Show filters
Presentation Prize 2026 (Doktorandentag, Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, ETH Zurich)
Benjamin Hunkeler, PhD student in the “Nuclide Chemistry Group” received the price for the best oral presentation
Best Presentation Award 2025 (SwyMIC Day 2025 in Lausanne)
Jerome Schmid, PhD student in the “Nuclide Chemistry Group” received the price for the best oral presentation at the SwyMIC Day 2025 in Lausanne
Room-Temperature Magnetic Skyrmions and Intrinsic Anomalous Hall Effect in a Nodal-Line Kagomé Ferromagnet MnRhP
Topological magnetic semimetals with kagomé lattices have attracted significant attention due to their nontrivial electronic band structures and pronounced electromagnetic responses. The search for kagomé-lattice topological semimetals exhibiting magnetic ordering above room temperature is essential ...
Muon Knight Shift as a Precise Probe of the Superconducting Symmetry of Sr2RuO4
Muon spin rotation (𝜇SR) measurements of internal magnetic field shifts, known as the muon Knight shift, are used for determining pairing symmetries in superconductors. While this technique has been especially effective for 𝑓-electron-based heavy-fermion superconductors, it remains challenging ...
Low-frequency electrochemical pulsing to manage flooding and salt precipitation in zero-gap CO2-to-ethylene electrolyzers
The electrochemical conversion of CO2 to ethylene offers a promising approach to expand manufacturing of commodity chemicals and fuels. Specifically, ethylene is a critical precursor for polyethylene a $240B industry. Expanding productivity ...
Driving forces of mineral recrystallization in aqueous solutions derived from...
Curti et al., 2026
Recrystallization in aqueous solutions is a ubiquitous process susceptible to control the entrapment and release of toxic contaminants in the subsurface. However, unraveling the underlying mechanisms and driving forces has proven to be elusive, as recrystallization frequently follows different kinetic pathways even for the same mineral, depending on its initial state and pre-treatment. To obtain a better insight, a large body of experimental data from isotope tracer experiments carried out....
Swelling of Na-montmorillonite in the presence....
Owusu et al., 2026
Various dissolved gases, such as CO, H, and CH, may be present in the near-field geological repository due to metal corrosion or the degradation of organic waste. However, the influence of dissolved gases on the swelling behavior of bentonites, commonly used as backfill material, is still poorly understood. In this study, classical molecular dynamics simulations are conducted to....
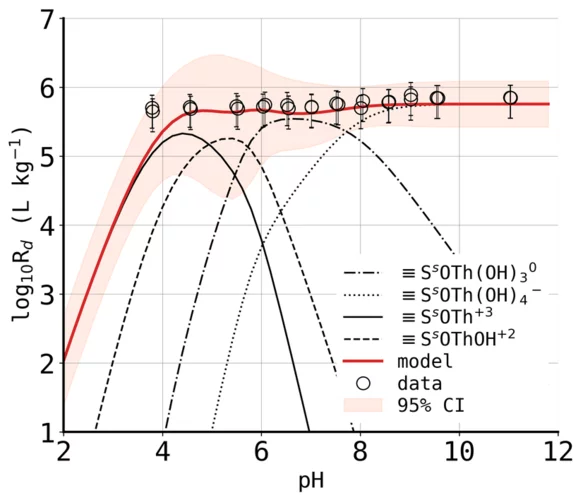
Examining the pH dependence of Fe behavior in.....
Ban et al., 2026
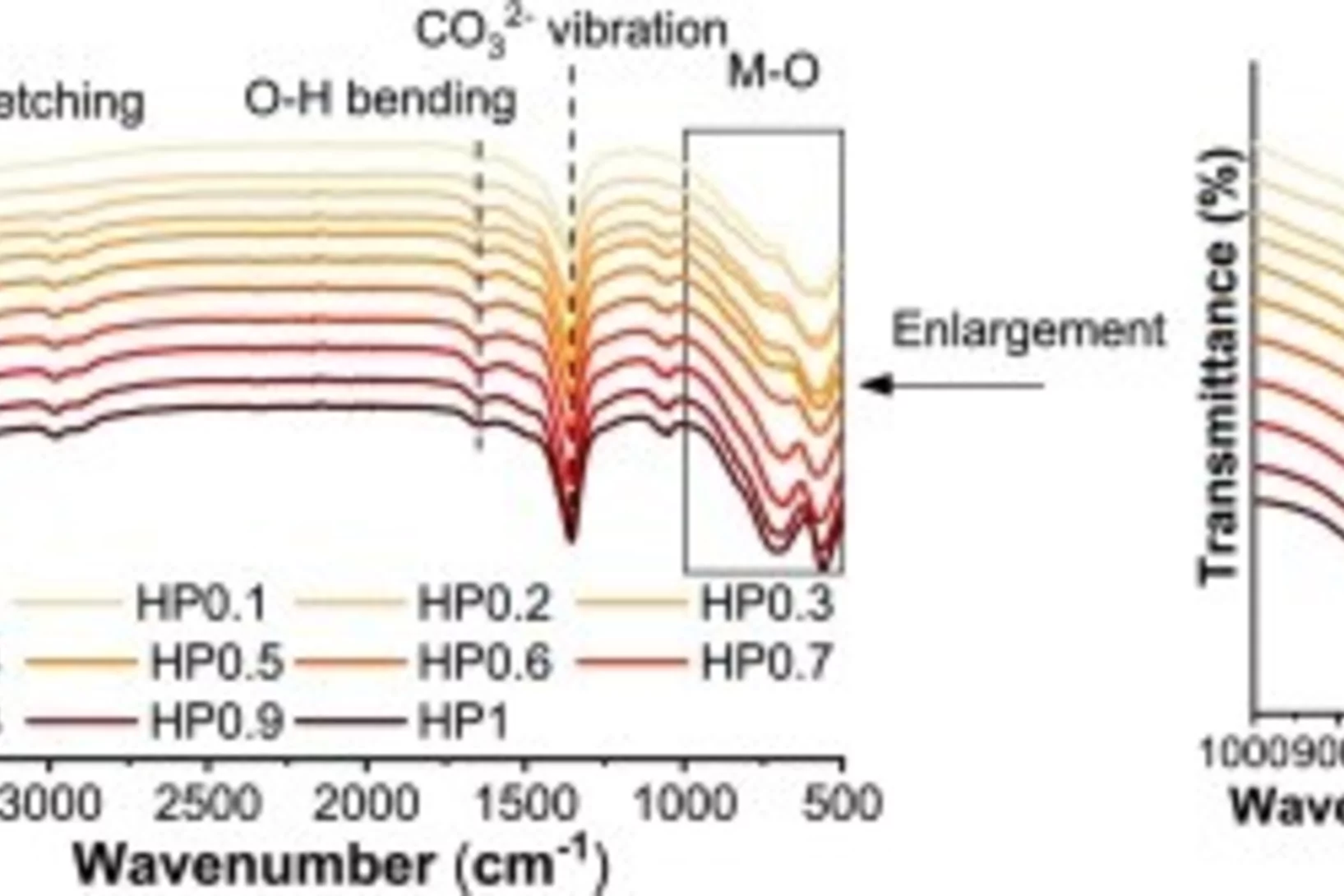
Hydrotalcite-group layered double hydroxide (LDH) phases are important in many technical and geological contexts, and in applications ranging from environmental processes to catalysts to cements. This study systematically investigates the roles of Fe in LDH structures across varying....
Advanced muon-spin spectroscopy with high lateral resolution using Si-pixel detectors
Muon-spin spectroscopy at continuous sources has stagnated at a stopped muon rate of ∼40kHz for the last few decades. The major limiting factor is the requirement of a single muon in the sample during the typical 10µsdata gate window. To overcome this limit ...
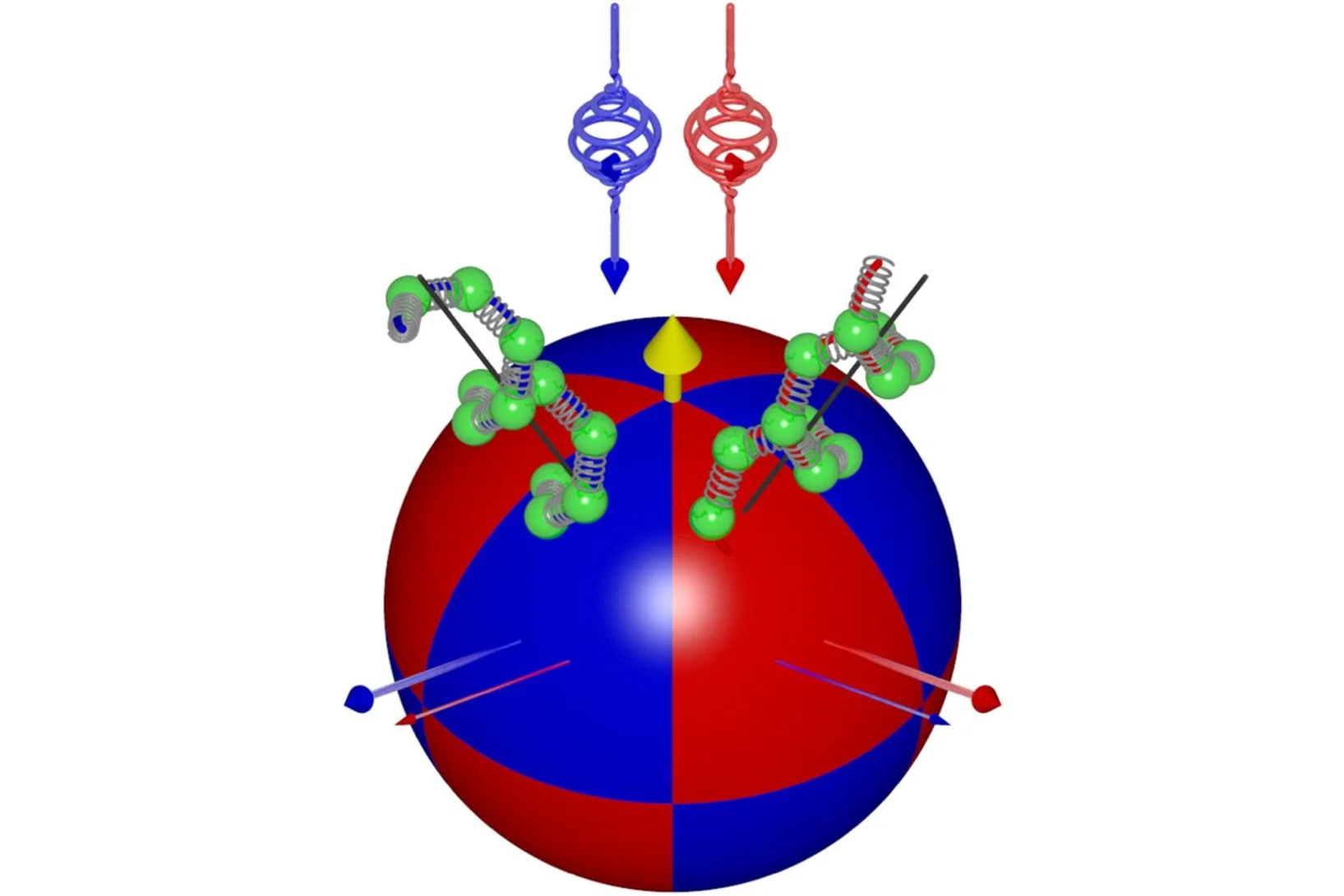
Realizing Blume-Capel Degrees of Freedom with Toroidal Moments in a Ruby Artificial Spin Ice
Realizing exotic Hamiltonians beyond the Ising model is a key pursuit in experimental statistical physics. Onesuch example is the Blume-Capel model, a three-state spin model, whose phase diagram features a tricritical point where second-order and first-order transition lines converge, leading to a coexistence of paramagnetic, ferromagnetic, and disordered phases. Here, we realize ...
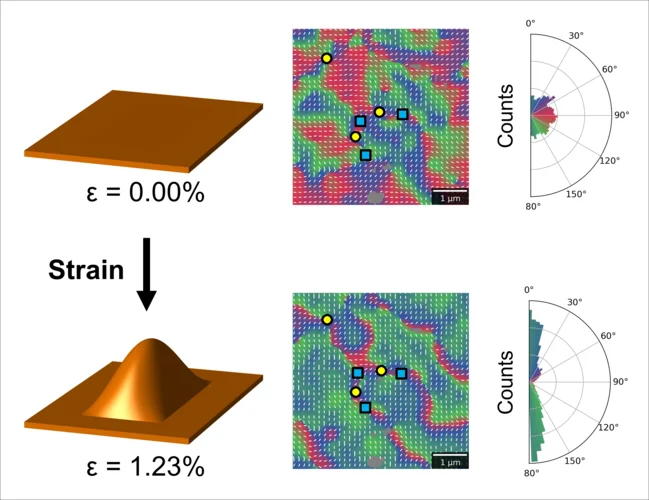
Designing antiferromagnetic domains by stretching membranes in STXM
Researchers from an international collaboration between the United Kingdom and Switzerland have performed imaging of an antiferromagnetic iron oxide membrane using soft X-ray microscopy. By stretching the membranes using a gas cell, the team investigated the modification of domain structures under strain.
ISS @SLS 2.0
ISS received the first light on 10.07.2025. After that, the endstation has been reconnected and aligned. During the shutdown period, the ScientaOmicron R4000 HiPP-2 analyser has undergone maintenance and upgrade. It features now a new detector (new MCP and 70 Hz camera) and ethernet communication.
First in-house and pilot users have measured in November and December 2025. A first official call for proposals will open in February 2026 (deadline March 16th 2026, beamtime periods scheduled from September to December 2026). Please contact Dr. Luca Artiglia for more information.
Surface-localized magnetic order in RuO2 thin films revealed by low-energy muon probes
Ruthenium dioxide (RuO2) has recently emerged as an altermagnetic candidate, but its intrinsic magnetic ground state in thin films remains widely debated. This study aims to clarify the nature and spatial extent of the magnetic order in RuO2thin films grown under different conditions ...
Investigating the hidden content of Tibetan bronze statues using modern neutron imaging techniques
Bronze statues hold deep significance in Buddhism and Bon, often containing relics sealed within their hollow interiors. Traditional scholarly methods, such iconographic analysis, cannot access the hidden contents of these statues without risking physical damage. This study proposes ...
Chiral phonons in polar LiNbO3
Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering reveals that lattice vibrations can be chiral in a polar material, with phonons having opposite handedness depending on their direction in momentum space.
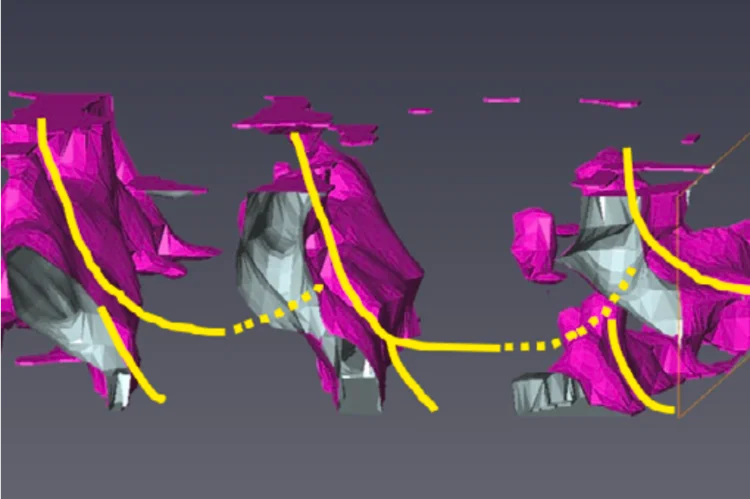
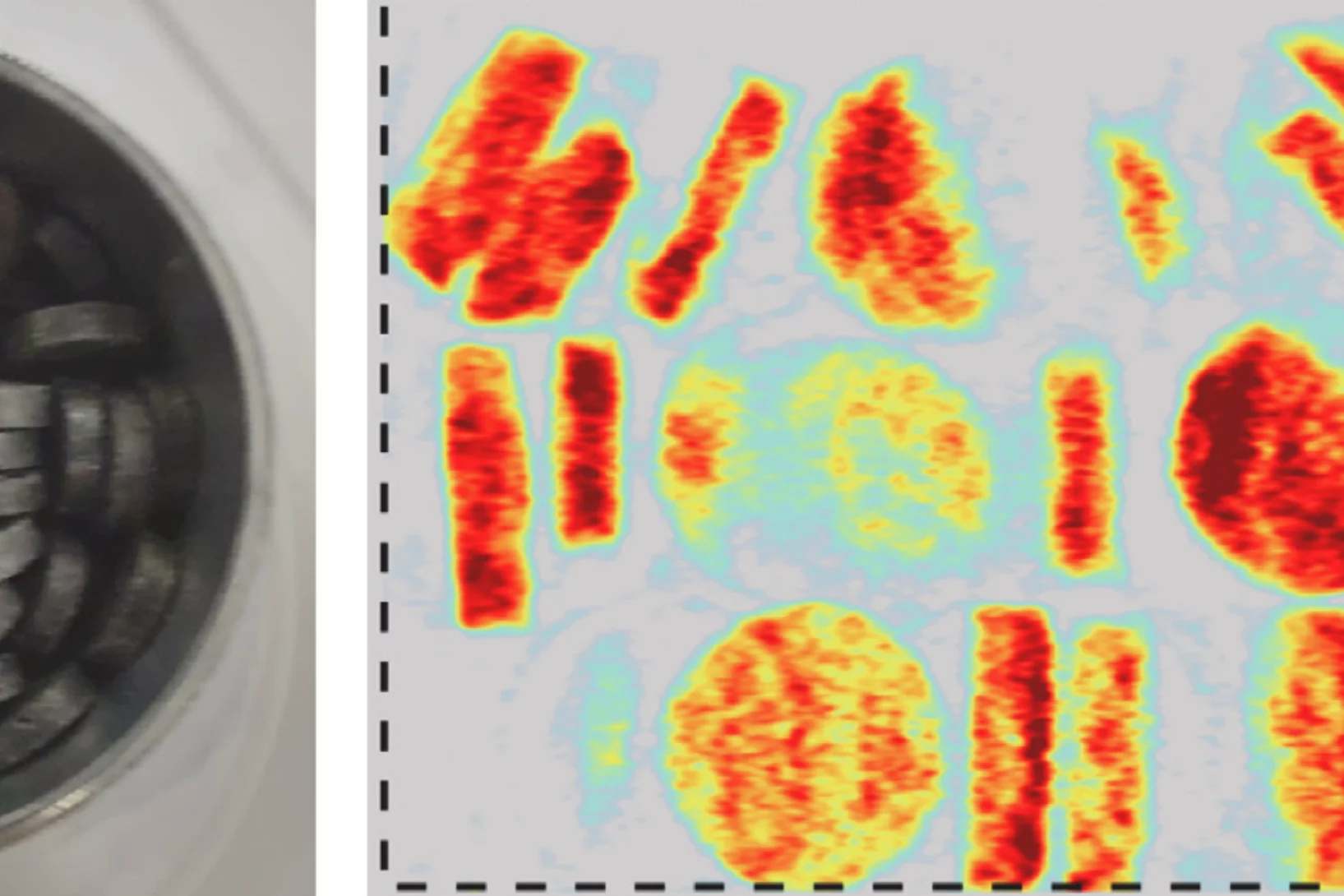
Uncovering Hidden Phases in 3D-Printed Fusion Steels
3D synchrotron X-ray mapping uncovered unexpected internal phase structures in laser-printed steels, showing how processing controls what we cannot see.
2nd GIF Molten Salt Reactor workshop at PSI
On 10 December 2025 the 2nd GIF Molten Salt Reactor workshop took place at PSI
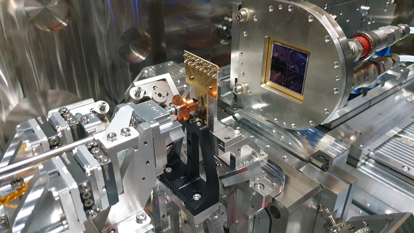
SOPHIE - A new endstation for high-resolution soft X-ray ptychography
A new PSI-designed and built soft X-ray ptychography endstation, SOPHIE, has been successfully commissioned. Routine sub-5nm imaging was demonstrated.
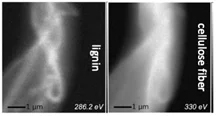
Preparing cellulose sample for soft-Xray spectro-microscopy
Different sample preparation techniques for ultrathin samples to be measured at the carbon-K-edge for chemical contrast are presented.
Two-dimensional gradients in magnetic properties created with direct-write laser annealing
Across the fields of magnetism, microelectronics, optics, and others, engineered local variations in material properties can yield groundbreaking functionalities that play a crucial role in enabling future technologies. One-dimensional lateral gradients in material properties give rise to a plethora of new effects in thin-film magnetic systems. However, extending such gradient-induced behaviors to two dimensions has been challenging to realize experimentally. Here, we demonstrate the creation of two-dimensional complex patterns with continuous variations in magnetic anisotropy, interlayer exchange coupling, and ferrimagnetic compensation at the mesoscopic scale in numerous application-relevant magnetic materials. We exploit our engineered gradients in material properties to demonstrate novel magnetic functionalities, including the creation of a spin wave band pass filter and an architecture for passively resetting the position of a magnetic domain wall. Our results highlight the exciting new physics and device applications enabled by two-dimensional gradients in thin film properties.
Anisotropic Band-Split Magnetism in Magnetostrictive CoFe2O4
Single crystal spinel CoFe₂O₄ exhibits the largest room-temperature saturation magnetostriction among non-rare-earth compounds and a high Curie temperature (T₍c₎ ∼ 780 K), properties that are critical to a wide range of industrial and medical applications. Neutron spectroscopy ...
Hydrotalcite-pyroaurite solid solution in cement system...
Wang et al., 2025
Hydrotalcite-pyroaurite solid solutions, which are common minerals both in nature and in modern cementitious materials, hold significant potential for waste immobilization and cement properties yet remain insufficiently studied. In this work, we first synthesized a series of hydrotalcite...
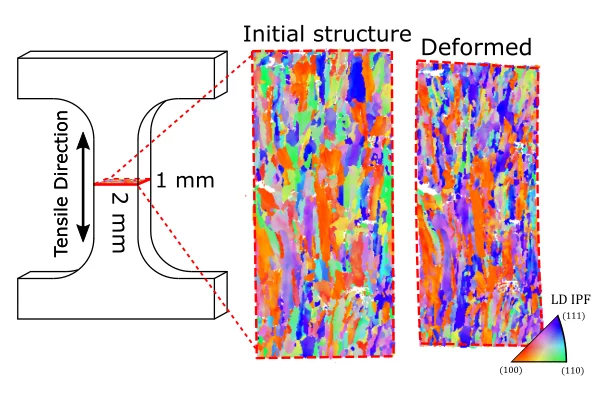
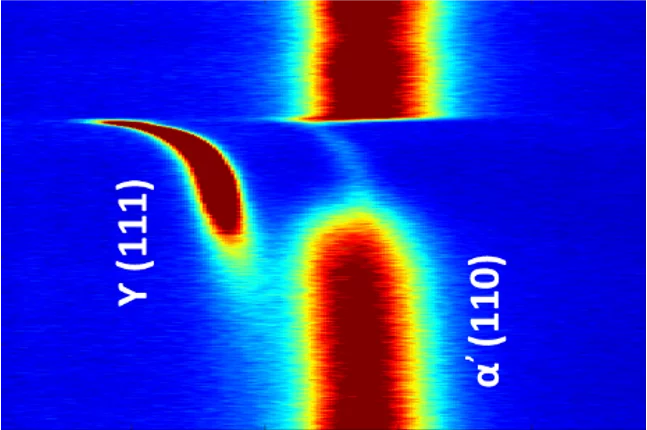
Following Twin-Formation in 3D Printed Steel
Using hard-xray microscopy to study the deformation of 3D printed steel.
Acidity scale of carbenium ions in ZSM-5
A combination of Fourier transformed IR spectroscopy and density functional theory elucidates the higher reactivity of benzenium ions over cyclopentenyl cations in ZSM-5.
Operando neutron imaging of an alkaline electrolysis cell for mapping gas distributions
Optimizing hydrogen and oxygen transport within porous electrodes is essential for improving the efficiency of industrial alkaline electrolyzers. In this study, we utilize operando dynamic neutron radiographic measurements to investigate ...
Unravelling the coexistence of insulating and metallic-like excitations in SrIrO₃
A team led by researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI used resonant inelastic X-ray scattering to probe spin and charge fluctuations in atomically engineered SrIrO₃. The results revealed that insulator-like and metallic-like modes can simultaneously emerge in a correlated 5d semimetal, advancing the understanding of “strange metal” behaviour in spin–orbit coupled systems.
MADICES Conference at PSI
The MADICES 3 workshop was about bringing representatives from the open research data (ORD) community, including research data management (RDM) platform developers/maintainers, ontology/semantics experts, those leveraging AI/LLM for RDM tasks, and FAIR principles advocators together to discuss (and implement solutions for) the problems hindering the adoption of ORD and FAIR principles and practices in the sciences.
From Melt to Martensite
Real-time synchrotron X-ray diffraction reveals how different phases of steel emerge and evolve under the intense heat of laser powder bed fusion.
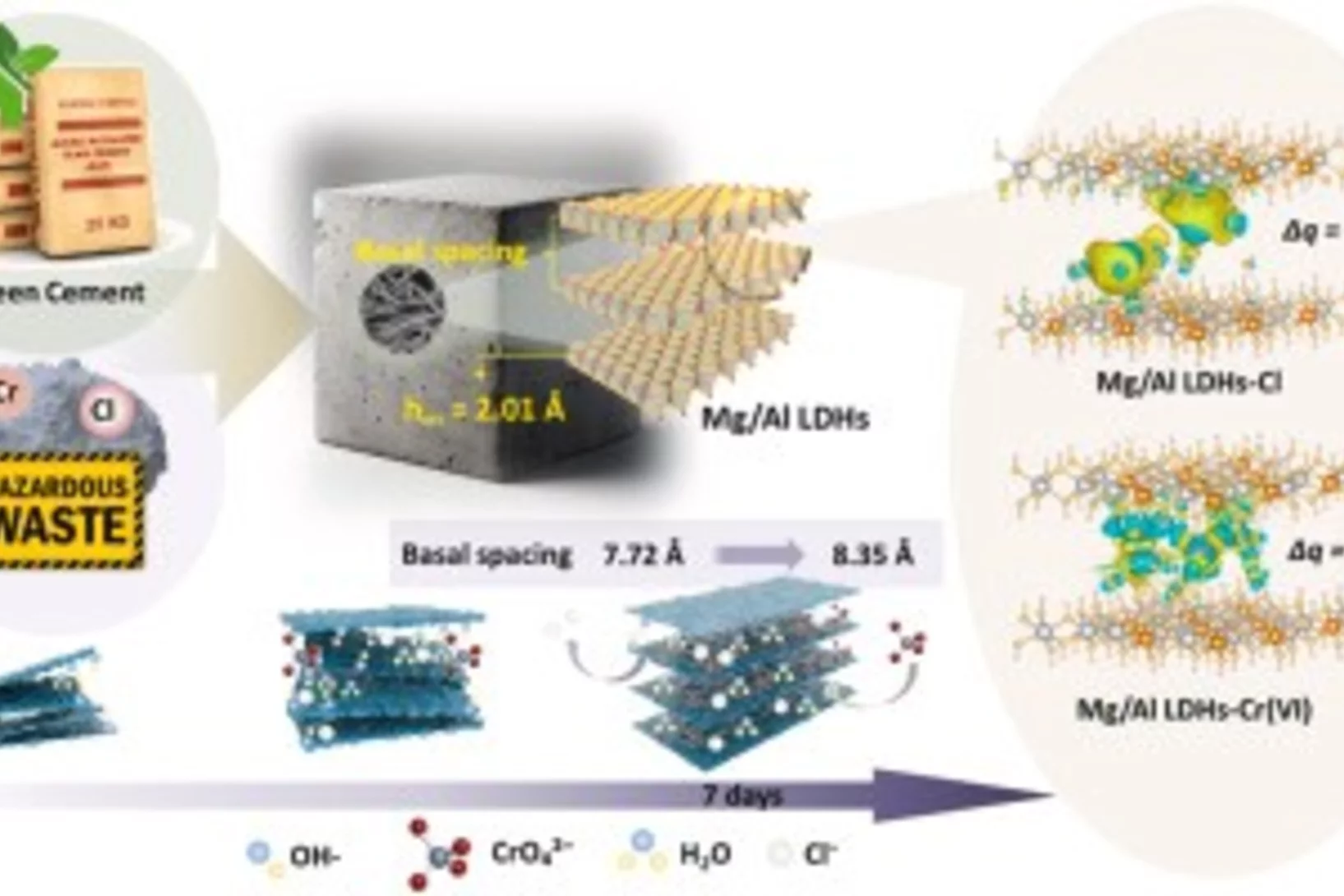
Reconstruction kinetics and structural evolutions of chromate and...
Zhang et al., 2025
Understanding the early-stage reconstruction of Mg/Al layered double hydroxide (LDH) is critical for enhancing anion immobilization in low-carbon cementitious systems. Here, we combined in-situ and ex-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analyses to reveal the time-dependent and reversible layered structure transformation of Mg/Al-LDH from calcined Mg/Al-LDH (CLDH) in cementitious environments enriched with...
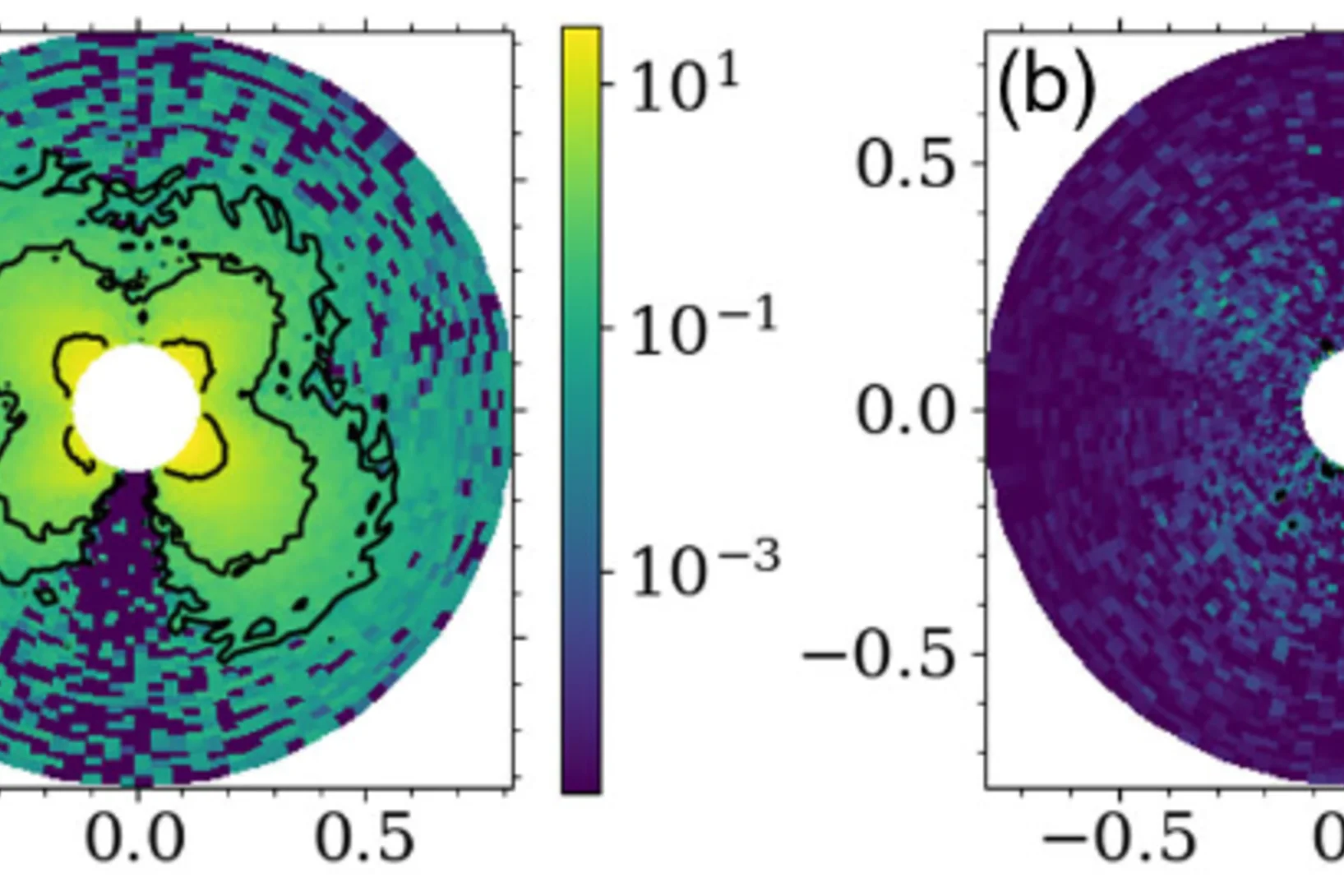
Spin-Disorder-Induced Angular Anisotropy in Polarized Magnetic Neutron Scattering
We experimentally report a hitherto unseen angular anisotropy in the polarized small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) cross section of a magnetically strongly inhomogeneous material ...
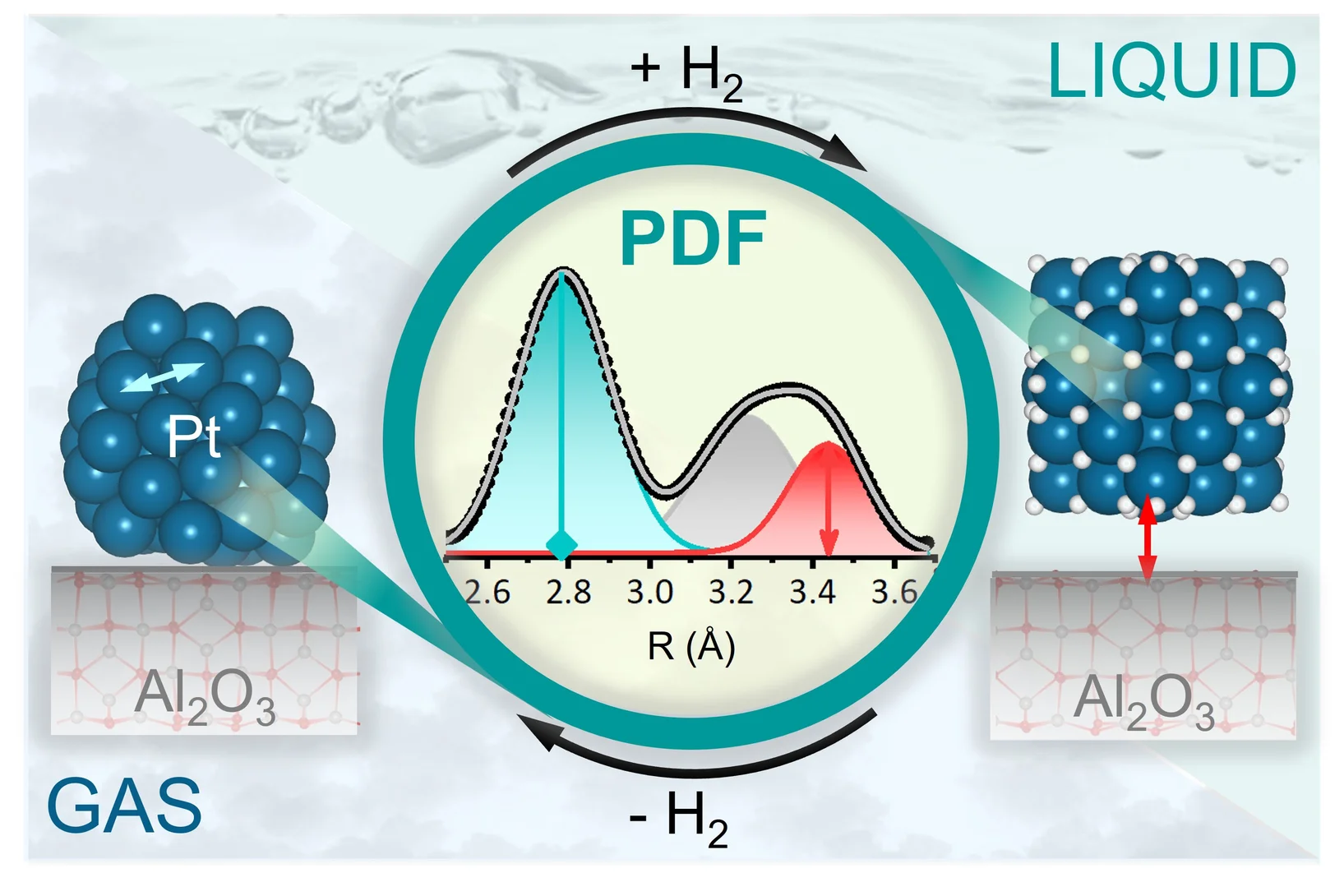
Seeing the subtle structural changes of Pt nanoparticles induced by hydrogen
We show that Pt nanoparticles reversibly expand and detach from Al2O3 in the presence of gas phase H2 and H2 dissolved in solvent.
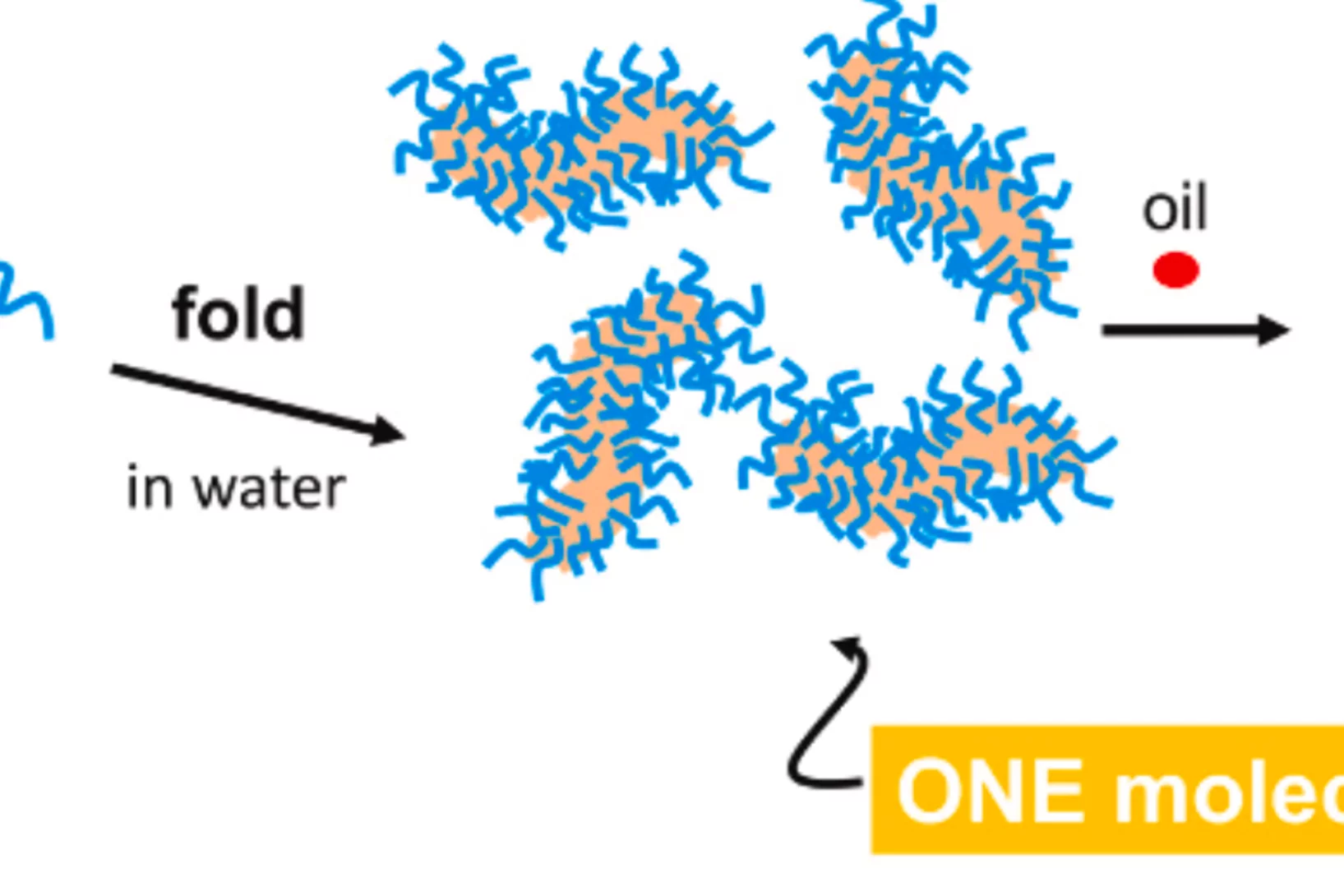
Single-chain polymer nanoparticles for oil solubilization
We report on the oil solubilization of amphiphilic single chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) based on random copolymers composed of oligo(ethyleneglycol) methacrylate (OEGMA) and anthracene methacrylate (AnMA). Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) combined with molecular dynamics simulations reveal ...
Coexistence of Insulatorlike Paramagnon and Metallic Spin-Orbit Exciton Modes in SrIrO3
We probe the spectrum of elementary excitations in SrIrO3 by using heterostructured [(SrIrO3)m / (SrTiO3)l] samples to approach the bulk limit. Our resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) measurements at the Ir L3 edge reveal ...
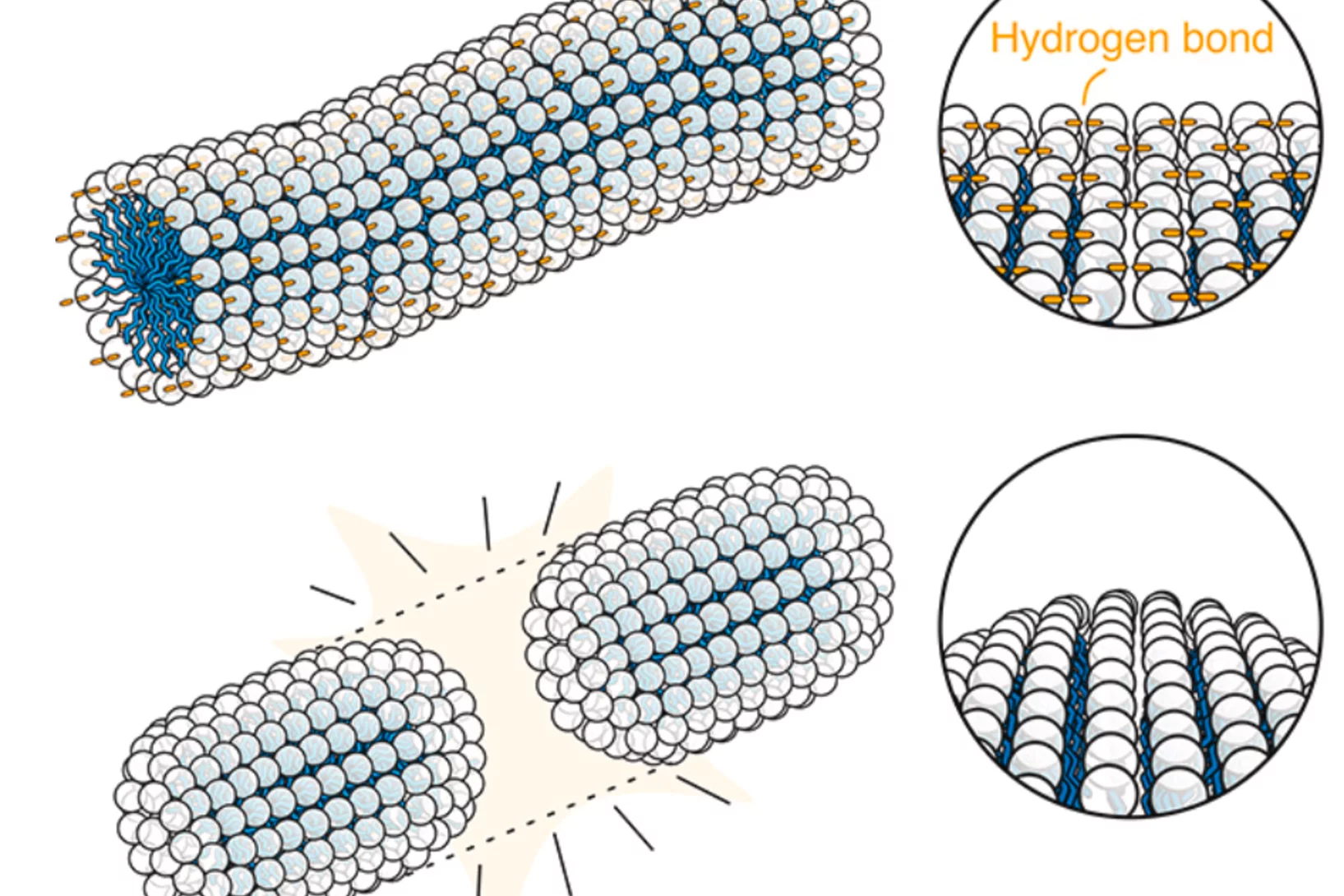
Hydrogen bonding exacerbates viscoelasticity of amino acid– and betaine surfactant self-assemblies
Many day-to-day materials rely on formulations of surfactants to control flow, texture and application. Inspired by the pairing of bases between DNA strands, we demonstrate enhanced control ...
Both natural and human emissions shape cloud formation high above Earth
What happens inside the CLOUD chamber?
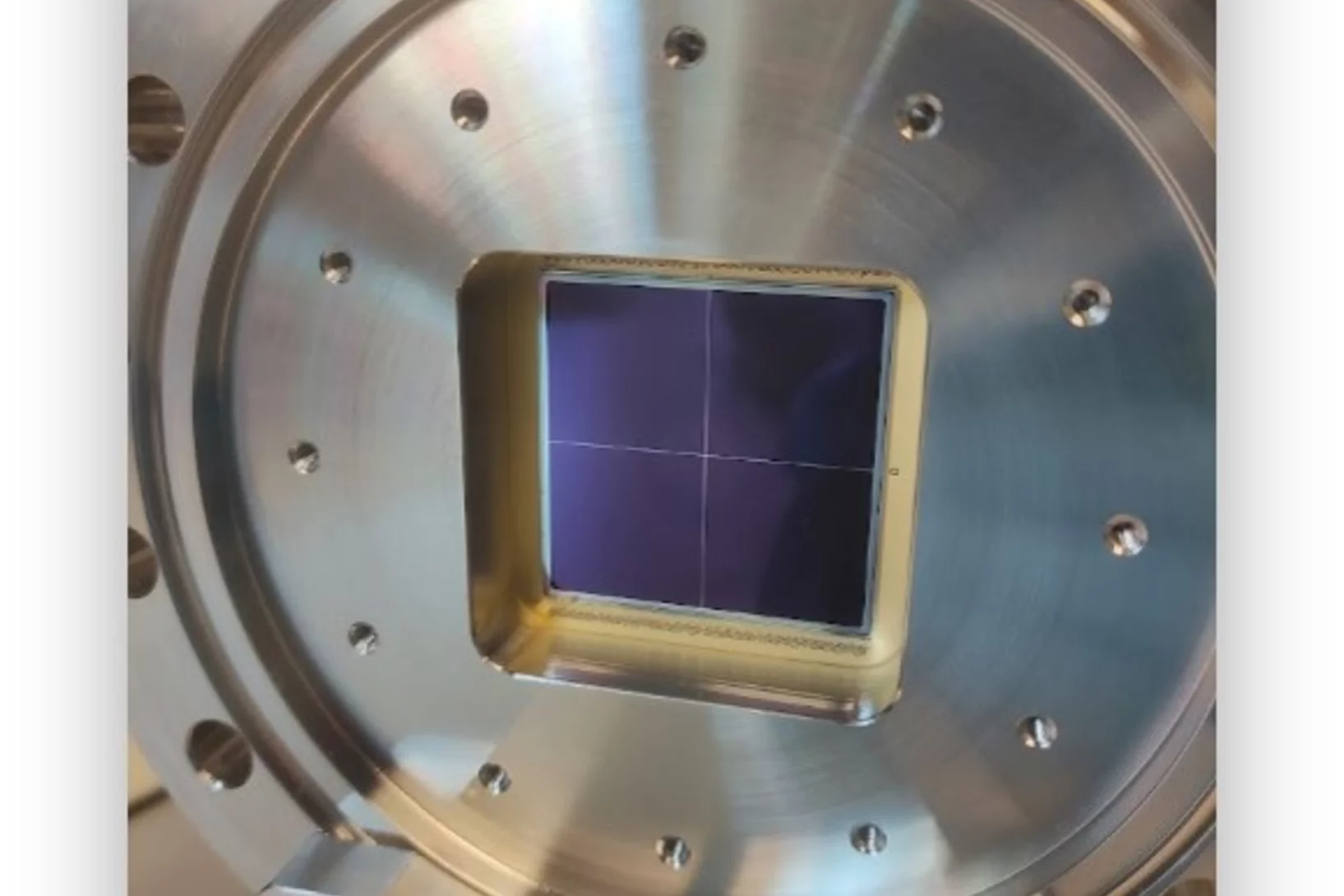
Single-Photon-Counting Detection for Soft X-rays Down to 530 eV
The PSI Photon Science Detector Group has developed the first single-photon-counting pixel detector capable of detecting soft X-rays down to 530 eV. This breakthrough was achieved by combining EIGER readout chips with novel inverse LGAD sensors, developed in collaboration with and fabricated at Fondazione Bruno Kessler (Italy). The detector is now in user operation for ptychographic applications, where it has already enabled significant scientific results at the Fe L₃-edge (707 eV) and even at the O K-edge (530 eV), demonstrating superior detection performance compared to commercially available state-of-the-art detectors.
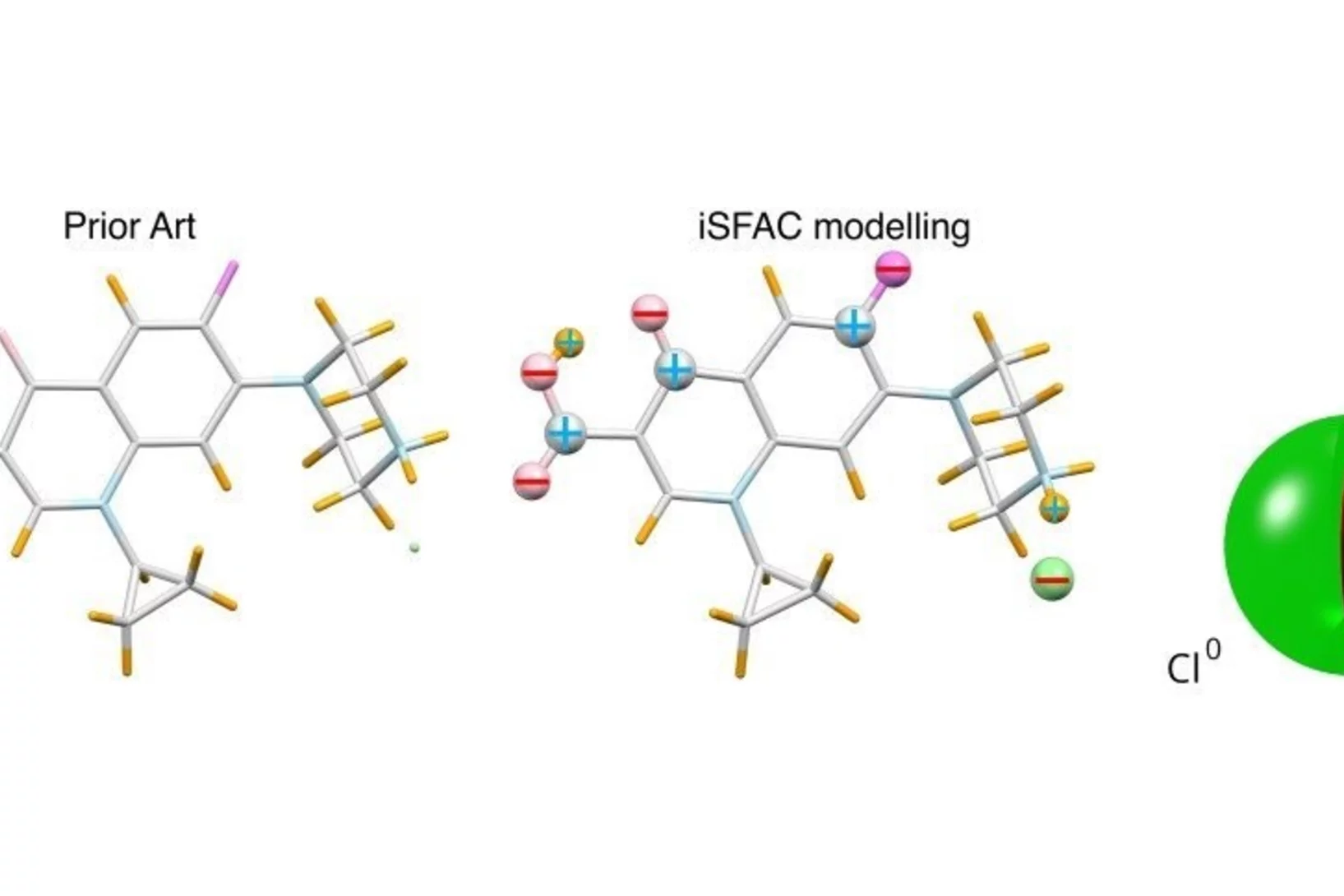
Measuring How Molecules Communicate
A collaboration between PSI and the University of Vienna has resulted in a new experimental method that, for the first time, enables the direct measurement of partial charges in molecules. Partial charges are fundamental to understanding molecular structure, interactions, and reactivity, yet until now no general technique existed to determine them experimentally.
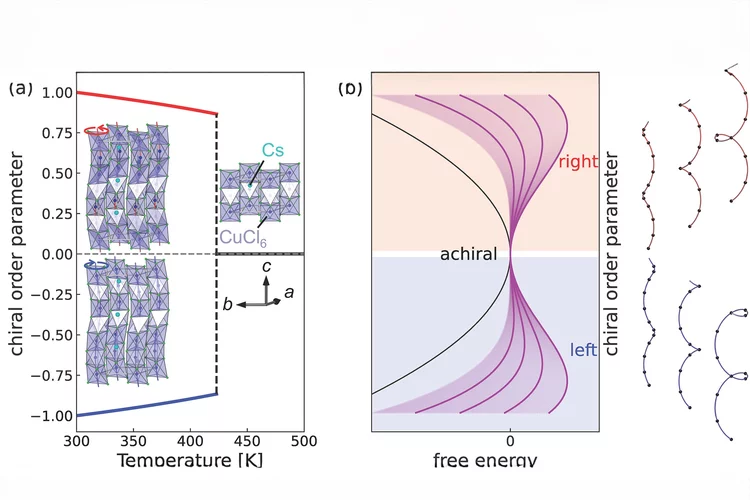
Tuning chirality amplitude at ultrafast timescales in chiral CsCuCl3
We quantify “how chiral” a crystal is, and demonstrate its tunability at ultrafast timescales. This achievement does open up a new direction in chirality-related condensed matter physics and on emergent phenomena, which have both attracted significant attention recently.
Depth-resolved magnetic order in superconducting topological insulator/FeTe thin film heterostructures
The search for chiral topological superconductivity in magnetic topological insulator (TI)-FeTe heterostructures is a key frontier in condensed matter physics, with potential applications in topological quantum computing. The combination of ferromagnetism, superconductivity, and topologically nontrivial surface states brings together the key elements required for chiral Majorana physics. In this work ...
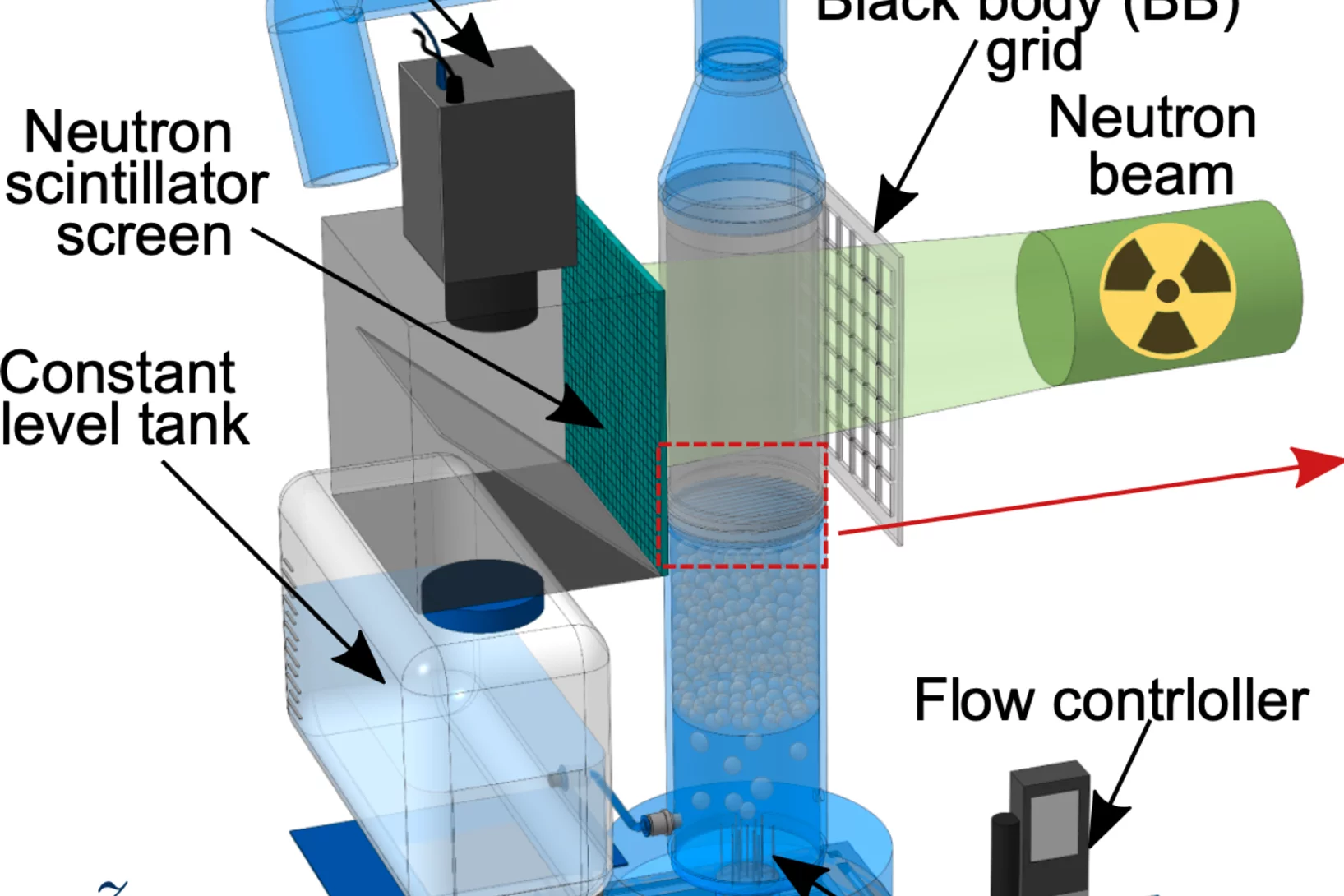
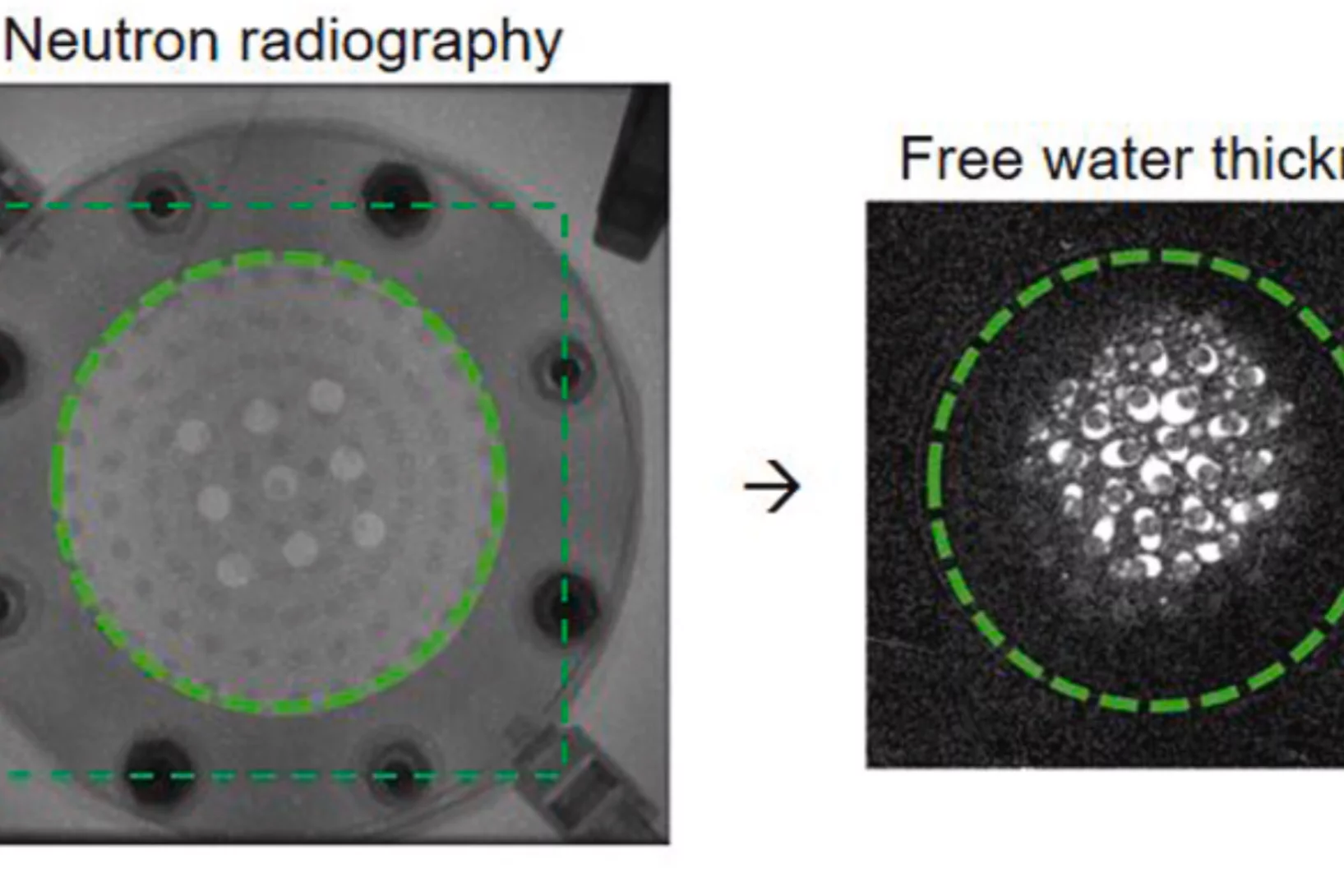
In-situ neutron tomography study of a dehydrating and hydrating packed bed for thermochemical heat storage
To study the heat and water vapor transport and reaction kinetics in a packed bed of thermo-chemical material on both reactor and tablet level, an in-situ neutron imaging study of a dehydrating and subsequently hydrating packed bed consisting of cylindrical K2 CO3 tablets was performed at the Paul Scherrer Institute ...
Field-Induced Magnon Decay, Magnon Shadows, and Rotonlike Excitations in the Honeycomb Antiferromagnet YbBr3
The search for new quantum many-body phenomena in magnetic materials has a strong focus on highly frustrated systems and the resulting quantum spin-liquid state. However, even unfrustrated magnetic materials show a multitude of unconventional features in their spin excitation spectra. By using the synergy of ...
ClaySor 2023: Implementation of the 2SPNE SC/CE sorption model and...
Marinich et al., 2025
The ClaySor 2023 model package within the GEM-Selektor software includes an updated version of the two-site protolysis non-electrostatic surface complexation and cation exchange model for illite and montmorillonite, as well as the first implementation of the generalised caesium sorption model for illite. These models have been harmonised with the most recent PSI Chemical Thermodynamic Database 2020, resulting in the updated.....
Generating structured foam via flowing through a wire array
Efficient manufacturing methods could unlock foams with tailored, anisotropic properties. Conventional foam production methods rely on the self-arrangement of bubbles, typically leading to isotropic materials, or involve intricate additive layering processes. This study presents a simple, passive technique to modify the foam structure. A set of thin parallel wires ...
Neutron radiography analysis of water management in a passive proton-exchange membrane fuel cell with superhydrophobic catalyst layers
Water transport in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) with superhydrophobic catalyst layers (CLs) has been studied with neutron radiography. Superhydrophobic CLs were deposited by electrospray on the membrane to be tested on the cathode and anode sides of the cells. The cells are operated under ...
HPCP Summer School FHNW/PSI
The institute for Data Science of the FHNW in Brugg - Windisch and AWI department of PSI held a joint course on high performance computing. The course addressed computer science students of FHNW and interested individuals at PSI. Two full days at the FHNW (with Apero) were followed by two full days at PSI using Merlin6 (with tour).
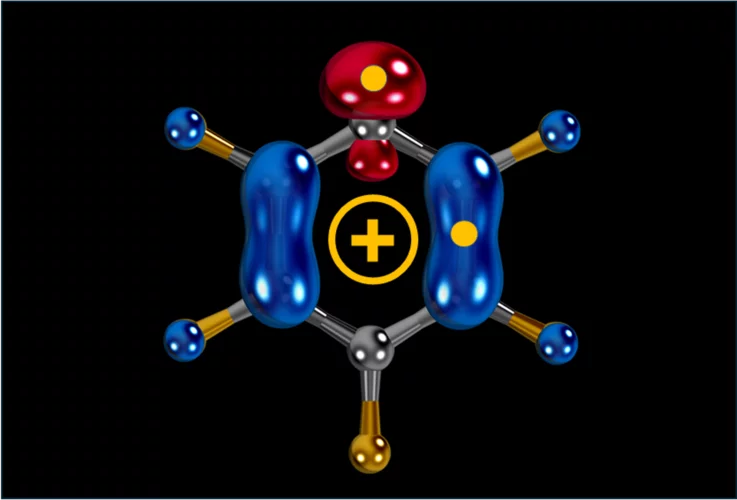
Carbocation, diradical, and superelectrophile in one molecule?
The pentafluorophenyl cation (C₆F₅⁺) breaks these rules with a borderline “crazy” reactivity.
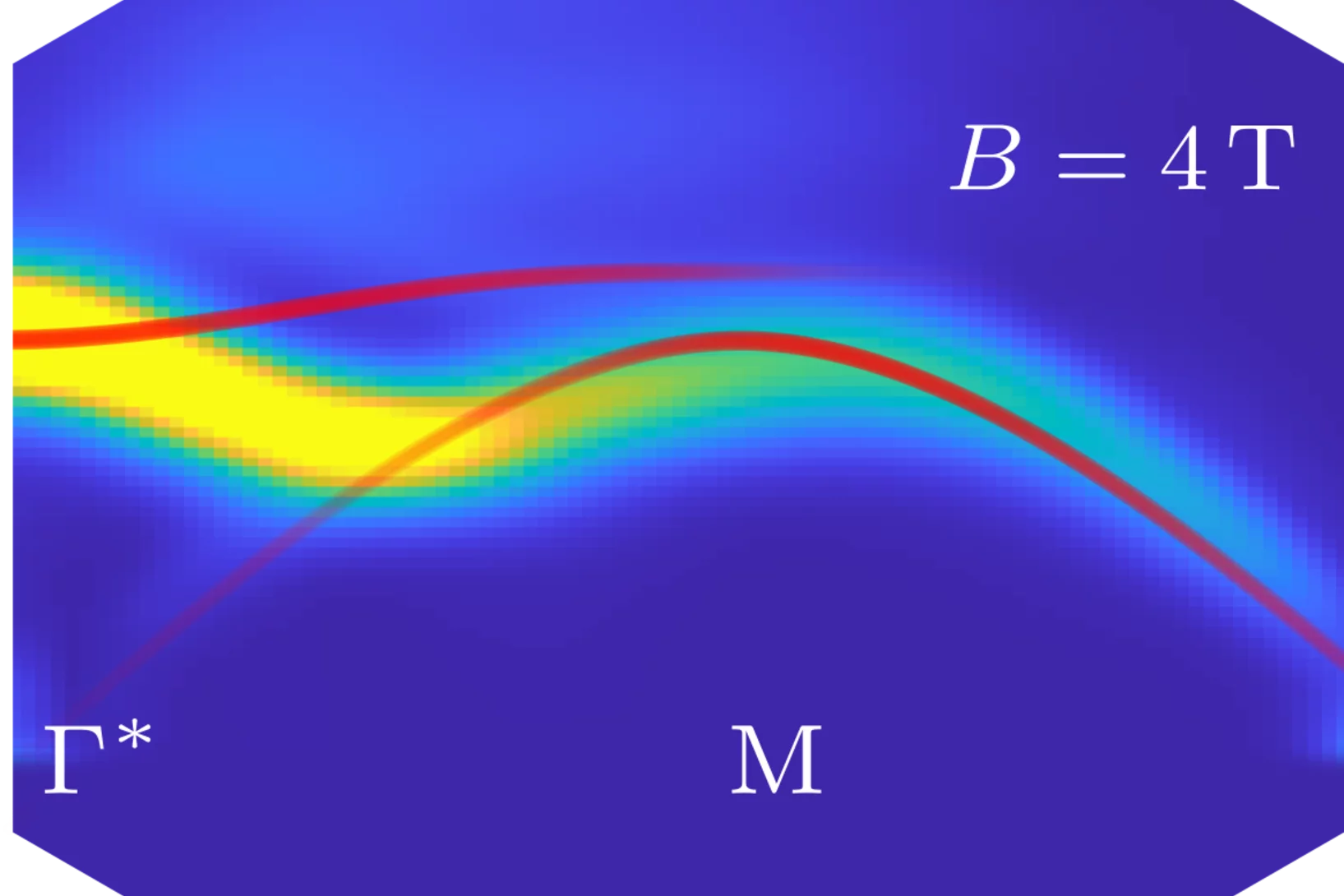
Discovery of Nodal-Line Superconductivity in Chiral Crystals
Chiral crystals, whose key feature is the structural handedness, host exotic quantum phenomena driven by the interplay of band topology, spin-orbit coupling (SOC), and electronic correlations. Due to the limited availability of suitable chiral-crystal materials, their unconventional superconductivity (SC) remains largely unexplored.
Here, the discovery ...
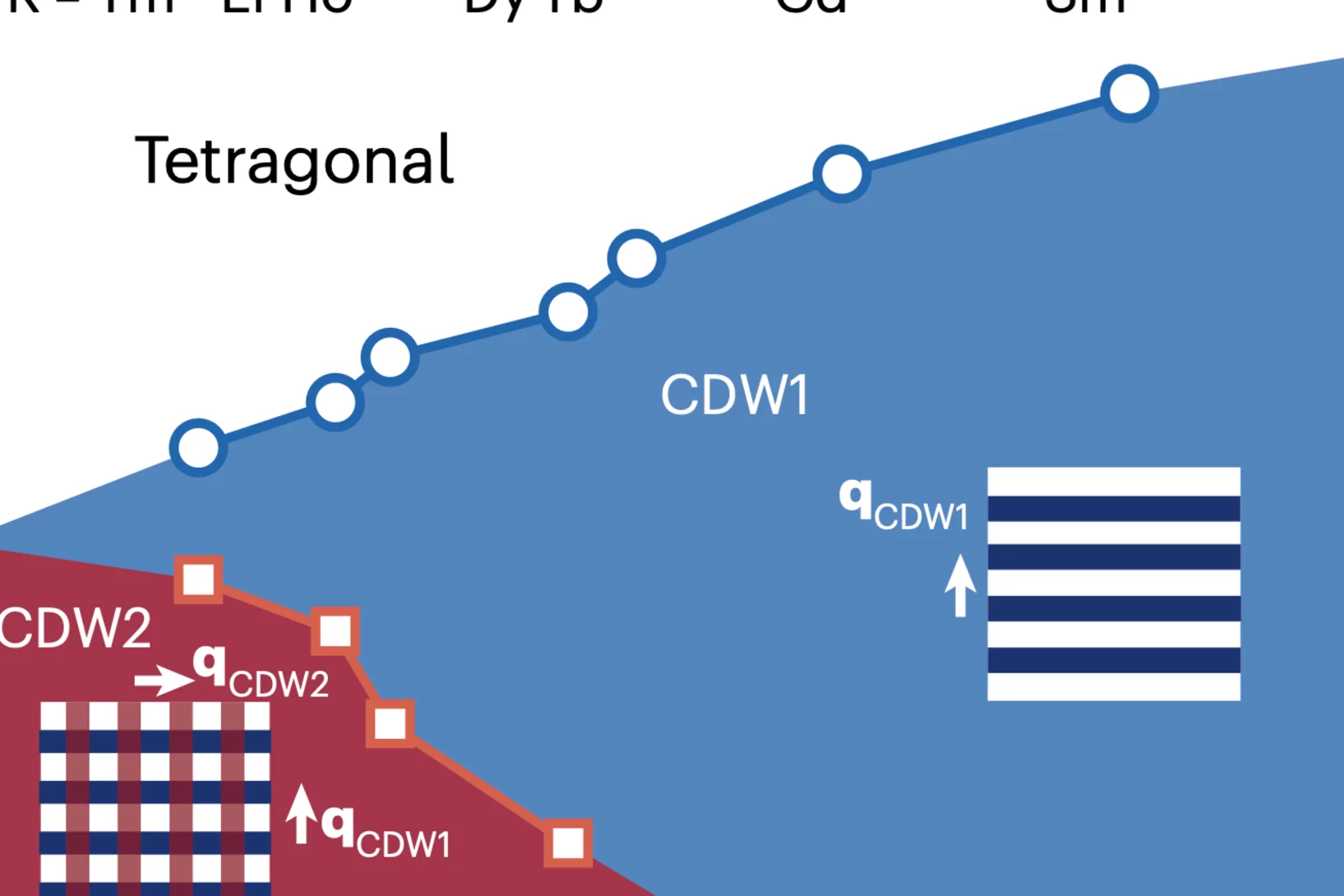
Ferroaxial density wave from intertwined charge and orbital order in rare-earth tritellurides
The discovery of the axial amplitude mode—commonly referred to as the Higgs mode—in charge density wave systems, such as rare-earth tritellurides, indicates the presence of a hidden order. A theoretical study proposed that this axial Higgs mode arises from a hidden orbital texture of the charge density wave, which produces a ferroaxial charge order.
However, experimental evidence ...