IEEE Early Career Award 2022
For contributions to the development of detectors for XFELs and specifically for their verification, characterization, and calibration
Commissioning of the novel Continuous Angle Multi-energy Analysis spectrometer at the Paul Scherrer Institut
We report on the commissioning results of the cold neutron multiplexing secondary spectrometer CAMEA (Continuous Angle Multi-Energy Analysis) at the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source at the Paul Scherrer Institut, Switzerland. CAMEA is optimized for ...
Simulations on "Piz Daint" explain surprising mineral behaviour
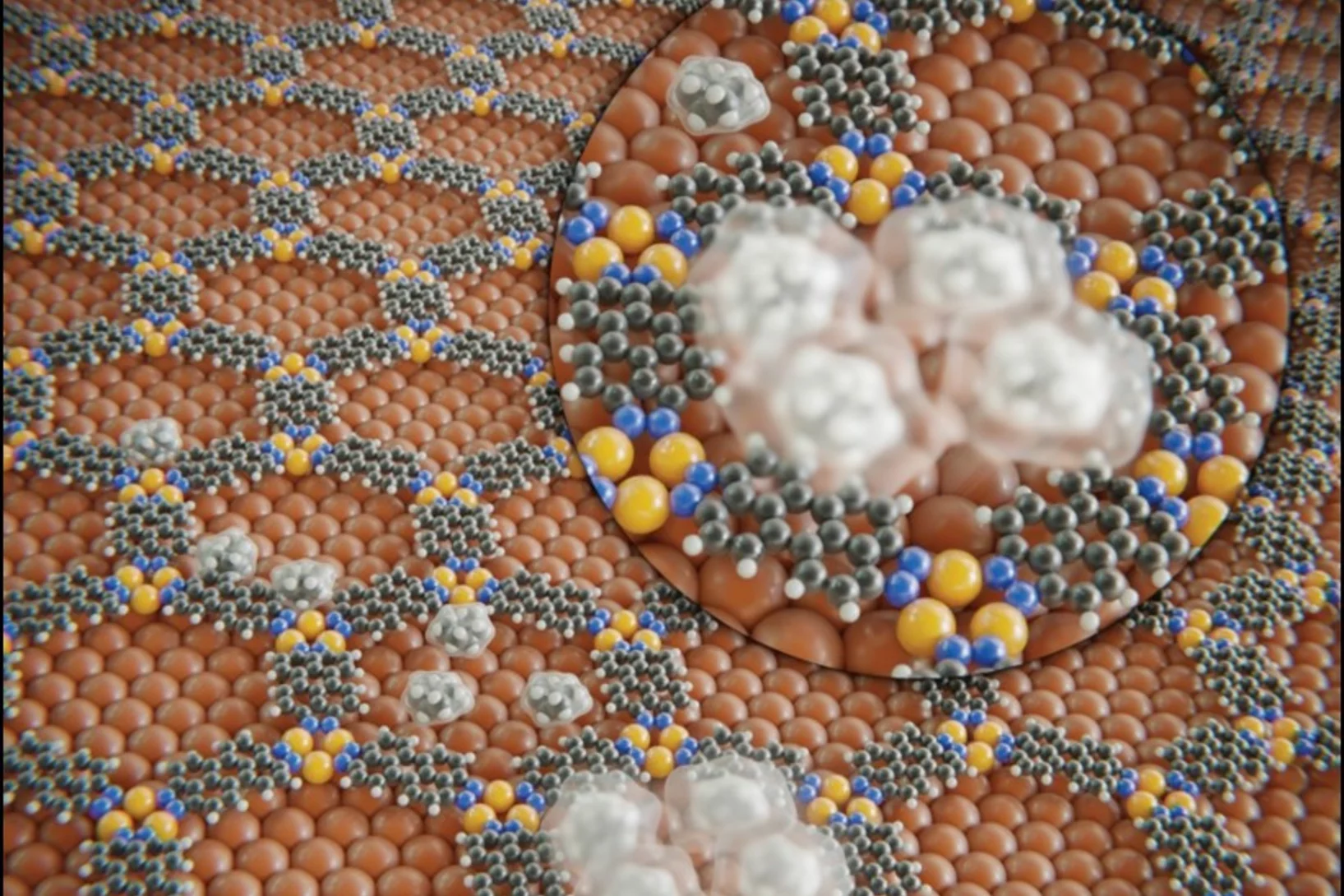
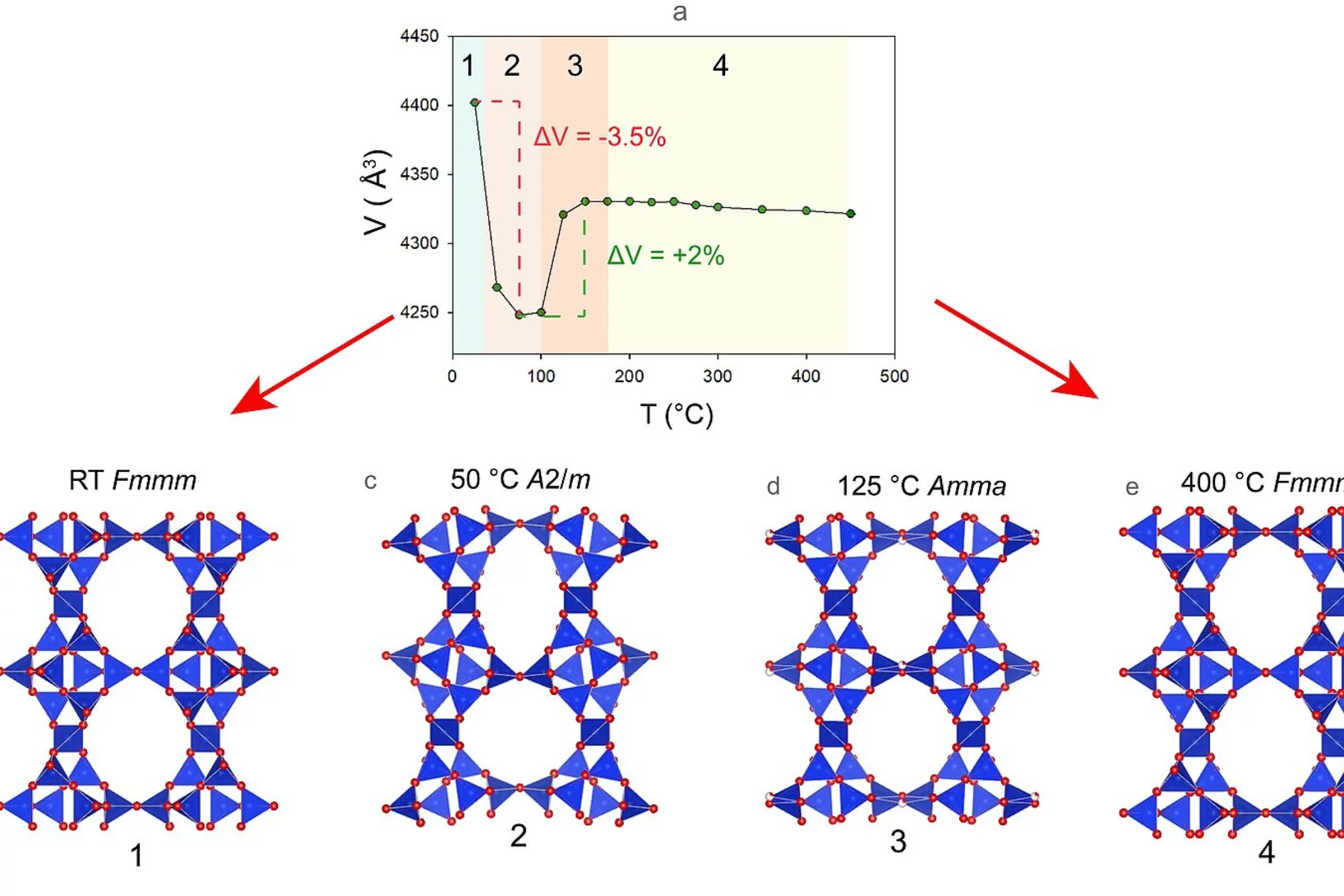
Zeolites are a class of shapely, colourful minerals with very special properties, making them omnipresent in our surroundings. They accelerate chemical reactions, absorb hazardous contaminants and water to a high degree, for example. Their only limitation is that they usually lose their peculiar crystalline structure at high temperatures. Now researchers at the University of Bern have found an unexpected exception.
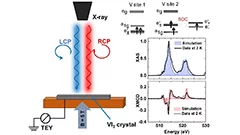
Discovery of a large unquenched orbital moment in a 2D van der Waals ferromagnet
3d transition metals often exhibit a quenched orbital moment when in a solid state system. Therefore, the proposition of a large unquenched orbital moment for V in VI3 caused some surprise and discussion in the scientific community. Experimental and theoretical works diverge on the fact of whether the orbital moment is quenched or not. In our work we have been able to give an answer this open issue, proposing also a model for the ground state of VI3.
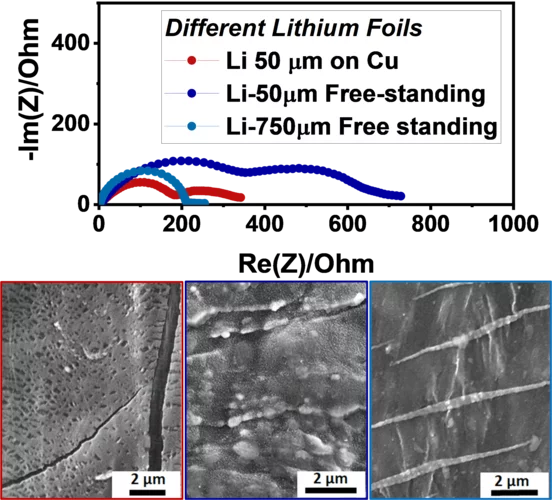
Updated electrochemical impedance model for understanding the interface of metallic lithium
Lithium metal negative electrodes are often used as counter electrodes while testing other electrochemically active materials, and are considered to be equivalent, independently of their thickness, supplier and production processes used. Here, we clearly demonstrate, using Electrochemical Impedance spectroscopy (EIS) that it is not the case, as well as the often-used symmetric cells are actually not so symmetric, when EIS spectra are disentangled using Thee-electrode cells.
CHART MagDev CCT Dipole achieves record field
As one of the first CHART projects, the MagDev activity at PSI designed and built a canted-cosine theta (CCT) demonstrator magnet, wound from Nb3Sn conductor.
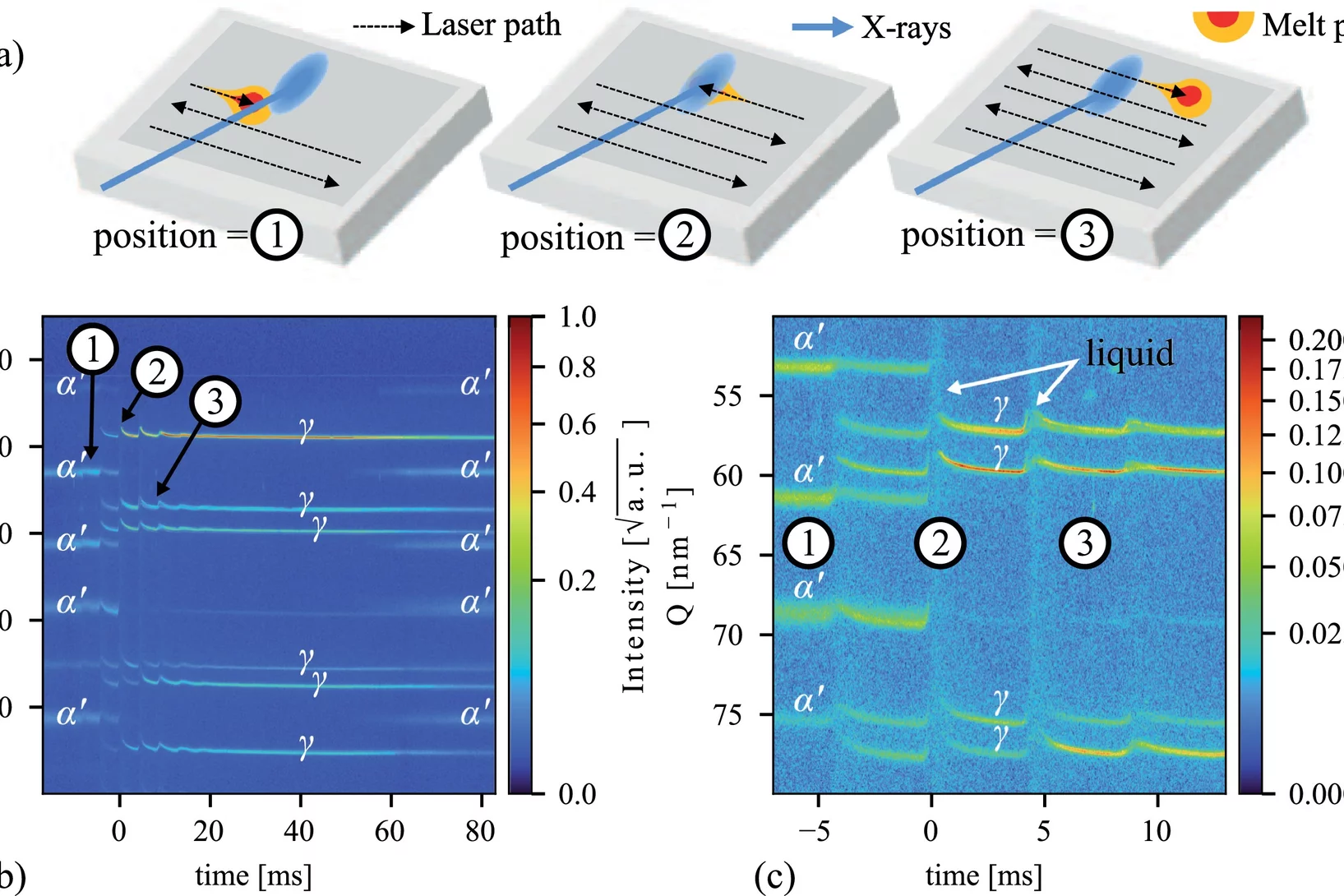
Solidification modes during additive manufacturing
The thermal conditions during laser-based additive manufacturing are inferred from high-speed X-ray diffraction data and can be linked to a model for rapid solidification.
PLD plasma plume analysis, a summary of the PSI contribution
We report on the properties of laser-induced plasma plumes generated by ns pulsed excimer lasers as used for pulsed laser deposition to prepare thin oxide films. A focus is on the time and spatial evolution of chemical species in the plasma plume as well as the mechanisms related to the plume expansion. The overall dynamics of such a plume is governed by the species composition in particular if three or more elements are involved. We studied the temporal evolution of the plume, the composition of the chemical species in the plasma, as well as their electric charge. In particular, ionized species can have an important influence on film growth. Likewise, the different oxygen sources contributing to the overall oxygen content of an oxide film are presented and discussed. Important for the growth of oxide thin films is the compositional transfer of light element such as oxygen or Li. We will show and discuss how to monitor these light elements using plasma spectroscopy and plasma imaging and outline some consequences of our experimental results.
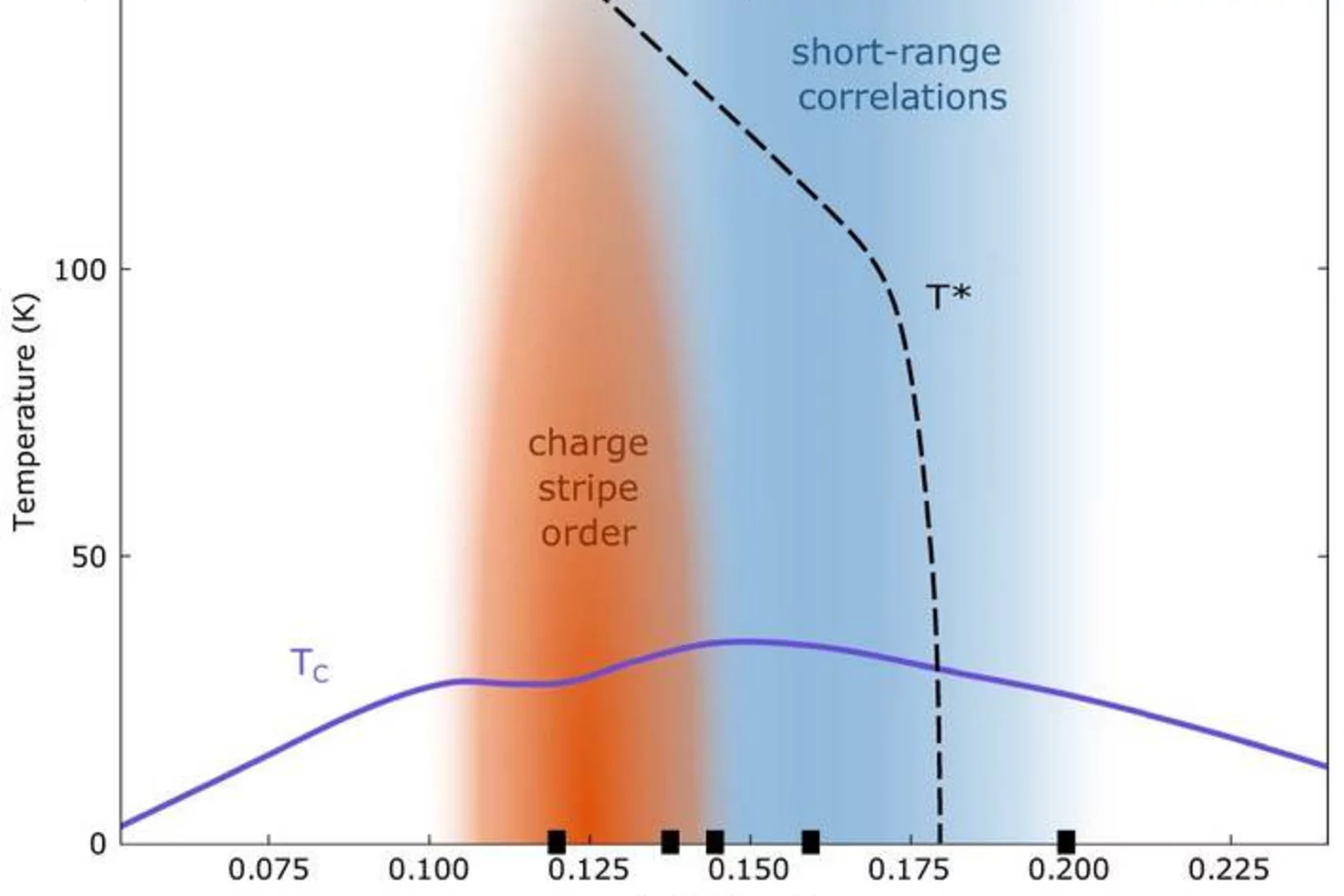
Fate of charge order in overdoped La-based cuprates
In high-temperature cuprate superconductors, stripe order refers broadly to a coupled spin and charge modulation with a commensuration of eight and four lattice units, respectively. How this stripe order evolves across optimal doping remains a controversial question. Here we present a systematic resonant inelastic x-ray scattering study of weak charge correlations in La2−xSrxCuO4 and La1.8−xEu0.2SrxCuO4. Ultra high energy resolution experiments demonstrate the importance of the separation of inelastic and elastic scattering processes. Long-range temperature-dependent stripe order is only found below optimal doping. At higher doping, short-range temperature-independent correlations are present up to the highest doping measured. This transformation is distinct from and preempts the pseudogap critical doping. We argue that the doping and temperature-independent short-range correlations originate from unresolved electron–phonon coupling that broadly peaks at the stripe ordering vector. In La2−xSrxCuO4, long-range static stripe order vanishes around optimal doping and we discuss both quantum critical and crossover scenarios.
Fate of charge order in overdoped La-based cuprates
In high-temperature cuprate superconductors, stripe order refers broadly to a coupled spin and charge modulation with a commensuration of eight and four lattice units, respectively. How this stripe order evolves across optimal doping remains a controversial question. Here we present a systematic resonant inelastic x-ray scattering study of weak charge correlations in La2−xSrxCuO4 and La1.8−xEu0.2SrxCuO4. Ultra high energy resolution experiments demonstrate the importance of the separation of inelastic and elastic scattering processes.
Unusual ferrimagnetism in CaFe2O4
Rare ferrimagnet states in a phase competing antiferromagnet.
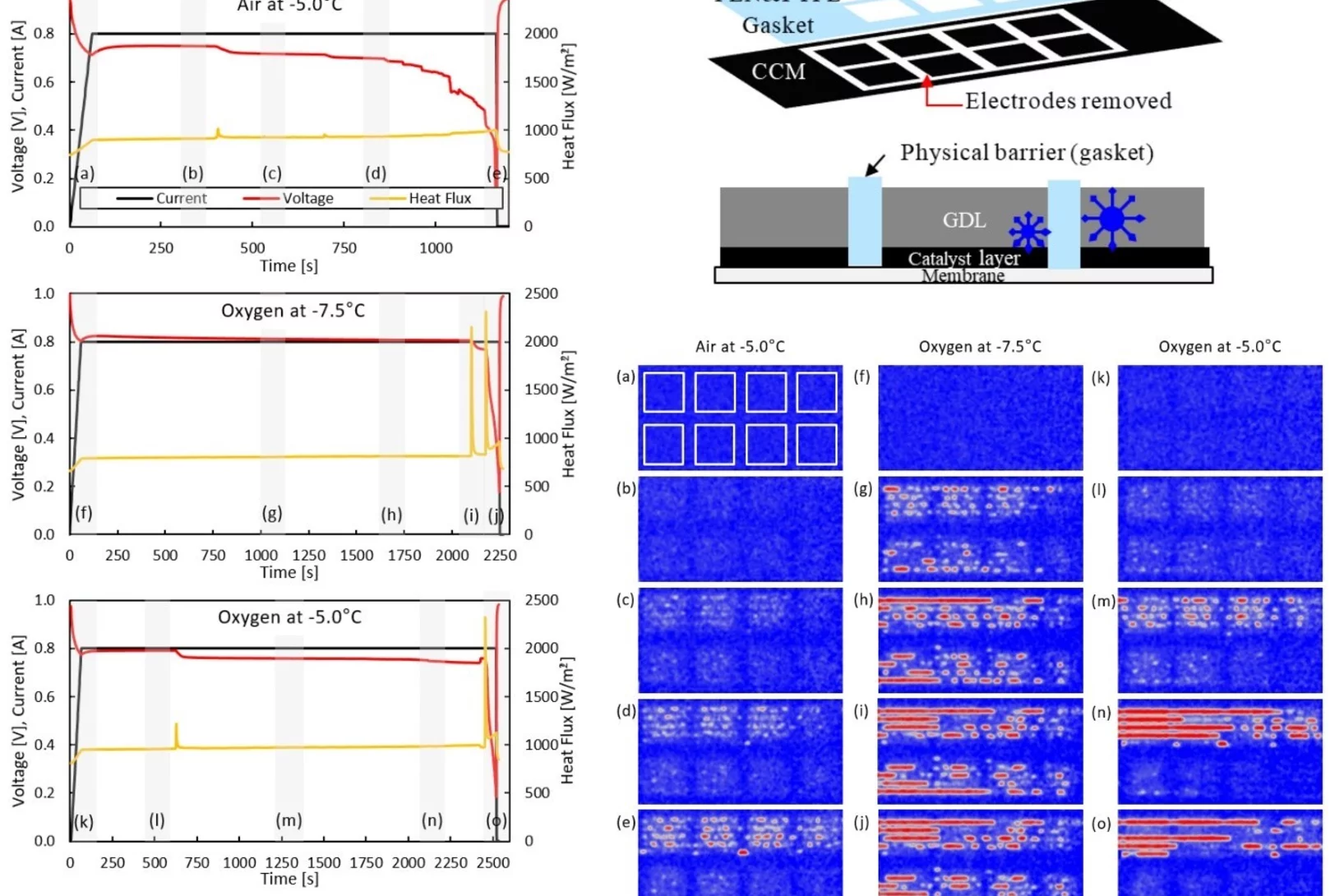
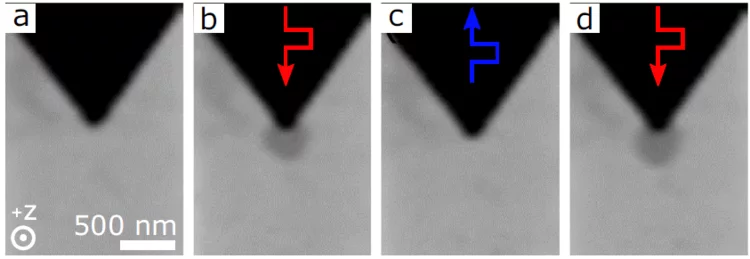
Prevention of freezing propagation in fuel cells using segmentation
The ability to start-up in extreme environmental conditions, including sub-freezing temperatures, is essential to the deployment of the fuel cell technology. Water produced in fuel cells at these temperatures can be in the super-cooled state, and freezing can lead to a rapid shutdown, as water cannot be removed anymore as a liquid. By segmenting a fuel cell, it is possible to prevent the propagation of freezing, which enables the cell operation even after the first freezing event occurred.
Topological magnetic structures in MnGe: Neutron diffraction and symmetry analysis
From new neutron powder diffraction experiments on the chiral cubic (P213) magnet manganese germanide (MnGe), we analyze all of the possible crystal symmetry-allowed magnetic superstructures that are determined successfully from the data. The incommensurate propagation vectors k of the magnetic structure are found to be aligned with the [100] cubic axes, and correspond to a magnetic periodicity of about 30 Å at 1.8 K. Several maximal crystallographic symmetry magnetic structures are found to fit the data equally well and are presented. These include topologically nontrivial magnetic hedgehog and “skyrmion” structures in multi-k cubic or orthorhombic 3+3 and orthorhombic 3+2 dimensional magnetic superspace groups respectively, with either potentially responsible for topological Hall effect. The presence of orthorhombic distortions in the space group P212121 caused by the transition to the magnetically ordered state does not favor the cubic magnetic hedgehog structure, and leave both orthorhombic hedgehog and skyrmion models as equal candidates for the magnetic structures. We also report on a combined mechanochemical and solid-state chemical route to synthesize MnGe at ambient pressures and moderate temperatures, and compare with samples obtained by the traditional high pressure synthesis.
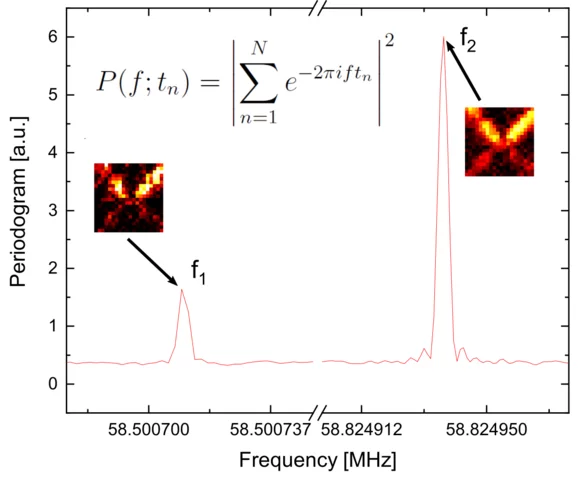
From light-years to nanometers: reconstruction of unknown oscillations in STXM
From light-years to nanometers: by repurposing an algorithm originally developed for the investigation of oscillatory dynamics in astronomical objects, scientists have been able to image non-locked dynamical processes at the nanosecond and nanometer scale.
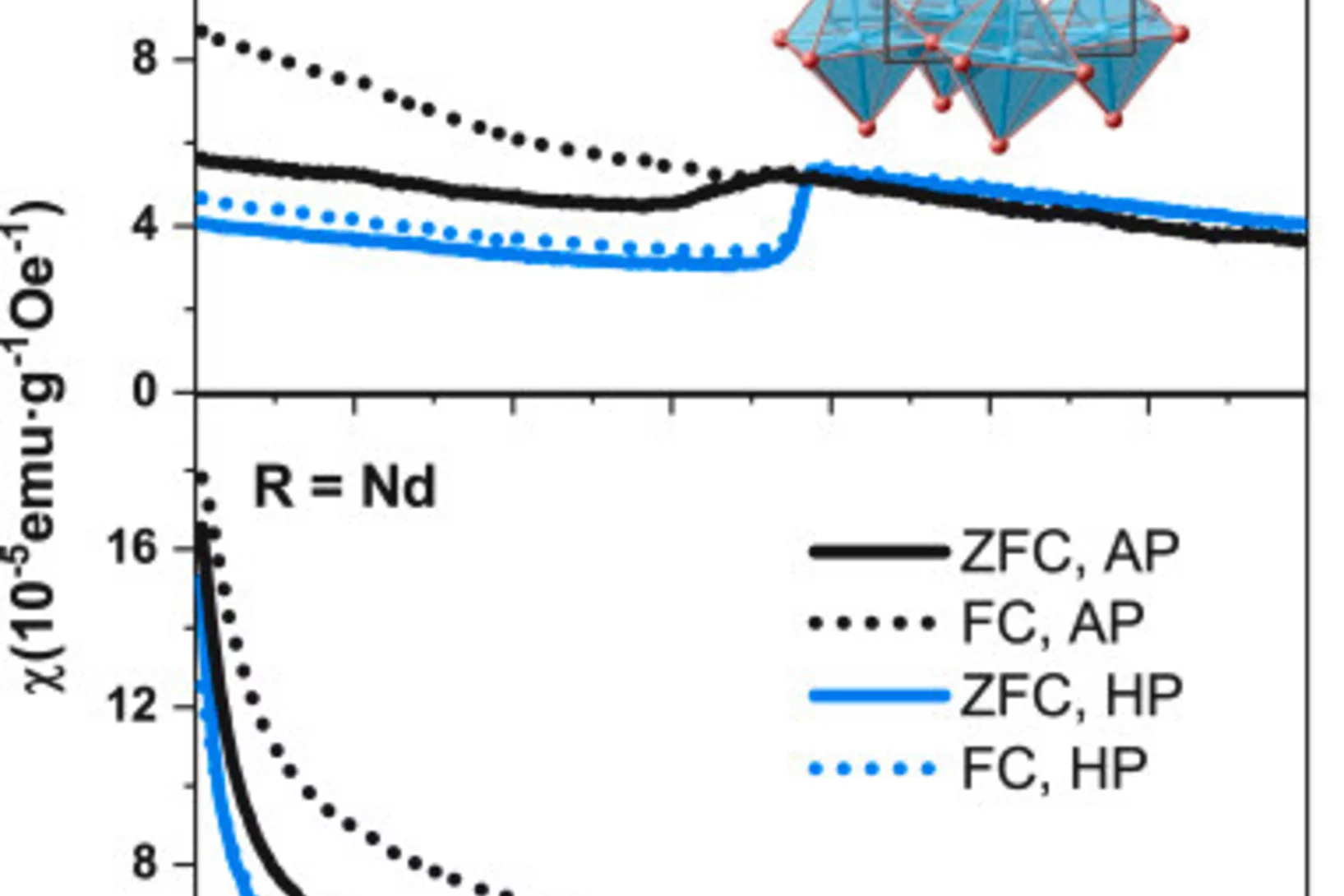
Magnetic structure of R1/3Sr2/3FeO (R = Pr, Nd)
We present magnetization and neutron powder diffraction studies in the temperature range 2K to 300K for oxygen stoichiometric R1/3Sr2/3FeO (R = Pr and Nd). From full symmetry analysis, we proposed two magnetic models by a combined application of irreducible representations and magnetic space groups. Both models fit equally well the neutron powder diffraction data.
Manuel Guizar-Sicairos appointed as Associate Professor at EPF Lausanne and head of the Computational X-ray Imaging group at PSI
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos, currently Senior Scientist at PSI, was appointed as Associate Professor of Physics in EPF Lausanne and head of the Computational X-ray Imaging group in PSI.
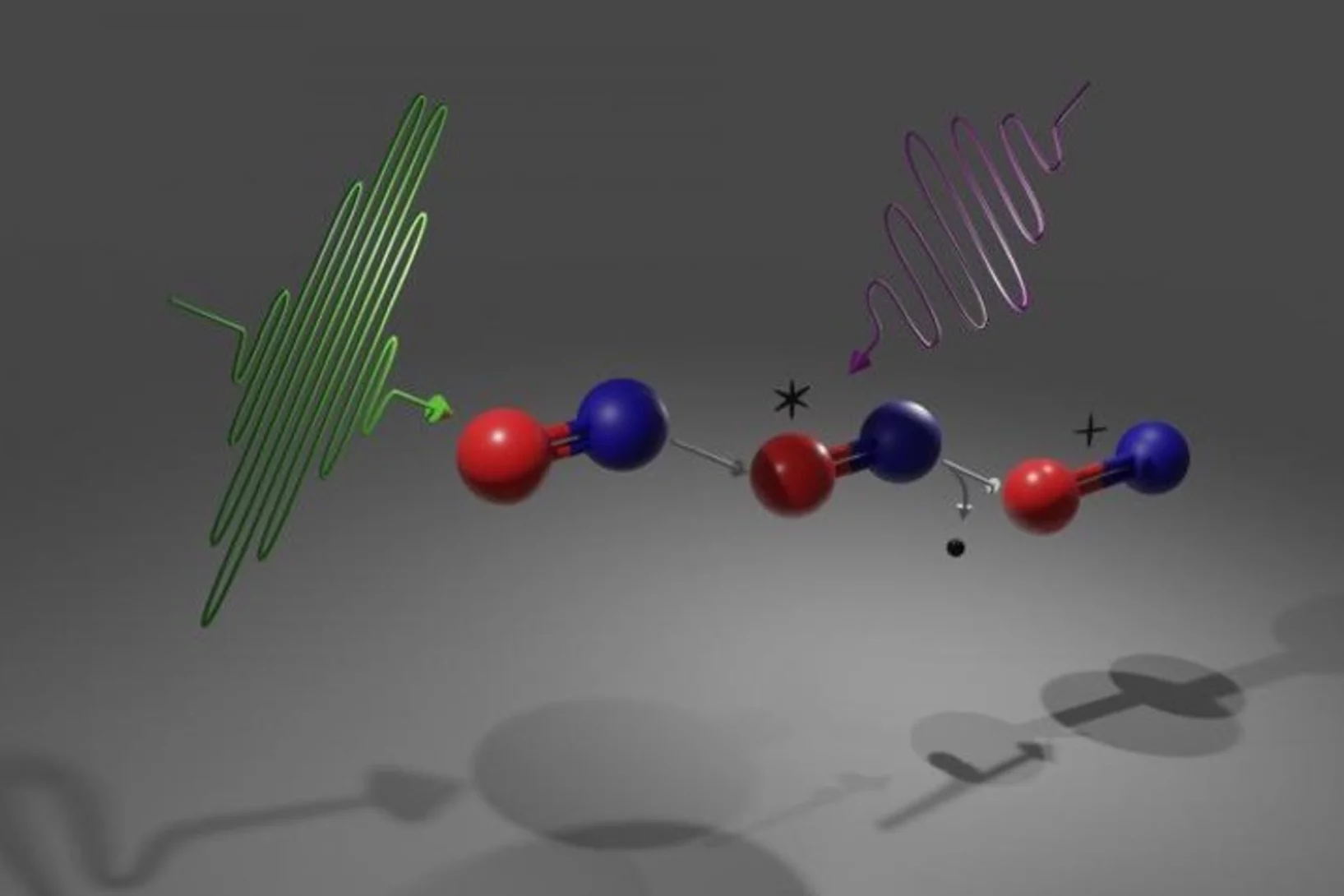
Tracking chemical bond changes with element selectivity and in real time
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy probes the chemical environment in a molecule at a specific atomic site. Now the concept is extended with a site selective trigger to follow chemical bond changes as they occur on the femtosecond time scale.
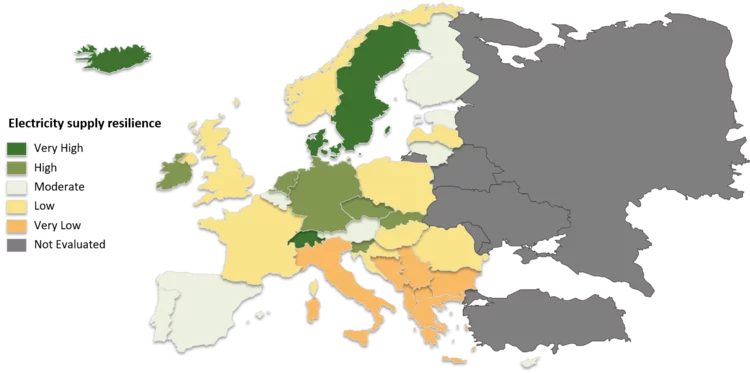
Evaluation of European electricity supply resilience
The increasing risk of extended electricity supply disruptions and severe electricity price fluctuations strongly motivate an evaluation of electricity supply resilience. In this direction, this research proposes a multicriteria decision support framework to assess resilience at a country level, based on three major dimensions: Resist, Restabilize and Recover. In total, 35 European countries are ranked according to their performance on 17 indicators, through a synergy of MCDA methods, techniques and communication protocols. The assessment framework has been extended to incorporate the Choquet Integral method, in order to accommodate potentially interacting pairs of criteria and negate their arbitrary effects on the final evaluation results. The analysis incorporates country data from credible international databases, as well as the preference information of a European energy expert. The results are envisaged to support energy policymakers in Europe and provide guidelines and areas for improvement at a country level.
Magnetic and crystal structure of the antiferromagnetic skyrmion candidate GdSb0.71Te1.22
GdSb0.46Te1.48, a nonsymmorphic Dirac semimetal with Dirac nodes at the Fermi level, has a rich magnetic phase diagram with one of the phases predicted to be an antiferromagnetic skyrmion state. In the current work, we investigate GdSb0.71Te1.22 through bulk magnetization measurements, single-crystal, and powder synchrotron X-ray diffraction, as well as single-crystal hot-neutron diffraction. We resolve a weak orthorhombic distortion with respect to the tetragonal structure and charge density wave (CDW) satellites due to incommensurate modulations of the crystal structure. At 2 K the magnetic structure is modulated with two propagation vectors, kI = (0.45 0 0.45) and kII = (0.4 0 0), with all their arms visible. While kI persists up to the transition to the paramagnetic state at TN = 11.9 K, kII disappears above an intermediate magnetic transition at T1 = 5 K. Whereas magnetic field applied along the c-axis has only a weak effect on the intensity of antiferromagnetic reflections, it is effective in inducing an additional ferromagnetic component on Gd atoms. We refine possible magnetic structures of GdSb0.71Te1.22 and discuss the possibility of hosting magnetic textures with non-trivial 3D+ 2 topologies in the GdSb1−xTe1+x series.
Thermal cycling during 3D laser printing
High-speed in situ X-ray diffraction is used to measure temperature profiles and cooling rates during 3D printing of a a Ti-6Al-4V single-track wall.
A unique environment for research on highly radioactive materials
PSI has a unique (worldwide) environment for the investigation of highly radioactive / toxic materials:
> Materials (different fuel types, very high burn-up, different cladding materials, materials activated in SINQ).
> The hot lab with advanced tools for microsample analysis and preparation.
> The large-scale equipment for advanced material analysis.
This unique combination at PSI allows us to meet the needs of our industrial partners to improve plant safety / efficiency, up to fundamental research.
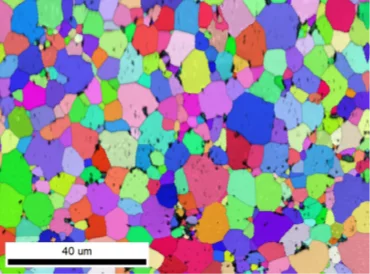
The quantitative distribution of fission products over the cross-section of a pellet with a shielded electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA) used for verification analysis of the material behavior to validate the model. In this context, Xe behavior during transients/failure (LOCA, RIA) is an important safety parameter that can’t be measured with the EPMA at the periphery. Microstructural EBSD investigations on a microsample extend the information horizon, which is deepened at the microXAS beamline by detailed X-ray analyses.
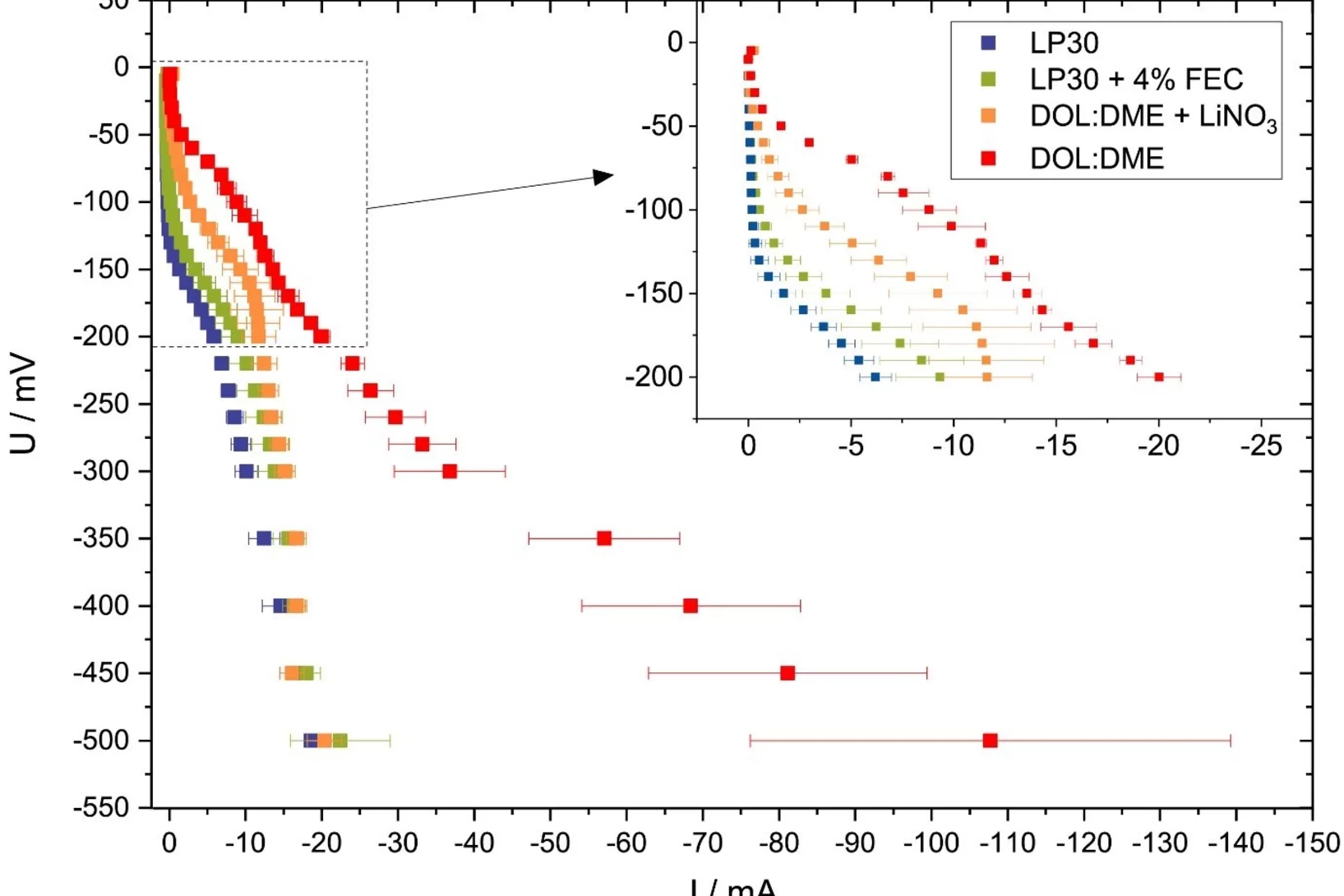
Versatile and Fast Methodology for Evaluation of Metallic Lithium Negative Battery Electrodes
Evaluating potential electrolyte candidates is typically a lengthy procedure requiring long-term cycling experiments. To speed this process up, we have investigated potentiostatic lithium plating as a potential method for fast electrolyte suitability investigation. The applications of this methodology is not limited to liquid electrolytes, - effects of solid-state electrolytes, coatings, and other modifications can be readily assessed.
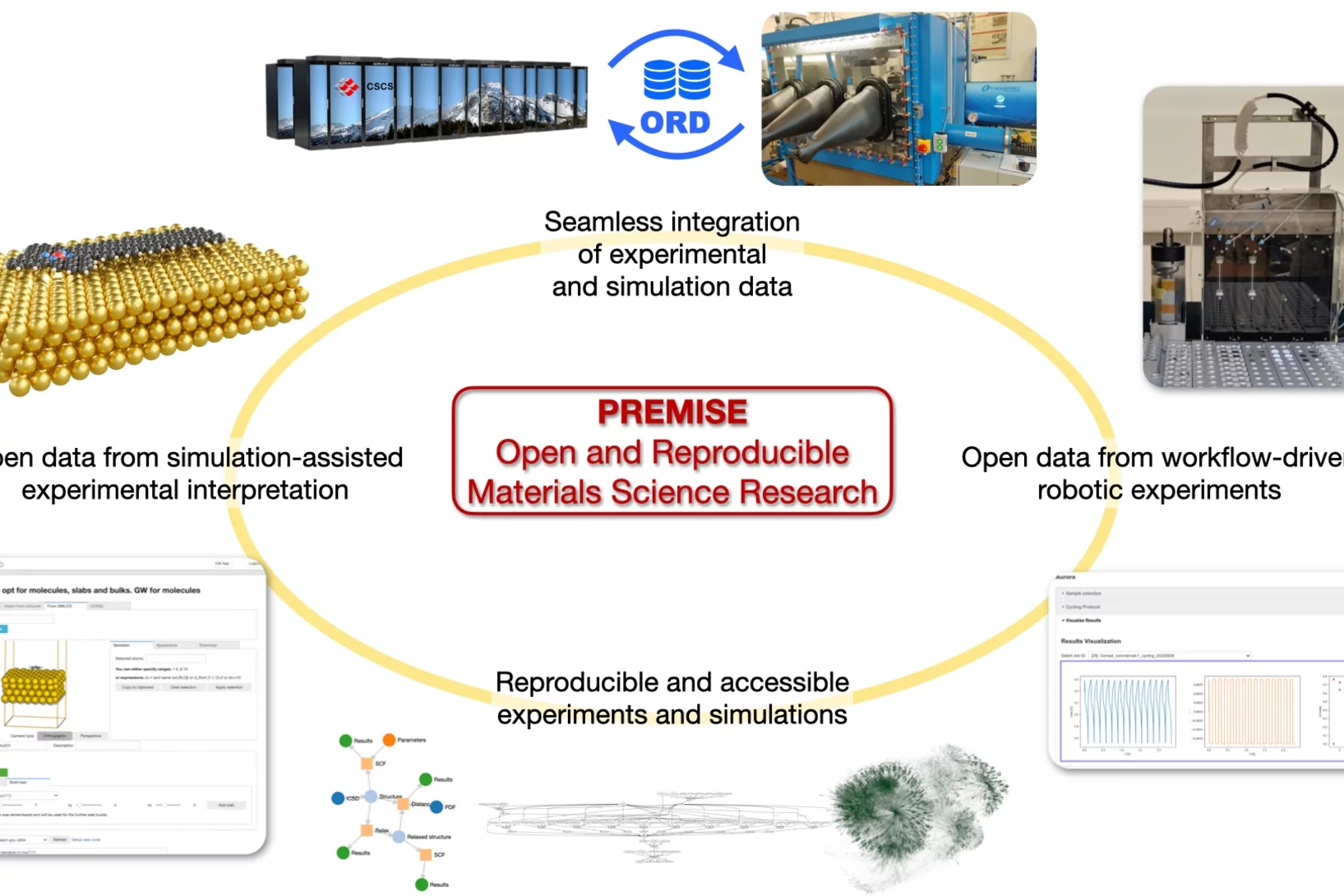
Consortium led by LMS wins funding to establish ORD practices
A consortium led by Dr. Giovanni Pizzi, Group leader of the “Materials Software and Data” group in the Laboratory for Materials Simulations, has won funding of almost CHF1.3 million for a three-year project dubbed PREMISE: “Open and reproducible materials science research.”
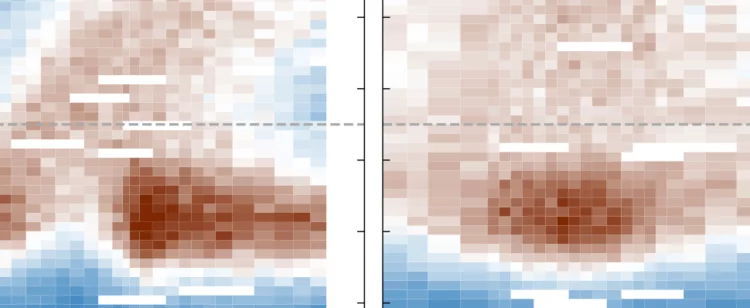
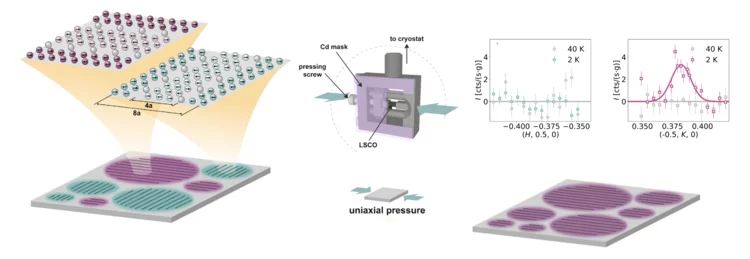
Single-domain stripe order in a high-temperature superconductor
The coupling of spin, charge and lattice degrees of freedom results in the emergence of novel states of matter across many classes of strongly correlated electron materials. A model example is unconventional superconductivity, which is widely believed to arise from the coupling of electrons via spin excitations. In cuprate high-temperature superconductors, the interplay of charge and spin degrees of freedom is also reflected in a zoo of charge and spin- density wave orders that are intertwined with superconductivity ...
Dancing molecules
When cycloalkanes are enclosed in a nanometer-sized pore, they adapt their shape - similar to the induced fit concept described in #biochemistry. The molecules do not all behave in the same way and surprisingly start to move when there is a lack of space at 5K.
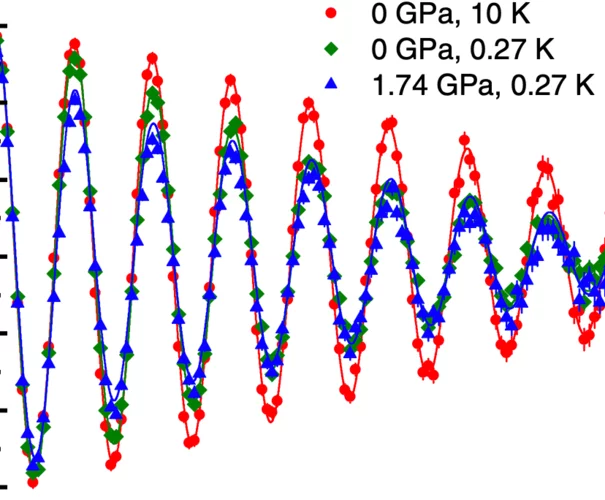
Perspective on muon-spin rotation/relaxation under hydrostatic pressure
Pressure, together with temperature, electric, and magnetic fields, alters the system and allows for the investigation of the fundamental prop- erties of matter. Under applied pressure, the interatomic distances shrink, which modifies the interactions between atoms and may lead to the appearance of new (sometimes exotic) physical properties, such as pressure-induced phase transitions; quantum critical points; new structural, magnetic, and/or superconducting states; and changes of the temperature evolution and symmetry of the order parameters...
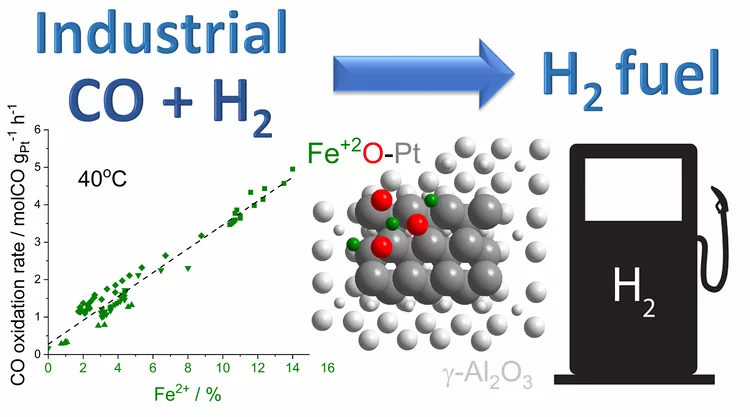
Platinum-Iron(II) Oxide Sites Directly Responsible for Preferential Carbon Monoxide Oxidation at Ambient Temperature: An Operando X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study
Operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy revealed a linear correlation between the amount of oxidic Fe2+ and the ambient temperature activity of Pt−FeOx preferential carbon monoxide oxidation catalysts. The hydrogen prereduction temperature and pressure determines the amount of active Fe2+ sites for alumina- and silica-supported Pt−Fe catalysts. Catalyst deactivation is linked with the oxidation of these sites.
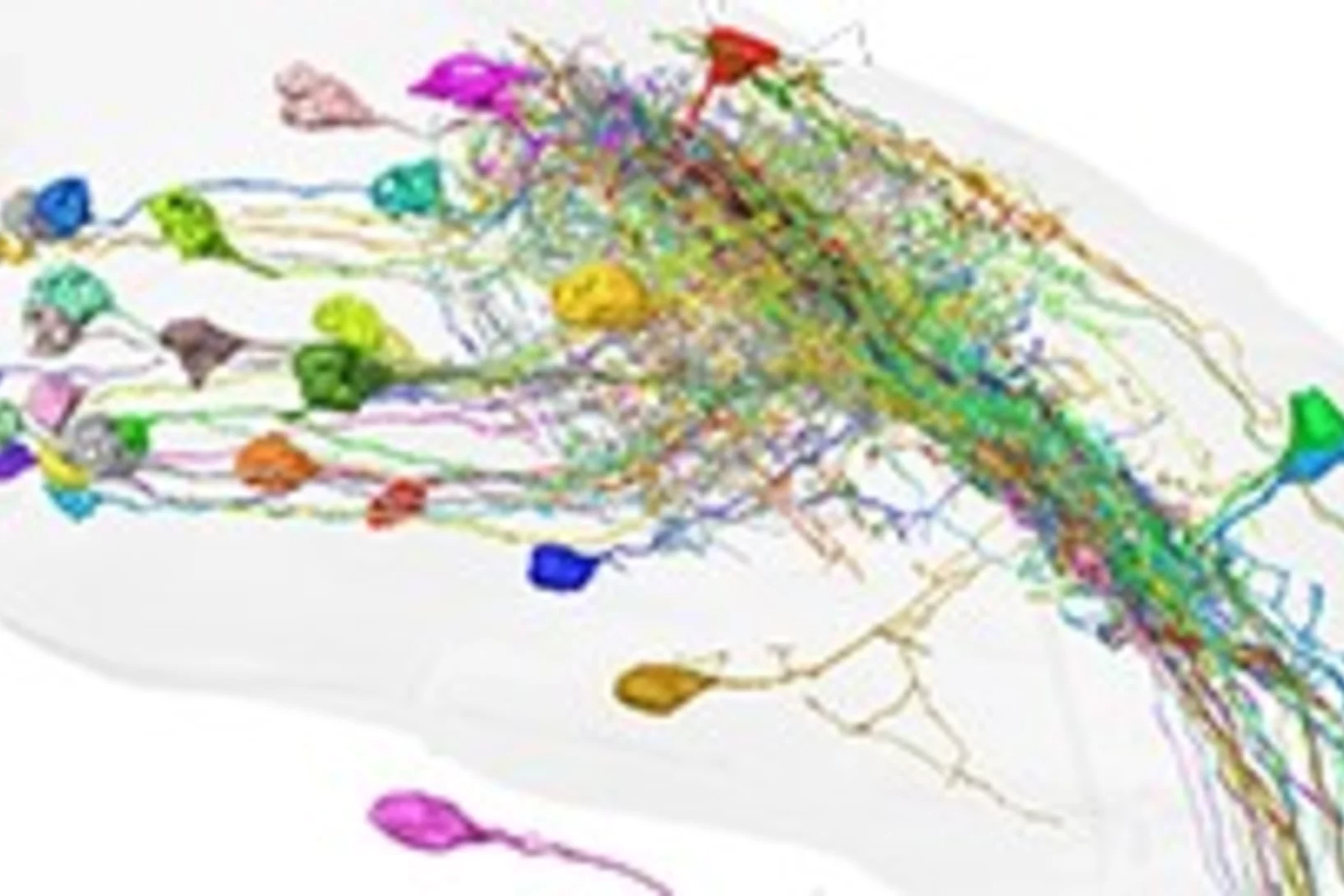
Automated synapse-level reconstruction of neural circuits in the larval zebrafish brain
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Biological Intelligence, Google Inc. and the Paul Scherrer Institute published a new method and data resource that makes connectomic analyses of the entire larval zebrafish brain possible.
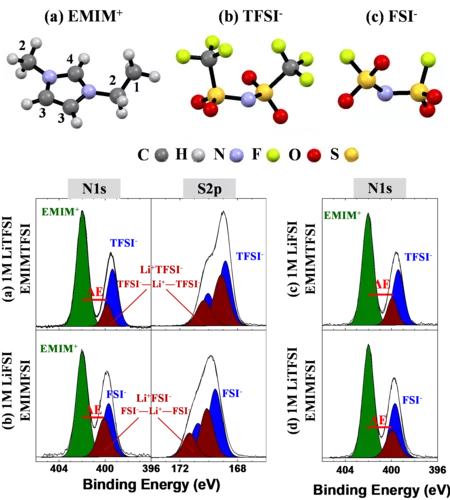
Li-ion solvation in TFSI and FSI - based ionic liquid electrolytes probed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
We demonstrate the capability of conventional laboratory XPS to determine the anions solvation shell of Li+ cation within 1M of LiTFSI and 1M of LiFSI salts dissolved in (EMIM+-FSI-) and (EMIM+-TFSI-) ionic liquids. The binding energy difference between the N1s components originating from the EMIM+ cation and from TFSI- or FSI- anions, solvating the Li+, confirms that both TFSI- and FSI- contribute simultaneously to the Li+ solvation. Additionally, the degradation of the TFSI and FSI -based electrolytes under X-ray exposure is proved.
ETSON Workshop at PSI Towards Artificial Intelligence Informed Nuclear Safety Assessments
Data science (DS) and artificial intelligence (AI) methods opens up an immense range of new opportunities and challenges in the context of continuously enhancing the complex methodologies used as basis for nuclear safety assessments. To this aim, following discussions in the ETSON Technical Board on Reactor Safety, the PSI laboratory for reactor physics and thermal-hydraulics organized on October 20-21, 2022, an international workshop to review and discuss DS/AI within ETSON, the network of European research and expert organizations providing scientific support to national nuclear authorities. With close to 40 participants, the workshop, organized as a hybrid meeting, allowed to put in evidence that similarly as at PSI, a wide and growing range of developments with integration of DS/AI methods are currently taking place in order to complement and/or inform nuclear safety analysis methodologies.
Award winning work on high-resolution X-ray radiography methods for boiling experiments at high pressure.
Light Water Reactors (LWRs) such as the ones operating in Switzerland work at relatively high temperatures and pressures. As a consequence, thermal-hydraulics experiments investigating relevant LWRs phenomena at prototypical conditions require test sections with relatively thick steel walls. This poses significant challenges for the implementation of suitable instrumentation to capture phenomena of interest, such as the flow regimes during transition from liquid to steam. The characterization of flow regimes in the presence of boiling is rather complex, and their better understanding would allow to develop mathematical modeling tools that can be used to optimize equipment and better assess safety margins. To perform in-situ measurements of the boiling process under high-pressure conditions, the team of authors from PSI, ETH, and the University of Michigan has developed a new high-fidelity and high-speed imaging system based on x-ray radiography, which provides high-resolution details on the boiling process while being non-intrusive. Since the instrumentation is located outside of the test section, it has also the advantage that can be easily moved to take measurements in different region of the test sections.
PSI researcher Patrick Hemberger honored in the Rising Stars special issue in Energy & Fuels
To celebrate contributions of highly influential early and mid-career researchers in energy research, the journal Energy & Fuels established an annual recognition of Energy and Fuels Rising Stars.
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos elected as SPIE Fellow member
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos was elected as a 2022 SPIE Fellow Member for his contributions to coherent lensless imaging, including ptychography and X-ray nano-tomography. The distinction was awarded in the SPIE’s Optics & Photonics conference in San Diego, California.
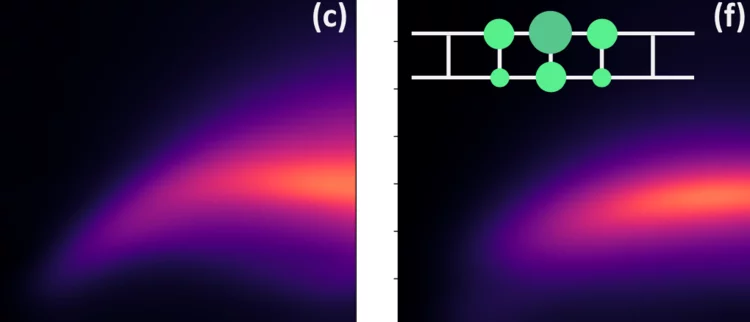
Emergence of spinons in layered trimer iridate Ba4Ir3O10
Spinons are well-known as the elementary excitations of one-dimensional antiferromagnetic chains, but means to realize spinons in higher dimensions is the subject of intense research. Here, we use resonant x-ray scattering to study the layered trimer iridate Ba4Ir3O10, which shows no magnetic order down to 0.2 K. An emergent one-dimensional spinon continuum is observed that can be well-described by XXZ spin-1/2 chains with magnetic exchange of ∼55 meV and a small Ising-like anisotropy. With 2% isovalent Sr doping ...
Clarifying the fate of collective metallic quantum states
Many complex metals exhibit collective states in which electrons appear to collaborate to generate novel and frequently functional behavior. These states develop when metals are cooled down to remove the effects of thermal fluctuations, enabling collective states in which electrons move coherently through the material. These collective electronic states are of tremendous importance because they are the foundation for many quantum states of interest such as unconventional superconductivity, frustrated magnetism, hidden order, as well as topologically non-trivial and electronic-nematic states.
Strong modulation of carrier effective mass in WTe2 via coherent lattice manipulation
Schematic ultrafast surface diffraction setup used for monitoring the crystal lattice in multiple directions.
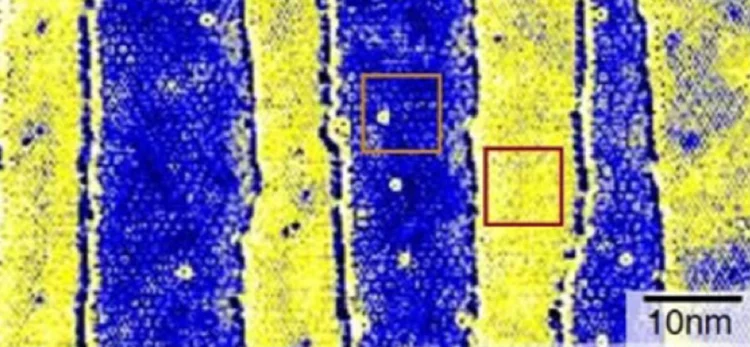
Discovery of Charge Order and Corresponding Edge State in Kagome Magnet FeGe
Kagome materials often host exotic quantum phases, including spin liquids, Chern gap, charge density wave, and superconductivity. Existing scanning microscopy studies of the kagome charge order have been limited to nonkagome surface layers. Here, we tunnel into the kagome lattice of FeGe to uncover features of the charge order. Our spectroscopic imaging identifies a 2 × 2 charge order in the magnetic kagome lattice, resembling that discovered in kagome superconductors. Spin mapping across steps of unit cell height demonstrates the existence of spin-polarized electrons with an antiferromagnetic stacking order.
Ready for SLS2.0: First magnet series measurement completed
The first magnet series consisting of 112 quadrupole electromagnets for SLS2.0 were measured to high precision using a special home-made rotating coils measurement system. This is an important step forward for the realization of SLS2.0, the upgrade of the Swiss Light Source (SLS) at PSI, and a milestone for the members of the Magnet Section in GFA.
IPW Young Investigator Award 2022
Dr. Francesca Borgna, former Marie Curie Fellow at the Center for Radiopharmaceutical Sciences awarded by the Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences in 2022 and gave the IPW Young Scientist lecture entitled: "Combination of Terbium-161 with Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists: a Potential Paradigm Shift for the Treatment of Neuroendocrine Neoplasm.
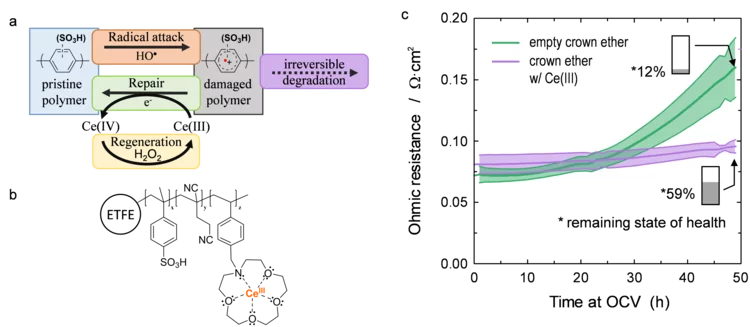
Damage-Repair Cycle in Hydrocarbon Based Membranes for Fuel Cells
The development of next generation fuel cell membranes based on aromatic hydrocarbon chemistry calls for a new antioxidant strategy to tackle radical induced membrane degradation. Although damage by radicals cannot be prevented, the formed aromatic intermediates can be repaired by a suitable additive. Fuel cell experiments demonstrate that the approach is viable on the device level and that repair is a catalytic mechanism.
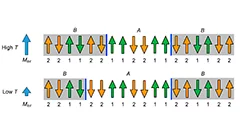
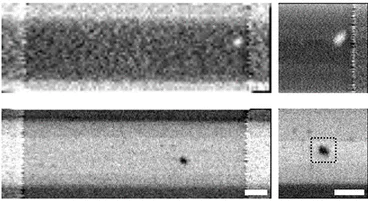
Nucleation of synthetic antiferromagnetic skyrmions
Magnetic skyrmions stabilized in synthetic antiferromagnets hold promise as nanoscale information carriers in novel non-volatile magnetic memory designs. In this work, scientists in a worldwide collaborative effort have demonstrated the electrically-induced nucleation of magnetic skyrmions in synthetic antiferromagnets, which is a vital stepping stone towards the applicability of these magnetic textures in devices.
Ferrimagnetic Skyrmions: fast and straight
Scientists have demonstrated, through magnetic X-ray microscopy, that magnetic skyrmions stabilized in ferrimagnetic heterostructures can be displaced by electrical currents at high velocities, and exhibit low deflection angles, proving that ferrimagnetic skyrmions are good candidates for fast skyrmionic devices.
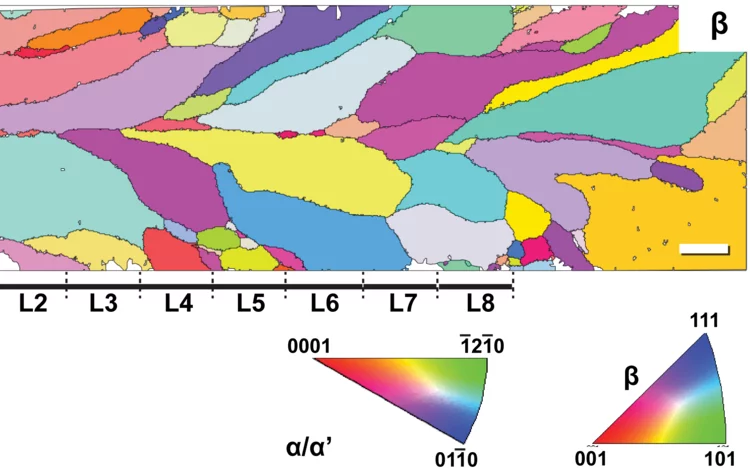
In situ alloying during additive manufacturing
In situ alloying is an effective method to engineer microstructures of additively manufactured Ti6Al4V3Fe alloys.
Alexander Grimm wins 2022 Nicholas Kurti prize
We are happy to announce that Alex has been awarded the 2022 Nicholas Kurti Science prize. The prize recognises his work on non-linear effects in Josephson junctions for quantum information processing.
Two types of charge order with distinct interplay with superconductivity in the kagome material CsV3Sb5
The kagome metals of the family AV3Sb5, featuring a unique structural motif, harbor an array of intriguing phenomena such as chiral charge order and superconductivity. CsV3Sb5 is of particular interest because it displays a double superconducting dome in the region of the temperature-pressure phase diagram where charge order is still present. However, the microscopic origin of such an unusual behavior remains an unsolved issue. Here, to address it, we combine high-pressure, low-temperature muon spin relaxation/rotation with first-principles calculations. We observe ....
Crossover of high-energy spin fluctuations from collective triplons to localized magnetic excitations in Sr14−xCaxCu24O41 ladder
We studied the magnetic excitations in the quasi-one-dimensional (q-1D) ladder subsystem of Sr14−xCaxCu24O41 (SCCO) using Cu L3-edge resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). By comparing momentum-resolved RIXS spectra with high (x = 12.2) and without (x = 0) Ca content, we track the evolution of the magnetic excitations from collective two-triplon (2 T) excitations (x = 0) to weakly- dispersive gapped modes at an energy of 280 meV (x = 12.2)...
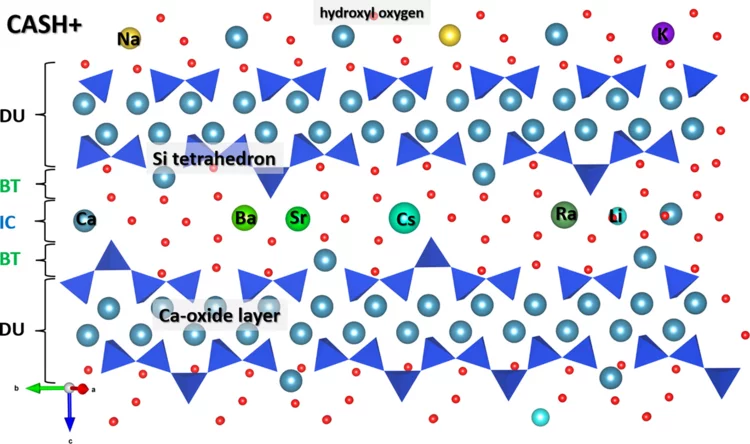
CASH+ solid solution cement model
A new incrementally extendable thermodynamic model, CASH+, was developed, aimed at accurately describing equilibrium composition, solubility, and elemental uptake of C-A-S-H gel-like phases at varying chemical conditions in cement systems. Cement is widely used as matrix and backfill for low and intermediate level waste. Calcium-Aluminum-Silicate Hydrates (C-A-S-H) are the most important binding phases in cement. They are also responsible for the initial entrapment of radionuclides via sorption or solid solution formation mechanisms. Therefore, the thermodynamic modelling of C-A-S-H stability, solubility and interaction with radionuclides in cement porewater is crucial for understanding hydration, blending, degradation of cement-based materials and for the performance assessment of cementitious repositories.
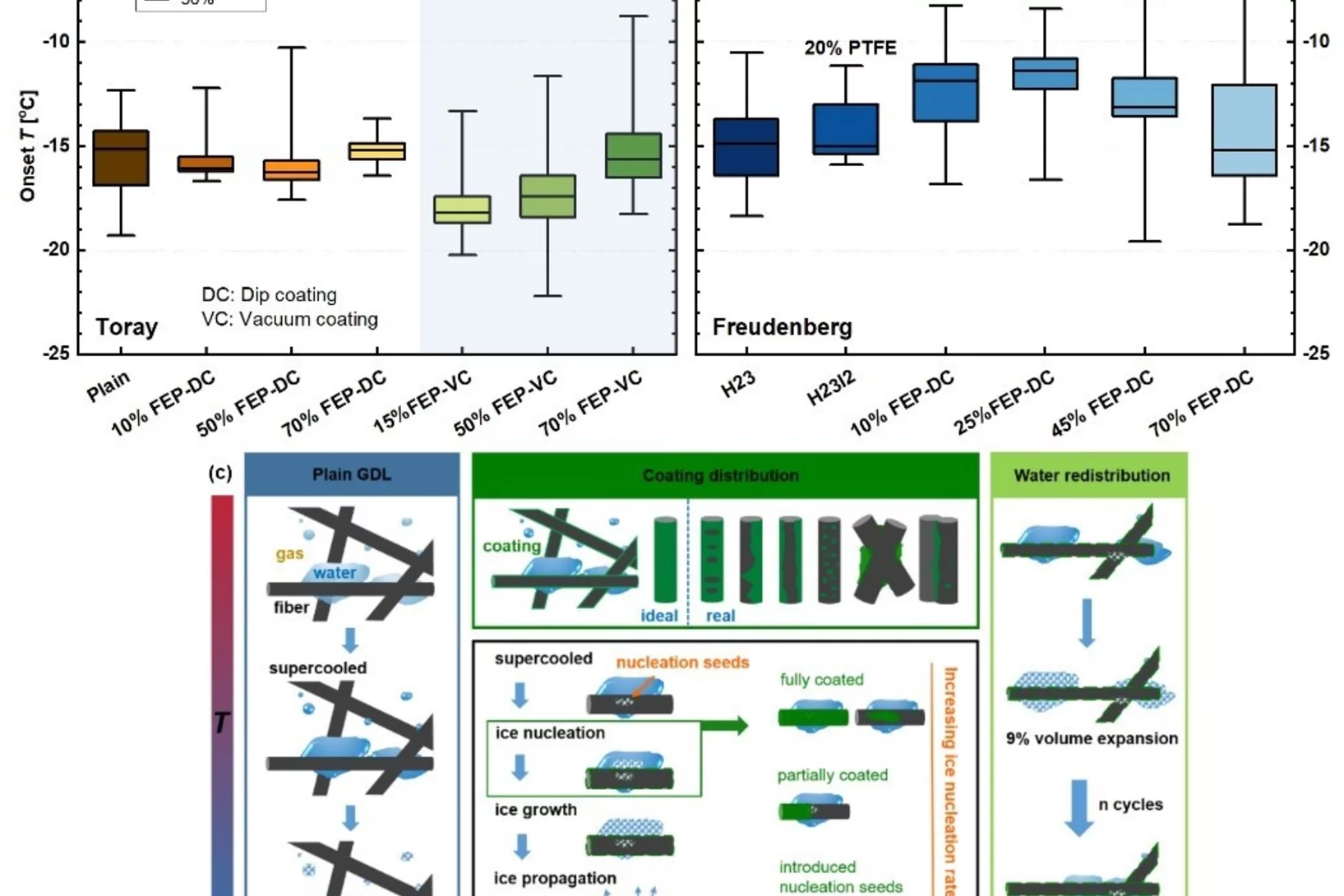
The Effects of Hydrophobicity Treatment of Gas Diffusion Layer on Ice Crystallization in PEFCs
Water management is crucial to the successful cold-start in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs). The sudden freeze of supercooled water blocks the reactant gas in the cathode and causes rapid voltage failure. In this work, we statistically evaluated the effects of the gas diffusion layer (GDL) substrate, size, saturation, and the coating loads and methods of hydrophobic polymer on the freezing probability of supercooled water by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC).