Show filters
Synchronising ultrashort X-ray pulses
Attosecond coherent pulses at SwissFEL will open new experimental possibilities
PSI Year in Review 2025
Twelve PSI research highlights in 2025
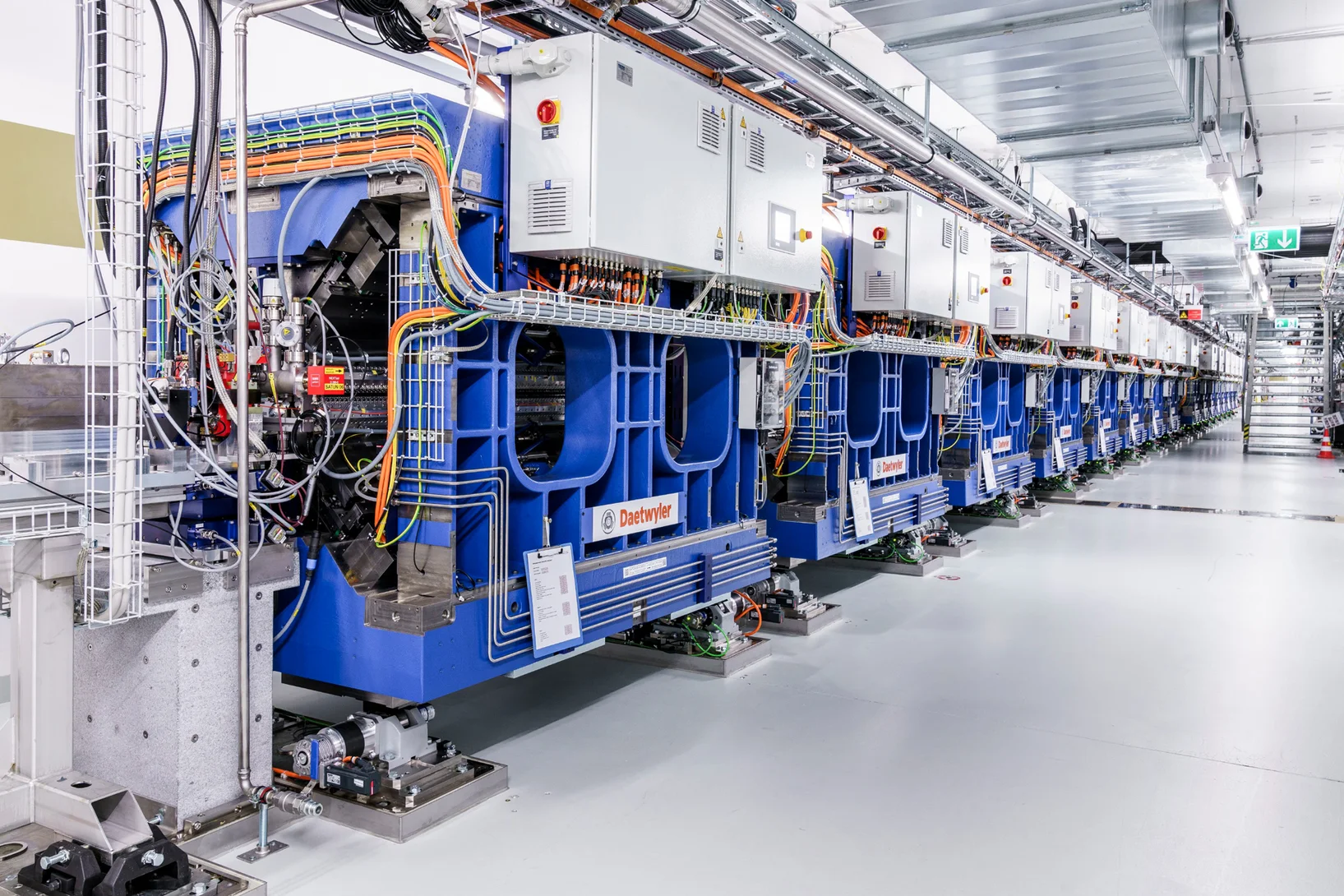
Engineering skill and perseverance
Credit for the on-time completion of the major SLS 2.0 upgrade project is due in part to a team of dedicated electrical engineers.
Kelvin: The low-temperature scale
The art of engineering means, first of all, the skill required to design and manufacture devices that enable top technical performance. This gallery shows, in five pictures, that this term can also be understood differently if the devices are regarded as works of art with their very own aesthetic, apart from their actual function.
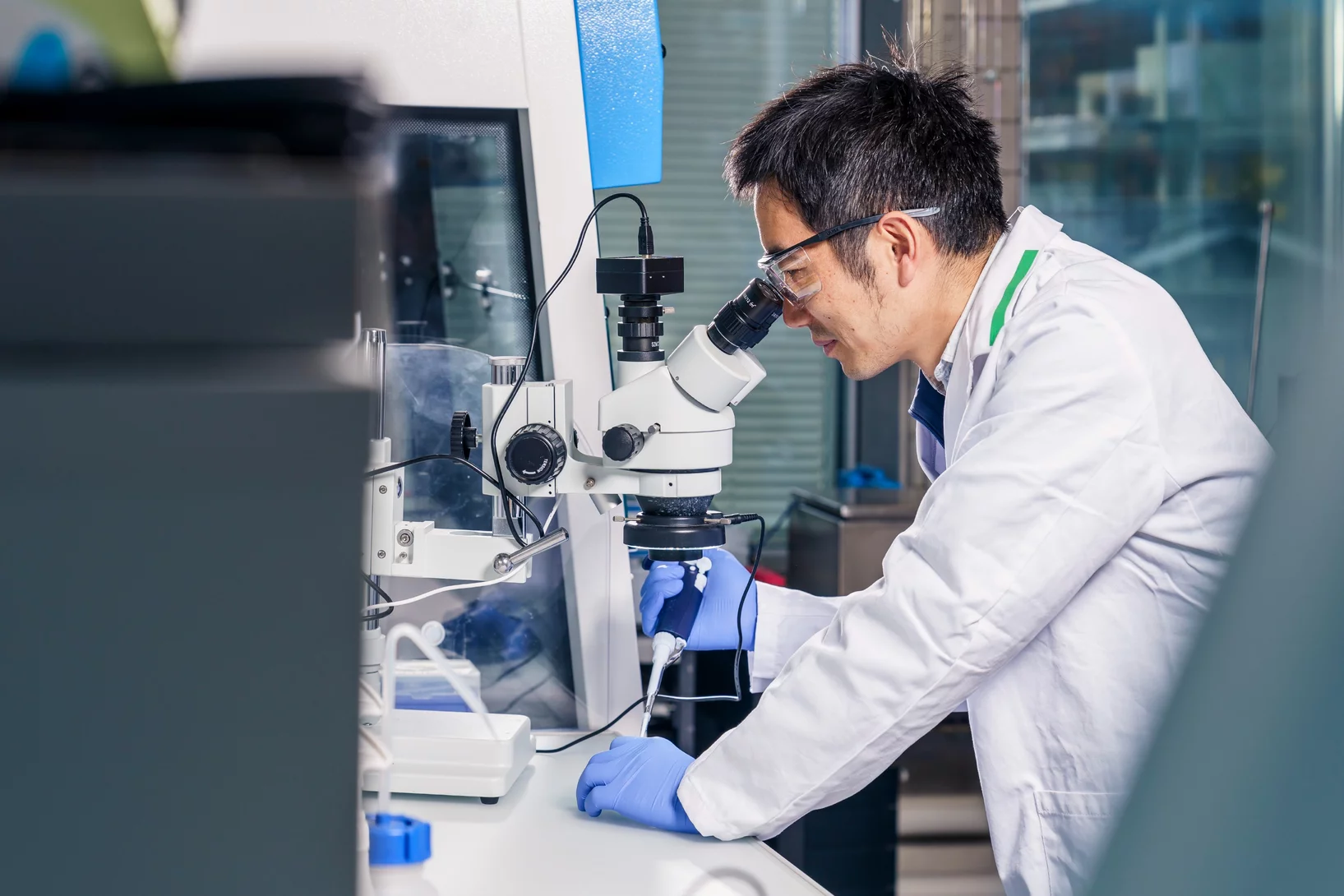
“Collaboration is particularly important in quantum research”
PSI researcher Kirsten Moselund talks about quantum technologies – about their importance and the current situation in Switzerland. And about her own research in the field of nanophotonics.
Laser draws made-to-order magnetic landscapes
Researchers at PSI have found a surprisingly inexpensive and fast method to make localised alterations in magnetic materials.
How microtubules take part in cellular signal processing
Researchers at PSI have investigated on the molecular level how the cytoskeleton transmits commands within the cell. Their findings could provide the medical field with new options for intervention in the event of malfunctions within the organism.
Optimising the treatment of eye tumours
The Insel Group and PSI are expanding their collaboration to provide faster and better coordinated access to proton therapy for patients with eye tumours.
Predicting component lifetimes in nuclear facilities
For 30 years, experiments have been providing unique insight into how metals and ceramics degrade under high-energy proton bombardment.
X-rays bring high-resolution brain mapping within reach
A new imaging breakthrough could reveal brain connectivity in 3D detail never before accessible.
Clean biogas – measurable everywhere
A new analytical method can detect even tiny amounts of critical impurities.
Swiss PIC technology transfer centre is inaugurated
Jointly founded by scientific and industrial partners with PSI researchers: the Swiss Photonics Integration Center celebrated its inauguration on 24 November 2025.
How the cheese-pasta principle could help counter Alzheimer's
PSI researchers have discovered cellular mechanisms that could help to mitigate diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Atoms under pressure
Zurab Guguchia puts pressure on matter – and in doing so, creates exciting quantum effects such as superconductivity at more easily achievable temperatures.
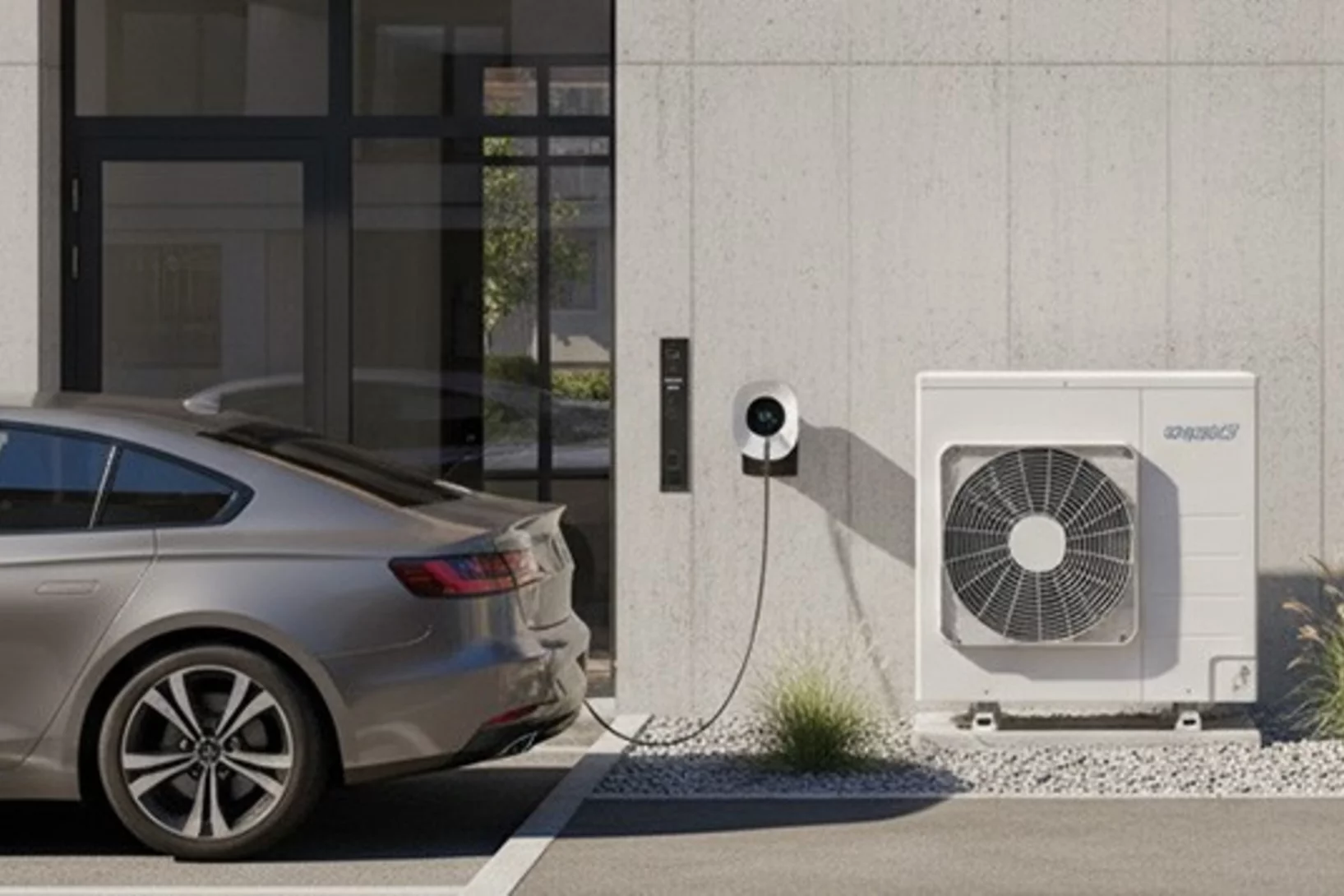
Electric cars and heat pumps can help the Energy Strategy
In future, flexibly operated heat pumps and electric cars could reduce both electricity imports and electricity prices. That is according to a new study by a Swiss research consortium led by ETH Zurich.
Terbium duet and other quantum art
To create more stable qubits, PSI researchers make terbium ions perform in pairs. Elsewhere, they are using optical tweezers to position atoms with high precision.
Particulate pollution re-evaluated
A new study provides data from 43 sites across Europe, showing the respective oxidative stress on the lungs.
Slowing time and trapping ions
Cornelius Hempel uses quanta to perform calculations on quantum phenomena. While this sounds logical, it’s actually highly complex. His latest coup: a quantum simulator that slows down time.
Disorder begins at the surface of quantum materials
Ultrafast X-rays from SwissFEL reveal unexpected light responses in quantum materials.
Data for a better vanadium flow
Scientists at PSI have developed a dynamic database on the global vanadium economy. This is meant to advance the use of special energy storage systems – and thus the energy transition.
Big heart, acute senses key to explosive radiation of early fishes
X-rays of a 400-million-year-old fossil illuminate a key moment in our deep evolutionary past.
POLIZERO: PSI project shows paths to climate neutrality
The net-zero target is achievable – if Switzerland sets the right political course now.
Merlin-7: New model for high-performance computing
An innovative computing cluster is ushering in a new era of computer-aided research at PSI.
PSI’s cement whisperer
John Provis has dedicated his research career to a building material that is far more exciting than you might think.
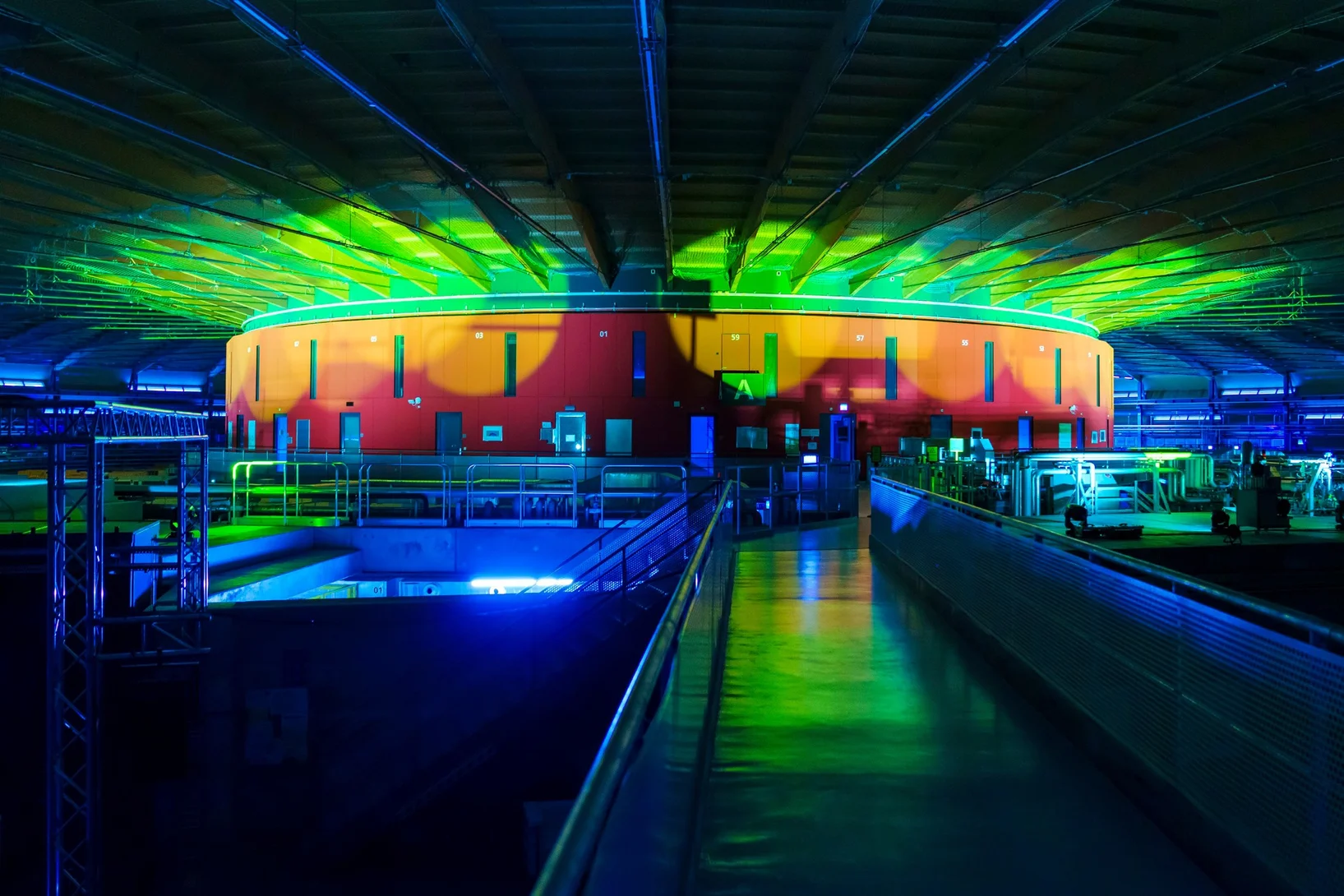
A bright light for Switzerland
The new Swiss Light Source is inaugurated
The Quantum Revolution: What's Next?
A century on from the birth of quantum mechanics, 2025 marks the UNESCO International Year of Quantum Science and Technology. What does the future hold? Our experts share their opinions.
X-rays reveal fossil stealth technology
PSI imaging helps to uncover the hunting strategy of a prehistoric predator.
New insights into a rare disease
Researchers at PSI have uncovered how genetic defects damage human cilia in different ways – a step towards improving the diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia, a disease that has until now been poorly understood.
Zinc detected in clogged syringes
With the help of researchers at PSI, ANAXAM has been investigating, on behalf of the pharmaceutical company MSD, whether zinc may contribute to clogging of pre-filled syringes.
Peering into matter with ultrashort X-ray ripples
An all-X-ray transient grating experiment allows scientists to study the dynamics of quantum particles at the nanoscale.
Attorney for cutting-edge technology
Former PSI doctoral candidate Stephanie Smit now works as a patent attorney for a company that is among the most important in the world. That’s because this company builds machines that are worth a fortune and are highly sought after.
PSI research at Switzerland’s most-visited museum
Making energy research something visitors can experience: The Swiss Museum of Transport is creating a platform for political and social dialogue on energy issues.
AI paves the way towards green cement
Researchers at PSI are using artificial intelligence to develop environmentally friendly formulations for cement.
Prestigious research grant for photonic networks
PSI researcher Kirsten Moselund has been awarded a major research grant from the European Research Council ERC.