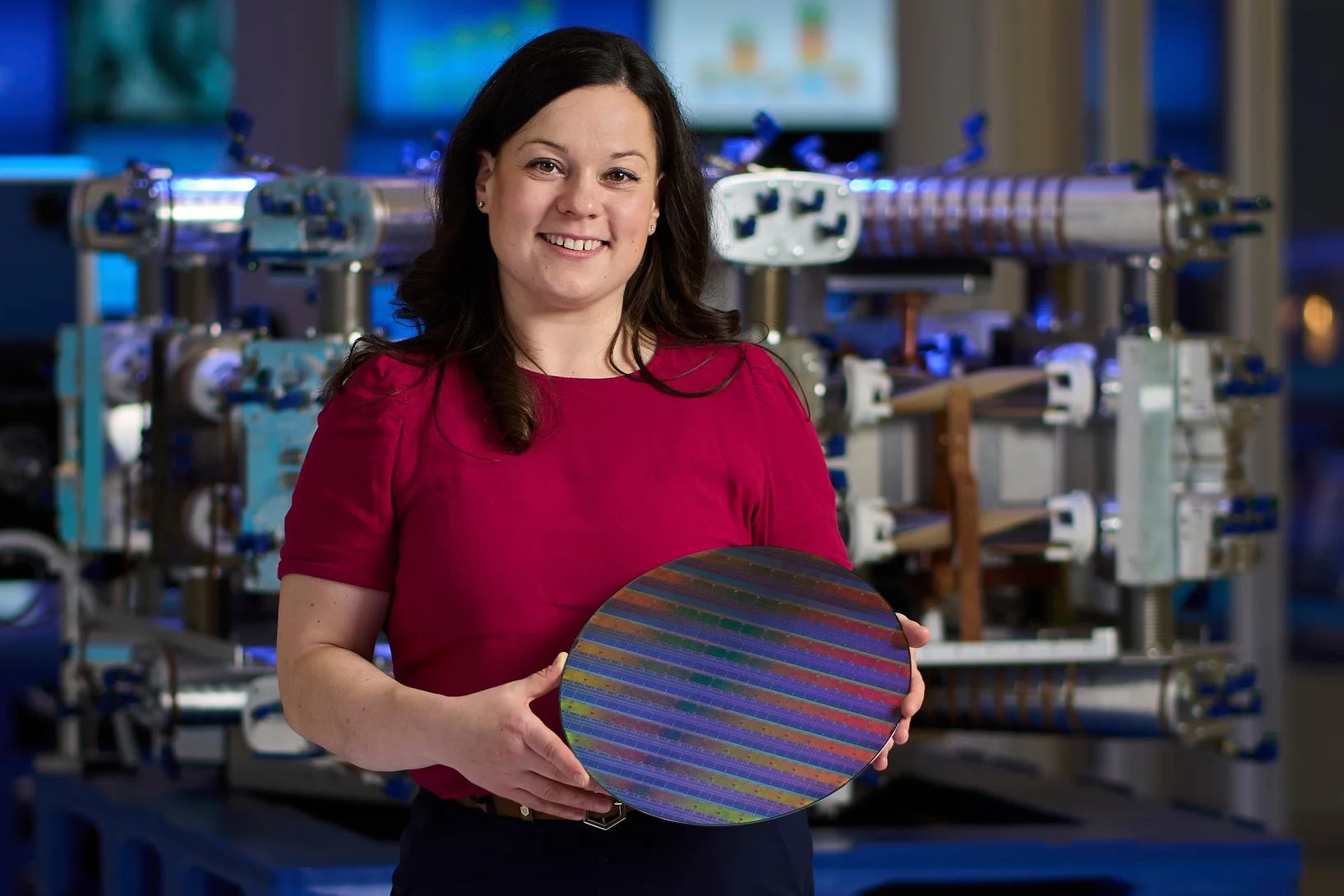
Plus rapide, précise et fiable: la production et son avenir
Le terme de fabrication avancée désigne des méthodes de fabrication ultramodernes. Les scientifiques du PSI améliorent la fiabilité de ces technologies, comme l’impression 3D, et continuent de faire progresser la miniaturisation de puces à haute performance.
Correcting quantum errors with neutral-atom architectures
Wenchao Xu talks about the benefits and challenges of building quantum computers from neutral atoms.
L’aluminium devient visible
Des scientifiques du PSI ont réussi une première: déterminer précisément la position des atomes d’aluminium dans des zéolithes, qui font de ces matériaux des catalyseurs si performants.
Identifier les perturbations génétiques dans les images de cellules grâce à l’IA
Une nouvelle IA détecte les perturbations génétiques dans la chromatine: une approche possible pour le diagnostic et le développement de médicaments.
Des scientifiques réalisent une mesure attoseconde record au SwissFEL
Les scientifiques du SwissFEL peuvent mesurer des impulsions de rayons X avec une résolution temporelle de l’ordre de l’attoseconde.
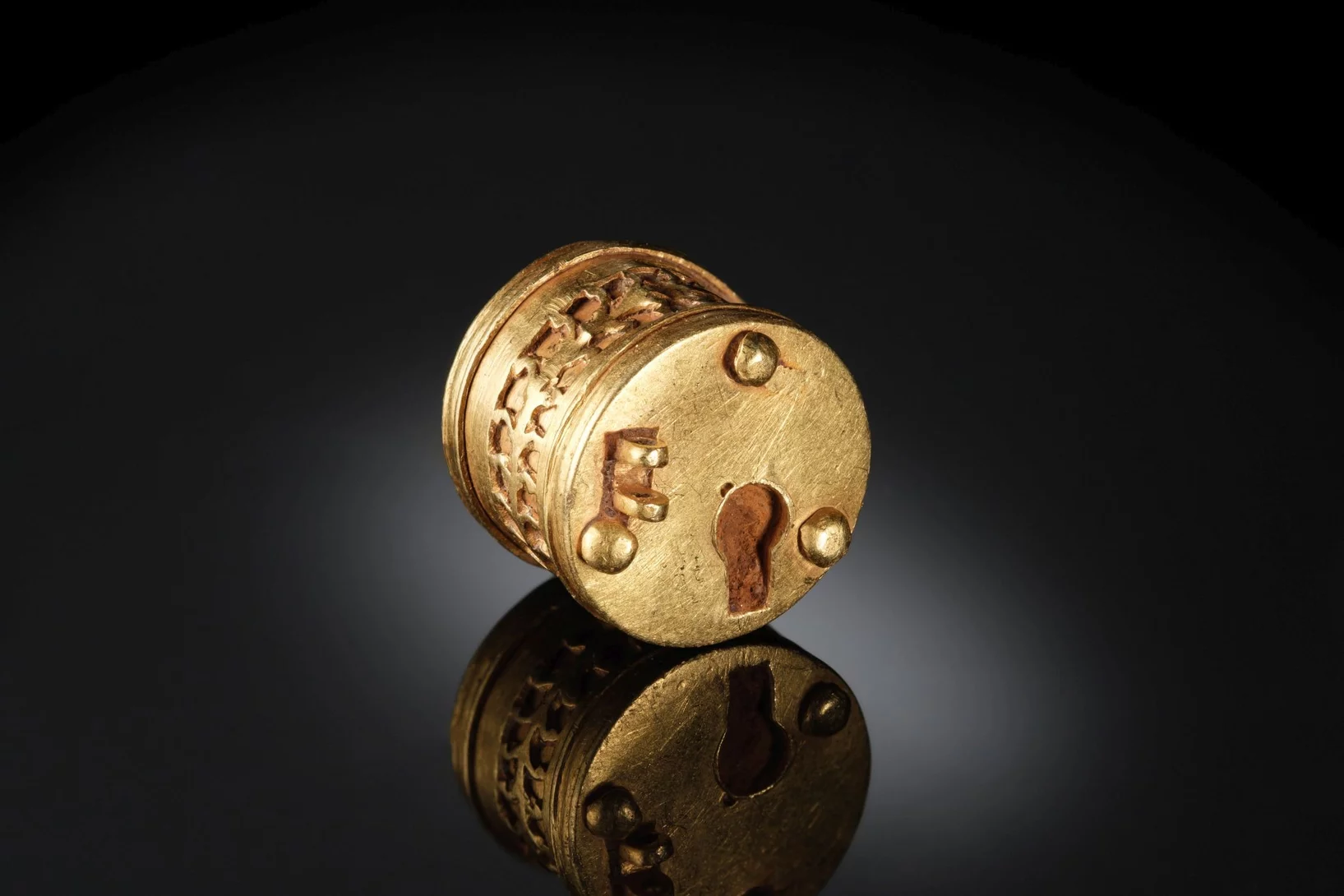
Une minuscule serrure en or de l’époque romaine
Grâce aux neutrons, David Mannes du PSI a percé le secret d’un fascinant artefact archéologique.
Une promotion ciblée de l'innovation pour la transition énergétique
Comment les innovations naissent-elles et comment peuvent-elles être encouragées de façon ciblée en vue de la transition énergétique? Michael Weinold, chercheur au PSI, a tenté de répondre à cette question en prenant pour exemple les lampes LED.
Plus vite vers l’hydrogène vert
Si l’on utilise du cobalt comme catalyseur, le pH détermine la facilité avec laquelle on pourra fabriquer de l’hydrogène par électrolyse de l’eau. Des scientifiques du PSI viennent de découvrir pourquoi.
Neutralité carbone: inclure les matières premières
Un nouveau modèle de calcul du PSI visualise les interactions complexes entre technologie, besoins en matières premières critiques et impacts environnementaux nécessaires à la transition du système énergétique vers «zéro émission nette» de gaz à effet de serre.
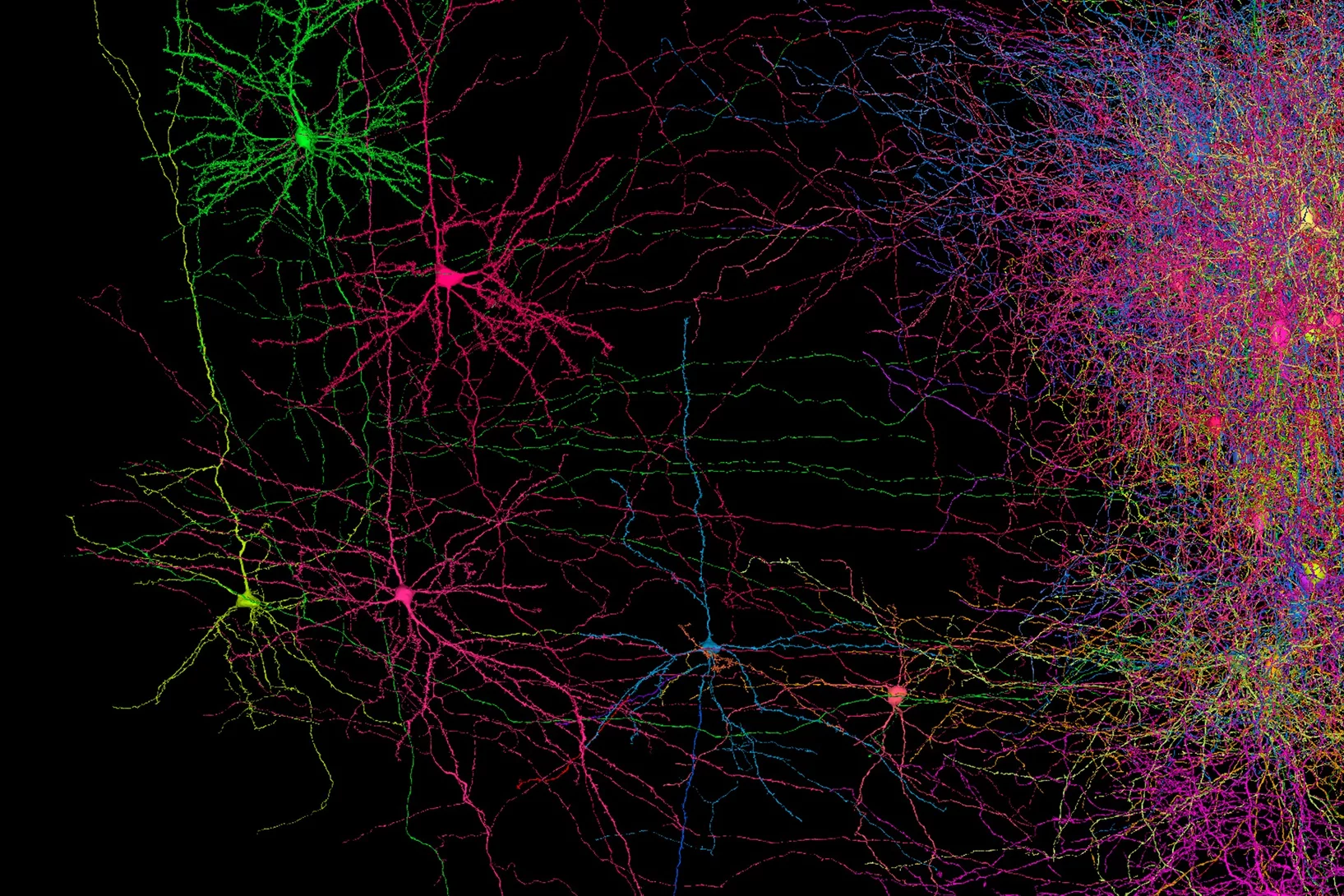
Etablir les schémas de connexions du cerveau
Comprendre la maladie d’Alzheimer grâce aux schémas de connexions du cerveau.
Les polluants ne se forment souvent que dans l'air
Dans le cadre de l’expérience CLOUD au CERN, des scientifiques du PSI ont mesuré avec une précision jamais atteinte à ce jour comment les polluants atmosphériques organiques se forment et se répartissent.
Un incroyable succès
Araris Biotech AG, spin-off du PSI, obtient une valorisation au niveau «licorne»
«La protonthérapie pourrait aider davantage de patientes et de patients»
Un livre qui vient de paraître retrace le développement de la protonthérapie au PSI. Damien Weber explique pourquoi le potentiel de cette méthode n’est pas encore pleinement exploité, alors qu’elle sauve des vies.
Bloc-notes, crayon et algorithmes
Dominik Sidler, physicien au PSI, développe des théories fondamentales pour des phénomènes restés inexpliqués à ce jour.
SLS 2.0: démarrage d’un accélérateur de particules
Les électrons sont de retour: après sa mise à niveau, la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS reprend peu à peu du service.
Subvention prestigieuse pour la recherche au PSI
Béton, catalyse chimique et quête d’une nouvelle physique: trois chercheurs du PSI ont reçu chacun un grant du Fonds national pour ces thèmes de recherche