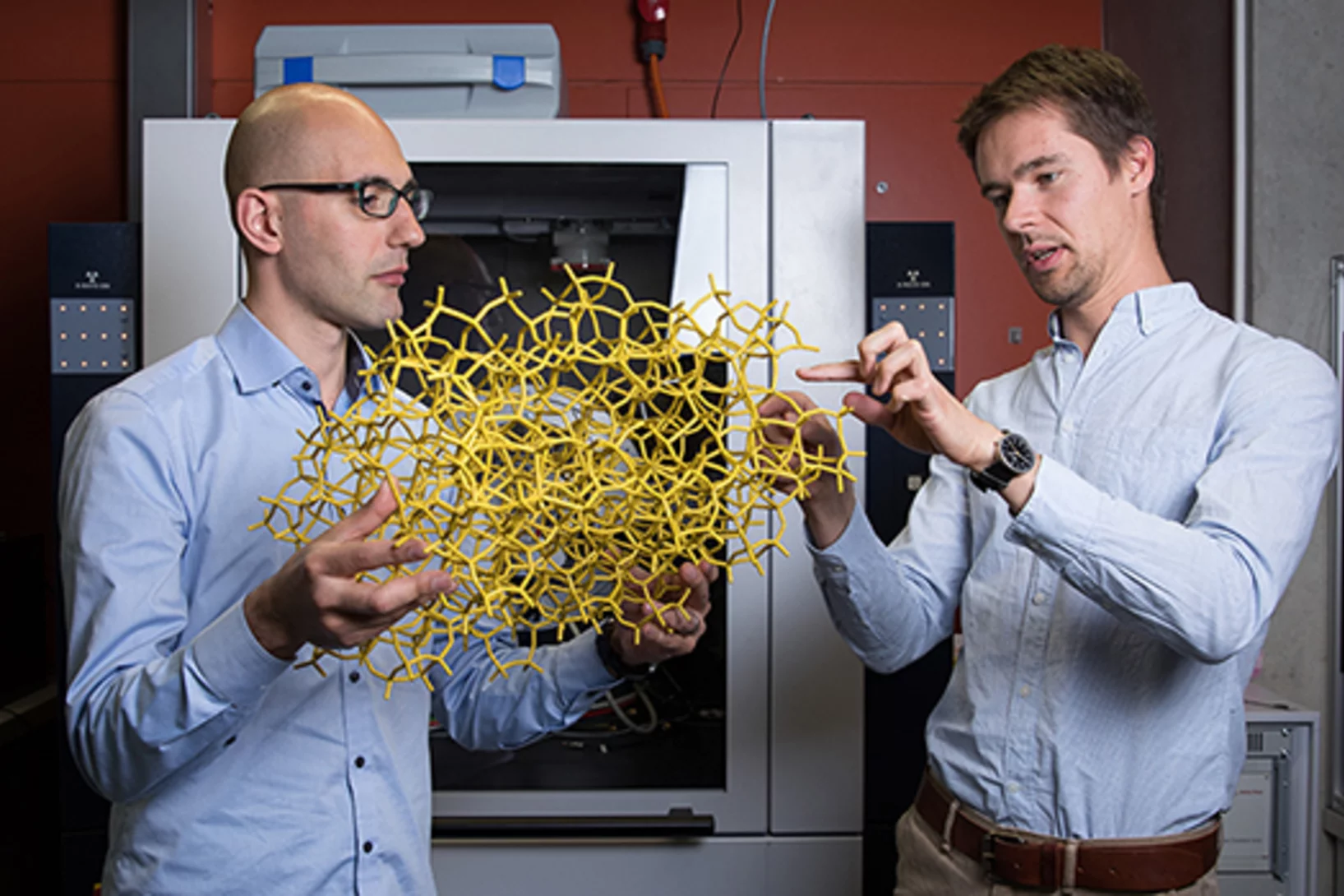
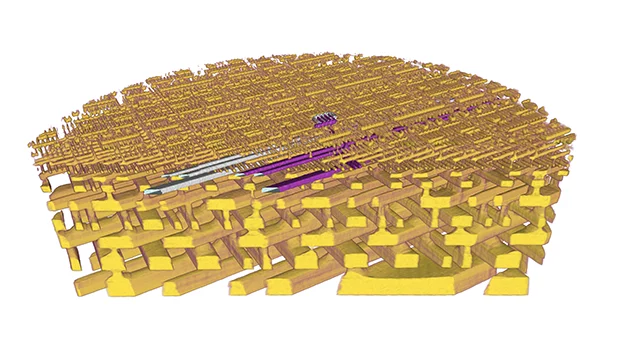
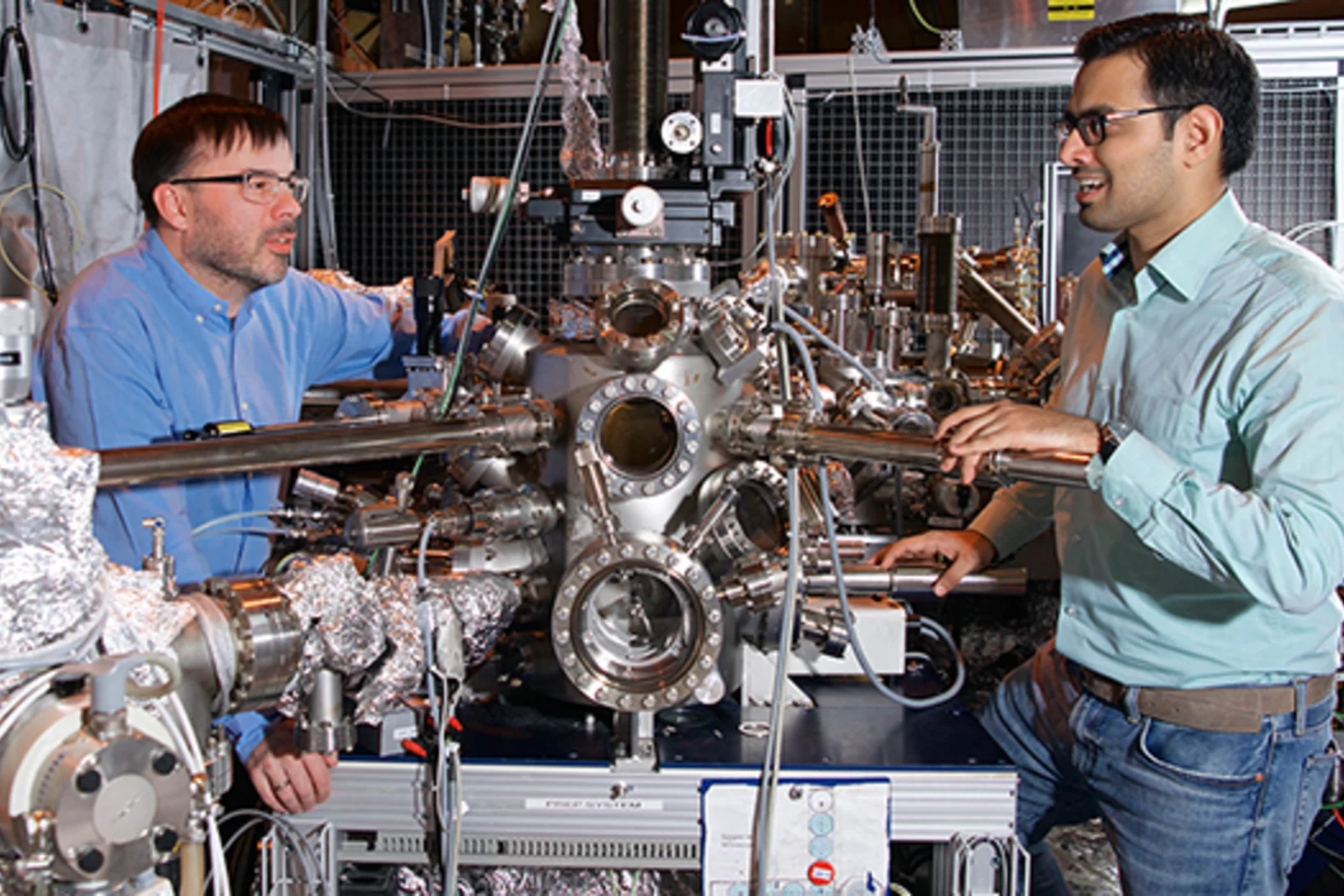
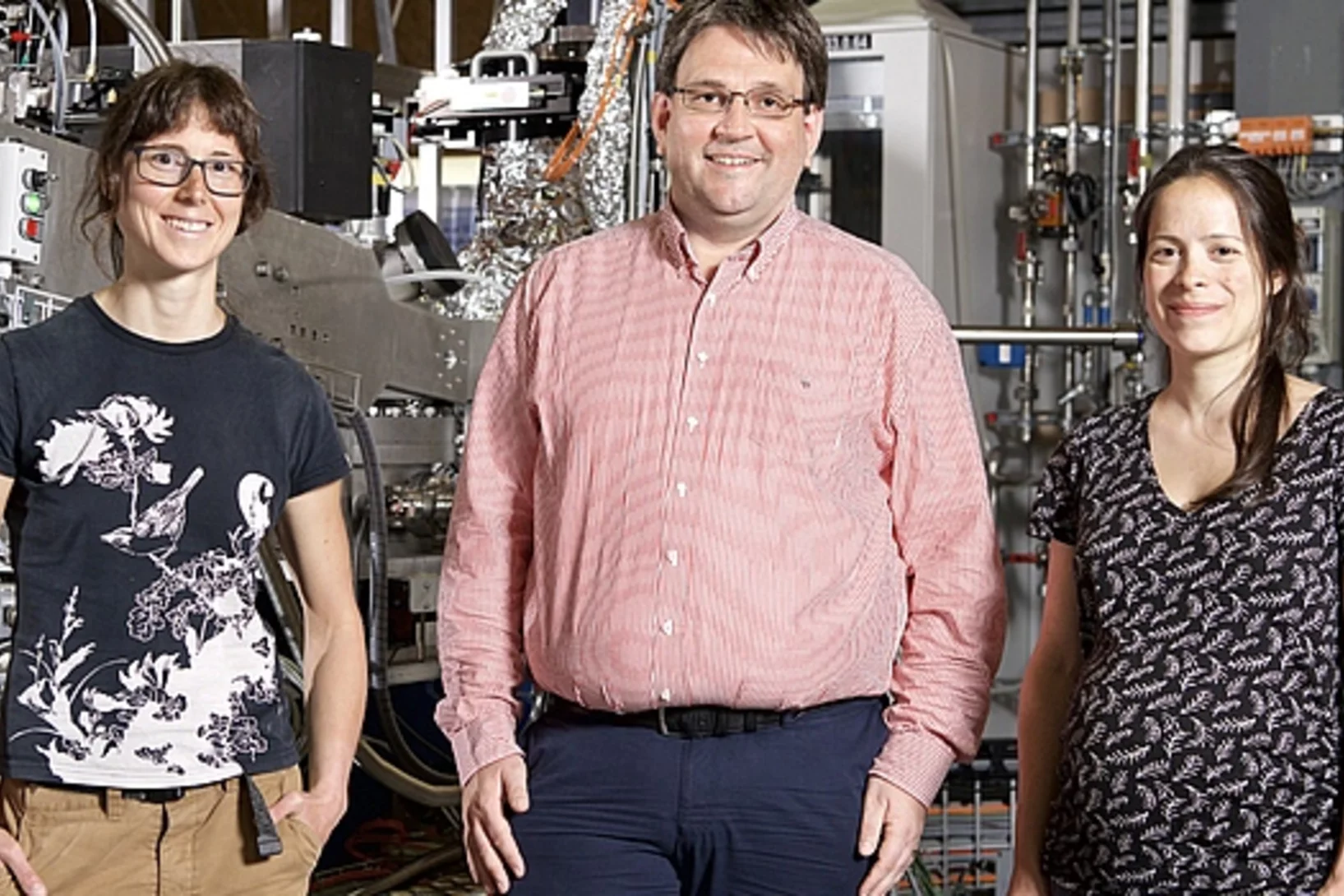
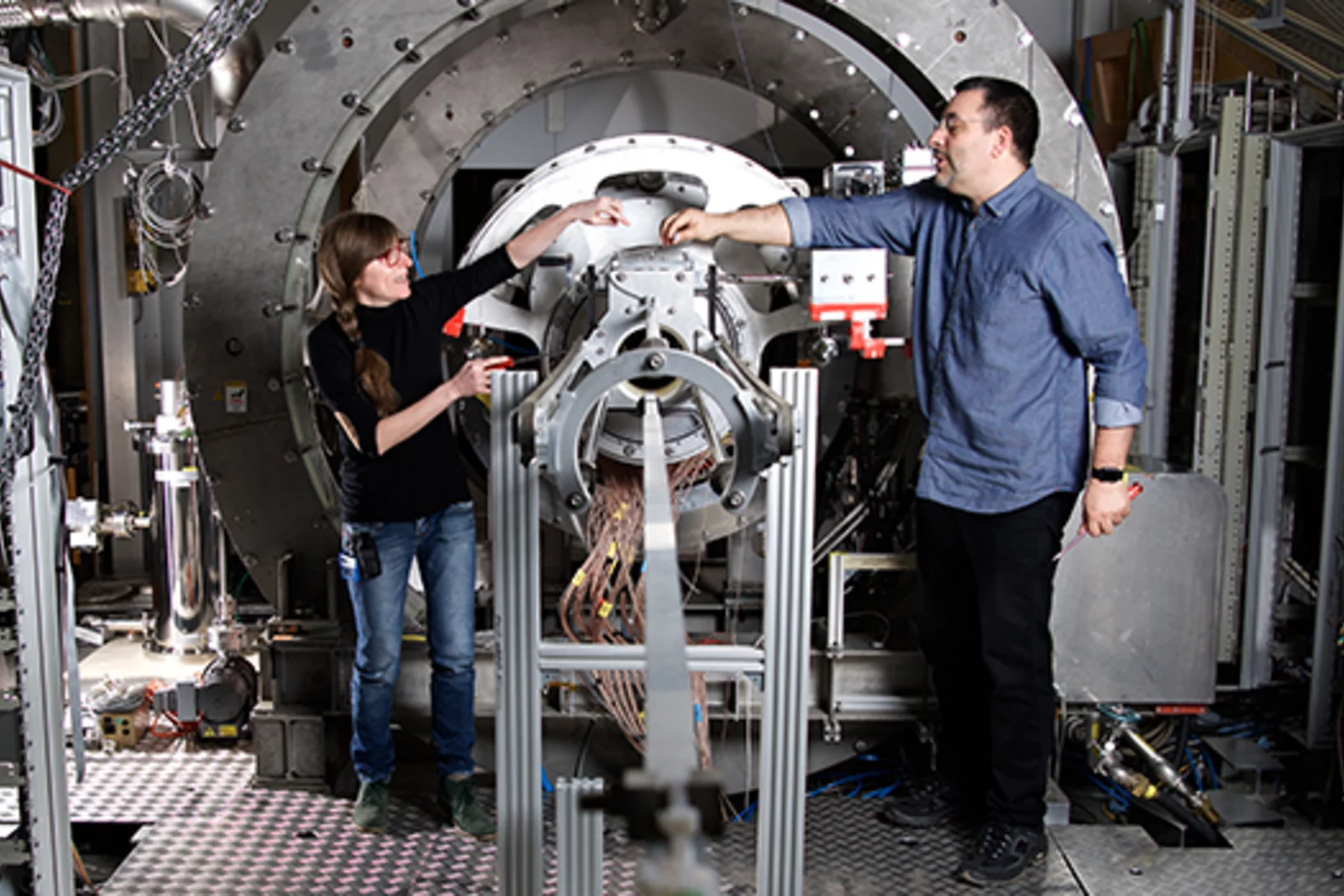
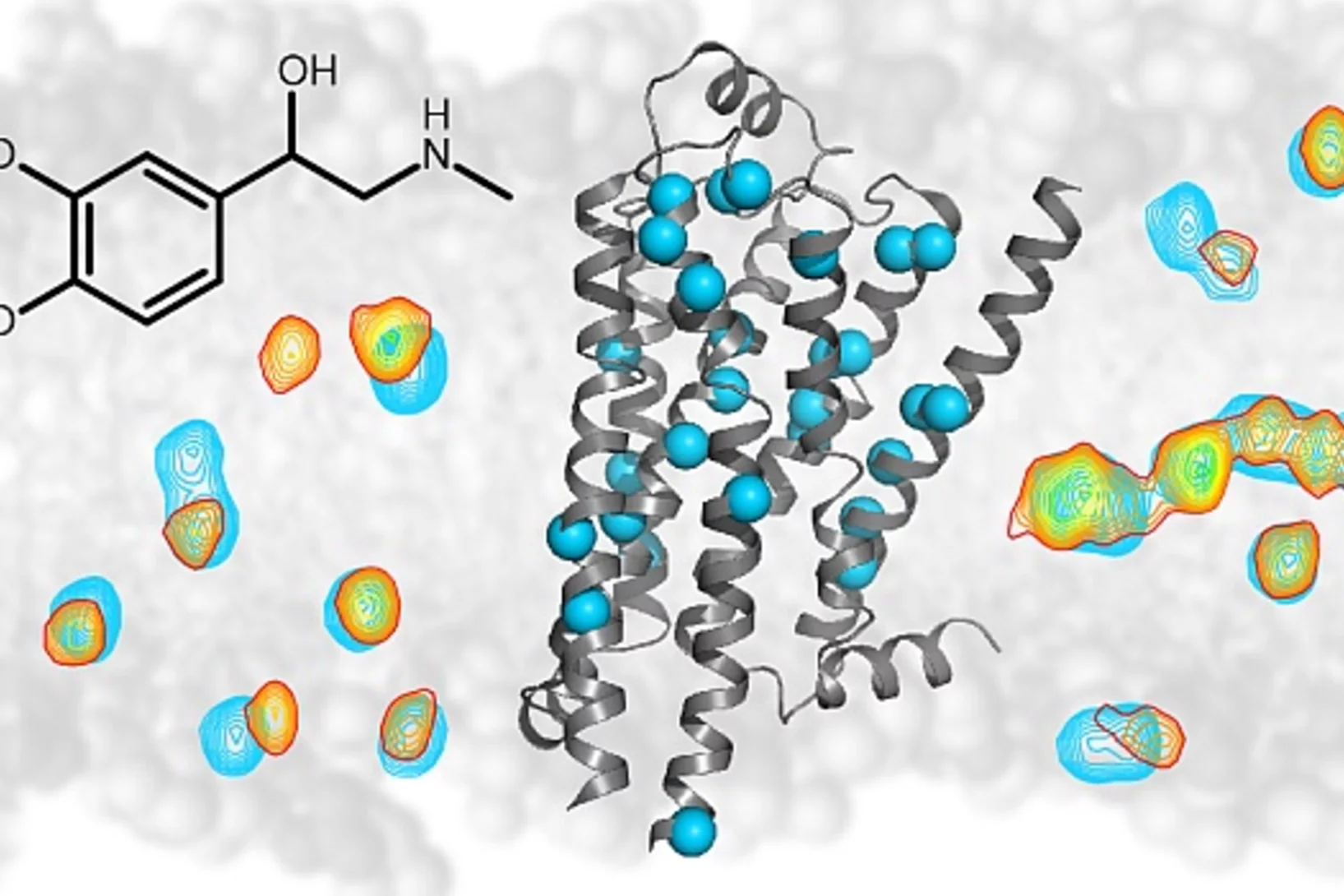
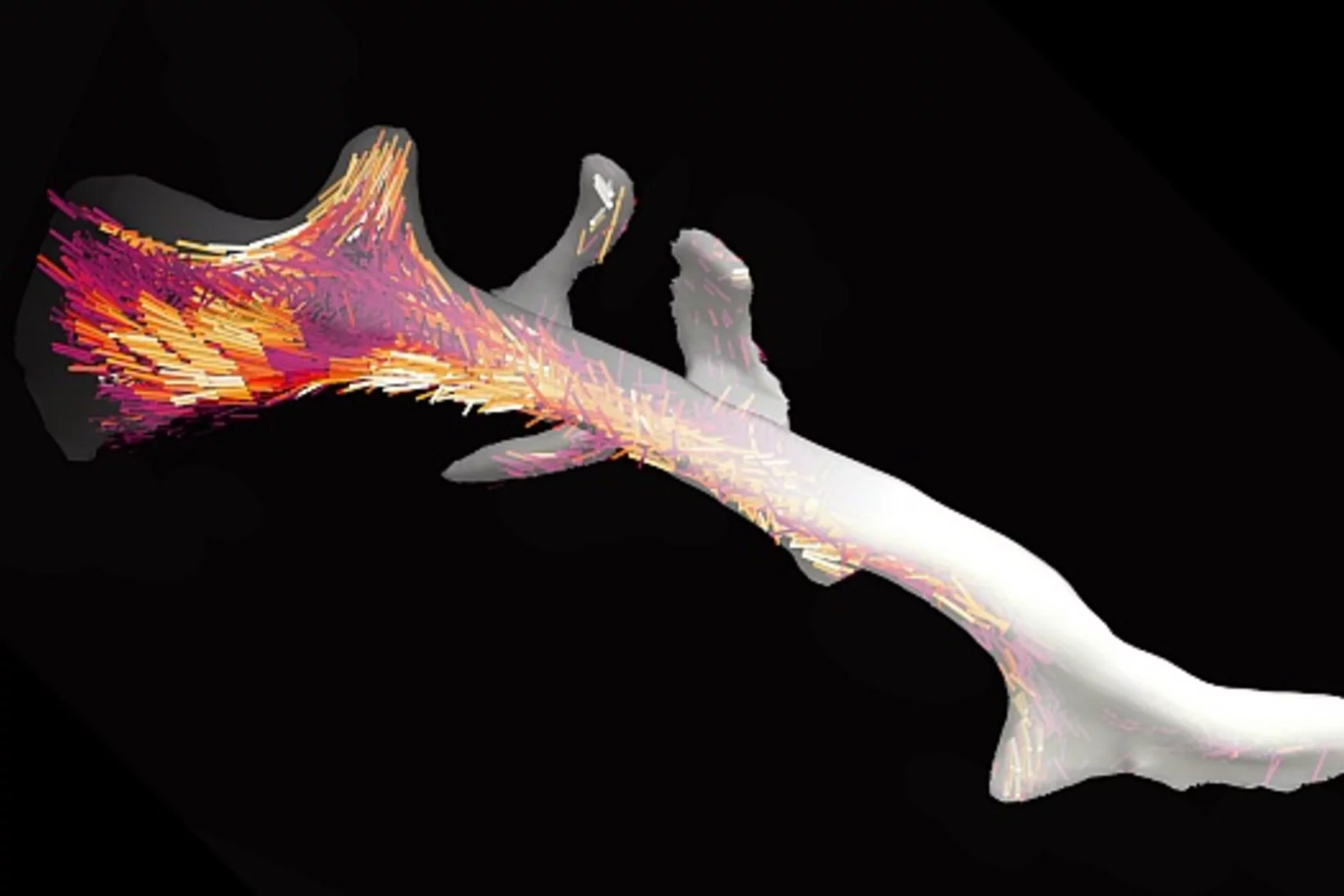
More than a prototype
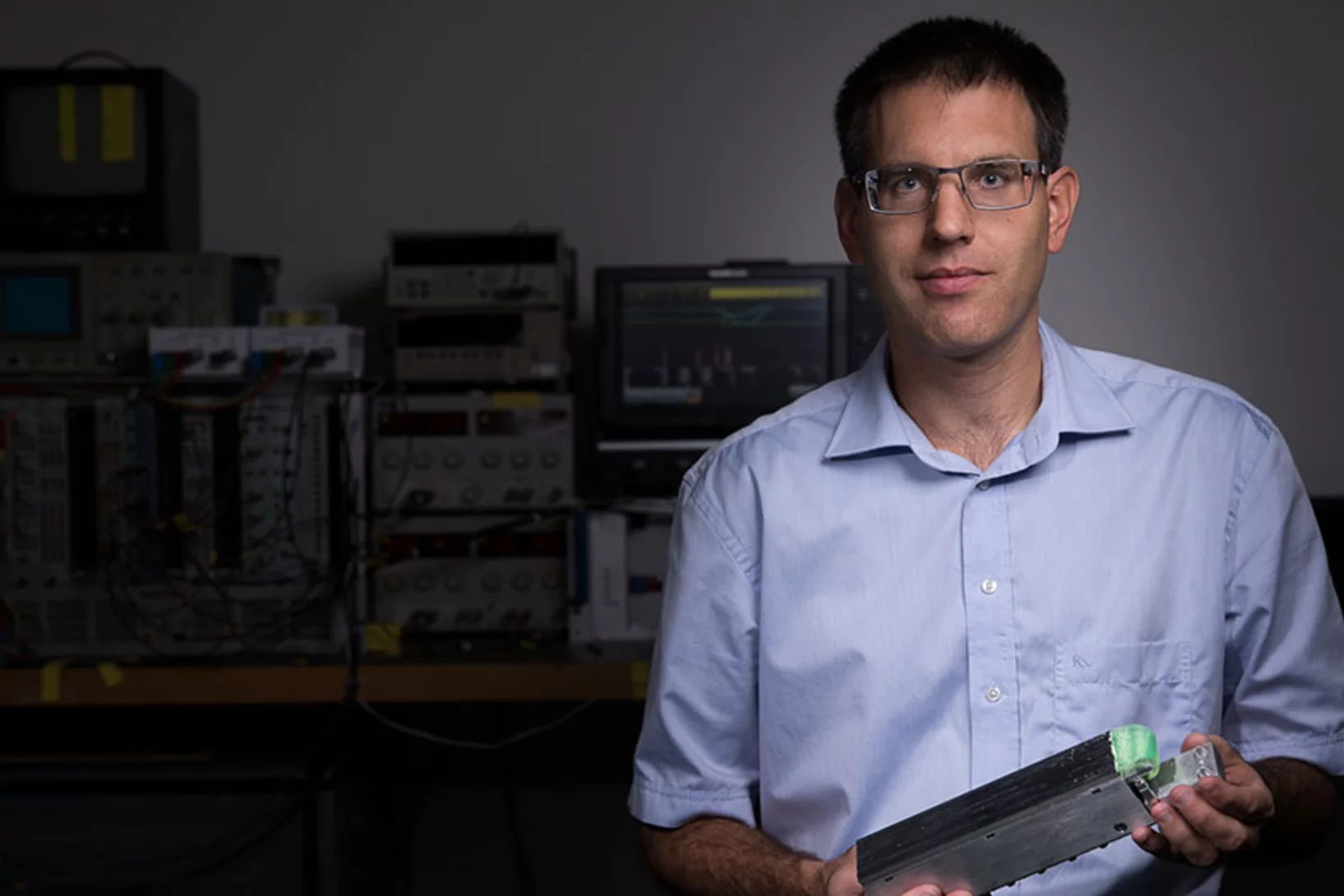
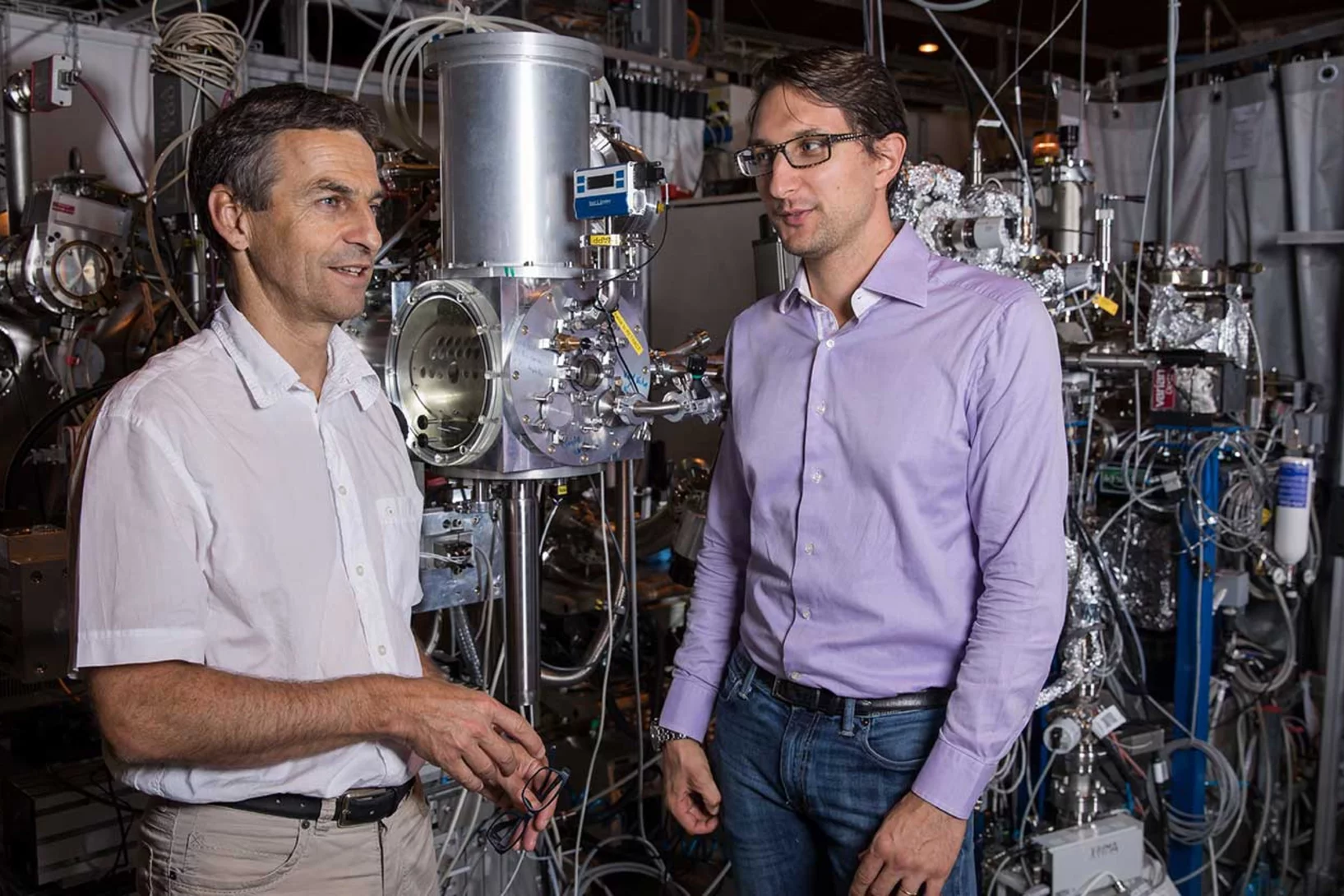
Jean-Baptiste Mosset, winner of a Founder Fellowship at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, wants to commercialise a neutron detector to spot plutonium and uranium.
Still no sign of dark matter
No evidence of dark matter made of axions – result of an experiment at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI further constrains theories about the nature of dark matter.
A new bio-robot
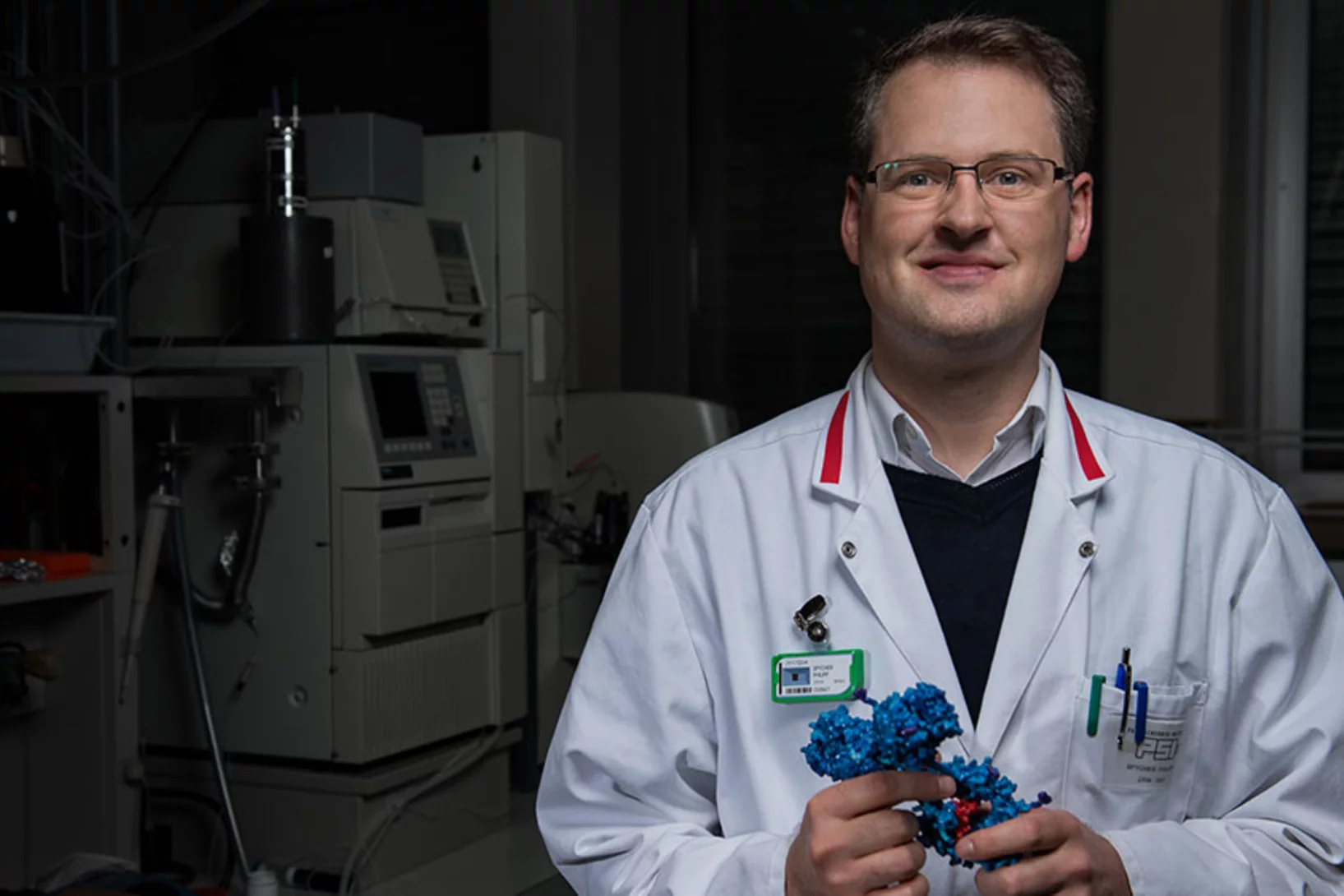
With a new method for modifying antibodies, Philipp Spycher, winner of a Founder Fellowship at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, wants to develop drugs that are more stable and, thus, have fewer side-effects.
Atmosphere in X-ray light
PSI researchers have developed an experimental chamber in which they can recreate atmospheric processes and probe them with unprecedented precision, using X-ray light from the Swiss Light Source SLS. In the initial experiments, they have studied the production of bromine, which plays an essential role in the decomposition of ozone in the lower layers of the atmosphere. In the future, the new experiment chamber will also be available for use by researchers from other scientific fields.
More than just spilling the beans
Because of their high nitrogen content, spent coffee grounds are a popular garden fertilizer. Recycled in this manner, they already contribute to an environmentally friendly waste management. But they have the potential to deliver much more: a new procedure developed at the PSI allows high quality methane to be formed from spent coffee grounds. PSI researchers involved in a pilot project carried out in cooperation with the Swiss food producer Nestlé were able to show that spent coffee grounds left over during the production of instant coffee can be efficiently re-used elsewhere.
Diving into magnets
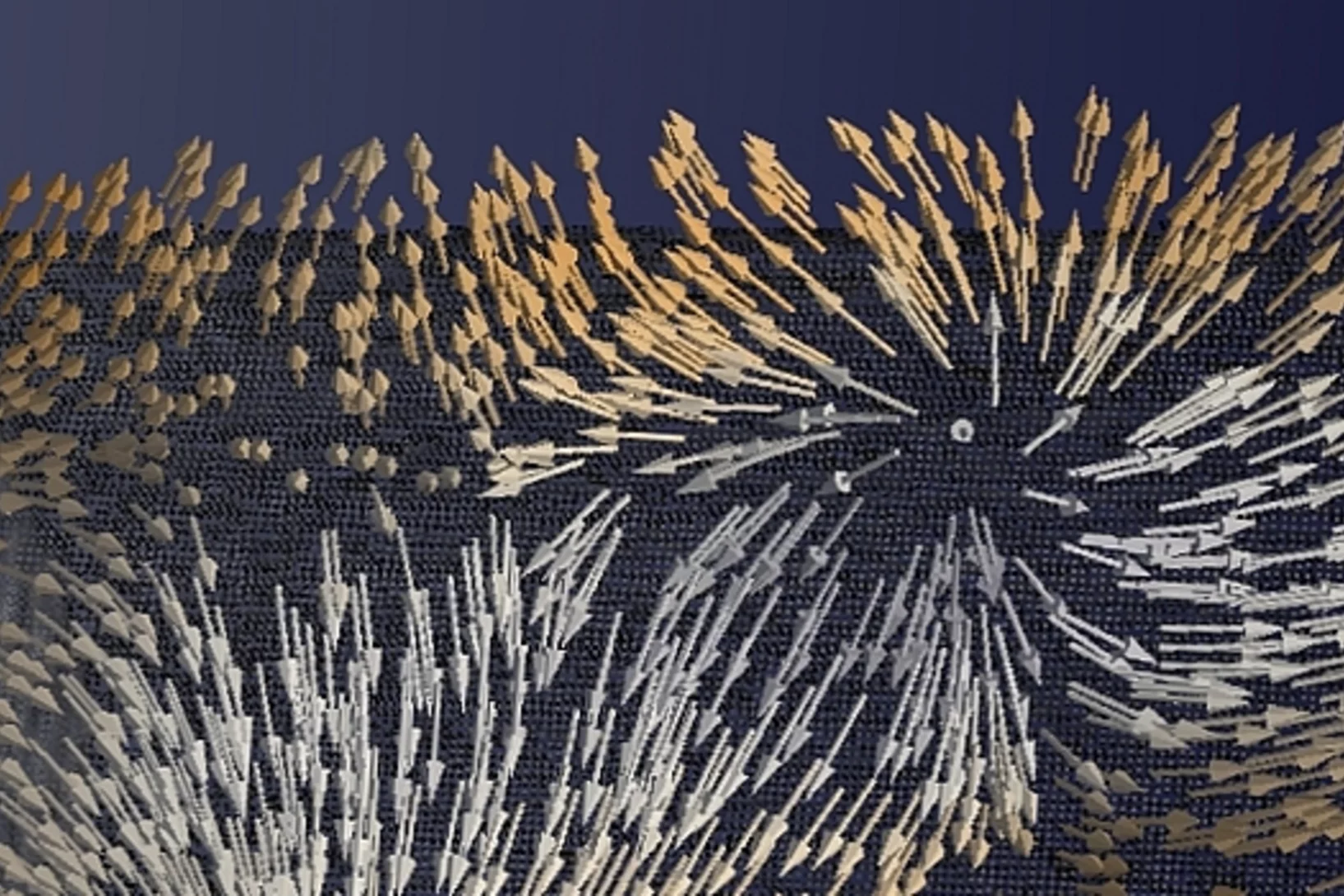
For the first time, scientists have made visible the directions of the magnetisation inside a 3D magnetic object. The smallest details in their visualisation were ten thousand times smaller than a millimetre. Among others, the magnetic structure contained one outstanding kind of pattern: magnetic singularities called Bloch points, which up to now were only known in theory.
Nanomaterial helps store solar energy: efficiently and inexpensively
Efficient electrolysers are needed in order to store sun and wind energy in the form of hydrogen. Thanks to a new material developed by researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and Empa, these devices are likely to become less costly and more efficient in the future. Researchers were also able to demonstrate that this new material can be reliably produced in large quantities, showing its performance capability in an electrolysis cell—the main component of an electrolyser.
Research experience from California benefits Swiss X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL
An X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) is capable of visualizing extremely fast structural and electronic processes. Pilot experiments will take place at the PSI's Swiss Free-Electron Laser (SwissFEL) from the end of 2017 on. Two current publications in Science and Nature Communications demonstrate the kind of outstanding scientific work that is enabled by such facilities. The work was carried out at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) in California. Two of the leading authors behind these studies have now relocated to the PSI in order to share their expertise as SwissFEL expands its capabilities.
Fuel and chemicals from plant waste
Lignin, as a constituent of many plants, accumulates in large quantities and could theoretically be used as a precursor material for production of fuels and chemicals. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and ETH Zurich have developed a method with which the processes that take place in the catalytic breakdown of lignin can be observed in detail. The knowledge thus gained could enable targeted improvement of production methods in the future.
Quartz powder for the battery of the future
PSI materials researchers have developed a method that provides crucial insights into the charging and discharging processes of lithium-sulphur batteries. And the method revealed: with quartz powder added to the battery, its available energy increases and the gradual loss of capacity is much weaker.
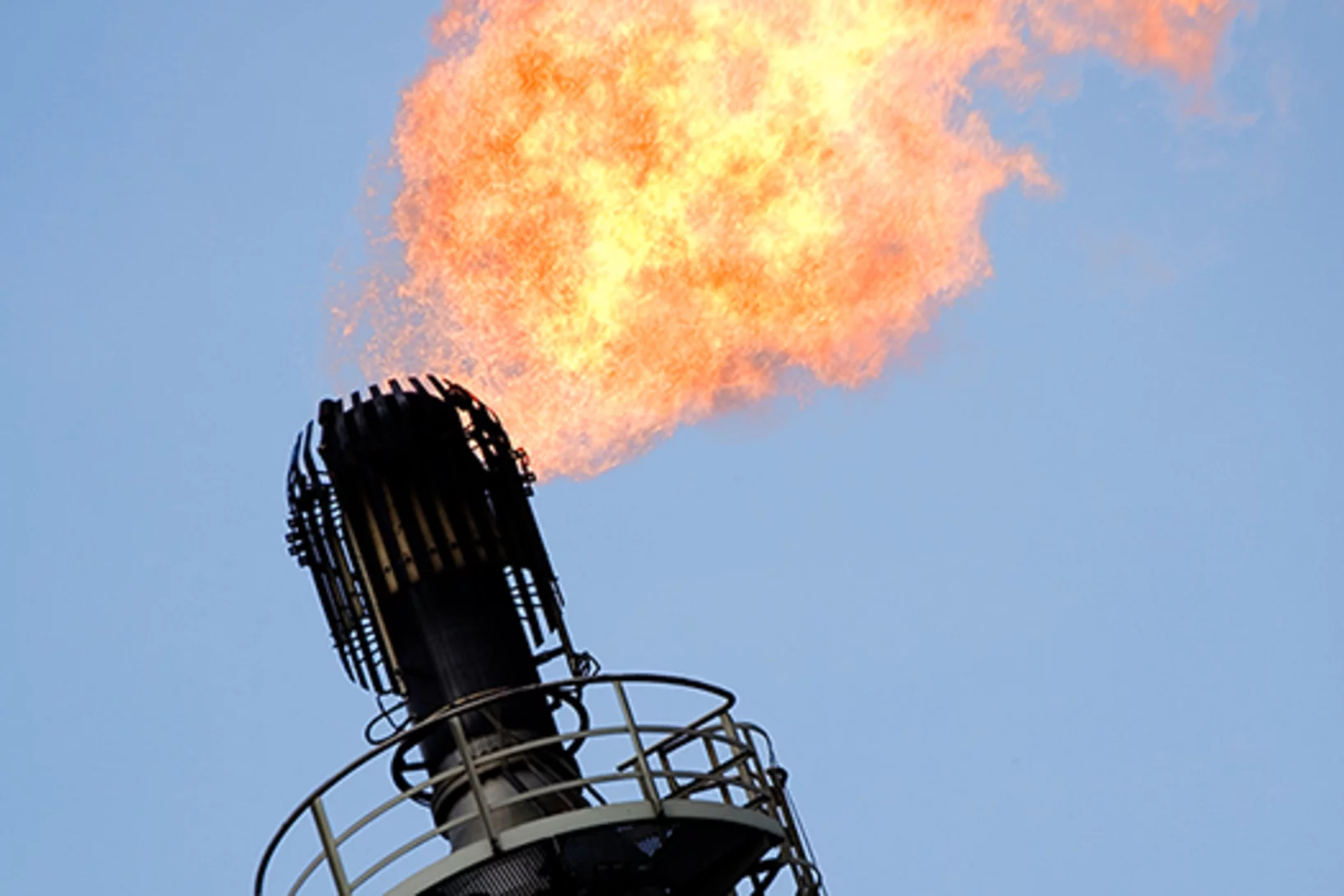
Making a valuable resource usable with water
In oil extraction sites, gaseous methane is simply burned, even though it could actually be a useful precursor material for fuels and products of the chemical industry. One way to make methane usable is to convert it to methanol. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and ETH Zurich have now developed a new chemical process that allows this conversion in an efficient and inexpensive way.
Successful for 20 years: Probing materials with particles
Whether they study materials for the electronics of the future, batteries, or swords from the Bronze Age — for 20 years researchers from a range of disciplines have been using the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source SINQ of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI for their investigations. At a symposium on 18 April, researchers looked back on the facility's successes and presented plans for modernisation.
3-D X-ray imaging makes the finest details of a computer chip visible
Researchers at the PSI have made detailed 3-D X-ray images of a commercially available computer chip. In their experiment, they examined a small piece that they had cut out of the chip beforehand. This sample remained undamaged throughout the measurement. It is a major challenge for manufacturers to determine if, in the end, the structure of their chips conforms to the specifications. Thus these results represent one important application of an X-ray tomography method that the PSI researchers have been developing for several years.
Welcome to Esiville
A new visitor’s station at PSI tells the story of a Swiss town that makes the change from a conventional energy supply to one with new renewable energy sources.
Historical copper, trapped in ice
Until now, the onset of copper production in South America was still unclear. Hardly any written records or artefacts from the early high cultures in Peru, Chile, and Bolivia have been preserved. Now, however, researchers of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI in Villigen (Switzerland) have tracked down the evidence. Through analysis of ice from the Illimani glacier in the Bolivian Andes, they found out that copper was being mined and smelted in South America since around 700 BC.
Nanotechnology enables new insights into chemical reactions
Eighty percent of all products of the chemical industry are manufactured with catalytic processes. Catalysis is also indispensable in energy conversion and treatment of exhaust gases. Industry is always testing new substances and arrangements that could lead to new and better catalytic processes. Researchers of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI in Villigen and ETH Zurich have now developed a method for improving the precision of such experiments, which may speed up the search for optimal solutions.
Towards energy-saving data storage
A new material could become the basis for future data storage devices, since it may enable significant reductions in energy demands in comparison to present-day hard drives. It is a material from the class of so-called magnetoelectric multiferroics, exhibiting the necessary magnetic properties even at room temperature.
SwissFEL inauguration
Today, on 5 December 2016, the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI held an inauguration ceremony for its new large-scale research facility SwissFEL, with Johann N. Schneider-Ammann, President of the Swiss Confederation, in attendance.
The substances that brighten up the clouds
Clouds consist of tiny droplets. These droplets form when water condenses around so-called aerosols – small particles in the atmosphere. To understand how in turn aerosols come into existence scientists have now created a comprehensive computer model simulation based on profound experimental data. This simulation revealed that in addition to sulphuric acid, two other substances are crucially involved in the formation of aerosols: organic compounds and ammonia. These results have now been published in the renowned journal Science.
Selectively conductive or insulating
The material neodymium nickel oxide is either a metal or an insulator, depending on its temperature. The possibility to control this transition electrically makes the material a potential candidate for transistors in modern electronic devices. By means of a sophisticated development of X-ray scattering, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have now been able to track down the cause of this transition: electrons around the oxygen atoms are rearranging.
ERC funding of €2.4 million for research on fundamental interactions in magnets
Christian Rüegg has been awarded a prestigious Consolidator Grant from the European Research Council (ERC). With this funding he will continue to investigate how the smallest magnetic building blocks of matter interact.
Renewable energy: Experimental platform ESI is starting up
This fall, the time has come: The Energy System Integration Platform at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI goes into operation. Today, in the framework of the double conference Networked Energy Research Switzerland, it was presented to the media and around 150 representatives from politics, industry, and science.
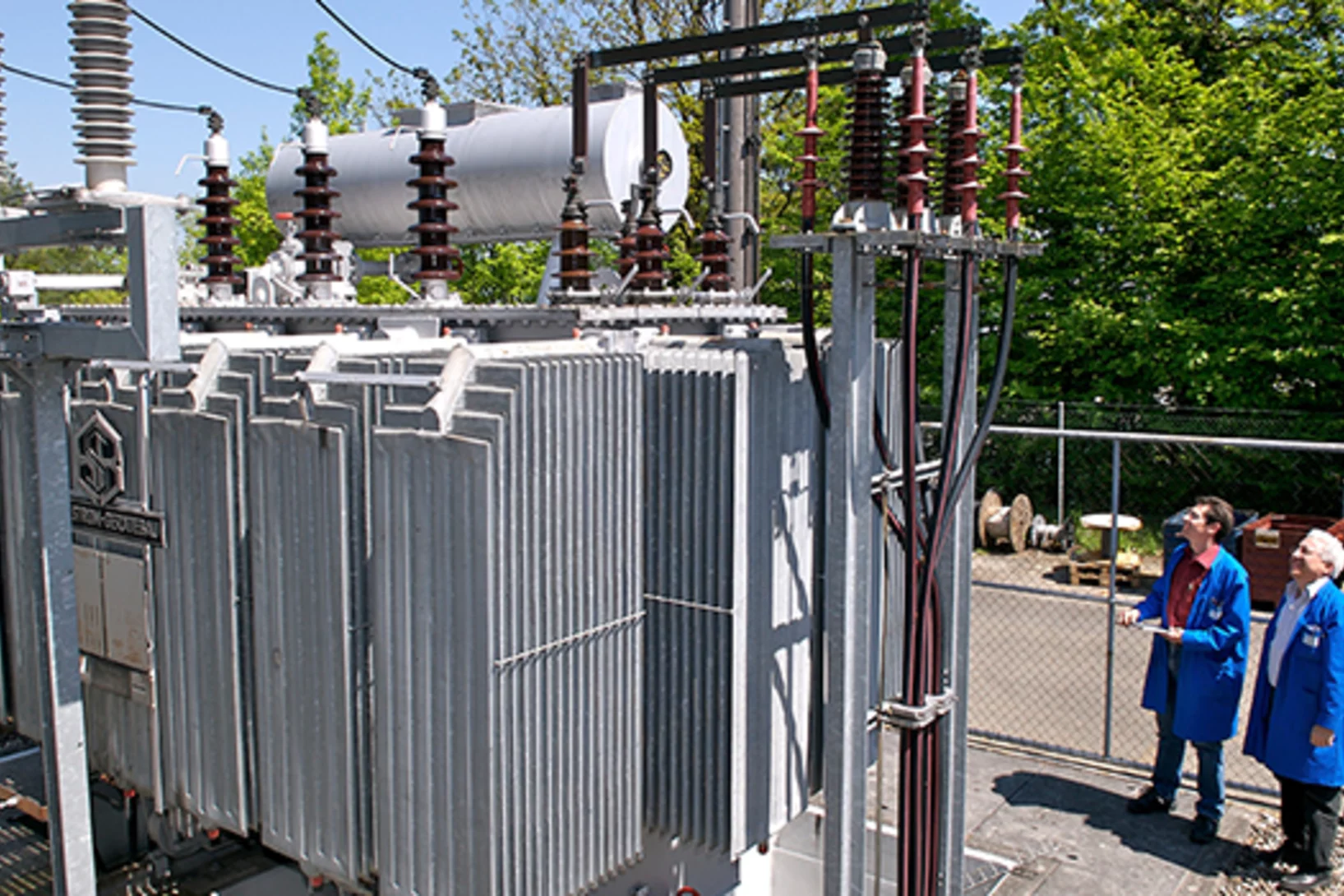
En route to better transformers
Thanks to an ultramodern research method, scientists have successfully looked inside transformers and observed the magnetic domains at work in the interior of a transformer’s iron core. Transformers are indispensable in regulating electricity both in industry and in domestic households. The current research results show that the new examination method can be profitably applied to develop more efficient transformers.
Catching proteins in the act
Proteins are indispensable building blocks of life. They play a vital role in many biological processes. Researchers have now been able to show how the ultrafast processes by which proteins do their work can be studied with free-electron X-ray lasers such as SwissFEL at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI. Free-electron X-ray lasers generate extremely short and intense pulses of X-ray light. Currently there are just two such facilities in operation, worldwide. The results were published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
The deuteron too poses a mystery
The deuteron — just like the proton — is smaller than previously thoughtThe deuteron — one of the simplest atomic nuclei, consisting of just one proton and one neutron — is considerably smaller than previously thought. This new research finding fits with a 2010 study in which, similarly, the proton was measured at the Paul Scherrer Institute and, likewise, a smaller value than expected was found. The result from 2010 formed the basis for what has been known since then as the proton radius puzzle.
Hitching a ride to gamma-ray bursts
Researchers at the PSI have developed a detector called POLAR. It is designed to search out and investigate extreme eruptions of energy from the depths of the universe. This coming September, POLAR will be launched into orbit with a Chinese space mission.
Sun-Petrol
Despite its great potential, solar energy still faces one big problem: the sun doesn’t always shine and its energy is hard to store. Now, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and the ETH Zurich have unveiled a chemical process that uses the sun’s thermal energy to convert carbon dioxide and water directly into high-energy fuels: a procedure developed on the basis of a ground-breaking material combination of cerium oxide and rhodium.
Rechargeable batteries that last longer and recharge more rapidly
Researchers at the Swiss Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and ETH Zurich have developed a simple and cost-effective procedure for significantly enhancing the performance of conventional Li-ion rechargeable batteries. Whether in wristwatches, smartphones, laptops or cars, the use of rechargeable batteries will be optimized in all areas of application, considerably extending storage capacity as well as cutting down charging times.
Present-day measurements yield insights into clouds of the past
Researchers have shown how fine particles are formed from natural substances in the atmosphere. These findings will improve our knowledge about clouds in the pre-industrial era and thus will contribute to a more accurate understanding of both the past and future evolution of our climate.
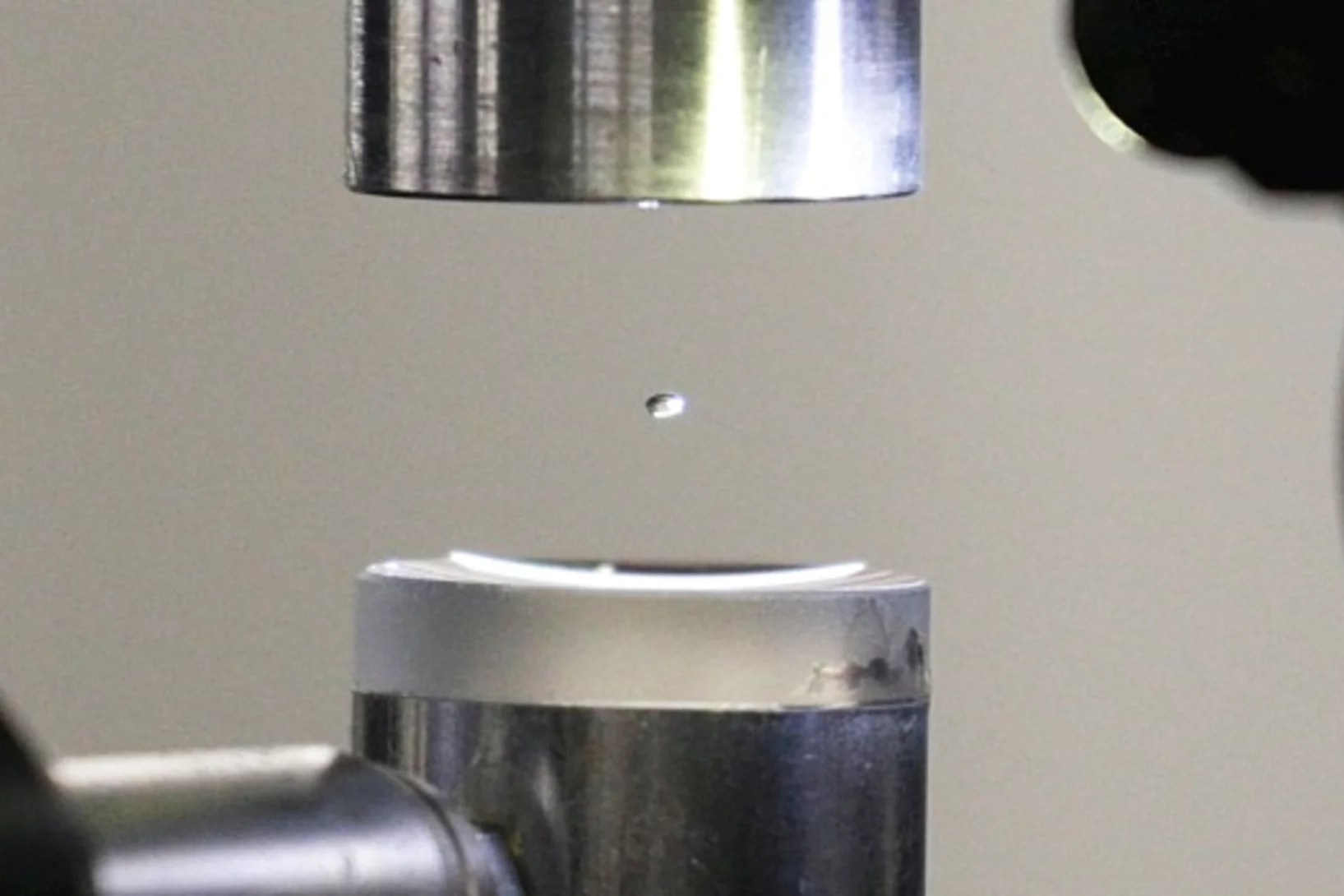
Experiment in a hovering droplet
At the PSI, the exact structure of proteins is deciphered in the standard way, with X-rays. Now two PSI researchers have used a clever trick to advance this method further: Instead of pinning down the proteins, they are studying them within a levitating drop of liquid.
Using methane rather than flaring it
Chemists at ETH Zurich and the Paul Scherrer Institute have found a new, direct way to convert gaseous methane into liquid methanol. This offers industry the interesting prospect of using the gas, rather than simply burning it off, as is currently the case.
New particle could form the basis of energy-saving electronics
The Weyl fermion, just discovered in the past year, moves through materials practically without resistance. Now researchers are showing how it could be put to use in electronic components.
From the Higgs boson to new drugs
A picture-perfect example of how basic research makes concrete contributions to the economy is the company DECTRIS — a PSI spin-off founded in 2006 and already highly successful. The latest development from DECTRIS is a detector called EIGER, which is used for X-ray measurements at large research facilities. There EIGER contributes, among other things, to the search for new drugs.
Five hundred thousand times less likely than winning the lottery
Measuring the rarity of a particle decayIn the so-called MEG experiment at the PSI, researchers are searching for an extremely rare decay signature from a certain kind of elementary particles known as muons. More precisely, they are quantifying its improbability. According to their latest number, this decay occurs less than once in 2.4 trillion events. By means of this result, theoretical physicists can sort out which of their approaches to describing the universe will hold up against reality.
Transport von aufgelösten Plutoniumlager des Bundes in die USA ist erfolgt
Im Januar und Februar 2016 wurden unter strengen Sicherheitsvorkehrungen rund 20kg Plutonium im Eigentum des Bundes in die USA transportiert. Es handelt sich dabei um Material, das seit den 1960er Jahren auf dem Areal des heutigen Paul Scherrer Instituts (PSI) gelagert worden war. Das Plutonium stammte aus wiederaufbereiteten Brennstäben des von 1960 bis 1977 betriebenen Forschungsreaktors Diorit. Der Bundesrat beschloss 2014 im Rahmen des Nuclear Security Summit-Prozesses, das Plutoniumlager aufzulösen und damit zur weltweiten Sicherung von Nuklearmaterial beizutragen.This news release is only available in French and German.
A micrometer-sized model of the Matterhorn
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have produced large numbers of detailed models of the Matterhorn, each one less than a tenth of a millimetre in size. With this, they demonstrated how 3-D objects so delicate could be mass-produced. Materials whose surface is covered with a pattern of such tiny 3-D structures often have special properties, which could for example help to reduce the wear and tear of machine parts.
Probing what sets the heart racing
New insights into the workings of important drug receptorsMany medical drugs operate on specific receptors located in the outer walls of our body’s cells. One of these is called the beta-1 adrenergic receptor. Among other things, it is responsible for palpitation, the racing pulse that we feel with stage fright or infatuation. How it transmits signals to the cellular interior can now be revealed in detail. These findings could help scientists better understand many drugs' mode of action.
Slowed down current could point the way to energy-saving computers
Computers and other electronic devices account for a substantial portion of worldwide energy use. With today’s technologies, it is not possible to reduce this energy consumption significantly any further; chips in the energy-saving electronics of the future will hence have to be made from novel materials. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have now found important clues in the search for such materials.
Reappointment of the Directors of PSI and WSL
On application of the ETH Board, the Federal Council reappointed the Director of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, Joël Mesot, and the Director of the Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research WSL, Konrad Steffen, for another four years on 20 January 2016. Joël Mesot’s third term of office will start on 1 August 2016, Konrad Steffen’s second term of office on 1 July 2016.
Neutrons reveal distribution of flux-tube islands
Usually, superconductors expel magnetic fields. In type II superconductors, however, thin channels – so-called flux tubes – are formed. The magnetic field is guided through these tubes while the rest of the material remains field-free and superconducting. In the metal niobium, the flux tubes bunch together into small islands that create complex patterns similar to those found in other fields of nature. A team of researchers from PSI and TU München were the first to conduct neutron experiments to study these patterns in niobium and determine the distribution of the islands in detail.
3D nanostructure of a bone made visible
Bones are made up of tiny fibres that are roughly a thousand times finer than a human hair. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have developed a new computer-based algorithm with which they were able to visualize the localised order and alignment of these nanostructures inside an entire piece of bone for the first time.
Structure of concrete disease
solved
When bridges, dam walls and other structures made of concrete are streaked with dark cracks after a few decades, the culprit is the so-called the concrete disease. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and Empa have now solved the structure of the material produced in these cracks at atomic level - and have thereby discovered a previously unknown crystalline arrangement of the atoms.
Put in perspective
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded in using commercially available camera technology to visualise terahertz light. In doing so, they are enabling a low-cost alternative to the procedure available to date, whilst simultaneously increasing the comparative image resolution by a factor of 25. The special properties of terahertz light make it potentially advantageous for many applications. At PSI, it will be used for the experiments on the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL.
New method will enable most accurate neutron measurement yet
Our universe consists of significantly more matter than existing theories are able to explain. This is one of the great puzzles of modern science. One way to clarify this discrepancy is via the neutron’s so-called electric dipole moment. In an international collaboration, researchers at PSI have now devised a new method which will help determine this dipole moment more accurately than ever before.
Water pathways make fuel cells more efficient
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have developed a coating technique in the laboratory conditions that could raise the efficiency of fuel cells. The PSI scientists have already applied to patent the technique, which is suitable for mass production.
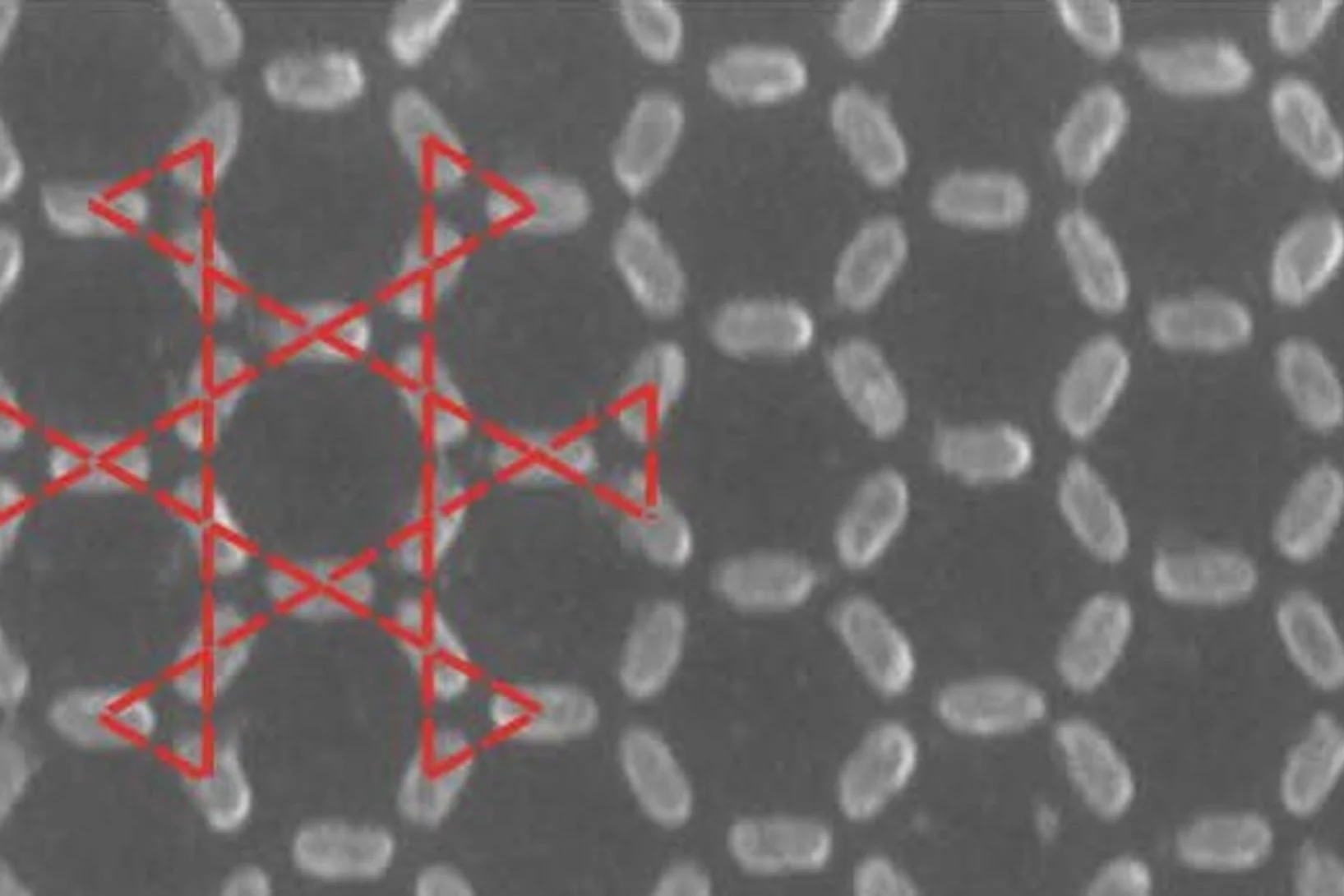
Tiny magnets mimic steam, water and ice
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) created a synthetic material out of 1 billion tiny magnets. Astonishingly, it now appears that the magnetic properties of this so-called metamaterial change with the temperature, so that it can take on different states; just like water has a gaseous, liquid and a solid state.
The key to charging a lithium-ion battery rapidly
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are very durable and can be charged relatively quickly. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), ETH Zurich and Japanese car manufacturer Toyota reveal the reasons for these properties in a new study. The findings were made possible thanks to measurements using a new method at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) at PSI.
New details of the transmission of stimuli in living organisms unveiled
Researchers unveil new details of how cells in a living organism process stimuli. So-called G-proteins, which help conduct external stimuli that reach a cell into its interior, play a central role here. For the first time, the study shows which parts of the G-proteins are vital for their function. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, ETH Zurich, the pharmaceutical company Roche and the British MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology report their results in the journals Nature and Nature Structural and Molecular Biology.