Interfacial Phase Formation in 316L–CuCrZr Hybrids
In-situ X-ray diffraction reveals how phase separation and fluid flow shape microstructure in laser-welded multi-material metal builds.
Sarbajit Banerjee wins Royal Society of Chemistry’s Centenary Prize
ETH Zürich and the Paul Scherrer Institut PSI scientist Professor Sarbajit Banerjee has been named winner of the Royal Society of Chemistry’s Centenary Prize in recognition of brilliance in research and innovation.
PSI research at Switzerland’s most-visited museum
Making energy research something visitors can experience: The Swiss Museum of Transport is creating a platform for political and social dialogue on energy issues.
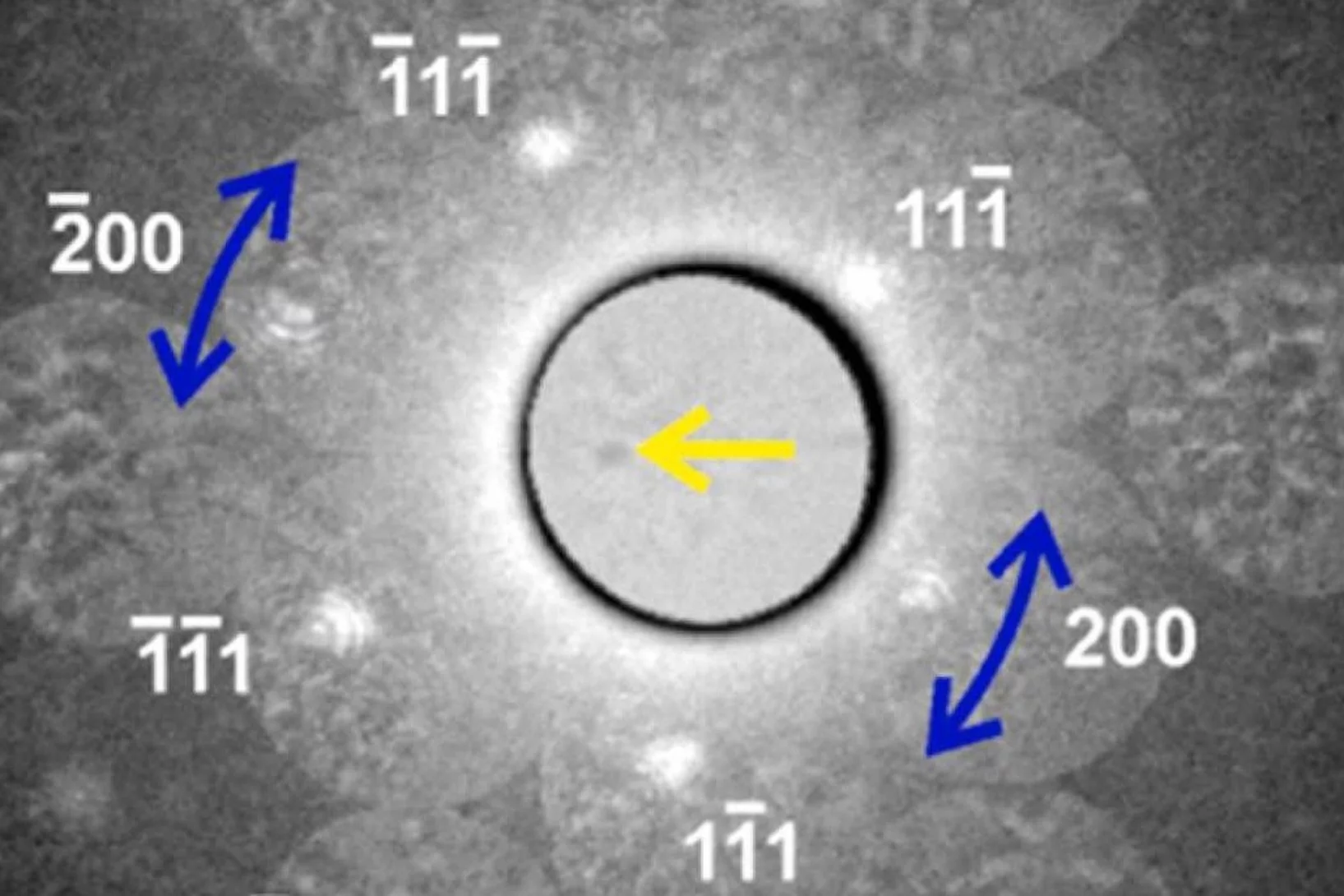
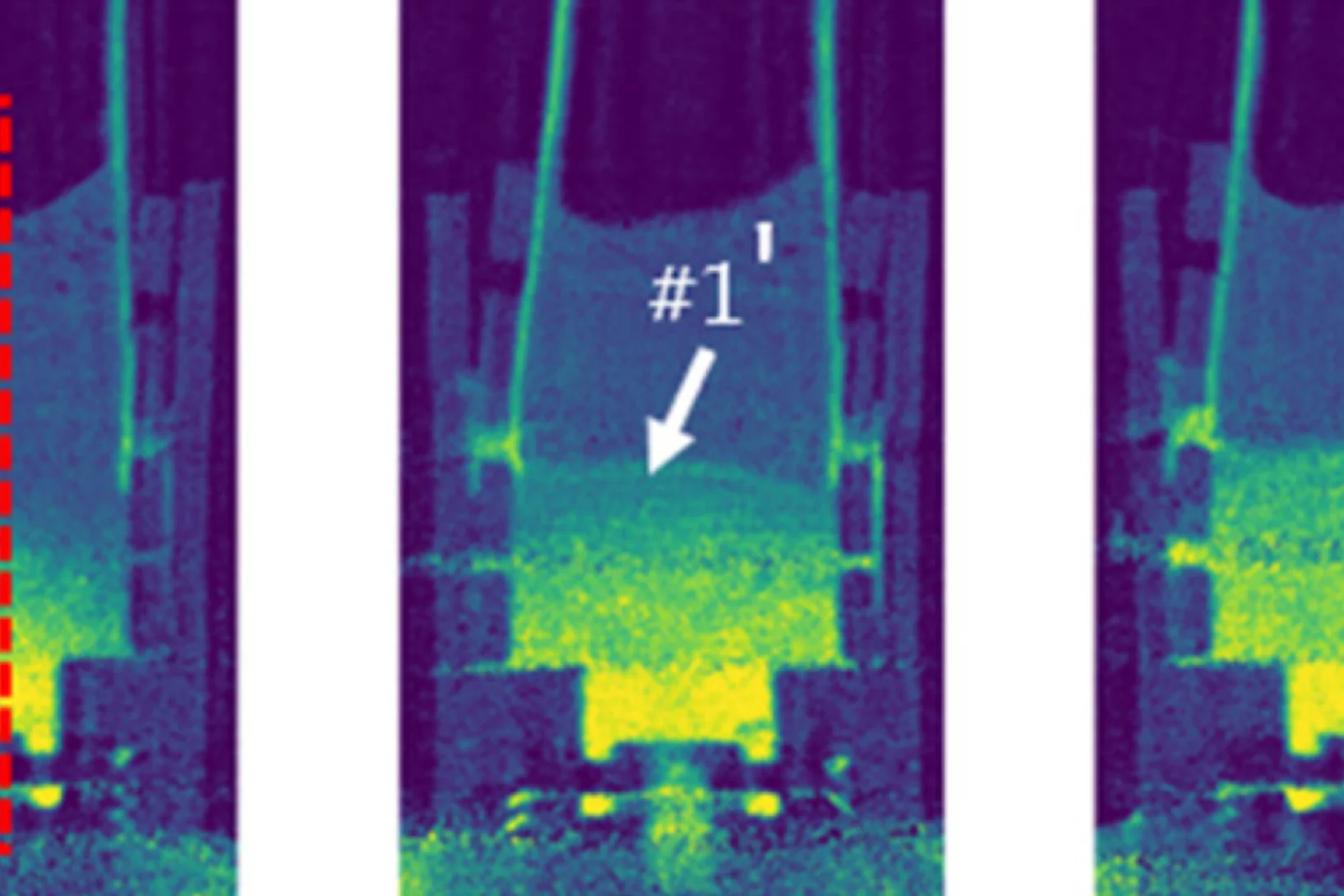
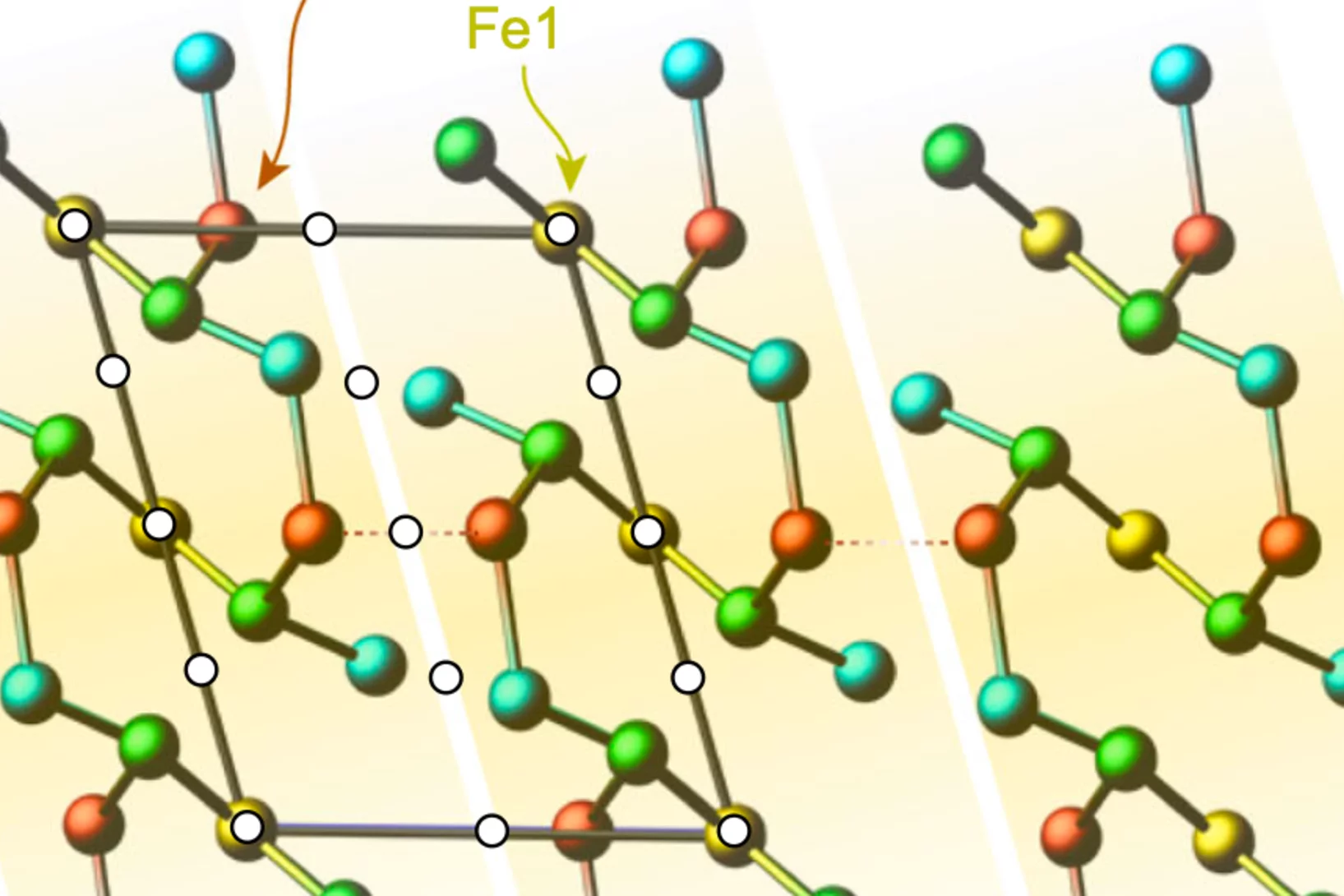
Phase by Phase: How Stainless Steel and IN625 Solidify Together
Where steel meets superalloy: real-time X-ray snapshots reveal how composition and cooling shape metal during 3D printing
AI paves the way towards green cement
Researchers at PSI are using artificial intelligence to develop environmentally friendly formulations for cement.
Prestigious research grant for photonic networks
PSI researcher Kirsten Moselund has been awarded a major research grant from the European Research Council ERC.
Steering magnetic textures with electric fields
Neutrons reveal a new way to control magnetism at the nanoscale
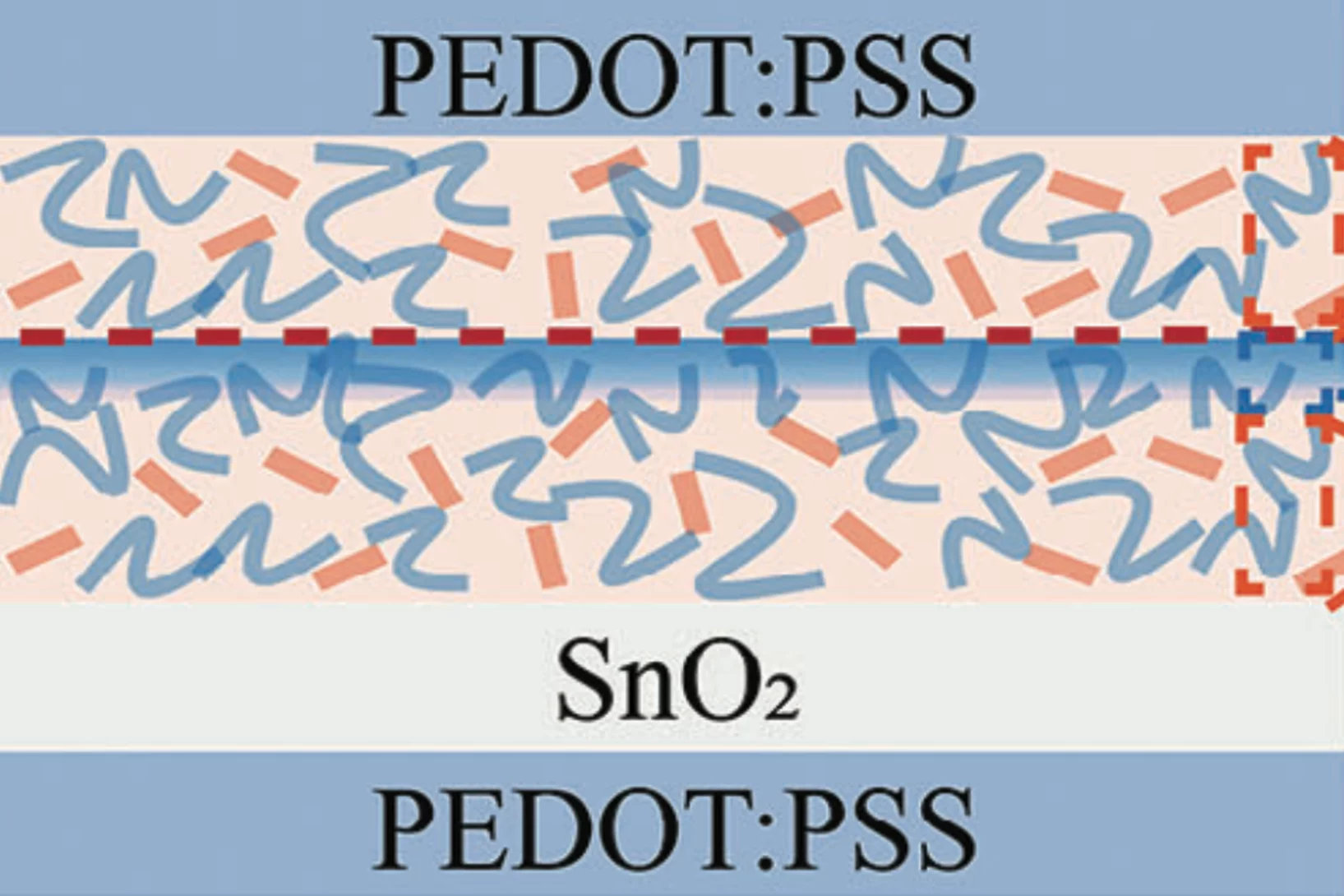
Understanding and Addressing the Performance Asymmetry Issue in Semitransparent Laminated Organic Photovoltaic Devices
Organic photovoltaics (OPVs) offer a promising solution for indoor energy harvesting. However, fundamental investigations to understand and optimize industrial processes such as roll-to-roll lamination for upscaling remain limited. This study investigates a critical failure mode in the upscaling of OPVs.
One major challenge ...
Stabilising fleeting quantum states with light
X-rays from SwissFEL probe emergent properties of quantum materials
Gold nanoparticle dynamics on graphene probed by convergent beam electron diffraction.
Dynamics of single Au nanoparticles on graphene were probed simultaneously in real- and diffraction space by time-series convergent beam electron diffraction.
Science meets industry – innovation with an impact
Hans Priem and Cees Maris of VDL ETG explain what advanced manufacturing means in industry and talk about their collaboration with PSI.
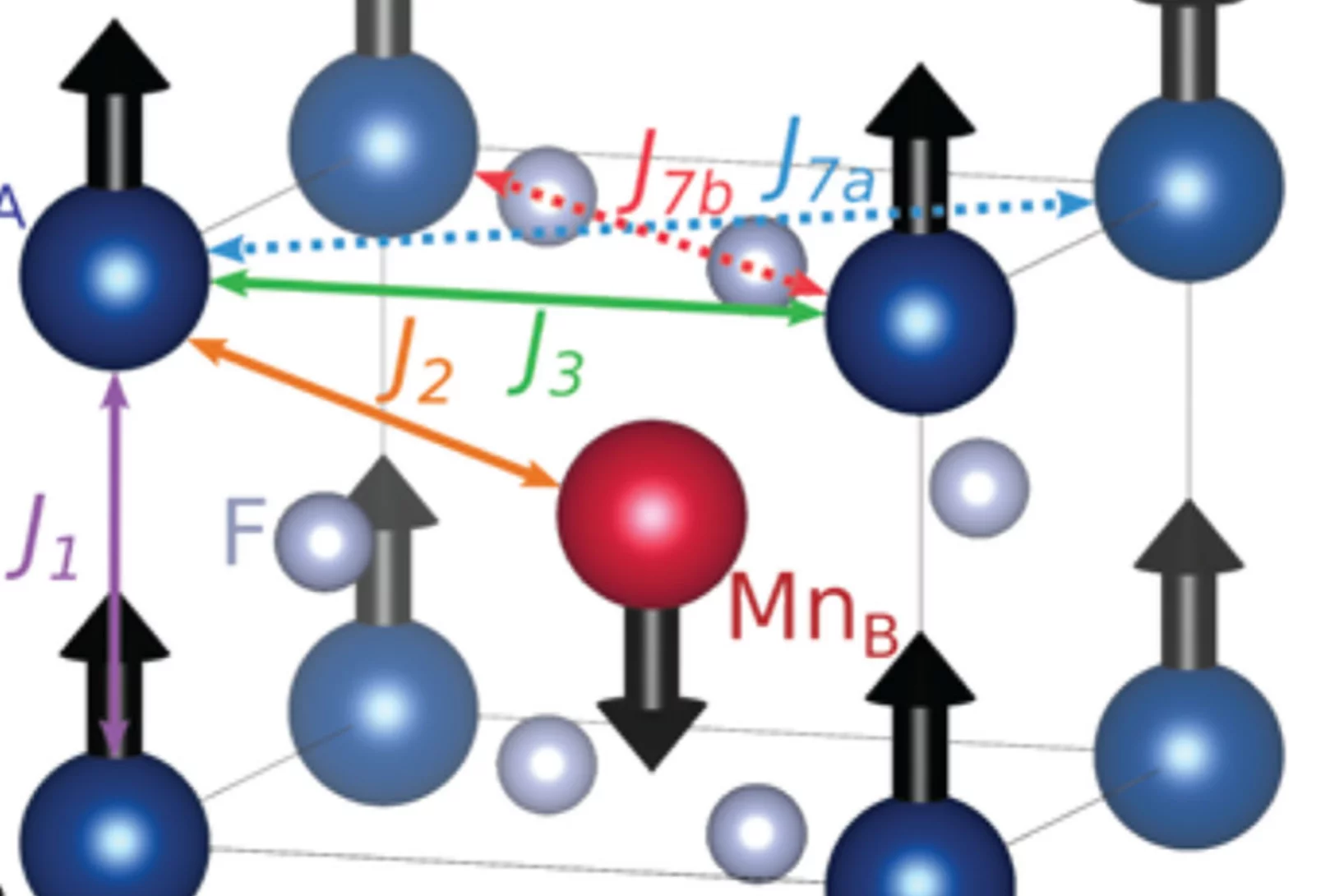
Absence of Altermagnetic Magnon Band Splitting in MnF2
Altermagnets are collinear compensated magnets in which the magnetic sublattices are related by rotation rather than translation or inversion. One of the quintessential properties of altermagnets is the presence of split chiral magnon modes. Recently, such modes have been predicted in MnF2.
Here, we report inelastic neutron scattering results ...
Using terbium against lymphoma
Promising laboratory experiments at PSI show that radionuclide therapy with the radioactive element terbium could combat lymphoma effectively.
Pressure effect on the spin density wave transition in La2PrNi2O6.96
High-pressure studies reveal a stark contrast between the superconducting properties of double-layer Ruddlesden-Popper (RP) nickelates La2PrNi2O7 and La3Ni2O7. While La2PrNi2O7 exhibits bulk superconductivity, La3Ni2O7 displays filamentary behavior, suggesting that superconductivity is confined to phase interfaces rather than the bulk. Since magnetism emerges ...
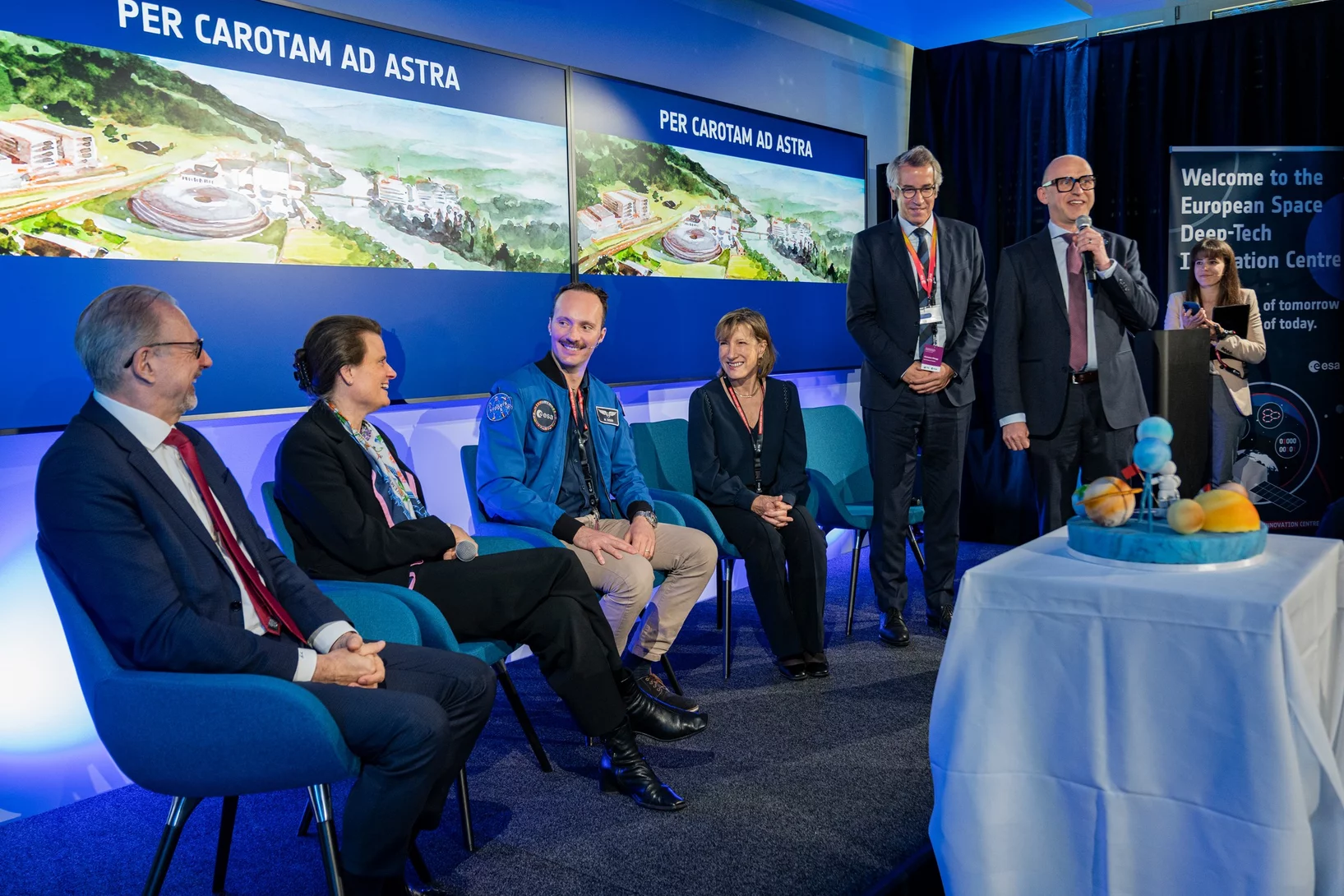
ESA Centre of Excellence opens in Switzerland
The opening ceremony of the “European Space Deep-Tech Innovation Centre” ESDI brought together distinguished guests.
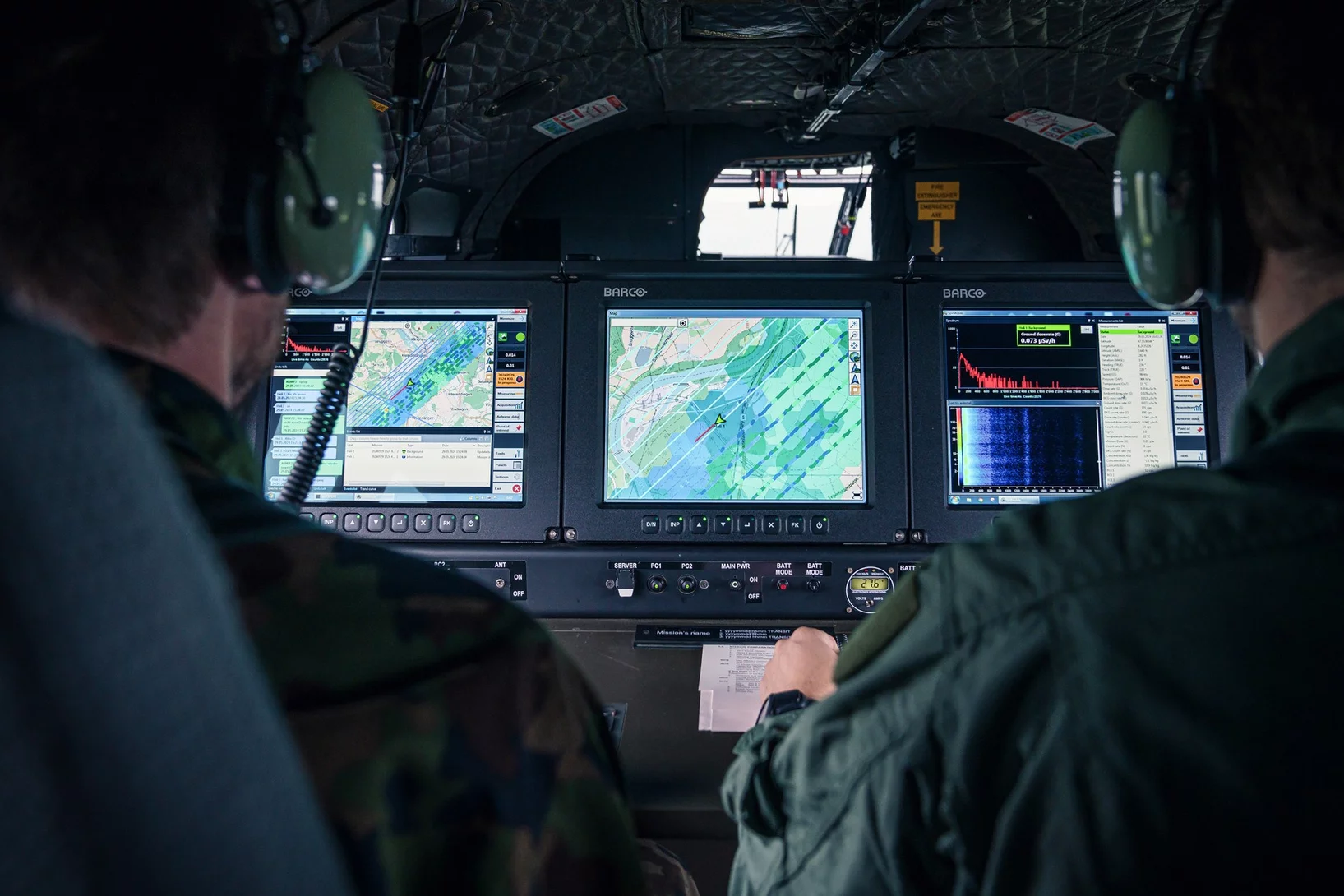
Decoding radiation
Searching for radiation from the sky. How a sensitive detector and a clever algorithm are making ionising radiation visible.
New standards in nuclear physics
With unprecedented precision: PSI researchers measure the nuclear radius of muonic helium-3 and put the theories of atomic physics to the test.
Research Software Engineering (RSE) Movement at PSI
The online information event on the “Research Software Engineering (RSE) Movement” at PSI on Wednesday 7th May, 2025 was a quite success with an unexpected high number of 100+ participants!
Successful Swiss DeepTech CVC Day 2025
On May 21, 2025, the Swiss DeepTech CVC Day took place at the Switzerland Innovation Park Innovaare – a significant event that brought together leading representatives from the Corporate Venture Capital (CVC) sector and innovative DeepTech start-ups from Switzerland.
Faster, more precise, more reliable – the future of manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing means using state-of-the-art production methods. Researchers at PSI are helping to make techniques such as 3D printing more reliable and to advance the miniaturisation of high-performance chips.
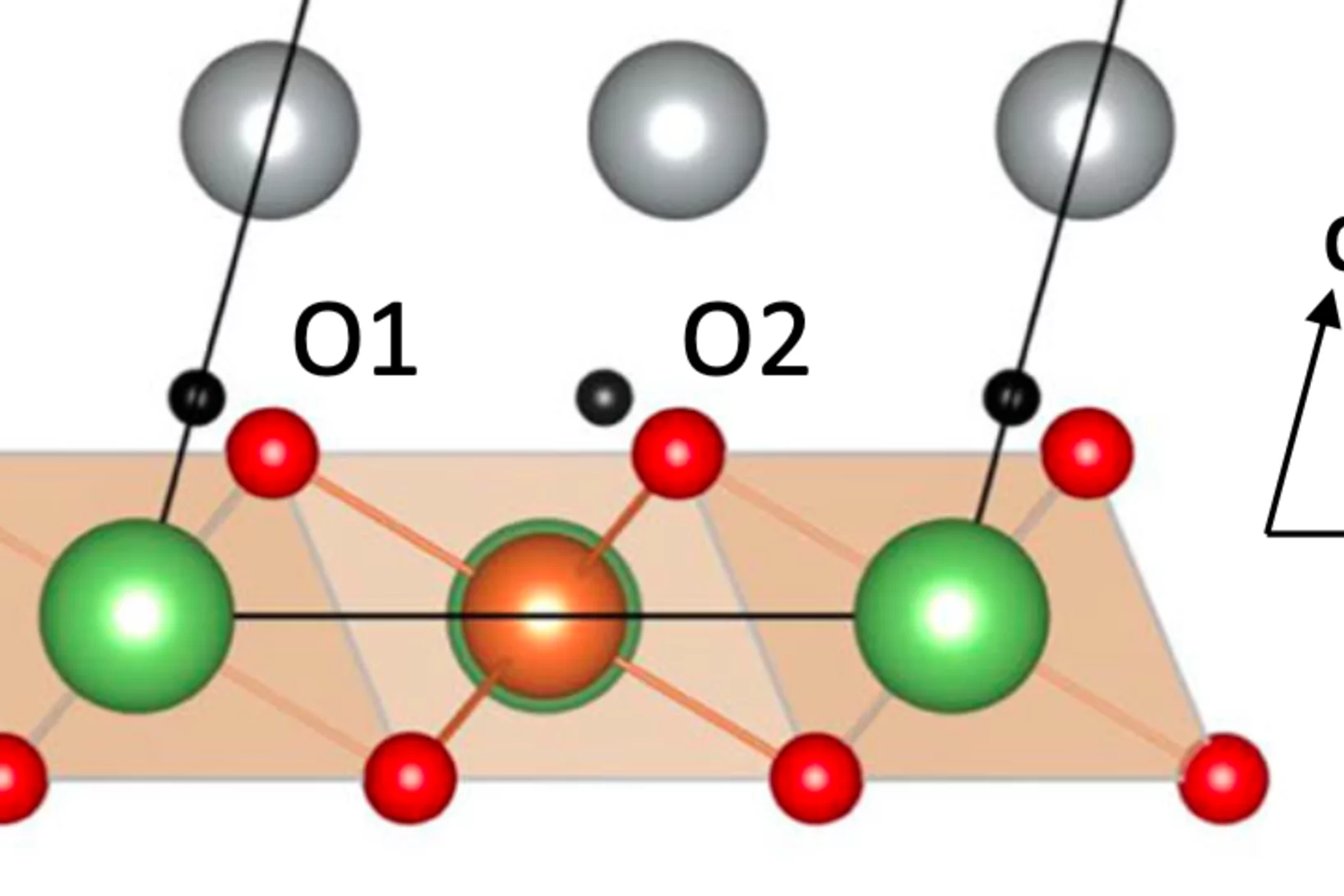
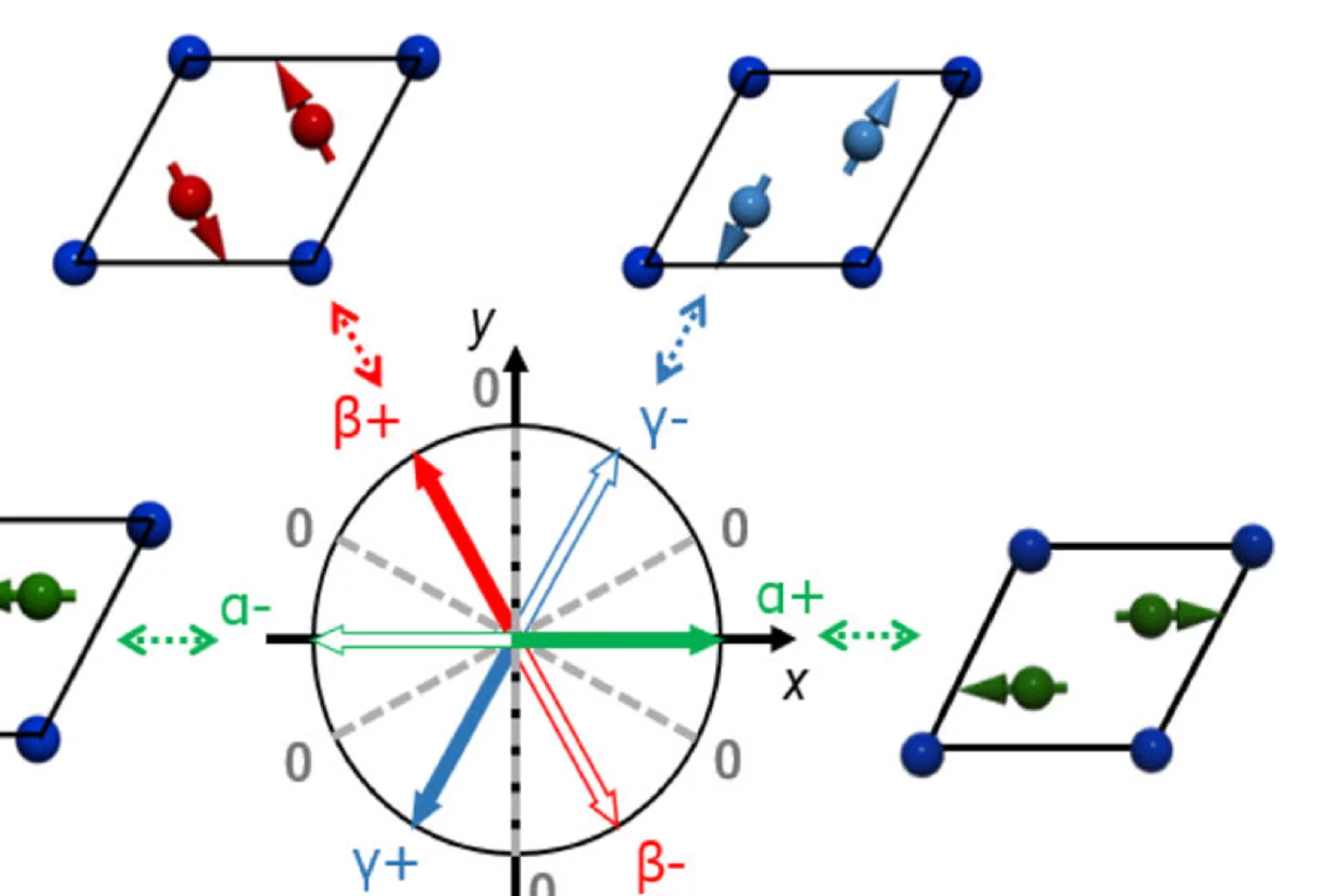
Pressure tuning of competing interactions on a honeycomb lattice
Exchange interactions are mediated via orbital overlaps across chemical bonds. Thus, modifying the bond angles by physical pressure or strain can tune the relative strength of competing interactions. Here we present a remarkable case of such tuning between the Heisenberg (J) and Kitaev (K) exchange, which respectively establish magnetically ordered and spin liquid phases on a honeycomb lattice. We observe ...
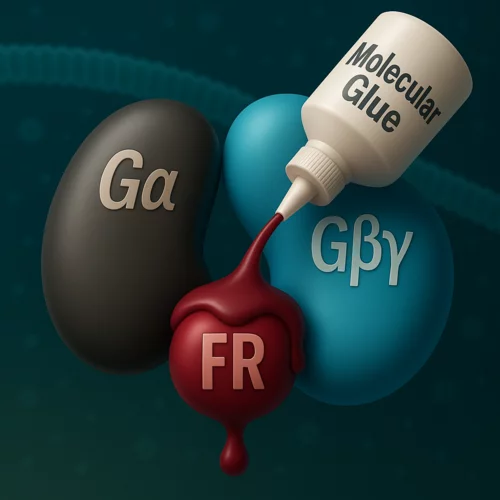
From coral berries to new therapies: uncovering the molecular glue mechanism of natural compounds
Researchers at the Center for Life Sciences and the Center for Scientific Computing, Theory, and Data at the Paul Scherrer Institute have identified the mechanism by which certain natural compounds interfere with cellular signaling. These ‘molecular glues’ have a therapeutic potential for the treatment of specific cancer types. Their latest study on this topic has been published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
Dr. Yingfang He has been honored with the Alavi-Mandell Award 2025
We congratulate Dr. Yingfang He for the excellent research work she did during her time at the Center for Radiopharmaceutical Sciences.
Correcting quantum errors with neutral-atom architectures
Wenchao Xu talks about the benefits and challenges of building quantum computers from neutral atoms.
Aluminium made visible
PSI researchers have for the first time determined the exact position of the aluminium atoms in zeolites, which make these materials such good catalysts.
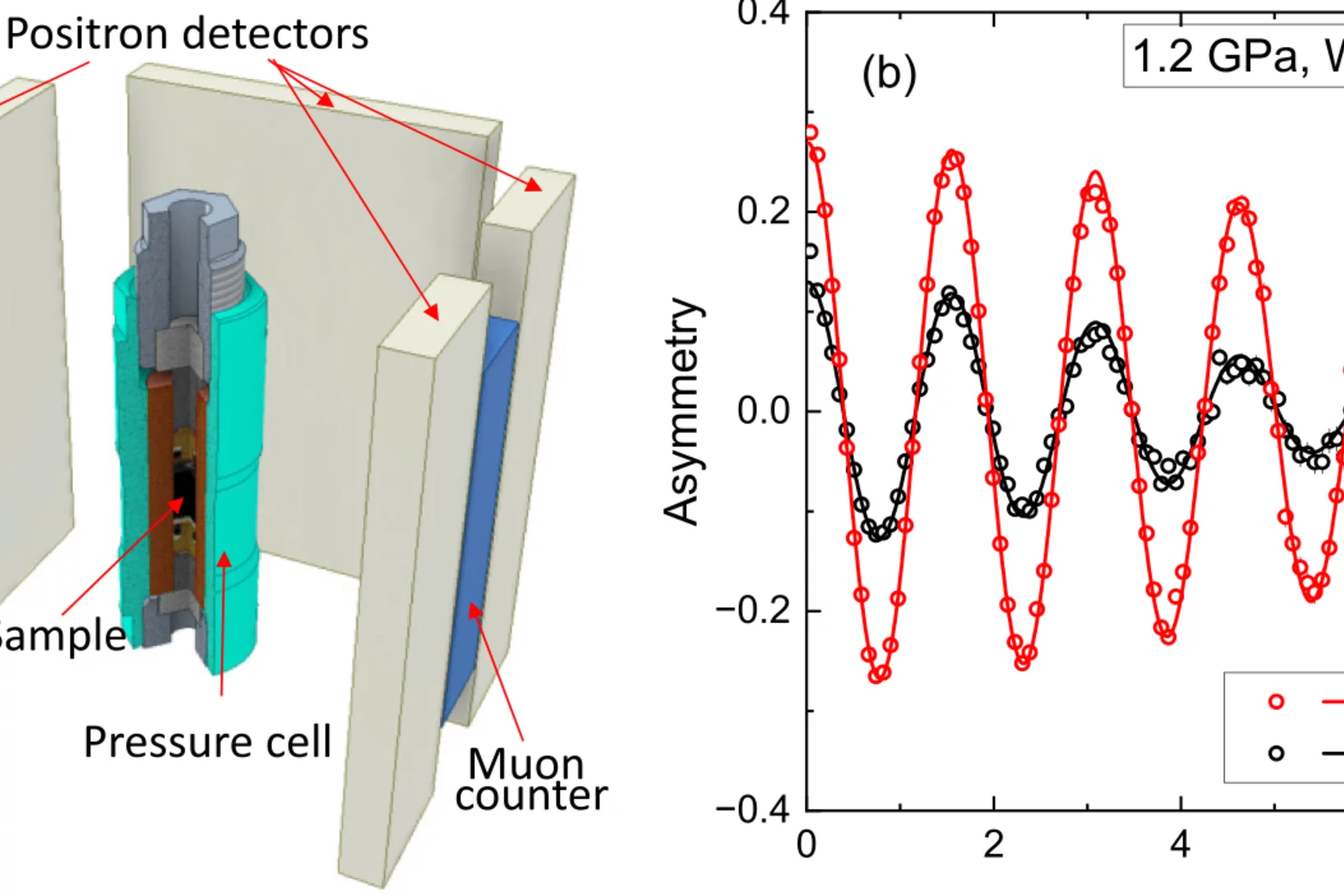
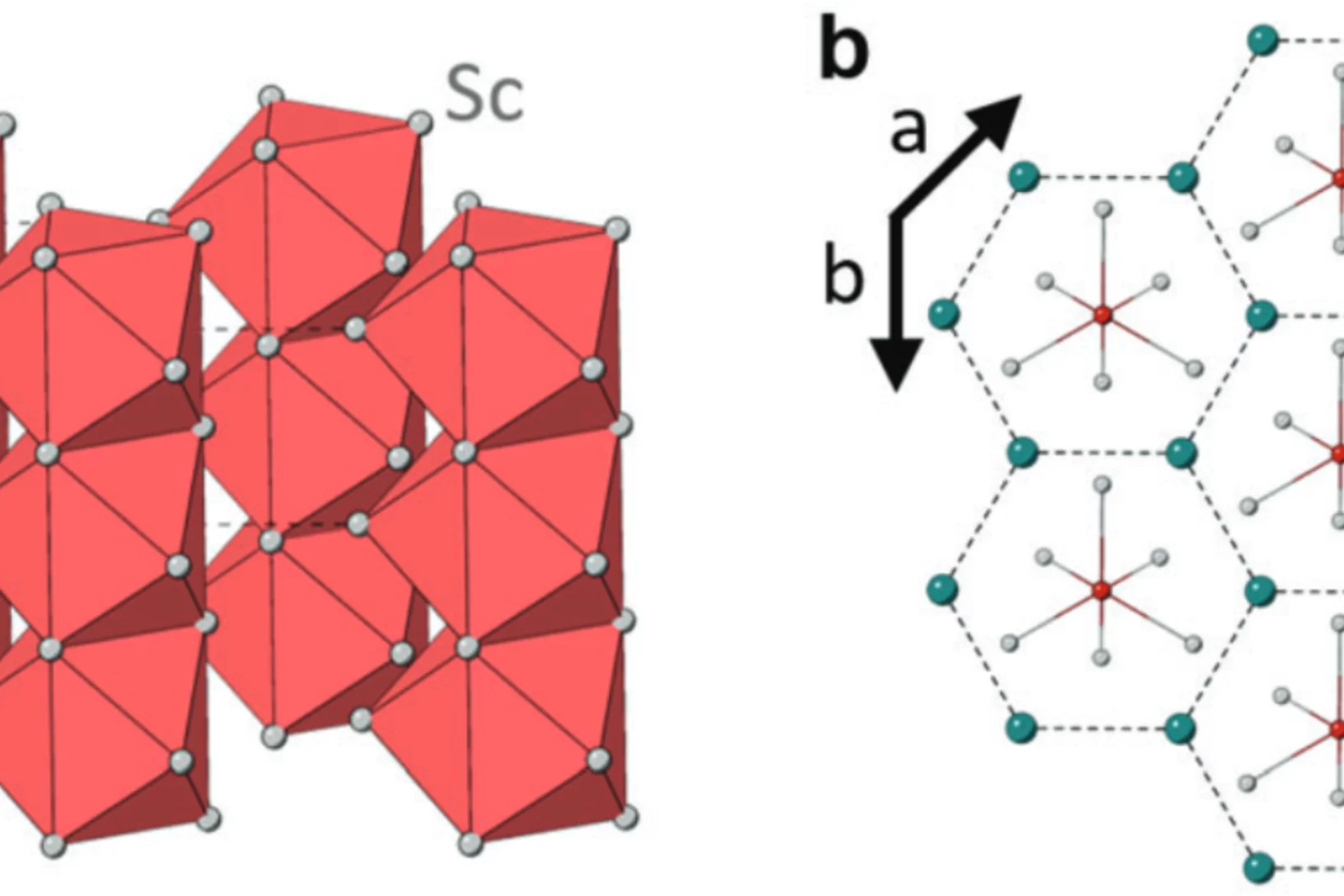
Tailoring the Normal and Superconducting State Properties of Ternary Scandium Tellurides, Sc6MTe2 (M = Fe, Ru, and Ir) Through Chemical Substitution
The pursuit of a unifying theory for non-BCS superconductivity has faced significant challenges. One approach to overcome such challenges is to perform systematic investigations into superconductors containing d-electron metals in order to elucidate their underlying mechanisms. Recently, the Sc6MTe2 (M = d-electron metal) family has emerged as a unique series of isostructural compounds exhibiting superconductivity across a range of 3d, 4d, and 5d electron systems.
In this study, muon spin rotation, neutron diffraction, and magnetization techniques are employed to probe ...
Achieving Uniform Phase Structure for Layer-by-Layer Processed Binary Organic Solar Cells with 20.2% Efficiency
Layer-by-layer (LBL) deposition has become a facile and promising method to fabricate highly efficient organic solar cells (OSCs). However, characterization and optimization of 3D morphology remain a grand challenge for LBL- processed active layers, and their correlation with photovoltaic properties of OSC devices is not clear to date.
Here, to address this issue, ...
Using AI to identify genetic perturbations from cell images
New AI identifies genetic perturbations in chromatin – a potential approach in diagnostics and drug development.
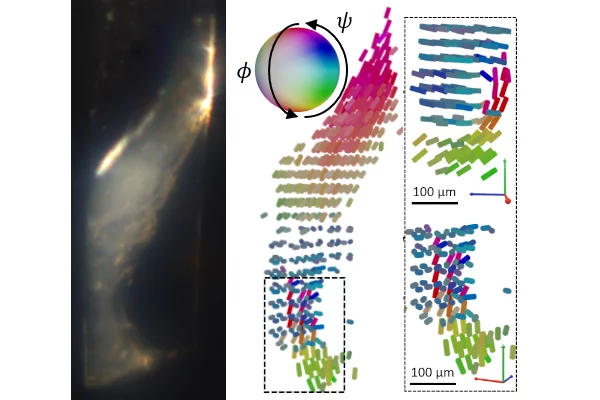
Nanostructure orientation in 3D with visible light by Tomographic Müller-Polarimetric Microscopy
We developed a new method, tomographic Müller-polarimetric microscopy (TMPM), that allows to retrieve at three-dimensional microscopic resolution the nanoscale structural information of the ultrastructure probed with polarized light in a non-destructive manner using a low cost and experimentally simple optical setup.
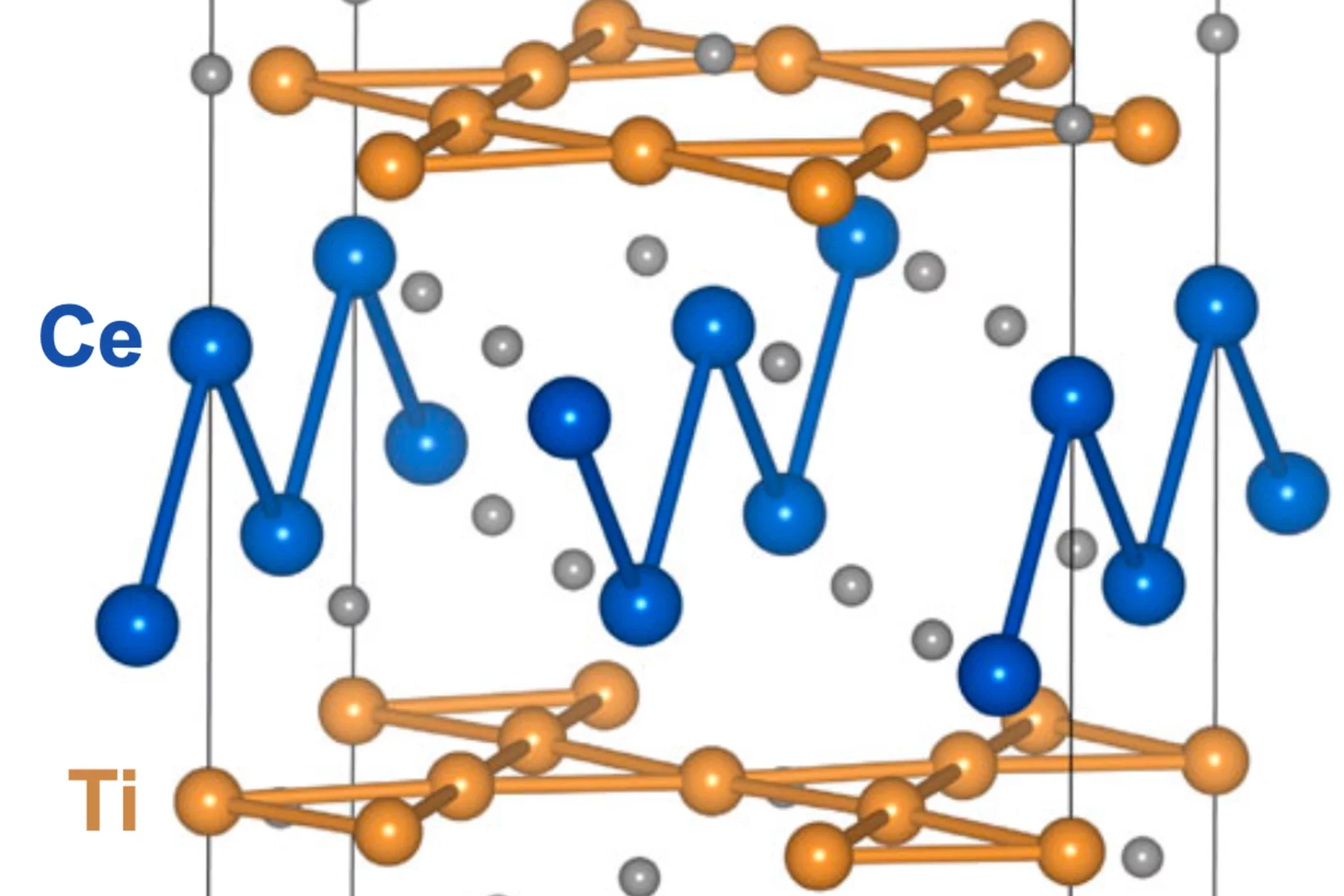
Spin density wave and van Hove singularity in the kagome metal CeTi3Bi4
Kagome metals with van Hove singularities near the Fermi level can host intriguing quantum phenomena such as chiral loop currents, electronic nematicity, and unconventional superconductivity. However, to our best knowledge, unconventional magnetic states driven by van Hove singularities–like spin-density waves–have not been observed experimentally in kagome metals. Here, we report ...
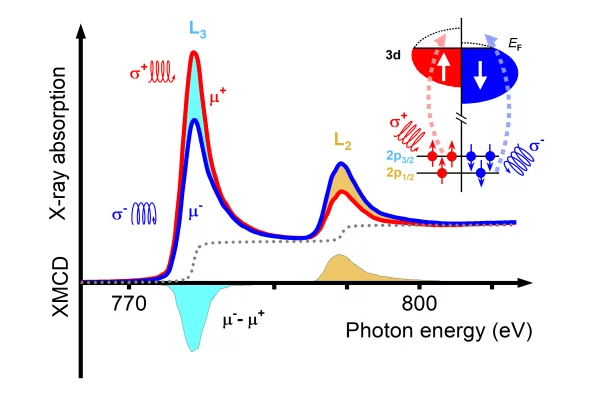
Primer on X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) is a magneto-optical effect that describes the difference in absorption between left and right circularly polarized X-rays by a magnetized material. It has been widely applied to the study of magnetic systems and of magnetic phenomena and its unique capabilities make it a fundamental tool for the study of novel magnetic phenomena and new materials systems.
Advancing Biogas Quality: Tackling Siloxane Challenges for Smooth Energy Transition
Siloxanes, present in everyday items, can compromise the efficiency and durability of bioenergy systems, even at trace levels. Monitoring and quantifying these impurities are critical for improving biogas quality and expanding its role in renewable energy. However, sampling biogas and storing samples containing siloxanes for analysis remain a significant challenge.
World record attosecond measurement at SwissFEL
Scientists at SwissFEL can measure X-ray pulses with attosecond time resolution.
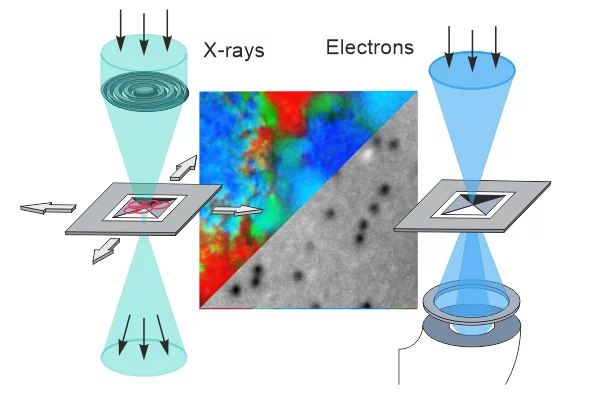
Correlating transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy to bridge atomic- and mesoscales
Transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy have contributed significantly to our understanding of phenomena in fields ranging from biology to materials science. In this review, we present recent developments in combining transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy techniques, including progress in sample environment, and in situ and operando approaches and highlight the unique opportunities offered by fully correlative transmission electron and soft x-ray microscopy.
4D imaging of frost heave and ice lens growth in silt using neutron and x-ray computed tomography
There are substantial changes in soil structure in regions where the soil is freezing. Water movements in the freezing soil introduce level changes beyond what can be expected by the expansion of water when it freezes. The impact of frost heave is seasonal damage to our built environment ...
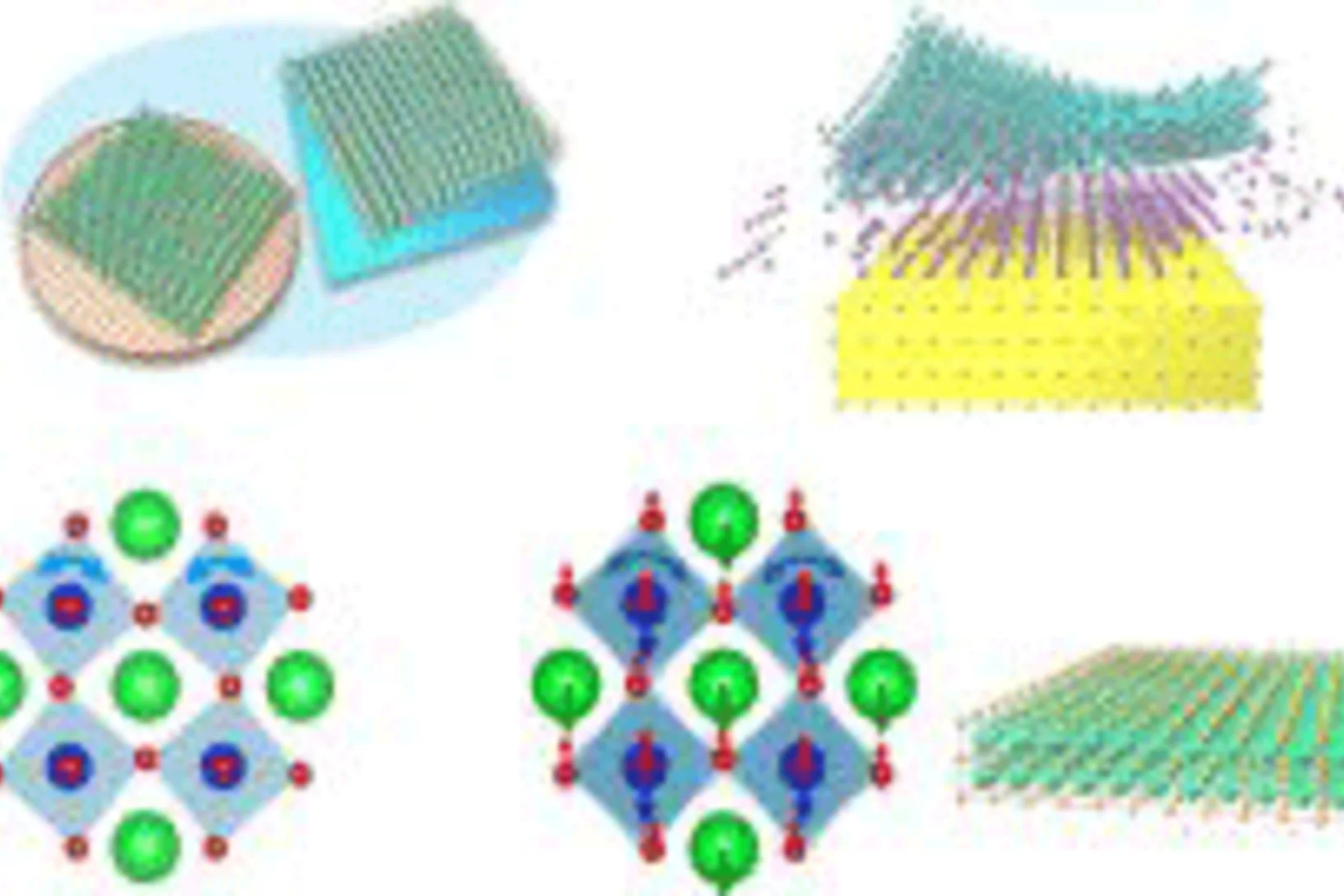
Antiferrodistortive and ferroeletric phase transitions in freestanding films of SrTiO3
Epitaxially grown thin films are commonly used to strain engineer electronic properties by the choice of a substrate, and therefore do not match bulk properties (leading to properties that deviate from the bulk material). Free standing ultrathin oxide films are expected to preserve the bulk-like properties due to the absence of substrate influence. However, we show that this expectation is not fulfilled with ultrathin free standing SrTiO3, as they get ferroelectric at 80K.
PSI Spin-off "novoMOF" secures 4.4 Million CHF for promising CO2 technology
The PSI spin-off novoMOF has successfully completed a funding round, raising 4.4 million CHF. With this support, the company will further develop and bring its groundbreaking CO2 capture technology to market.
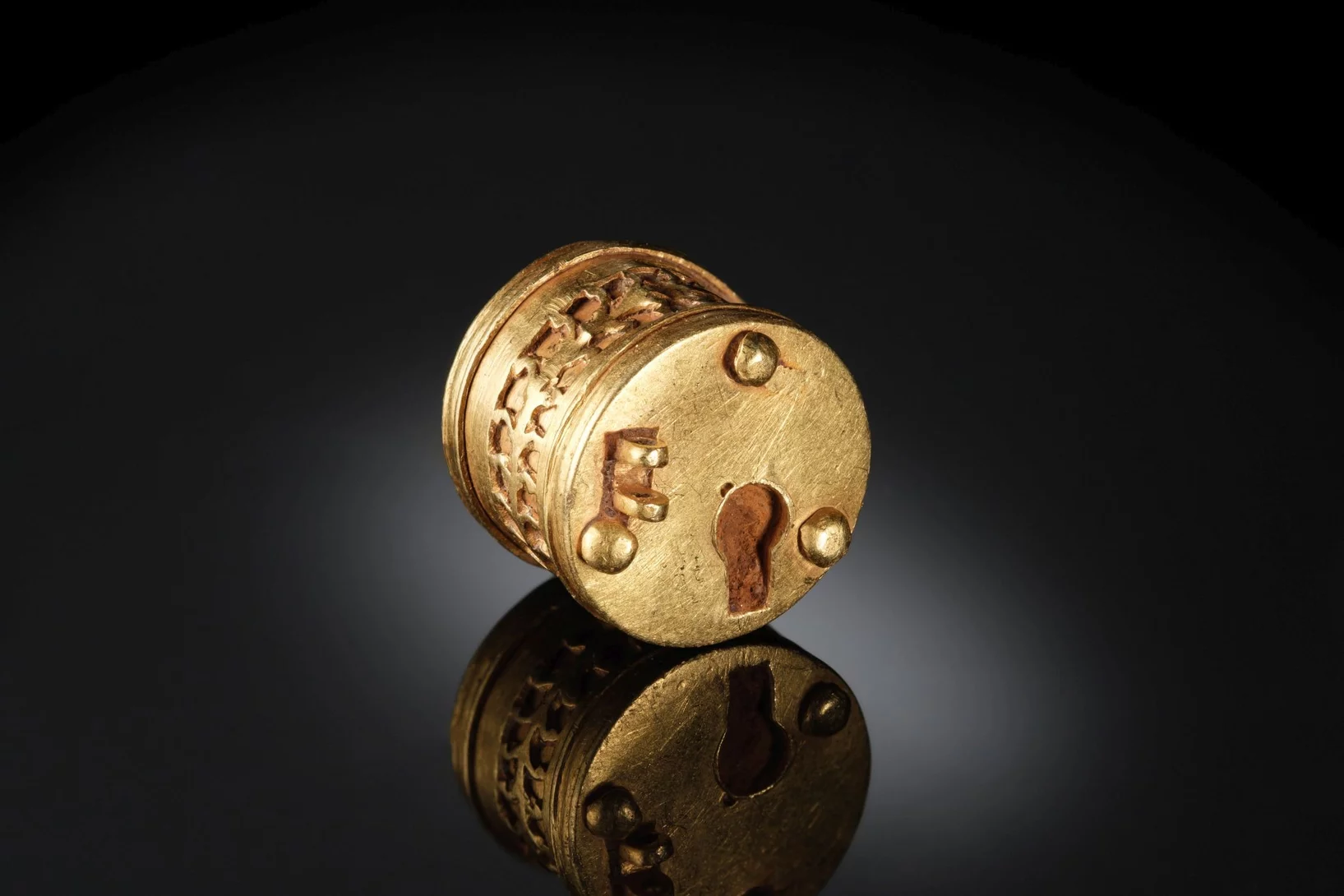
A tiny golden object from Roman times
PSI’s David Mannes has used neutrons to unravel the mystery of a fascinating archaeological artefact.
Momentum-resolved fingerprint of Mottness in layer-dimerized Nb3Br8
Crystalline solids can become band insulators due to fully lled bands, or Mott insulators due to strong electronic correlations. While Mott insulators can theoretically occur in systems with an even number of electrons per unit cell, distinguishing them from band insulators experimentally has remained a longstanding challenge.
In this work, we present ...
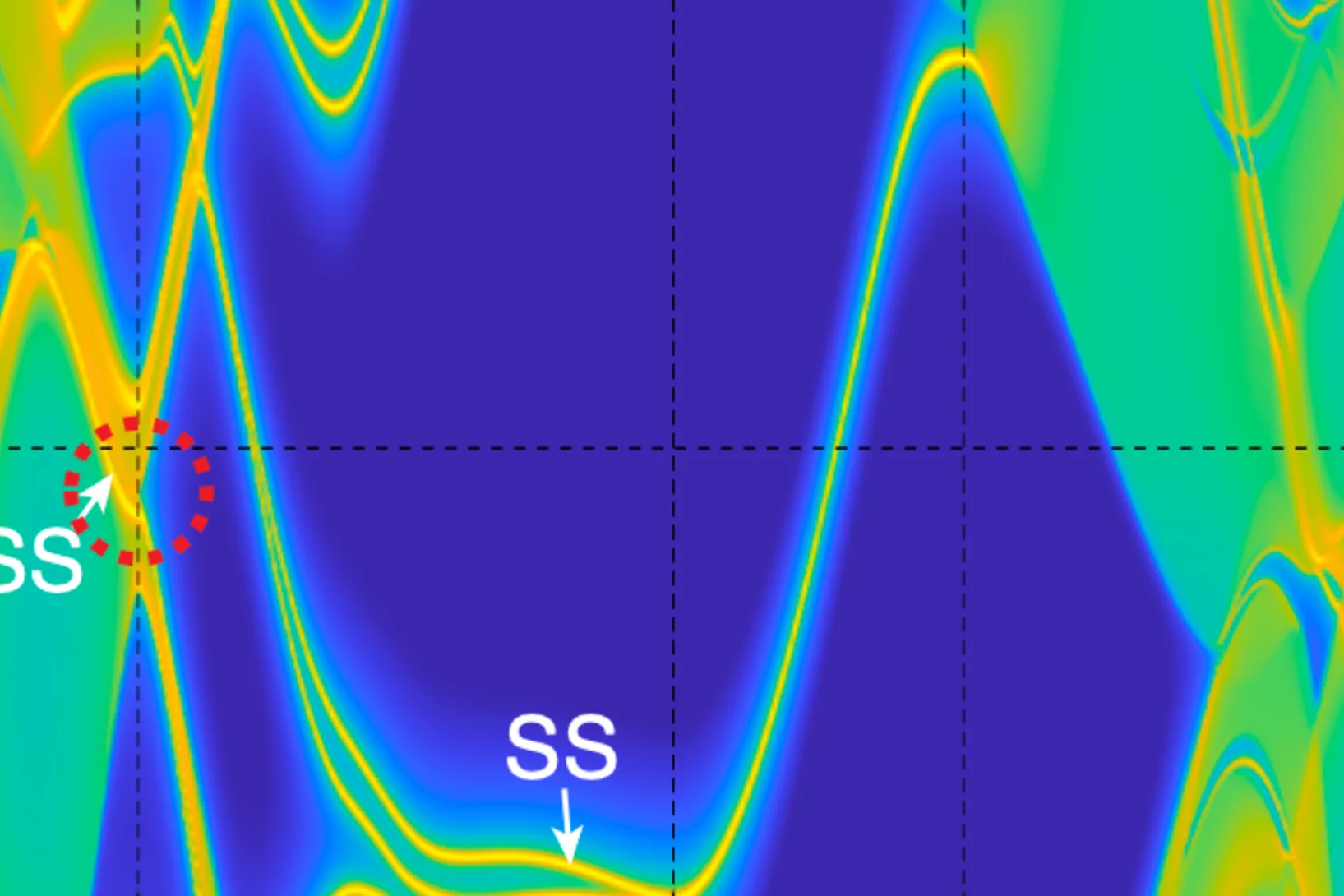
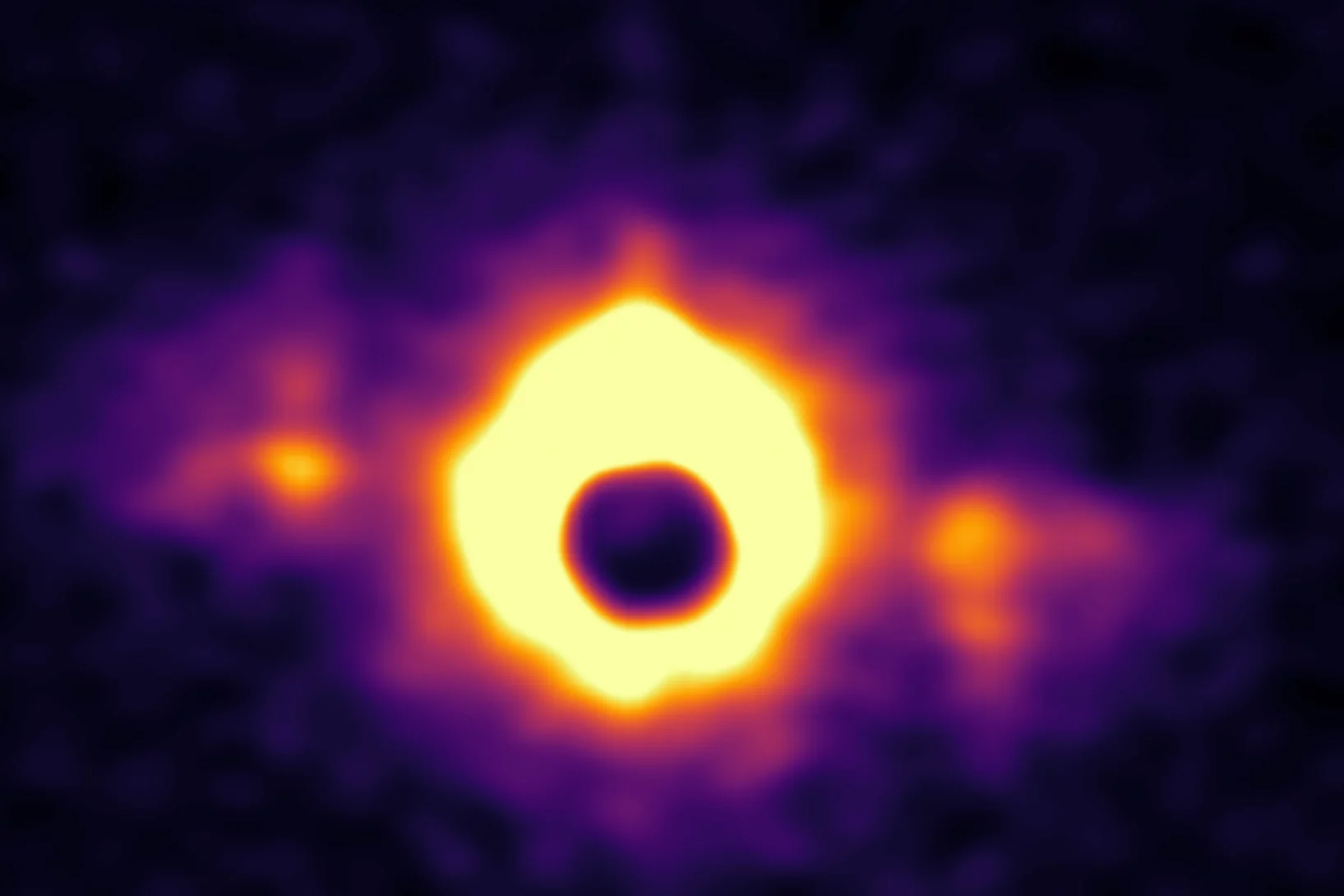
Superconductivity and a van Hove singularity confined to the surface of a topological semimetal
The interplay between topology and superconductivity generated great interest in condensed matter physics. Here, we unveil an unconventional two-dimensional superconducting state in the Dirac nodal line semimetal ZrAs2 which is exclusively con ned to the top and bottom surfaces within the crystal’s ab plane.
As a remarkable consequence ...
Promising Innovation in Cancer Diagnostics
What if modern medicine could select the most effective cancer treatment for each patient more precisely and faster?
Targeted funding of innovation for the energy transition
How do innovations arise and how can they be specifically encouraged for the energy transition? PSI researcher Michael Weinold has been looking into this question using LED lamps as an example.
Emergence of topological Hall effect from a fluctuation-based dynamic origin
The topological nature of the electronic bands or spin structure has direct manifestation in experimentally measured Hall conductivity. The extra topological (or geometrical) component to the Hall effect (THE) usually emerges due to multi-k structures, which inherently possess a finite static scalar spin chirality (SSC). Generating a THE in a single-k structure necessitates the consideration of the dynamical origin of SSC, the real material examples of such cases remain scarce to date.
Water gets in shape for VUV absorption
Nanometre‑thin, free‑flowing liquid sheets now let Swiss Light Source users record pristine VUV absorption spectra of water, and soon any solvent.
Zero-field Hall effect emerging from a non-Fermi liquid in a collinear antiferromagnet V1/3NbS2
Magnetically intercalated transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) provide a versatile three-dimensional (3D) material platform to explore quantum phenomena and functionalities that emerge from an intricate interplay among magnetism, band structure, and electronic correlations.
Generation of Neutron Airy Beams
The Airy wave packet is a solution to the potential-free Schrödinger equation that exhibits remarkable properties such as self-acceleration, nondiffraction, and self-healing. Although Airy beams are now routinely realized ....
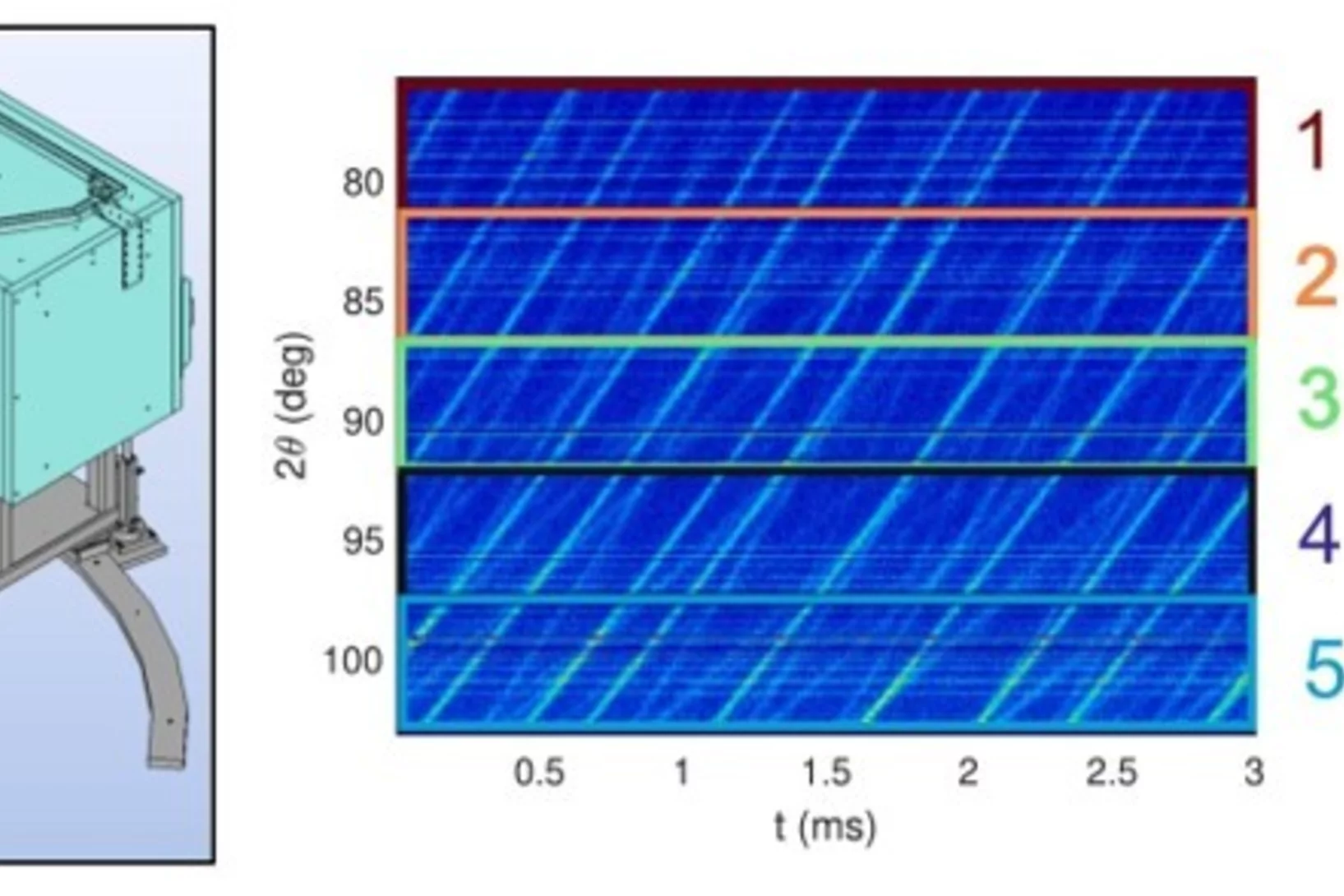
Texture analysis implementation at the neutron strain diffractometer POLDI
This study presents the implementation of a novel data analysis methodology to perform spatially resolved crystallographic texture analyses in bulk specimens at POLDI, the pulsed frame overlap diffractometer at SINQ, Paul Scherrer Institute. The method is based on the determination of several incomplete pole figures. To increase the angular resolution, the POLDI diffraction bank is split into several virtual units of smaller angular coverage. The diffraction data of each virtual unit can then be analyzed individually and used to create experimental pole figures from the Euler angles of the explored sample orientations. Additionally, to help the analyses, a new numerical tool was developed and implemented at POLDI to calculate neutron flight path of each virtual detector as a function of sample size, geometry, and orientation. Leveraging on the SALOME platform’s Geom module (open-source CAD modeler), the tool allows inserting CAD objects into a virtual detailed PODI geometry. This allows to automate sample positioning and orientation within the instrument frame and computes flight path intersections. It serves two main purposes: enhancing texture analysis through precise path calculations and aiding experimental design by visually evaluating orientation feasibility and estimating counting times. Finally, to complete the analysis path from the experiments to the results, the experimental and numerical evaluations are processed together with POLTex (MATLAB-based toolbox) to obtain the orientation distribution functions. To demonstrate the analysis routine, the crystallographic texture of an additively manufactured steel sample and Zircaloy-4 sample were characterized.
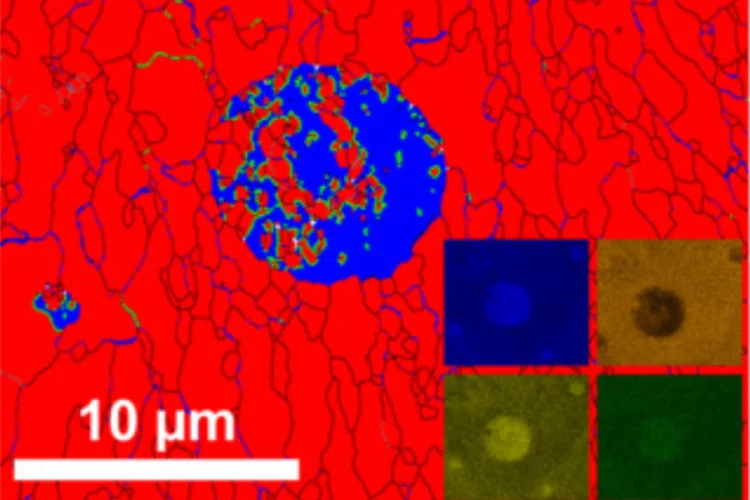
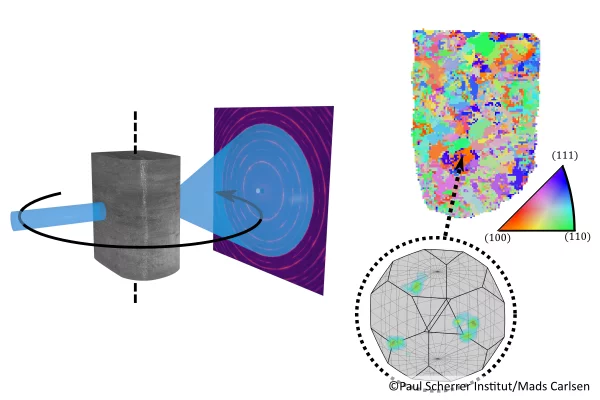
Mapping crystallite orientation in bulk polycrystals
A new experimental technique allows the orientation distribution of small-grained polycrystal materials to me mapped in 3D.