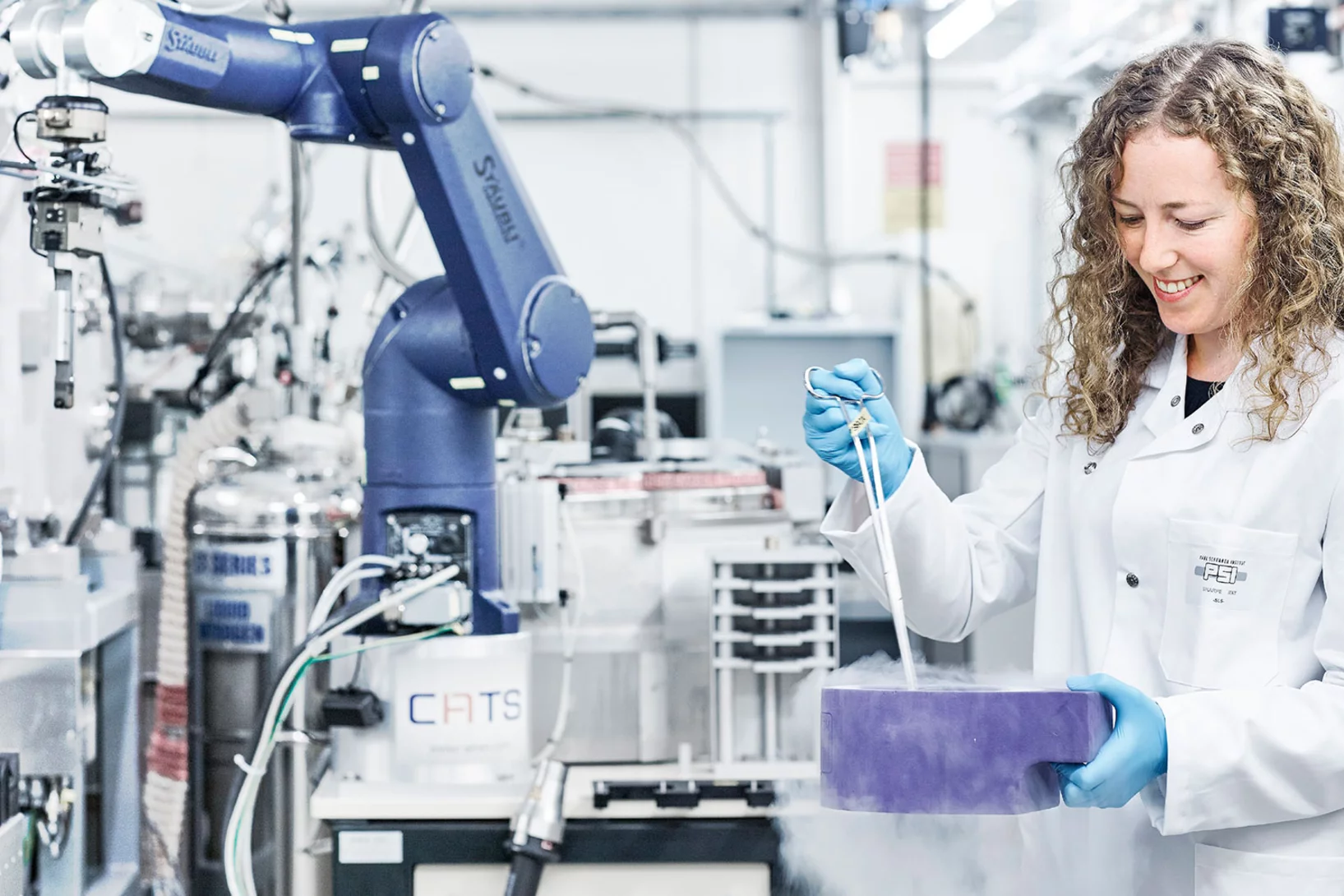
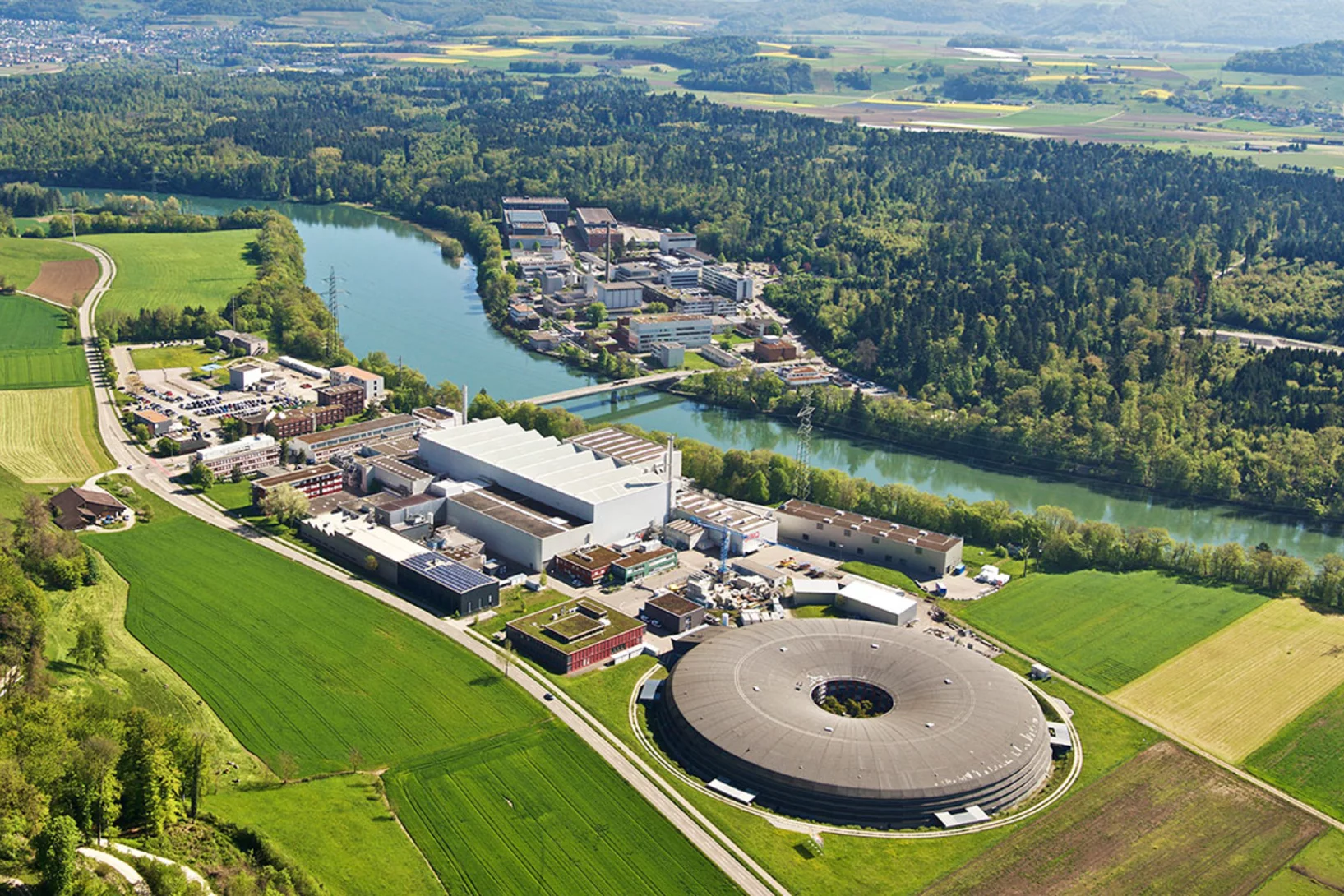
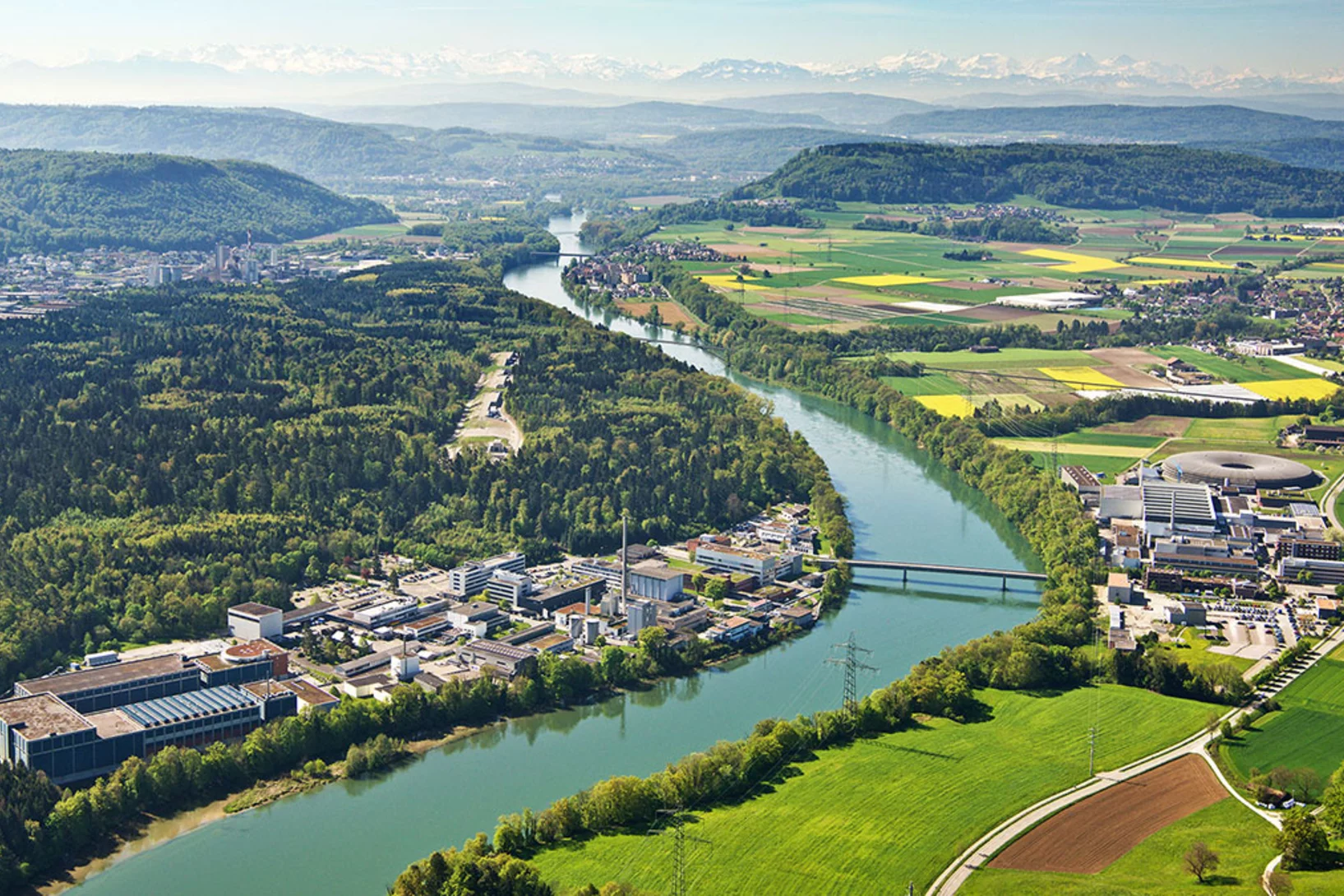
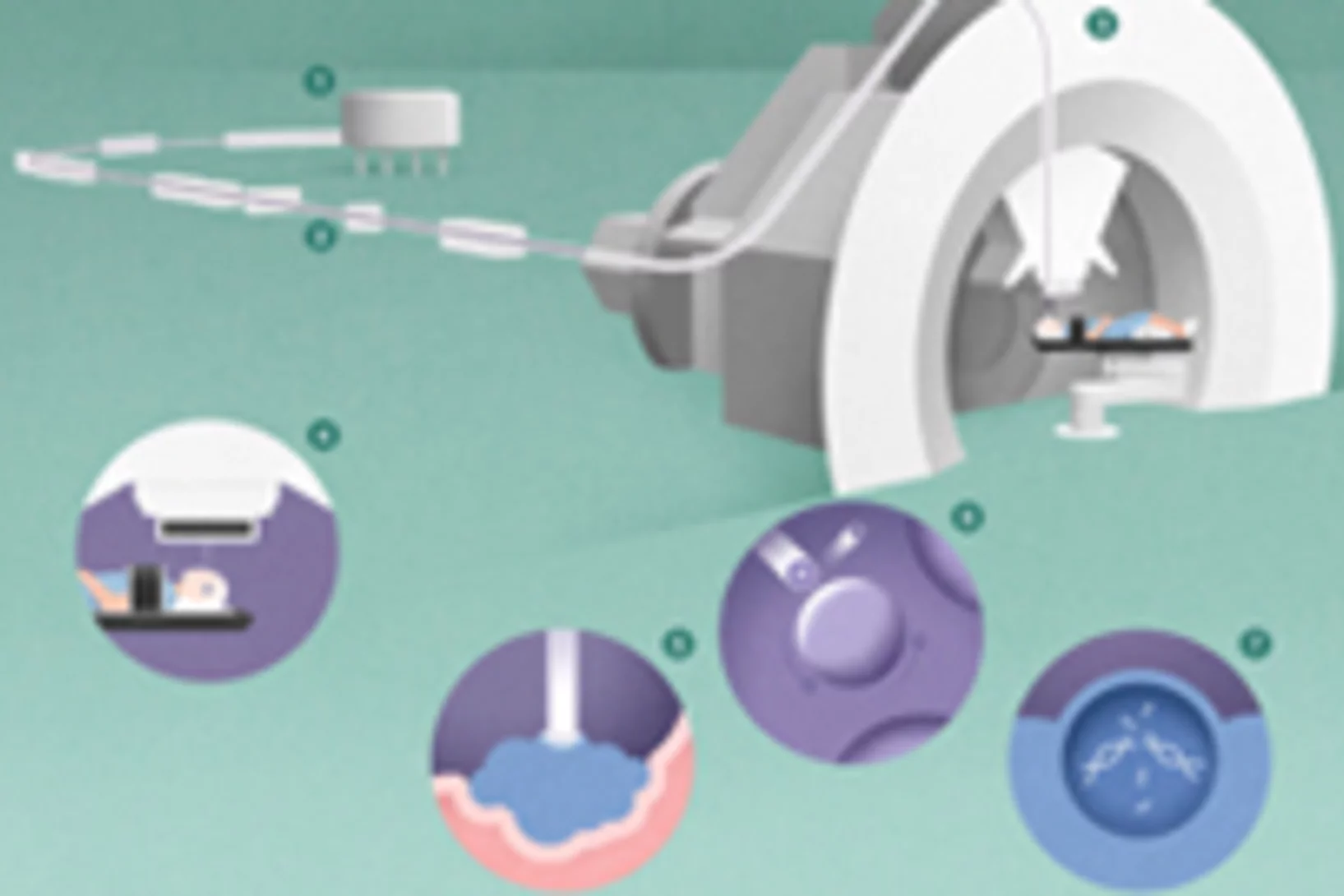
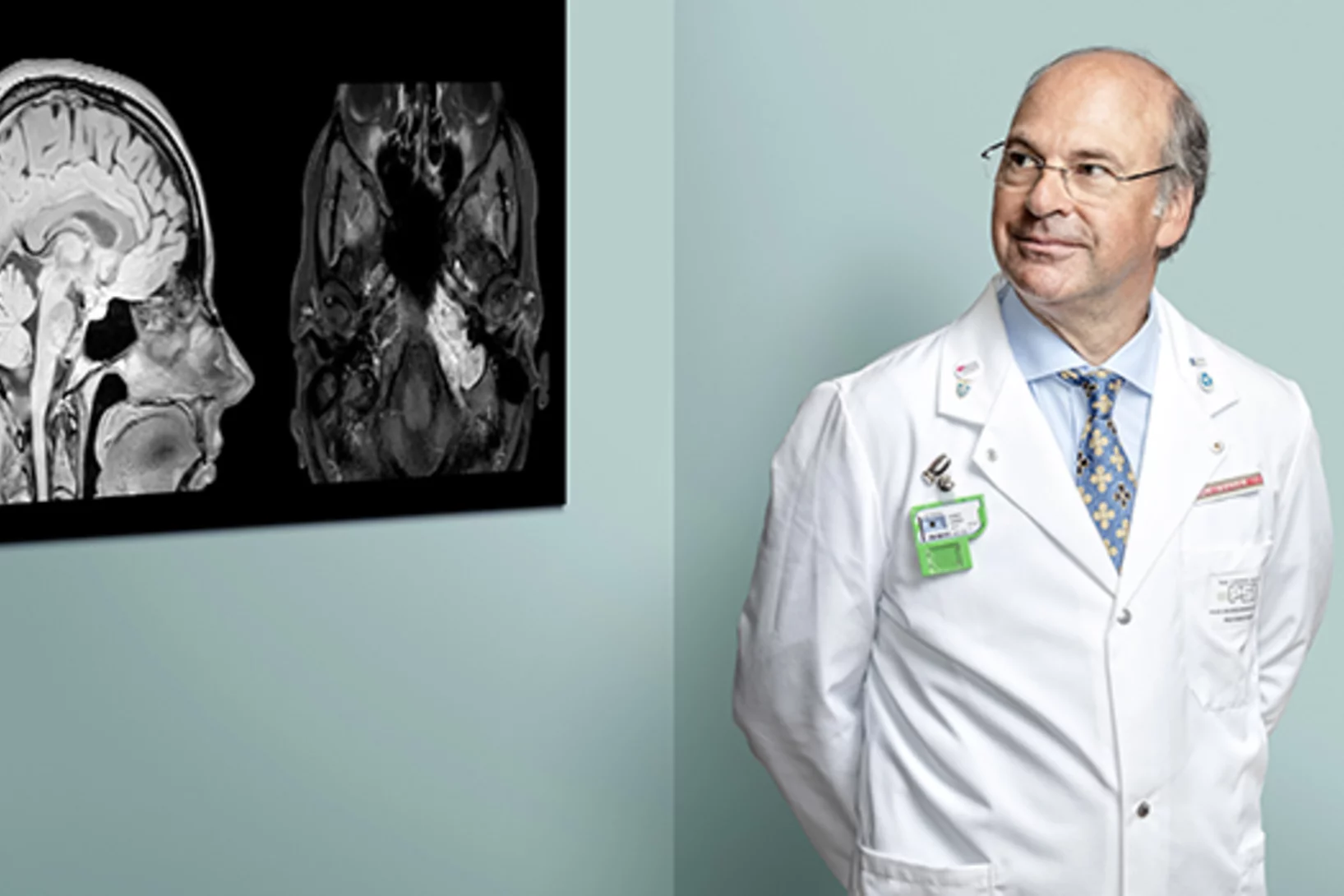
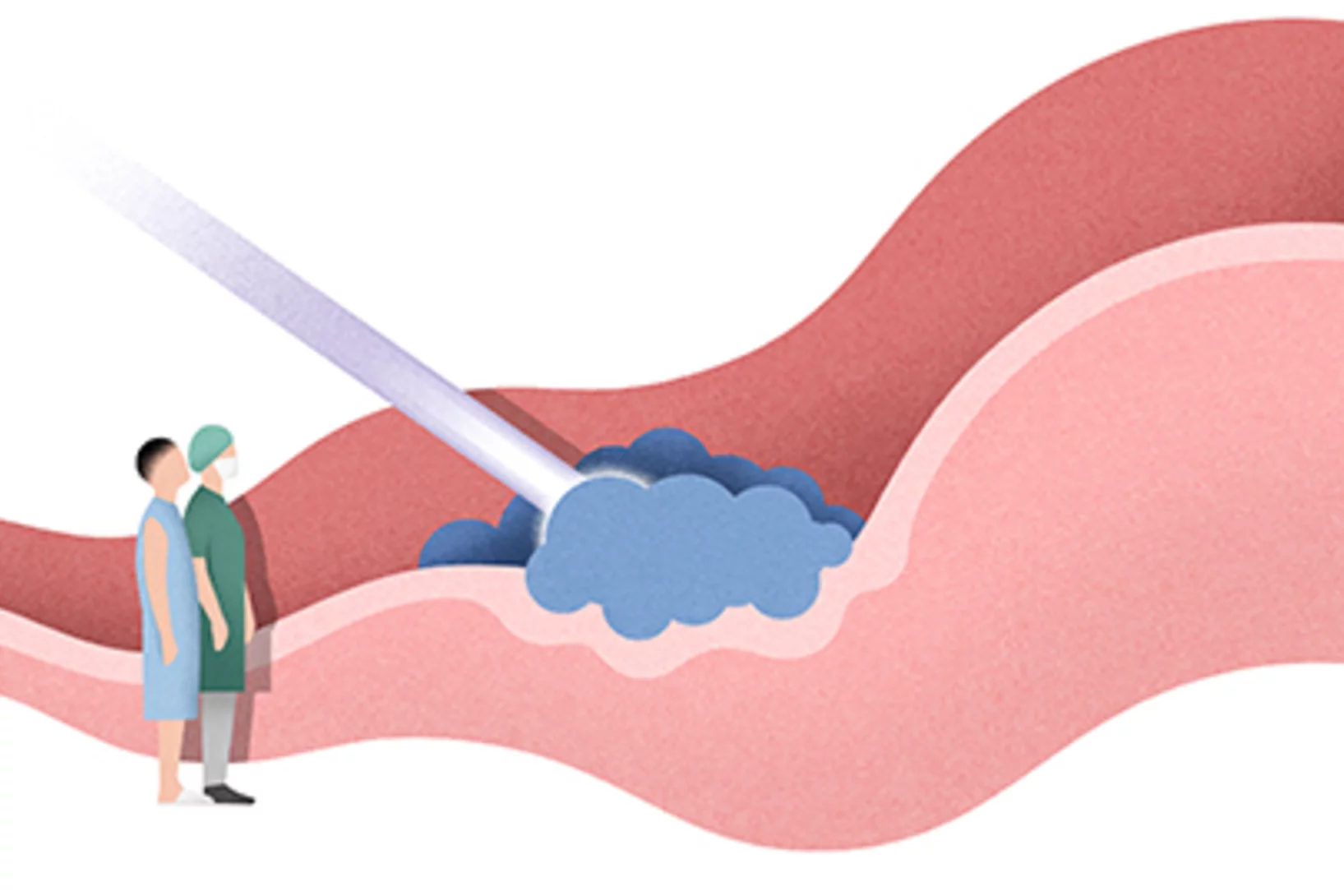
Covid-19 research: Anti-viral strategy with double effect
Frankfurt scientists identify a possible weakness of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. They carried out part of their measurements at PSI's Swiss Light Source SLS. The research results are published this week in the scientific journal Nature.
In search of new physics
With the high-intensity proton accelerator HIPA, the Paul Scherrer Institute generates elementary particles to clarify how the universe is structured. Using pions, muons, and neutrons, the researchers conduct experiments to test the standard model of particle physics.
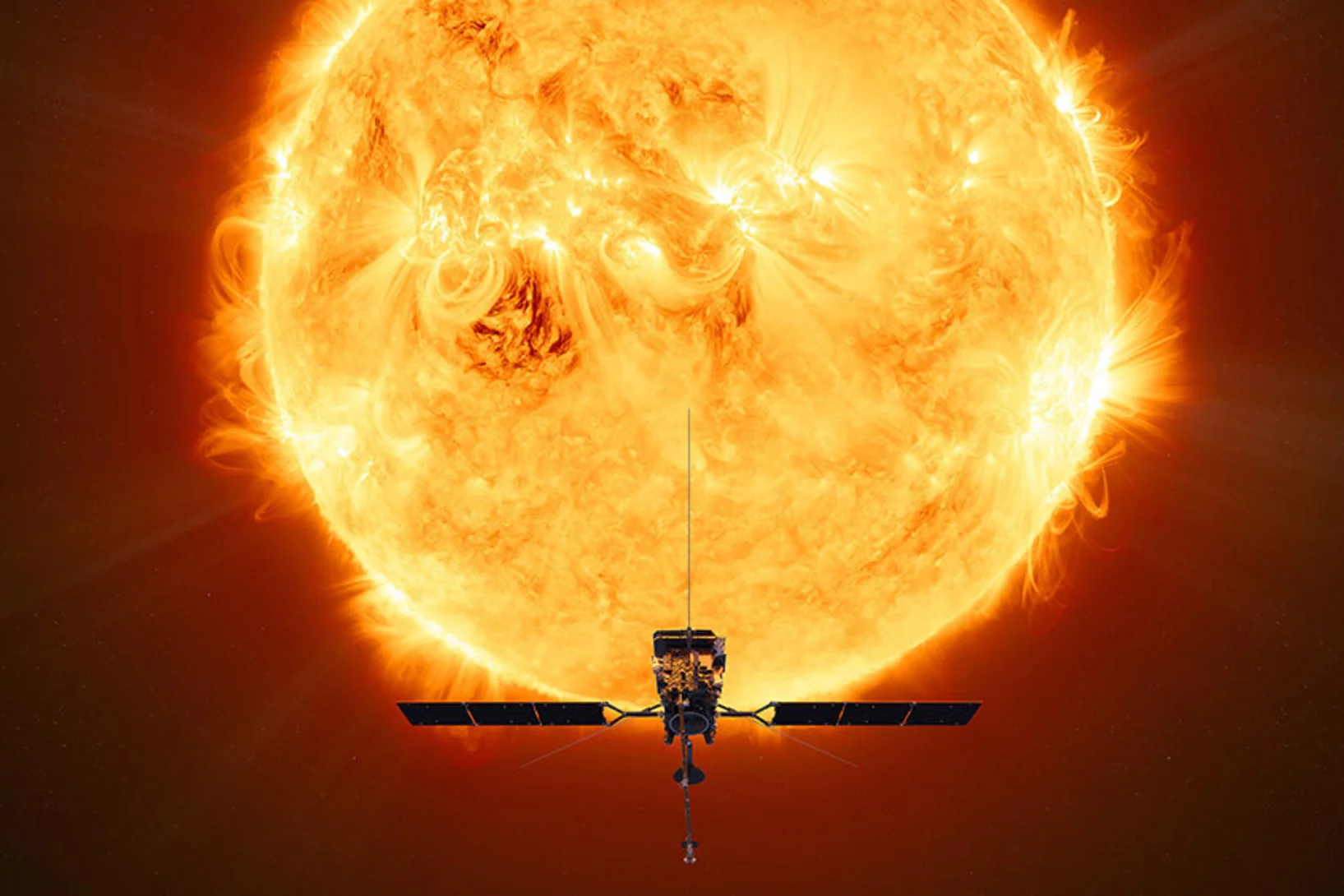
To the sun and beyond
PSI takes part in space research projects. This not only expands knowledge about our astronomical home, but also reinforces Switzerland's reputation as a reliable developer of sophisticated space equipment.
Long-lived pionic helium: Exotic matter experimentally verified for the first time
Exotic atoms, in which electrons are replaced by other particles, allow deep insights into the quantum world. After eight years, an international group of scientists have succeeded in a challenging experiment conducted at PSI’s pion source: they created an artificial atom called “pionic helium”.
Why Covid-19 hits older people especially hard
The older you are, the higher the risk of dying from a coronavirus infection. G. V. Shivashankar, a group leader at PSI and professor at ETH Zurich, now presents an unusual thesis in a publication in Nature Reviews: that the stiffness of cells might play a decisive role in the course of the disease. In this interview, he explains why.
«Every day counts in the battle against the virus»
The outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic has changed the way research is carried out at PSI but has not brought it to a standstill. Gabriel Aeppli, head of the Photon Science Division at PSI, talks about the exceptional threat that Covid-19 represents and how PSI researchers are studying this new virus at SLS, and possibly soon at SwissFEL as well.
Priority research continues
The Paul Scherrer Institute PSI is in limited operation due to the Covid-19 pandemic, and most employees are working from home in accordance with the Federal Council's specifications. Nevertheless, essential research facilities and projects continue to operate in accordance with all the necessary safety precautions.
"We want to understand how this virus works"
The Swiss Light Source SLS at PSI is still in operation despite the Covid-19 pandemic – and may be urgently needed, especially in these difficult times. Oliver Bunk, head of the Laboratory for Macromolecules and Bioimaging, explains why.
"Strategy and networking are enormously important"
Gebhard Schertler, head of the Biology and Chemistry Division at PSI and professor of structural biology at ETH Zurich, explains what research is being done on the coronavirus at PSI and why collaboration with researchers from other institutions plays such an important role in this.
«SLS is something very special right now, across Europe»
The Swiss Light Source SLS is one of just a few facilities of its kind in Europe that are still in operation during these pandemic times. In an interview, Mirjam van Daalen, chief of staff of the Photon Science Division, emphasises how important international cooperation is these days.
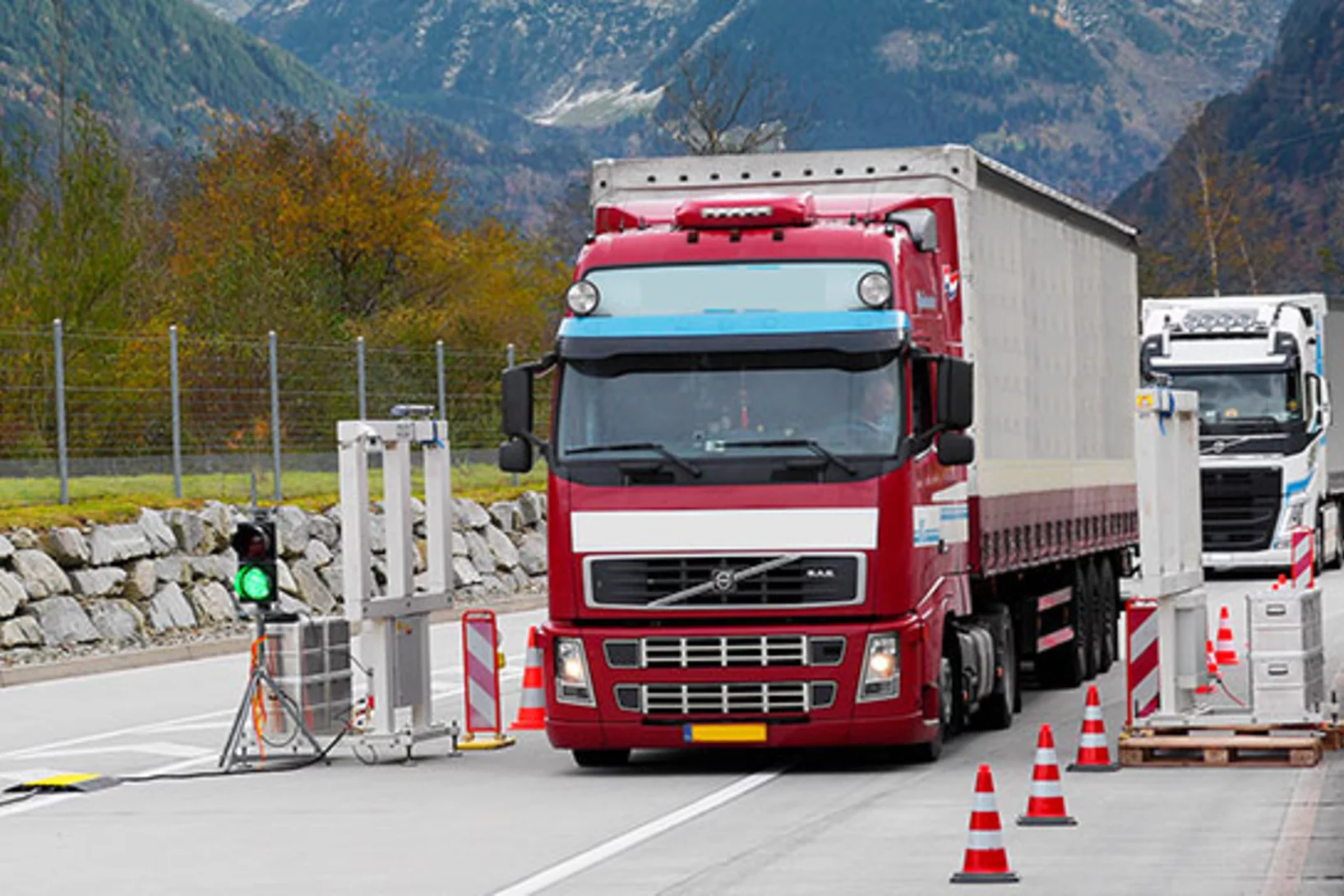
Sniffing out radioactive substances in freight transport
With a mobile measurement portal, PSI regularly carries out radioactivity checks on heavy goods vehicles. The purpose of this work, on behalf of the Swiss Federal Office of Public Health, is to discover stray radiation sources.
Athos is making great strides
The new beamline at PSI's X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL will soon be ready for action. In December, Athos delivered laser light for the first time − even sooner than expected, to the delight of the researchers responsible for its construction.
Nanoworlds in 3-D
Tomographic images from the interior of fossils, brain cells, or computer chips are yielding new insights into the finest of structures. These 3-D images are made possible by the X-ray beams of the Swiss Light Source SLS, together with detectors and sophisticated computer algorithms developed at PSI.
"Electric is already the right choice today"
An interview on automotive power systems with Christian Bauer, a scientist at PSI's Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis who specialises in life cycle and sustainability analyses.
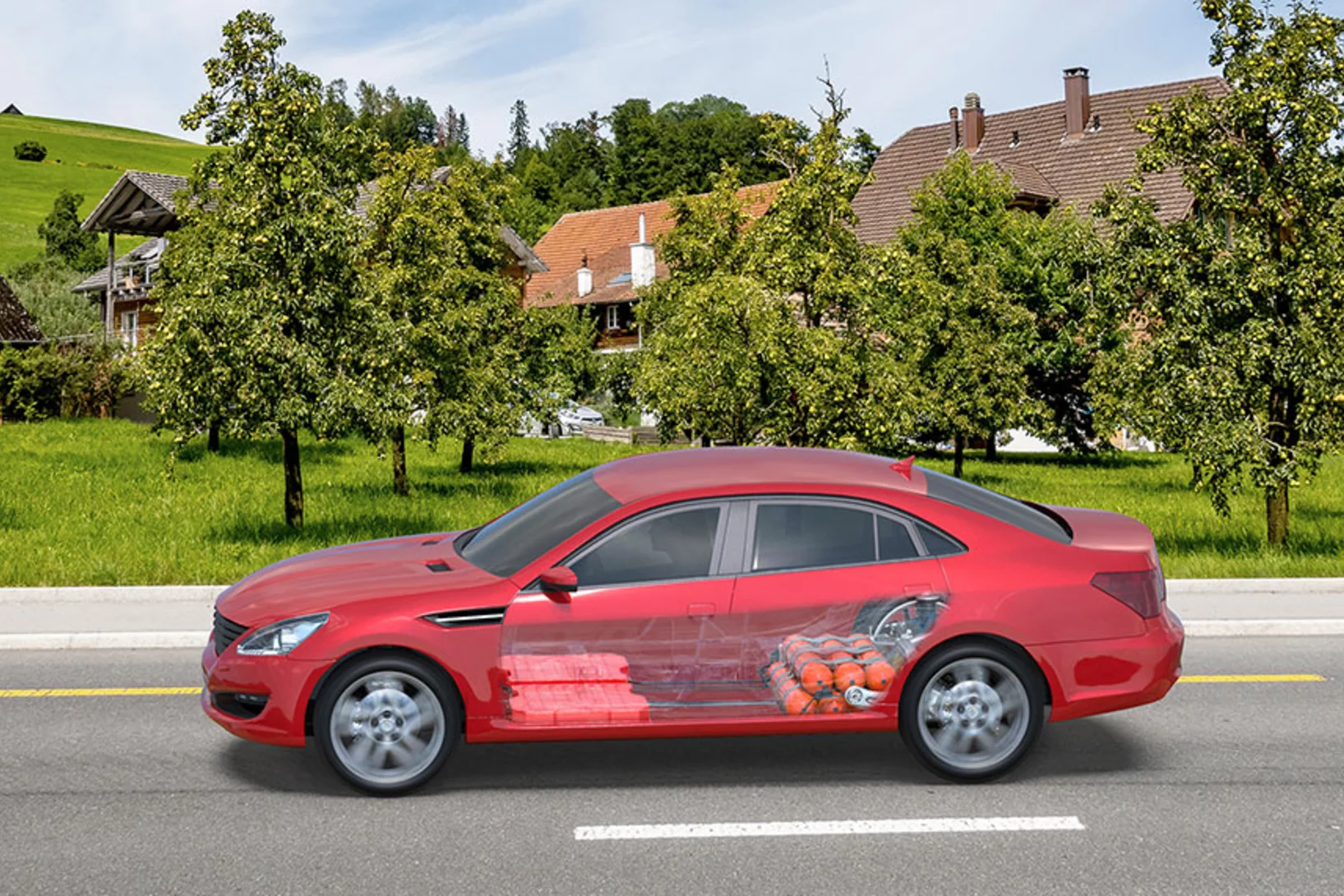
Make way for electric cars
Petrol, diesel, fuel cell or electric – which is the automobile of the future? A PSI study has examined the overall climate impact of various vehicle engines in use today and also projected it to the year 2040.
Toward better motors with X-ray light
Making Switzerland's road traffic fit for the future calls for research, first and foremost. In the large-scale research facilities of PSI, chemists and engineers are investigating how to improve the efficiency of motors and reduce their emissions.
Simulation: The third pillar of science
PSI researchers simulate and model large research facilities as well as experiments, for example, in the materials and biological sciences. Andreas Adelmann, head of PSI's Laboratory for Scientific Computing and Modelling, explains how they do it.
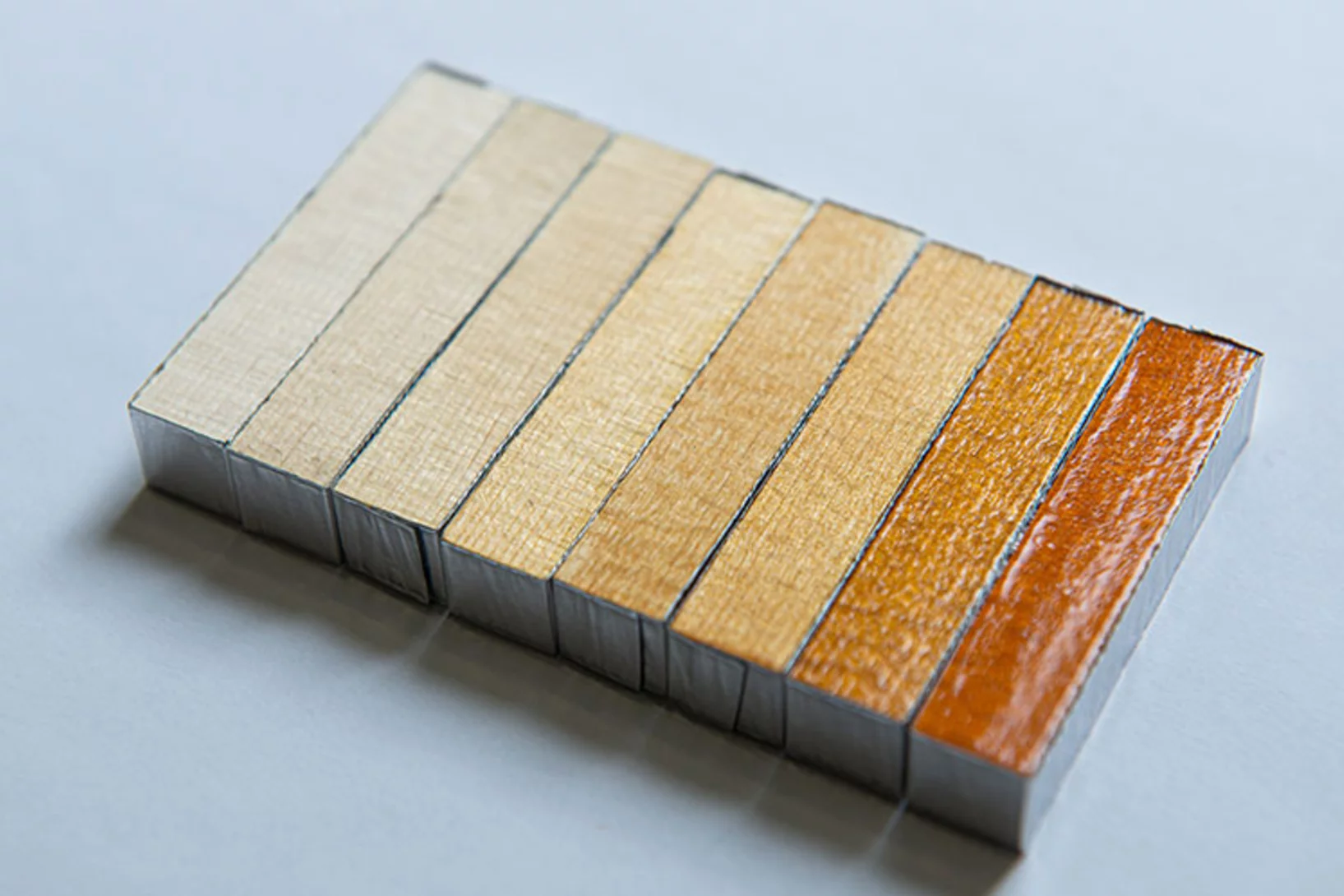
Well varnished violins play longer
Traditionally, violins are varnished to protect them from humidity and other environmental influences. At PSI, a scientific team has investigated how different coatings affect the instrument. Under no circumstances, they found, should anyone try to do without varnish completely.
Modelling and simulation pay off
Researchers in PSI's Laboratory for Scientific Computing and Modelling solve the most complex problems through a combination of theory, modelling, and high-performance computing. With powerful computers, they simulate the smallest molecules or large research facilities.
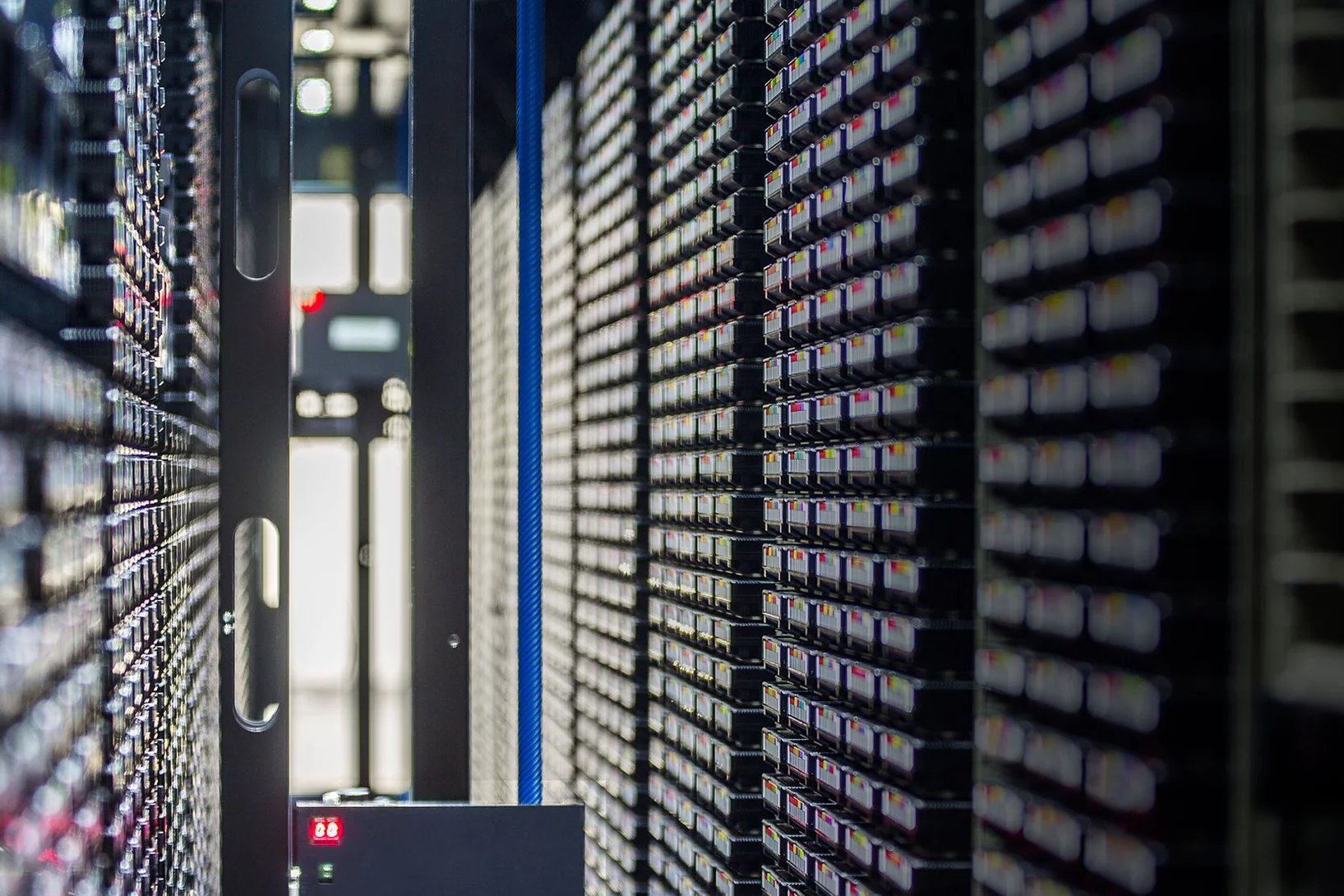
5,000,000,000,000,000 bytes from Villigen to Lugano
During investigations of tiny structures with large research facilities, huge amounts of data accumulate at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI. This data is archived at the CSCS supercomputer centre in Lugano, and the researchers use the supercomputer there for their simulations and modelling.
More magnets, smoother curves: The SLS upgrade
The Swiss Light Source SLS is set to undergo an upgrade in the coming years: SLS 2.0. The renovation is made possible by the latest technologies and will create a large research facility that will meet the needs of researchers for decades to come.
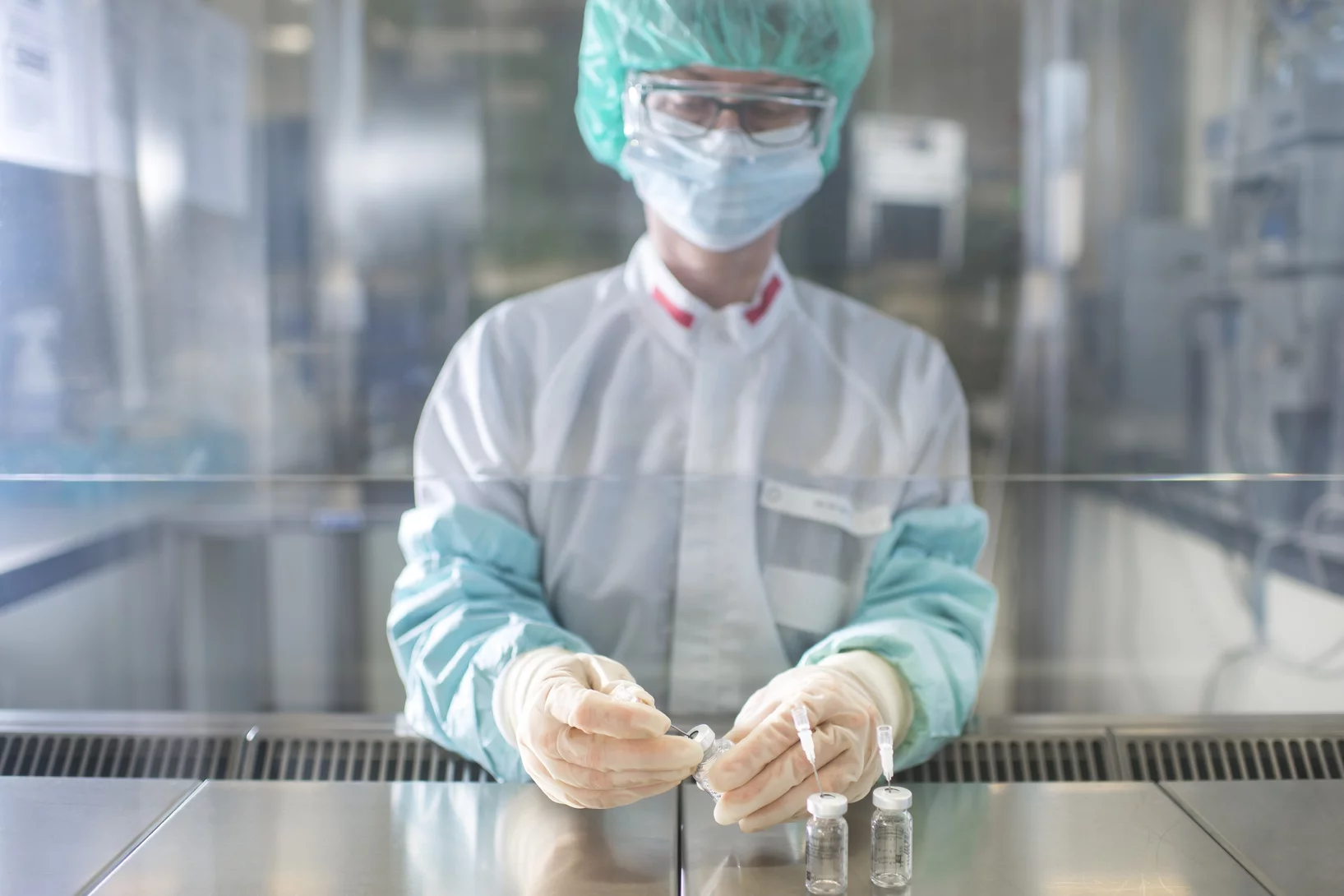
Brilliant medicines
In the service of health, scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI work with radionuclides and develop agents to treat cancer and to detect tumours. Their research provides support to hospitals and is of great interest to Swiss industry.
Radionuclides for cancer therapy are in great demand
Radionuclides open up new options for treating cancer. Christian Rüegg, head of the Research with Neutrons and Muons Division at PSI, explains the significance of the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source SINQ at PSI.
Cancer medicine using PSI’s neutron source
At the neutron source SINQ, PSI researchers are producing special radionuclides that aid in the development of new and more effectively targeted cancer therapies. In this they collaborate closely with the clinics in the surrounding area.
Open fire on tumours
At the treatment stations of the Centre for Proton Therapy at PSI, tumours can be precisely irradiated from any direction. An interactive graphic explains how the protons get from the source to the body in order to trigger the elimination of tumour tissue.
"It's important to keep doing research"
Proton therapy is time-consuming and more costly than conventional radiation therapy, but its accuracy in targeting tumours is unsurpassed. An interview with Damien Weber, head of the Centre for Proton Therapy at PSI.
Cancer cells under attack
At PSI, cancer patients receive a therapy that is unique in Switzerland. Bombardment with protons wipes out cancer cells – and does so more precisely than with any other form of irradiation.
Thirteen months in the Arctic
A PSI research project investigating atmospheric chemistry will be on board the icebreaker Polarstern on 20th September 2019. Researcher Julia Schmale talks about the upcoming expedition and her role in it.
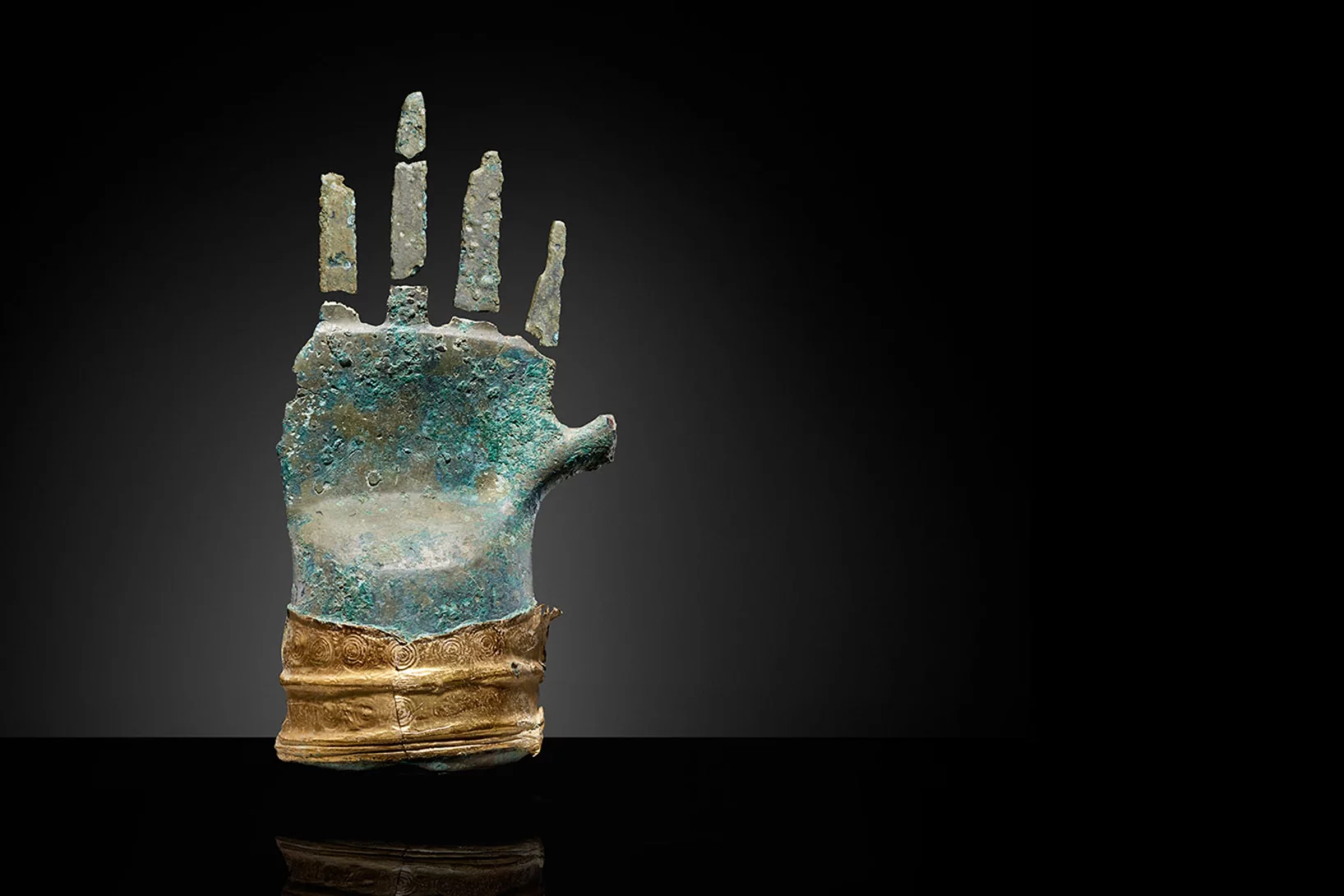
A hand like no other
A 3,500-year-old bronze sculpture is being examined at PSI's SINQ neutron source. This will enable conservators to get a unique view into the interior of the sensational find – and gain insights into how it was made.
"This is incredibly ambitious"
Every three years, the World Energy Council explores possible developments of the global energy system under different scenarios. Tom Kober, head of the Energy Economics Group in PSI’s Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis and one of the lead authors of the study, explains what the individual scenarios mean and how global warming could be mitigated.
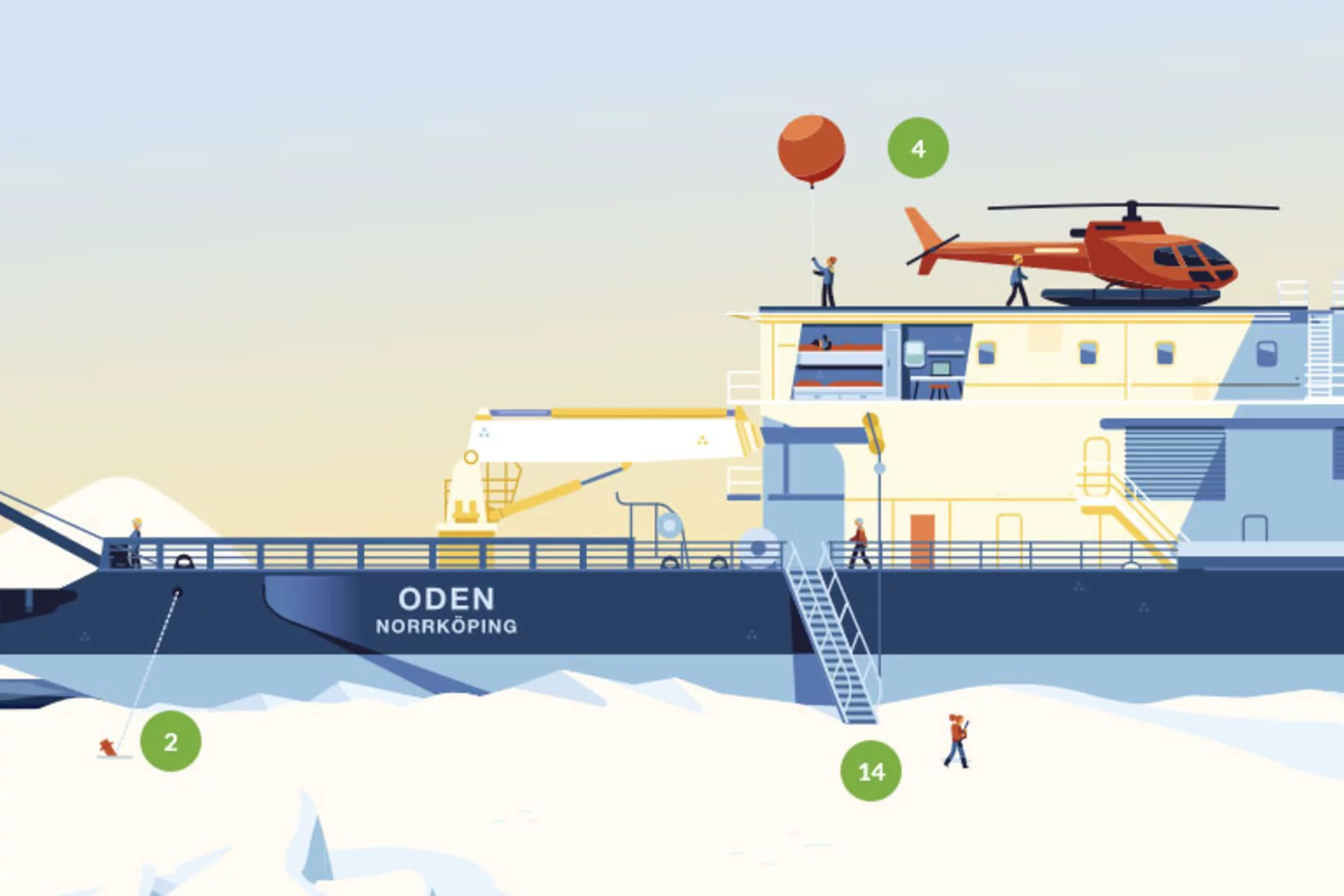
A floating lab
To investigate Arctic water, ice, and air, 40 scientists cruised to the North Pole on the icebreaker Oden in the summer of 2018. Two atmospheric researchers from PSI were on board.
Research and tinkering – SwissFEL in 2019
The newest large research facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute, SwissFEL, has been completed. In January 2019 it began regular operation. Henrik Lemke, head of the SwissFEL Bernina research group, gives an interim report.
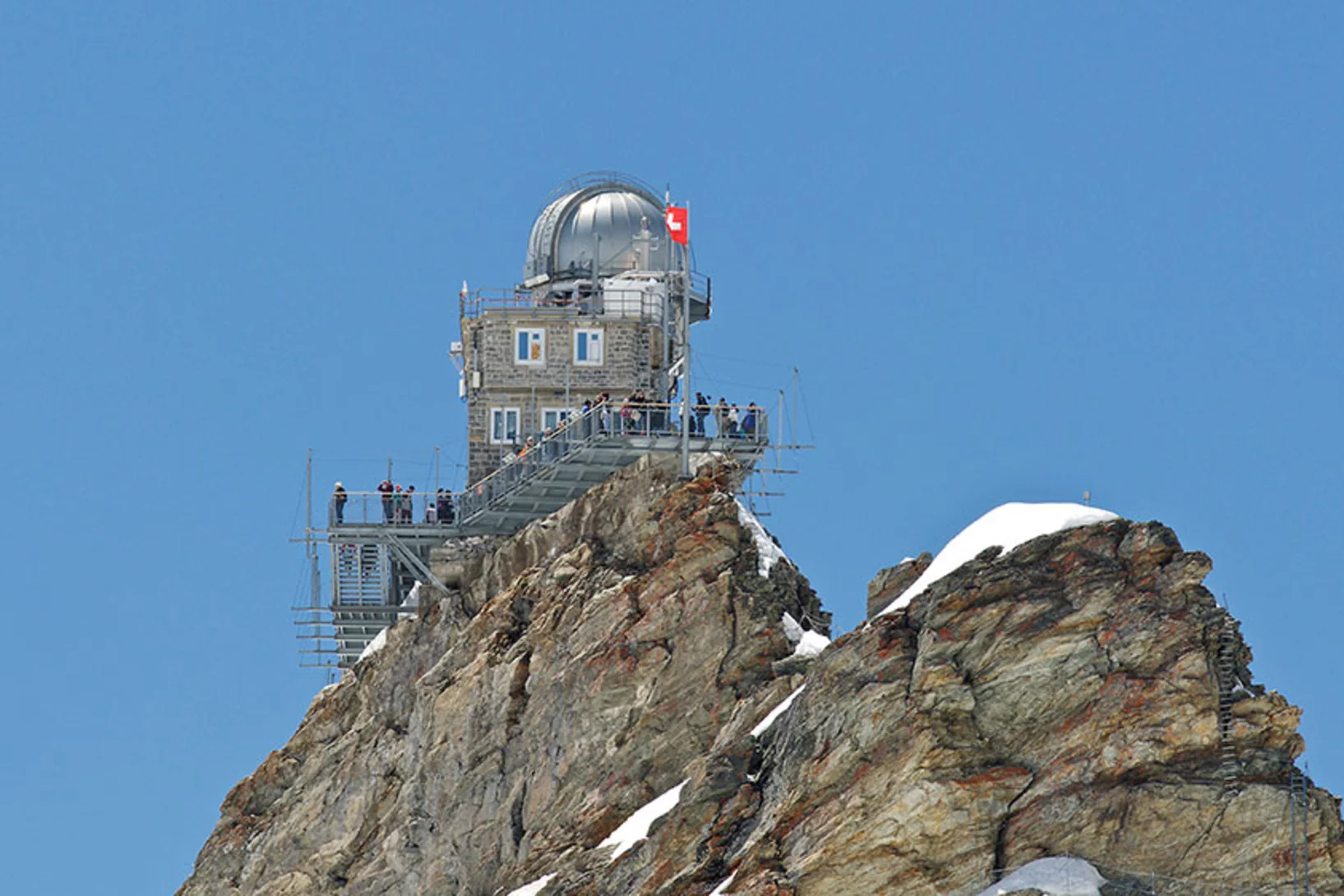
Research above – and about – the clouds
At the Jungfraujoch research station, PSI scientists study particulate matter in the atmosphere. And have to deal with the fact that the human body is not made for life at 3,500 metres above sea level.
In fresh air and in smog
PSI researchers drill through millennia-old glacier ice in the high mountains and analyse the world's highest particulate concentrations in Delhi, India. They are helping to address questions regarding climate change and to reduce air pollution.
Testing the energy system of the future today, as realistically as possible
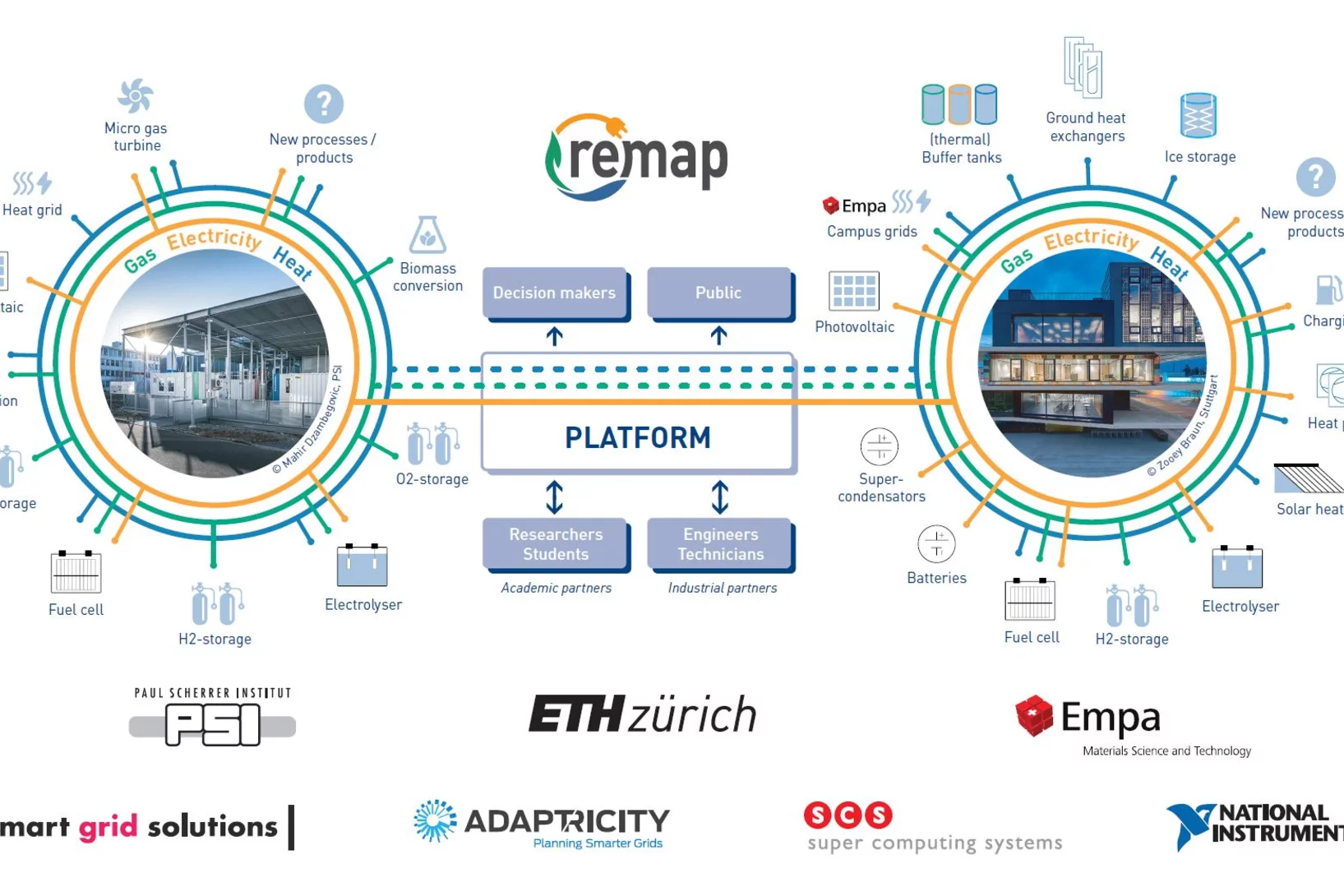
With the kick-off of the ReMaP project, companies have another opportunity to test their vision for the energy system of the future now. PSI's ESI platform helps to make better and more intelligent use of renewable energy in the future.
Cladding tubes and their properties
In the Nuclear Energy and Safety Research Division at PSI, Johannes Bertsch focuses on the so-called cladding tubes that are used in nuclear power plants.
Watching electrons and switching bits on
Electronics should get smaller, faster, and above all more energy-efficient. These themes are also present in several research groups at PSI. From incremental improvements to complete rethinking – who is currently working on what?
Now it's time for something new
If you make electronic components smaller, they unfortunately get hotter. Also, we will soon reach the limit of technically feasible miniaturisation. At PSI, Gabriel Aeppli and Christian Rüegg are working on fundamentally new, physical solutions for better computers and data storage devices.
30 years Paul Scherrer Institute PSI
Ceremony with invited guests from politics, business and sciencePSI held its 30 Years of PSI ceremony. The PSI showed guests what it has achieved over the past three decades, with results that could be of benefit to everyone in Switzerland.
The Swiss Federal Interim Storage Facility
In medicine, industry, and research as well as in power generation radioactive waste occurs. In Switzerland, there are currently two central interim storage facilities. The Federal interim storage facility for waste stemming from medicine, industry and research is located on the grounds of PSI.
A biotechnological revolution
Gebhard Schertler is head of the research division Biology and Chemistry at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and professor for Structural Biology at ETH Zurich. In this interview he talks about biological research at PSI and the future of drug development.
Fast-moving plot
How do dye-sensitised solar cells work, and what's behind the brilliant new mobile phone displays? The ultrashort X-ray pulses at SwissFEL reveal the chemical reactions that take place inside these devices and could help to make them even more efficient and cost-effective.
Movie directors with extra roles
Data storage devices based on novel materials are expected to make it possible to record information in a smaller space, at higher speed, and with greater energy efficiency than ever before. Movies shot with the X-ray laser show what happens inside potential new storage media, as well as how the processes by which the material switches between two states can be optimised.
Hollywood in the Würenlingen woods
With the X-ray laser SwissFEL, researchers at PSI want to produce movies of biomolecules in action. This can reveal how our eyes function or how new drugs work.
A day as a young scientist
Physics isn't everyone's favourite subject. At the iLab of the Paul Scherrer Institute, students experience the material in a different way: with experiments instead of memorising formulas.
Investigation into violation of research integrity is concluded
Last summer a violation of research integrity was reported to the Paul Scherrer Insitute PSI. The results of the investigation are now available. PSI has taken several measures as a consequence.
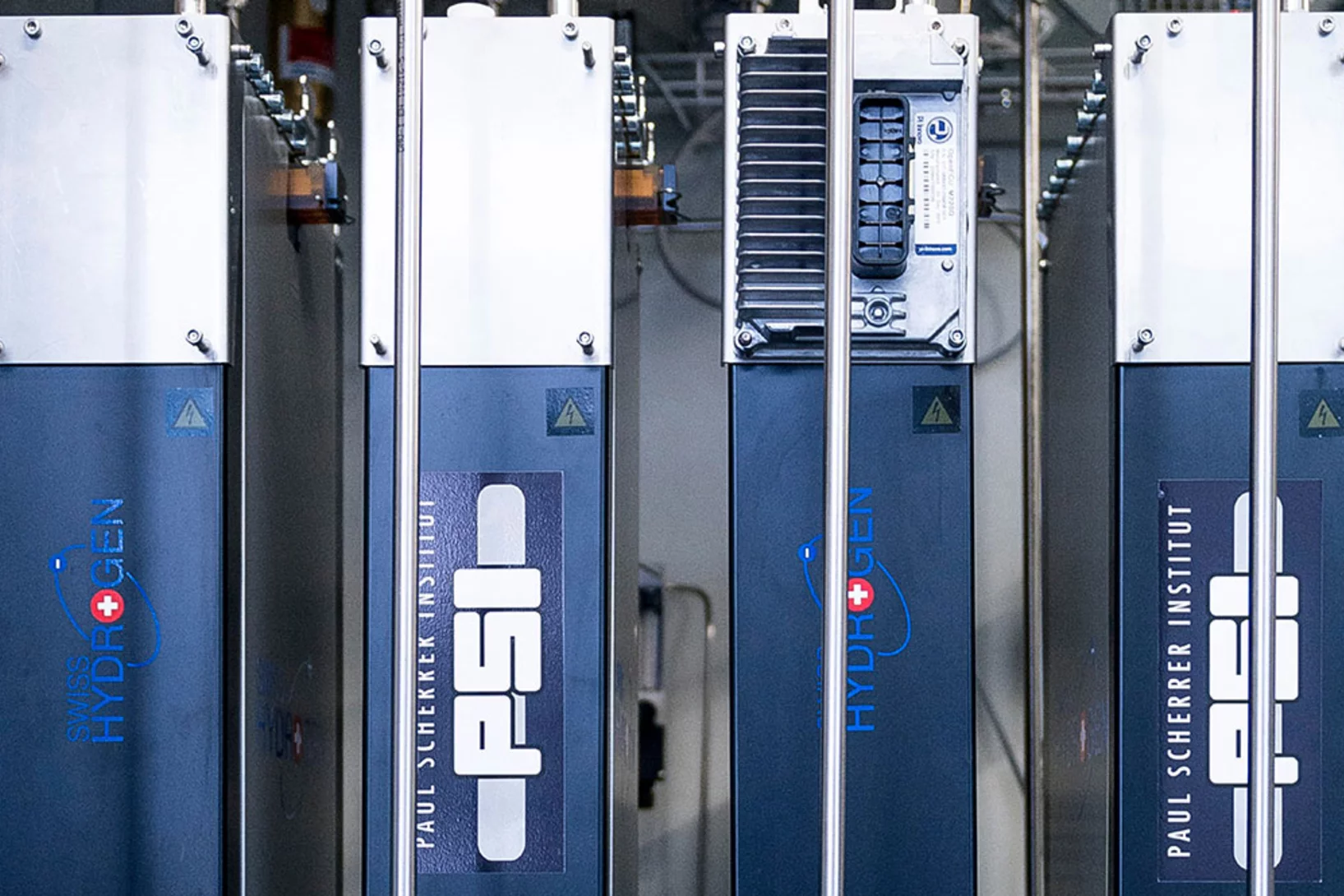
Power on demand
If photovoltaic or wind power plants produce more electricity than the network can absorb, valuable energy is lost. At the ESI Platform, PSI researchers are investigating how fuel cells can contribute to making this energy usable in a targeted way through storage.
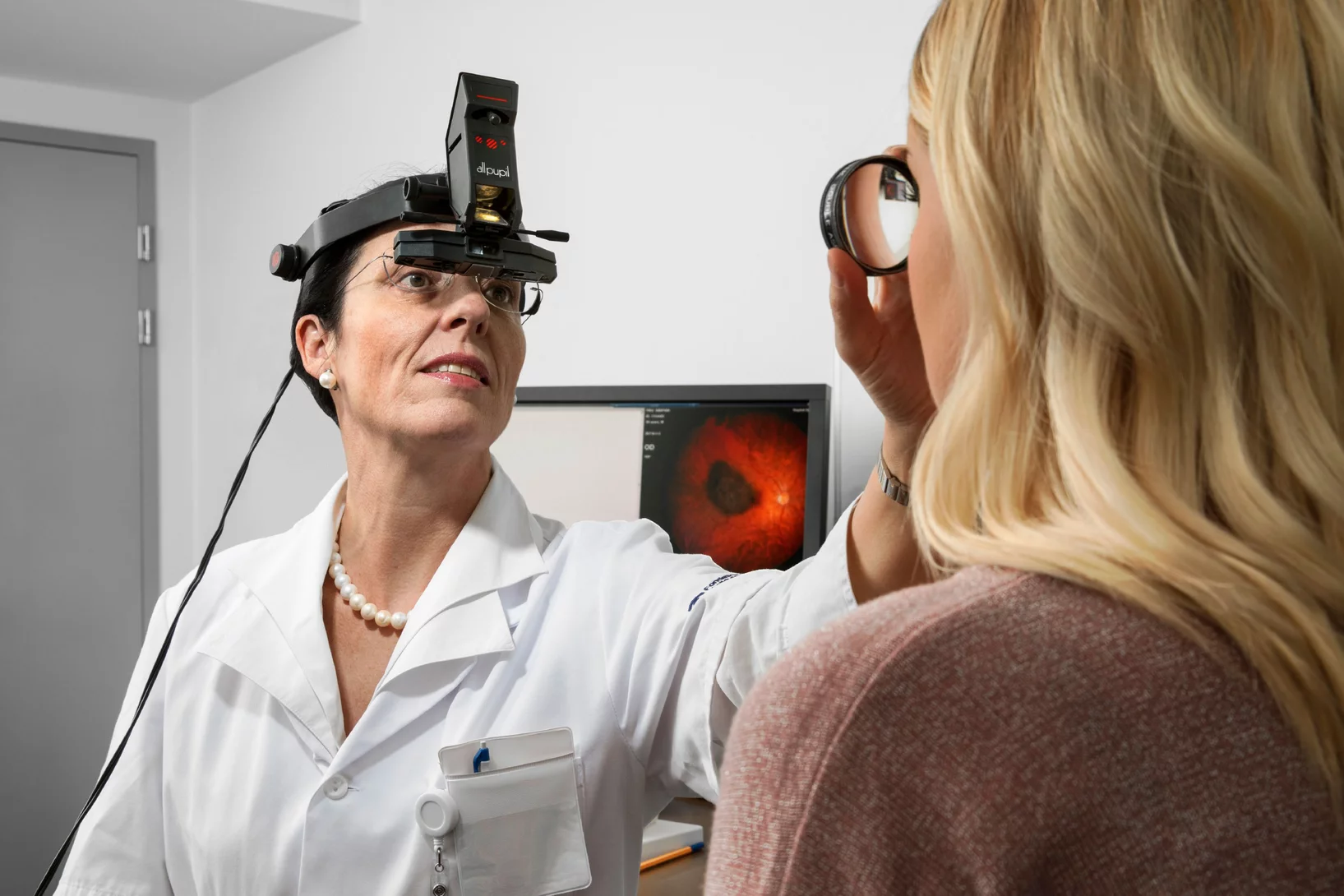
Lausanne-Villigen return
Nowhere in the world have so many ocular tumours been irradiated with protons as at PSI. But before the affected patients go to Villigen, they have to visit Lausanne: for pretreatment at the Jules Gonin Ophthalmic Hospital. The more than 30-year-long collaboration between the hospital and PSI is unique, and in most cases it saves the patient's diseased eye.