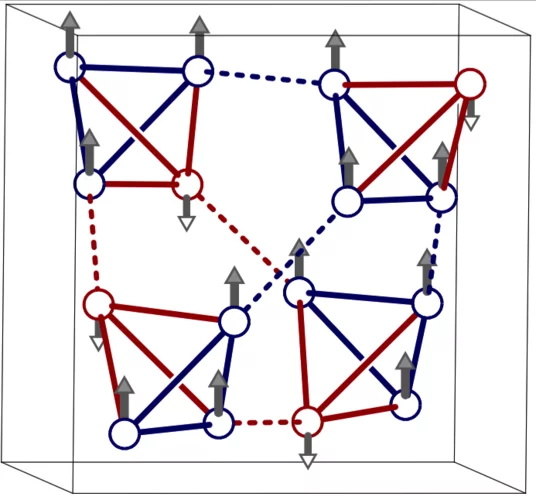
Spin excitations in copper selenate, a skyrmion host material
G.S. Tucker et al., Physical Review B 93, 054401 (2016). Inelastic neutron scattering measurements performed at EIGER and TASP have mapped the magnetic excitation spectrum along high-symmetry directions of the first Brillouin zone for the magnetic skyrmion host copper selenate, Cu2OSeO3.
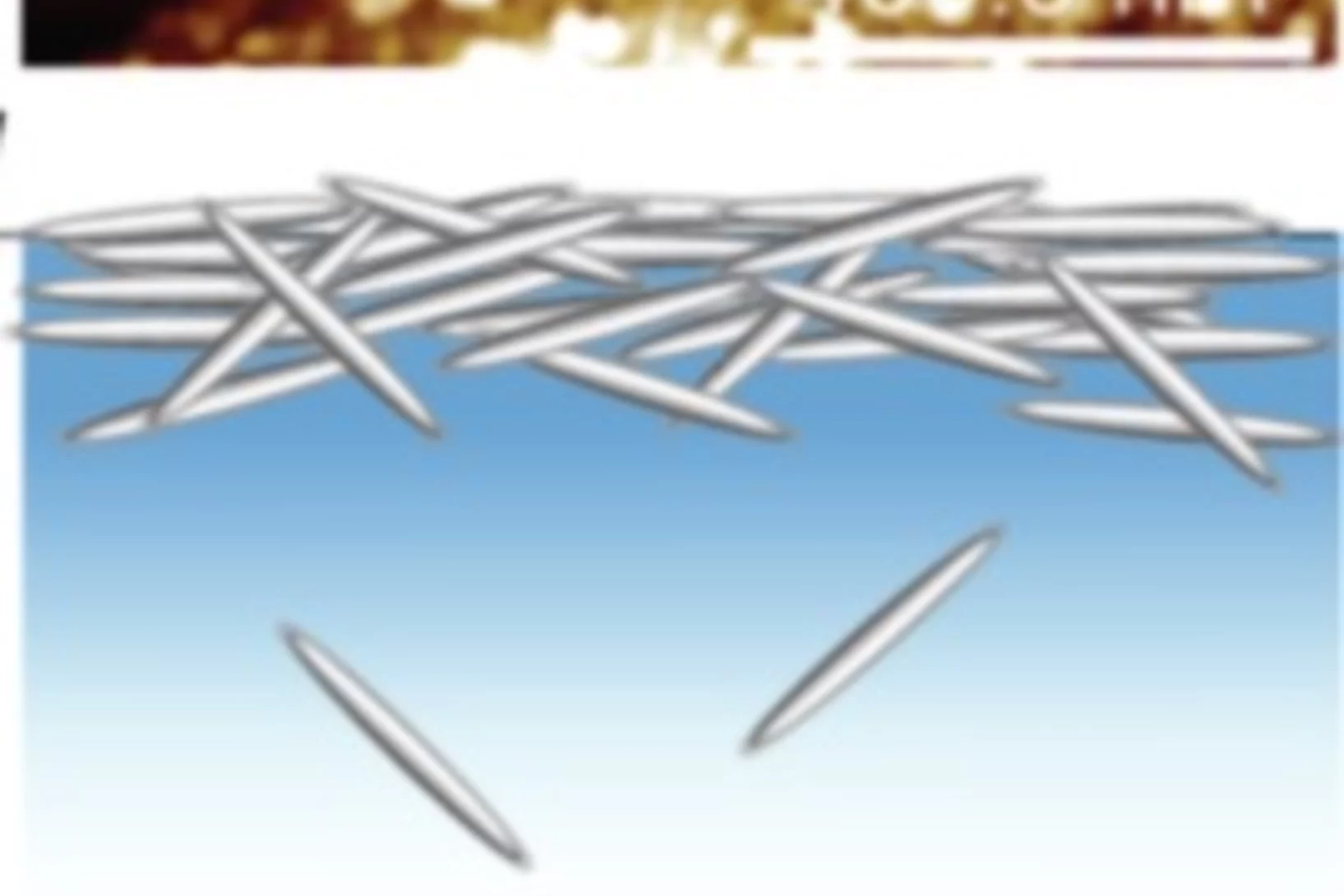
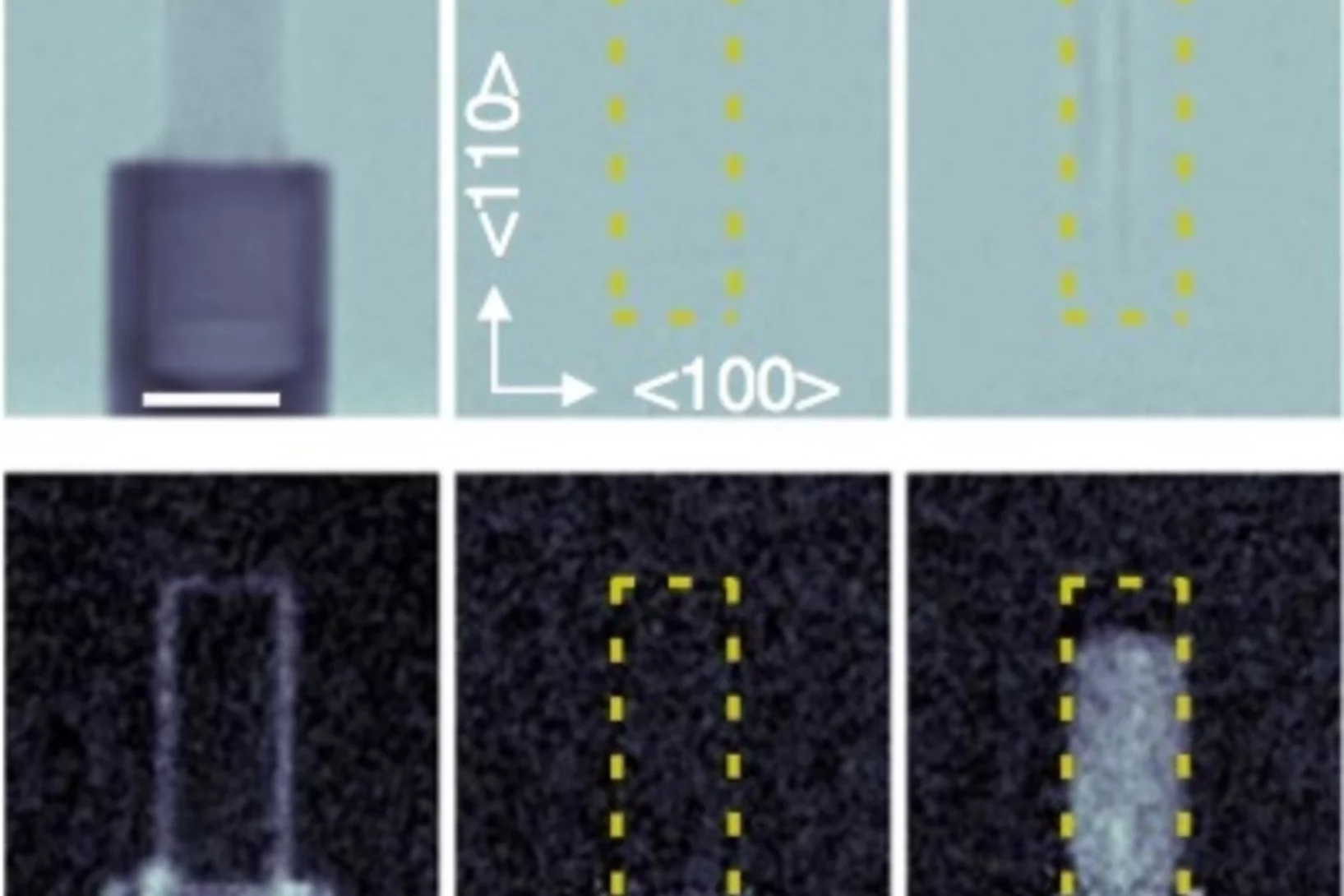
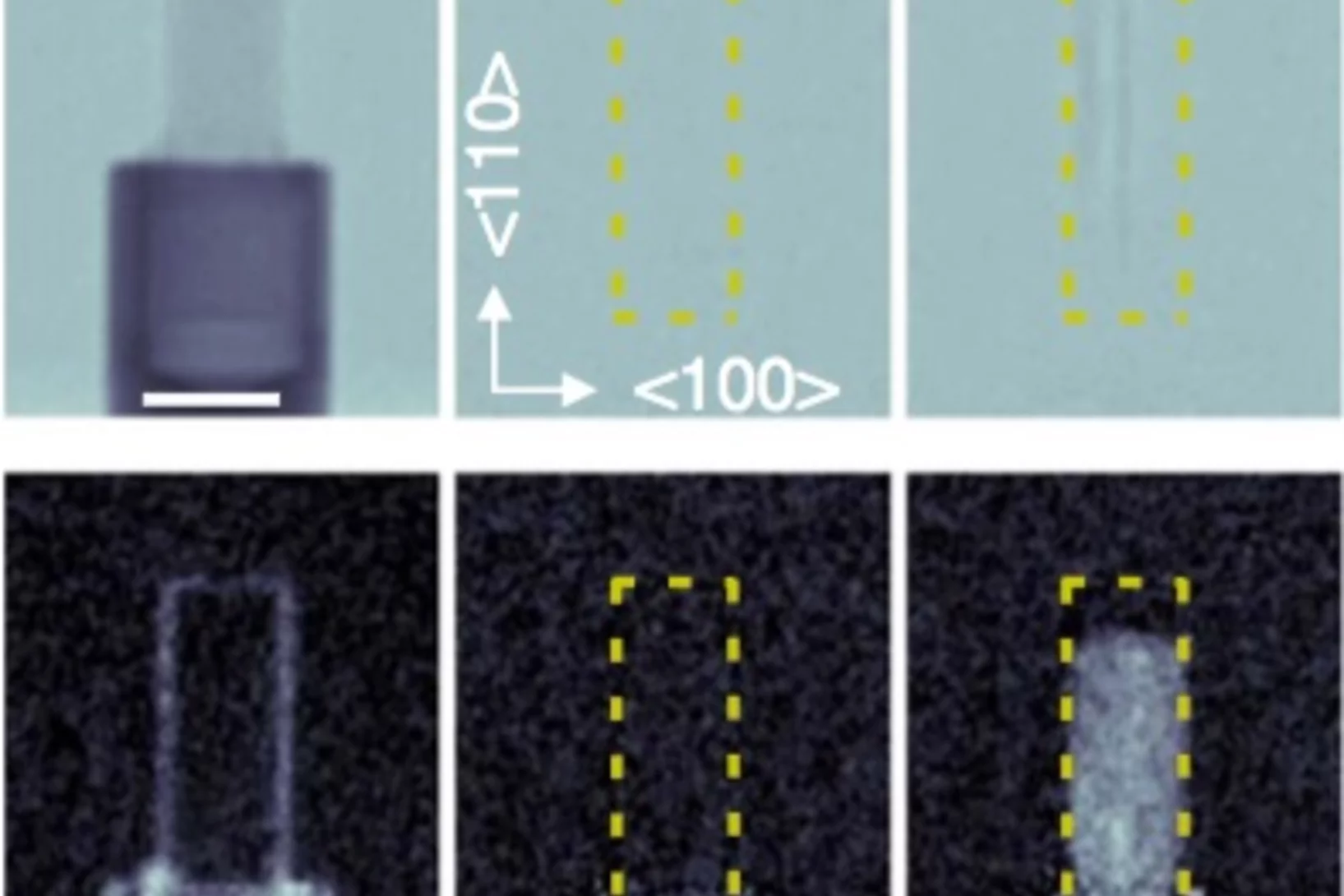
In-situ visualization of stress-dependent bulk magnetic domain formation by neutron grating interferometry
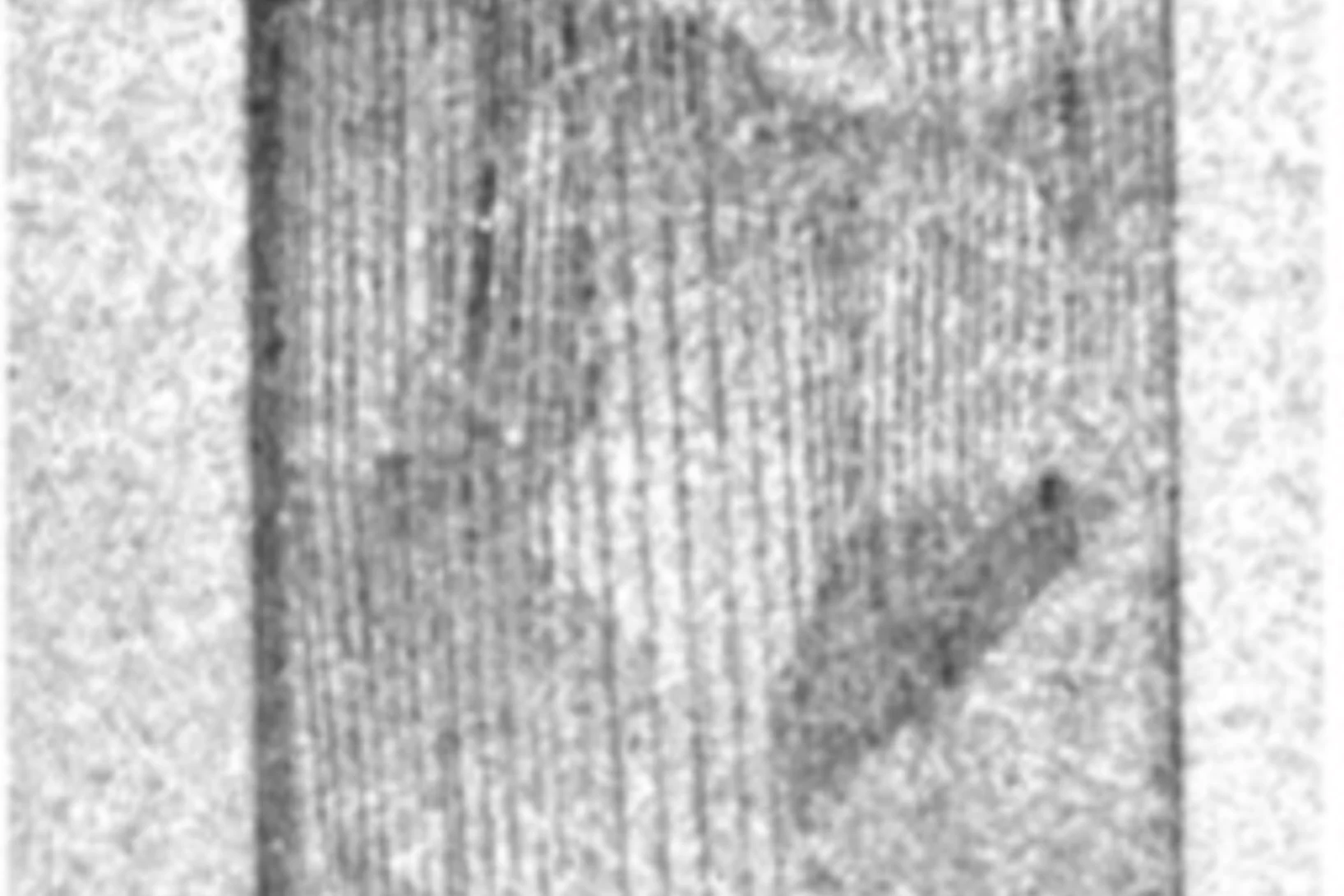
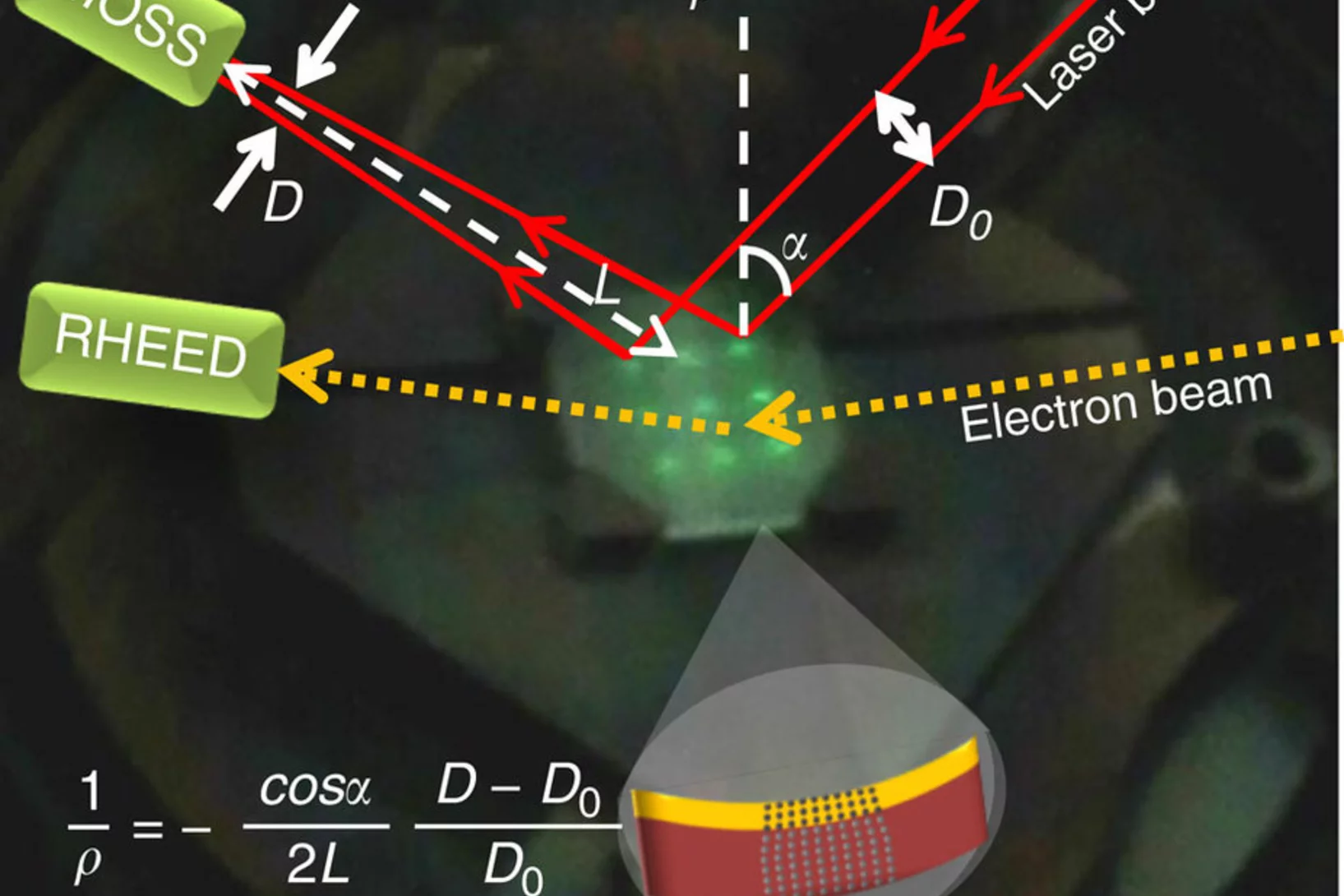
The efficiency of industrial transformers is directly influenced by the magnetic properties of high-permeability steel laminations (HPSLs). These laminations are coated by insulating layers, to reduce eddy-current losses in the transformer core. In addition, the coating induces favorable inter-granular tensile stresses that significantly influence the underlying magnetic domain structure.
Stratified Micellar Multilayers - Toward Nanostructured Photoreactors
Polyelectrolyte multilayers (PEMs) with stratification of the internal structure were assembled from statistical amphiphilic copolyelectrolytes of opposite charges. These polyelectrolytes organize in aqueous solutions into micellar structures with fluoroalkyl and aromatic nanodomains, respectively, that were also preserved after deposition as thin films via layer-by-layer (LbL) electrostatic self-assembly.
Giant Controllable Magnetization Changes Induced by Structural Phase Transitions in a Metamagnetic Artificial Multiferroic
The realization of a controllable metamagnetic transition from AFM to FM ordering would open the door to a plethora of new spintronics based devices that, rather than reorienting spins in a ferromagnet, harness direct control of a materials intrinsic magnetic ordering. In this study FeRh films with drastically reduced transition temperatures and a large magneto-thermal hysteresis were produced for magnetocaloric and spintronics applications.
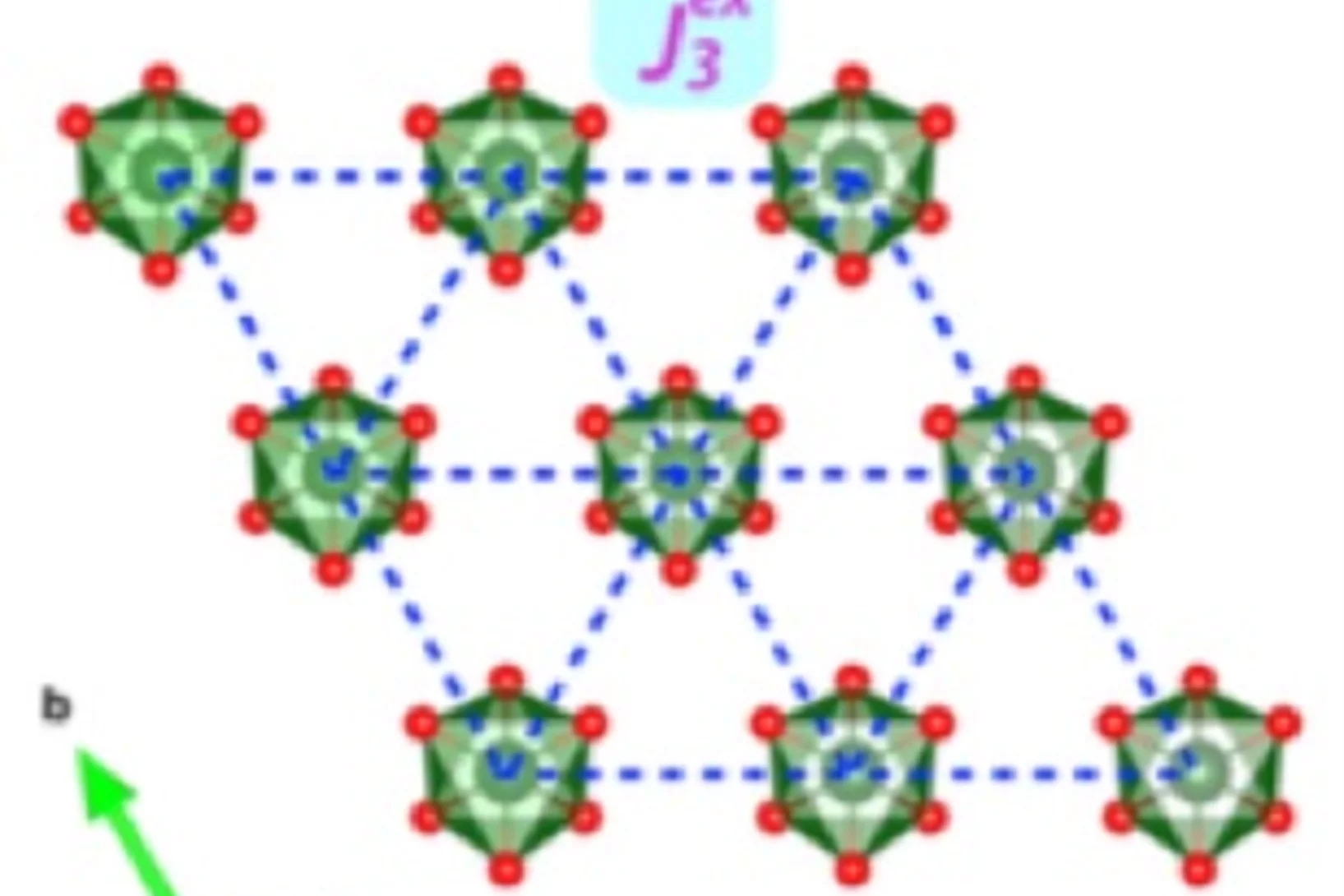
Origin of the Spin-Orbital Liquid State in a Nearly J=0 Iridate Ba3ZnIr2O9
We show using detailed magnetic and thermodynamic studies and theoretical calculations that the ground state of Ba3ZnIr2O9 is a realization of a novel spin-orbital liquid state. Our results reveal that Ba3ZnIr2O9 with Ir5+ (5d4) ions and strong spin-orbit coupling (SOC) arrives very close to the elusive J 1⁄4 0 state but each Ir ion still possesses a weak moment.
Textbook on XAS and XES
During the last two decades, remarkable and often spectacular progress has been made in the methodological and instrumental aspects of x–ray absorption and emission spectroscopy. This progress includes considerable technological improvements in the design and production of detectors especially with the development and expansion of large-scale synchrotron reactors All this has resulted in improved analytical performance and new applications, as well as in the perspective of a dramatic enhancement in the potential of x–ray based analysis techniques for the near future.
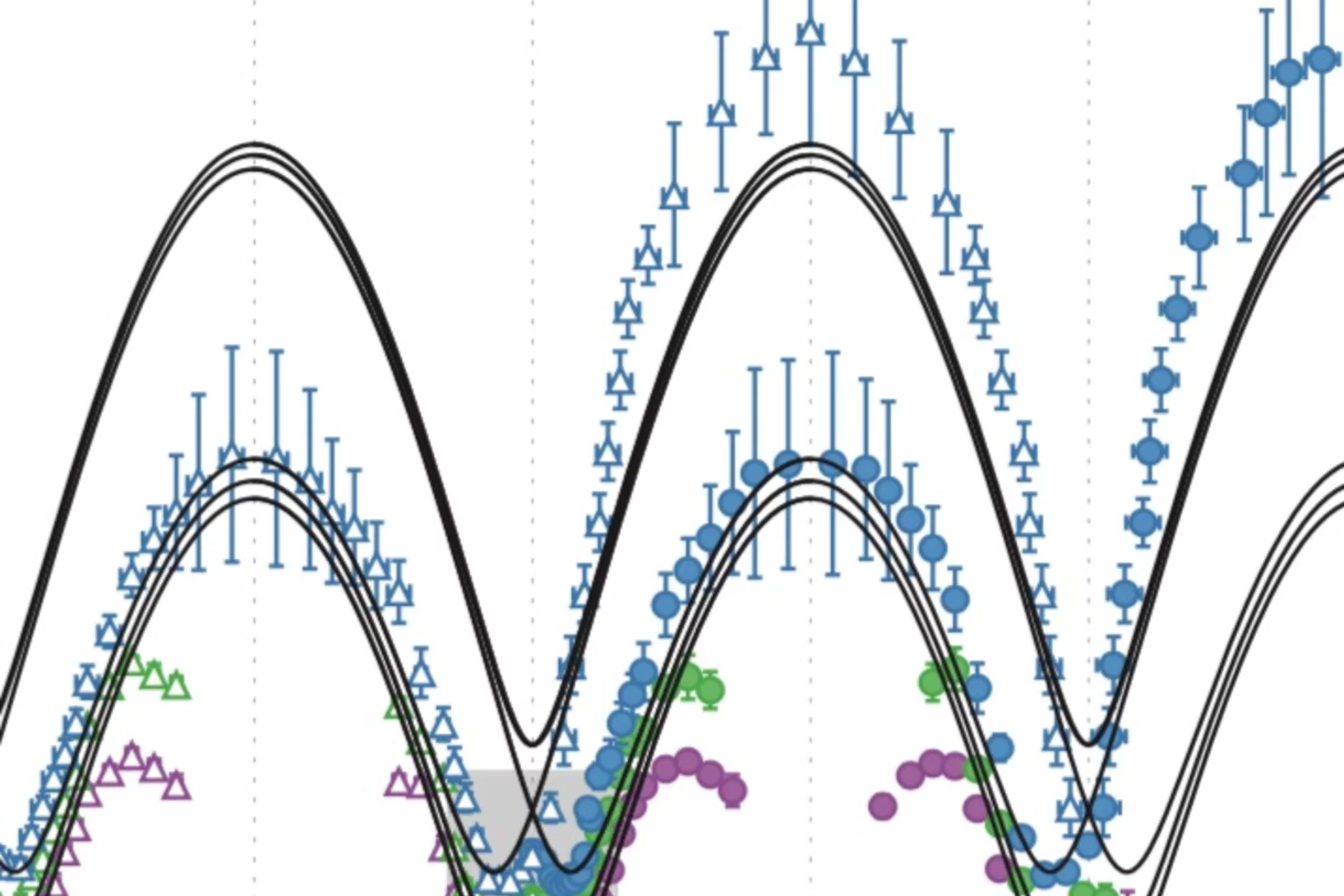
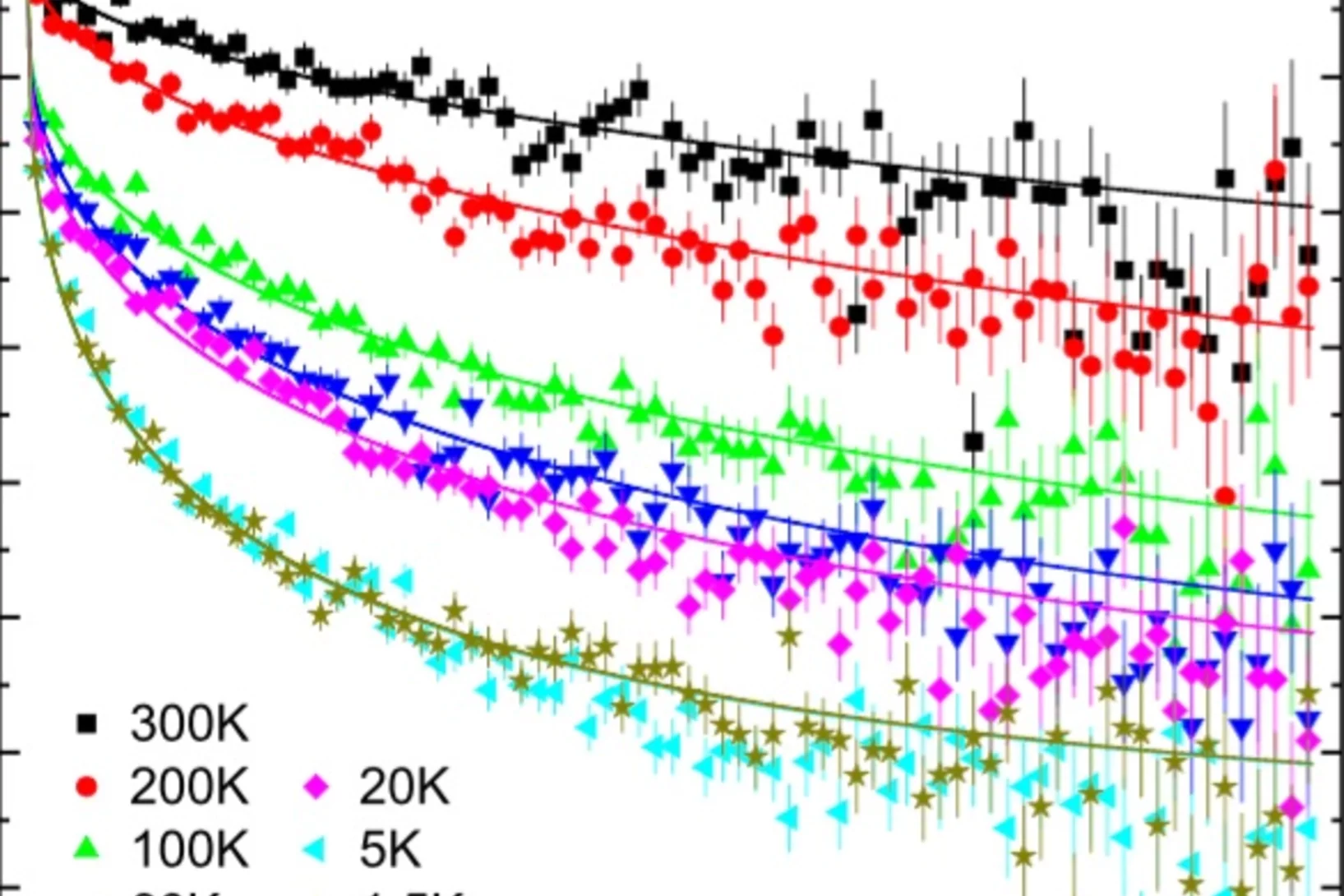
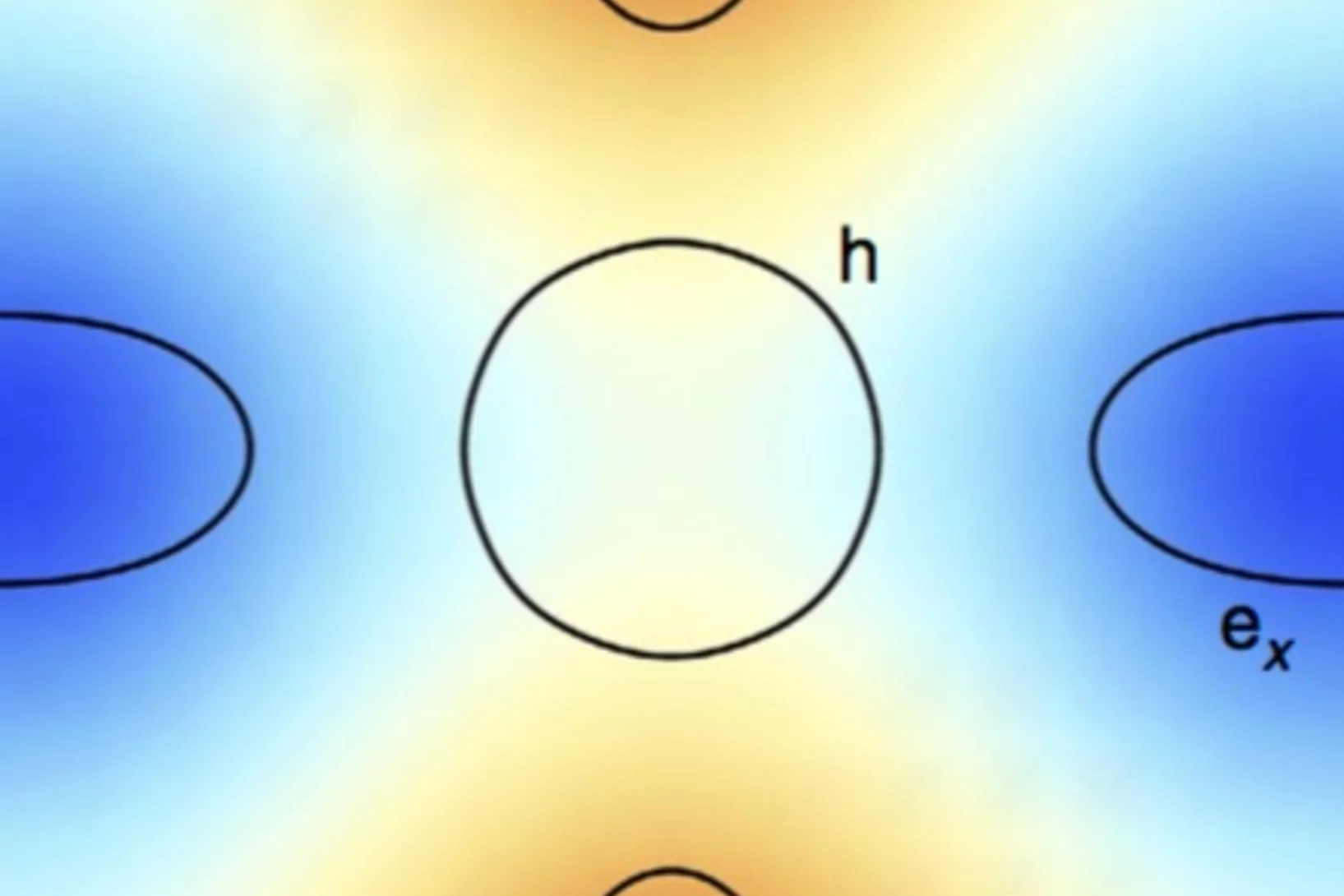
Quasiparticle-continuum level repulsion in a quantum magnet
When the energy eigenvalues of two coupled quantum states approach each other in a certain parameter space, their energy levels repel each other and level crossing is avoided. Such level repulsion, or avoided level crossing, is commonly used to describe the dispersion relation of quasiparticles in solids.
In situ stress observation in oxide films and how tensile stress influences oxygen ion conduction
Many properties of materials can be changed by varying the interatomic distances in the crystal lattice by applying stress. Ideal model systems for investigations are heteroepitaxial thin films where lattice distortions can be induced by the crystallographic mismatch with the substrate. Here we describe an in situ simultaneous diagnostic of growth mode and stress during pulsed laser deposition of oxide thin films.
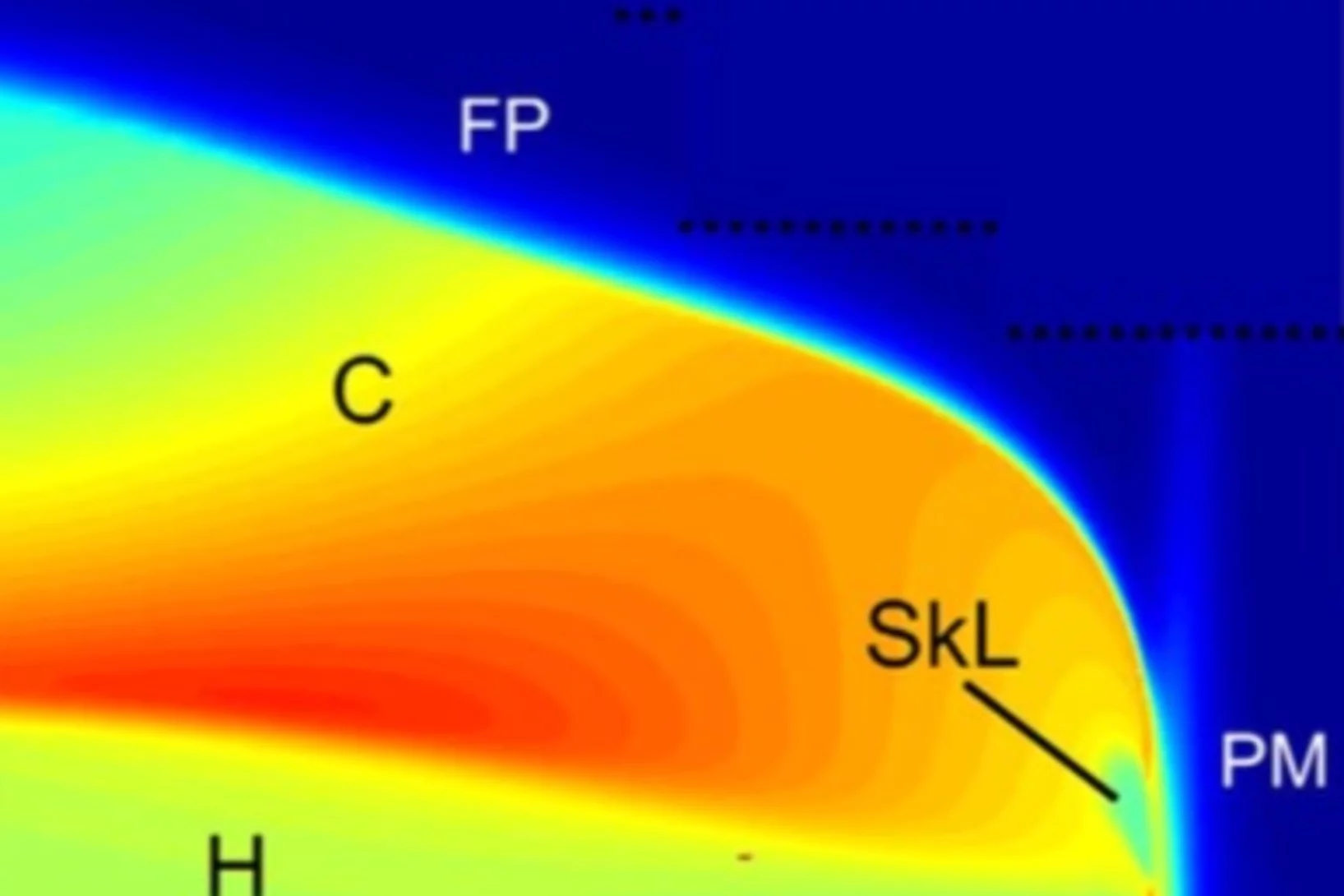
Dramatic pressure-driven enhancement of bulk skyrmion stability
The recent discovery of magnetic skyrmion lattices initiated a surge of interest in the scientic community. Several novel phenomena have been shown to emerge from the interaction of conducting electrons with the skyrmion lattice, such as a topological Hall-effect and a spin-transfer torque at ultra-low current densities.
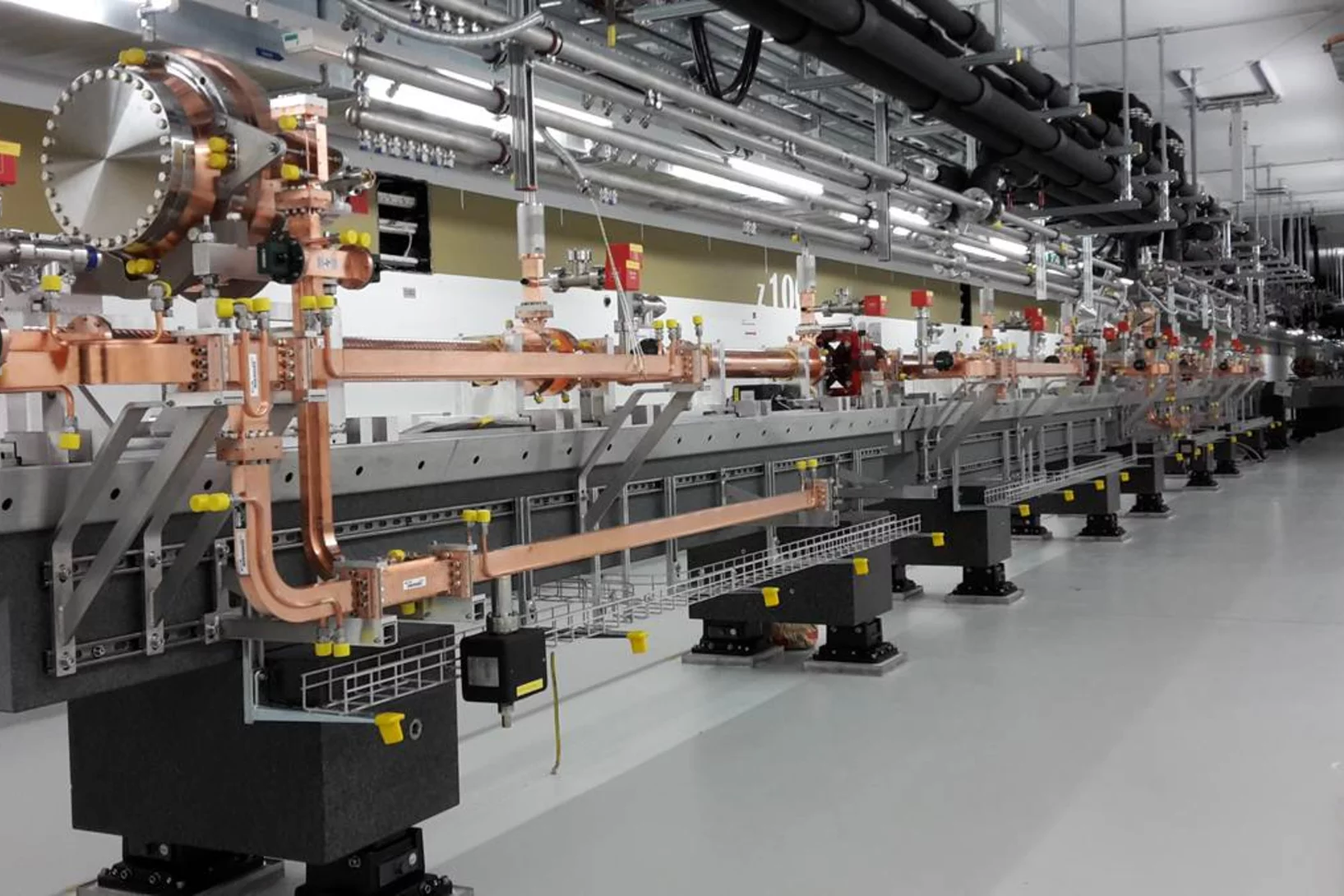
Installation progress of the SwissFEL Linac
The installation of the linear accelerator (Linac) progresses very well. This week, the last girder of the so-called “Linac 1” was installed in the SwissFEL tunnel. The entire C-band accelerator consists out of Linac 1, Linac 2, and Linac 3, and a total amount of 104 accelerating structures. Meanwhile, 38 accelerating structures are installed in the SwissFEL tunnel. The assembly work on the remaining Linac modules will take place until end of September of this year. By then it is planned to finish the installation of all Linac modules in the SwissFEL tunnel.
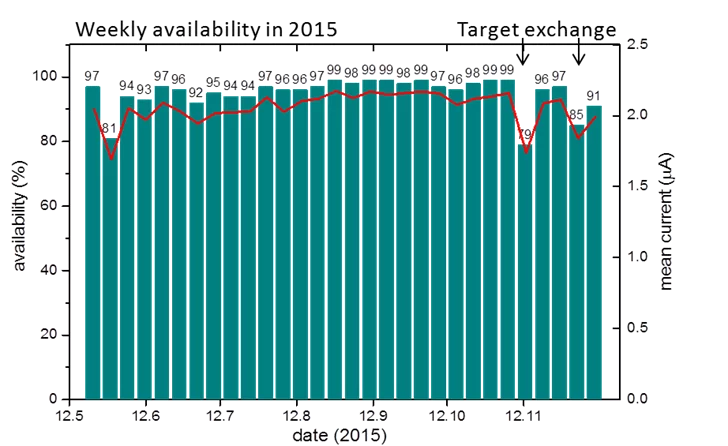
Proton Accelerator Operation Statistics 2015
For the first time in the history of the High Intensity Proton Accelerator the availability of the facility reached an outstanding value of 95% in 2015 with a record value of 99.3% in week 44. In comparison to the two previous years this corresponds to a reduction of the downtime by 50%. The user operation in 2015 was started as scheduled and already in the first week the machine was available 97% of the scheduled beam time. In addition to the smooth operation of the facility, high intensity beam experiments could regularly be performed with currents of up to 2.4 mA. nu
Coexistence of low-moment magnetism and superconductivity in tetragonal FeS and suppression of Tc under pressure
The family of iron-based superconductors has recently acquired a new member material, FeS. Theoretically, this compound has been shown to have electronic structure similar to that of the superconducting FeSe. However, contradictory ground states have been predicted for FeS. In this work, a collaboration of authors from Switzerland and Germany use muon spin rotation and relaxation to show that weak-moment magnetism microscopically coexists with bulk superconductivity.
Porträt Jenna Poonoosamy: Die Vermesserin der Gesteinsporen
Drei Jahre in Folge hat Jenna Poonoosamy den Preis für die beste Präsentation am Doktorandentag im Bereich Nukleare Energie und Sicherheit (NES) am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI erhalten. Poonoosamy stammt ursprünglich von der Insel Mauritius im Indischen Ozean. Schon in der Schule interessierte sie sich vor allem für Chemie. «Die meisten meiner Freunde wollten in die Wirtschaft», erzählt sie. «Mich dagegen haben die Naturwissenschaften fasziniert.» Und so zog sie nach der Schule zum Chemie-Studium nach Paris. Und kam später für ihre Doktorarbeit ans PSI.
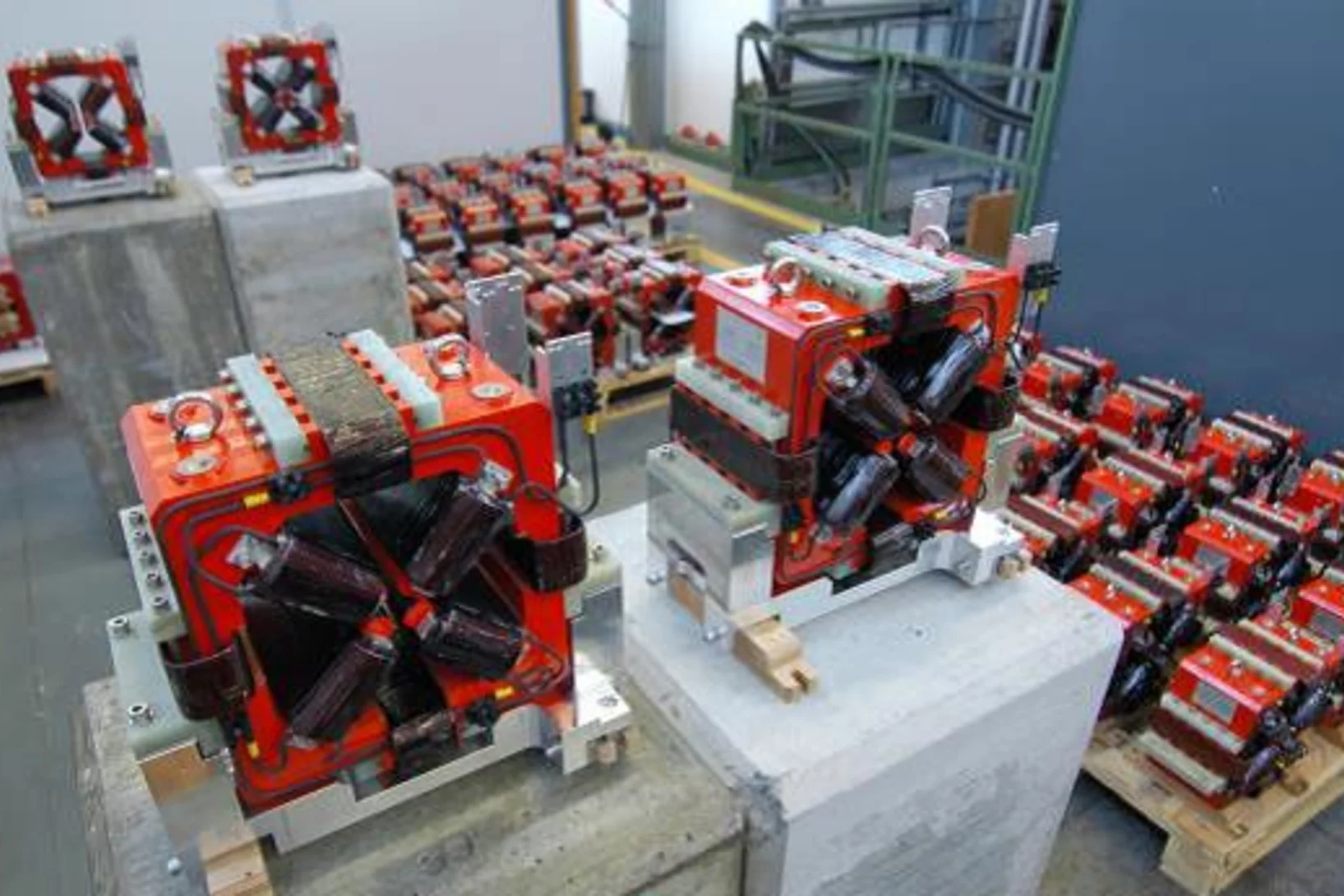
GFA delivers the SwissFEL magnets on schedule
The Paul Scherrer Institut is building an X-ray free electron laser (SwissFEL) providing a source of intense, ultra-short pulses of coherent radiation in the wavelength range of 0.1 nm to 0.7nm. For the hard X-ray beam line, the magnet section in GFA/ATK has the responsibility for the design, the procurement and the magnetic qualification of 267 electro-magnets of 22 different types. Several design studies were performed in an attempt to meet the required magnet specifications while optimizing construction and operation cost.
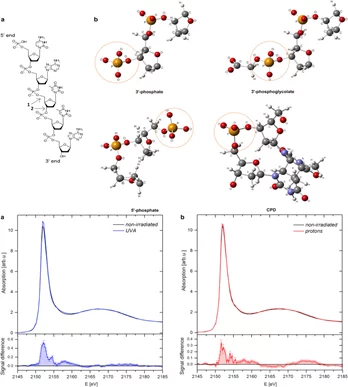
Biophysical effects of UV radiation on biological samples
The biological influence of radiation on living matter has been studied for years; however, several questions about the detailed mechanism of radiation damage formation remain largely unanswered. Among all biomolecules exposed to radiation, DNA plays an important role because any damage to its molecular structure can affect the whole cell and may lead to chromosomal rearrangements resulting in genomic instability or cell death.
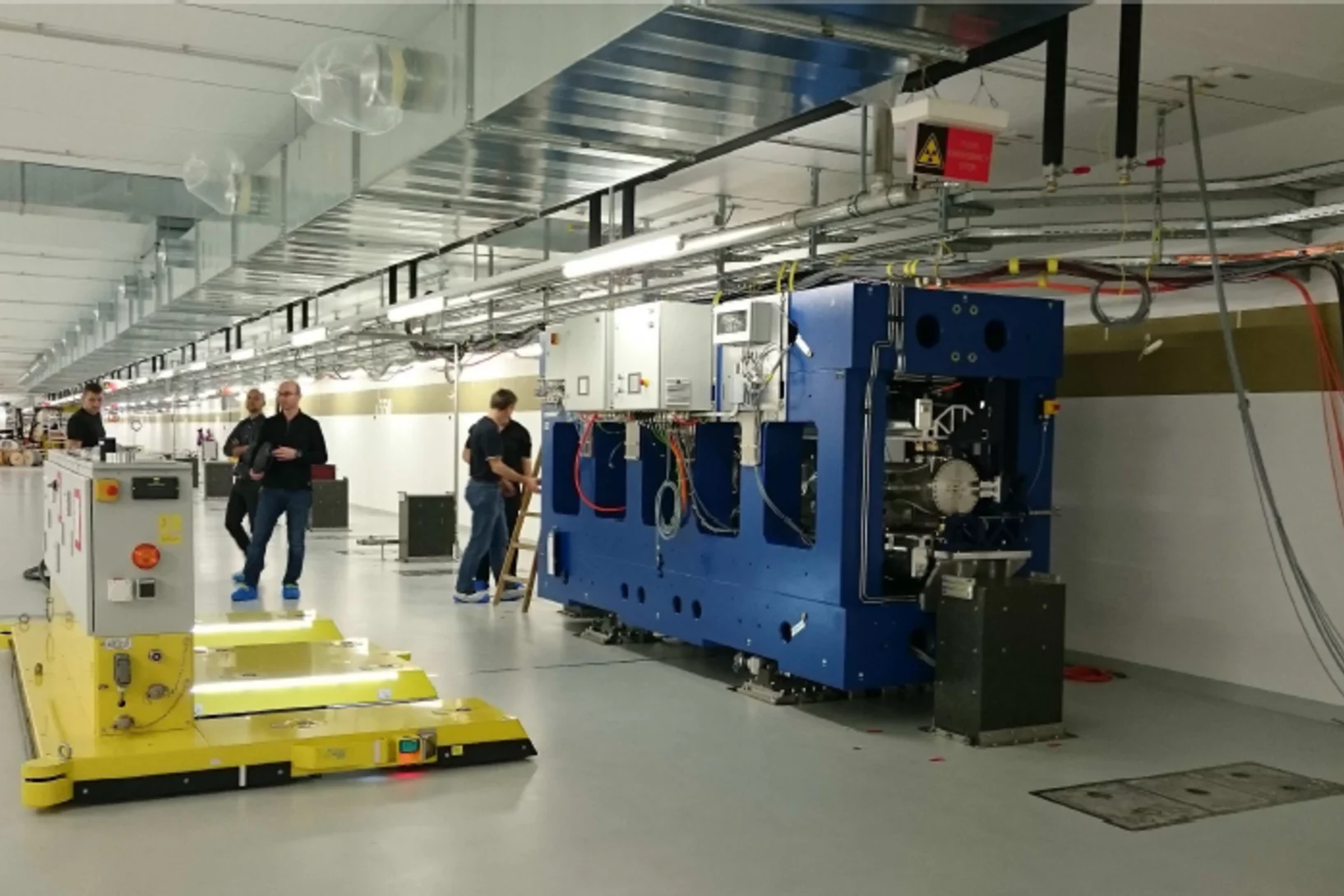
Transport of first "completed" Undulator into the SwissFEL Tunnel
On the 25th of January, the first "completed" undulator has been transported to its final position in the SwissFEL tunnel. The 1064 permanent magnets of this undulator where shimmed to the sub-micrometer level and the magnetic profile has been carefully measured for the full gap range. Twelve of such undulators will be installed until October 2016!
Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Study of Interplay of Attractive and Repulsive Interactions in Nanoparticle-Polymer System
The phase behavior of nanoparticle (silica)−polymer (polyethylene glycol) system without and with an electrolyte (NaCl) has been studied. It is observed that nanoparticle−polymer system behaves very differently in the presence of electrolyte. In the absence of electrolyte, the nanoparticle−polymer system remains in one-phase even at very high polymer concentrations.
Mechanically Enhanced Liquid Interfaces at Human Body Temperature Using Thermosensitive Methylated Nanocrystalline Cellulose
The mechanical performance of materials at oil/water interfaces after consumption is a key factor affecting hydrophobic drug release. In this study, we methylated the surface of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) by mercerization and dimethyl sulfate exposure to produce thermosensitive biopolymers. These methylated NCC (metNCC) were used to investigate interfacial thermogelation at air/water and medium-chain triglyceride (MCT)/water interfaces at body temperature.
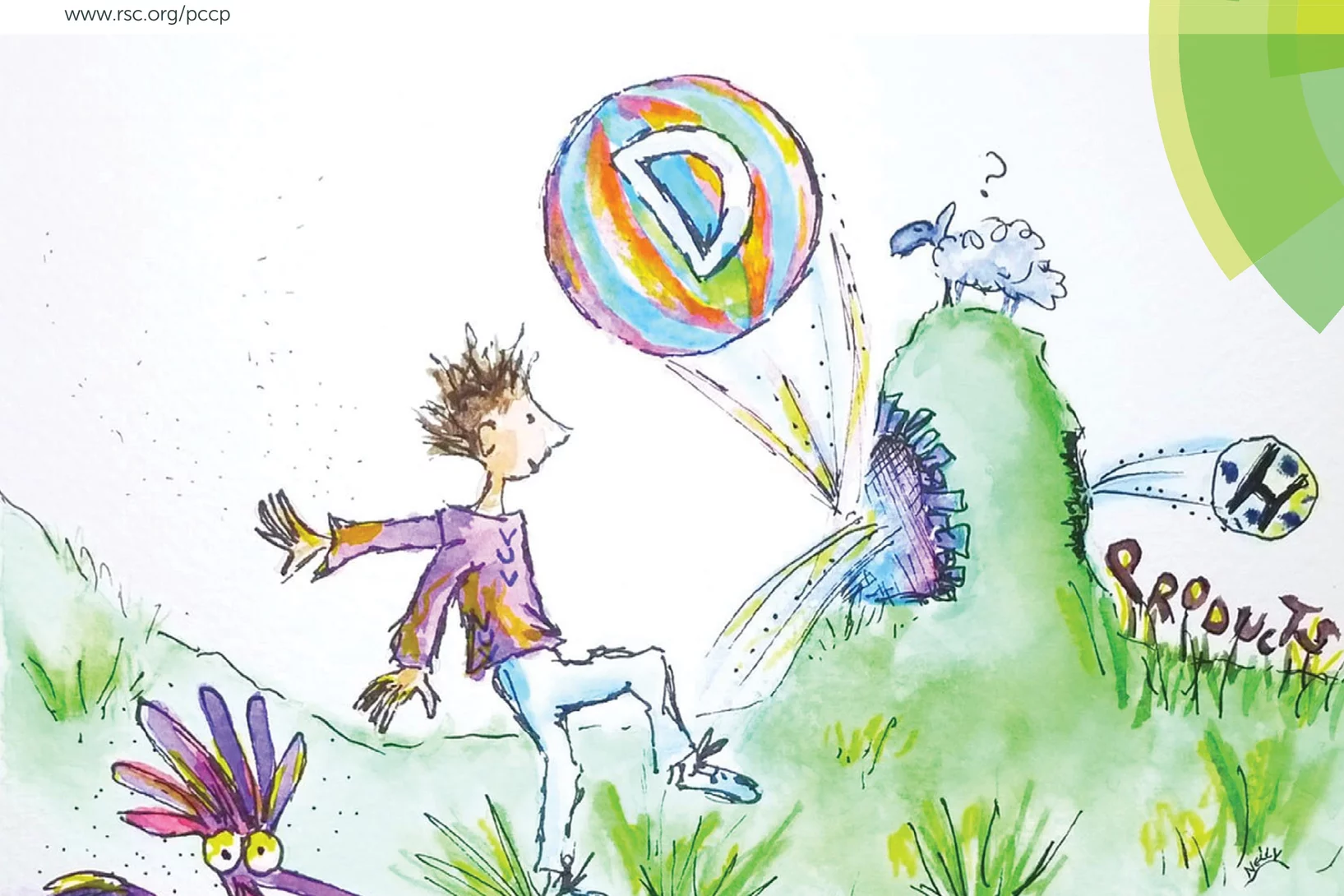
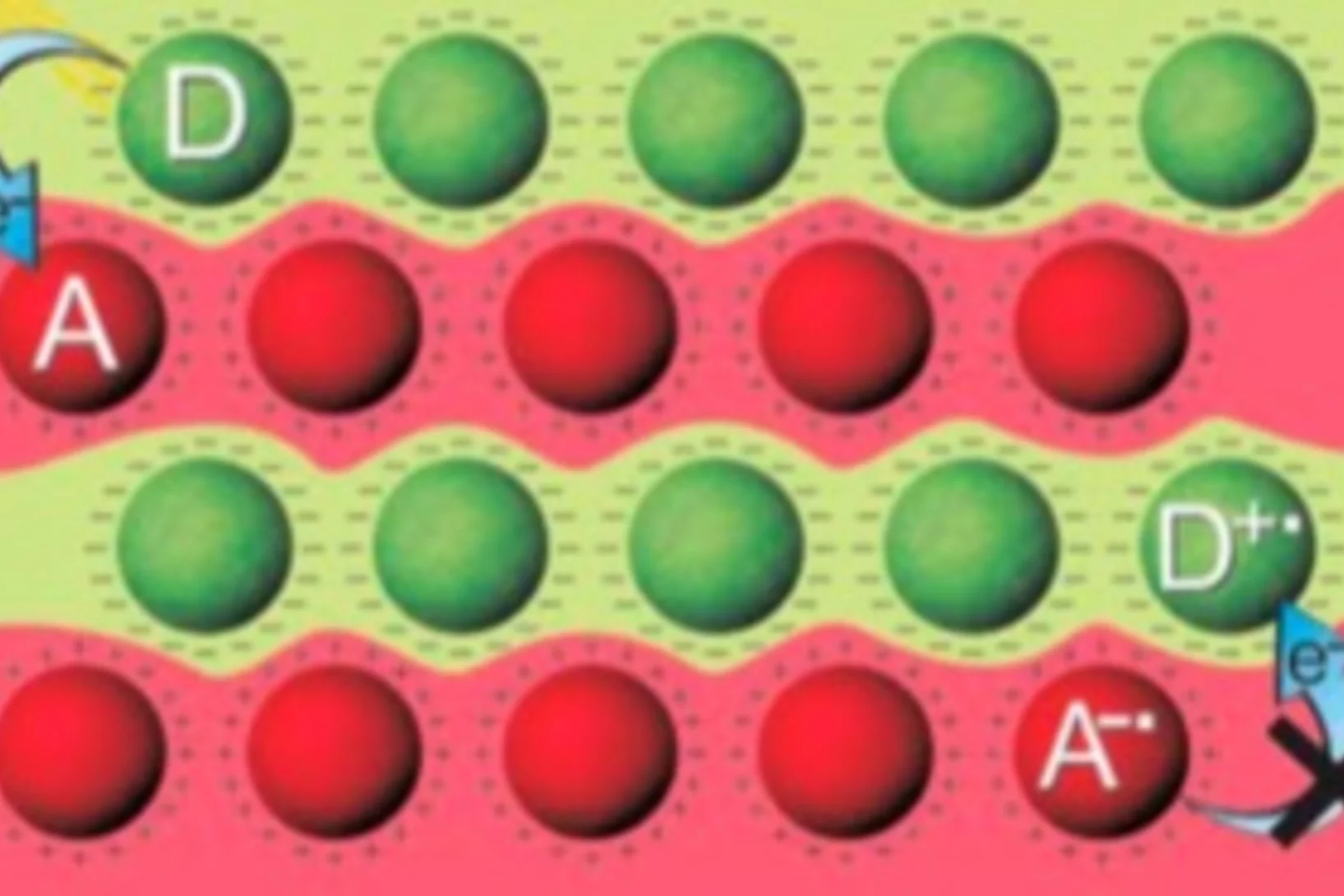
Controlling tunnelling in methane loss from acetone ions by deuteration
If a ball is rolled up a hill with less kinetic energy than the potential energy at the top, it will return eventually, and stays bound in the valley. Tunnelling is a distinctly quantum mechanical phenomenon, in which such balls can magically cross the hill, and appear in the neighbouring valley, as if going through a tunnel. In order for this to happen with a non-negligible probability, the ball has to be small and the barrier, i.e. the hill, sharp.
Self-Diffusion in Amorphous Silicon
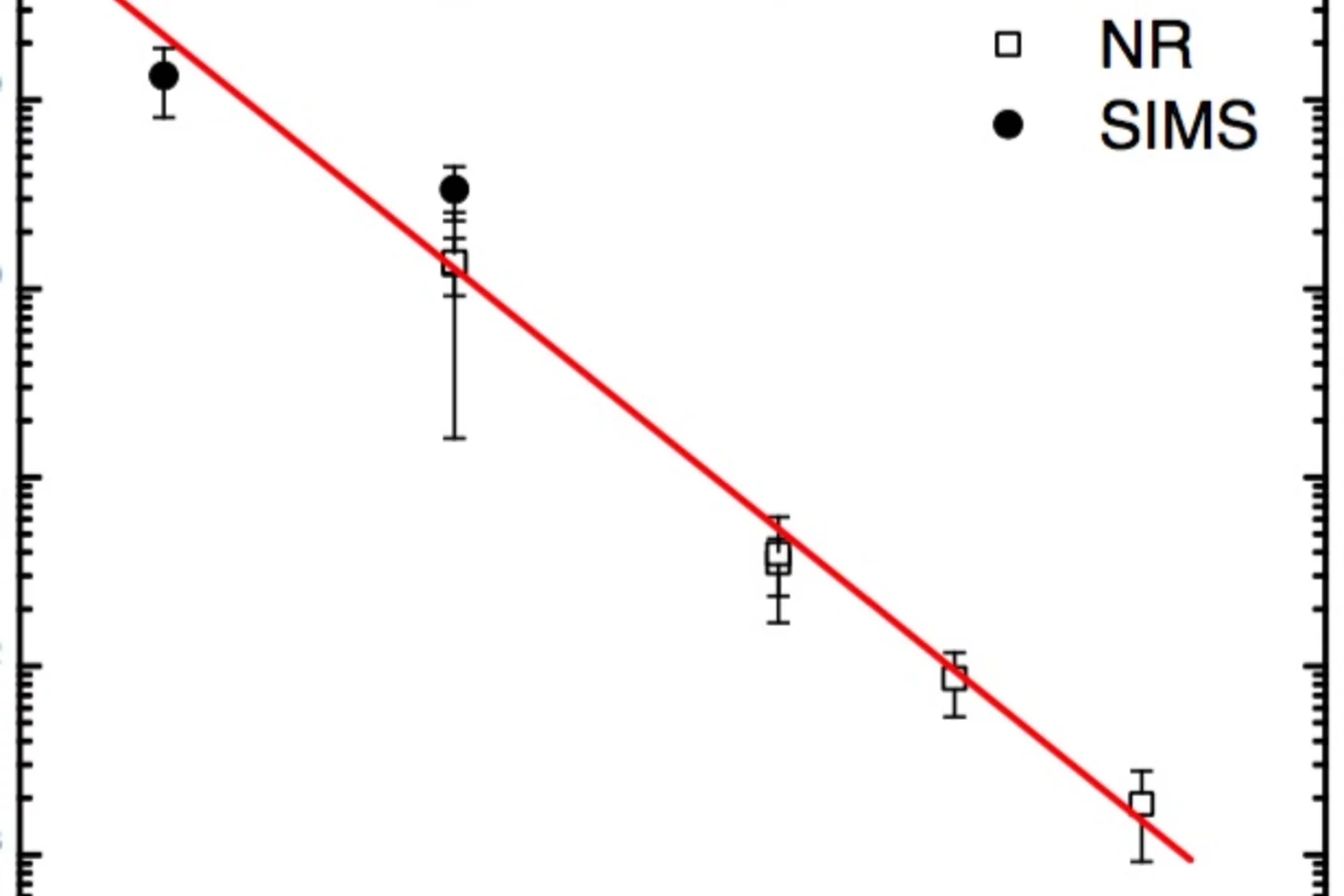
The present Letter reports on self-diffusion in amorphous silicon. Experiments were done on 29Si/natSi heterostructures using neutron reflectometry and secondary ion mass spectrometry. The diffusivities follow the Arrhenius law in the temperature range between 550 and 700°C with an activation energy of (4.4 ± 0.3) eV.
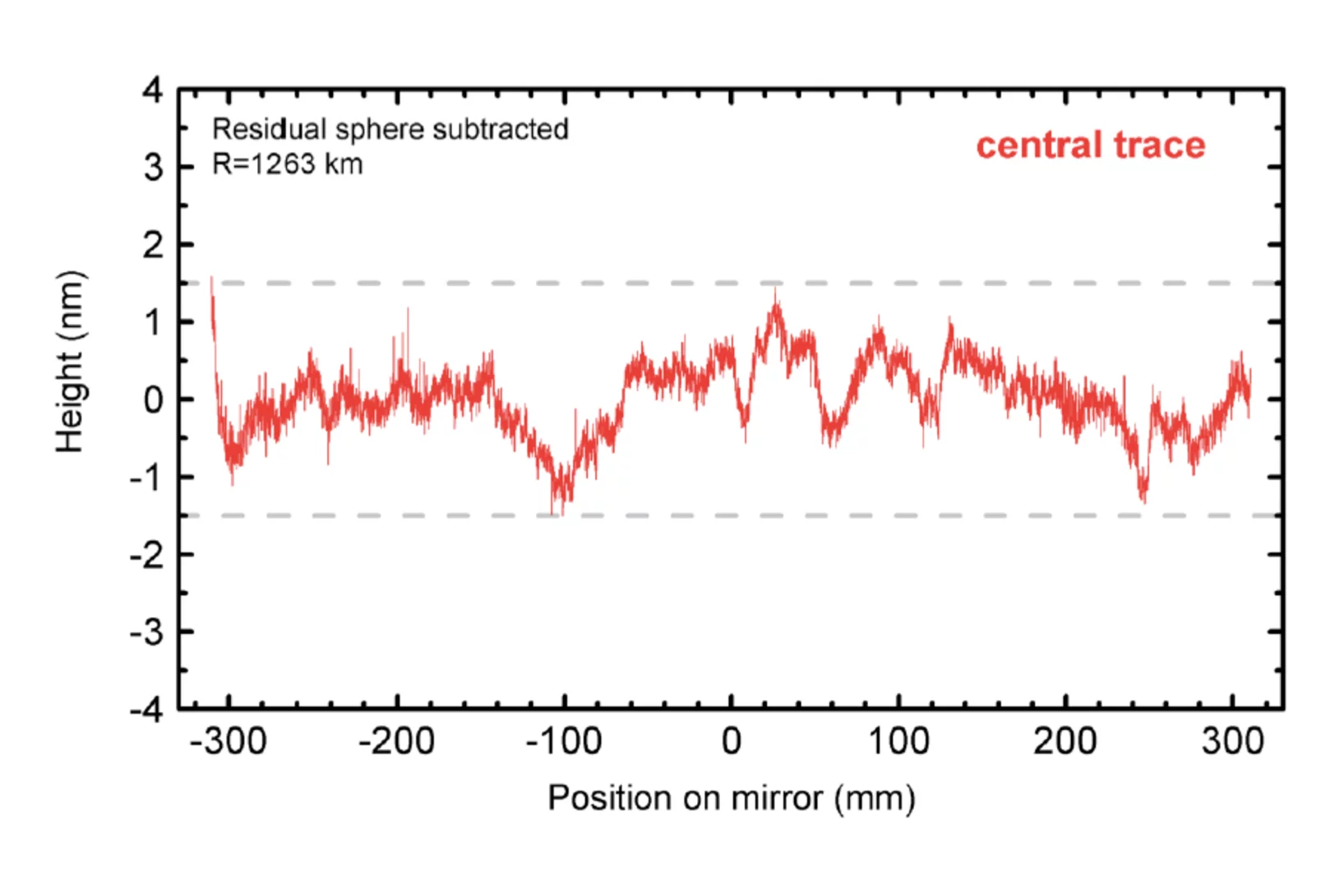
First ultraprecise mirror for SwissFEL arrived at PSI
Mirrors are key elements to distribute and shape the Xray beam generated by the undulators of the SwissFEL facility. They are essential tools to guide and focus the light according to the specific users requirements and should do this without noticeable effects on the beam quality. A quantitative measure is the quality of the beam wavefront.
First ultraprecise mirror for SwissFEL arrived at PSI
Mirrors are key elements to distribute and shape the Xray beam generated by the undulators of the SwissFEL facility. They are essential tools to guide and focus the light according to the specific users requirements and should do this without noticeable effects on the beam quality. A quantitative measure is the quality of the beam wavefront. The wavefront must be conserved by the optical elements in the SwissFEL beamlines within a fraction of the wavelength which can be as short as one Angstrom in the case of Aramis. There are only few companies in the world, who are able to fabricated such ultraprecise mirrors.
In-situ visualization of stress-dependent bulk magnetic domain formation by neutron grating interferometry
The performance and degree of efficiency of industrial transformers are directly influenced by the magnetic properties of high-permeability steel laminations (HPSLs). Industrial transformer cores are built of stacks of single HPSLs. While the insulating coating on each HPSL reduces eddy-current losses in the transformer core, the coating also induces favorable inter-granular tensile stresses that significantly influence the underlying magnetic domain structure.
Endlagersuche: Viele 100'000 Jahre sicher im Ton
Obwohl die Schweiz aus der Kernenergie aussteigt, muss sie eine Lösung für das in den Kernkraftwerken, aber auch in Medizin, Industrie und Forschung entstandene, radioaktive Material finden. Daher stellt sie sich einer aussergewöhnlichen, verantwortungsvollen Aufgabe: Sie sucht einen Ort, an dem sie ihre radioaktiven Abfälle mehrere hunderttausend Jahre lang sicher lagern kann. So lange, bis sie von selbst die Radioaktivität natürlicher Gesteine erreicht haben.
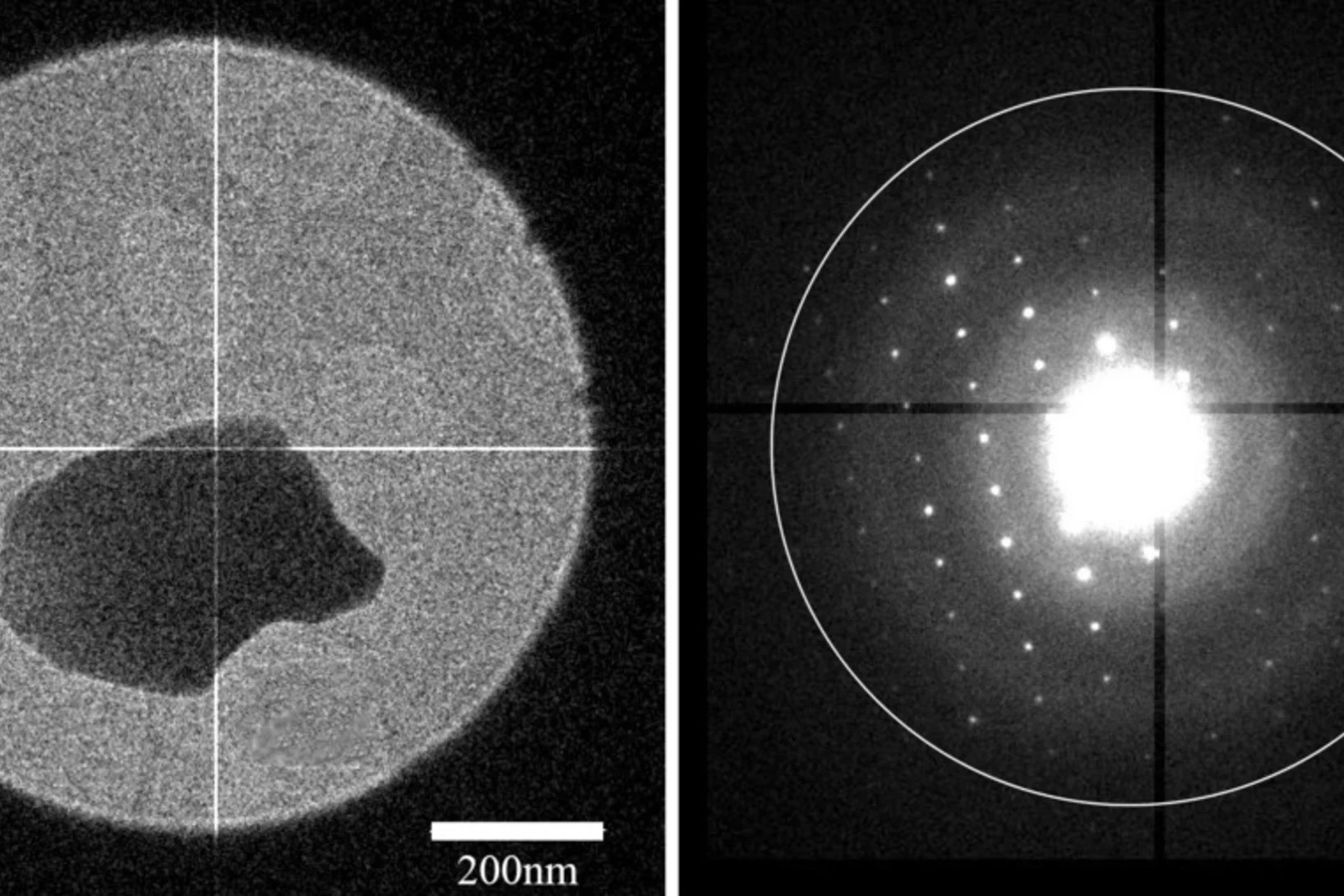
Determining the structures of nanocrystalline pharmaceuticals by electron diffraction
A new type of detector developed by Dr. van Genderen enables the structure determination of pharmaceutical compounds with electron diffraction at room temperature. The group concentrate on expanding this new technique to macromolecular compounds.
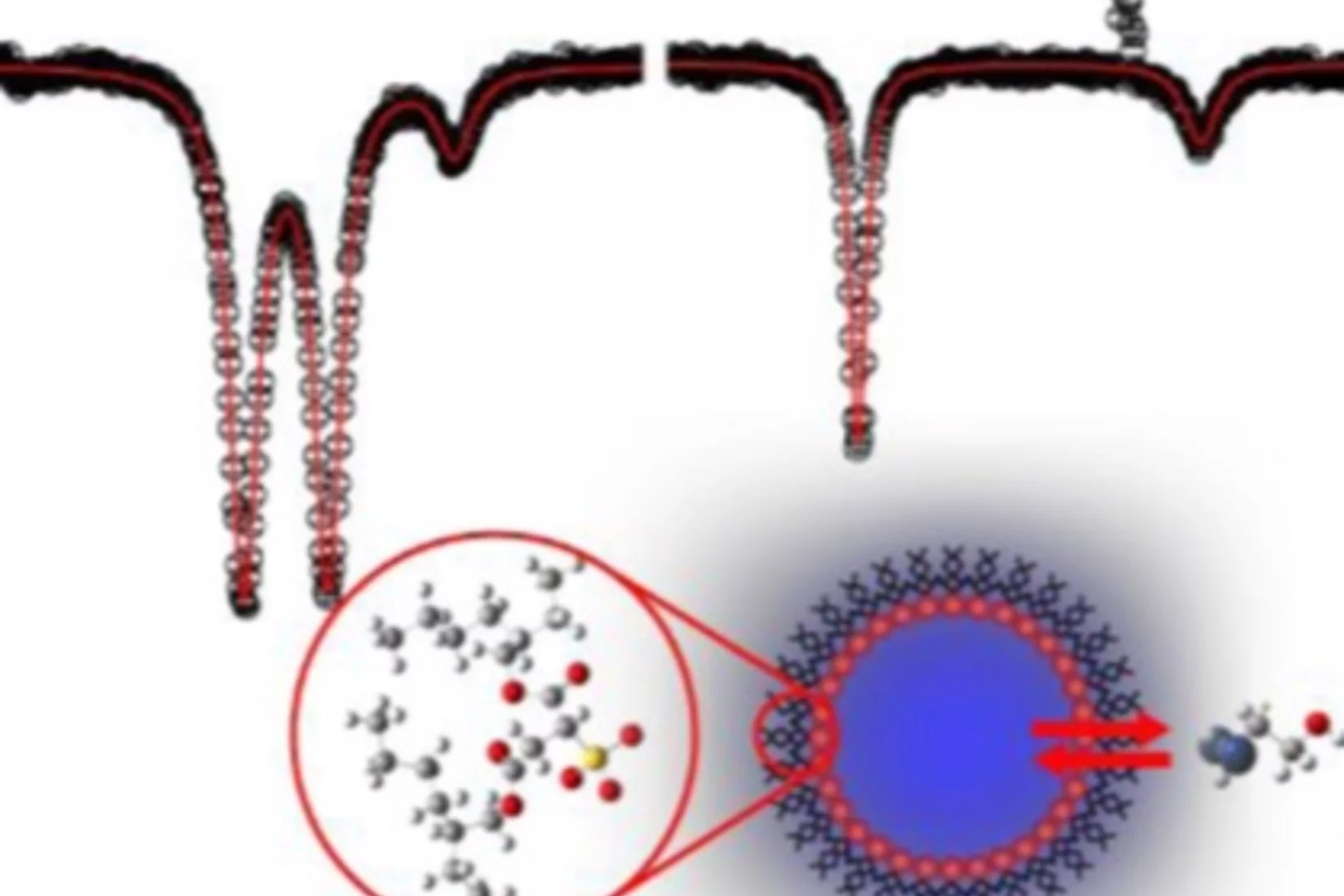
Rate of Molecular Transfer of Allyl Alcohol across an AOT Surfactant Layer Using Muon Spin Spectroscopy
The transfer rate of a probe molecule across the interfacial layer of a water-in-oil (w/o) microemulsion was investigated using a combination of transverse field muon spin rotation (TF-μSR), avoided level crossing muon spin resonance (ALC-μSR), and Monte Carlo simulations. Reverse micro-emulsions consist of nanometer-sized water droplets dispersed in an apolar solvent separated by a surfactant monolayer.
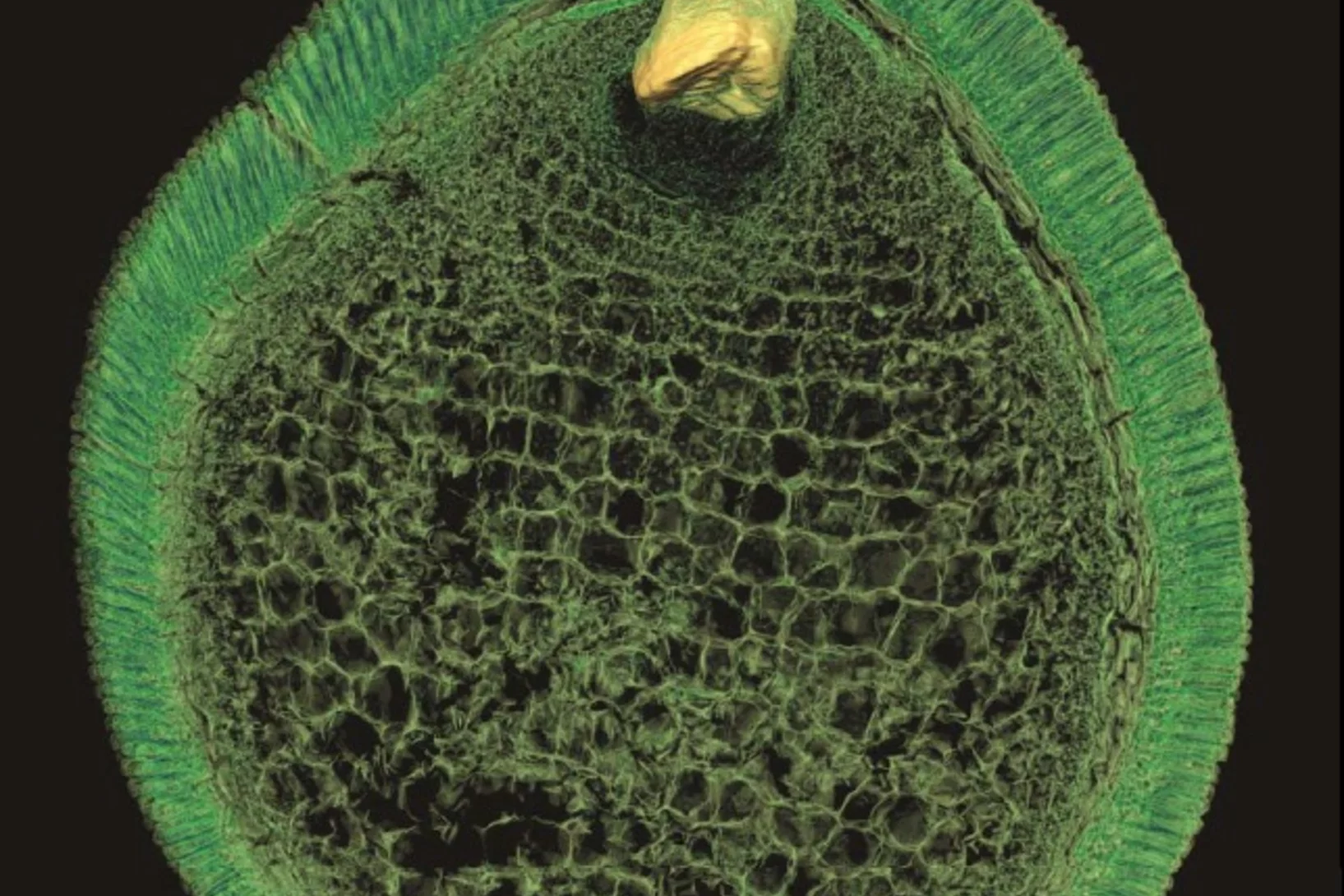
Preserved Embryos Illustrate Seed Dormancy in Early Angiosperms
The discovery of exceptionally well-preserved, tiny fossil seeds dating back to the Early Cretaceous corroborates that flowering plants were small opportunistic colonizers at that time, according to a new Yale-led study.
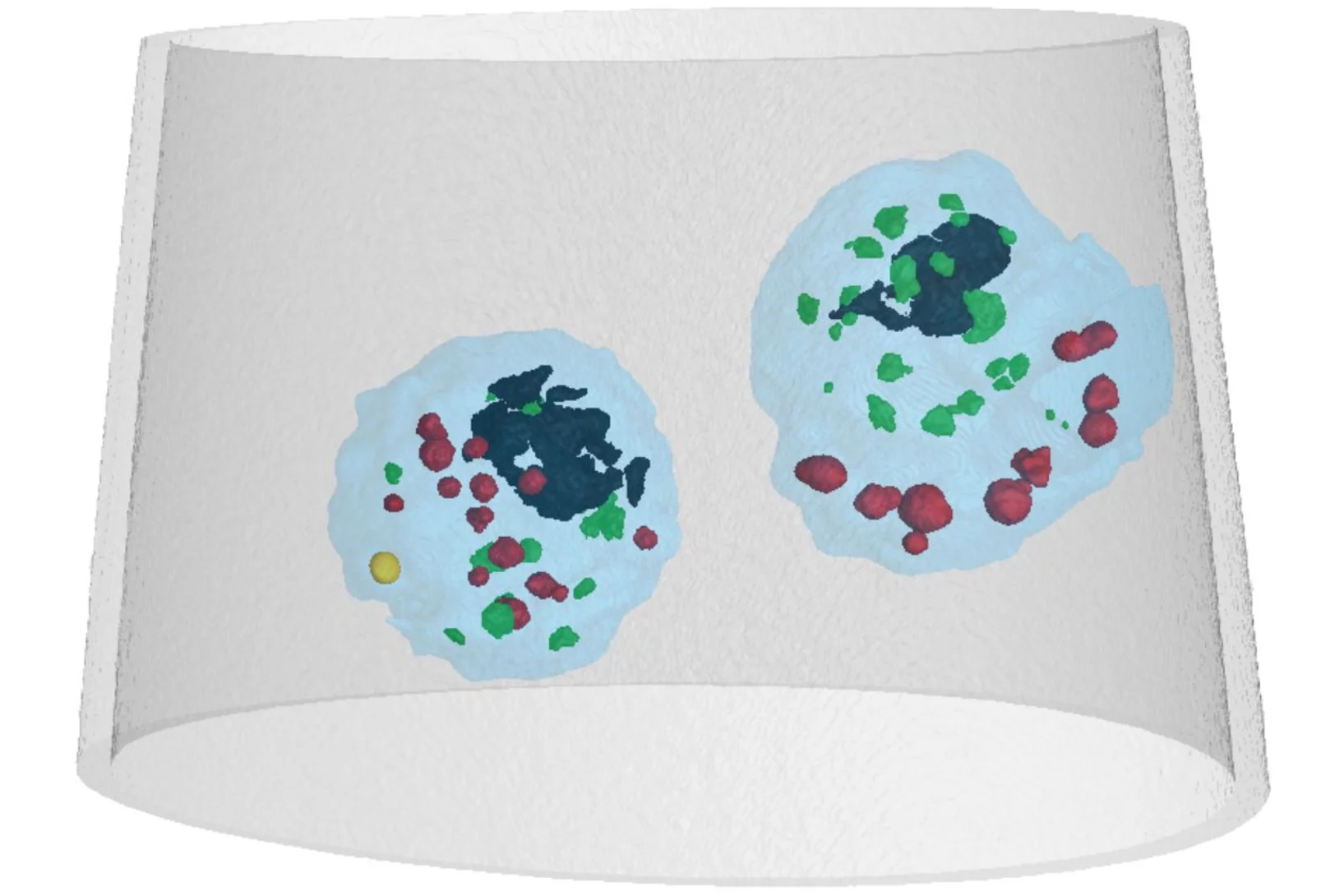
Mass density distribution of intact cell ultrastructure
The determination of the mass density of cellular compartments is one of the many analytical tools that biologists need to unravel the extremely complex structure of biological systems. Cryo X-ray nanotomography reveals absolute mass density maps of frozen hydrated cells in three dimensions.
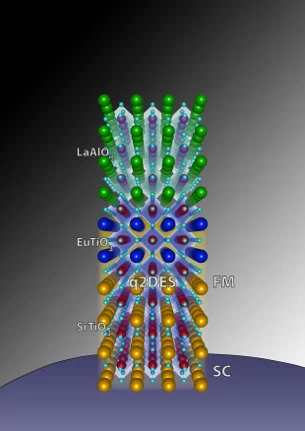
Tunable spin polarization and superconductivity in engineered oxide interfaces
A new kind of 2DEG is found by inserting two atomic layers of the antiferromagnetic and insulating compound EuTiO3 between LaAlO3 and SrTiO3. The 2DEG is found to exhibit besides a superconducting ground state, a strong spin-polarization. The magnetism of Eu and Ti was studied by XMCD at the X-Treme beamline in SLS.
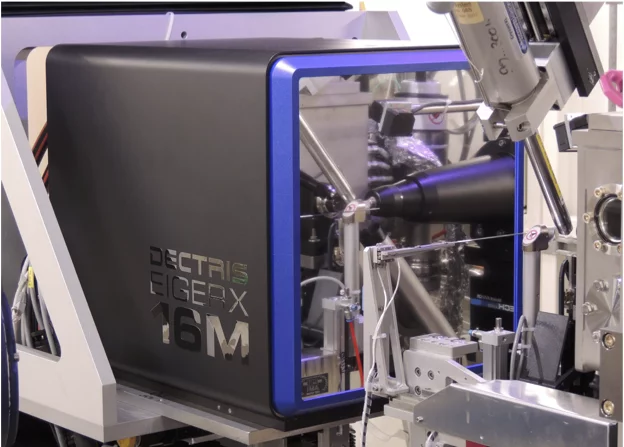
First EIGER X 16M in operation at the Swiss Light Source
The macromolecular crystallography beamline X06SA at the Swiss Light Source, a synchrotron operated by Paul Scherrer Institute, is the first one in the world to upgrade its detector to an EIGER X 16M.
The flip-over effect in pulsed laser deposition: Is it relevant at high background gas pressures?
In pulsed laser deposition the use of a rectangular or elliptical beam spot with a non 1:1 aspect ratio leads to the so called flip-over effect. Here, the longest dimension of the laser spot results in the shortest direction of plasma plume expansion.
Controlling tunnelling in methane loss from acetone ions by deuteration
If a ball is rolled up a hill with less kinetic energy than the potential energy at the top, it will return eventually, and stays bound in the valley. Tunnelling is a distinctly quantum mechanical phenomenon, in which such balls can magically cross the hill, and appear in the neighbouring valley, as if going through a tunnel. In order for this to happen with a non-negligible probability, the ball has to be small and the barrier, i.e. the hill, sharp.
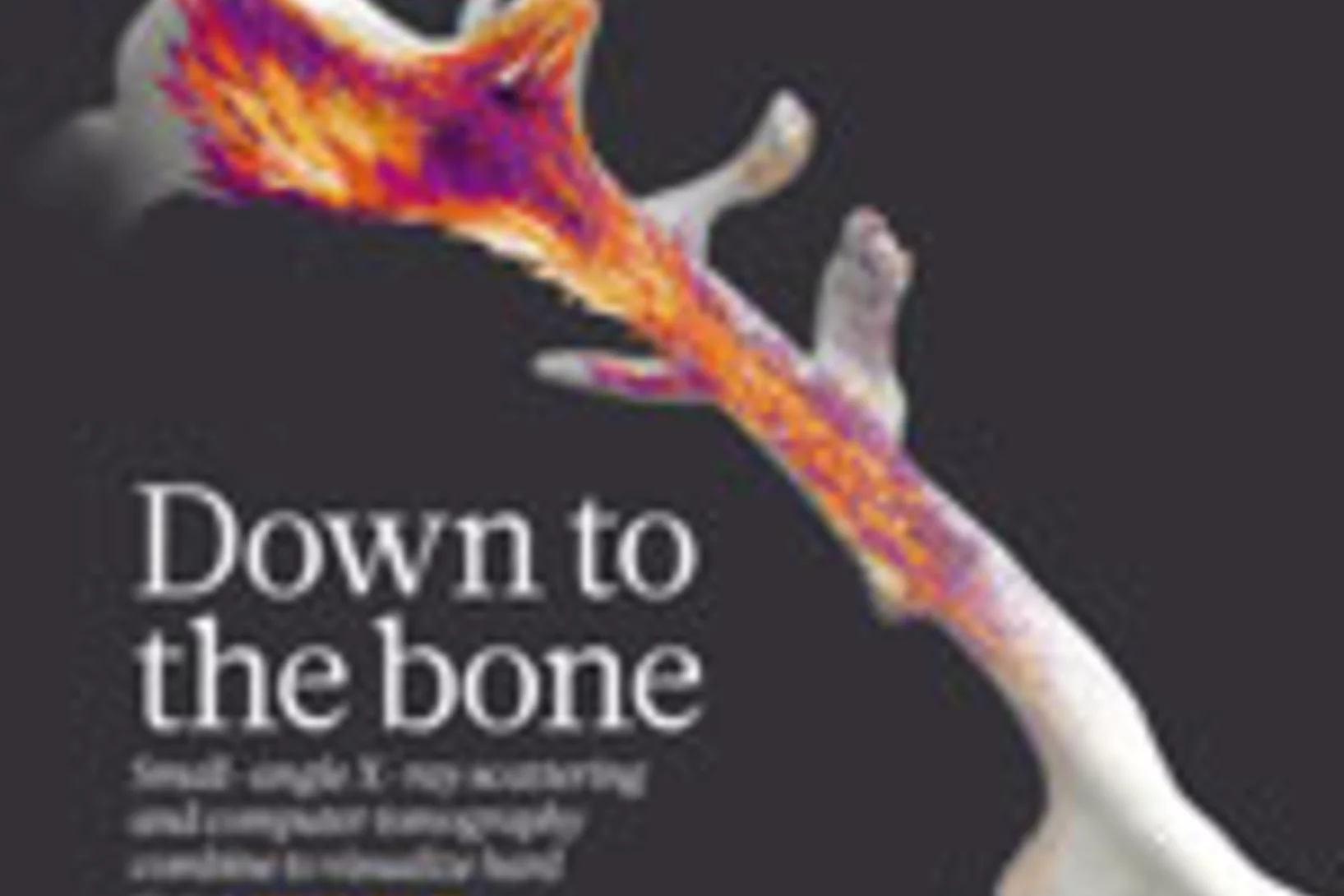
Nanostructure surveys of macroscopic specimens by small-angle scattering tensor tomography
The mechanical properties of many materials are based on the macroscopic arrangement and orientation of their nanostructure. This nanostructure can be ordered over a range of length scales. In biology, the principle of hierarchical ordering is often used to maximize functionality, such as strength and robustness of the material, while minimizing weight and energy cost.
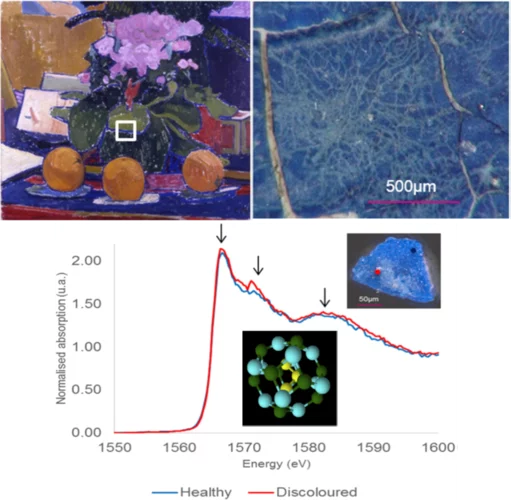
Aluminium X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy analysis of discoloured ultramarine blue in 20th century oil paintings
A specific case of synthetic ultramarine degradation was observed in three oil paintings from the early 20th century. Pigment particleswere found to have been discoloured, resulting in intricate patterns ofwhite lines, approximately 10 to 30 microns wide, criss-crossing the paint surface. Colour in ultramarine pigments comes from the encapsulated sulphur radical anions, chromophores, inside the cage framework built from SiO4 4 − and AlO4 5 −
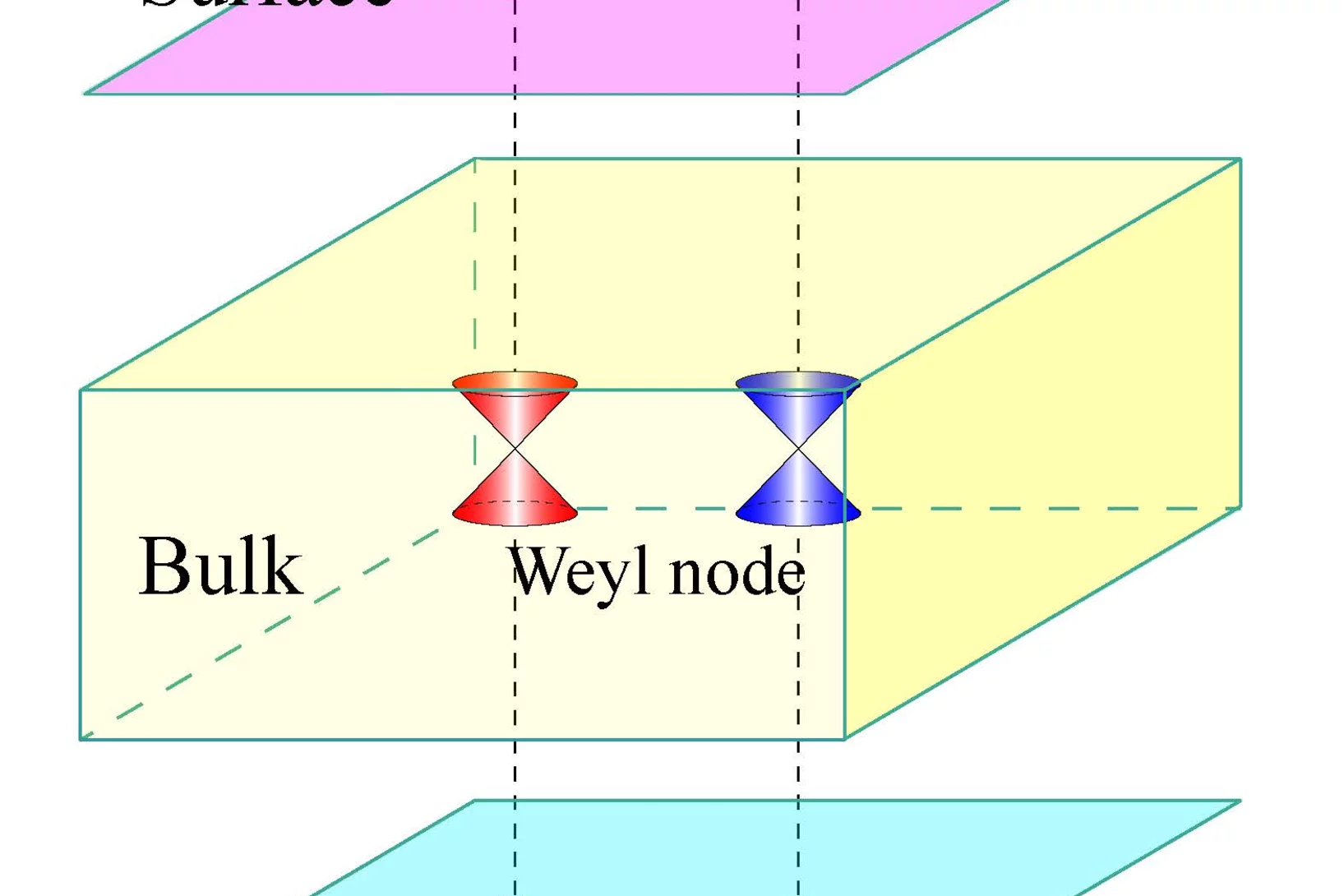
Observation of Fermi-Arc Spin Texture in TaAs
The study of nontrivial topological semimetals (TSM) is an emerging subject, providing a new frontier in topological aspects beyond insulators. Here, we have investigated the spin texture of surface Fermi arcs in the recently discovered Weyl semimetal TaAs using spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. The experimental results demonstrate that the Fermi arcs are spin polarized. The measured spin texture fulfills the requirement of mirror and time-reversal symmetries and is well reproduced by our first-principles calculations, which gives strong evidence for the topologically nontrivial Weyl semimetal state in TaAs. The consistency between the experimental and calculated results further confirms the distribution of chirality of the Weyl nodes determined by first principles calculations.
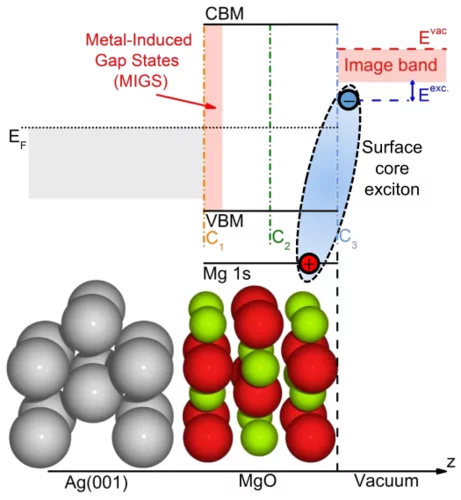
Excited states at interfaces of a metal-supported ultrathin oxide film
At the PEARL beamline, metal-supported ultrathin oxide films have been studied which are a class of materials of technological importance in various research fields such as catalysis, spintronics, or nanoelectronics.
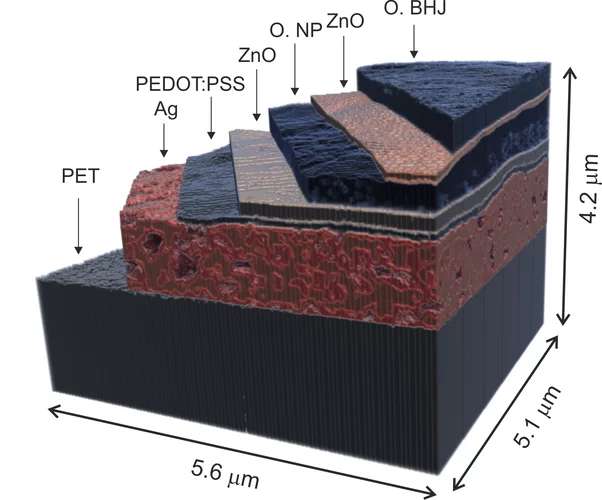
X-ray nanotomography aids the production of eco-friendly solar cells
Polymer solar cells are in the spotlight for sustainable energy production of the future. Characterization of these devices by X-ray nanotomography helps to improve their production using environmentally friendly materials.
Controlling tunnelling in methane loss from acetone ions by deuteration
At the imaging Photoelectron Photoion Coincidence (iPEPICO) endstation of the VUV beamline evidence of H-atom tunneling was shown.
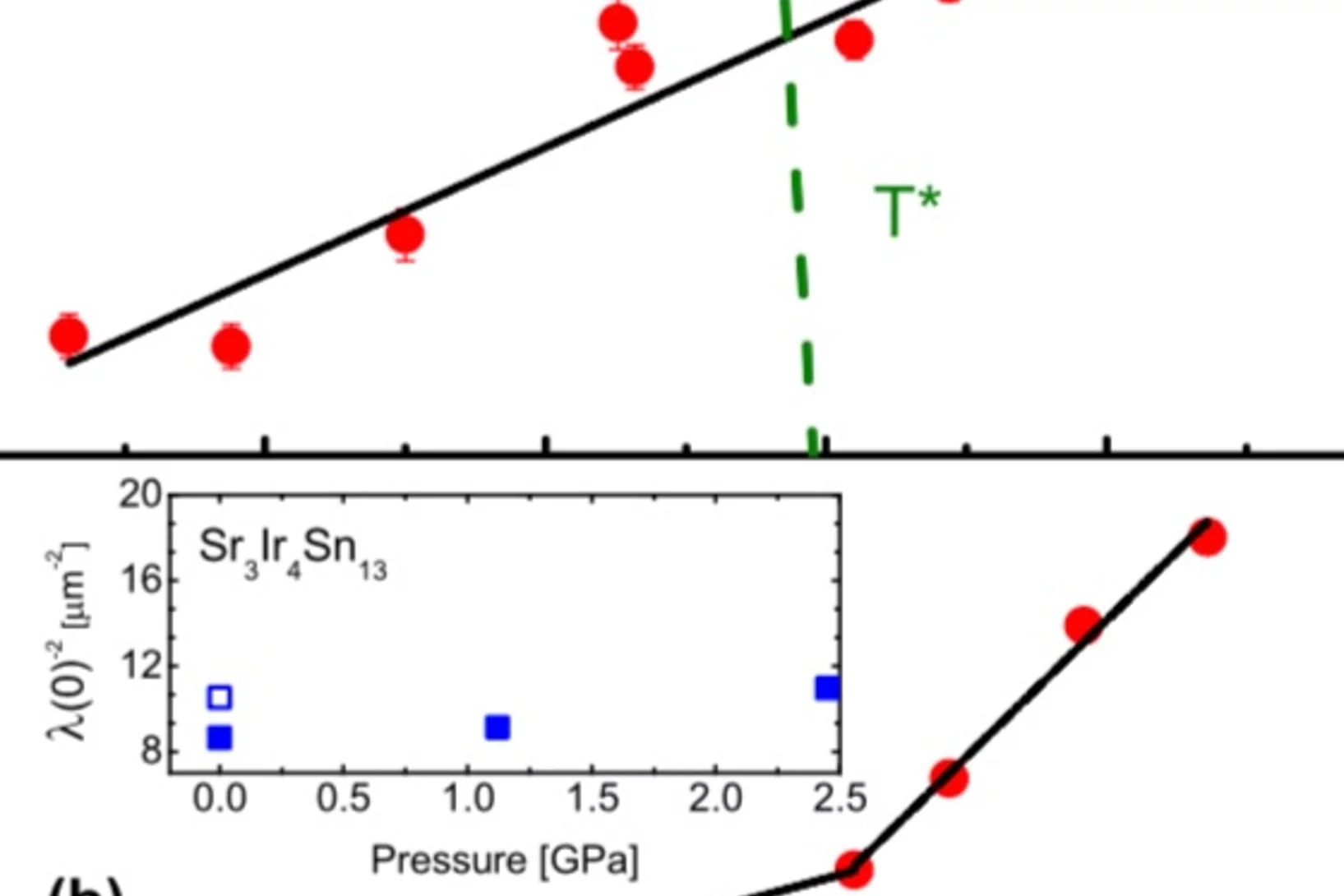
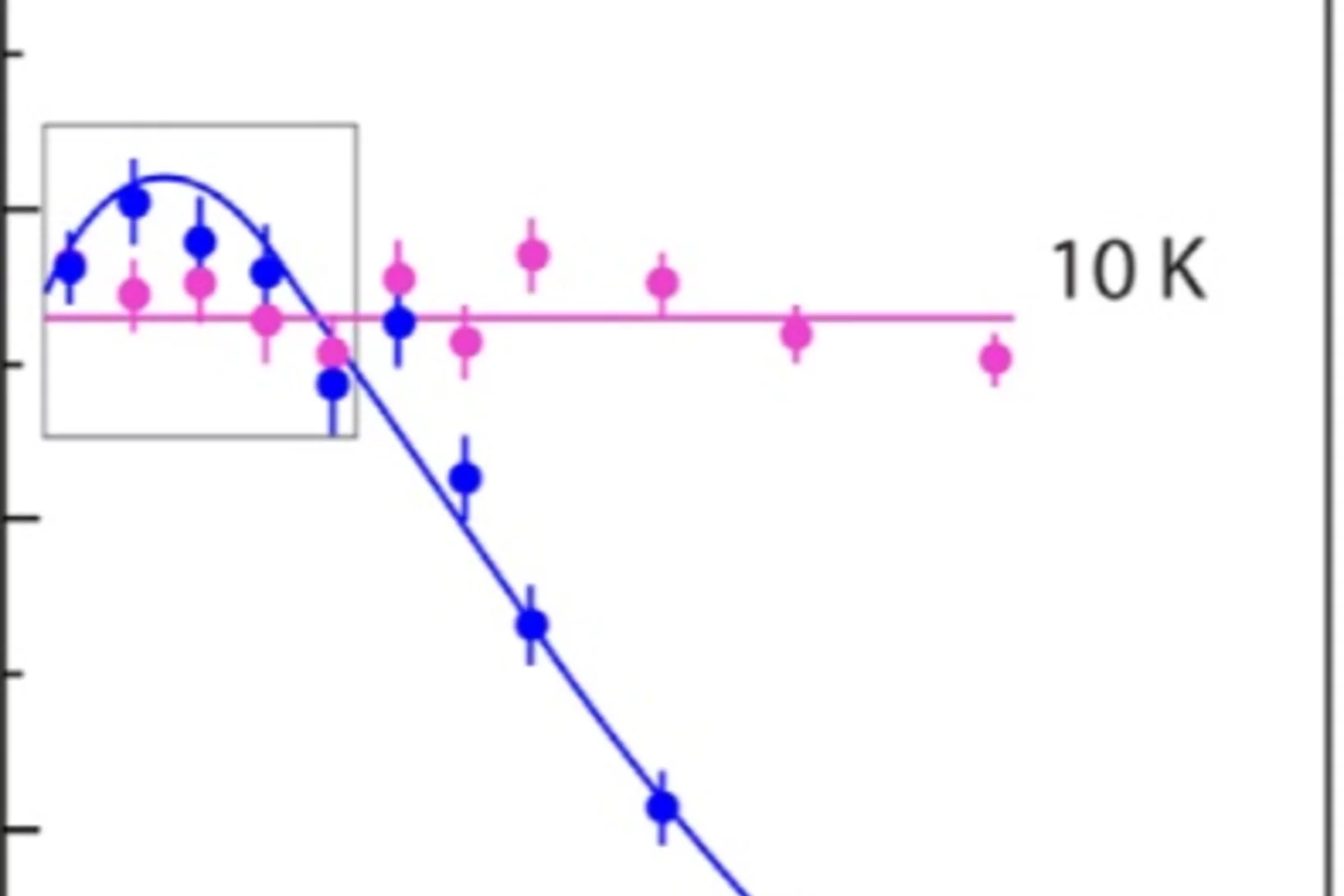
Strong enhancement of s-wave superconductivity near a quantum critical point of Ca3Ir4Sn13
We report microscopic studies by muon spin rotation/relaxation as a function of pressure of the Ca3Ir4Sn13 and Sr3Ir4Sn13 cubic compounds, which are members of the (Ca1−xSrx)3Ir4Sn13 system displaying superconductivity and a structural phase transition associated with the formation of a charge density wave (CDW).
Direct evidence for a pressure-induced nodal superconducting gap in the Ba0.65Rb0.35Fe2As2 superconductor
The superconducting gap structure in iron-based high-temperature superconductors (Fe-HTSs) is non-universal. In contrast to other unconventional superconductors, in the Fe-HTSs both d-wave and extended s-wave pairing symmetries are close in energy. Probing the proximity between these very different superconducting states and identifying experi- mental parameters that can tune them is of central interest.
Intrinsic Paramagnetic Meissner Effect Due to s-Wave Odd-Frequency Superconductivity
In 1933, Meissner and Ochsenfeld reported the expulsion of magnetic flux - the diamagnetic Meissner effect - from the interior of superconducting lead. This discovery was crucial in formulating the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory of superconductivity. In exotic superconducting systems BCS theory does not strictly apply.
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
New EU project: Guiding light for the world's brightest light sources
EUCALL will build bridges between major laser and X-ray research centres: For the past half-century, two special kinds of light have changed the landscape of research. Advanced visible-spectrum optical lasers have propelled studies into ultrafast processes, new materials, telecommunications, and many other fields, while intense X-rays produced at synchrotrons have helped image tiny structures and otherwise invisible parts of matter, enabling huge leaps in biochemistry, pharmacology, and materials science. New developments have enhanced the generation of X-rays at optical-laser and accelerator facilities, resulting in the creation of large international research centres. The European Union is now funding a 7 million-euro effort to bring these research centres together through the European Cluster of Advanced Laser Light Sources (EUCALL) project.
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
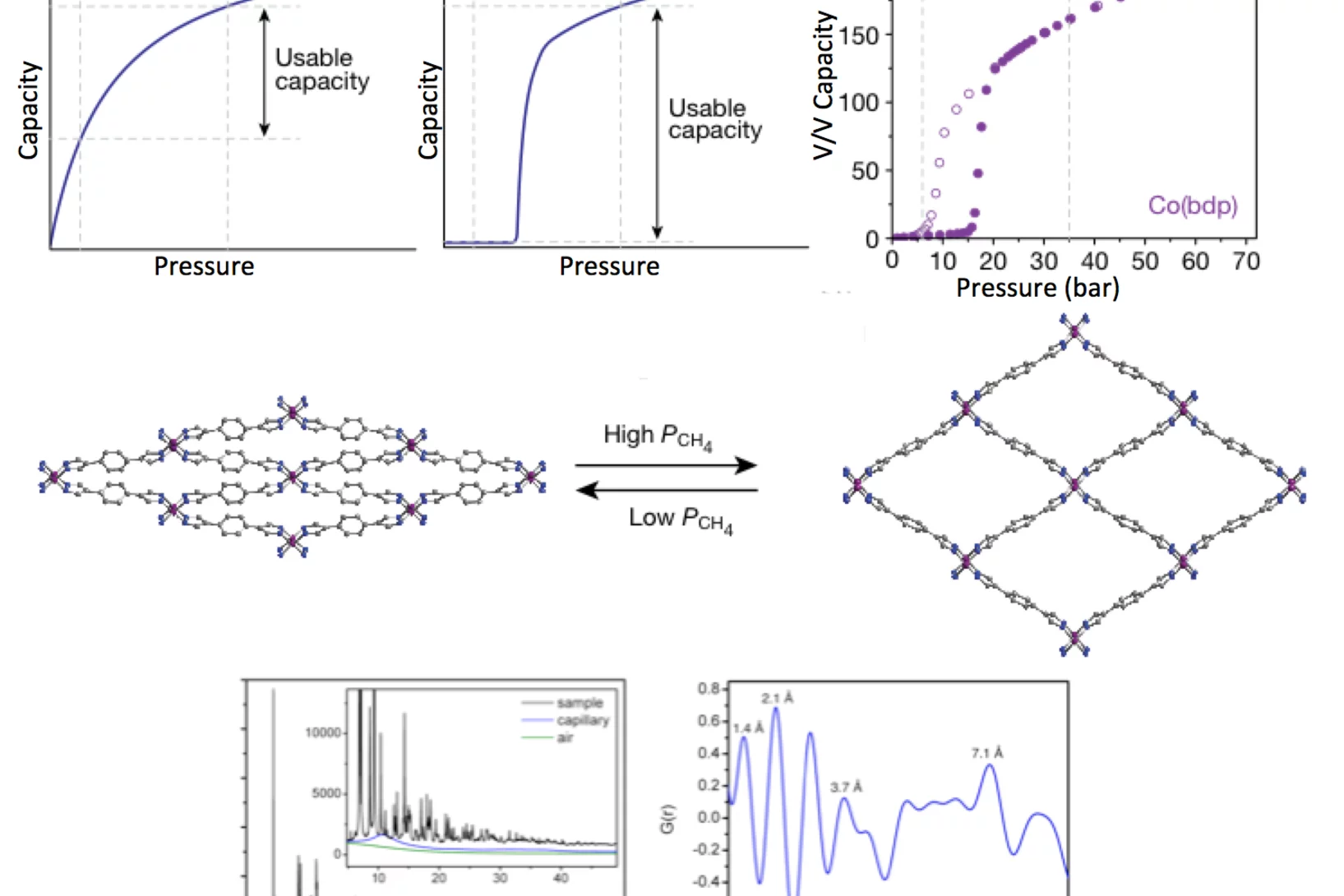
Methane storage in flexible metal–organic frameworks with intrinsic thermal management
As a cleaner, cheaper, and more globally evenly distributed fuel, natural gas has considerable environmental, economic, and political advantages over petroleum as a source of energy for the transportation sector. Despite these benefits, its low volumetric energy density at ambient temperature and moderate pressure presents substantial challenges, particularly for light-duty vehicles with little space available for on-board fuel storage.
Put in perspective
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded in using commercially available camera technology to visualise terahertz light. In doing so, they are enabling a low-cost alternative to the procedure available to date, whilst simultaneously increasing the comparative image resolution by a factor of 25. The special properties of terahertz light make it potentially advantageous for many applications, from safety technology to medical diagnostics.
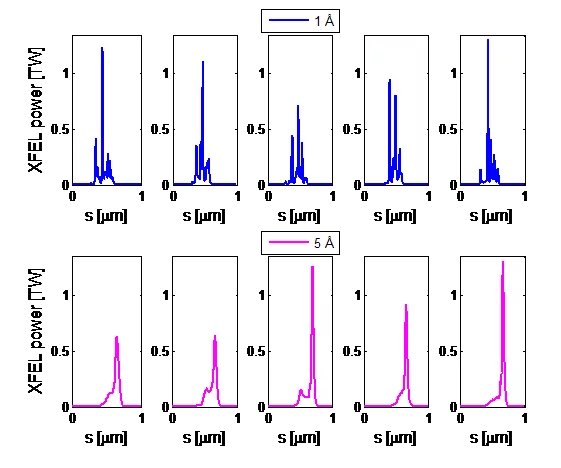
New methods to generate short and high-power X-ray Free-Electron-Laser pulses
State-of-the-art X-ray Free-Electron-Laser (XFEL) facilities like SwissFEL are able to provide radiation pulses with pulse powers of a few tens of gigawatts and pulse durations of several tens of femtoseconds and shorter. There is, however, a strong demand in research fields such as bioimaging and nonlinear optics to obtain higher radiation powers and shorter pulses than in standard facilities. In this context, we have developed two new methods able to generate terawatt-attosecond XFEL pulses. Both proposals are based on superradiance, a regime with quadratic growth of the radiation power and a shortening of the spike while it slips into unspoiled (good-beam) regions of the bunch.
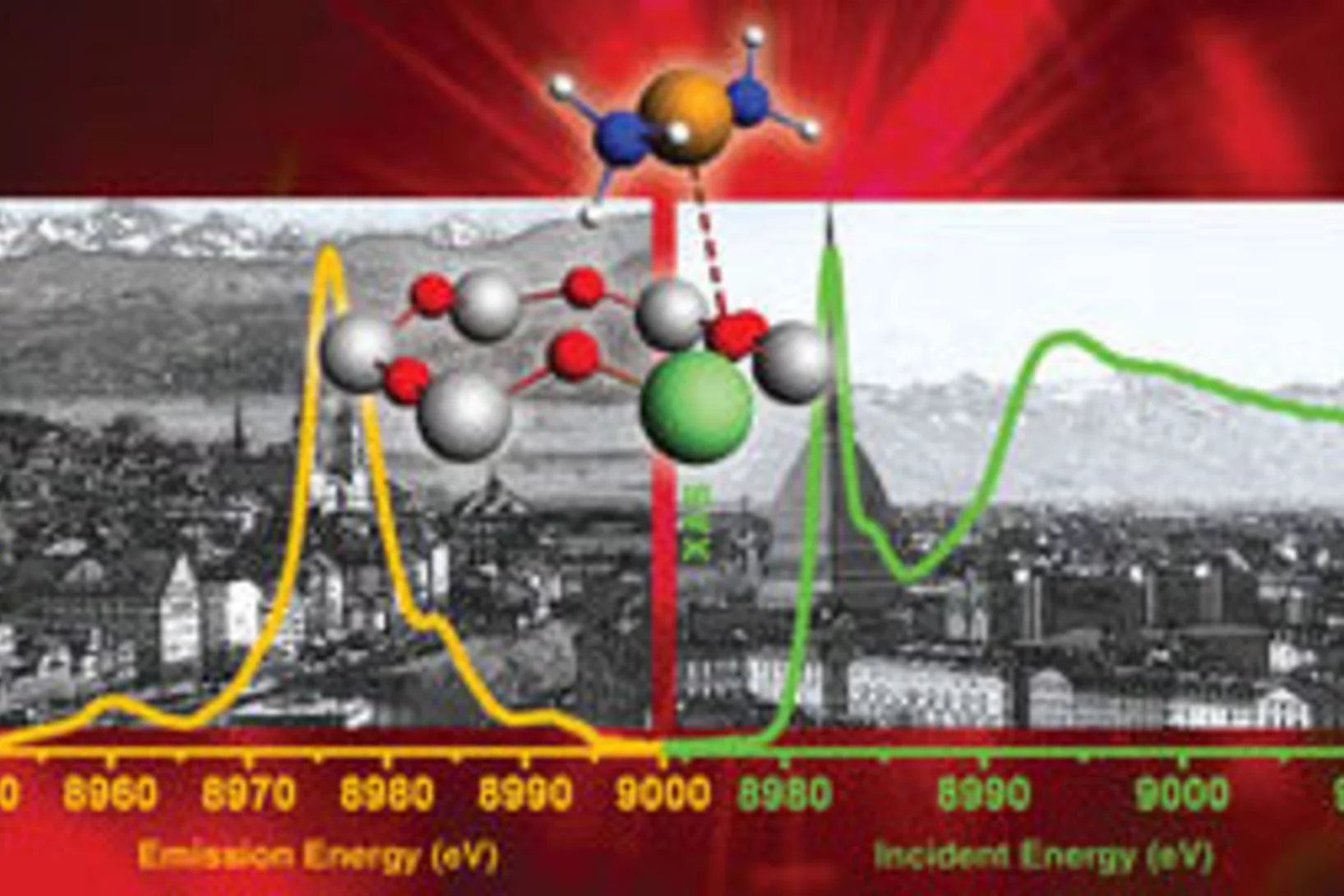
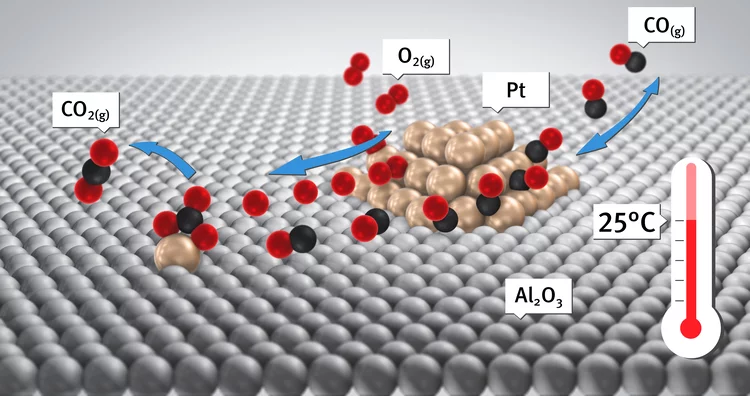
Room-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation by oxygen over Pt-Al2O3 mediated by reactive platinum carbonates
A new possibility for the attainment of low-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide is demonstrated. Here we report using time-resolved DRIFTS, XAS, and mass spectrometry a platinum carbonate-mediated mechanism for the room-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide.