SINQ
EU grants 14 million to Swiss Researchers
A team with three researchers from the ETH Domain has been awarded a prestigious EU grant. Today, they received the contract signed by the EU confirming the extraordinary 14 million euros funding. With it, they will investigate quantum effects which could become the backbone of future electronics.
Making the impossible possible
Use of multiferroic materials promises more energy-efficient computers because in these, an electric field would suffice to achieve magnetic data storage. Researchers at PSI have now made such a material suitable for computer operating temperatures.
Material from PSI helps to check inconsistencies in the Big Bang theory
Shortly after the Big Bang, radioactive Beryllium-7 atoms were formed, which today, throughout the universe, they have long since decayed. A sample of beryllium-7 artificially produced at PSI has now helped researchers to better understand the first minutes of the universe.
Imaging the inside of injection needles with neutrons
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, the University of Basel and Roche have used neutron imaging to investigate why cool storage is crucial for syringes pre-filled with a liquid medication.
Imaging at Paul Scherrer Intitute helps to increase production at ABB site in Aargau
The ABB facility in Wettingen got practical recommendations on increasing production of ceramic components. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI examined the components by means of neutron imaging. With the help of these images, ABB employees were able to see where there is still potential for process optimisation. This feasibility study was funded by the Hightech Zentrum Aargau.
More than a prototype
Jean-Baptiste Mosset, winner of a Founder Fellowship at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, wants to commercialise a neutron detector to spot plutonium and uranium.
Still no sign of dark matter
No evidence of dark matter made of axions – result of an experiment at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI further constrains theories about the nature of dark matter.
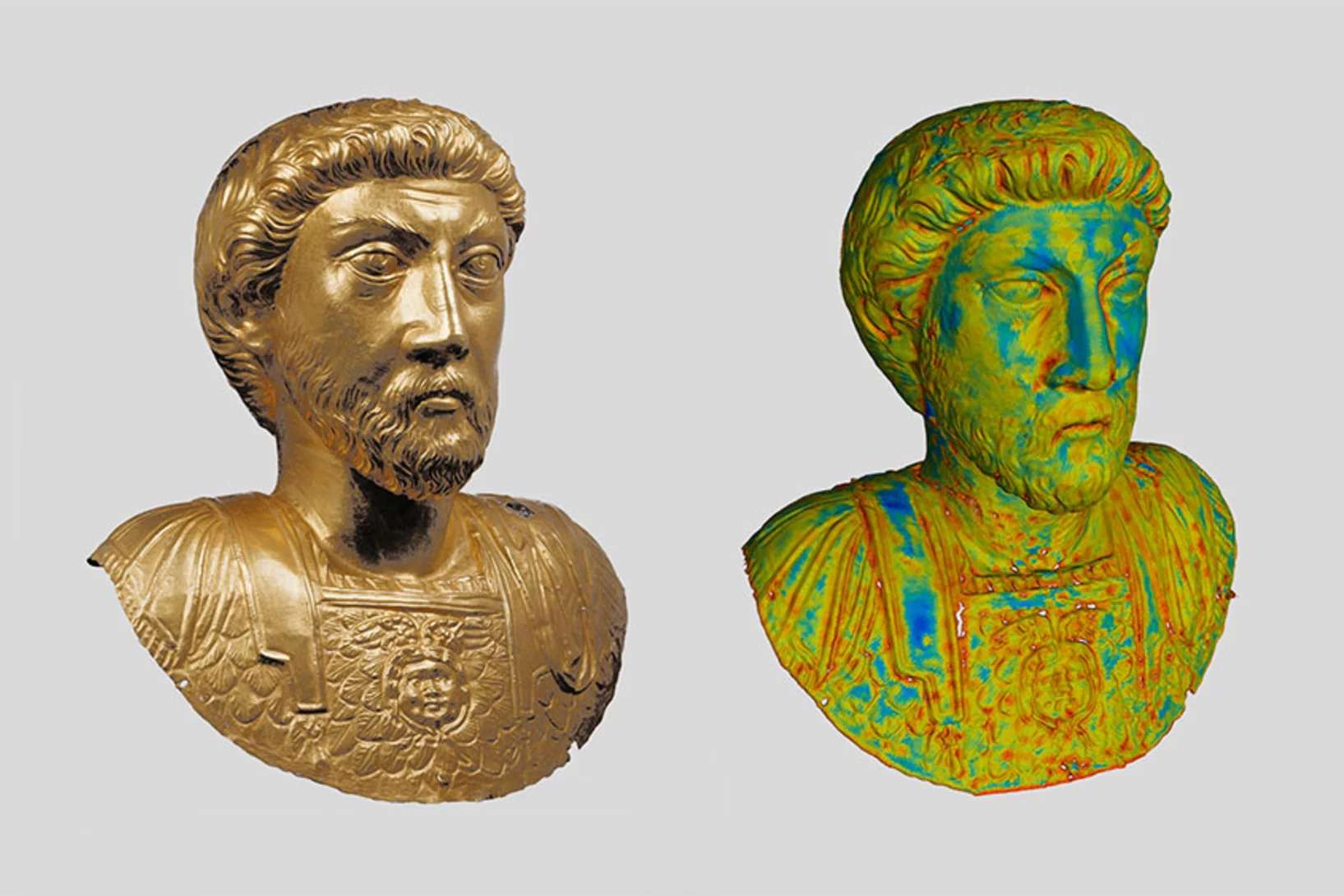
From golden emperor to filled Buddha
Ancient metal objects are illuminated by neutrons at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI. This enables researchers to discover what is hidden inside them, how they were made and how they can be preserved.
X-ray and neutron imaging for palaeontologists and archaeologists
Federica Marone illuminates objects with high-intensity X-ray beams, Eberhard Lehmann with neutrons. Both have used their methods to give palaeontologists and archaeologists a new view into the past.
From the garage to the world
In 1999, PSI researchers founded the spin-off firm SwissNeutronics. Today the company has a staff of 15, sells high-precision components to research institutions all over the world, and still is based in the small town of Klingnau – not far from PSI.