SLS
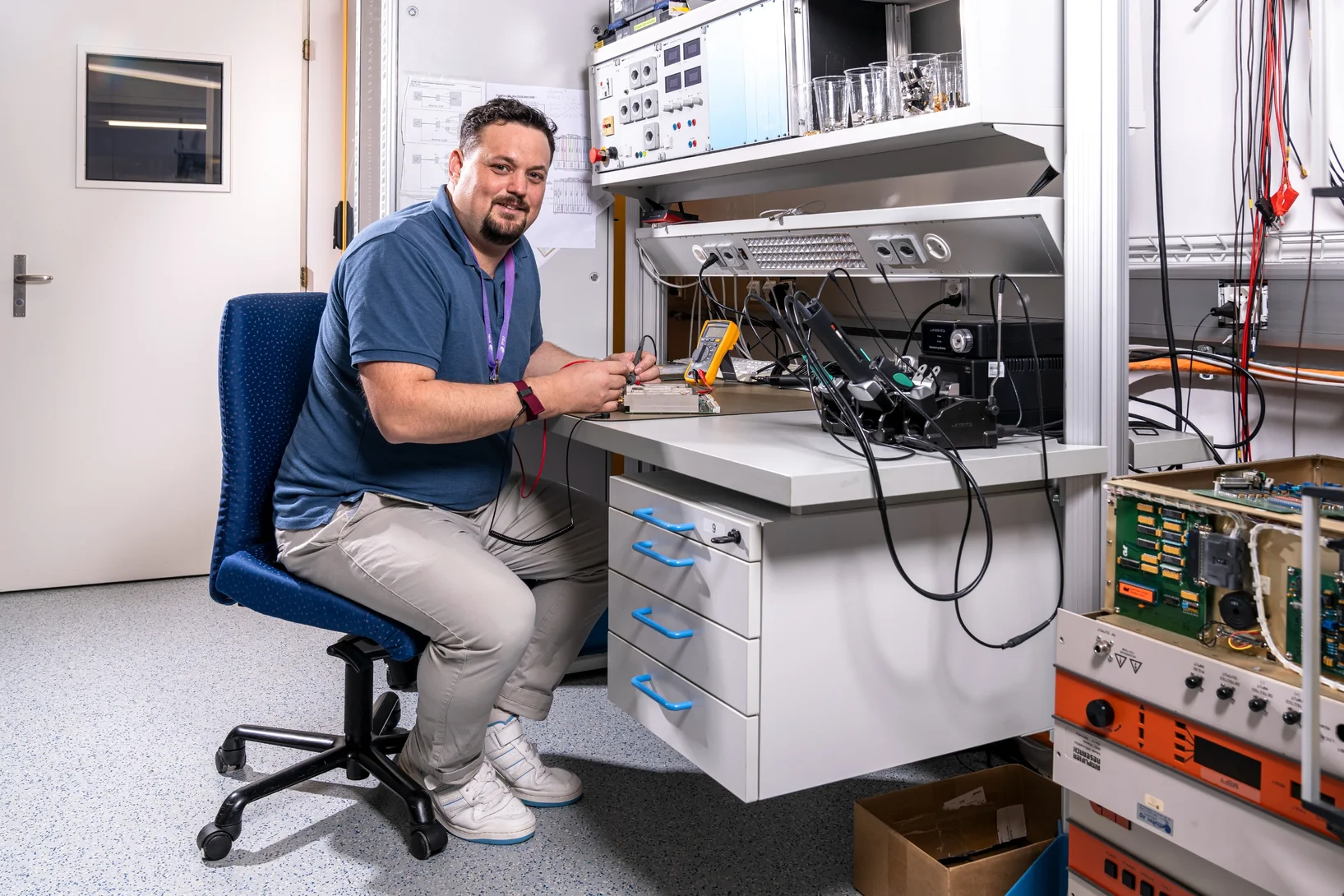
Engineering skill and perseverance
Credit for the on-time completion of the major SLS 2.0 upgrade project is due in part to a team of dedicated electrical engineers.
Uncovering Hidden Phases in 3D-Printed Fusion Steels
3D synchrotron X-ray mapping uncovered unexpected internal phase structures in laser-printed steels, showing how processing controls what we cannot see.
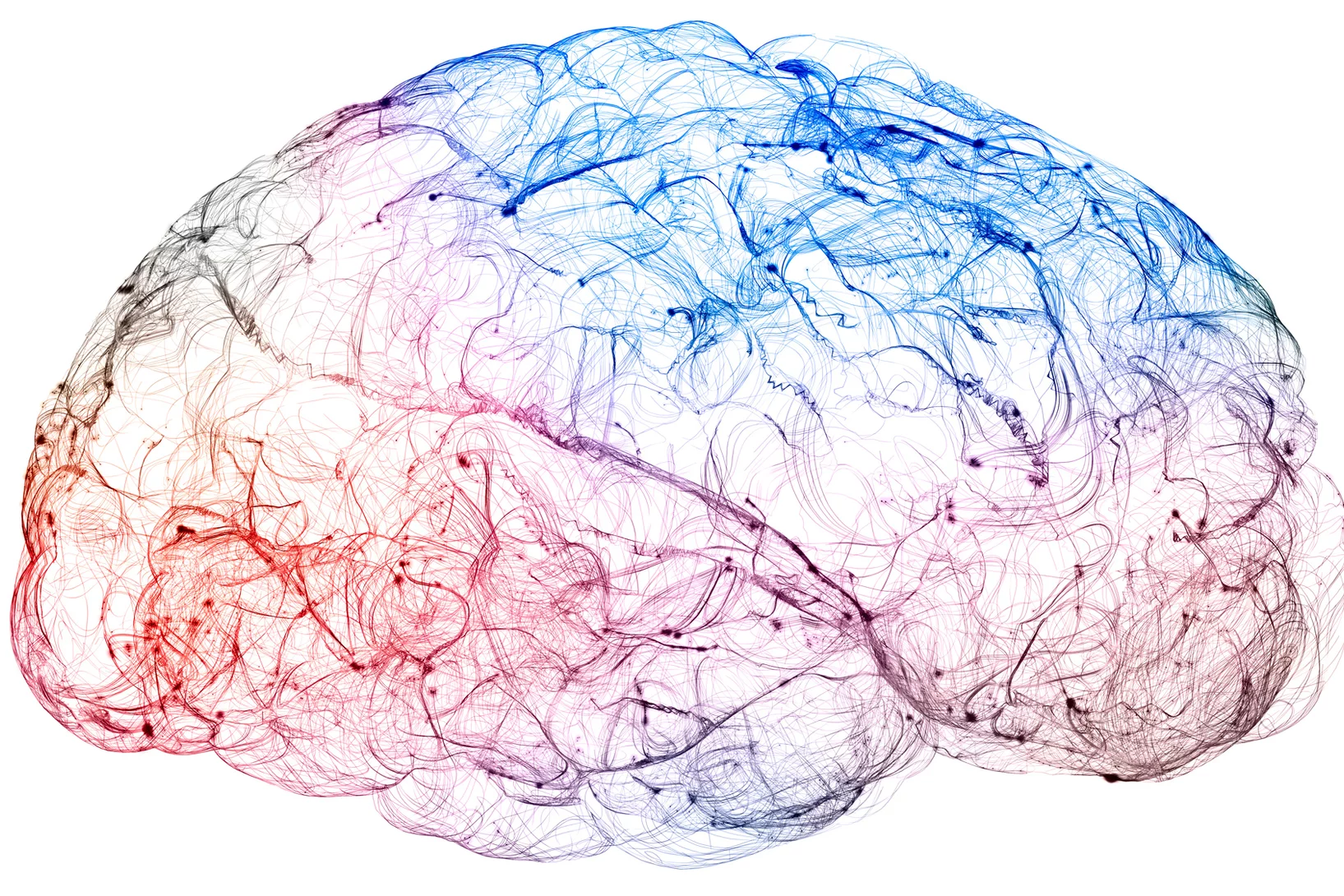
X-rays bring high-resolution brain mapping within reach
A new imaging breakthrough could reveal brain connectivity in 3D detail never before accessible.
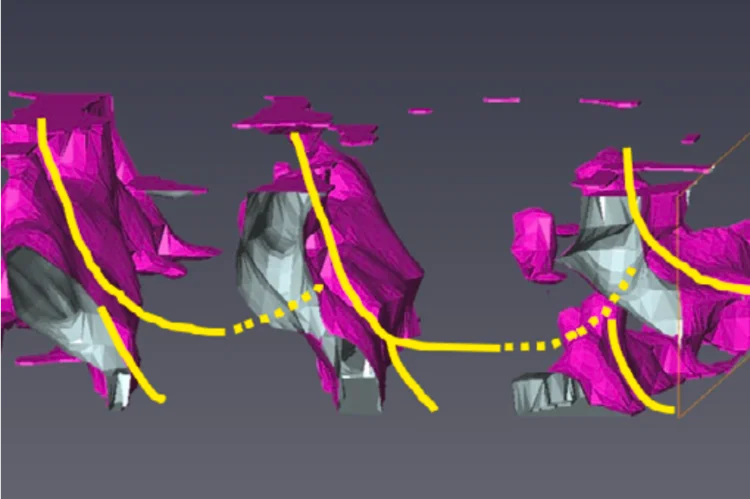
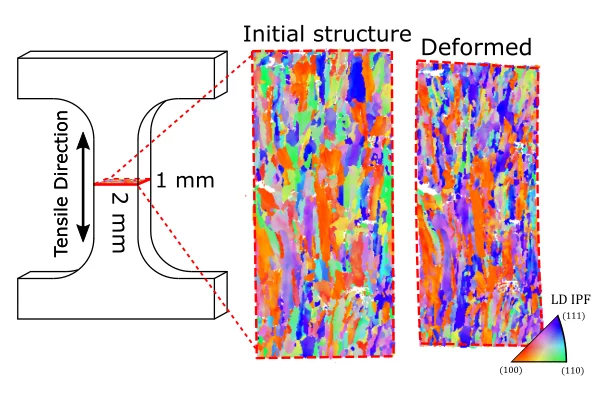
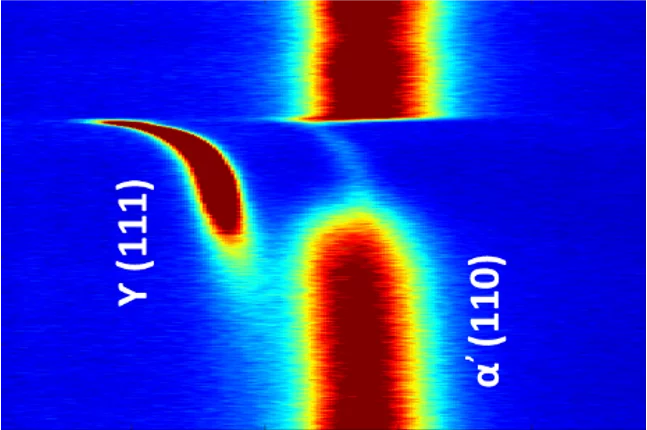
Following Twin-Formation in 3D Printed Steel
Using hard-xray microscopy to study the deformation of 3D printed steel.
How the cheese-pasta principle could help counter Alzheimer's
PSI researchers have discovered cellular mechanisms that could help to mitigate diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
From Melt to Martensite
Real-time synchrotron X-ray diffraction reveals how different phases of steel emerge and evolve under the intense heat of laser powder bed fusion.
Coexistence of Insulatorlike Paramagnon and Metallic Spin-Orbit Exciton Modes in SrIrO3
We probe the spectrum of elementary excitations in SrIrO3 by using heterostructured [(SrIrO3)m / (SrTiO3)l] samples to approach the bulk limit. Our resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) measurements at the Ir L3 edge reveal ...
Big heart, acute senses key to explosive radiation of early fishes
X-rays of a 400-million-year-old fossil illuminate a key moment in our deep evolutionary past.
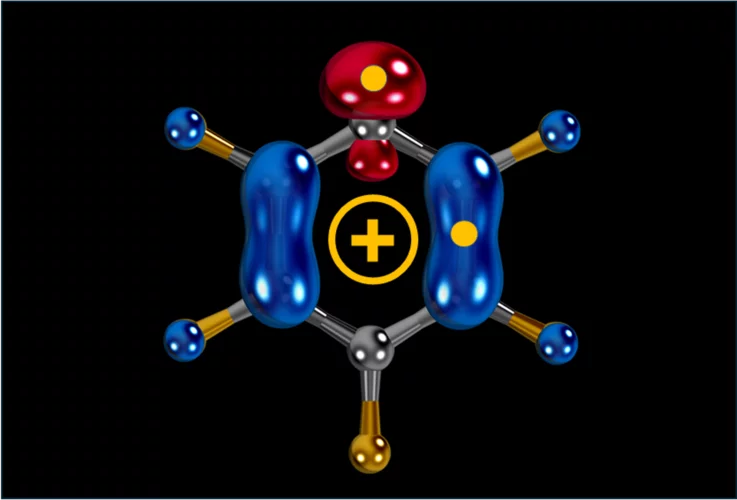
Carbocation, diradical, and superelectrophile in one molecule?
The pentafluorophenyl cation (C₆F₅⁺) breaks these rules with a borderline “crazy” reactivity.
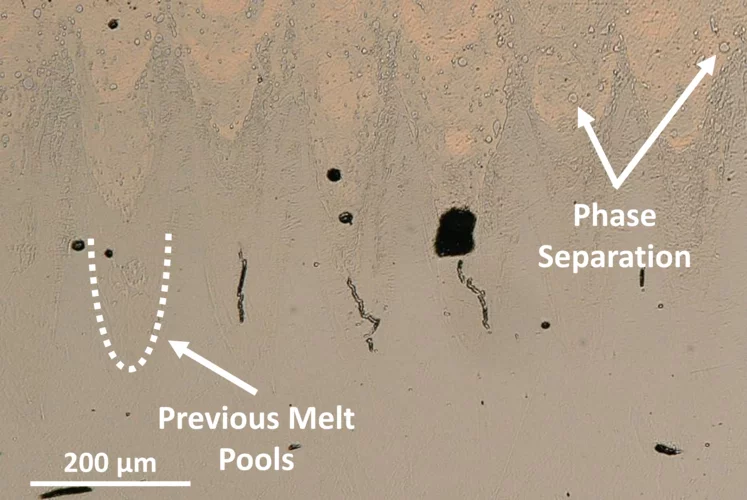
Why Ni-Cu Alloys Fail in 3D Printing
3D printing with nickel–copper alloys holds great promise — but hidden mechanisms can cause them to crack. Our latest study reveals why.