Show filters
Blue hydrogen can help protect the climate
The key is to eliminate methane leaks.
«Price tags» of the Swiss energy transition
NZZ am Sonntag has picked up this highlight in its issue on March 7th, 2021: The highlight refers to the analysis performed in SCCER Joint Activity Scenarios and Modelling, where PSI-LEA performed the analysis of the energy transition pathways.
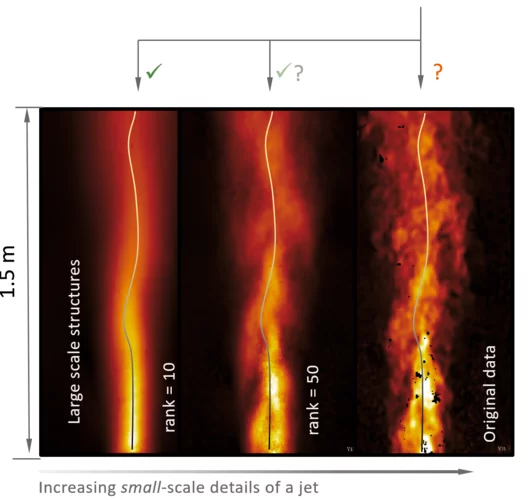
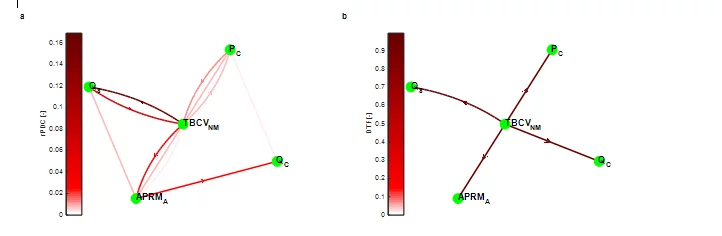
Analysis of a large-scale turbulent round jet
The entire study is an investigation into the self-similarity behavior [1] of first and second order statistical quantities derived from a large-scale jet flow taken from one of the experiments in the PANDA facility using the Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD).
What is presented, are the merits, the potential and the characteristics of the corresponding underlying POD analysis. Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) is a mathematical framework to extract large-scale structures which are otherwise eventually masked by the complexity of the fully turbulent flow; example: the meandering of a jet which is not so obvious for the original data.
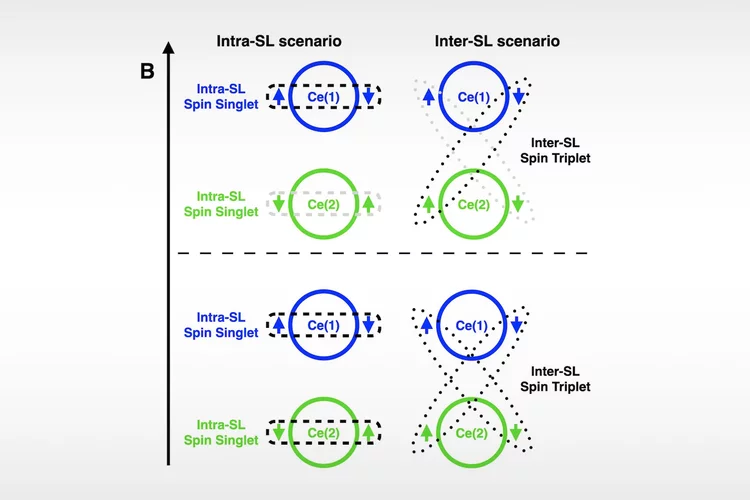
Two scenarios for superconductivity in CeRh2As2
CeRh2As2, a nonsymmorphic heavy fermion material, was recently reported to host a remarkable temperature versus z-axis magnetic-field phase diagram with two superconducting phases. In this material, the two inequivalent Ce sites per unit cell, related by inversion symmetry, introduce a sublattice structure corresponding to an extra internal degree of freedom. In this work, we propose a classification of the possible superconducting states in CeRh2As2 from the two Ce-sites' perspective.
“Without these technologies, we will hardly achieve our climate targets”
To achieve carbon neutrality, technologies need to be deployed which remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Improving the resilience of Switzerland’s energy supply
The SURE research project is up and running.
Safely stored for a million years
Switzerland plans to construct a deep repository for its radioactive waste. There are three potential locations, and data obtained by PSI researchers can aid in selection of the best one.
Switzerland's energy transition
Can Switzerland, as planned, reduce its CO2 emissions to zero by 2050? What is needed to achieve this? What could it cost?
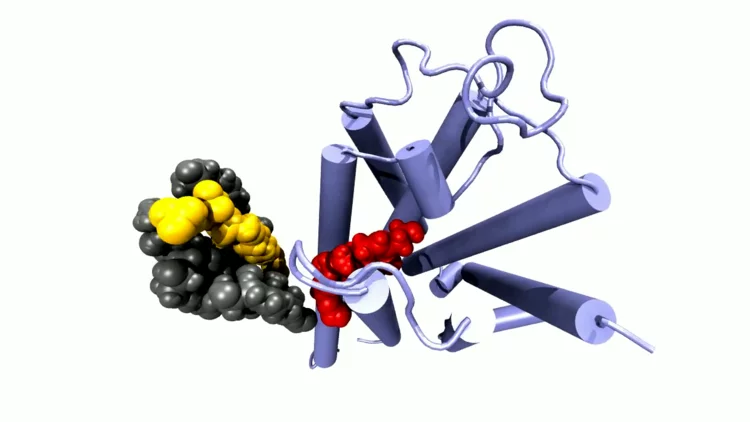
Watching receptor proteins changing shape
In our bodies, G protein-coupled receptors mediate countless processes. PSI researcher Ramon Guixà talks about how he brings those receptor molecules to life on the computer screen.
New blueprint for more stable quantum computers
PSI researchers have shown how faster and better defined quantum bits can be created. The central elements are magnetic atoms from the class of so-called rare-earth metals, selectively implanted into the crystal lattice of a material.
Weissbuch Radiochemie Schweiz
In December 2020, the Swiss Academy of Sciences (SCNAT) published its white book on radiochemical education in Switzerland. The report was authored under the lead of Prof. Dr. Roger Alberto (University of Zurich), Dr. Mario Burgener (Spiez Laboratory), and Prof. em. Dr. Heinz W. Gäggeler (University of Bern/Paul Scherrer Institute) and comprises contributions from many experts on the topic from various institutions throughout Switzerland. The white book highlights the imminent loss of experts in the field of radiochemistry and provides solutions to counteract this development.
Radiochemistry at ETH Zurich
As of December 10, 2020, the ETH Zurich appointed PSI’s Prof. Dr. Patrick Steinegger as assistant professor of radiochemistry (tenure track). Thus, the ETH domain took first counter measures against the imminent loss of radiochemical expertise in Switzerland, emphasized in the “Weissbuch Radiochemie Schweiz” by the Swiss Academy of Sciences (SCNAT). Furthermore, the December issue of CHIMIA (Swiss Chemical Society) invited to present the diverse radiochemical activities throughout the country.
CHIMIA: Radiochemistry in Switzerland
The December issue of CHIMIA of the Swiss Chemical Society (SCS) focused on the radiochemical activities throughout Switzerland. Scientists of the Laboratory of Radiochemistry contributed with a number of articles ranging from topics of fundamental sciences to applied research, thereby reflecting on the diverse projects carried out in our laboratory.
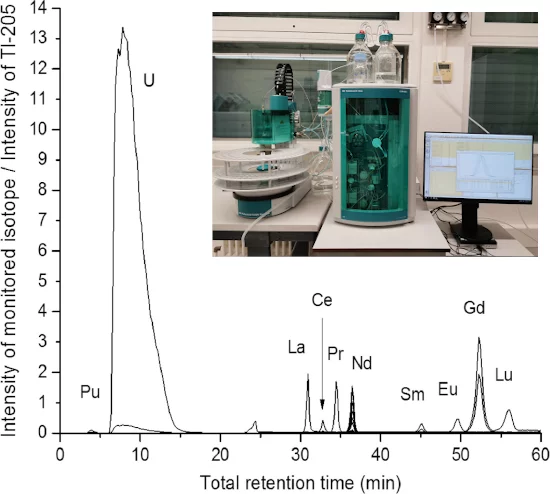
New element and speciation specific analytical options at AHL
The Hot Laboratory division (AHL) within PSI’s Nuclear Energy and Safety (NES) division continually upgrades and advances its analytical infrastructure to provide cutting-edge scientific service to PSI’s researchers and industrial customers. A new, fully automatable and highly flexible Ion Chromatograph (IC) furthers AHL’s efforts in sample miniaturization and extends the spectrum of destructive analytical capabilities to element and speciation specific analyses. With the new IC and its modern ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) facilities, AHL offers innovative scientific options for nuclear and general research. Moreover, speciation analyses by IC-ICP-MS for polyvalent inorganic water pollutants such as Cr or As and the acquisition of a new ICP-OES system (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry) enable future autonomy in wastewater management.
Deep geological disposal of radioactive waste in clay rocks
Geological waste disposal, cement clay interaction
• A considerable reduction of HTO and 36Cl− was observed after 6 years interaction.
• The chloride flux showed a much stronger reduction compared to HTO.
• For HTO the relation between the De and the porosity in the clay part can be described using Archie's law.
• No complete clogging of the porosity was observed after 6 years interaction.
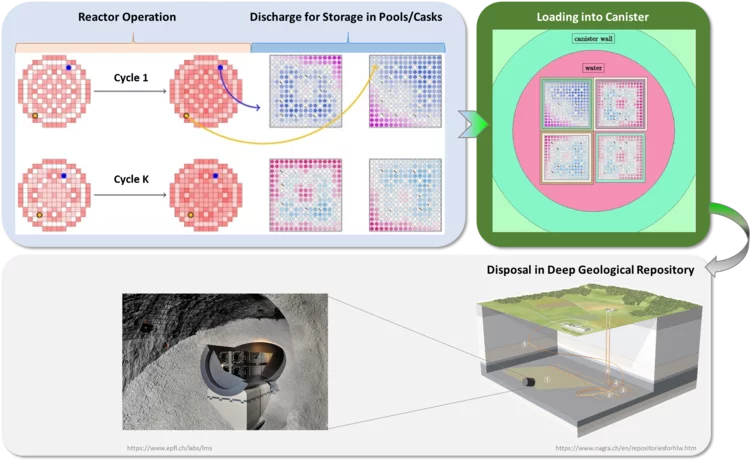
Used Nuclear Fuel: from Better Characterization to Better Optimization
A safe, economical and environmental friendly disposal of used nuclear fuel represents an essential objective of relevance for all. This guides the approach under development at the laboratory for reactor physics and thermal-hydraulics. Establish higher resolution simulation methods to gain more detailed knowledge on the content of each single nuclear fuel rod ever irradiated in a reactor. Thereafter, use this knowledge to explore optimization approaches that could potentially enlarge the range of disposal options allowing to fulfill the highest level of safety standards while reducing economical costs and geological footprints at the same time.
Hydrogen uptake into Zr-based fuel claddings
At the hot surface of a fuel rod cladding in the reactor water, the water is partially dissociated in hydrogen and oxygen, leading to corrosion of the cladding and to the uptake of a part of the created hydrogen. Hydrogen in solid solution and in precipitated form changes the mechanical properties of the cladding tube. The uptake of the hydrogen through the dense oxide layer is unclear. The structure and physical properties of the oxide near the metal-interface is critical The resistivity of the oxide increases with distance from the interface. Nb-containing alloys show lower resistivity in the oxide close to the metal interface, and exhibit a lower hydrogen pick-up. The time in the reactor is an important factor, leading to increasing resistivity in the oxide close to the metal interface, and a higher hydrogen uptake late in life.
Relevance of the findings: considering resistivity, the model of hydrogen uptake is better understood, revealing hints for further cladding development.
Life cycle assessment of cars – new web tool helps consumers and researchers
Decision support for car buyers: Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have developed a web tool called the Carculator that can be used to compare the environmental performance of passenger cars in detail.
Long-term developments of energy pricing and consumption in industry
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, on behalf of a research project funded by the Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE), have studied how energy consumption by Swiss industry develops depending on energy prices. One result: Price increases for energy usually affect energy consumption only over the long term.
"Electric is already the right choice today"
An interview on automotive power systems with Christian Bauer, a scientist at PSI's Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis who specialises in life cycle and sustainability analyses.
Make way for electric cars
Petrol, diesel, fuel cell or electric – which is the automobile of the future? A PSI study has examined the overall climate impact of various vehicle engines in use today and also projected it to the year 2040.
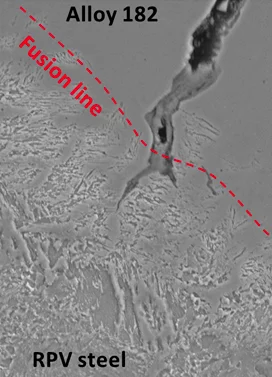
Assessment of stress corrosion cracking incidents in Alloy 182 – reactor pressure vessel dissimilar metal welds
Several stress corrosion cracking (SCC) incidents recently occurred in Alloy 182 - reactor pressure vessel (RPV) dissimilar metal welds in boiling water reactors (BWR). These SCC cracks tend to grow towards the RPV due to weld microstructure and residual stress profiles and might grow into the RPV. They thus represent a serious potential safety concern. PSI has evaluated under which conditions such cracks could grow into the RPV and also developed SCC crack growth disposition curves for the RPV steels that can be used for safety assessments of such cracks. With these curves that were recently accepted as a new Code Case N-896 in the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, sufficient safety margins could be demonstrated for such crack configurations with the current inspection intervals of the periodic in-service inspection.
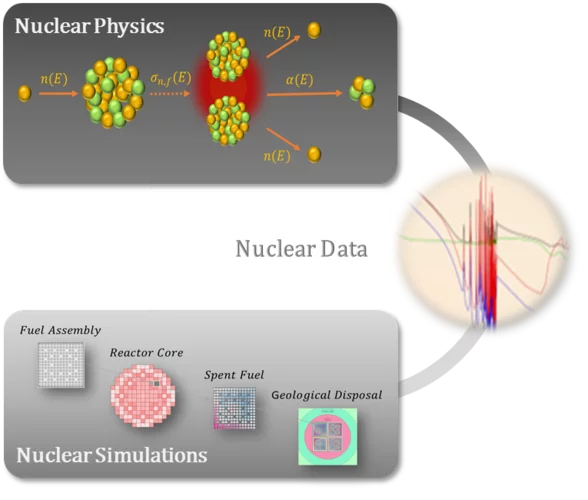
Nuclear Data – Towards a Stronger Link between Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Simulations
All matter in the universe is made of atoms and all atoms are made of particles. Spontaneous changes within atoms as well as collisions between atoms and surrounding particles are nuclear reaction processes guided by nuclear physics laws. To simulate these processes using computer models, probabilities for the various involved nuclear reactions are required. This is precisely the role of nuclear data: supply the computational models with evaluated quantities representing these nuclear reaction probabilities.
Through this, nuclear data can effectively be seen as the fundamental link between nature and any computer simulation involving nuclear reactions. It is thus of primary importance to continuously improve knowledge on nuclear data. In that context, researchers at the laboratory for reactor physics and thermal-hydraulics have recently focused on the development and application of Bayesian frameworks combining both differential and integral experiments for the improvement of nuclear data. By considering the different experiments together, the aim is to achieve enhancements of the nuclear data evaluations while preserving the basic nuclear physics sum rules.
Simulation: The third pillar of science
PSI researchers simulate and model large research facilities as well as experiments, for example, in the materials and biological sciences. Andreas Adelmann, head of PSI's Laboratory for Scientific Computing and Modelling, explains how they do it.
Modelling and simulation pay off
Researchers in PSI's Laboratory for Scientific Computing and Modelling solve the most complex problems through a combination of theory, modelling, and high-performance computing. With powerful computers, they simulate the smallest molecules or large research facilities.
Cancer medicine using PSI’s neutron source
At the neutron source SINQ, PSI researchers are producing special radionuclides that aid in the development of new and more effectively targeted cancer therapies. In this they collaborate closely with the clinics in the surrounding area.
World Energy Scenarios 2019
The Energy Economics Group quantified the new World Energy Scenarios 2019 in collaboration with the World Energy Council and Accenture Strategy. The three scenarios (named "Modern Jazz", "Unfinished Symphony", and "Hard Rock") depict possible future developments of the global energy systems until 2040 and were presented at the World Energy Congress 2019 in Dubai.
Identifying a disturbance root-cause from ... noise!
Nuclear reactors are complex systems with inherent stochastic behaviour. In simple words, the behaviour of various reactor processes are continuously fluctuating over their mean values, even under normal operation and steady-state conditions. The detailed and systematic analysis of this noisy behaviour can reveal valuable information about the operating status of the studied nuclear reactor. More importantly, designed modifications of the reactor’s operation or even unexpected deviations from the normal performance can be identified using advanced signal analysis techniques. The STARS program, at the Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Thermal-Hydraulics (LRT) in PSI, based on a tight collaboration with the Swiss nuclear industry, has developed a well-established signal analysis methodology, being continuously improved since more than two decades. The latest enhancements of the PSI signal analysis methodology allow a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms that drive the reactor’s operation, and can provide better insight on the root-cause of possible disturbances or malfunctions. Recently, the latest STARS activities in advanced signal analysis techniques were culminated by an international recognition through a special distinction from the AIP Chaos Journal.
"This is incredibly ambitious"
Every three years, the World Energy Council explores possible developments of the global energy system under different scenarios. Tom Kober, head of the Energy Economics Group in PSI’s Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis and one of the lead authors of the study, explains what the individual scenarios mean and how global warming could be mitigated.
New material with magnetic shape memory
PSI researchers have developed a material whose shape memory is activated through magnetism. Application areas for this new kind of composite material include, for example, medicine, space flight, electronics, and robotics.