Show filters
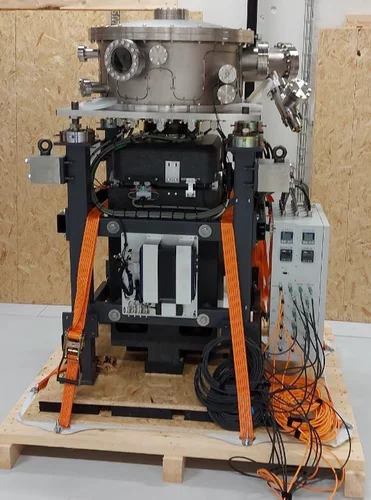
New Monochromators for SLS 2.0
The brand-new monochromators that have been built by XDS Oxford for the hard X-ray beamlines at SLS 2.0 have now arrived. They were unpacked beginning of the week, and are currently being tested in our new lab space at Park Innovaare. These advanced instruments will play a crucial role in enhancing the beamline performance, ensuring superior precision and efficiency in the upcoming experiments.
High-resolution ptychographic imaging at a seeded free-electron laser source using OAM beams
Electromagnetic waves possessing orbital angular momentum (OAM) are powerful tools for applications in optical communications, quantum technologies, and optical tweezers. Now, a consortium of collaborators in France, Italy, Slovenia, Spain, Switzerland, Sweden, and the US reports on using such beams in the extreme ultraviolet region for ptychographic imaging in the cover page article of Optica 11, Issue 3. By controlling the topological charge, the researchers achieve an improvement of 30% in image resolution.
SwissFEL: a next generation tool for Attosecond Science
The 2023 Nobel Prize in Physics recognises attosecond science’s pioneers. Past and future, this field’s evolution is entwined with SwissFEL.
Repairing genetic damage with sunlight
An international research team at SwissFEL of PSI has discovered how an enzyme repairs DNA damage with the help of sunlight.
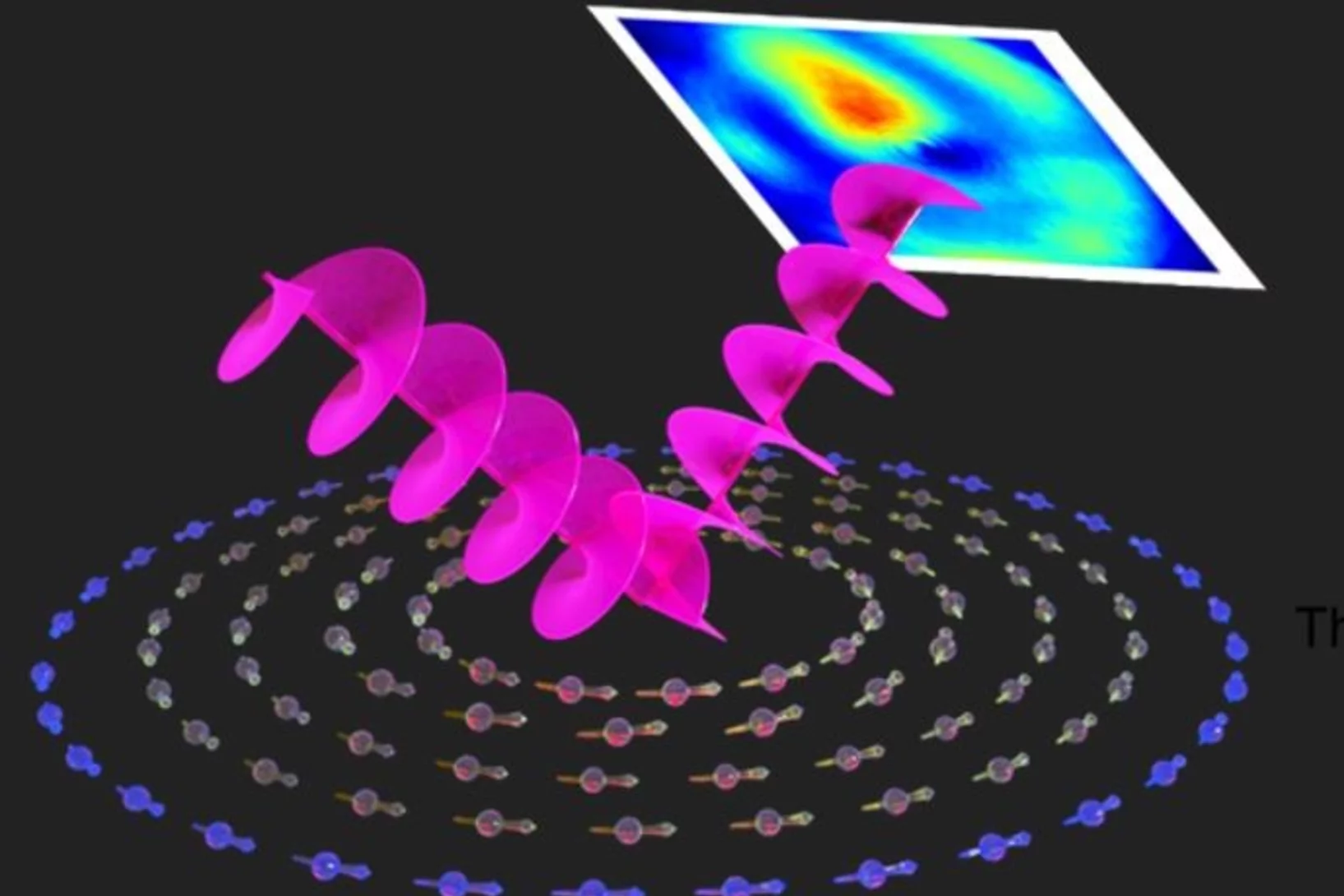
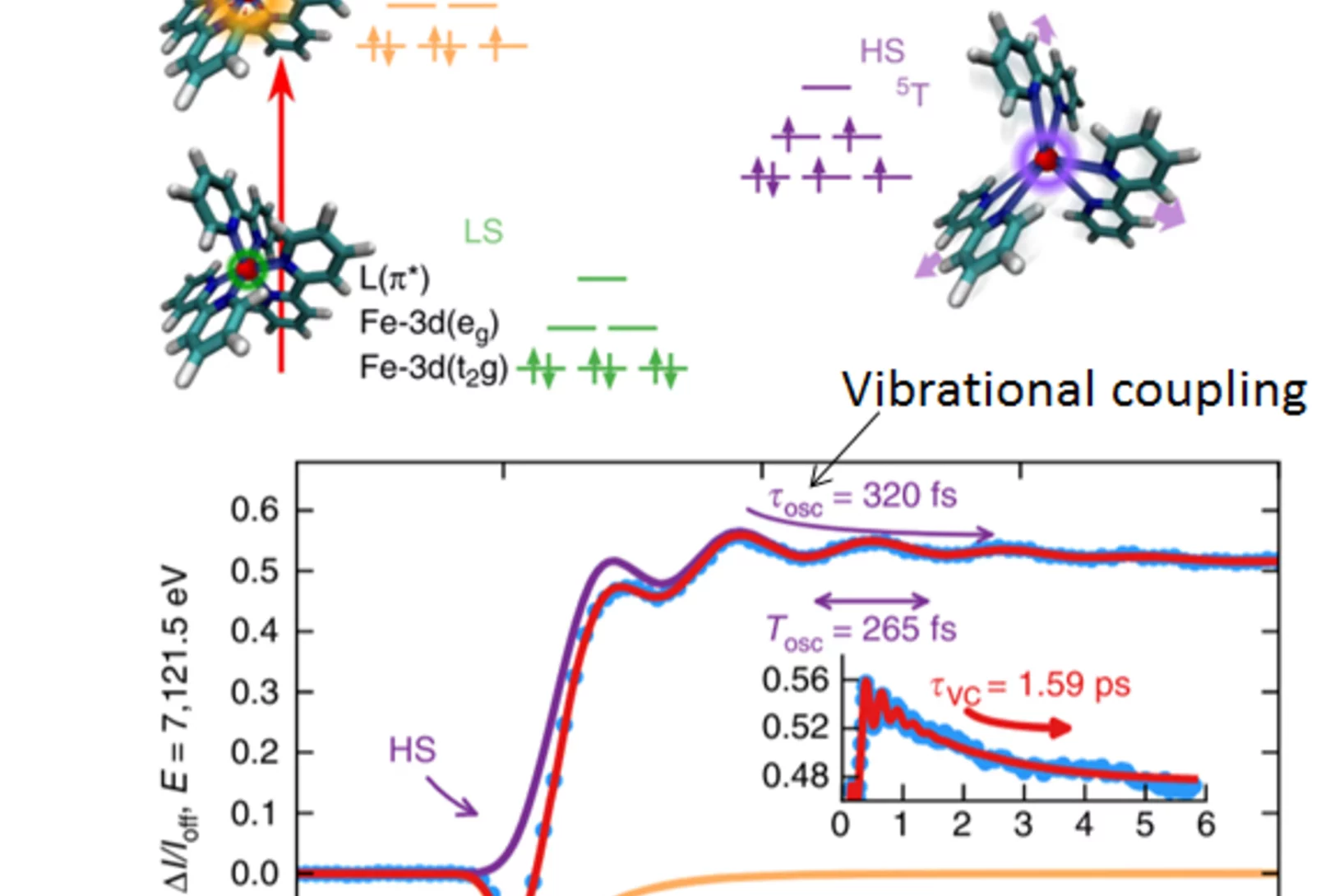
The secret life of an electromagnon
SwissFEL sheds light on how lattice and atomic spins jiggle together.
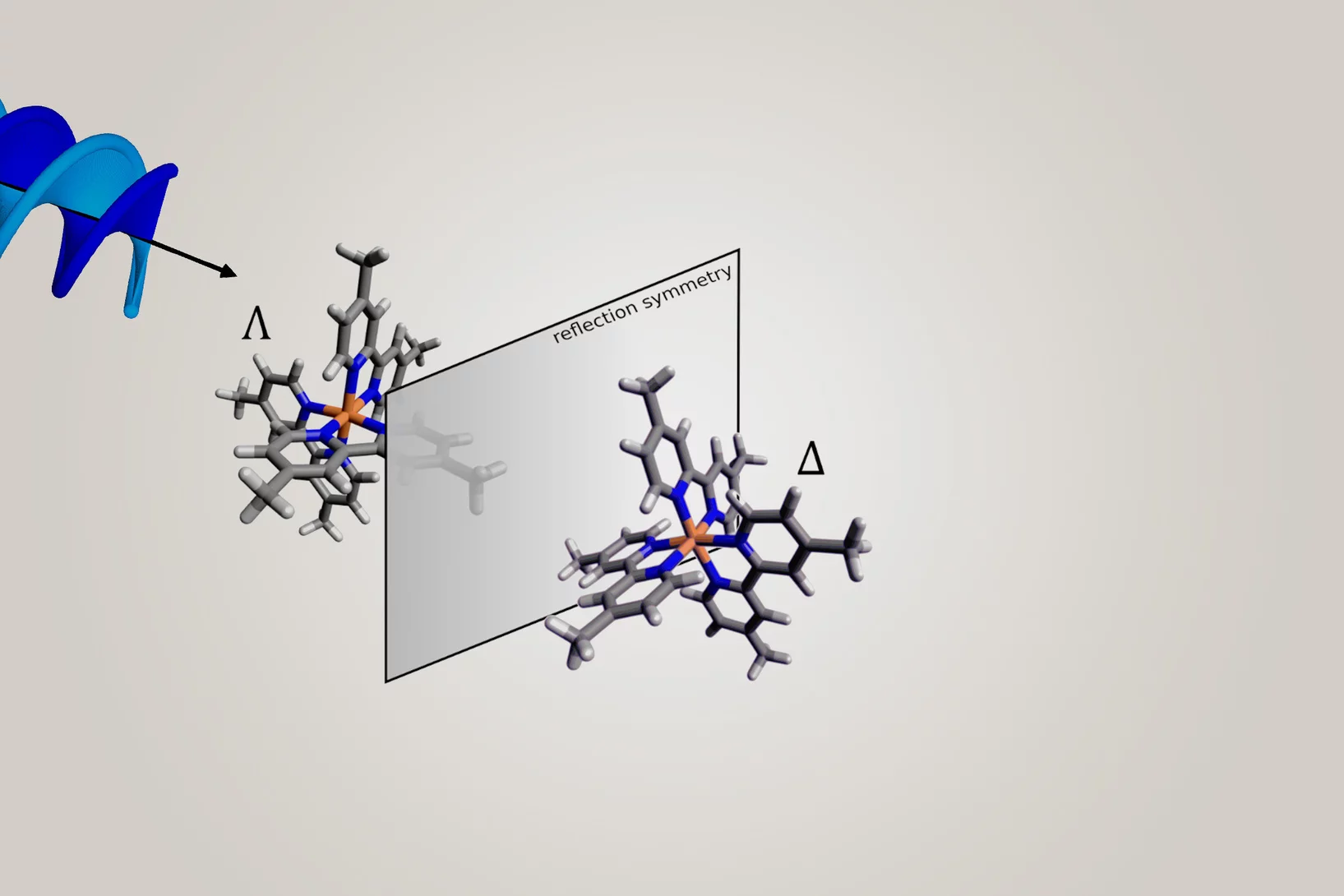
Making it easier to differentiate mirror-image molecules
Researchers have shown that mirror-image substances – so-called enantiomers – can be better distinguished using helical X-ray light.
Light-Induced Magnetization at the Nanoscale
Targeted manipulations of an atom's magnetic moment are tricky, as the charge currents used for this process are extremely difficult to control . Now, a consortium of collaborators in Germany, Switzerland, Slovenia and Italy reports on a solution to this problem in the cover page article of Physic Review Letters 128, Vol. 15. As it appears, the magnetization of an atomic gas can be altered by high-power lasers using a patterned wave front. The method is promising for studying and manipulating the magnetic properties of matter at the nanoscale.
Light springs and magnetic vortices: a new kind of dichroism
In contrast to circular dichroism that is dependent on the polarization, helicoidal dichroism induced by a twisted wave front profile is scarcely known. The first evidence of magnetic helicoidal dichroism has now been observed in an experiment using Spiral Fresnel Zone Plates developed at the Paul Scherrer Institut.
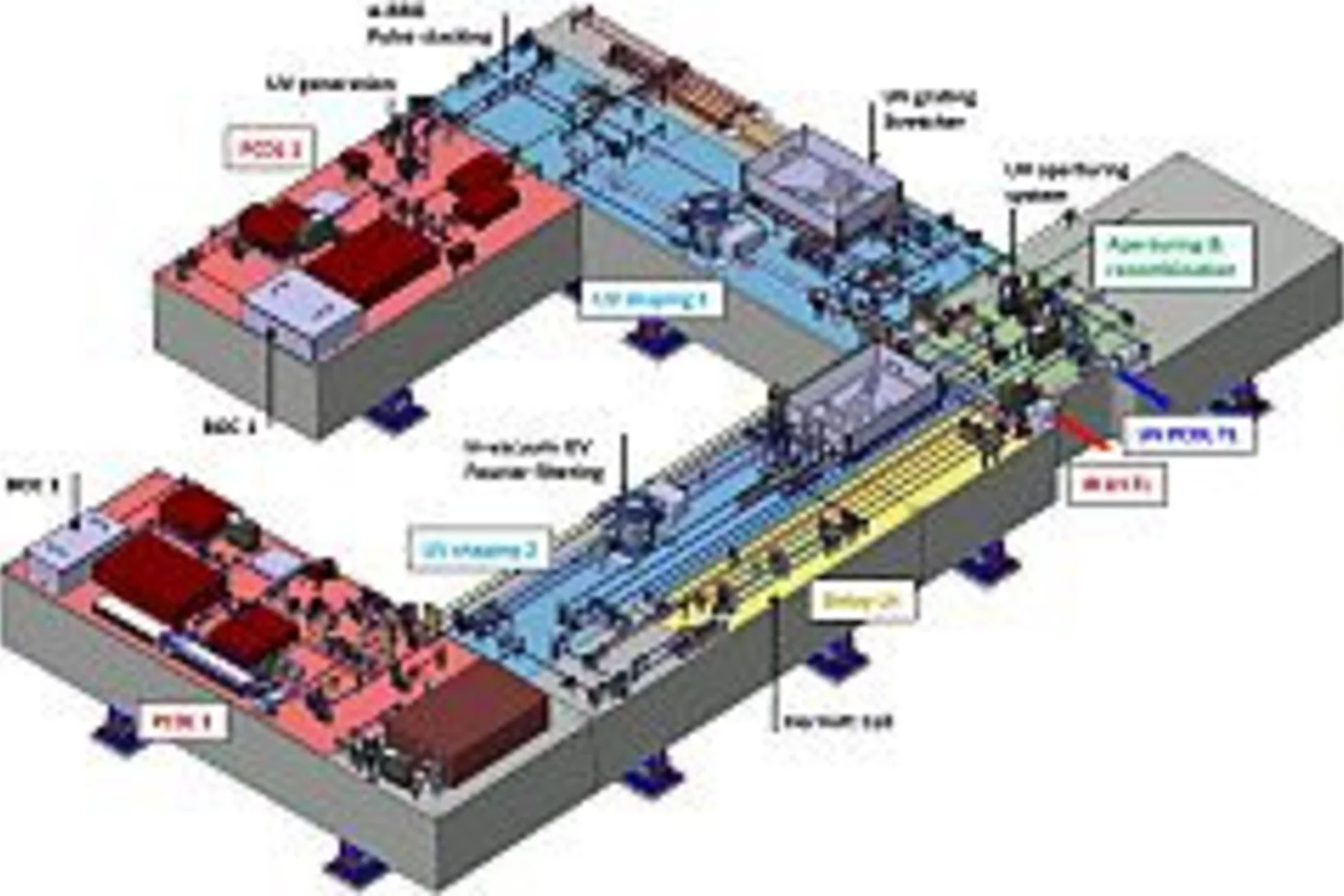
Overview of SwissFEL dual-photocathode laser capabilities and perspectives for exotic FEL modes
SwissFEL is a compact, high-brilliance, soft and hard X-ray Free Electron Laser (FEL) facility laser composed of two parallel beam lines seeded by a common linear accelerator (LINAC), and a two-bunch photo-injector. For the injector, an innovative dual-photocathode laser scheme has been developed based on state-of-the-art Ytterbium femtosecond laser systems. We just published an overview of the the SwissFEL Photo Cathode Drive Lasers (PCDL) performance, pulse shaping capabilities as well as the versatility of the systems, which allow many different modes of operation of SwissFEL [1]. The full control over the SwissFEL electron bunch properties via the unique architecture of the PCDL will enable in the future the advent of more advanced FEL modes; these modes are, but not restricted to, the generation of single or trains of sub-fs FEL pulses, multi-color FEL and finally the generation of fully coherent X-ray pulses via laser-based seeding.
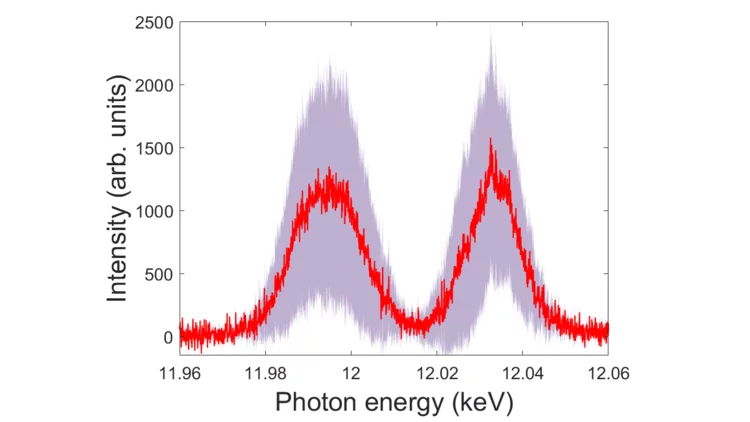
Two-color x-ray free-electron laser by photocathode laser emittance spoiler
A novel and noninvasive method for high-energy two-color x-ray FEL emission was demonstrated at SwissFEL. In the experiment, a laser emittance spoiler pulse is overlapped with the primary photocathode laser pulse to locally spoil the beam emittance and inhibit the FEL emission from the central part of the beam, ultimately resulting in X-ray emission at two wavelengths. High spectral stability and the possibility to independently control the duration and intensity ratio between the two-color X-ray pulses is demonstrated. The laser emittance spoiler also enables shot-to-shot selection between one and two-color FEL emission and further, as it does not contribute to beam losses, it is compatible with high repetition-rate FELs.
This article has been selected as the winner of the first Ernest Courant Outstanding Paper Recognition, a honor sponsored by the journal Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (PRAB) and the APS Division of Physics of Beams (DPB). This honor recognizes the most outstanding paper published in PRAB annually.
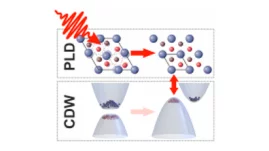
Structural involvement in the melting of the charge density wave in 1T-TiSe2
The authors find using resonant and non-resonant x-ray diffraction on an x-ray free electron laser that the structural distortion and the underlying electronic structure of the charge density wave in TiSe2 show different energetics at ultrafast timescales. This indicates that the lattice distortion stabilizes the charge density wave.
Clocking the movement of electrons inside an atom
Scientists pioneer an approach called self-referenced streaking, clocking Auger electrons with sub-femtosecond resolution. The breakthrough will unlock the broader potential for attosecond time resolution at X-ray free-electron lasers
A novel terahertz source for selective phonon excitation
Excitation of coherent phonons using light is an emerging approach for investigating condensed matter physics. It has the potential not only to reveal the dynamics of collective lattice vibrations but also to tailor them for the ultrafast control over the electronic, magnetic, and structural properties in solids. The optical phonons, in most solids, lie primarily in the spectral region between 1 and 10 THz. Unlike conventional laser sources, coherent radiation at these frequencies allows us to study time-resolved lattice displacements with only minor deposition of heat or generation of hot electrons. However, the available high-field terahertz sources, with their quasi-single cycle temporal shape and broadband spectrum, cannot be used to excite the individual phonon modes. By contrast, the challenge of understanding the transient dynamics of low-energy excitations calls for novel sources of narrow-band terahertz radiation at high intensities that can be tuned to the individual phonon resonances. Moreover, with strong enough fields tuned precisely to a phonon resonance, non-linearities in the material can be targeted and potentially exploited.
Long-lived pionic helium: Exotic matter experimentally verified for the first time
Exotic atoms, in which electrons are replaced by other particles, allow deep insights into the quantum world. After eight years, an international group of scientists have succeeded in a challenging experiment conducted at PSI’s pion source: they created an artificial atom called “pionic helium”.
Tailored electron bunch for SwissFEL
In order to achieve high-brillance and ultra-short FEL pulses, a flat current profile of the electron bunch is required. We achieve this by temporal shaping of the photo-cathode laser. From a femtosecond Gaussian pulse, we produce a picosecond long, flat-top laser pulse. At low charge, the photo-cathode laser pulse temporal profile is directly transferred into the electron bunch temporal profile.
New mid-IR pump source for SwissFEL with CEP capabilities installed
LNO has just installed a new CEP-capable mid-IR source for SiwssFEL experiments. The new source will enable a new class of experiments focused on understanding the unique properties of nonequilibrium driven states.
A new twist on a mesmerising story
The Einstein–de Haas effect, first demonstrated more than a century ago, provides an intriguing link between magnetism and rotation in ferromagnetic materials. An international team led by ETH physicist Steven Johnson now established that the effect has also a central role in ultrafast processes that happen at the sub-picosecond timescale — and thus deliver fresh insight into materials that might form the basis for novel devices.
Hollywood in the Würenlingen woods
With the X-ray laser SwissFEL, researchers at PSI want to produce movies of biomolecules in action. This can reveal how our eyes function or how new drugs work.
First Pilot Experiment at SwissFEL-Alvra: UV photo-induced charge transfer in OLED system
On the 17th of December 2017 SwissFEL saw its first pilot experiment in the Alvra experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline.
First experiment at SwissFEL carried out successfully
The years of careful planning and construction have paid off: At the newest large-scale research facility of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI – the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL – the first experiment has been carried out successfully. With that, two goals have been achieved: First, a new scientific result is already expected. Second, the interaction of the many individual components of the highly complex facility is being optimised.
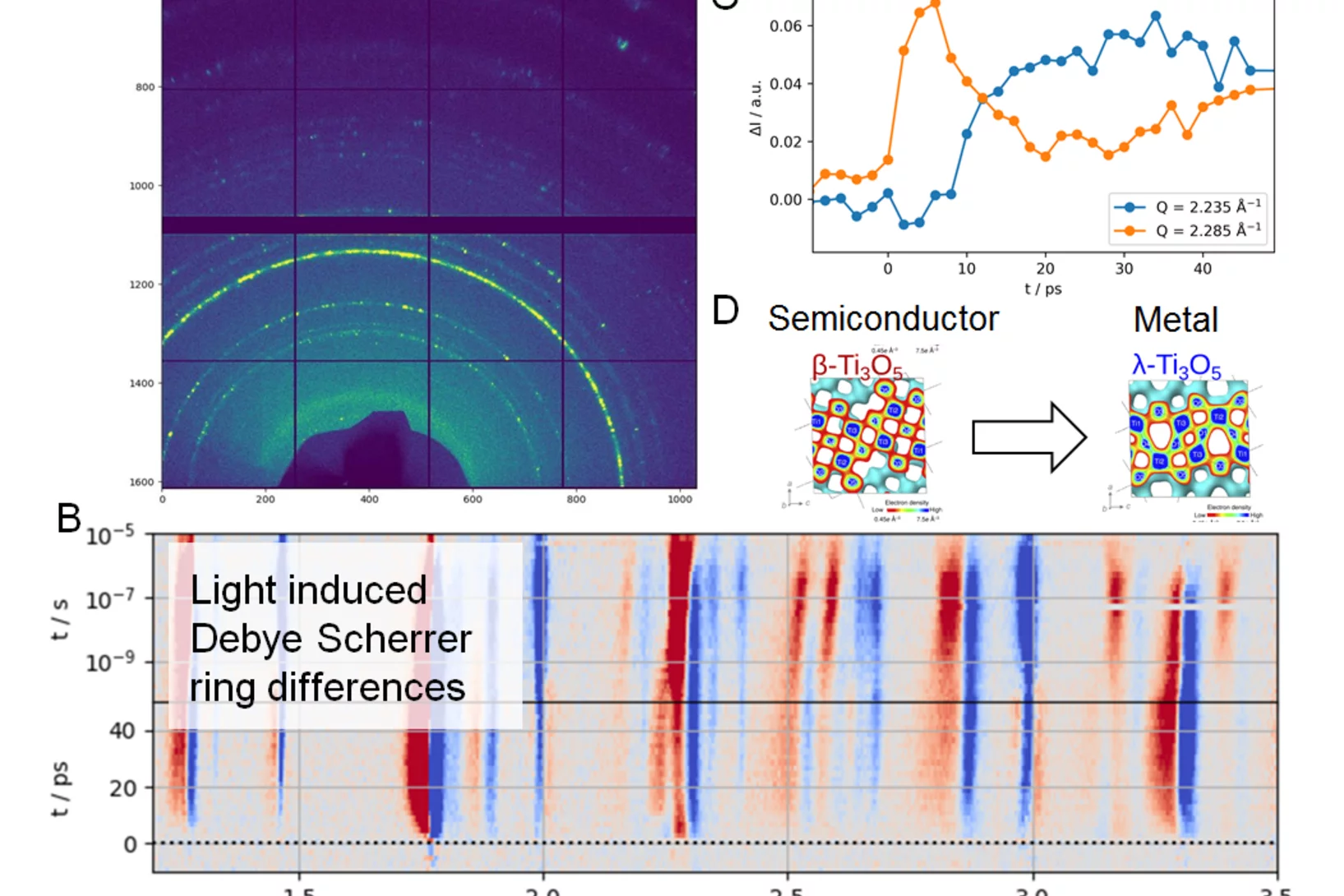
First time resolved Pilot Experiment by SwissFEL: Semiconductor to metal transition in Ti3O5 nanocrystals
On the 30th of November 2017 SwissFEL saw its first time resolved pilot experiment in the Bernina experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline. A team of scientists from the University of Rennes, ESRF and PSI, led by Marco Cammarata (Univ. Rennes) and Henrik Lemke (PSI), successfully started the experimental phase at SwissFEL.
How ‘super-microscopes’ are changing the face of European science
13 November 2017 – Brussels – 16 organisations representing 19 light sources facilities across Europe gathered to launch the LEAPS initiative and signed an agreement to strengthen their collaboration, in the presence of Robert-Jan Smits, Director General for Research and Innovation (RTD) at the European Commission, and Giorgio Rossi, Chair of the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures (ESFRI).
First light in SwissFEL Experimental Station Bernina
Friday, October 20th, 2017, we brought the first light (wavelength 1.2 nm) into the experimental hutch of Bernina. The beam passed the Alvra endstation, went through the diagnostic devices and hit the diagnostic screen in front of the refocussing KB-system of Bernina. The upper picture shows the pink beam on the last diagnostic screen of the beamline. The lower left at the entrance of Bernina-hutch, 133 m downstream of the undulator. The lower right picture shows the beam centered in the alignment iris in front of the KB-system.
ATHOS Conceptual Design Report (CDR)
The ATHOS Conceptual Design Report has recently been completed and describes the ATHOS project in detail. The CDR starts with a summary of the characteristics of the ATHOS undulator line. Especially the design parameters of the different ATHOS operation modes are explained and illustrated by simulation results. The core part of the report is a description of all key components, i.e. from the electron bunch extraction kicker down to the ATHOS experimental stations.
Scientists get first direct look at how electrons ‘dance’ with vibrating atoms
Scientists at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University - one of the leading authors, Simon Gerber, has in the meantime relocated to PSI - have made the first direct measurements, and by far the most precise ones, of how electrons move in sync with atomic vibrations rippling through an quantum material, in the present study an unconventional superconductor, as if they were “dancing" to the same beat.
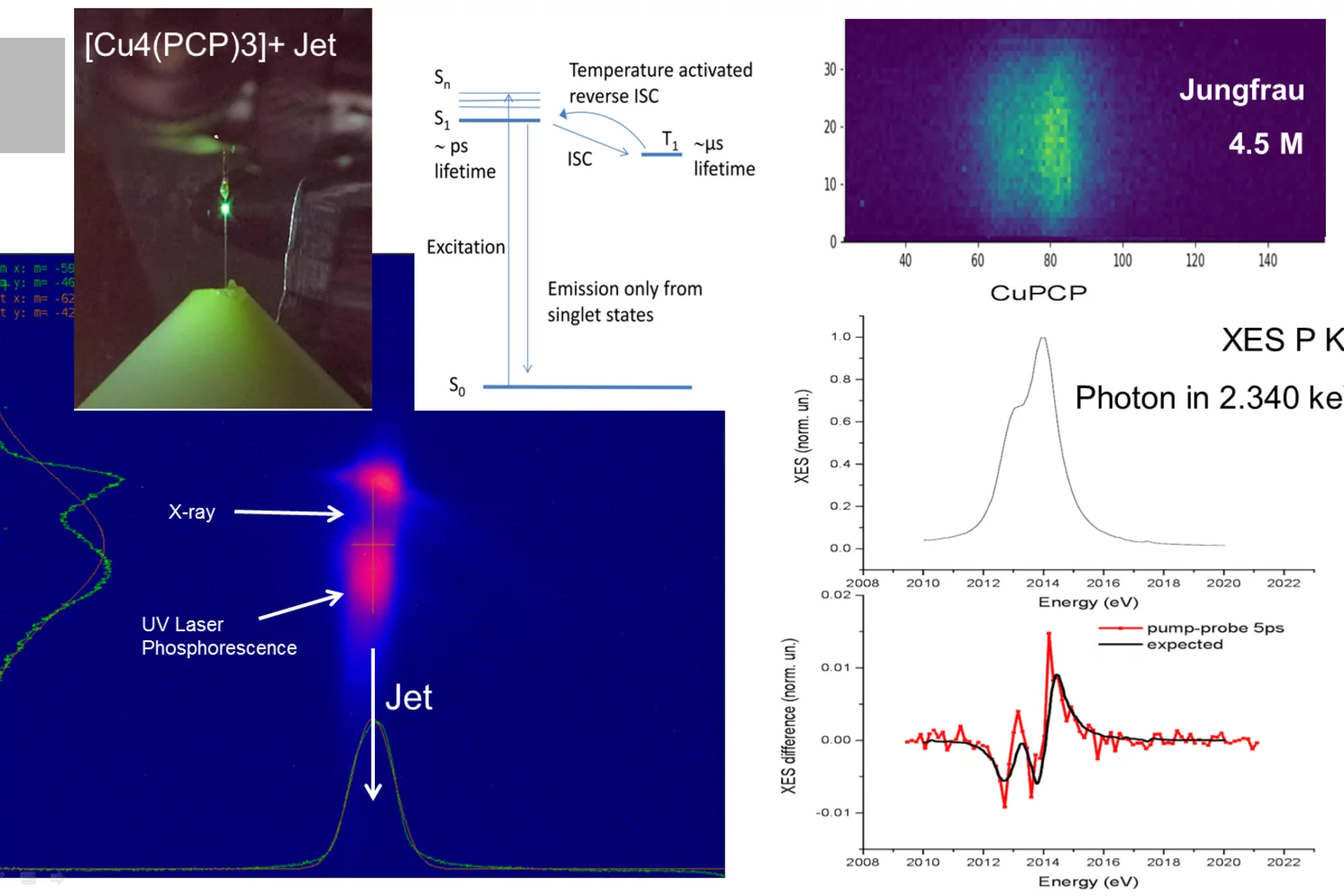
Observing switching of Molecules using Free Electron Lasers
Free electron lasers (FELs) like SwissFEL help scientists to understand the mechanisms that switch properties of materials which are the basis for functions in electronics, solar cells, chemistry and biology. By using ultrashort X-ray pulses it becomes possible to visualize the ultrafast rearrangements of electrons and atoms that enable the properties to switch in molecules or crystals.
First lasing at a wavelength of 4.1 nm
The electron beam energy of SwissFEL was recently increased to above 900 MeV by successfully bringing two new accelerating modules into operation. This allowed SwissFEL to produce laser radiation for the first time in the soft x-ray regime with a photon wavelength of 4.1 nm. During the next months, the electron beam energy will be progressively further increased with the goal of enabling first user experiments at a wavelength of around 0.5 nm towards the end of this year.