Covid-19 research: Anti-viral strategy with double effect
Frankfurt scientists identify a possible weakness of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. They carried out part of their measurements at PSI's Swiss Light Source SLS. The research results are published this week in the scientific journal Nature.
The tiniest secrets of integrated circuits revealed
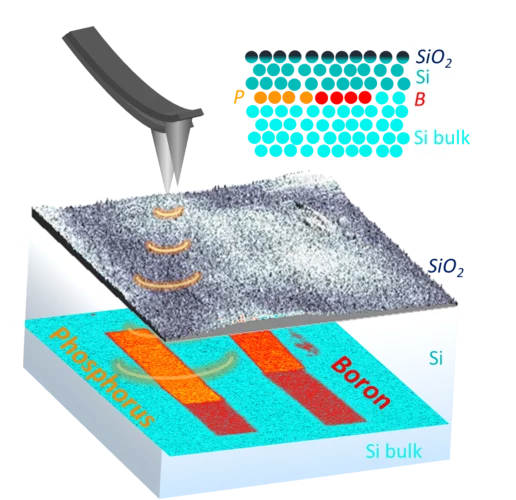
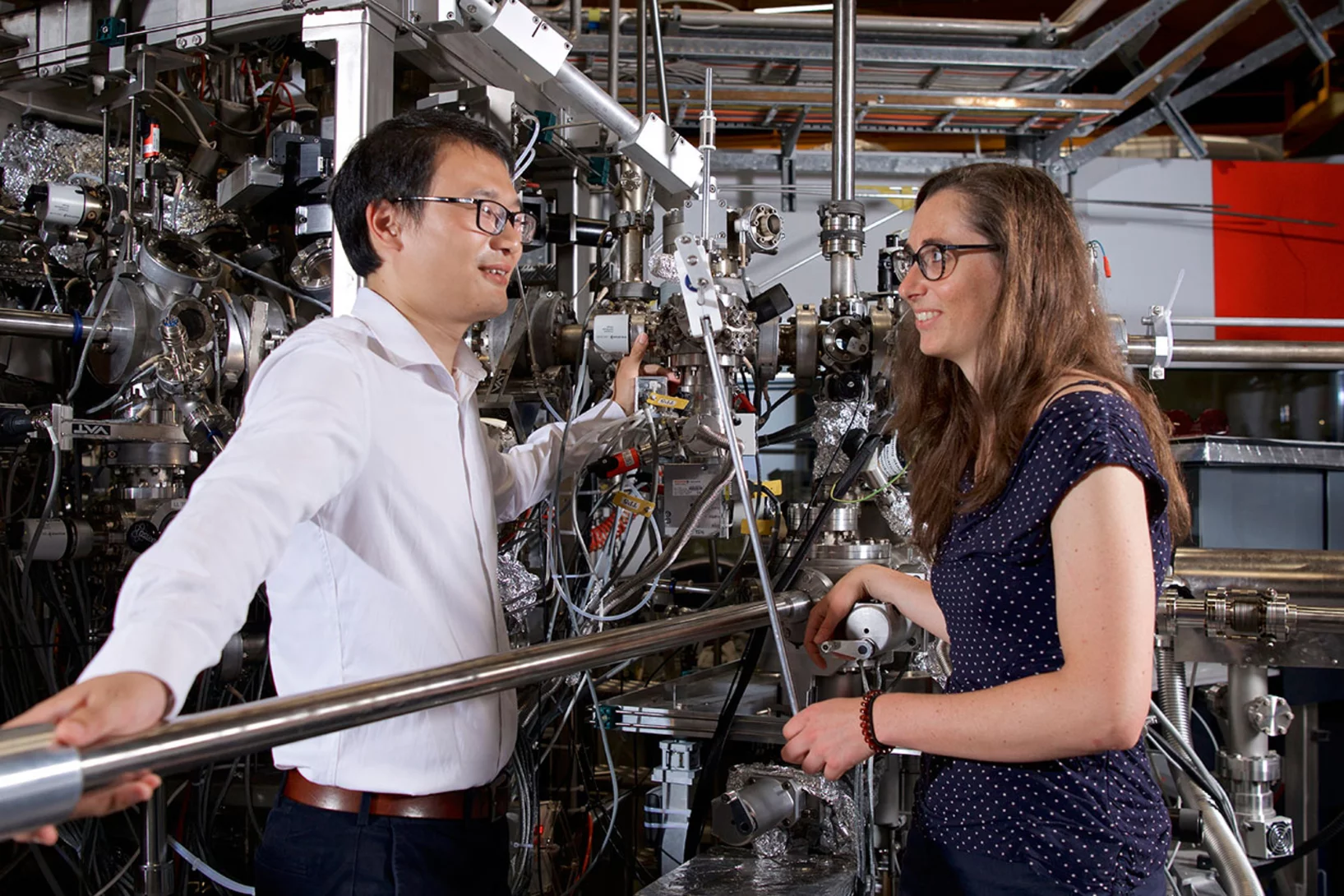
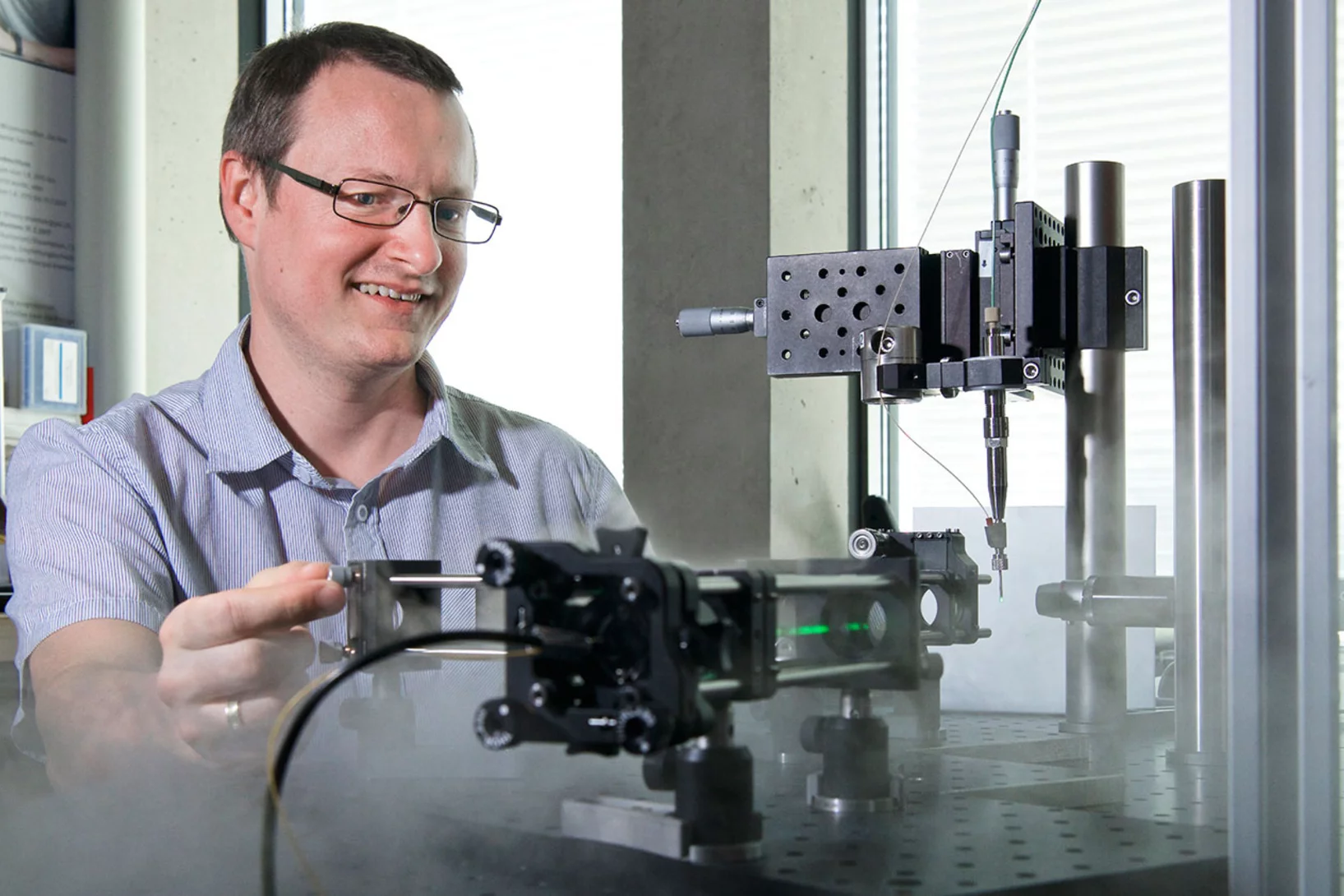
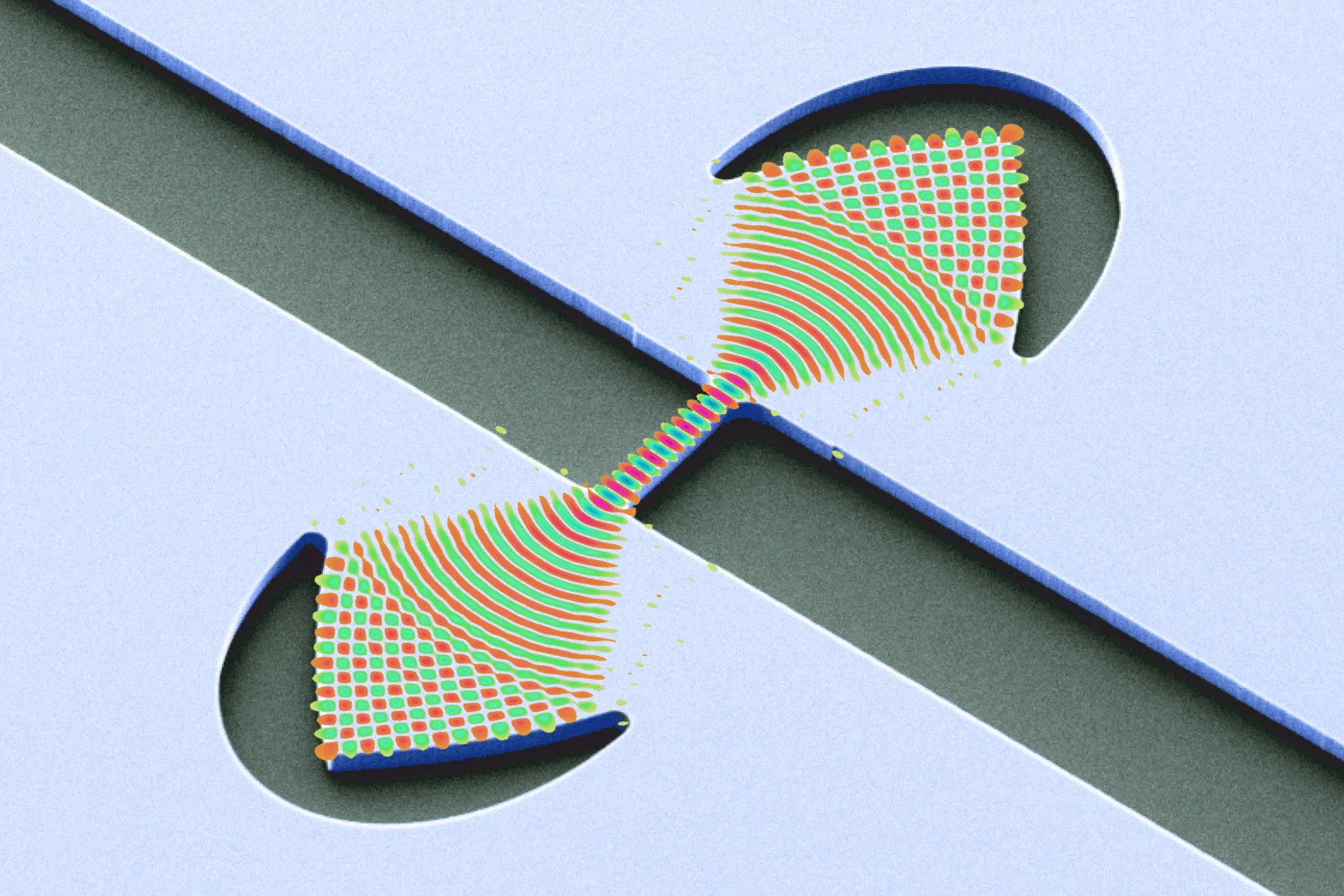
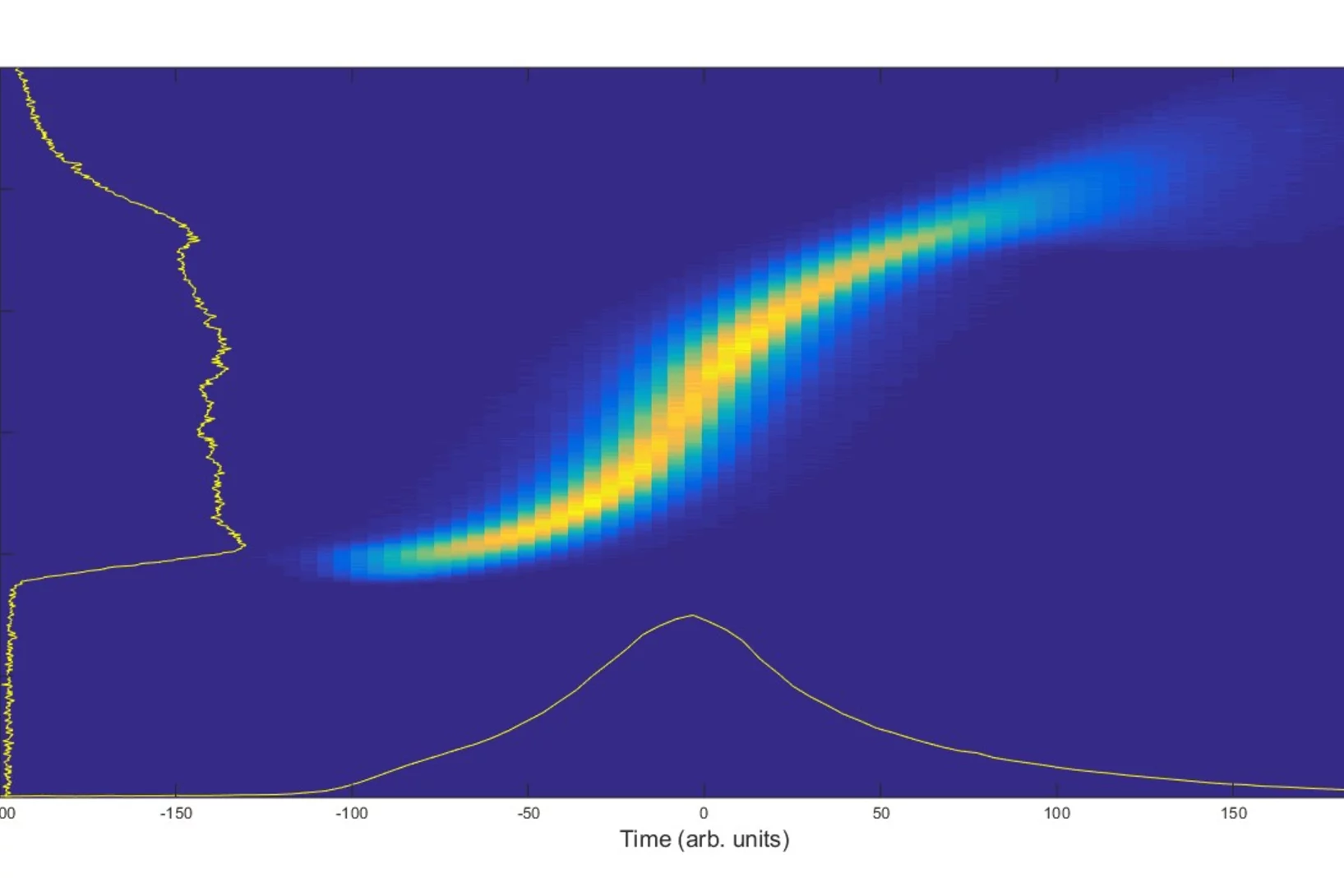
New research has demonstrated that the secrets of the tiniest active structures in integrated circuits can be revealed using a non-destructive imaging technique. The breakthrough required the efforts of an international team of scientists from JKU and Keysight Technologies (Austria), ETH/EPFL/PSI and IBM Research - Europe (Switzerland) and from UCL (UK).
Cherned up to the maximum
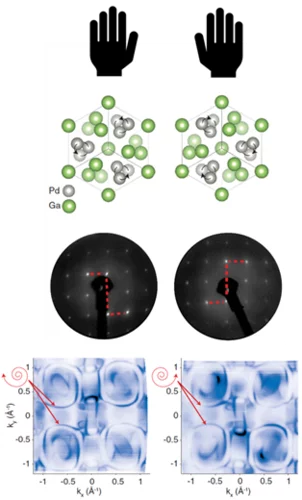
In topological materials, electrons can display behaviour that is fundamentally different from that in ‘conventional’ matter, and the magnitude of many such ‘exotic’ phenomena is directly proportional to an entity known as the Chern number. New experiments establish for the first time that the theoretically predicted maximum Chern number can be reached — and controlled — in a real material.
Analytical Research Infrastructures as key resources for the five Horizon Europe Missions
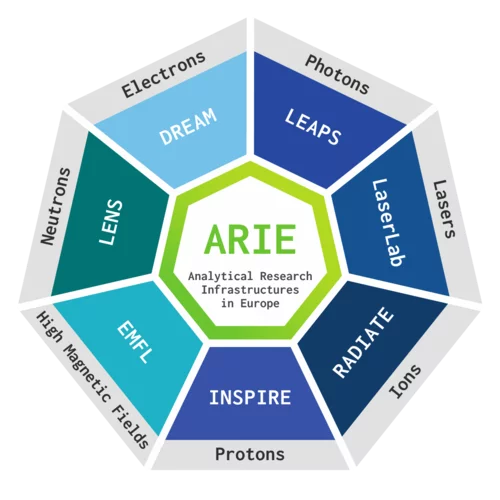
Moon-shot missions, such as those of Horizon Europe, require exceptional solutions, and the world-leading Analytical Research Infrastructures of Europe (ARIEs) are one of the key places those solutions can be sought. The ARIE Joint Position Paper highlighting how the common, complementary approach will help address the societal challenges of the Horizon Europe Missions framework programme was presented today.
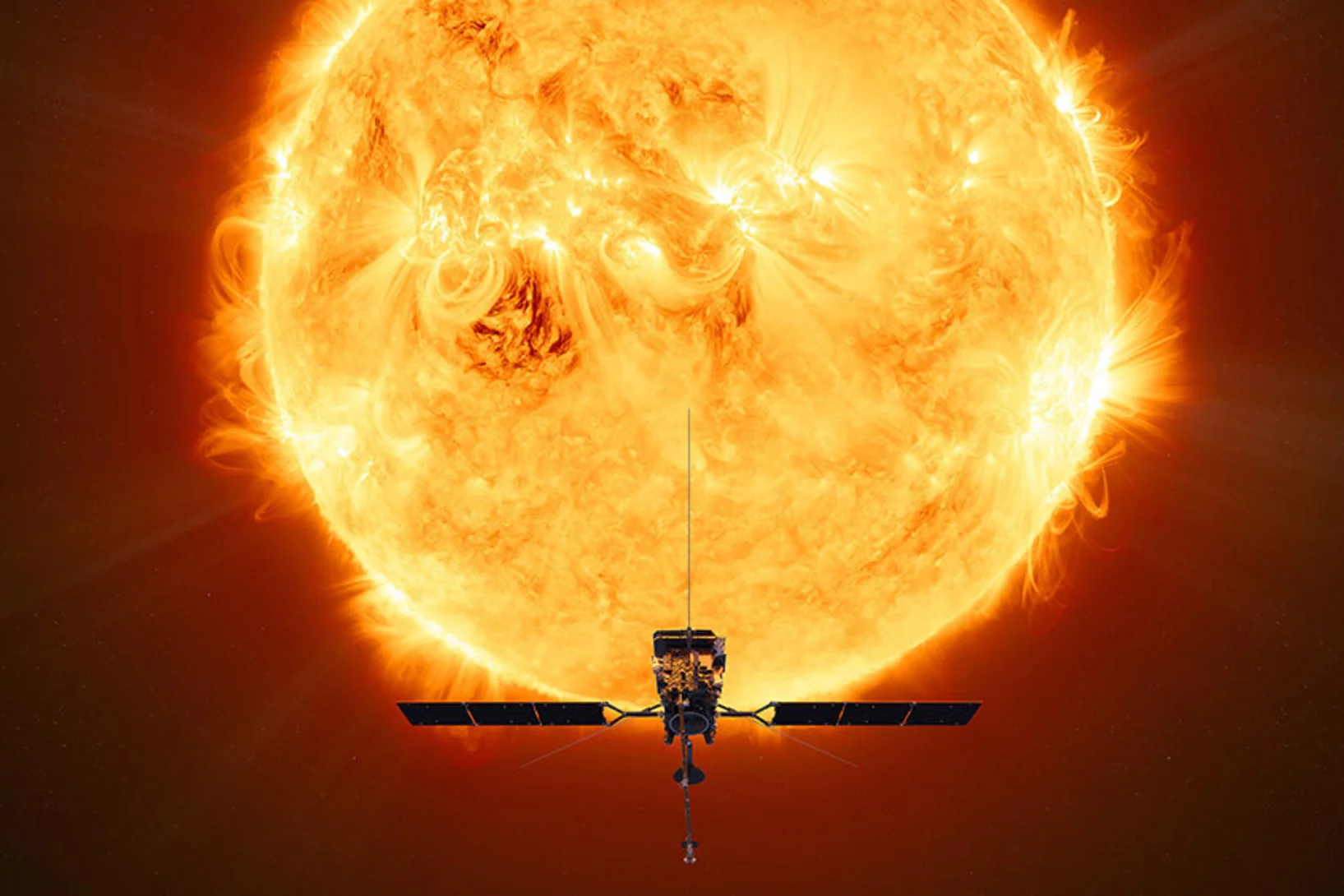
To the sun and beyond
PSI takes part in space research projects. This not only expands knowledge about our astronomical home, but also reinforces Switzerland's reputation as a reliable developer of sophisticated space equipment.
Grosser Rat bewilligt 2,4 Millionen für Technologiezentrum Anaxam
Der Kanton Aargau unterstützt das Technologietransferzentrum Anaxam in Villigen für die Dauer von vier Jahren mit insgesamt 2,4 Millionen Franken. Der Grosse Rat hat am Dienstag in Spreitenbach den entsprechenden Kredit mit 124 zu 3 Stimmen bewilligt.
Elucidating the mechanism of a light-driven sodium pump
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded for the first time in recording a light-driven sodium pump from bacterial cells in action. The findings promise progress in developing new methods in neurobiology. The researchers used the new X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL for their investigations.
First MX results of the priority COVID-19 call
The Dikic group at the Goethe University in Frankfurt am Main, Germany has published the first results following the opening of the "PRIORITY COVID-19 Call” at SLS.
Operando X-ray diffraction during laser 3D printing
Ultra-fast operando X-ray diffraction experiments reveal the temporal evolution of low and high temperature phases and the formation of residual stresses during laser 3D printing of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The profound influence of the length of the laser-scanning vector on the evolving microstructure is revealed and elucidated.
Long-lived pionic helium: Exotic matter experimentally verified for the first time
Exotic atoms, in which electrons are replaced by other particles, allow deep insights into the quantum world. After eight years, an international group of scientists have succeeded in a challenging experiment conducted at PSI’s pion source: they created an artificial atom called “pionic helium”.
In search of the lighting material of the future
At the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, researchers have gained insights into a promising material for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). This new understanding at the atomic level will help to develop new lighting materials that have higher light output and also are cost-efficient to manufacture.
SLS MX beamtime update
Update of the SLS MX beamline operation during the COVID-19 period
Athos is making great strides
The new beamline at PSI's X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL will soon be ready for action. In December, Athos delivered laser light for the first time − even sooner than expected, to the delight of the researchers responsible for its construction.
Nanoworlds in 3-D
Tomographic images from the interior of fossils, brain cells, or computer chips are yielding new insights into the finest of structures. These 3-D images are made possible by the X-ray beams of the Swiss Light Source SLS, together with detectors and sophisticated computer algorithms developed at PSI.
Short film of a magnetic nano-vortex
Using a newly developed imaging method, researchers were able to visualise the magnetic structure inside a material with nanoscale resolution. They succeeded in creating a short "film" consisting of seven movie frames that shows, for the first time in 3D, how tiny vortices of the magnetisation deep within a material change over time.
Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation 2019 for the development of XFEL detectors using the adaptive gain principle
The Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation 2019 was given to the researchers Prof. Heinz Graafsma from Desy and Dr. Aldo Mozzanica and Dr. Bernd Schmitt both from the Paul Scherrer Institute. The three physicists were honored for their contributions to the development of detectors for XFEL applications based on the dynamic gain switching principle enabling simultaneously single photon resolution and a large dynamic range. The laudation was held by Prof. Edgar Weckert from Desy. The Synchrotron Radiation Innovation Award is sponsored by SPECS GmbH and BESTEC GmbH.
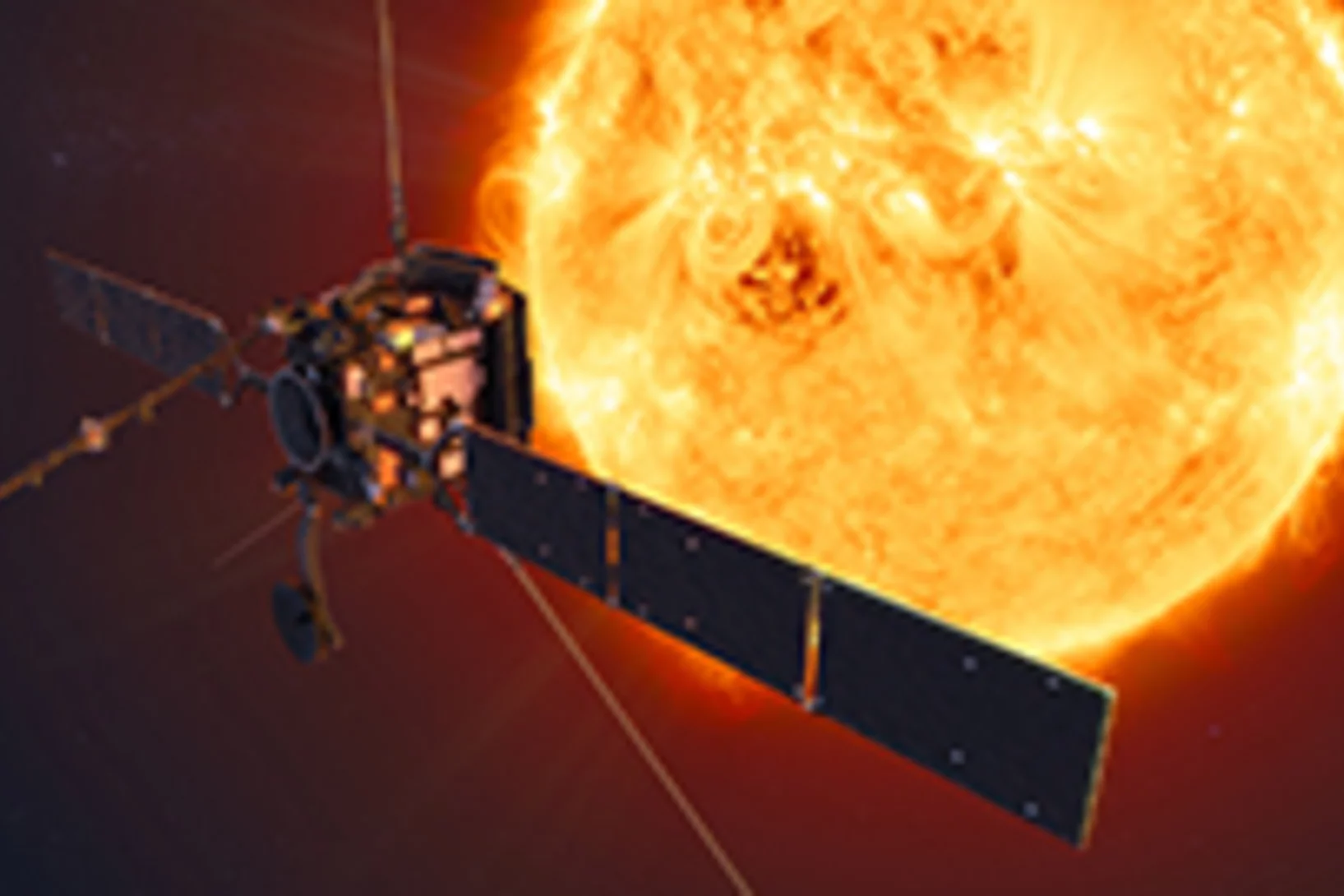
Swiss STIX X-ray telescope sets off for the sun
On 10 February, the ESA mission Solar Orbiter is scheduled to start. The Swiss X-ray telescope STIX will be launching too – with detectors developed at PSI.
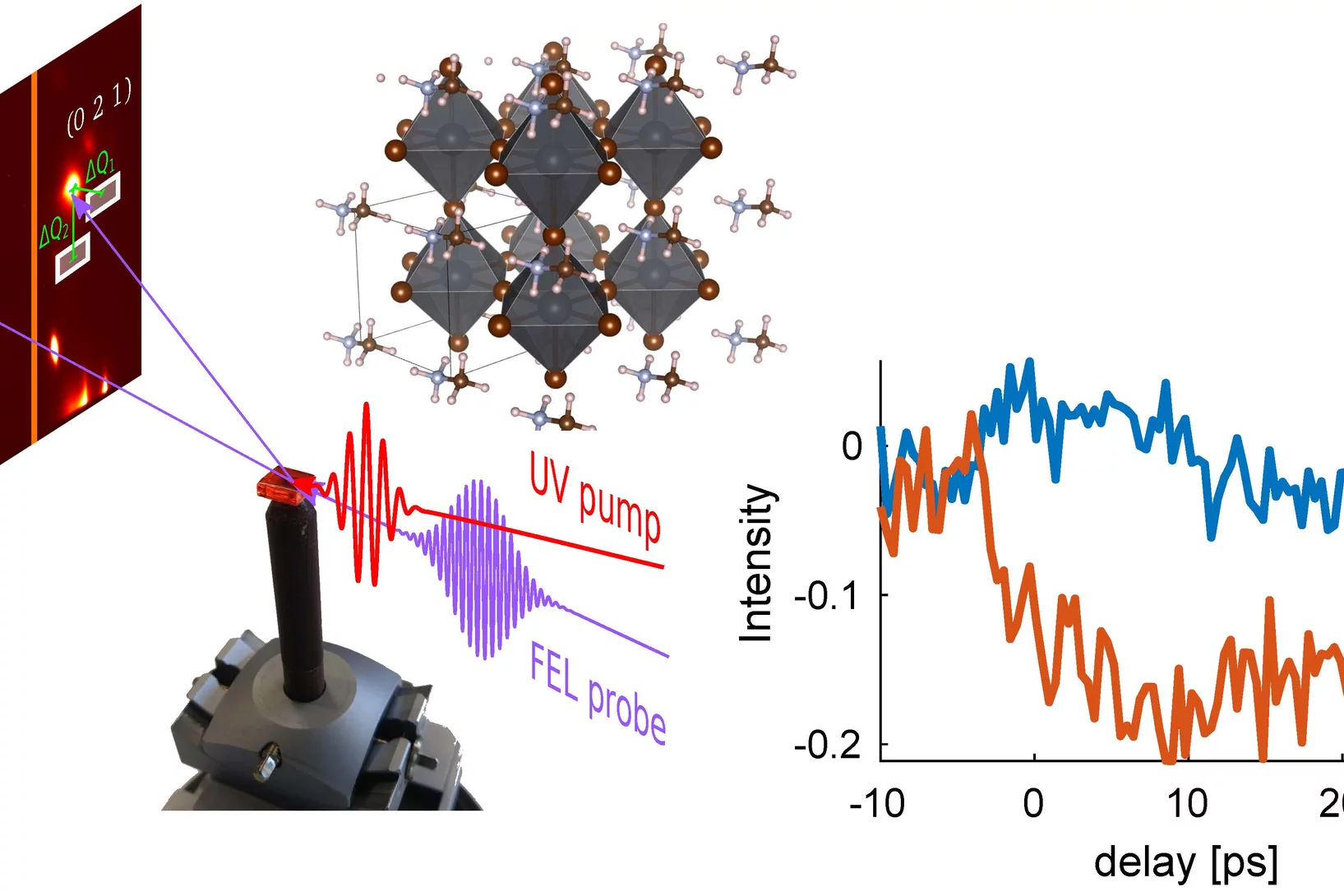
Ultrafast diffuse x-ray scattering of a hybrid perovskite crystal
Organic–inorganic ‘hybrid’ perovskites have recently gained attention as a low-cost alternative to silicon solar cells. However, many properties of these materials are still poorly understood. In particular, how imperfections in the crystals, which can be both static or dynamic, affect energy transport remains unclear.
More magnets, smoother curves: The SLS upgrade
The Swiss Light Source SLS is set to undergo an upgrade in the coming years: SLS 2.0. The renovation is made possible by the latest technologies and will create a large research facility that will meet the needs of researchers for decades to come.
A fast and precise look into fibre-reinforced composites
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have developed a new process with which fibre-reinforced composite materials can be precisely X-rayed. This could help to develop better materials with novel properties.
New 6M€ European grant awarded to ExPaNDS to drive open access data
A new 6M€ grant is being launched for the Photon and Neutron Data Services (ExPaNDS) to come together and work under the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC). This ambitious project will create enormous opportunities for scientific communities, and through their findings for humankind worldwide. It aims to publish and map the data behind the thousands of successful published scientific papers generated by Europe’s Photon and Neutron Research Infrastructures (PaN RIs) – which every year create petabytes of data – and make it available to all.
Research and tinkering – SwissFEL in 2019
The newest large research facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute, SwissFEL, has been completed. In January 2019 it began regular operation. Henrik Lemke, head of the SwissFEL Bernina research group, gives an interim report.
Preventing tumour metastasis
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, together with colleagues from the pharmaceutical company F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, have taken an important step towards the development of an active substance against the metastasis of certain cancers. Using the Swiss Light Source SLS, they deciphered the structure of a receptor that plays a crucial role in the migration of cancer cells.
Observing solid-state batteries during deformation
PSI researchers have observed mechanical processes in solid-state batteries with unprecedented precision. Using X-ray tomography at the Swiss Light Source SLS, they discovered how fissures inside the batteries propagate. These insights can help to make batteries for electric cars or smartphones safer and more efficient.
Weyl fermions discovered in another class of materials
A particular variety of particles, the so-called Weyl fermions, had previously only been detected in certain non-magnetic materials. But now researchers at PSI have experimentally proved their existence for the first time in a specific paramagnetic material.
Molecular energy machine as a movie star
Using the Swiss Light Source SLS, PSI researchers have recorded a molecular energy machine in action and thus revealed how energy production at cell membranes works. For this purpose, they developed a new investigative method that could make the analysis of cellular processes significantly more effective than before.
First demonstration of a Germanium laser
Scientist at the Paul Scherrer Institut and ETH Zürich, with colleagues from CEA Grenoble, have demonstrated and characterized a technology that, for the first time, yields lasing from strained elemental Germanium. This achievement underlines PSI’s leading role in the development of Silicon-compatible laser light sources.
PSI School for Master Degree Students - Introducing Photons, Neutrons and Muons for Condensed Matter Physics and Materials Science
From 17 – 21 June 2019 the Neutron and Muon Division (NUM) and the Photon Science Division (PSD) of PSI hosted 18 Master Degree students of physics, chemistry, materials and interdisciplinary science, as well as nuclear engineering to provide an introduction to the characterization of materials with large scale facilities like SINQ, SμS, SLS and SwissFEL. The course taught a basic understanding of how photons, neutrons and muons interact with matter, and how this knowledge can be used to solve specific problems in materials research.
Details of the program can be found at http://indico.psi.ch/event/PSImasterschool
First serial femtosecond crystallography experiment using SwissFEL’s large bandwidth X-ray pulses
The typical mode of operation at XFEL facilities uses the so-called self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) process to generate the short, bright X-ray pulses. This mode of operation is stochastic in nature, causing some variance in intensity and spectrum on a shot-to-shot basis, which makes certain types of crystallographic measurements much more challenging.
New material with magnetic shape memory
PSI researchers have developed a material whose shape memory is activated through magnetism. Application areas for this new kind of composite material include, for example, medicine, space flight, electronics, and robotics.