The Laboratory for Catalysis and Sustainable Chemistry studies functioning catalysts for energy conversion and storage and for sustainable chemicals synthesis.
Scientific Highlights & Lab News
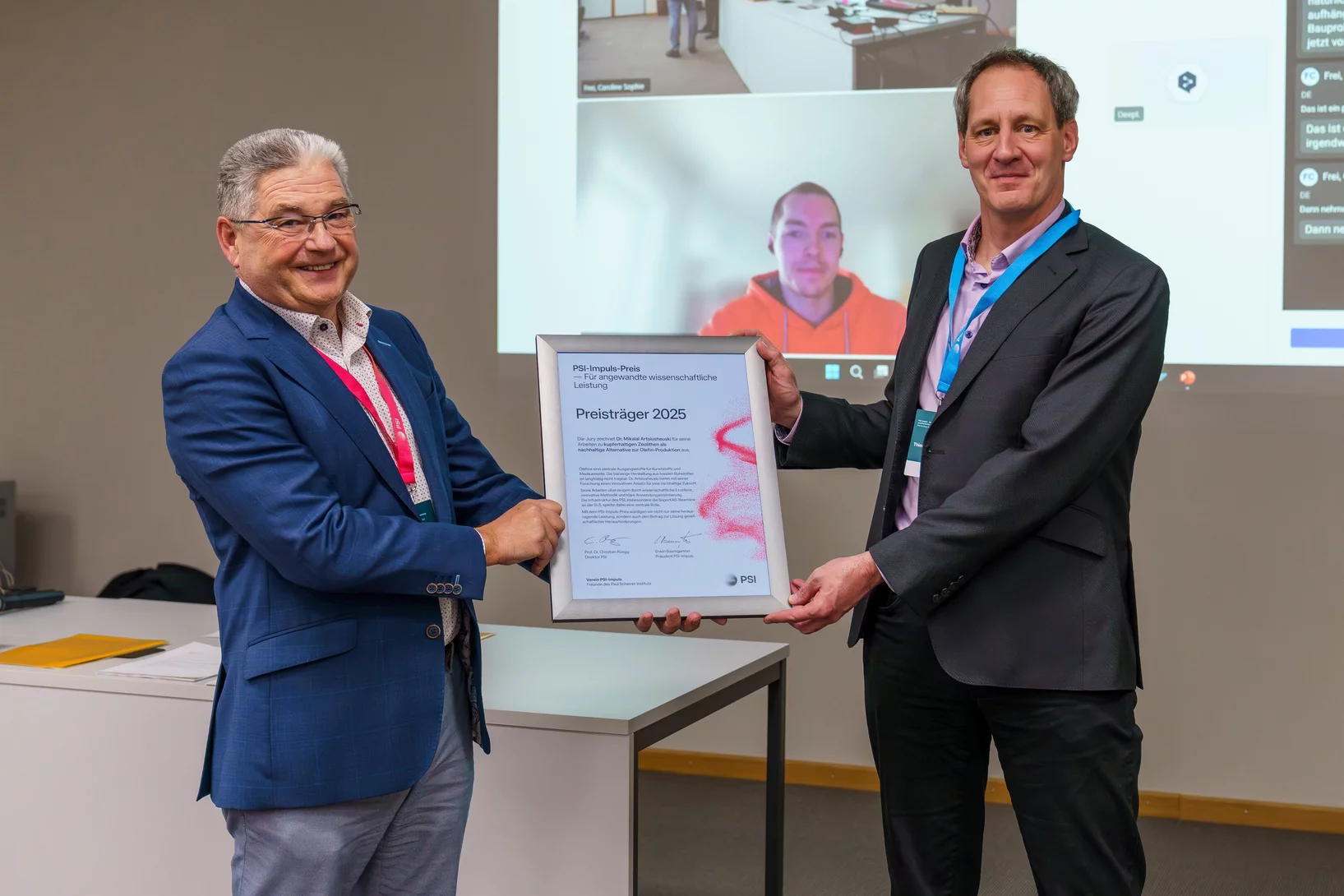
PSI-Impuls-Preis 2025
Der PSI-Impuls-Preis 2025 für anwendungsorientierte Forschung geht an Dr. Mikalai Artsiusheuski für seine herausragenden Arbeiten zur Entwicklung eines innovativen Chemical-Looping-Verfahrens zur nachhaltigen Herstellung von Ethylen und Propylen – zwei zentralen Bausteinen der modernen Chemie.
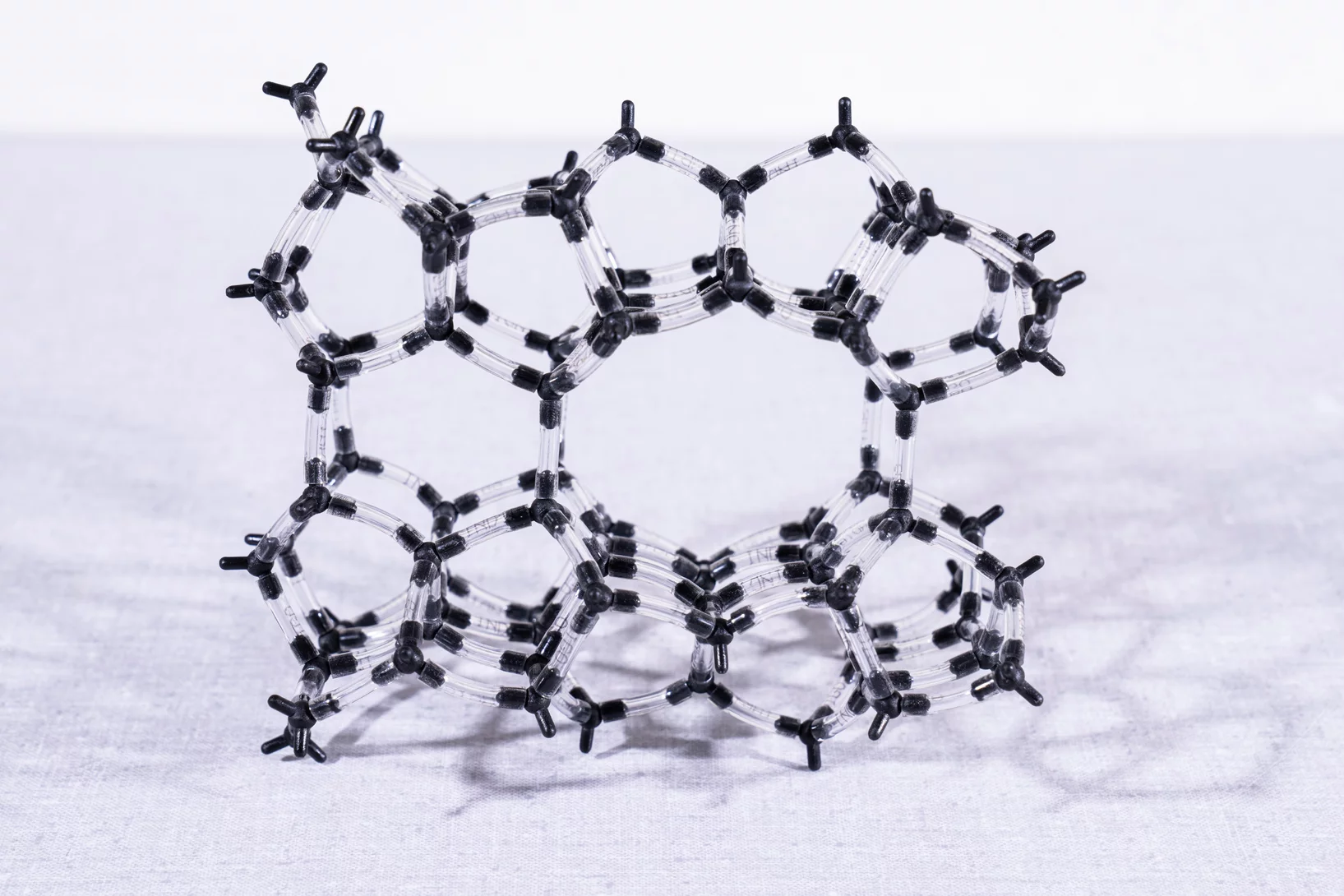
Aluminium sichtbar gemacht
PSI-Forschende haben in Zeolithen erstmals die genaue Lage der Aluminiumatome bestimmt, welche die Materialien zu so guten Katalysatoren machen.
Welcome to Archana Ramakrishnan!
A warm welcome to Archana Ramakrishnan.
She will work as a PhD student on the reFuel.ch project.
Publications
-
Aegerter D, Fabbri E, Novotny Z, Borlaf M, Yüzbasi NS, Comini N, et al.
Evaluation of dip-and-pull ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy for investigating oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts
ACS Applied Energy Materials. 2025; 8(19): 14554-14567. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.5c02252
DORA PSI -
Artsiusheuski M, Casati N, Clark A, Nachtegaal M, Verel R, van Bokhoven J, et al.
Controlling the mechanism of nucleation and growth enables synthesis of UiO‐66 metal‐organic framework with desired macroscopic properties
Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 2025; 64(4): e202415919 (13 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202415919
DORA PSI -
Artsiusheuski MA, Guo J, Kulkarni AR, van Bokhoven JA, Sushkevich VL
Low-temperature nonoxidative dehydrogenation of short-chain alkanes over copper(I) mordenite via chemical looping
Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2025; 147(18): 15880-15889. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c04229
DORA PSI