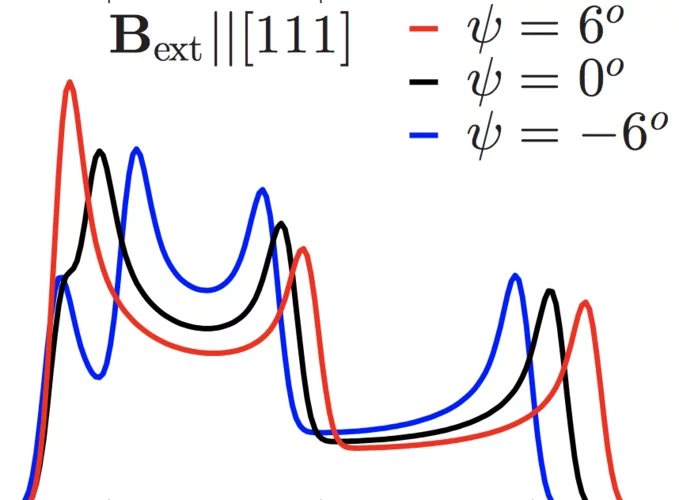
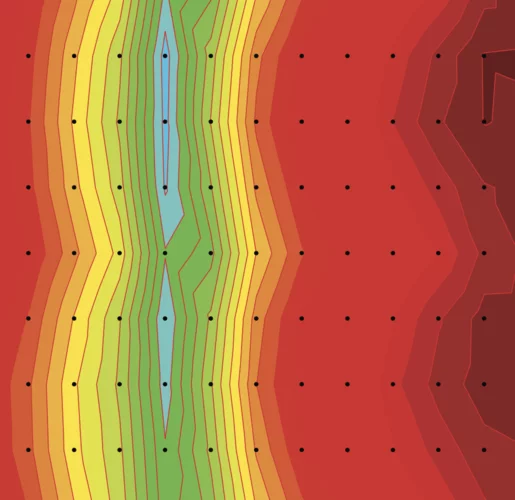
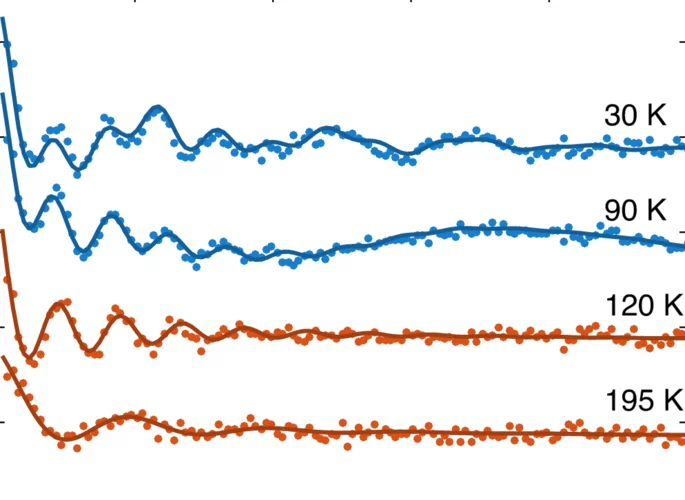
Pressure-induced magnetic order in FeSe: A muon spin rotation study
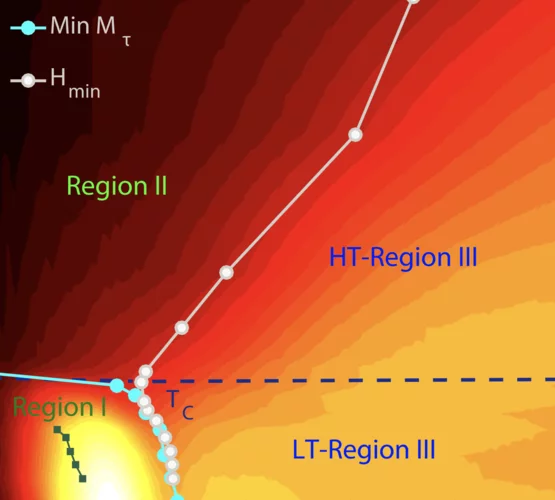
The magnetic order induced by the pressure was studied in FeSe by means of muon spin rotation (μSR) technique.
First lasing at a wavelength of 4.1 nm
The electron beam energy of SwissFEL was recently increased to above 900 MeV by successfully bringing two new accelerating modules into operation. This allowed SwissFEL to produce laser radiation for the first time in the soft x-ray regime with a photon wavelength of 4.1 nm. During the next months, the electron beam energy will be progressively further increased with the goal of enabling first user experiments at a wavelength of around 0.5 nm towards the end of this year.
First lasing at a wavelength of 4.1 nm
The electron beam energy of SwissFEL was recently increased to above 900 MeV by successfully bringing two new accelerating modules into operation. This allowed SwissFEL to produce laser radiation for the first time in the soft x-ray regime with a photon wavelength of 4.1 nm. During the next months, the electron beam energy will be progressively further increased with the goal of enabling first user experiments at a wavelength of around 0.5 nm towards the end of this year.
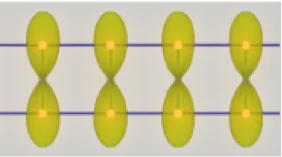
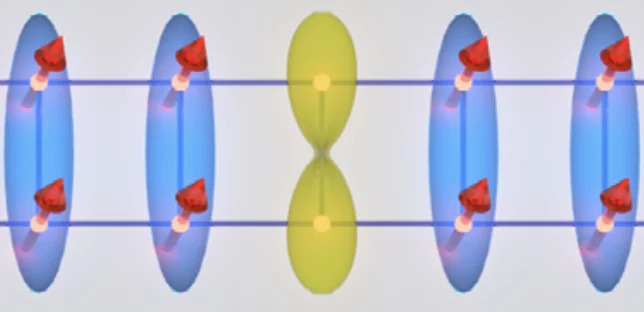
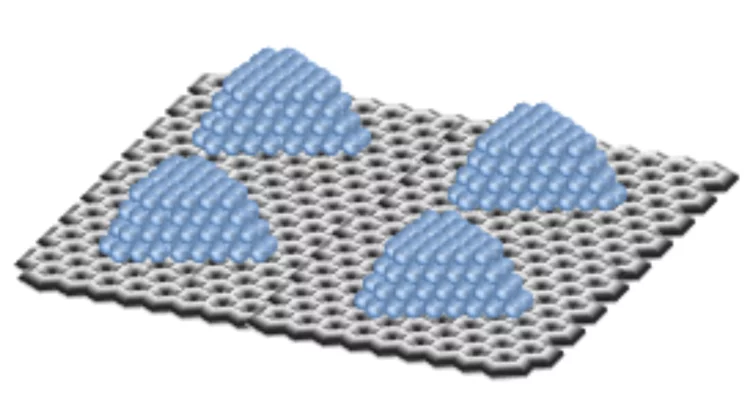
Emergent magnetism at transition-metal-nanocarbon interfaces
Interfaces are critical in quantum physics, and therefore we must explore the potential for designer hybrid materials that profit from promising combinatory effects. In particular, the fine-tuning of spin polarization at metallo–organic interfaces opens a realm of possibilities, from the direct applications in molecular spintronics and thin-film magnetism to biomedical imaging or quantum computing.
First SwissFEL Mirror Units ready to take X-rays
On May 11, 2017 the vacuum chambers of the first two offset mirrors have been closed eventually with the final gold- wire gasket and pumped down to ultra- high vacuum (goal: 1e-9 mbar). These mirrors are the key elements to switch the X-rays between the experimental stations. In pink beam mode they are the only optical elements for the X-rays on their way from the undulator down to the Alvra experiment.
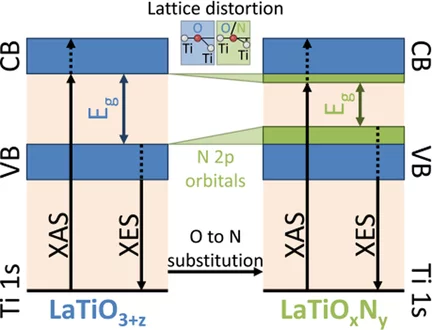
Determination of Conduction and Valence Band Electronic Structure of LaTiOxNy Thin Films
The nitrogen substitution into the oxygen sites of several oxide materials leads to a reduction of the band gap to the visible-light energy range, which makes these oxynitride semiconductors potential photocatalysts for efficient solar water splitting. Oxynitrides typically show a different crystal structure compared to the pristine oxide material.
Unconventional magnetic order in the conical state of MnSi
In the temperature-magnetic field phase diagram, the binary metallic compound MnSi exhibits three magnetic phases below Tc ≈ 29K.An unconventional helicoidal phase is observed in zero field. At moderate field intensity a conical phase sets in. Near Tc, in an intermediate field range, a skyrmion lattice phase appears.
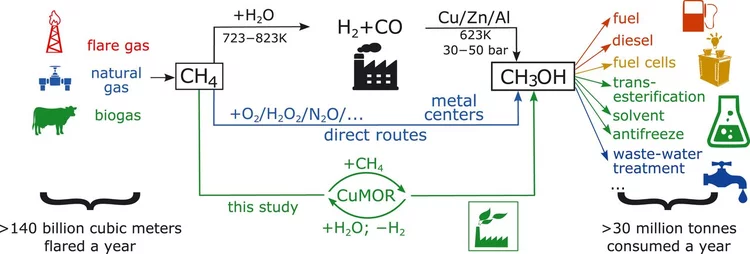
Selective anaerobic oxidation of methane enables direct synthesis of methanol
On the basis of in situ x-ray absorption spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, and density functional theory calculations, it was proposed a mechanism involving methane oxidation at Cu II oxide active centers, followed by Cu I reoxidation by water with concurrent formation of hydrogen.
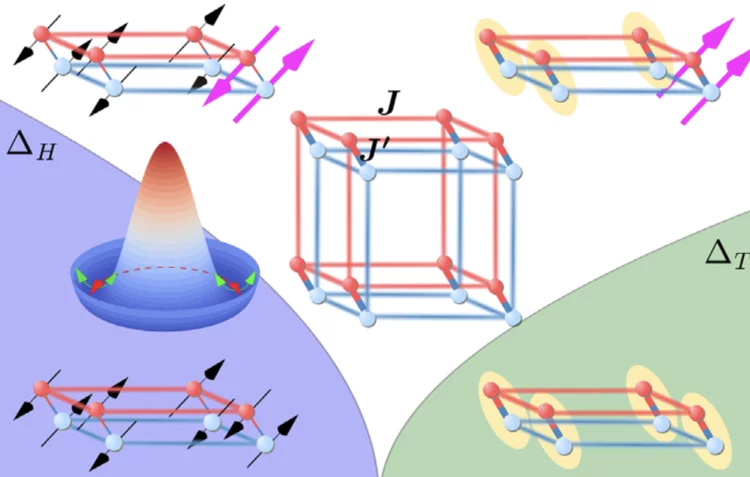
Anomalous Thermal Conductivity and Magnetic Torque Response in the Honeycomb Magnet α-RuCl3
We report on the unusual behavior of the in-plane thermal conductivity κ and torque τ response in the Kitaev-Heisenberg material α-RuCl3. κ shows a striking enhancement with linear growth beyond H = 7T, where magnetic order disappears, while τ for both of the in-plane symmetry directions shows an anomaly at the same field.
Climbing the ladder
Quantum phenomena can lead to intriguing effects in materials, but are famously difficult to predict and understand. A combined experimental and theoretical study of a model quantum system provides insight into excitations that involve multiple particles at once.
Bound States and Field-Polarized Haldane Modes in a Quantum Spin Ladder
The challenge of one-dimensional systems is to understand their physics beyond the level of known elementary excitations. By high-resolution neutron spectroscopy in a quantum spin-ladder material, we probe the leading multiparticle excitation by characterizing the two-magnon bound state at zero field.
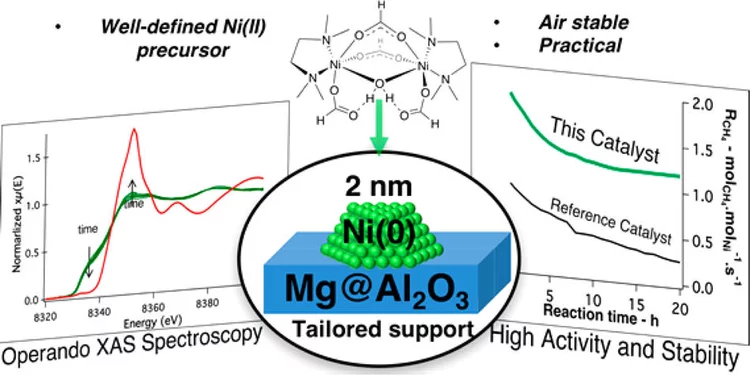
Molecularly Tailored Nickel Precursor and Support Yield a Stable Methane Dry Reforming Catalyst with Superior Metal Utilization
The superior performance of molecularly tailored methane dry reforming catalyst resulted in a maximization of the amount of accessible metallic nickel in the form of small nanoparticles preventing coke deposition. Operando X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy confirms that deactivation largely occurs through the migration of Ni into the support.
Amyloid fibril systems reduce, stabilize and deliver bioavailable nanosized iron
Iron-deficiency anaemia (IDA) is a major global public health problem. A sustainable and cost-effective strategy to reduce IDA is iron fortification of foods, but the most bioavailable fortificants cause adverse organoleptic changes in foods. Iron nanoparticles are a promising solution in food matrices, although their tendency to oxidize and rapidly aggregate in solution severely limits their use in fortification.
BKW and PSI agree on partnership for safety analysis services
BKW’s Engineering Division and the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) joined forces to provide risk and safety analysis services in the nuclear sector. By combining their expertise, the two companies are able to solve highly complex problems in the field of nuclear safety. The range of joint services is aimed at customers from the power plant sector and supply industry, as well as public and state institutions. The collaboration will focus exclusively on the international (non-Swiss) market.
Doping Dependence of Collective Spin and Orbital Excitations in the Spin-1 Quantum Antiferromagnet La2-xSrxNiO4 Observed by X-Rays
We report the first empirical demonstration that resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) is sensitive to collective magnetic excitations in S=1 systems by probing the Ni L3 edge of La2-xSrxNiO4 (x=0, 0.33, 0.45). The magnetic excitation peak is asymmetric, indicating the presence of single and multi-spin-flip excitations.
Amplitude Mode in Three-Dimensional Dimerized Antiferromagnets
The amplitude ("Higgs") mode is a ubiquitous collective excitation related to spontaneous breaking of a continuous symmetry. We combine quantum Monte Carlo (QMC) simulations with stochastic analytic continuation to investigate the dynamics of the amplitude mode in a three-dimensional dimerized quantum spin system.
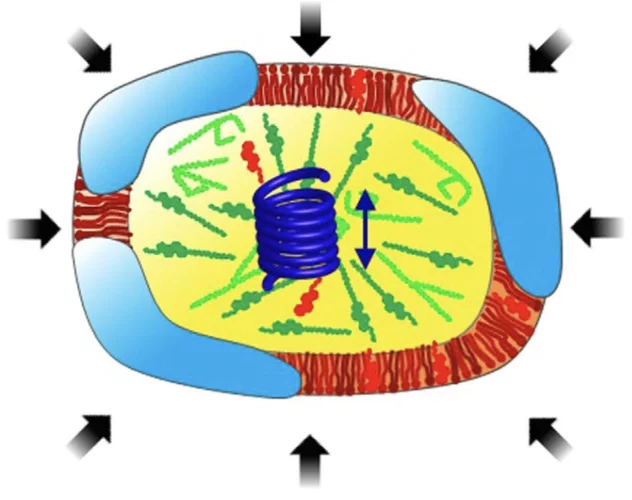
High hydrostatic pressure specifically affects molecular dynamics and shape of low-density lipoprotein particles
Lipid composition of human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and its physicochemical characteristics are relevant for proper functioning of lipid transport in the blood circulation. To explore dynamical and structural features of LDL particles with either a normal or a triglyceride-rich lipid composition we combined coherent and incoherent neutron scattering methods.
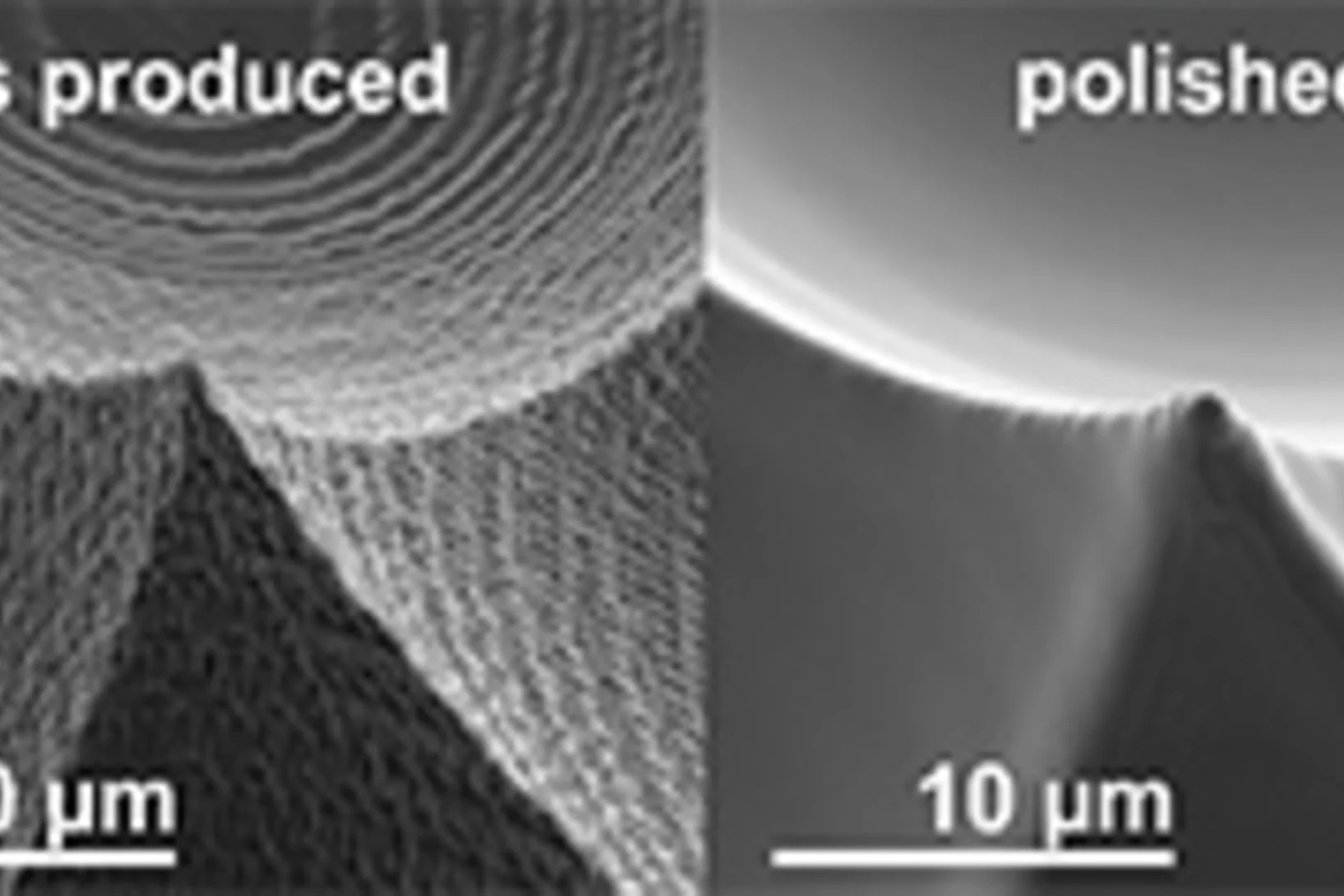
Contact-less micro-polishing
A new method of material modification using 172 nm UV photons enables to fabricate ultra-smooth and self-optimized polymer surfaces. The method, published in Advanced Materials Technologies, was used in the production of high quality micro-optics to remove typical process flaws after a 2-photon-lithography process.
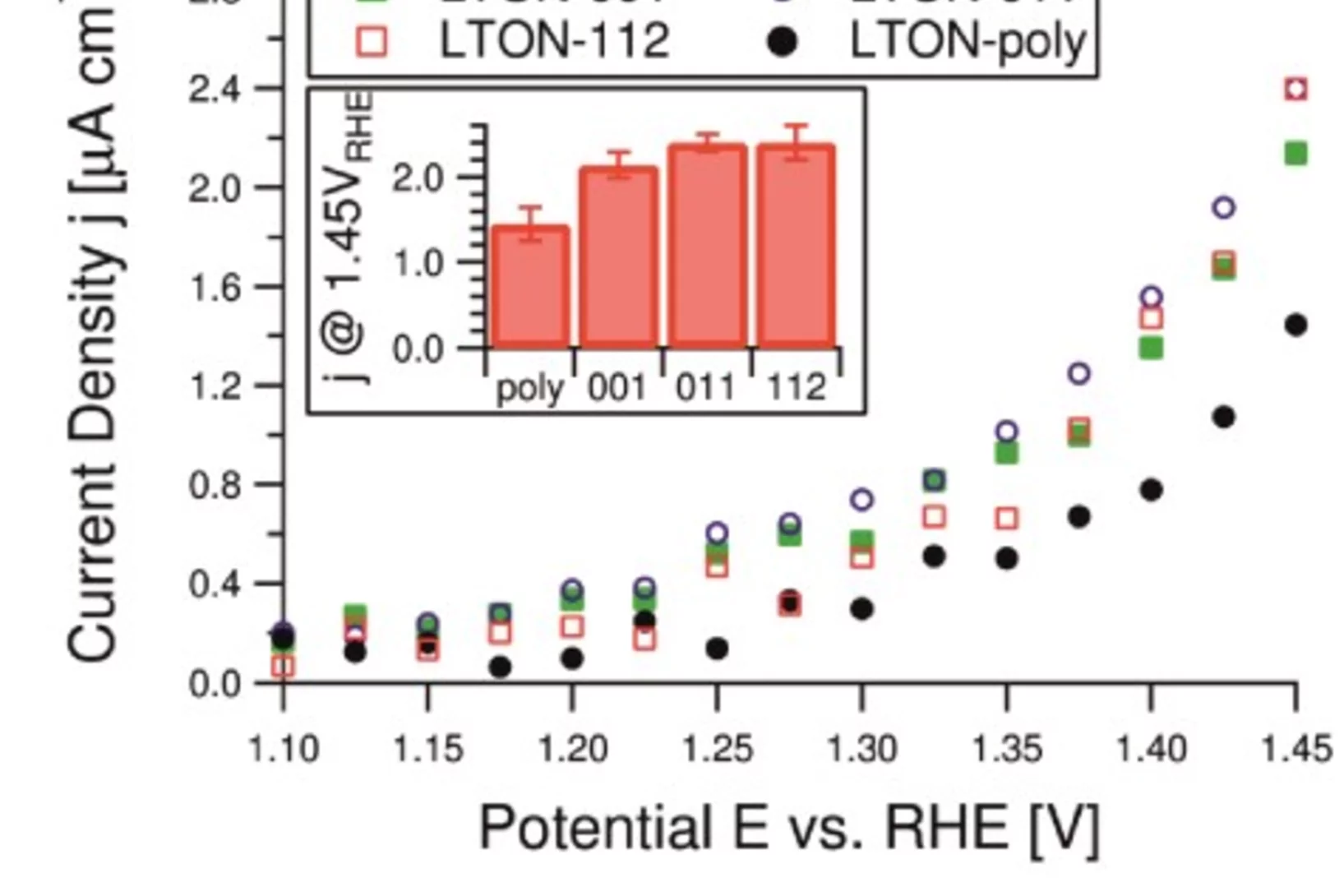
LaTiOxNy thin film model systems for photocatalytic water splitting: physicochemical evolution of the solid-liquid interface and the role of the crystallographic orientation
The size of the band gap and the energy position of the band edges make several oxynitride semiconductors promising candidates for efficient hydrogen and oxygen production under solar light illumination. The intense research efforts dedicated to oxynitride materials have unveiled the majority of their most important properties. However, two crucial aspects have received much less attention.
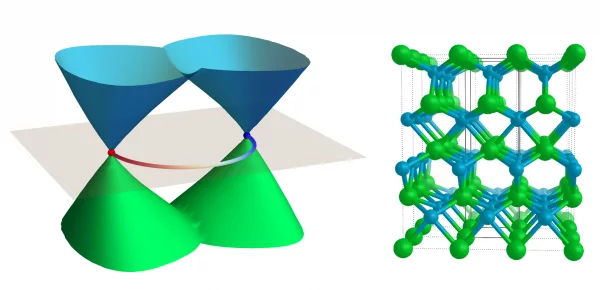
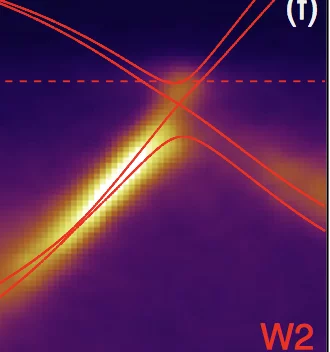
A breakthrough on Weyl semimetals
In their recent paper, Distinct Evolutions of Weyl fermion quasiparticles and Fermi arcs with bulk band topology in Weyl semimetals, two MARVEL groups — led by Prof. Ming Shi and Dr Nan Xu at PSI for the experimental part, and with Prof. Oleg Yazyev and Dr Gabriel Autès at EPFL for the theoretical side — joined forces to shed light (and soft X-rays) on the relationship between the bulk band topology in Weyl semimetals and two measurable signatures of Weyl fermion quasiparticles: magneto-transport effects in the bulk, and Fermi arcs on the surface.
Gapless Spin-Liquid Ground State in the S=1/2 Kagome Antiferromagnet
The defining problem in frustrated quantum magnetism, the ground state of the nearest-neighbor S=1/2 antiferromagnetic Heisenberg model on the kagome lattice, has defied all theoretical and numerical methods employed to date. We apply the formalism of tensor-network states, specifically the method of projected entangled simplex states, which combines infinite system size with a correct accounting for multipartite entanglement.
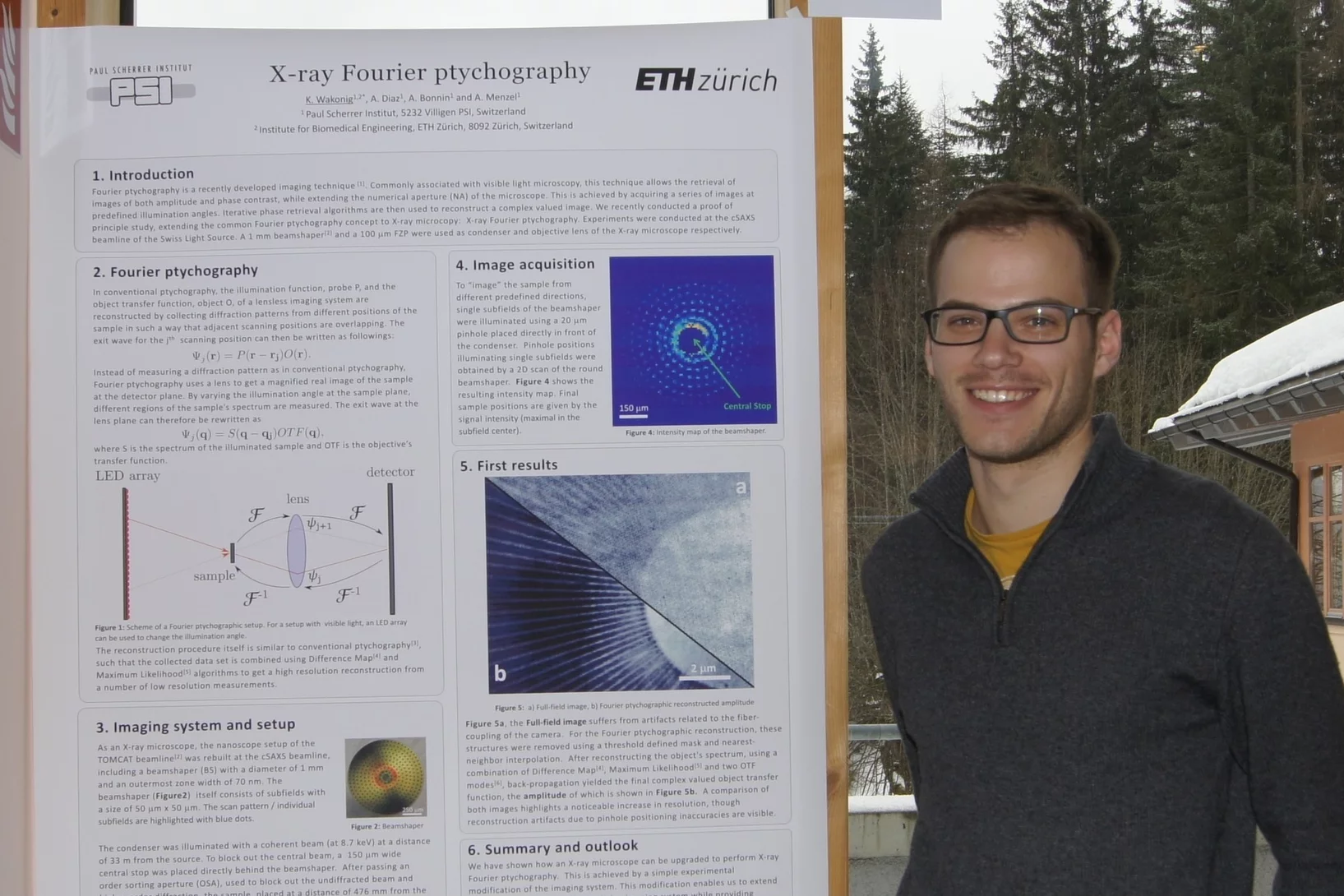
European NESY Winterschool Young Scientist Best Poster Prize
Klaus Wakonig was awarded the "Young Scientist Best Poster Prize" along with a cash prize at the 10th European NESY Winterschool & Symposium on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. Klaus is a PhD student at the coherent X-ray scattering group (CXS) in PSI. His poster, entitled "X-ray Fourier ptychography," details his latest results in the implementation of Fourier ptychography at X-ray wavelengths for nanoimaging. Image credit ©NESY/Montanuniversitaet Leoben
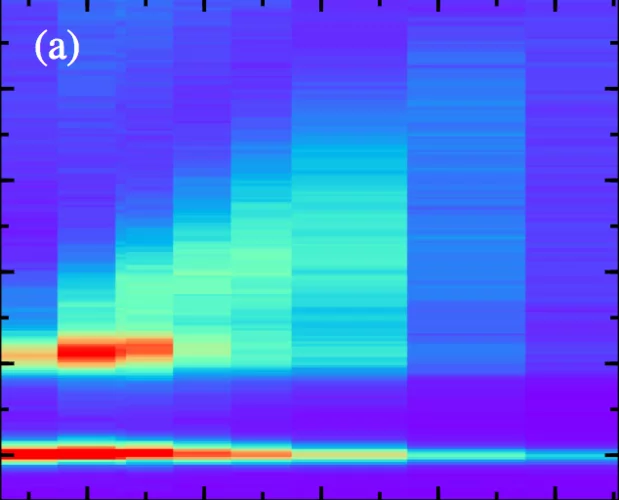
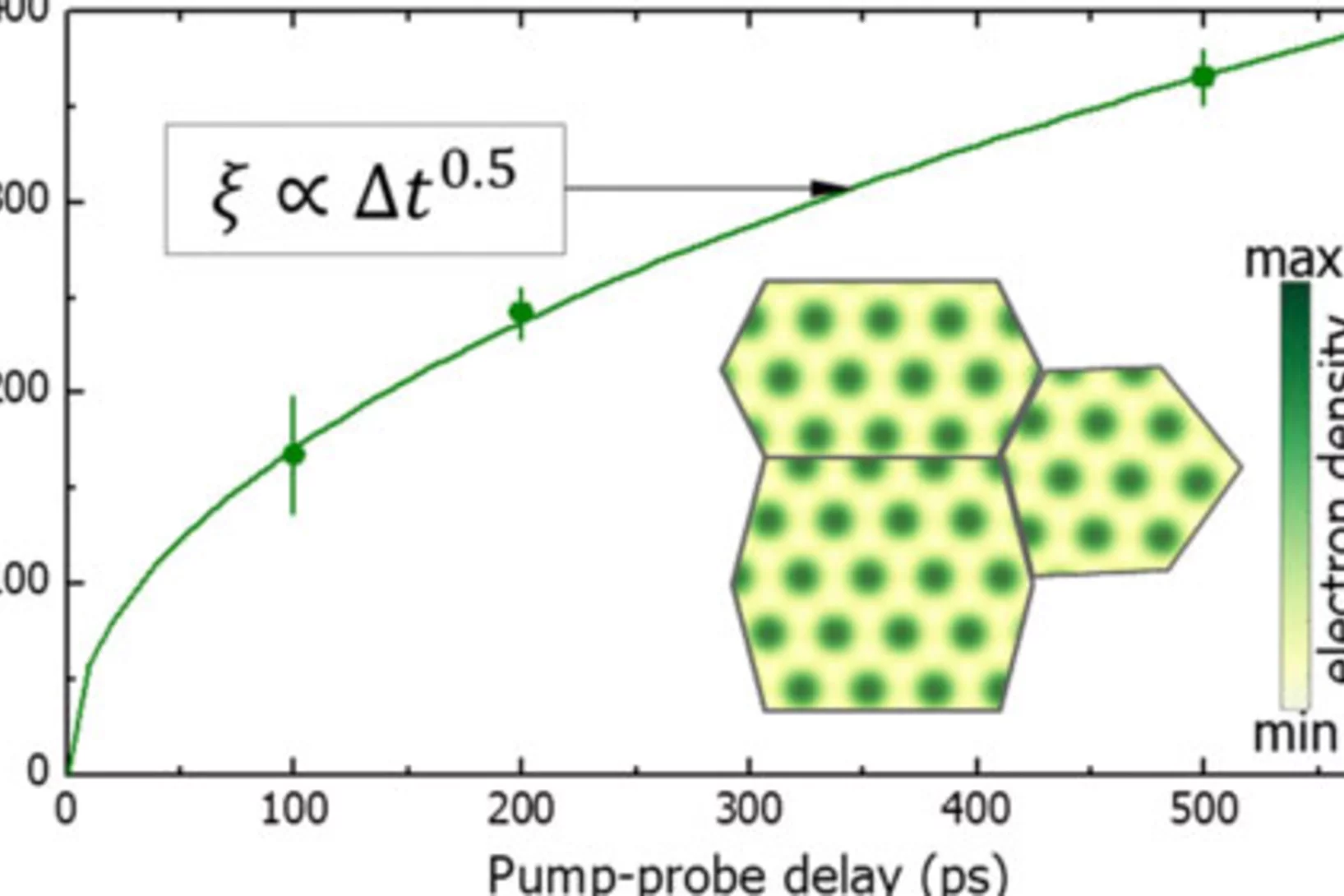
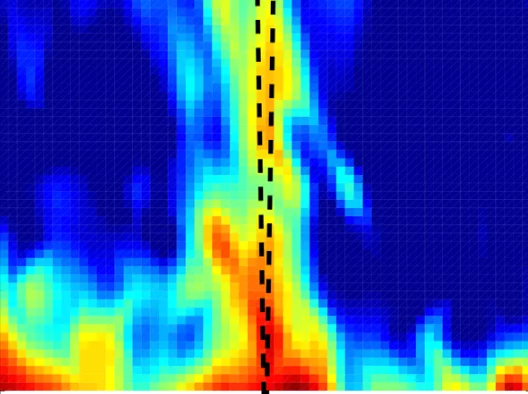
Ultrafast formation of a charge density wave state in 1T-TaS2: observation at nanometer scales using time-resolved X-ray diffraction
Femtosecond time-resolved x-ray diffraction is used to study a photoinduced phase transition between two charge density wave (CDW) states in 1T-TaS2, namely the nearly commensurate (NC) and the incommensurate (I) CDW states. Structural modulations associated with the NC-CDW order are found to disappear within 400 fs.
Better graphene nanoribbons for electronics applications
Turning the semimetal graphene into a technologically useful semiconductor is challenging. One way of opening a band gap is to cut graphene into nanometre-wide ribbons, but even atomic-level roughness at the ribbon edges can seriously degrade the mobility of charge carriers. Recent advances in on-surface chemistry have made it possible to obtain graphene nanoribbons with atomically precise edges through direct synthesis from molecular building blocks. Here, we report the synthesis, full structural and electronic characterization of 9-atom wide graphene nanoribbons with significantly improved electronic properties.
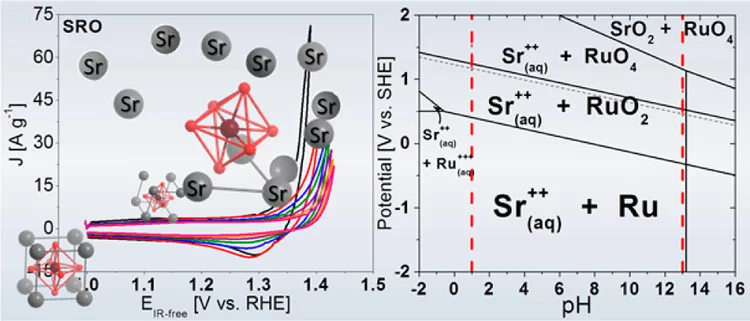
Unraveling Thermodynamics, Stability, and Oxygen Evolution Activity of Strontium Ruthenium Perovskite Oxide
Ru-based perovskites, i.e. SrRuO3 and LaRuO3, have been predicted as active perovskites to exhibit a particularly high oxygen evolution reaction activity. We highlight that understanding the origin of stability under a real operating environment is absolutely essential for the design of a sustainable electrocatalyst with optimal balance between activity and stability.
Magnetic states of MnP: muon-spin rotation studies
Muon-spin rotation data collected at ambient pressure (p) and at p = 2.42 GPa in MnP were analyzed to check their consistency with various low- and high-pressure magnetic structures reported in the literature. Our analysis con rms that in MnP the low-temperature and low-pressure helimagnetic phase is characterised by an increased value of the average magnetic moment compared to the high-temperature ferromagnetic phase.
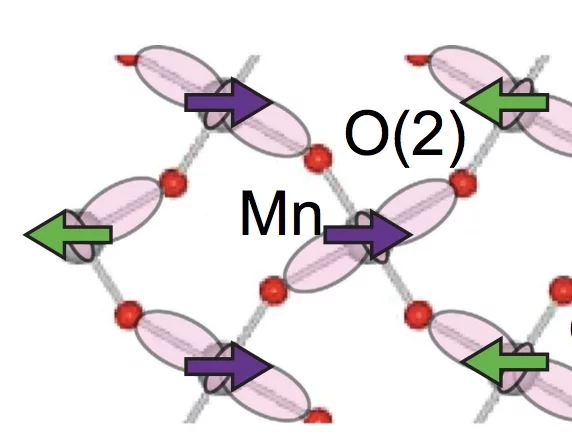
Tuning the multiferroic mechanisms of TbMnO3 by epitaxial strain
A current challenge in the field of magnetoelectric multiferroics is to identify systems that allow a controlled tuning of states displaying distinct magnetoelectric responses. Here we show that the multiferroic ground state of the archetypal multiferroic TbMnO3 is dramatically modified by epitaxial strain. Neutron diffraction reveals that in highly strained films the magnetic order changes from the bulk-like incommensurate bc-cycloidal structure to commensurate magnetic order.
Sub-pixel correlation length neutron imaging: Spatially resolved scattering information of microstructures on a macroscopic scale
Neutron imaging and scattering give data of significantly different nature and traditional methods leave a gap of accessible structure sizes at around 10 micrometers. Only in recent years overlap in the probed size ranges could be achieved by independent application of high resolution scattering and imaging methods, however without providing full structural information when microstructures vary on a macroscopic scale.
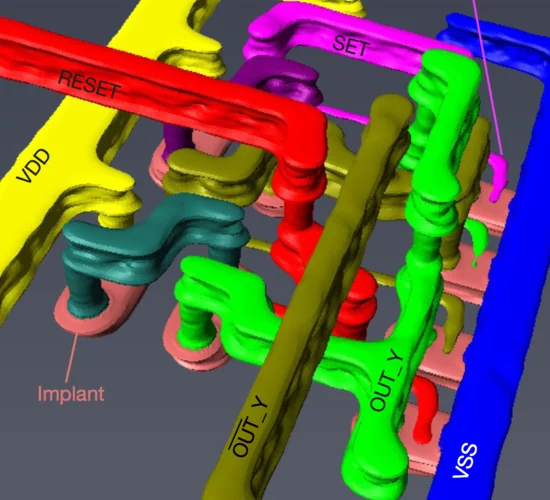
High-resolution non-destructive three-dimensional imaging of integrated circuits
Modern nanoelectronics has advanced to a point at which it is impossible to image entire devices and their interconnections non- destructively because of their small feature sizes and the complex three-dimensional structures resulting from their integration on a chip. This metrology gap implies a lack of direct feedback between design and manufacturing processes, and hampers quality control during production, shipment and use.
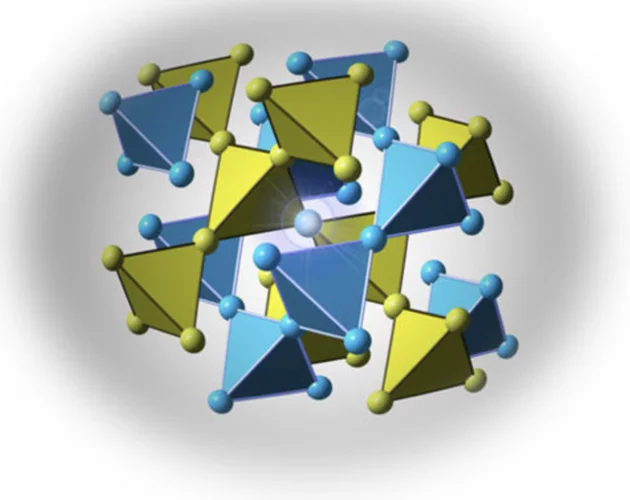
Ground state selection under pressure in the quantum pyrochlore magnet Yb2Ti2O7
A quantum spin liquid is a state of matter characterized by quantum entanglement and the absence of any broken symmetry. In condensed matter, the frustrated rare-earth pyrochlore magnets Ho2Ti2O7 and Dy2Ti2O7, so-called spin ices, exhibit a classical spin liquid state with fractionalized thermal excitations (magnetic monopoles).
Distinct Evolutions of Weyl Fermion Quasiparticles and Fermi Arcs with Bulk Band Topology in Weyl Semimetals
The Weyl semimetal phase is a recently discovered topological quantum state of matter characterized by the presence of topologically protected degeneracies near the Fermi level. These degeneracies are the source of exotic phenomena, including the realization of chiral Weyl fermions as quasiparticles in the bulk and the formation of Fermi arc states on the surfaces.
Effects of Quantum Spin-1/2 Impurities on the Magnetic Properties of Zigzag Spin Chains
We investigate the effect of Co2+ (spin-1/2) impurities on the magnetic ground state and low-lying spin excitations of the quasione-dimensional spin-1/2 antiferromagnet SrCuO2 by means of neutron scattering, muon spin spectroscopy, and bulk (ac and dc) magnetic susceptibilities. We found that dilute Co doping induces an Ising-like anisotropy and enhances the magnetic ordering temperature rather significantly, but preserves the gapless nature of the spin excitations.
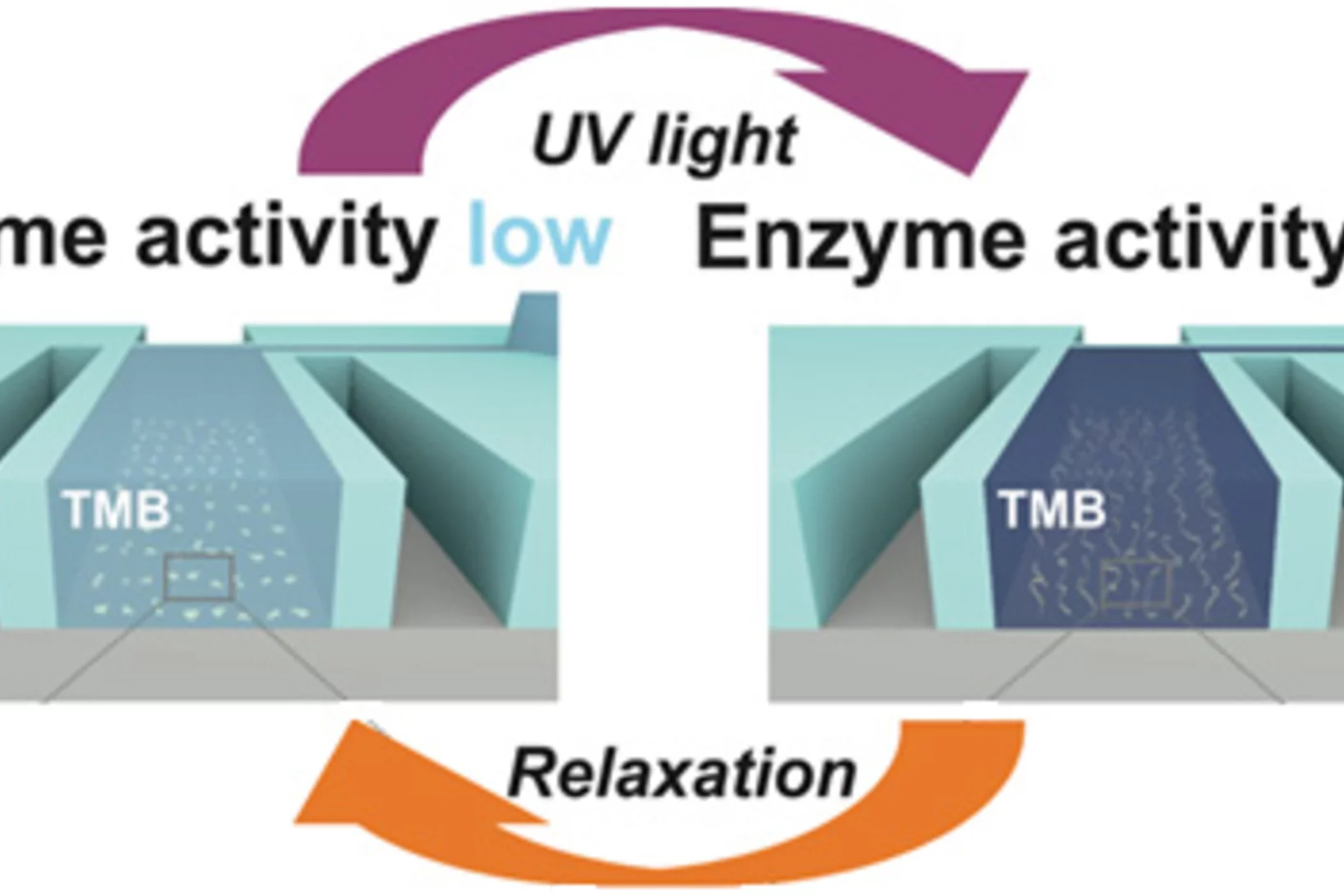
Light-switching of enzymatic activity on orthognonally functionalized polymer brushes
UV- and visible light-induced switching of enzymatic activity has been demonstrated using surface-grafted polymer brushes functionalized with microperoxidase MP-11 and spiropyran mojeties. Integration into an optofluidic device allowed reversible switching of the enzymatic activity under flow.
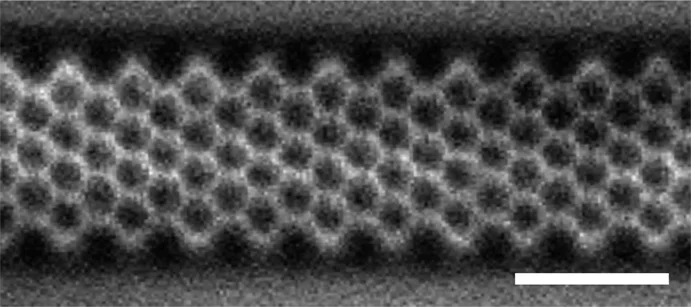
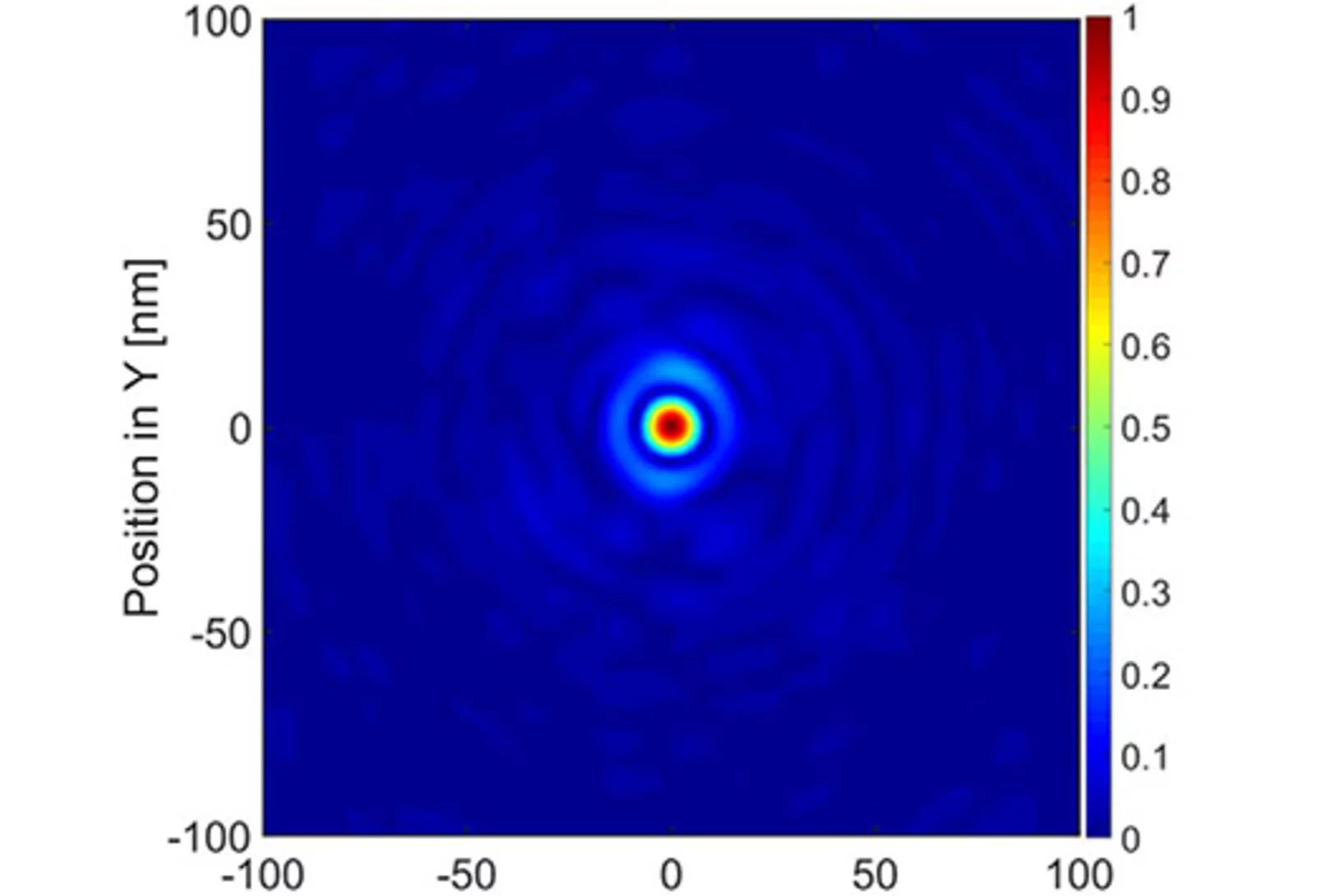
Interlaced zone plates push the resolution limit in x-ray microscopy
A novel type of diffractive lenses based on interlaced structures enable x-ray imaging at resolutions below 10 nm. The fabrication method and the test results of these novel x-ray lenses have been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
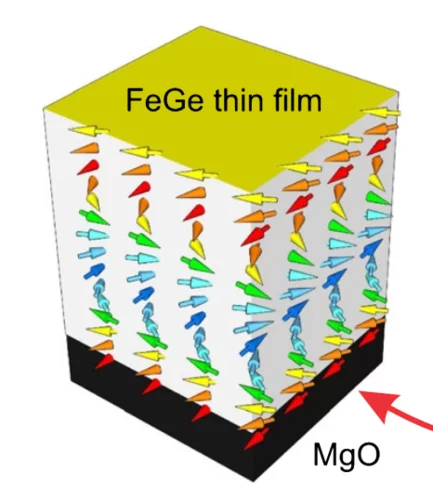
Room-temperature helimagnetism in FeGe thin films
Chiral magnets are promising materials for the realisation of high-density and low-power spintronic memory devices. For these future applications, a key requirement is the synthesis of appropriate materials in the form of thin films ordering well above room temperature. Driven by the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction, the cubic compound FeGe exhibits helimagnetism with a relatively high transition temperature of 278 K in bulk crystals.
Cover page of CHEMCATCHEM
A paper titled "Optimization of the Reaction Conditions for Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis of Pretreated Lignin over Zeolite for the Production of Phenol" by Zhiqiang Ma is published in ChemCatChem and made it on the cover of issue 6/2017.
Silicon pixel barrel detector successfully installed in the CMS experiment
Middle of February the upgraded CMS silicon pixel barrel detector has been moved from PSI to CERN and was successfully installed in the CMS experiment.
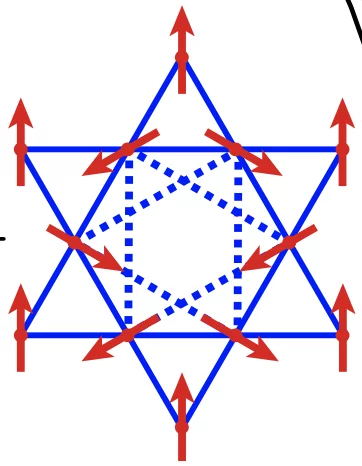
Spiral spin-liquid and the emergence of a vortex-like state in MnSc2S4
Spirals and helices are common motifs of long-range order in magnetic solids, and they may also be organized into more complex emergent structures such as magnetic skyrmions and vortices. A new type of spiral state, the spiral spin-liquid, in which spins fluctuate collectively as spirals, has recently been predicted to exist.
1000 Structures solved at X06DA-PXIII
The macromolecular crystallography beamline X06DA-PXIII has reached 1,000 structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) on February 22, 2017.
Intermicellar Interactions and the Viscoelasticity of Surfactant Solutions: Complementary Use of SANS and SAXS
In ionic surfactant micelles, basic interactions among distinct parts of surfactant monomers, their counterion, and additives are fundamental to tuning molecular self-assembly and enhancing viscoelasticity. Here, we investigate the addition of sodium salicylate (NaSal) to hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride and bromide (CTAC and CTAB) and 1-hexadecylpyridinium chloride and bromide (CPyCl and CPyBr), which have distinct counterions and headgroup structures but the same hydrophobic tail.
Switzerland at the Quantum Crossroads document endorsed by QTC@PSI members
“Switzerland at the Quantum Crossroads” outlines the current quantum science and technology landscape in Switzerland, explains the promises of this technology and outlines the required steps for Switzerland to leverage its leadership in this space.
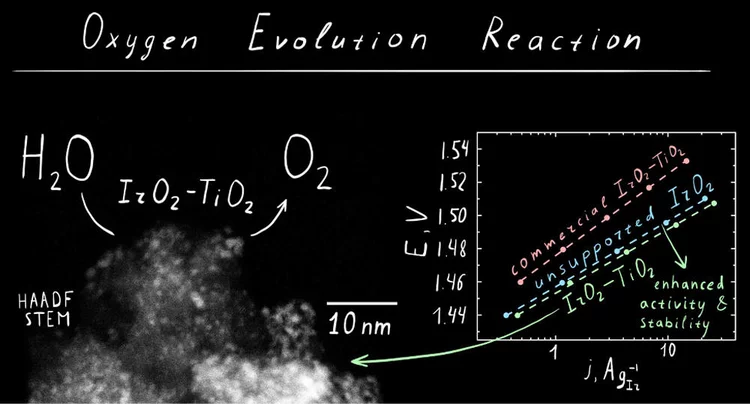
IrO2‑TiO2: A High-Surface-Area, Active, and Stable Electrocatalyst for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
We have developed a synthetic approach to highsurface-area chlorine-free iridium oxide nanoparticles dispersed in titania (IrO2-TiO2), which is a highly active and stable OER catalyst in acidic media. Operando X-ray absorption studies demonstrate the evolution of the surface species as a function of the applied potential, suggesting the conversion of the initial hydroxo surface layer to the oxo-terminated surface via anodic oxidation.
New magnetic phase in the nickelate perovskite TlNiO3
The RNiO3 perovskites are known to order antiferromagnetically below a material-dependent Néel temperature TN. We report experimental evidence indicating the existence of a second magnetically ordered phase in TlNiO3 above TN = 104K, obtained using nuclear magnetic resonance and muon spin rotation spectroscopy.
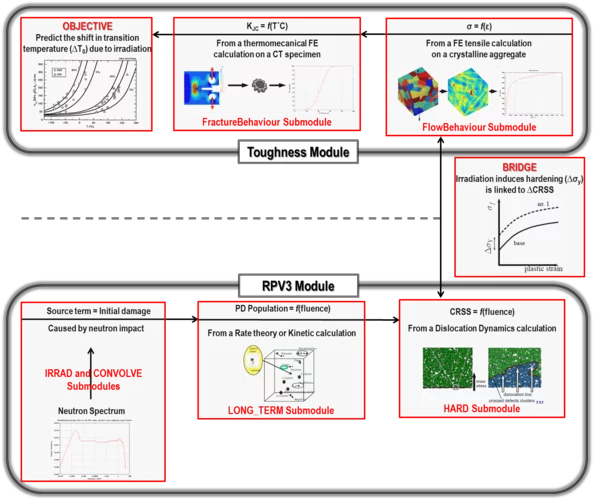
PERFORM-60: Modelling the Ageing of Reactor Vessel Steels
The main threat to the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) operational safety is certainly the radiation damage that hardens and embrittles the steel it is made of. Four decades of research worldwide have allowed understanding and monitoring the phenomena that come into play. At the computational level, a simulation platform, PERFORM-60, has the ambitious aim of predicting the steel evolution for most RPV and operational conditions. It was initially elaborated in the frame of the EU project of the same acronym and is currently further developed to be the end-product of the on-going H2020 EU project SOTERIA. As a contribution of the Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Systems Behaviour (LRS) to SOTERIA, the platform has been rigorously assessed for the first time since its release on a real case study of a Swiss RPV. This critical assessment has been acknowledged by the community and serves as basis for improvements and future developments of the platform within SOTERIA.
Carlos Vaz Honored by the American Physical Society as Outstanding Referee 2017
SIM beamline scientist Carlos Vaz was recognized as outstanding referee for providing high quality peer review for the journals of the American Physical Society (APS).
Magnetic Field Dependence of Excitations Near Spin-Orbital Quantum Criticality
The spinel FeSc2S4 has been proposed to realize a near-critical spin-orbital singlet (SOS) state, where entangled spin and orbital moments fluctuate in a global singlet state on the verge of spin and orbital order.
In-situ Studies of the Reactivity of Model Catalysts: Surface Chemistry from flat surfaces to nanoparticles
On 7th February Dr. Christian Papp from University Erlangen (Germany) is visiting the SIM beamline and will give a Photon Science Seminar talk with the title: "In-situ Studies of the Reactivity of Model Catalysts: Surface Chemistry from flat surfaces to nanoparticles"
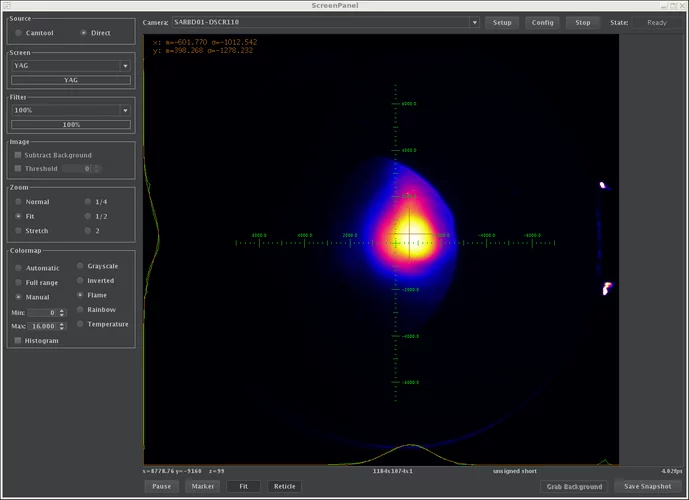
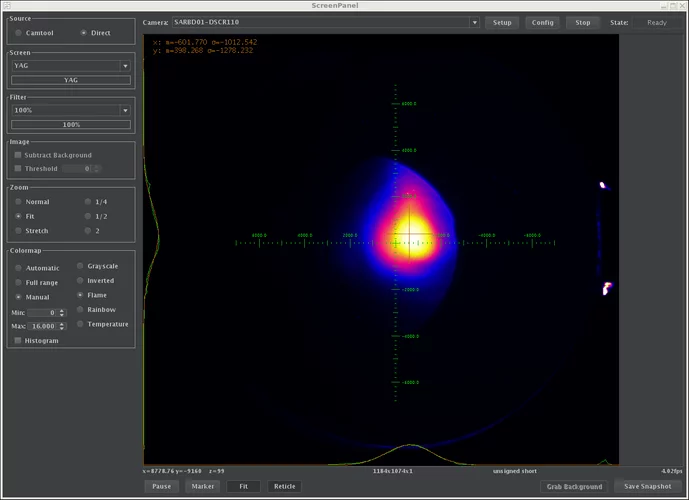
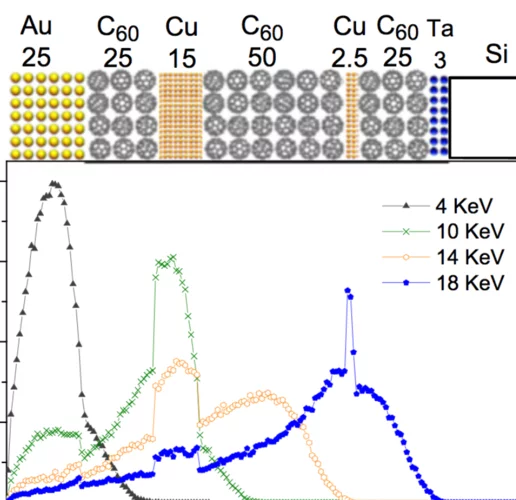
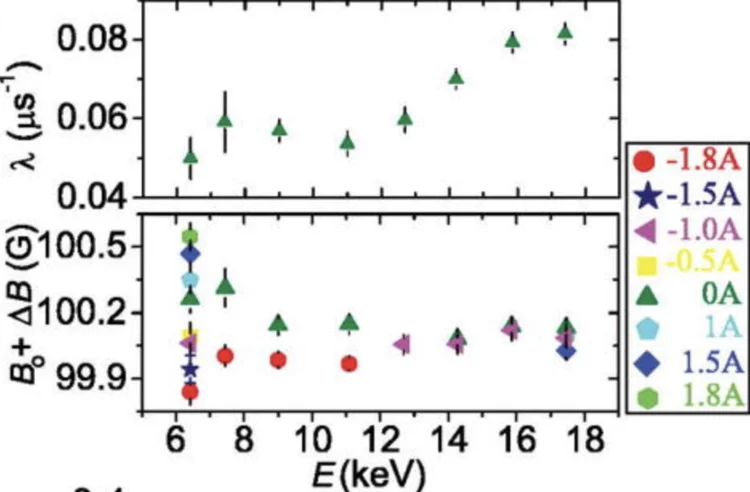
Probing current-induced magnetic fields in Au|YIG heterostructures with low-energy muon spin spectroscopy
We investigated the depth dependence of current-induced magnetic fields in a bilayer of a normal metal (Au) and a ferrimagnetic insulator (Yttrium Iron Garnet—YIG) by using low energy muon spin spectroscopy (LE-μSR). This allows us to explore how these fields vary from the Au surface down to the buried Au|YIG interface, which is relevant to study physics like the spin-Hall effect.