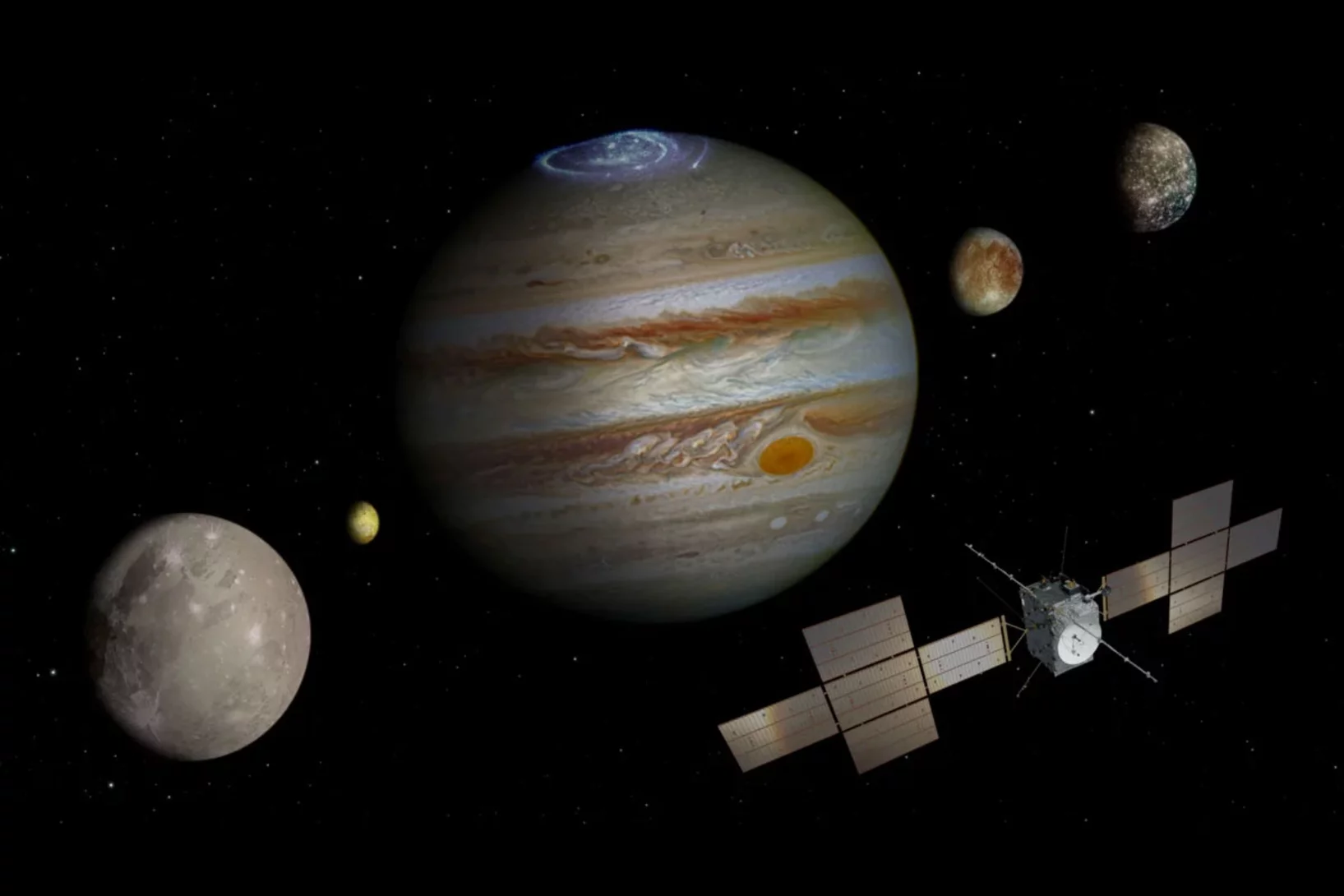
Jupiter mission to explore conditions conducive to life
Ganymede, Callisto and Europa: Jupiter’s icy moons are the destination of the upcoming ESA mission. On board: a high-tech detector developed by PSI.
How football-shaped molecules occur in the universe
An international research team reveals how fullerene is formed in the universe.
How vision begins
PSI scientists have discovered the very first step occurring in the eye when light hits the retina.
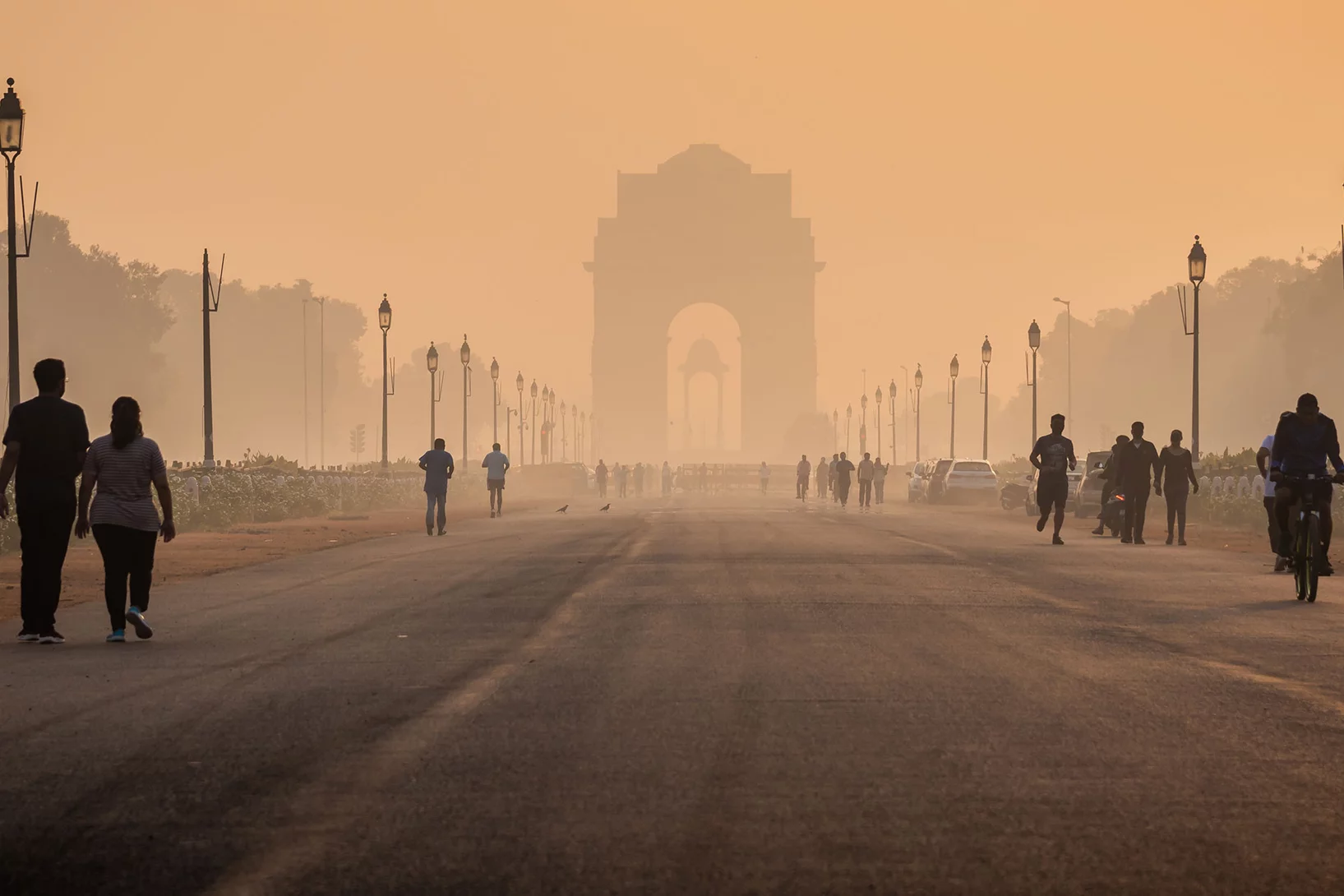
Extreme nighttime pollution in New Delhi air explained
PSI researchers find the cause of high nighttime air pollution in New Delhi
Using light to switch drugs on and off
PSI researchers record a molecular film of a cancer drug fitted with a photoswitch. This opens new insights for drug developers.
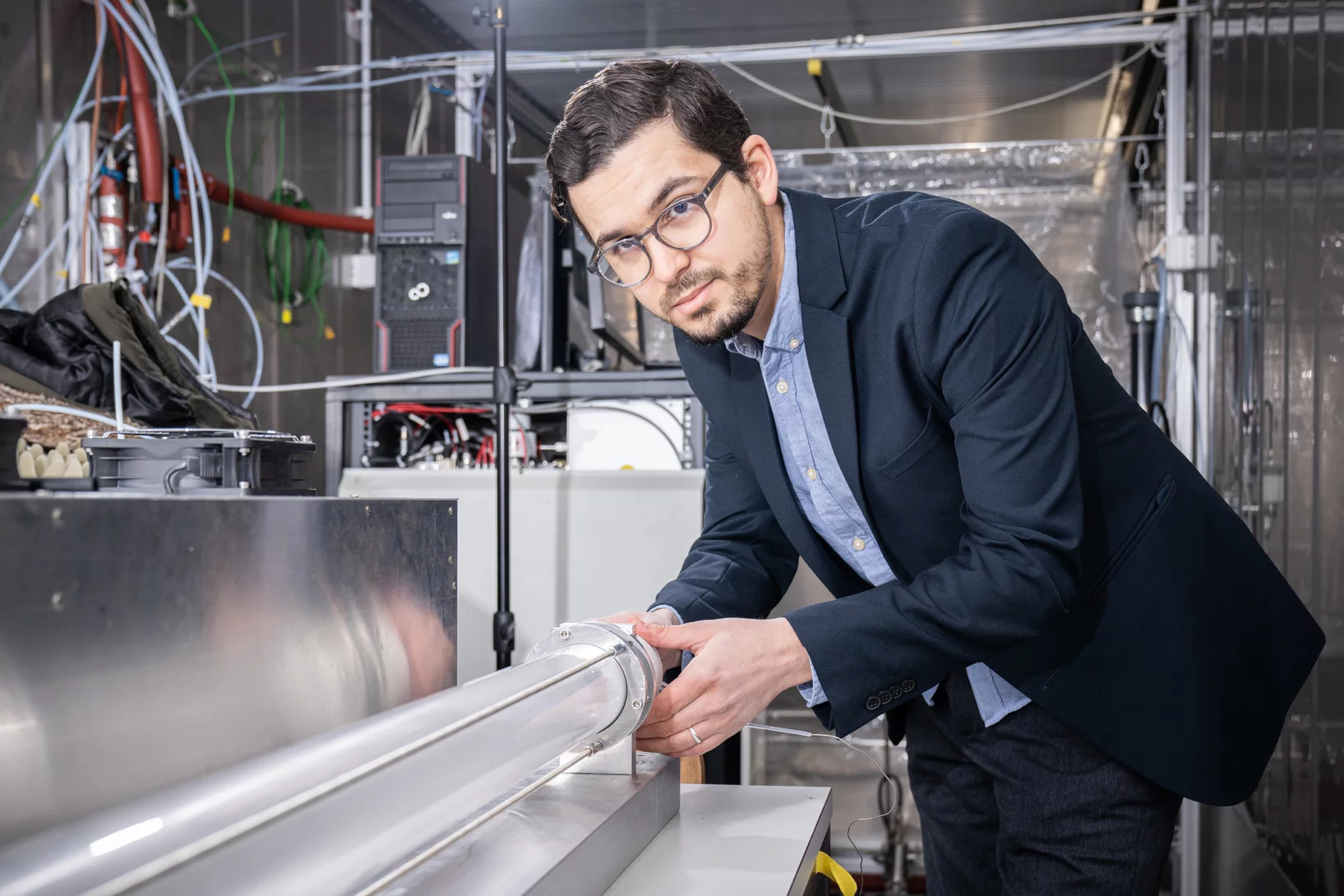
A greener alternative for aviation fuel
Air travel with no carbon footprint – PSI and the Metafuels AG develop a new technology to produce sustainable aviation fuel.
Swiss PIC to support Swiss photonics industry
The technology transfer centre Swiss PIC will be located in the Park Innovaare.
Further optimising car brakes
Research scientists at PSI and ANAXAM use neutrons to look inside brake callipers and identify potential ways of reducing CO2 emissions.
3.1 million in funding for new research projects at PSI
The PSI scientists Zurab Guguchia and Kirsten Schnorr are to receive grants totalling CHF 3.1 million from the Swiss National Science Foundation for ground-breaking projects.
New materials for the computer of the future
Researchers are identifying and studying material compounds whose unique properties could lead to the development of novel types of chip.
Paul Scherrer Institute and Apollo Health Ventures Launch Focal Biosciences
Newly established Focal Biosciences will focus on bringing together leading experts and scientific discoveries to harness cellular reprogramming in the fight against common age-related diseases.
Nanomaterial from the Middle Ages
Unlocking the secrets of Zwischgold at PSI.
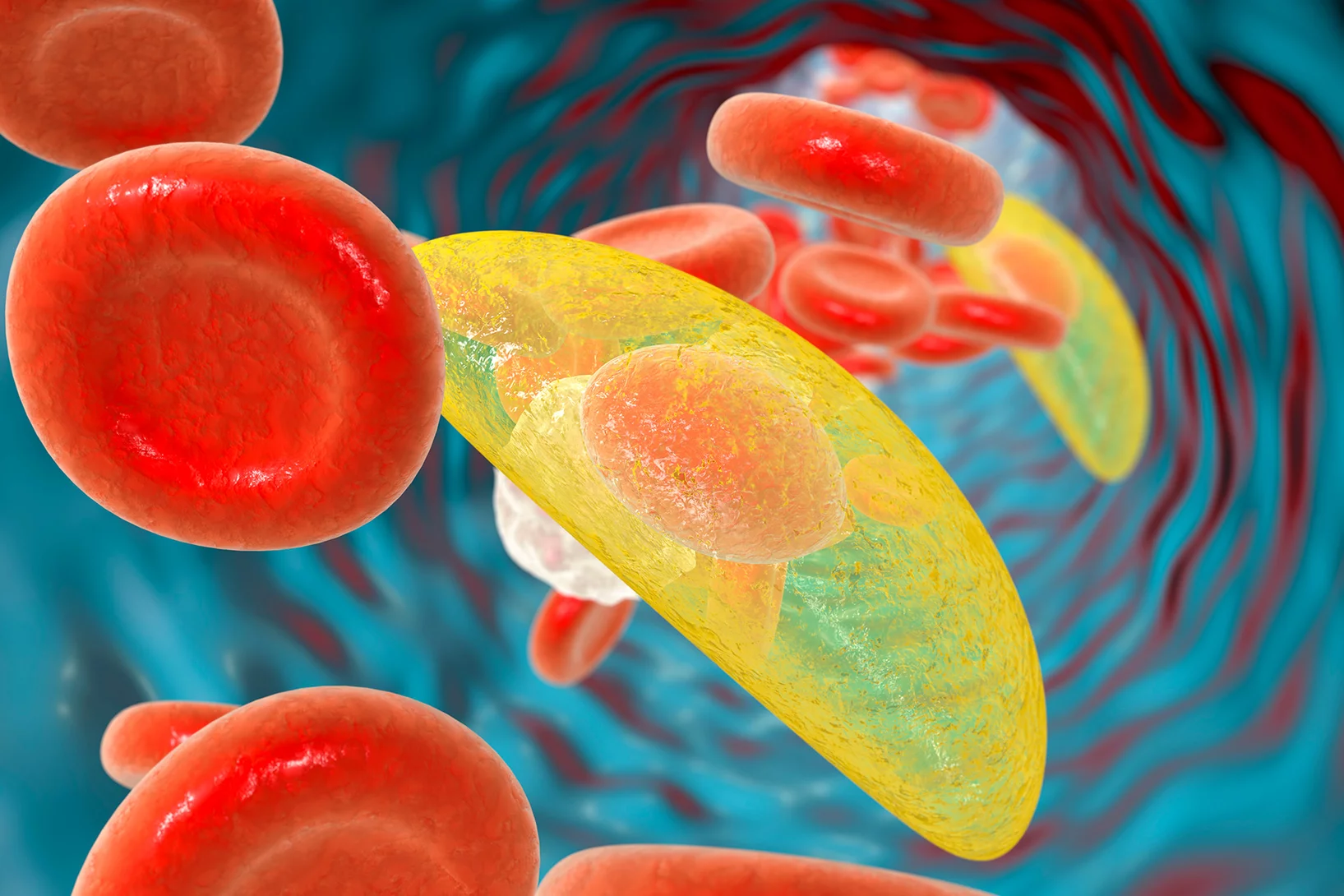
Making tumour diagnosis kinder to kidneys
Improved method thanks to a molecular trick
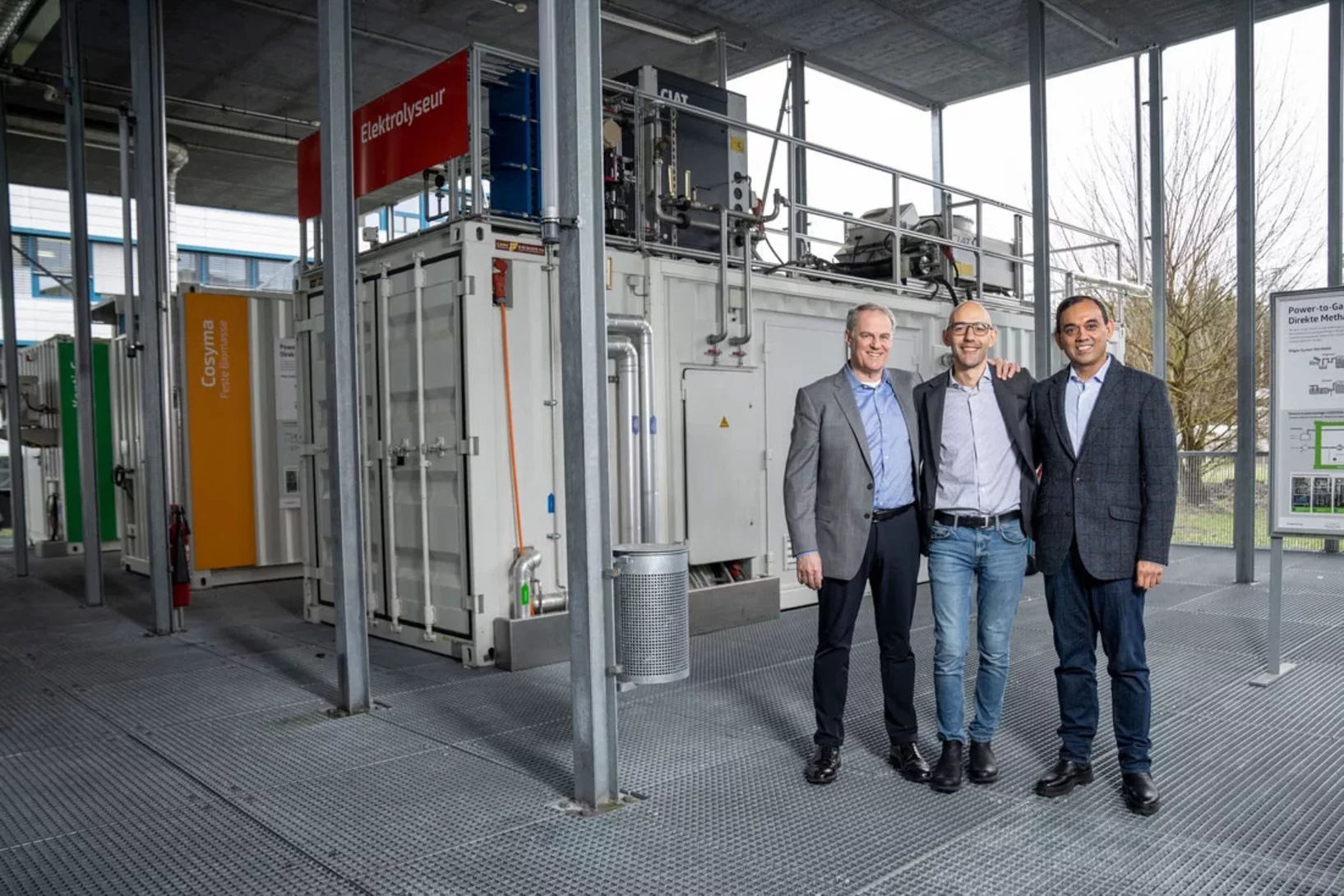
Combining forces for the energy transition
The Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and the start-up AlphaSYNT are piloting a new approach for storing energy in the form of methane gas.
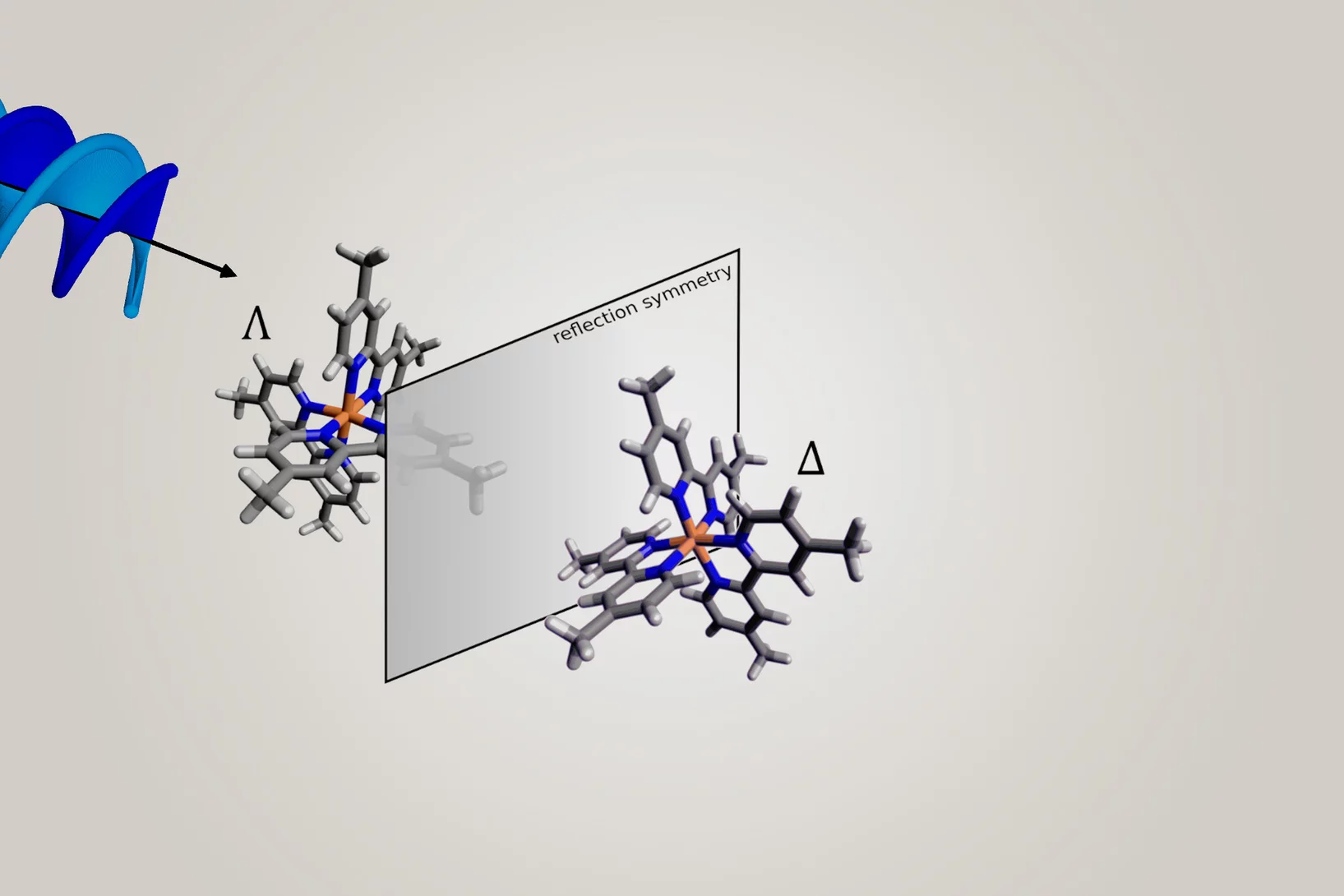
Making it easier to differentiate mirror-image molecules
Researchers have shown that mirror-image substances – so-called enantiomers – can be better distinguished using helical X-ray light.
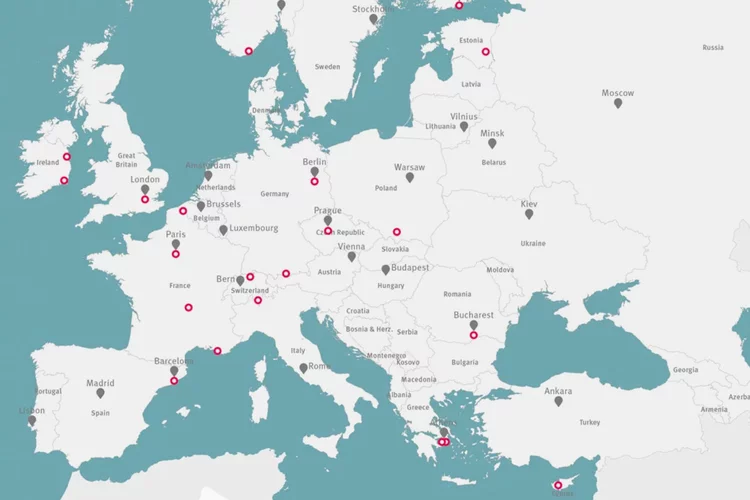
European map of aerosol pollution can help improve human health
Researchers have measured and determined the sources of aerosol pollution at 22 locations in Europe.
Visiting the researchers
New exhibition in the PSI Visitor Centre
How to find anti-cancer agents
PSI researchers have developed a new substance that disables a vital protein in the cell skeleton.
A look into the magnetic future
PSI researchers are the first to observe a specific behaviour of magnetic ice.
Novel X-ray lens facilitates glimpse into the nanoworld
PSI develops a revolutionary achromatic lens for X-rays.
New, better coronavirus rapid test
The test identifies different virus variants and improves disease prognosis.
Towards compact quantum computers, thanks to topology
In pursuit of particularly stable quantum bits, researchers have closely examined the electron distribution in two semiconductors.
More insight into how vision works
PSI scientists have shed light on the structure of an important component of the eye: CNG ion channels whose job is to relay optical signals to the brain.
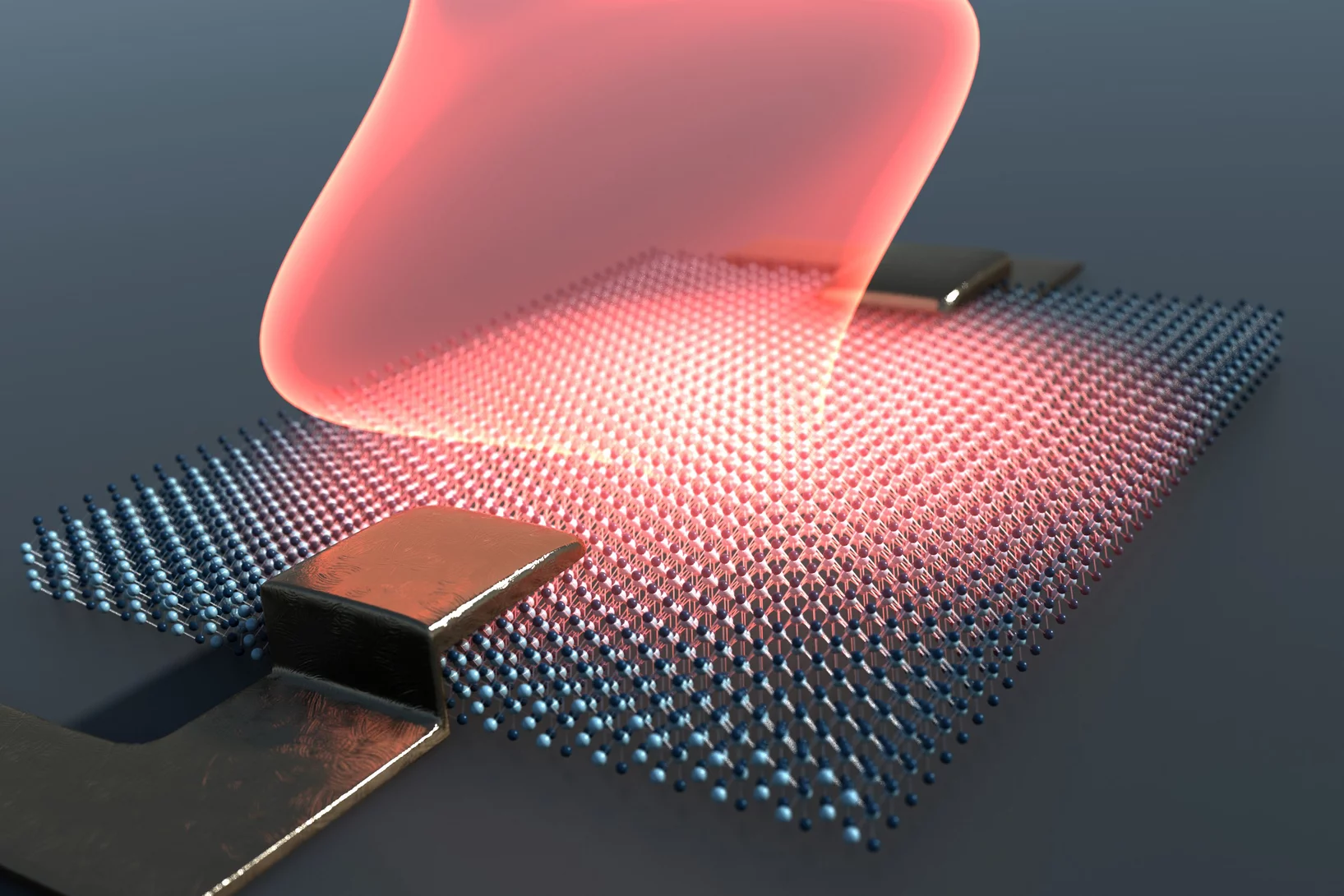
Semiconductors reach the quantum world
Boosted with superconductivity: Semiconductor technology can get a new twist by exploiting quantum effects in superconductors.
KSB and PSI forge a common research path
Kantonsspital Baden and the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have signed a cooperation agreement.
Effective combination cancer treatment
Combining two chemotherapeutic drugs inhibits tumour growth.
Blue hydrogen can help protect the climate
The key is to eliminate methane leaks.
Proton therapy: a success story that started 25 years ago
25 November 1996: a world first for PSI’s Center for Proton Therapy in treating a cancer patient using the spot-scanning technique.
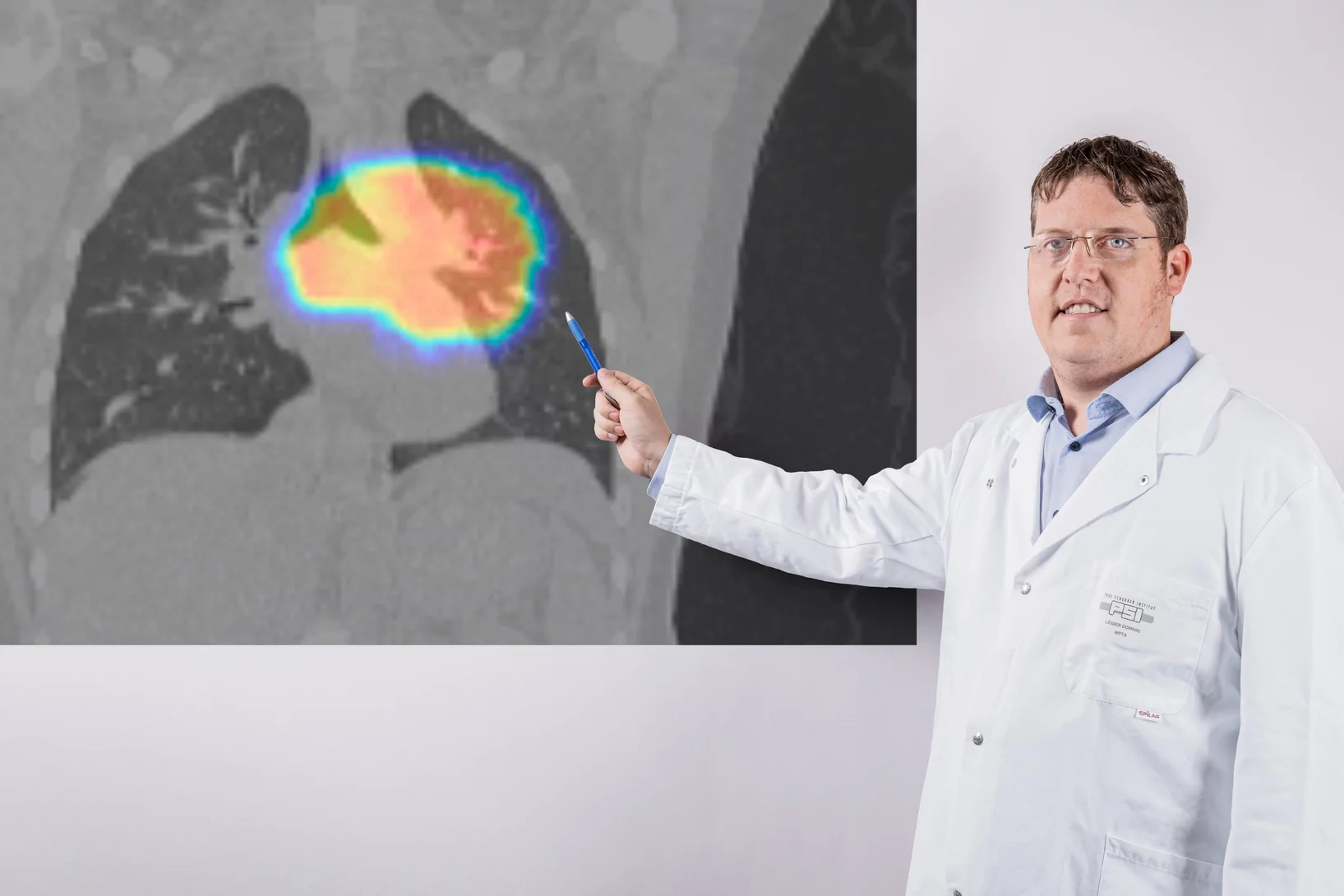
A first for Switzerland: proton therapy to treat lung cancer
On 9 November 2021 a lung cancer patient was given proton therapy at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI for the first time in Switzerland.
Carbon dioxide can be turned into a valuable resource
New study explores methods for using waste gas efficiently.
Ultrafast control of quantum materials
Using light to fundamentally change the properties of solids
New active agent against parasites
PSI researchers identify potential active agent against several unicellular parasites – including the pathogens that cause malaria and toxoplasmosis.
Protein distancing
PSI researchers have developed a new method to attach proteins to the surface of virus-like particles.
Novel and emerging medical radionuclides
Better treatment for disseminated cancer.
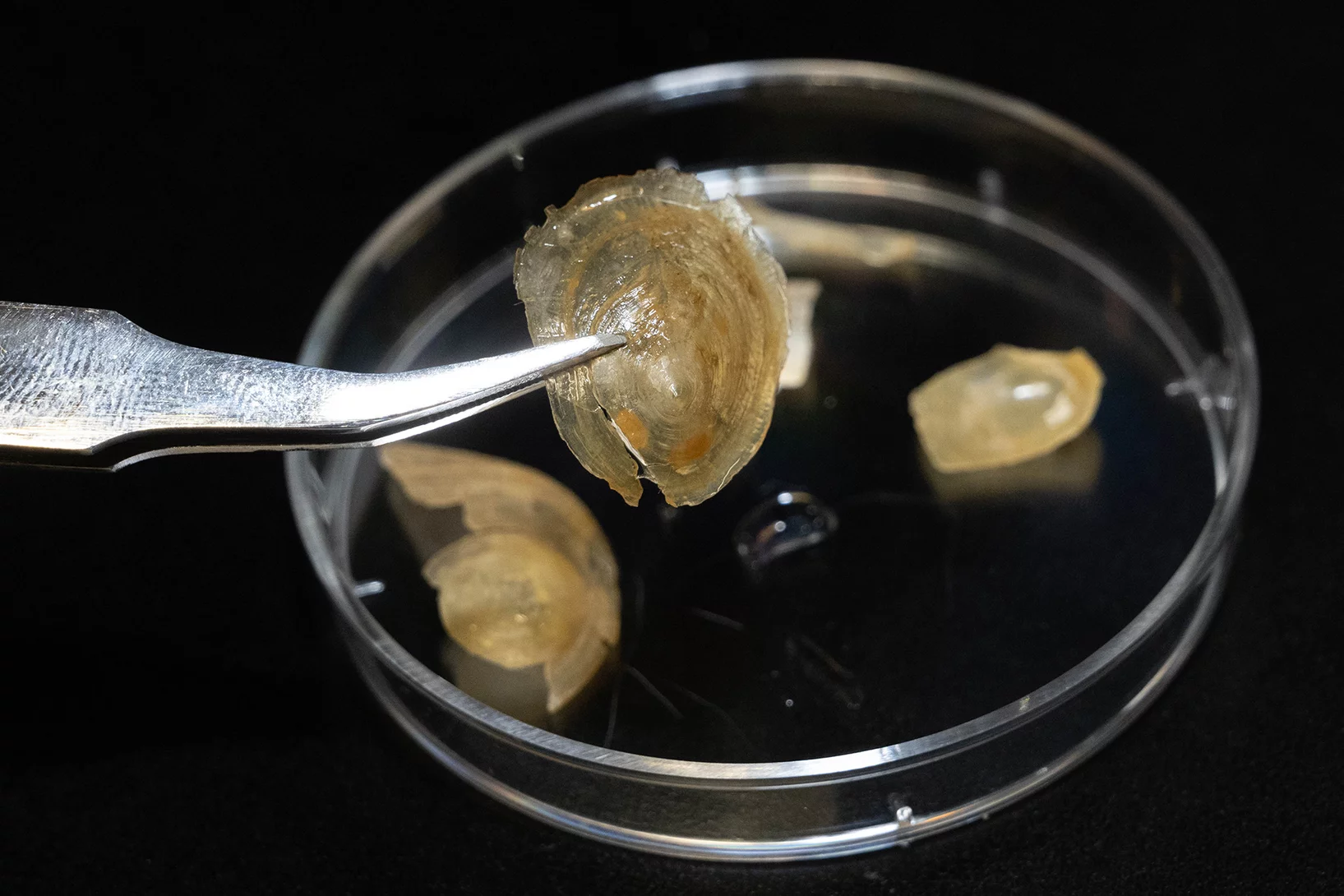
The mystery of the flexible shell
Why the shell of a marine animal is soft in water but hard in air.
Understanding the physics in new metals
Together with international colleagues, PSI researchers have now been able to make correlated metals more readily usable for applications in superconductivity, data processing, and quantum computers.
New research division at PSI points to the future of data
PSI is establishing a new research division: Scientific Computing, Theory, and Data.
How catalysts age
Catalysts used in industry change their material structure over the years. Using a new method, PSI researchers have now studied this on the nanoscale.
Cell cytoskeleton as target for new active agents
Using a combination of computer simulations and laboratory experiments, PSI researchers have identified new binding sites for active agents on the vital protein tubulin.
Improving the resilience of Switzerland’s energy supply
The SURE research project is up and running.
Uniquely sharp X-ray view
A new PSI method allows quantum-physical research on materials with the aid of X-ray lasers.
Aerosol formation in clouds
How chemical reactions in clouds can influence the global climate.
Particulates are more dangerous than previously thought
A precise look into the finest particles in the air shows how compounds harmful to human health are formed.
Switzerland's energy transition
Can Switzerland, as planned, reduce its CO2 emissions to zero by 2050? What is needed to achieve this? What could it cost?
Green fuels for aviation
In a new initiative, PSI and Empa want to jointly develop a process for producing kerosene from renewable resources.
Size of helium nucleus measured more precisely than ever before
In experiments at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, an international research collaboration has measured the radius of the atomic nucleus of helium five times more precisely than ever before. The new value can be used to test fundamental physical theories.
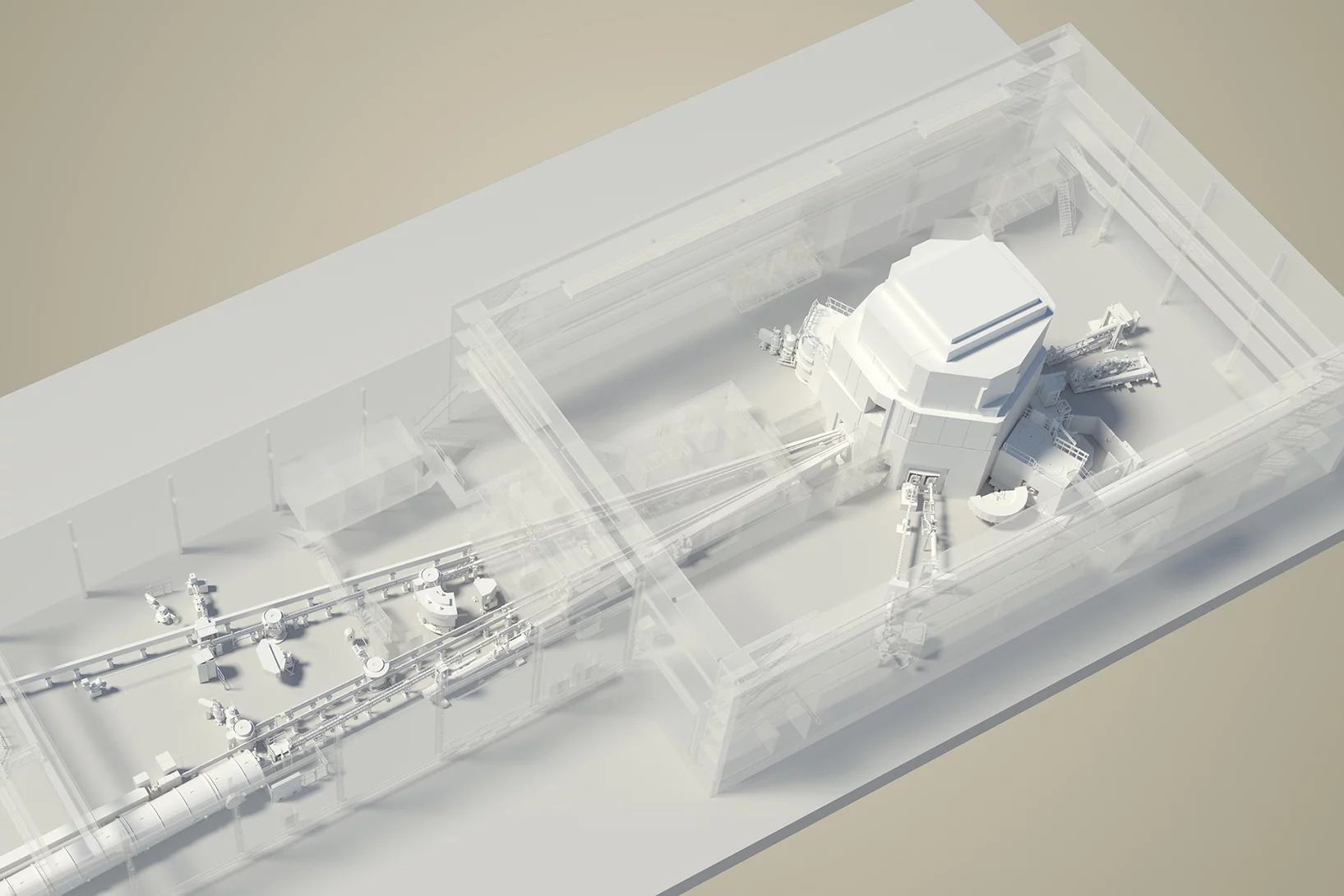
PSI equips the Swiss Light Source SLS for the future
Green light for SLS 2.0: The planned upgrade of the Swiss Light Source SLS can proceed; the funding is provided for within the framework of the ERI Dispatch for 2021-2024, which has been approved.
Which particulate air pollution poses the greatest health risk?
The composition of particulate matter can influence its harmfulness to human health just as much as the amount, PSI researchers show in a newly published study. Experiments and computational modelling showed that in Europe high concentrations of particulate matter harmful to human health occur mainly in metropolitan areas.