Show filters
Clean biogas for a successful energy transition
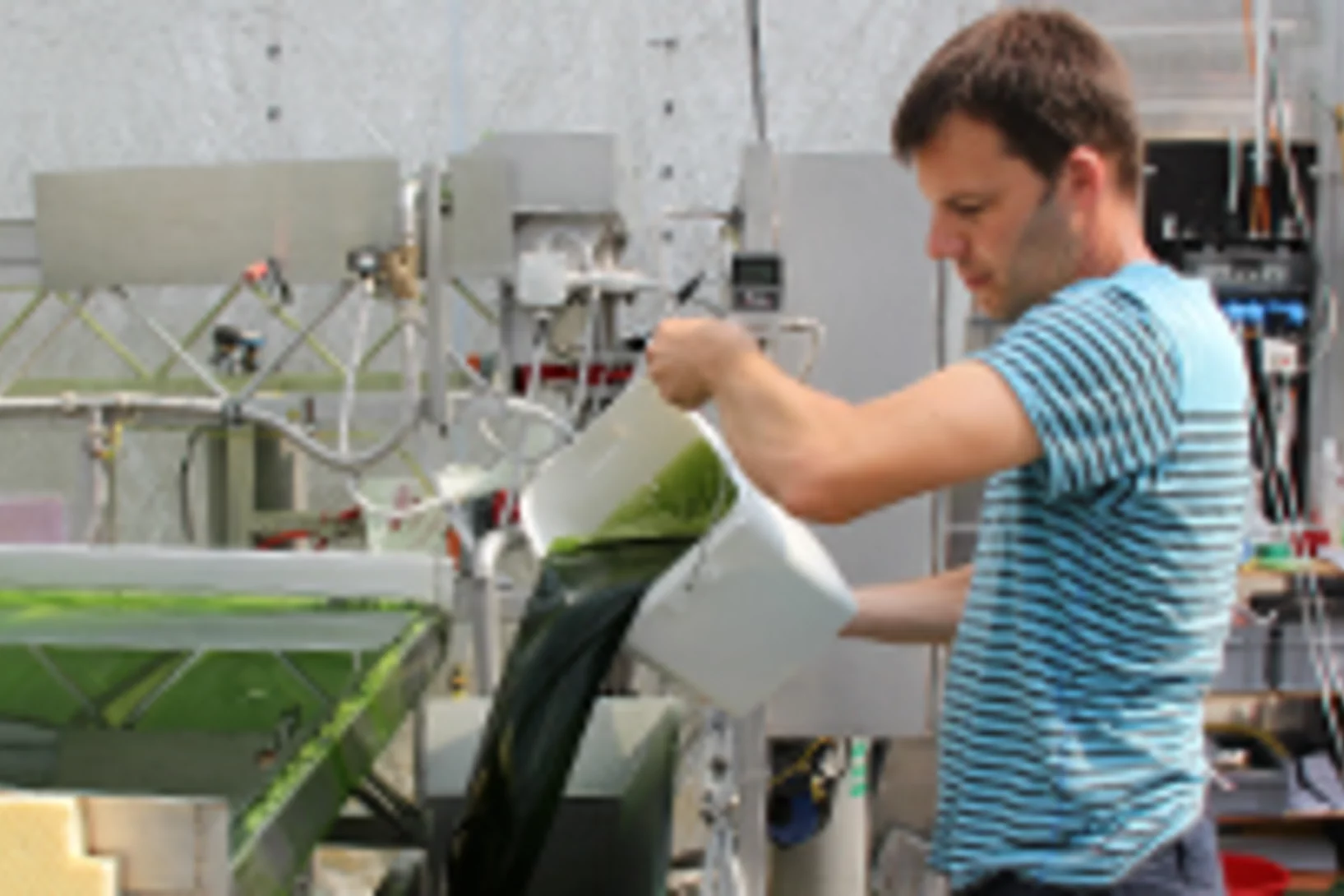
PSI researchers have set up camp at a biogas plant near Lucerne. Between meadows and gigantic fermenters, they are investigating how they can remove impurities from the biogas to make this energy source even more usable.
BATTERY 2030+ – large-scale European initiative for battery research starts up
Future batteries need to store more energy, have longer life, and be safer and more environmentally friendly than today's batteries. The European initiative BATTERY 2030+, in which PSI is participating, is intended to help achieve these goals.
Life cycle assessment of cars – new web tool helps consumers and researchers
Decision support for car buyers: Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have developed a web tool called the Carculator that can be used to compare the environmental performance of passenger cars in detail.
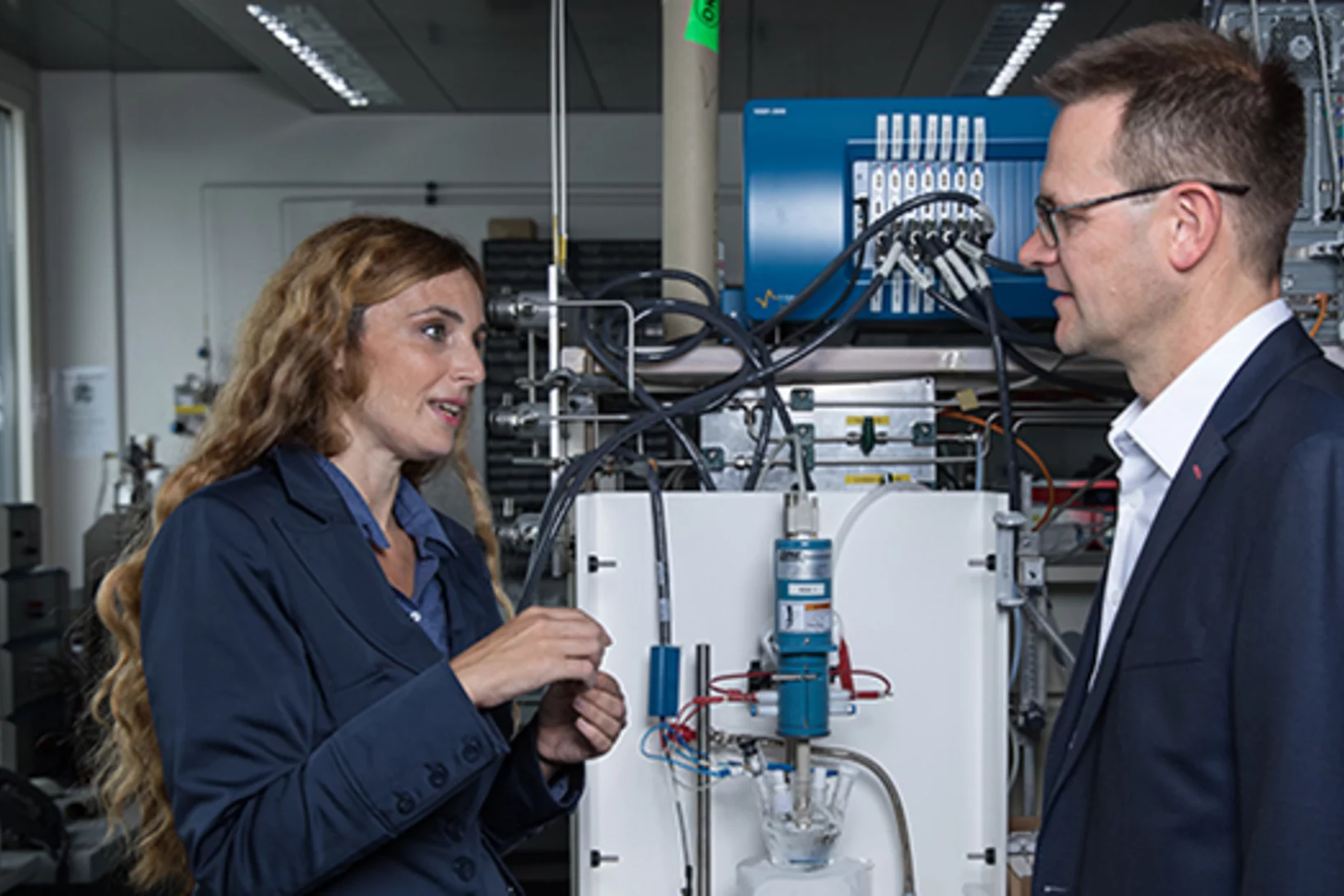
Long-term developments of energy pricing and consumption in industry
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, on behalf of a research project funded by the Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE), have studied how energy consumption by Swiss industry develops depending on energy prices. One result: Price increases for energy usually affect energy consumption only over the long term.
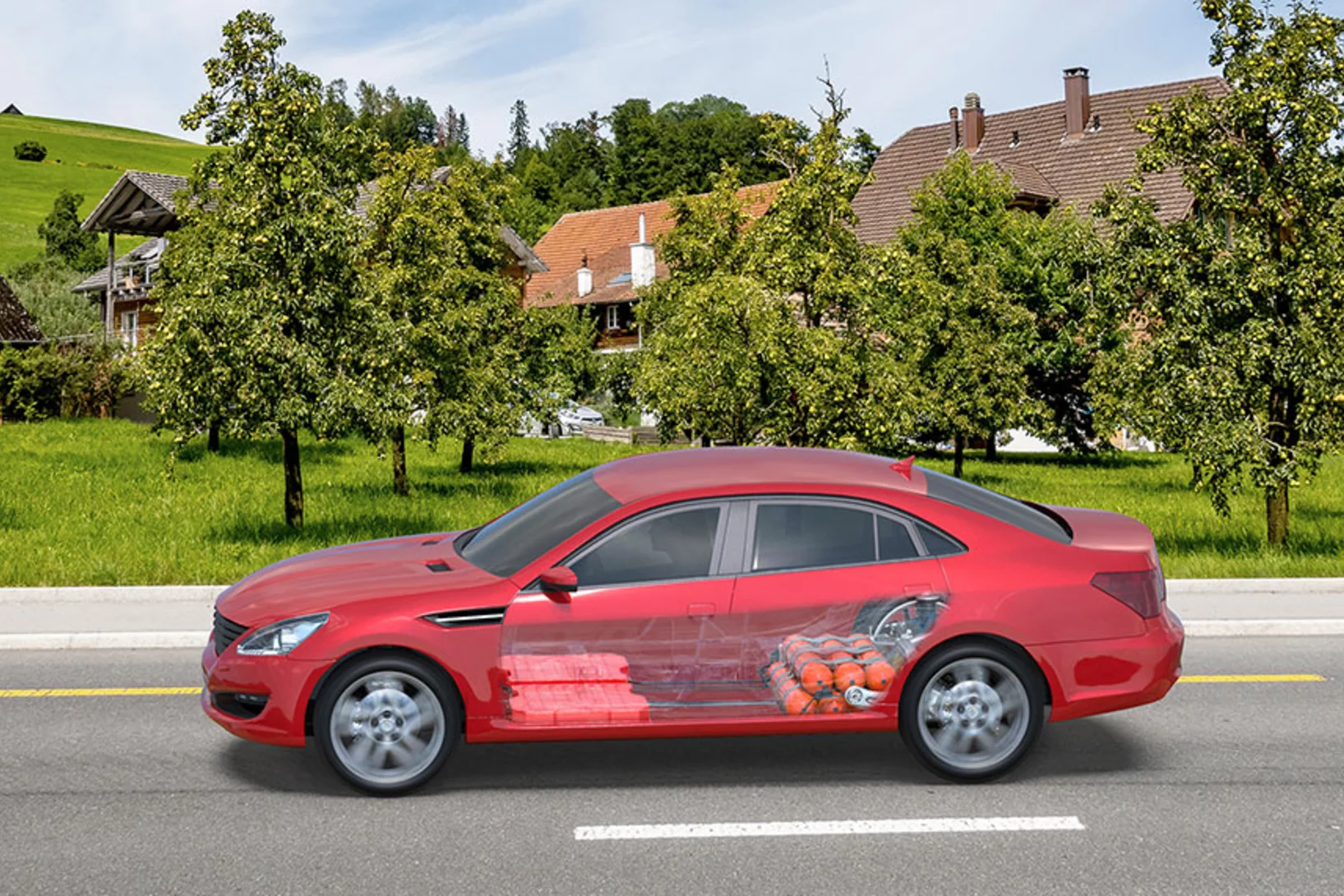
"Electric is already the right choice today"
An interview on automotive power systems with Christian Bauer, a scientist at PSI's Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis who specialises in life cycle and sustainability analyses.
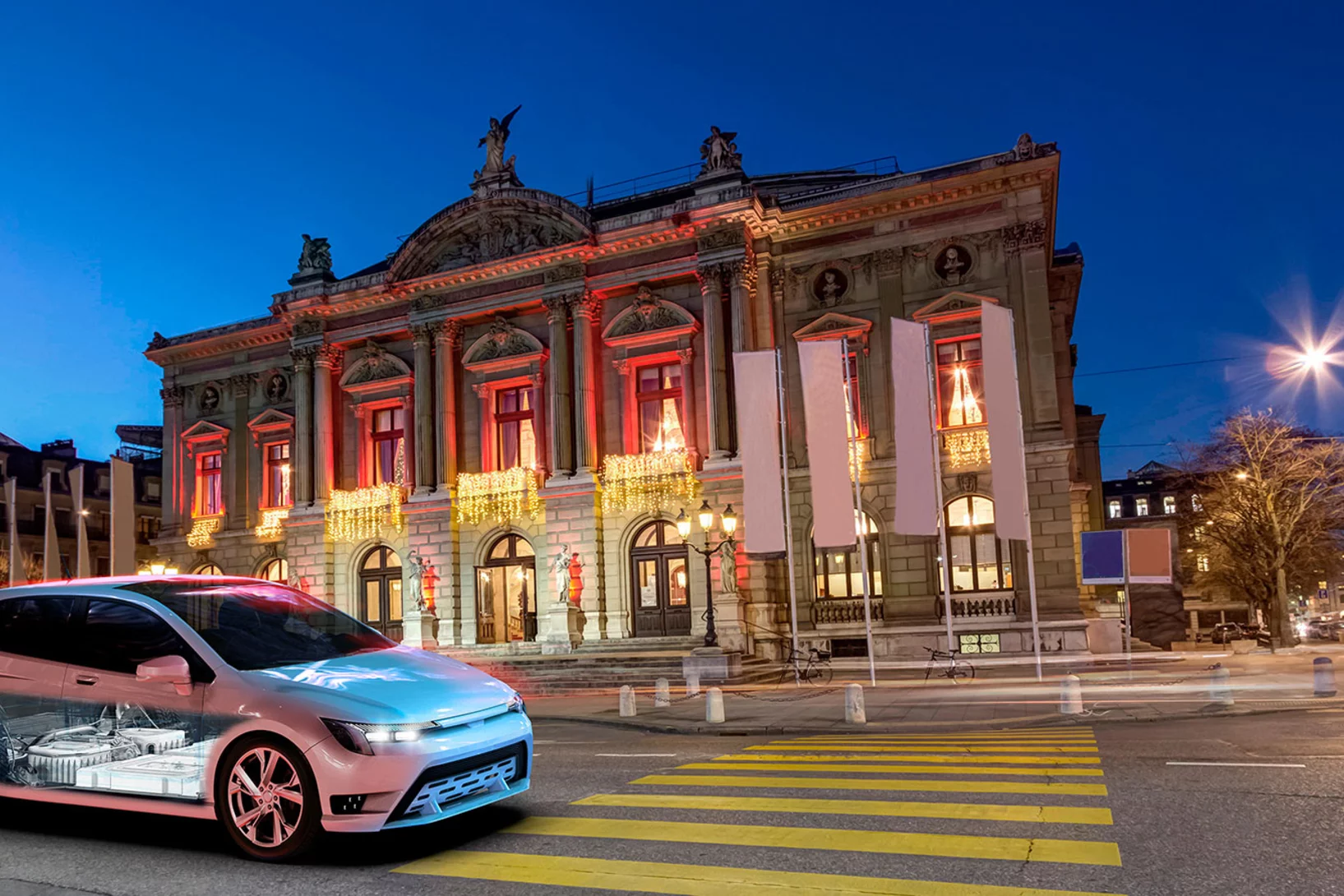
Make way for electric cars
Petrol, diesel, fuel cell or electric – which is the automobile of the future? A PSI study has examined the overall climate impact of various vehicle engines in use today and also projected it to the year 2040.
Toward better motors with X-ray light
Making Switzerland's road traffic fit for the future calls for research, first and foremost. In the large-scale research facilities of PSI, chemists and engineers are investigating how to improve the efficiency of motors and reduce their emissions.
"This is incredibly ambitious"
Every three years, the World Energy Council explores possible developments of the global energy system under different scenarios. Tom Kober, head of the Energy Economics Group in PSI’s Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis and one of the lead authors of the study, explains what the individual scenarios mean and how global warming could be mitigated.
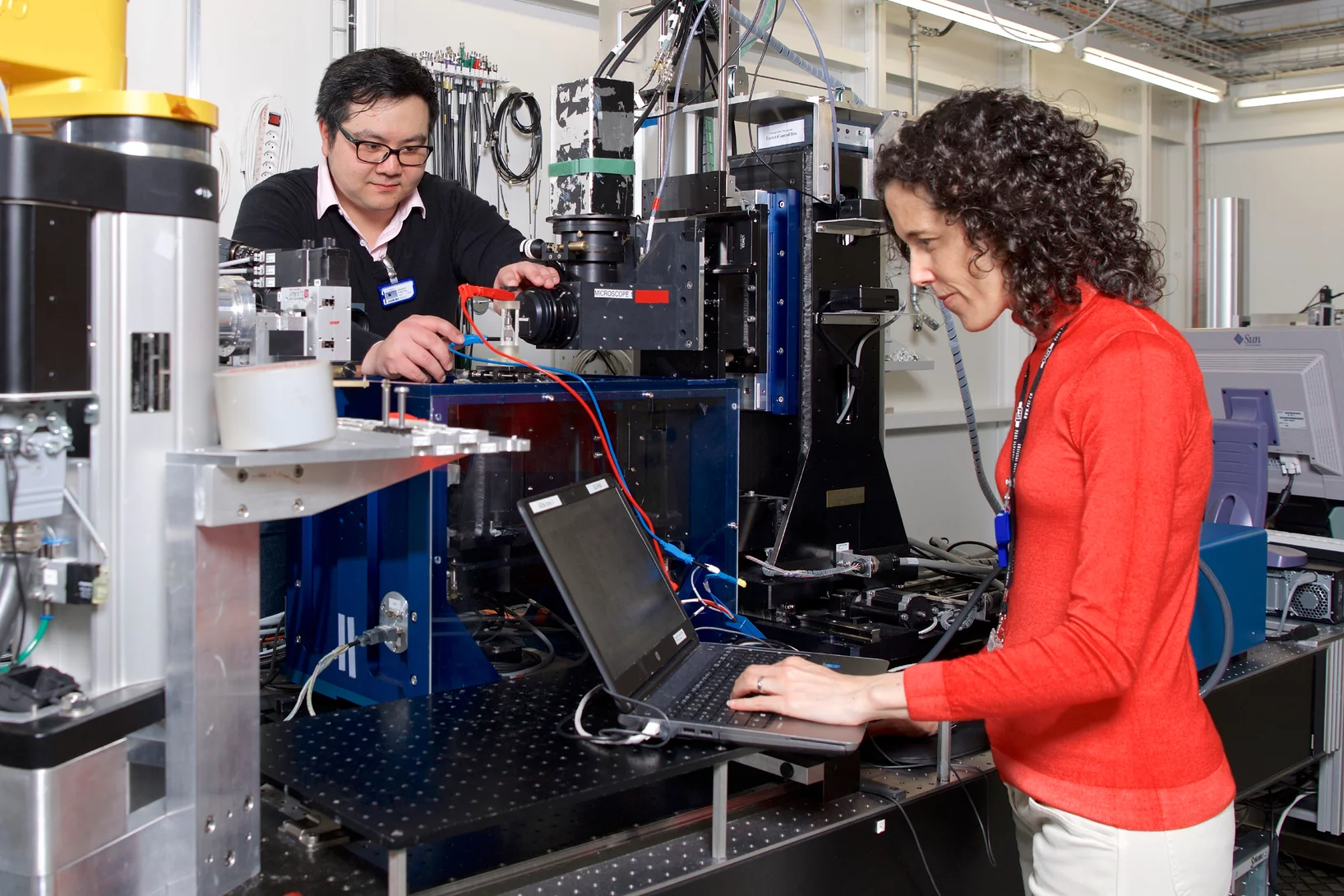
Observing solid-state batteries during deformation
PSI researchers have observed mechanical processes in solid-state batteries with unprecedented precision. Using X-ray tomography at the Swiss Light Source SLS, they discovered how fissures inside the batteries propagate. These insights can help to make batteries for electric cars or smartphones safer and more efficient.
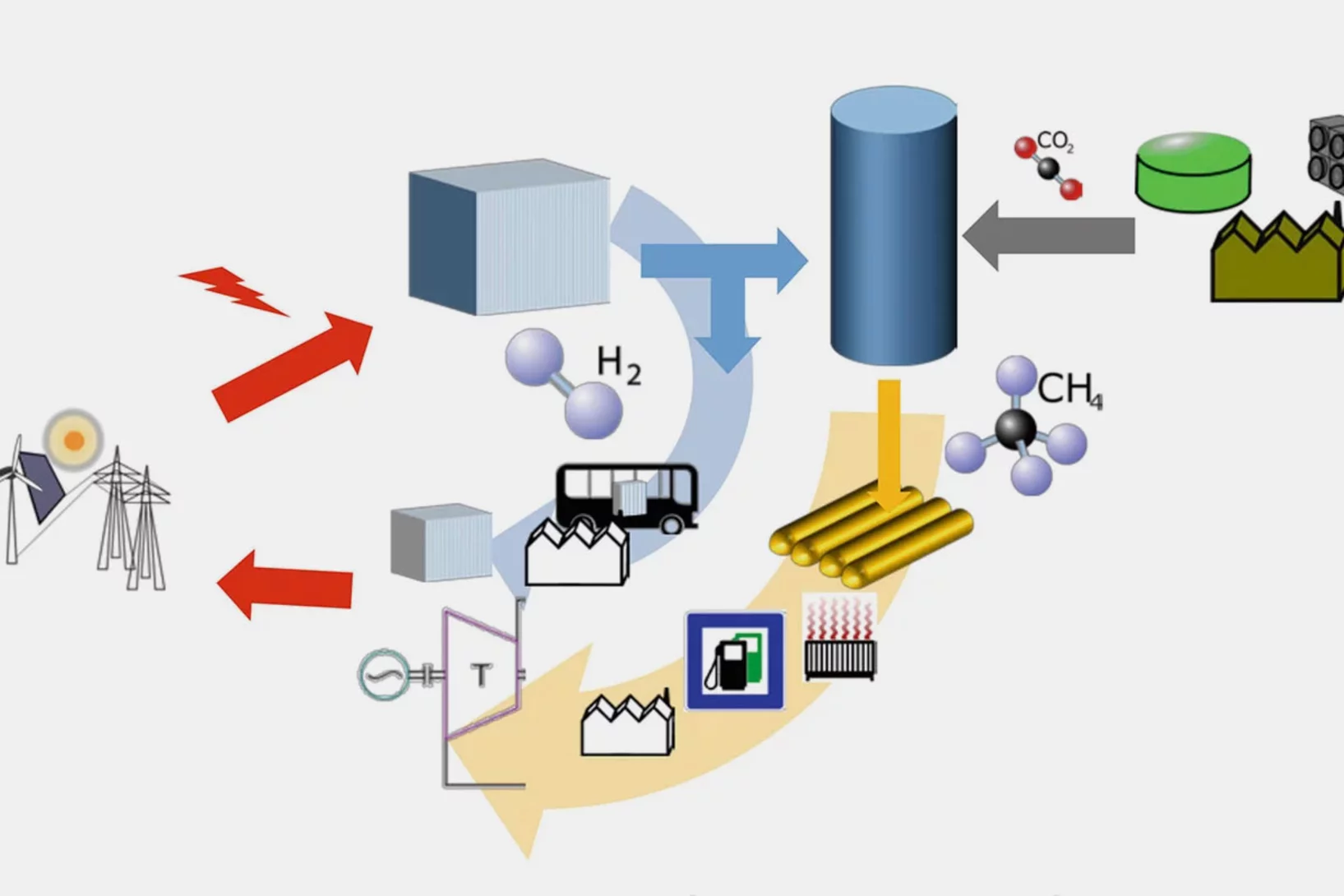
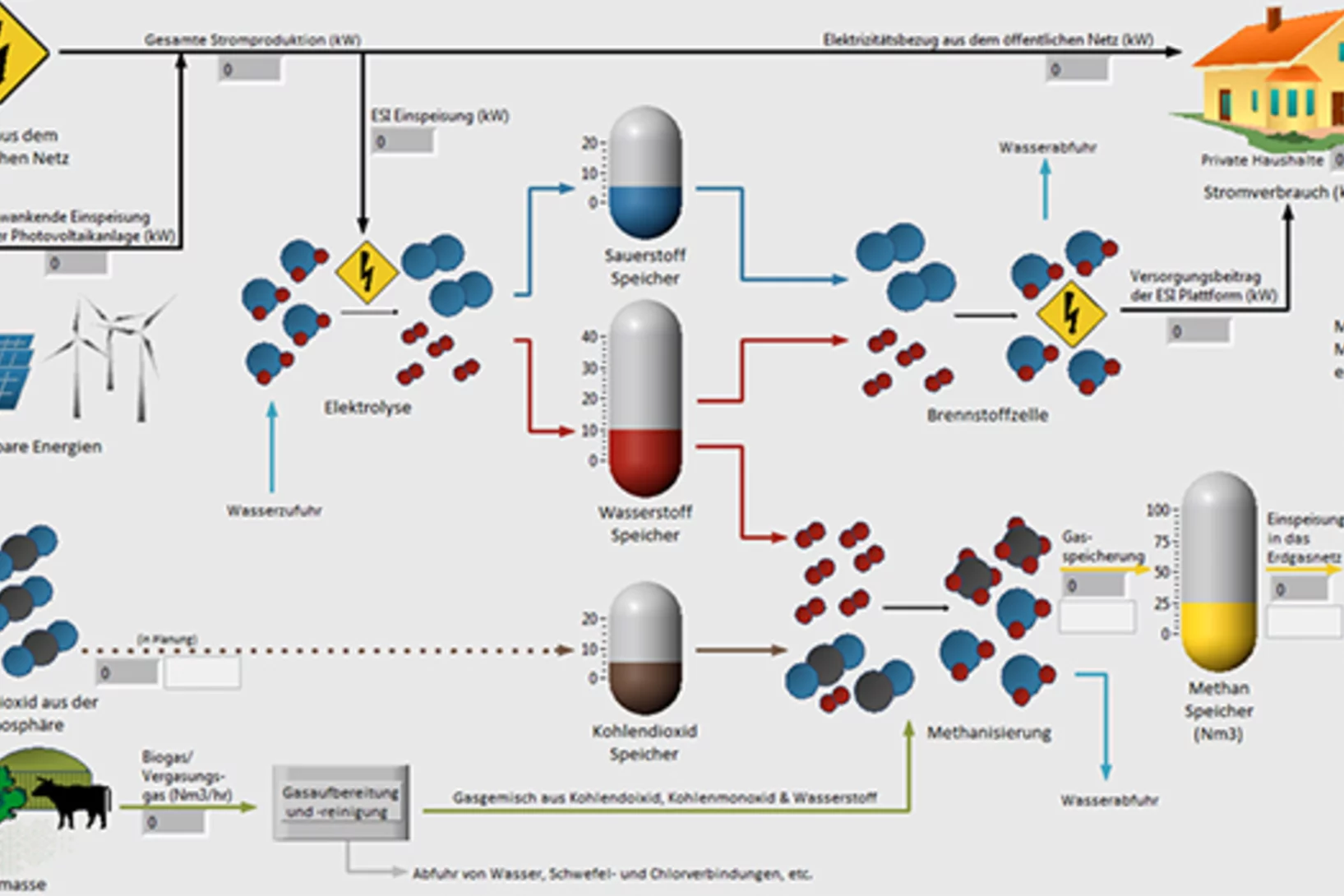
The energy system of the future and Power-to-X
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI analyse the potential of Power-to-X for Switzerland's energy supply and present their conclusions in a white paper. One finding: The costs for energy from Power-to-X could fall by up to one-third.
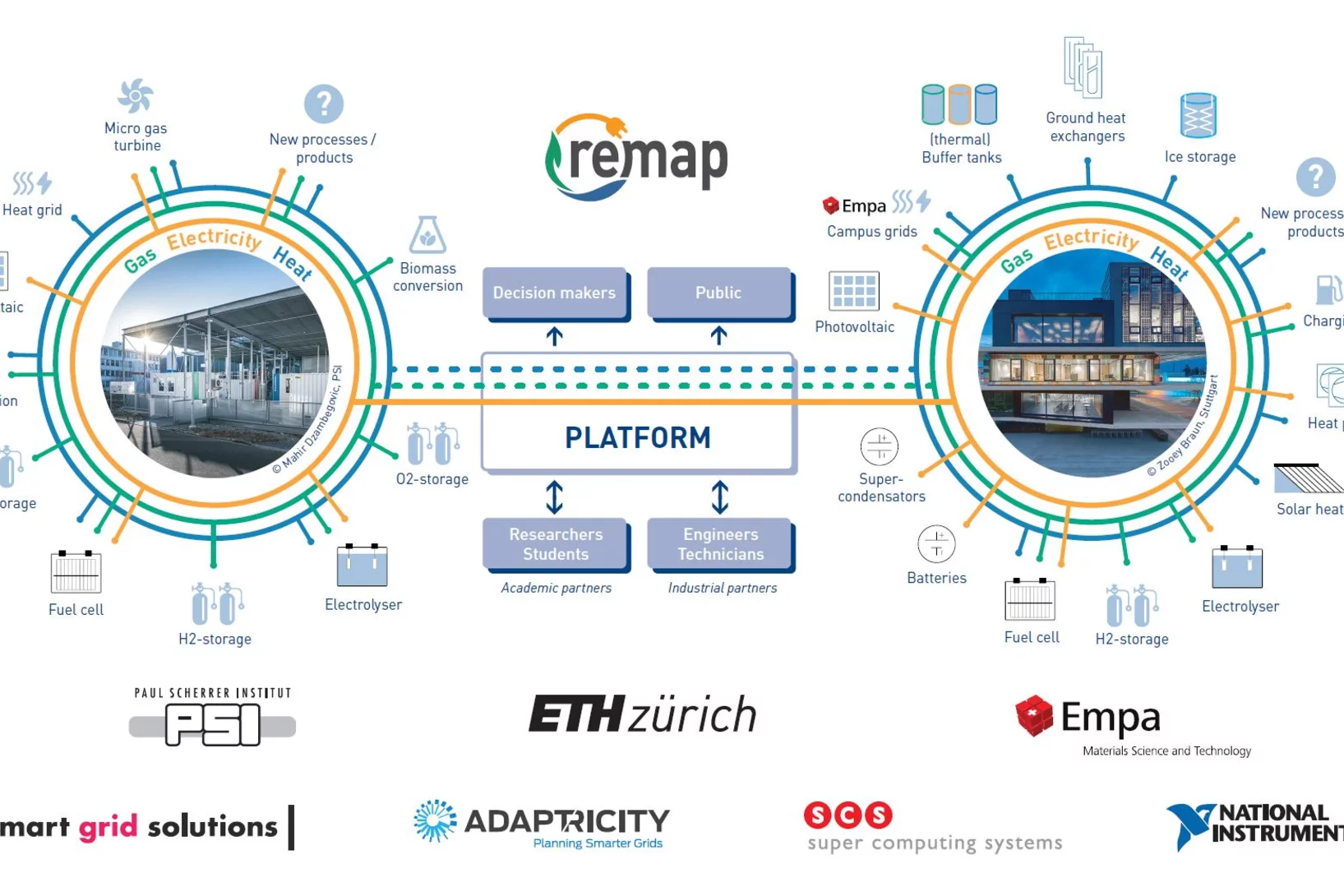
Testing the energy system of the future today, as realistically as possible
With the kick-off of the ReMaP project, companies have another opportunity to test their vision for the energy system of the future now. PSI's ESI platform helps to make better and more intelligent use of renewable energy in the future.
Power on demand
If photovoltaic or wind power plants produce more electricity than the network can absorb, valuable energy is lost. At the ESI Platform, PSI researchers are investigating how fuel cells can contribute to making this energy usable in a targeted way through storage.
Profitable for both sides
The young company Swiss Hydrogen is located in Fribourg. Here work is under way on competitive high-performance fuel cells that could be used in environmentally friendly vehicles or deployed as stationary power generators. In the company's collaboration with PSI, as CEO Alexandre Closset explains in this interview, both sides profit.
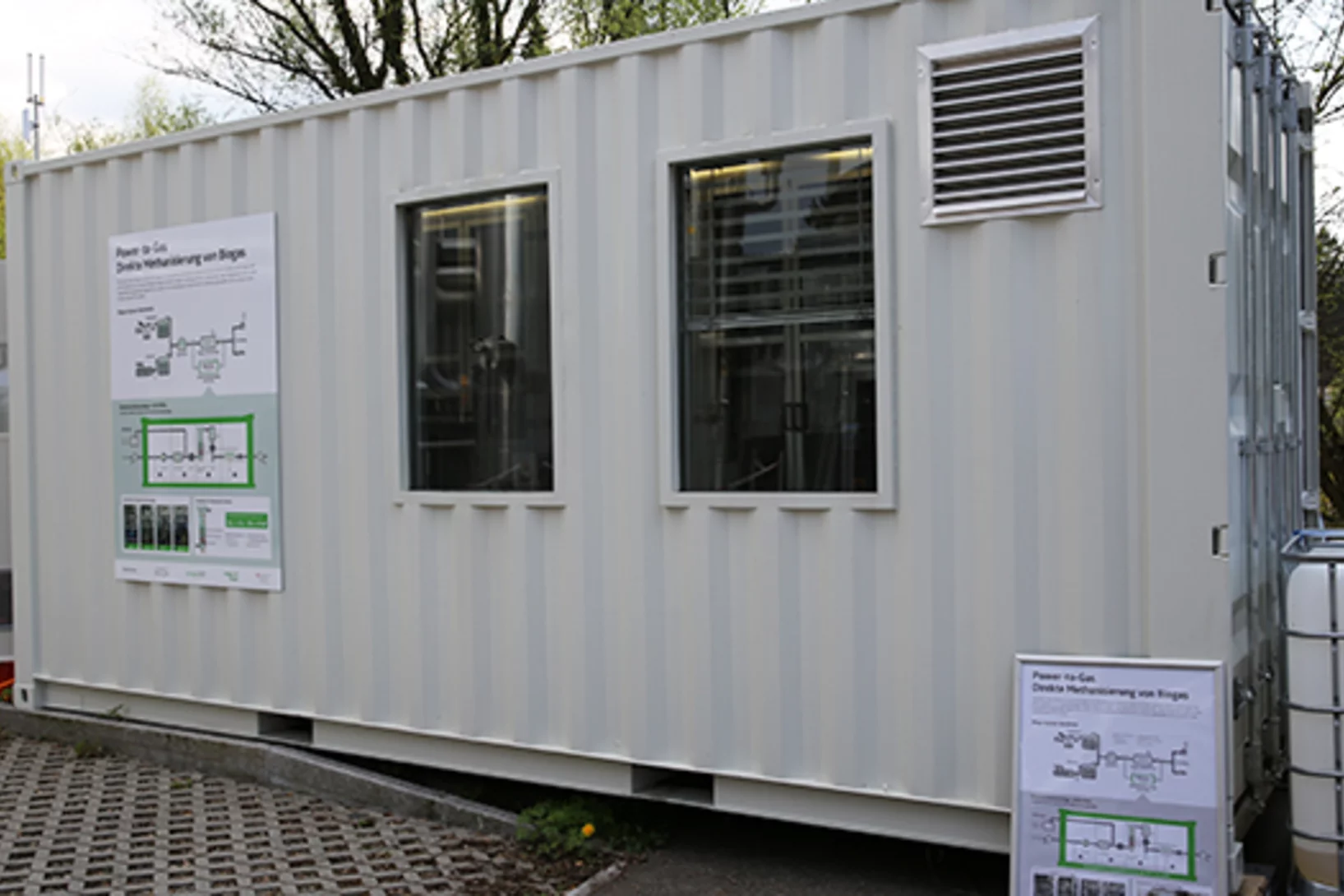
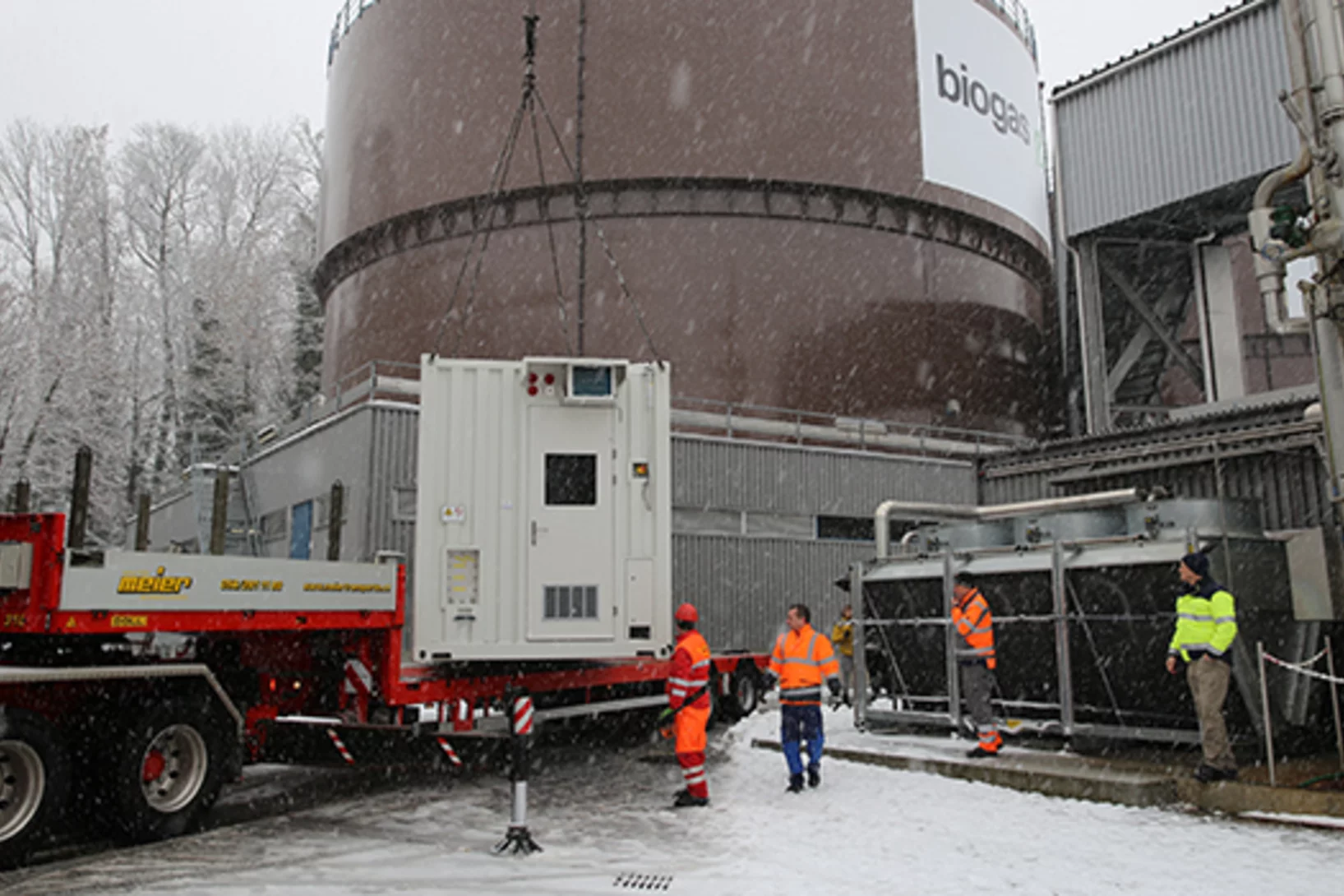
New technology undergoes real-world testing
The Zurich-based power company Energie 360° provides natural gas, biogas, and wood pellets throughout Switzerland. Now, with the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, it has successfully tested a new Power-to-Gas technology to be implemented in the area of biogas production. The joint project was awarded the Swiss energy prize Watt d'Or 2018. In this interview, division manager Peter Dietiker talks about the collaboration with PSI.
Using what's there
At the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, researchers are looking for solutions that enable energy from the sun, the wind, or biomass to be efficiently integrated into the Swiss energy system.
Efficient energy from biowaste – Watt d'Or for PSI and Energie 360°
Efficiently producing energy from biowaste: A technology developed at PSI and tested in collaboration with the Zurich-based energy provider Energie 360° makes it possible. It extracts significantly more methane from biowaste than conventional methods. For this important contribution to a sustainable energy supply, PSI and Energie 360° have now been awarded the Watt d'Or 2018 in the Renewable Energy category by the Swiss Federal Office of Energy.
Stress test passed
With a technology developed at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, around 60 percent more biogas can be produced from bio-waste than with conventional methods. But can it stand the test in practice as well? A 1,000-hour test at the Werdhölzli biowaste digestion and wastewater treatment plant in Zurich was able to answer this question with a clear yes. It was carried out in cooperation with the Zurich-based energy provider Energie 360°. The analysis of the stress test is now available.
More than just spilling the beans
Because of their high nitrogen content, spent coffee grounds are a popular garden fertilizer. Recycled in this manner, they already contribute to an environmentally friendly waste management. But they have the potential to deliver much more: a new procedure developed at the PSI allows high quality methane to be formed from spent coffee grounds. PSI researchers involved in a pilot project carried out in cooperation with the Swiss food producer Nestlé were able to show that spent coffee grounds left over during the production of instant coffee can be efficiently re-used elsewhere.
Nanomaterial helps store solar energy: efficiently and inexpensively
Efficient electrolysers are needed in order to store sun and wind energy in the form of hydrogen. Thanks to a new material developed by researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and Empa, these devices are likely to become less costly and more efficient in the future. Researchers were also able to demonstrate that this new material can be reliably produced in large quantities, showing its performance capability in an electrolysis cell—the main component of an electrolyser.
Fuel and chemicals from plant waste
Lignin, as a constituent of many plants, accumulates in large quantities and could theoretically be used as a precursor material for production of fuels and chemicals. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and ETH Zurich have developed a method with which the processes that take place in the catalytic breakdown of lignin can be observed in detail. The knowledge thus gained could enable targeted improvement of production methods in the future.
Welcome to Esiville
A new visitor’s station at PSI tells the story of a Swiss town that makes the change from a conventional energy supply to one with new renewable energy sources.
How Switzerland could supply its electric power in 2050
The Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI is investigating how Switzerland’s electricity supply might look, up to the year 2050, under a variety of boundary conditions. On the basis of their calculations, the lab’s researchers are able to generate insights on possible future developments of the energy sector, for example, determine how an ambitious reduction in CO2 emissions could be achieved at the lowest possible cost.
Higher methane yield from bio-waste
Within Switzerland’s bio-waste a huge amount of precious energy is hidden. That’s because valuable methane, the main constituent of natural gas, can be obtained from it. With a technology developed at PSI, the yield of methane from bio-waste could be increased considerably in the future. A long-term test conducted in cooperation with Energie 360° at the Werdhölzli fermentation and wastewater treatment plant is expected to advance this technology further along its path to industrial use.
Simulations for More Efficient Power Stations
In most cases, electricity is generated when water is heated and transformed into vapour. Vapour bubbles in the water play a decisive role in this process. Using computer simulation, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have succeeded in representing the behaviour of vapour bubbles – and in making their performance more calculable.
24 hours at the ESI Platform (video)
How can surplus power that can’t be fed into the electric grid be made usable? A fictitious day at the Energy System Integration Platform at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI.
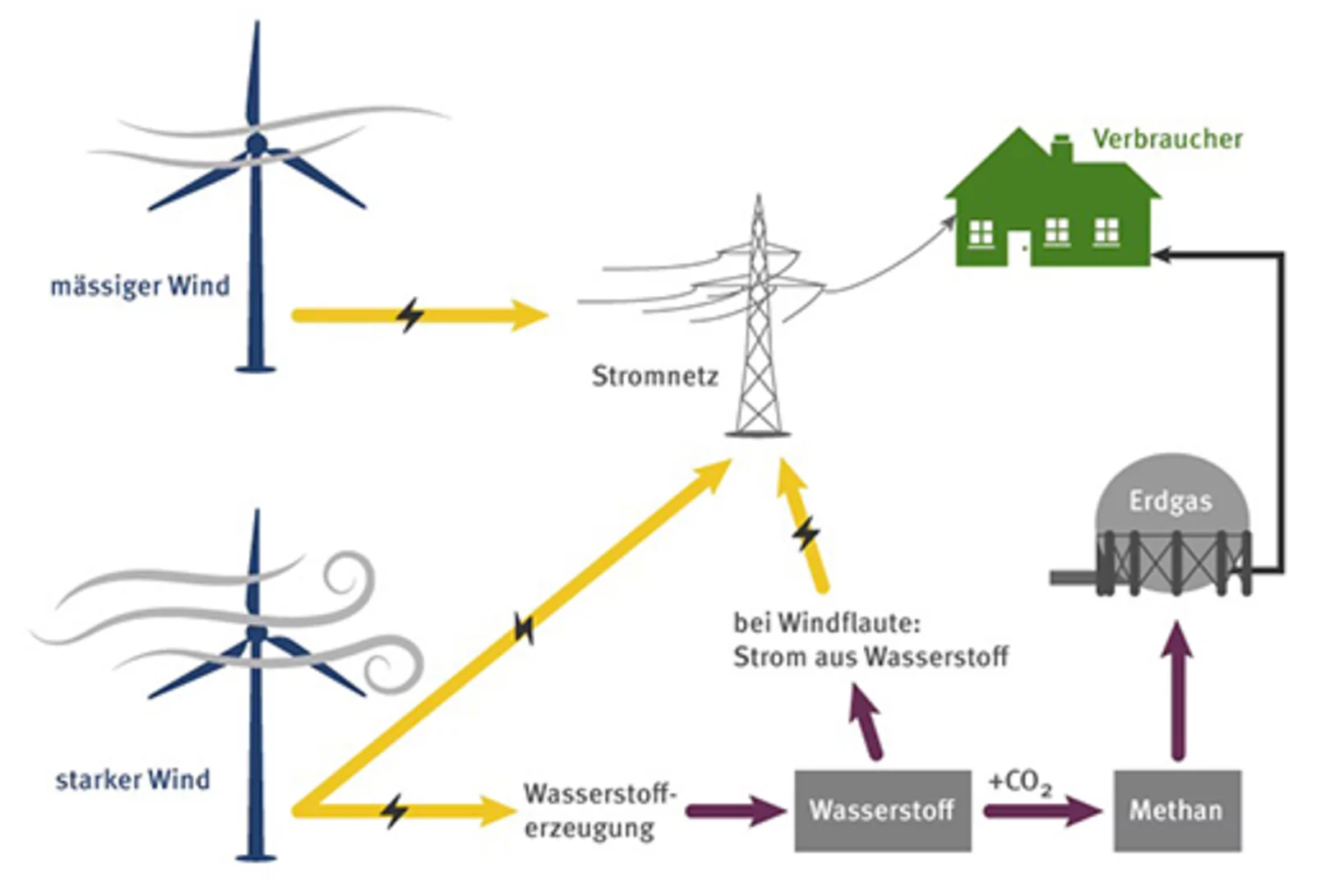
Turning Electricity into Gas – and back into Electricity
As capacities for producing solar and wind energy increase, integrating these into the existing energy system is becoming more of a challenge. The ESI platform is testing methods for successful integration. The answer: storing surplus energy as gas.
Kohlendioxid: Das Klimaproblem im Untergrund entsorgen?
Allen Warnungen vor den Folgen des Klimawandels zum Trotz und unbeeindruckt von politischen Absichtserklärungen: Die weltweiten Kohlendioxidemissionen steigen und steigen. Hauptverantwortlich dafür sind Kohle- und Gaskraftwerke, die den zunehmenden Strombedarf decken. Könnte man deren Kohlendioxidemissionen dauerhaft im Boden speichern, anstatt damit Atmosphäre und Klima zu belasten? Und wäre das auch für die Schweiz interessant? Diese Fragen beleuchtet der neueste Energie-Spiegel des PSI.This news release is only available in German.
PSI expertise boosts research for the energy transition
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) are involved in several projects under the new National Research Programme Energy Turnaround (NRP70) of the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF). The PSI experts tackle issues such as particle emissions from wood heating systems, the holistic evaluation of energy systems and the production of semiconductor components for novel transformers.
Keeping geothermal energy on the table
A study by the Centre for Technology Assessment TA-Swiss, coordinated by the Paul Scherrer Institute, recommends further pursuing deep geothermal energy in Switzerland. The energy resources underground are vast, environmentally friendly to extract and available around the clock, the authors conclude. The earthquake risk and the cost of electricity production, which are still too high, however, remain challenges that society needs to weigh up against the advantages of deep geothermal energy.
Energiewende in Reinkultur – in Wädenswil zu bestaunen
Der am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI entwickelte Prozess der hydrothermalen Methanierung von wässriger Biomasse erreicht einen wichtigen Meilenstein: Dank der Zusammenarbeit im neuen Kompetenzzentrum des Bundes für Bioenergie BIOSWEET konnten Forschende des PSI, der ZHAW, der ETH Lausanne, der Empa und der Hochschule für Technik Rapperswil die technische Machbarkeit der Methanherstellung aus Mikroalgen demonstrieren. Der dazu verwendete Algenbioreaktor sowie die Anlage zur Methanierung der Algen können am 24. September auf dem Campus Grüental der ZHAW in Wädenswil besichtigt werden. Für Medienschaffende gibt es von 14:00 bis 14:30 eine spezielle Führung.This news release is only available in German.
Method for producing energy from wet biomass gets the green light
On 28 March 2014 the topping-out ceremony for a new test facility to study energy production from wet biomass was celebrated at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI). The facility housed in a ship container is supposed to produce synthetic biogas from liquid manure, sewage sludge or algae.
How rock pores in deep repositories close over
Chemical reactions will change the nature of the deep repository and the surrounding rock (clay rock); that much is certain. But to what extent and with what impact on safety? Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute are looking to answer this question with the aid of a combination of experiments and computer simulations.