Show filters
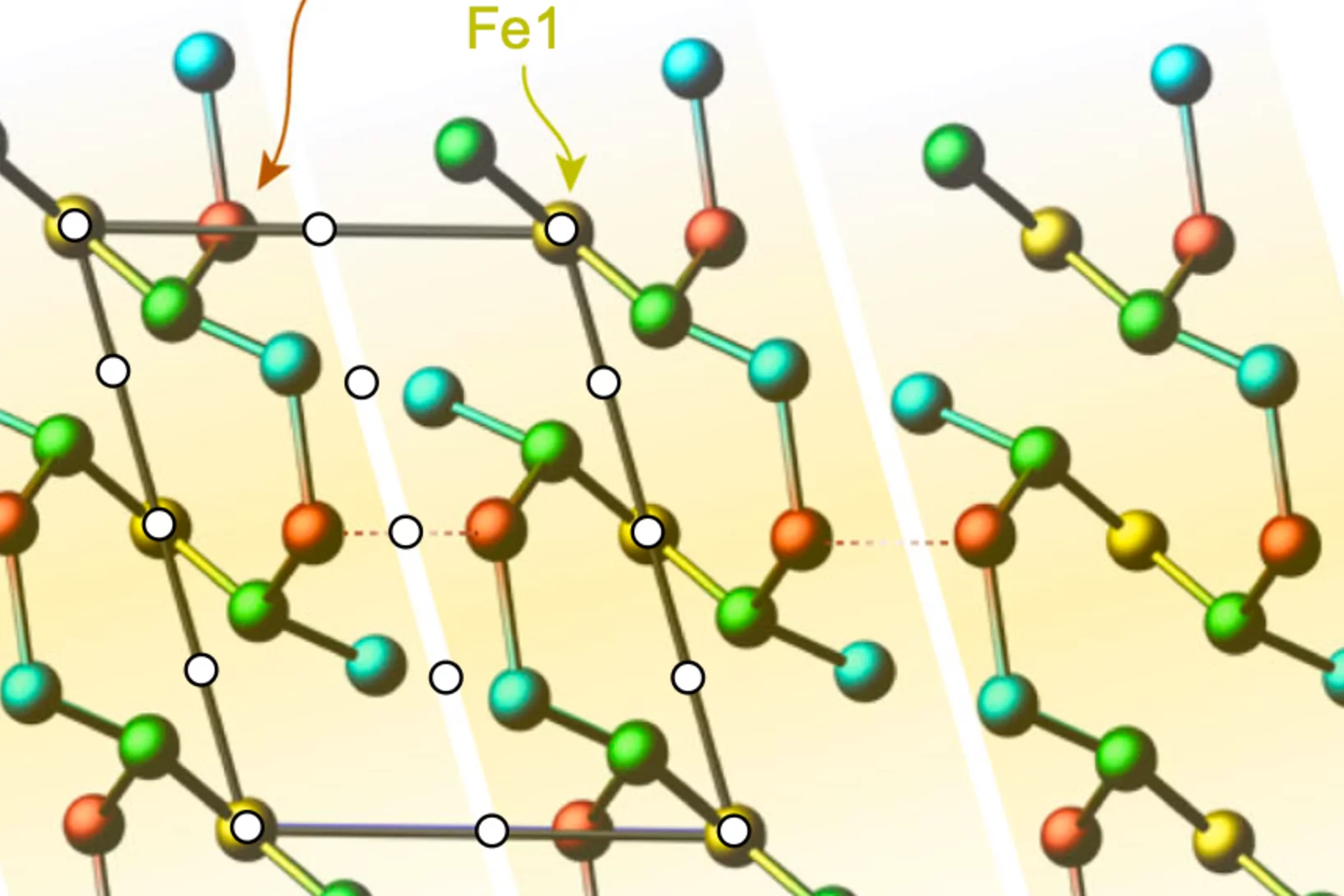
Pressure and oxygen-isotope substitution on density-wave transitions in La4Ni3O10
Understanding the interplay between magnetism and superconductivity in nickelate systems is a key objective in condensed matter physics. Gaining microscopic insights into magnetism—particularly as it emerges near superconductivity—requires a synergistic approach that combines complementary experimental techniques with controlled tuning of external parameters. In this paper, we present ...
Topological metal-insulator transition within the ferromagnetic state
A major challenge in condensed matter physics is integrating topological phenomena with correlated electron physics to leverage both types of states for next-generation quantum devices. Metal-insulator transitions are central to bridging these two domains while simultaneously serving as on-off switches for electronic states. Here, we demonstrate ...
How hydrogen affects titanium implants
Researchers use Swiss Spallation Neutron Source SINQ to study how medical implants change inside the body.
Room-Temperature Magnetic Skyrmions and Intrinsic Anomalous Hall Effect in a Nodal-Line Kagomé Ferromagnet MnRhP
Topological magnetic semimetals with kagomé lattices have attracted significant attention due to their nontrivial electronic band structures and pronounced electromagnetic responses. The search for kagomé-lattice topological semimetals exhibiting magnetic ordering above room temperature is essential ...
Low-frequency electrochemical pulsing to manage flooding and salt precipitation in zero-gap CO2-to-ethylene electrolyzers
The electrochemical conversion of CO2 to ethylene offers a promising approach to expand manufacturing of commodity chemicals and fuels. Specifically, ethylene is a critical precursor for polyethylene a $240B industry. Expanding productivity ...
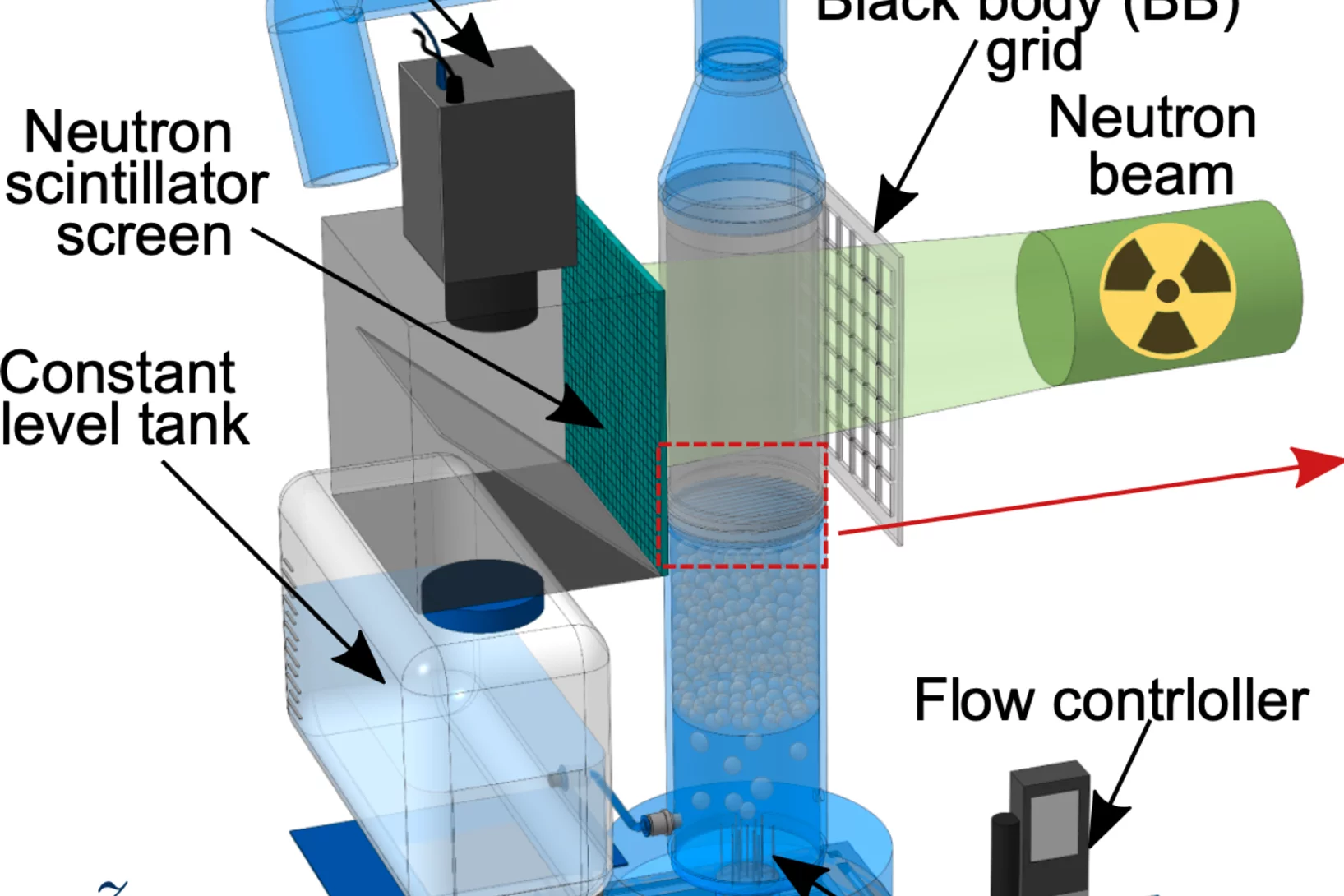
Investigating the hidden content of Tibetan bronze statues using modern neutron imaging techniques
Bronze statues hold deep significance in Buddhism and Bon, often containing relics sealed within their hollow interiors. Traditional scholarly methods, such iconographic analysis, cannot access the hidden contents of these statues without risking physical damage. This study proposes ...
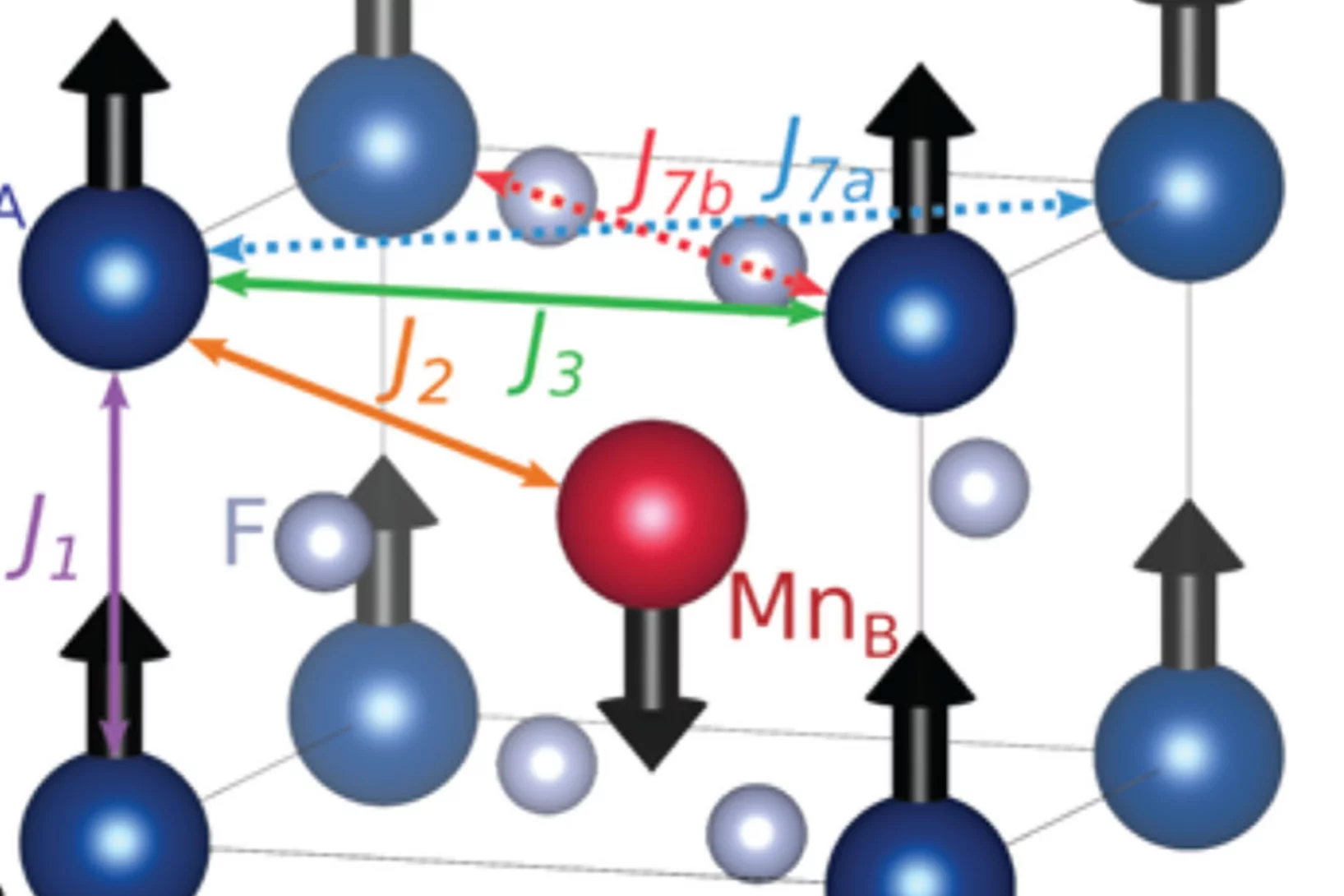
Anisotropic Band-Split Magnetism in Magnetostrictive CoFe2O4
Single crystal spinel CoFe₂O₄ exhibits the largest room-temperature saturation magnetostriction among non-rare-earth compounds and a high Curie temperature (T₍c₎ ∼ 780 K), properties that are critical to a wide range of industrial and medical applications. Neutron spectroscopy ...
Operando neutron imaging of an alkaline electrolysis cell for mapping gas distributions
Optimizing hydrogen and oxygen transport within porous electrodes is essential for improving the efficiency of industrial alkaline electrolyzers. In this study, we utilize operando dynamic neutron radiographic measurements to investigate ...
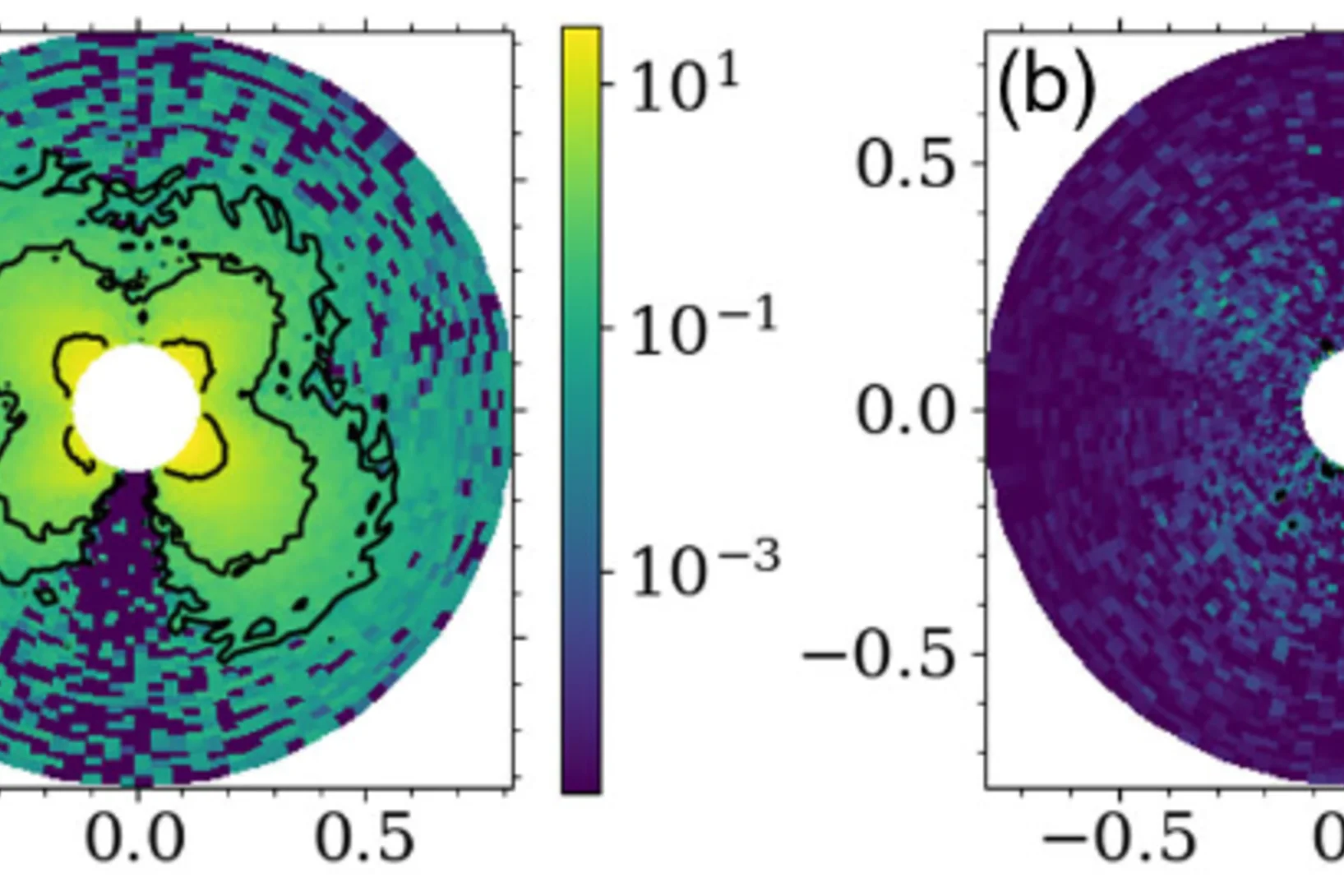
Spin-Disorder-Induced Angular Anisotropy in Polarized Magnetic Neutron Scattering
We experimentally report a hitherto unseen angular anisotropy in the polarized small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) cross section of a magnetically strongly inhomogeneous material ...
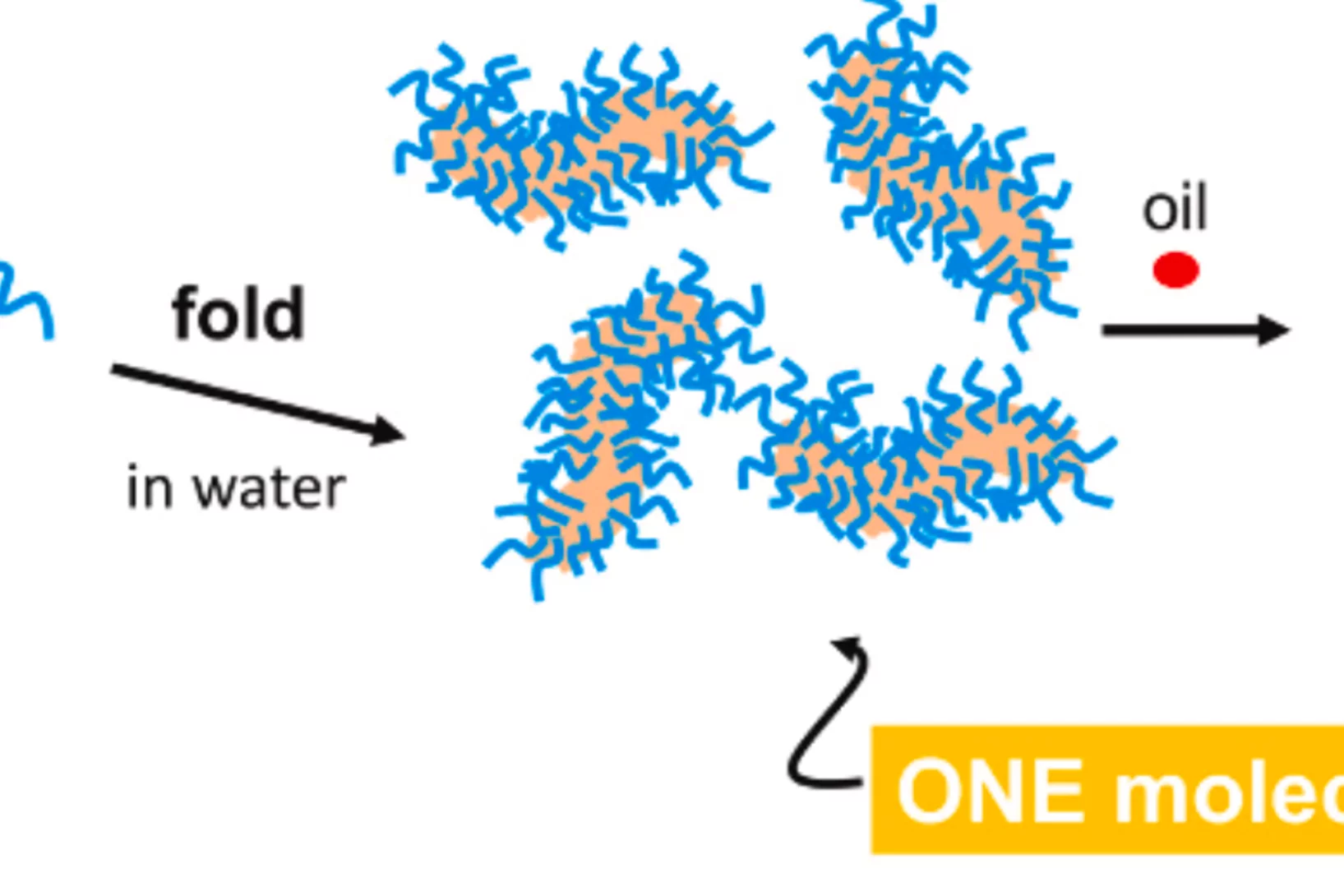
Single-chain polymer nanoparticles for oil solubilization
We report on the oil solubilization of amphiphilic single chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) based on random copolymers composed of oligo(ethyleneglycol) methacrylate (OEGMA) and anthracene methacrylate (AnMA). Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) combined with molecular dynamics simulations reveal ...
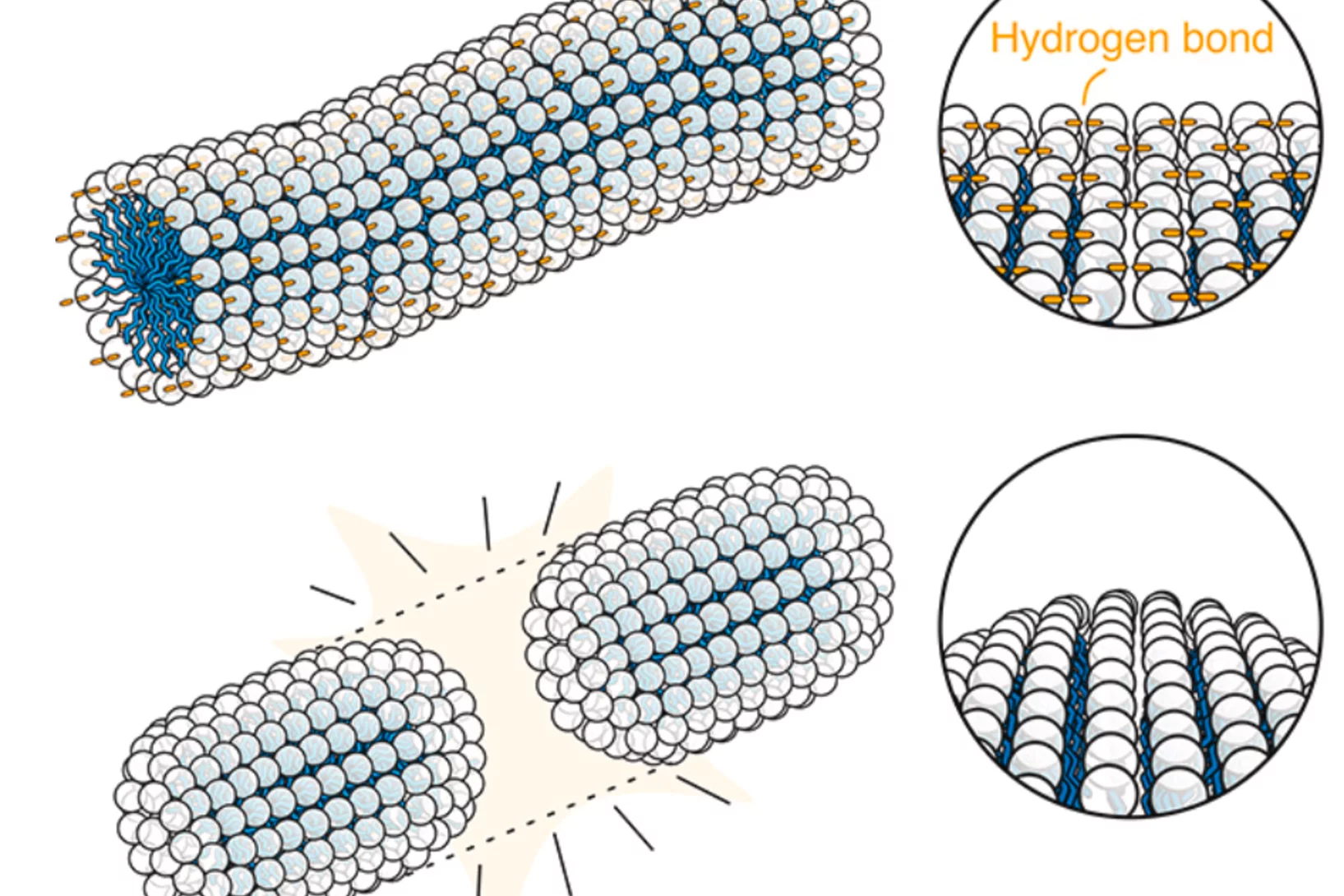
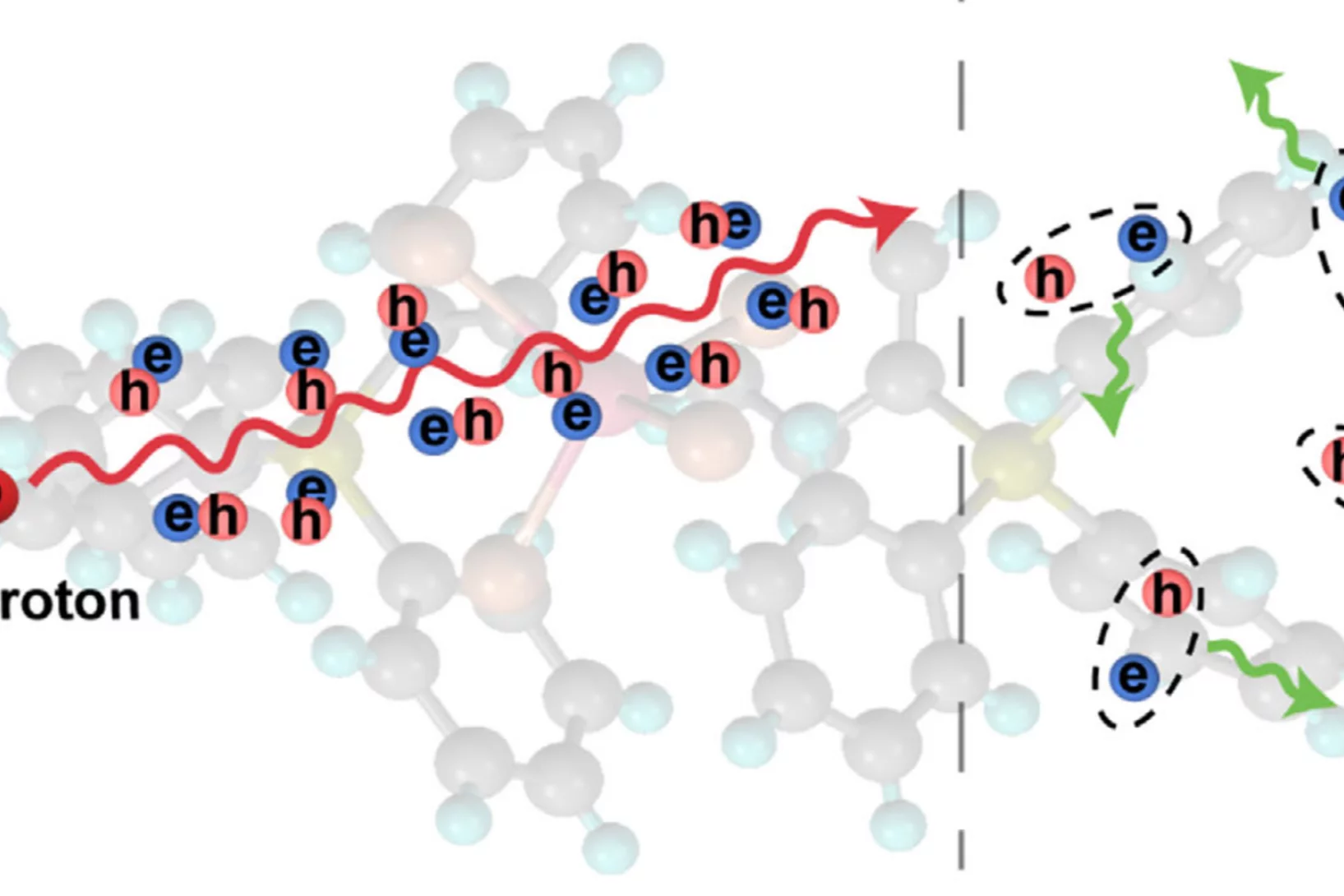
Hydrogen bonding exacerbates viscoelasticity of amino acid– and betaine surfactant self-assemblies
Many day-to-day materials rely on formulations of surfactants to control flow, texture and application. Inspired by the pairing of bases between DNA strands, we demonstrate enhanced control ...
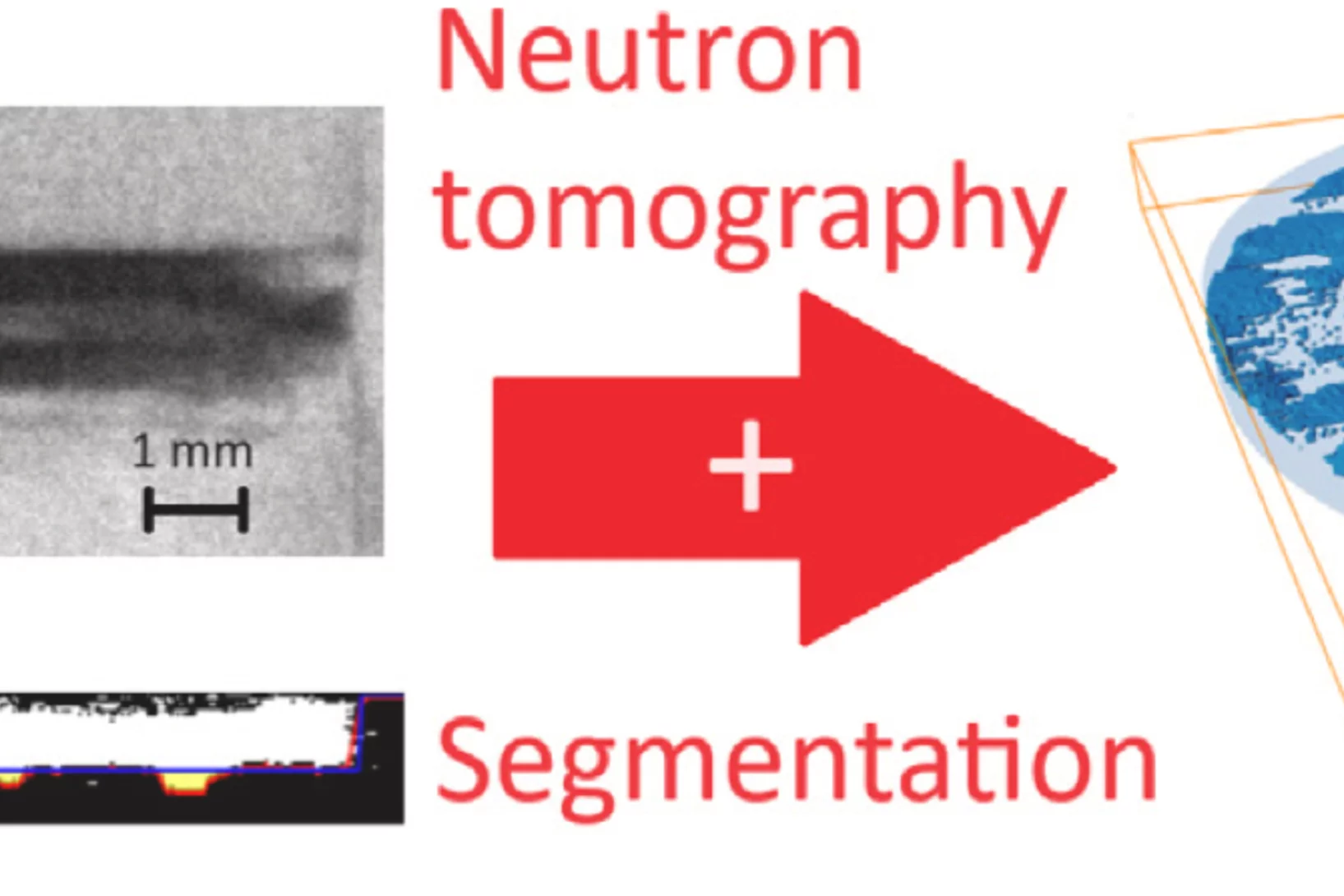
In-situ neutron tomography study of a dehydrating and hydrating packed bed for thermochemical heat storage
To study the heat and water vapor transport and reaction kinetics in a packed bed of thermo-chemical material on both reactor and tablet level, an in-situ neutron imaging study of a dehydrating and subsequently hydrating packed bed consisting of cylindrical K2 CO3 tablets was performed at the Paul Scherrer Institute ...
Field-Induced Magnon Decay, Magnon Shadows, and Rotonlike Excitations in the Honeycomb Antiferromagnet YbBr3
The search for new quantum many-body phenomena in magnetic materials has a strong focus on highly frustrated systems and the resulting quantum spin-liquid state. However, even unfrustrated magnetic materials show a multitude of unconventional features in their spin excitation spectra. By using the synergy of ...
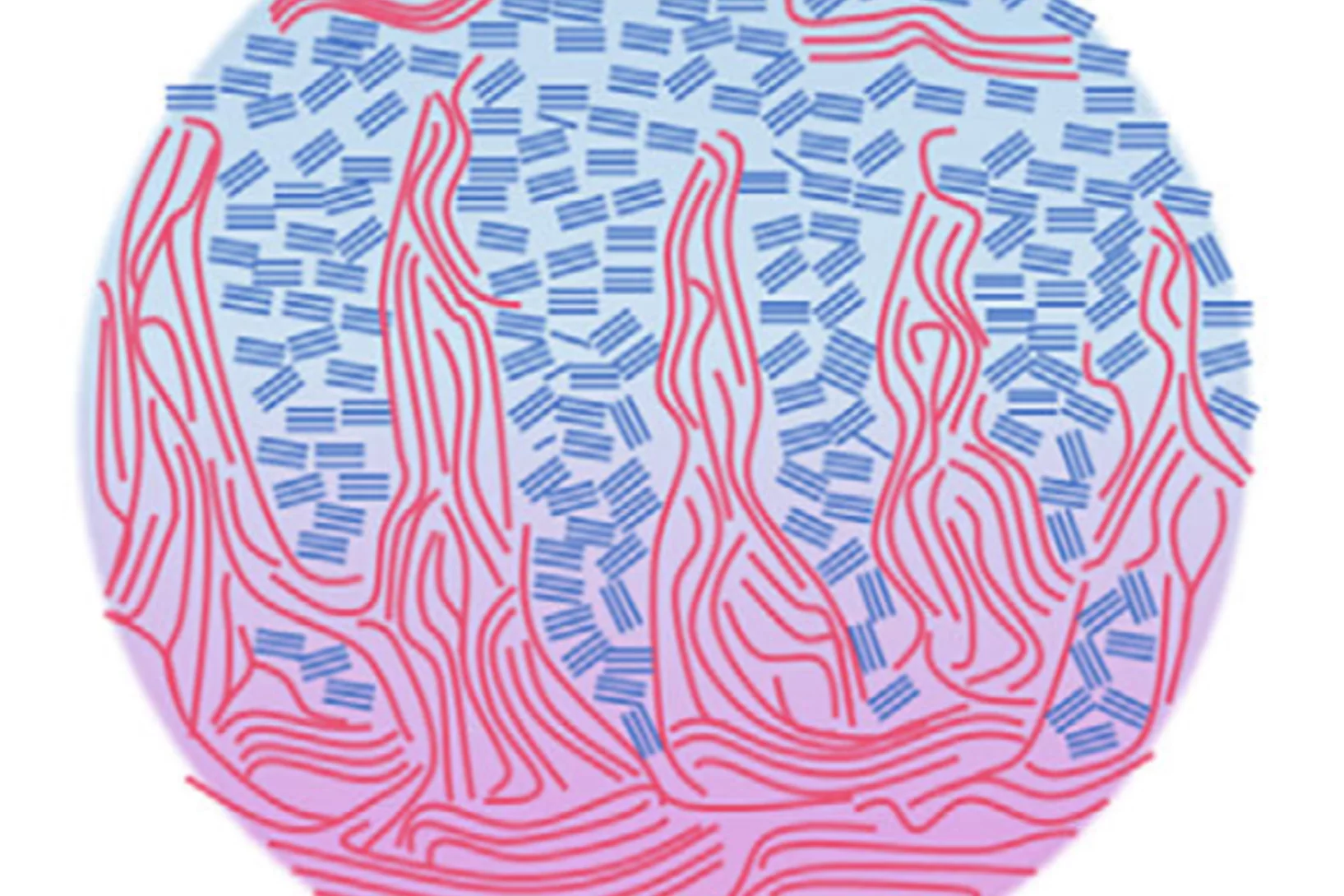
Generating structured foam via flowing through a wire array
Efficient manufacturing methods could unlock foams with tailored, anisotropic properties. Conventional foam production methods rely on the self-arrangement of bubbles, typically leading to isotropic materials, or involve intricate additive layering processes. This study presents a simple, passive technique to modify the foam structure. A set of thin parallel wires ...
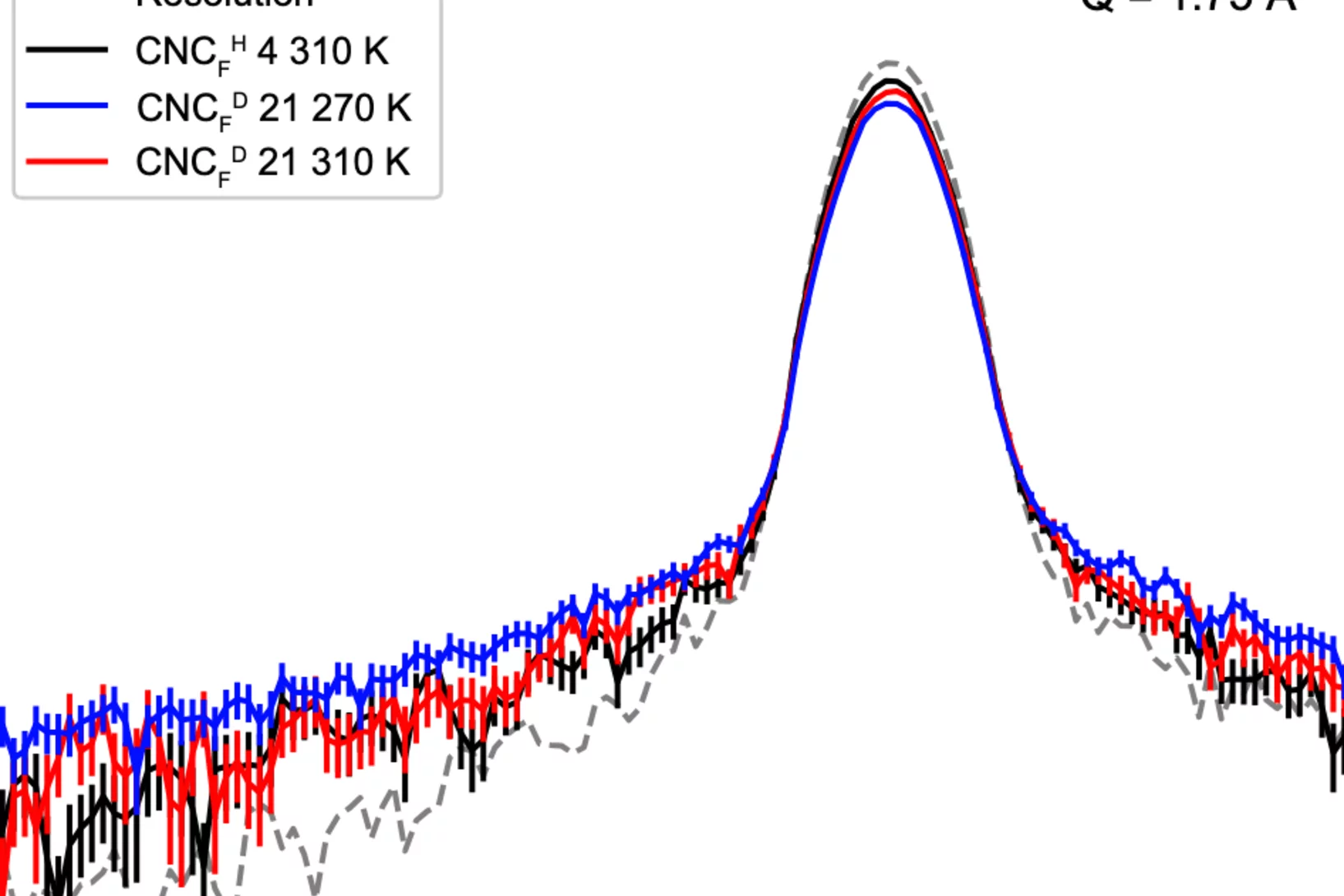
Hydration- and Temperature-Dependent Rotational Dynamics and Water Diffusion in Nanocellulose
Nanocellulose is a promising alternative to fossil-derived materials, but its development is hindered by a limited understanding of cellulose–water interactions. Herein, quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) is used to investigate how hydration and temperature affect the localized rotations in cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) and the diffusion of mobile water. QENS reveals ...
Bright Monocompound Metal Halide Scintillator for Fast Neutron Radiography
Fast neutron imaging is a promising technique for visualizing objects containing dense, mixed light-and-heavy-elements materials, such as combustion engines, nuclear fuel assemblies, and fossils, where X-rays and thermal neutrons are ineffectiv. However, the limited efficiency of current detection technologies hinders their widespread adoption. Recoil proton detection ...
Neutron imaging in 2D and 3D as a powerful tool to investigate electrolyte degradation and plating mechanisms in sodium-ion batteries
To develop durable and high-performance sodium-ion batteries, it is crucial to understand the degradation processes taking place during electrochemical cycling. This study presents the first demonstration of visualizing the effects of electrolyte degradation in sodium-ion batteries, via 2D and 3D neutron imaging thereby visualizing the degradation of the cells. The experiment ...
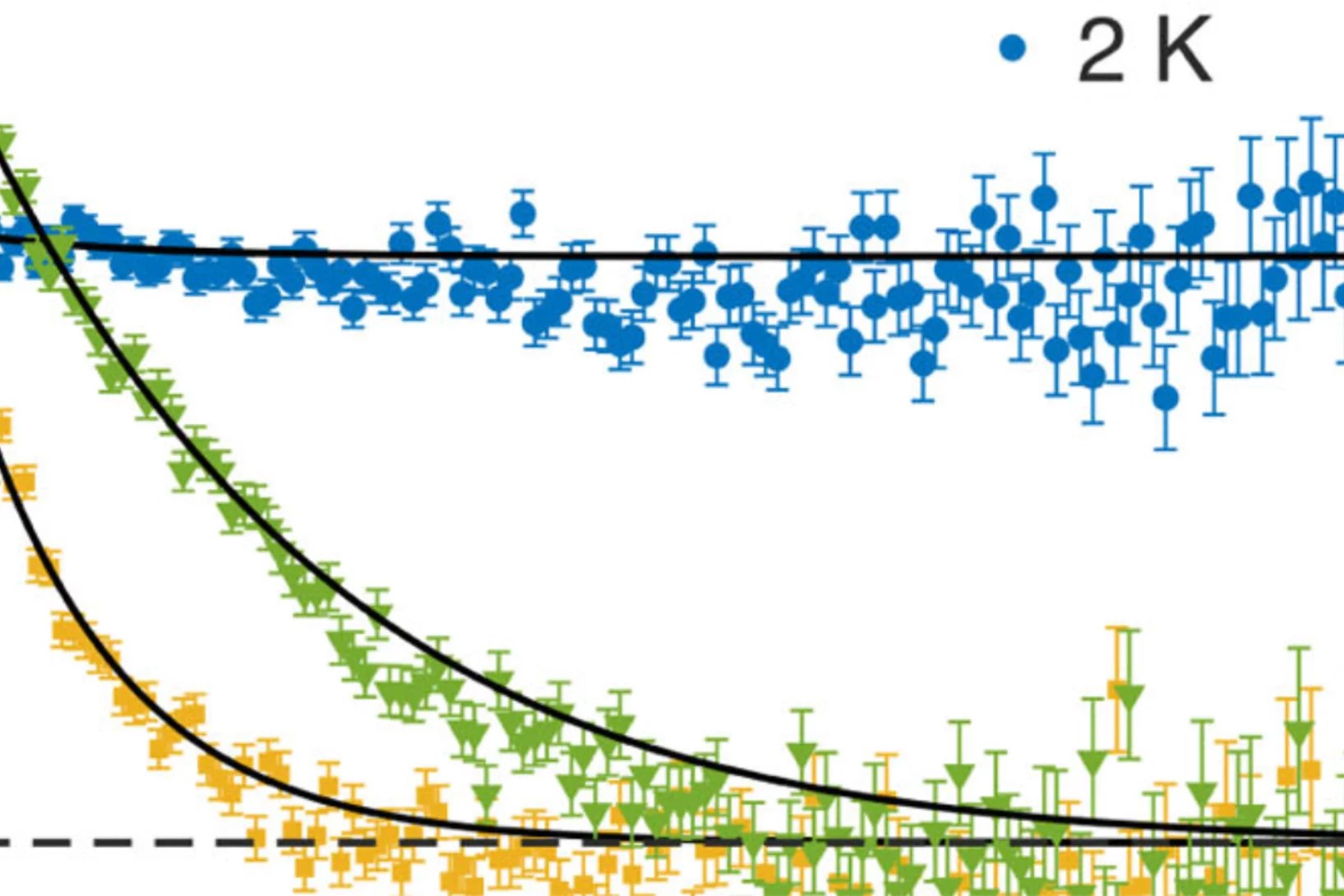
Microscopic Origin of Reduced Magnetic Order in a Frustrated Metal
Although magnetic frustration in metals provides a promising avenue for novel quantum phenomena, their microscopic interpretation is often challenging. Here, we use the face-centered cubic intermetallic HoInCu4 as model material to show that Hamiltonians neglecting the charge degree of freedom are appropriate for frustrated metals possessing low density of states at the Fermi surface ...
Steering magnetic textures with electric fields
Neutrons reveal a new way to control magnetism at the nanoscale
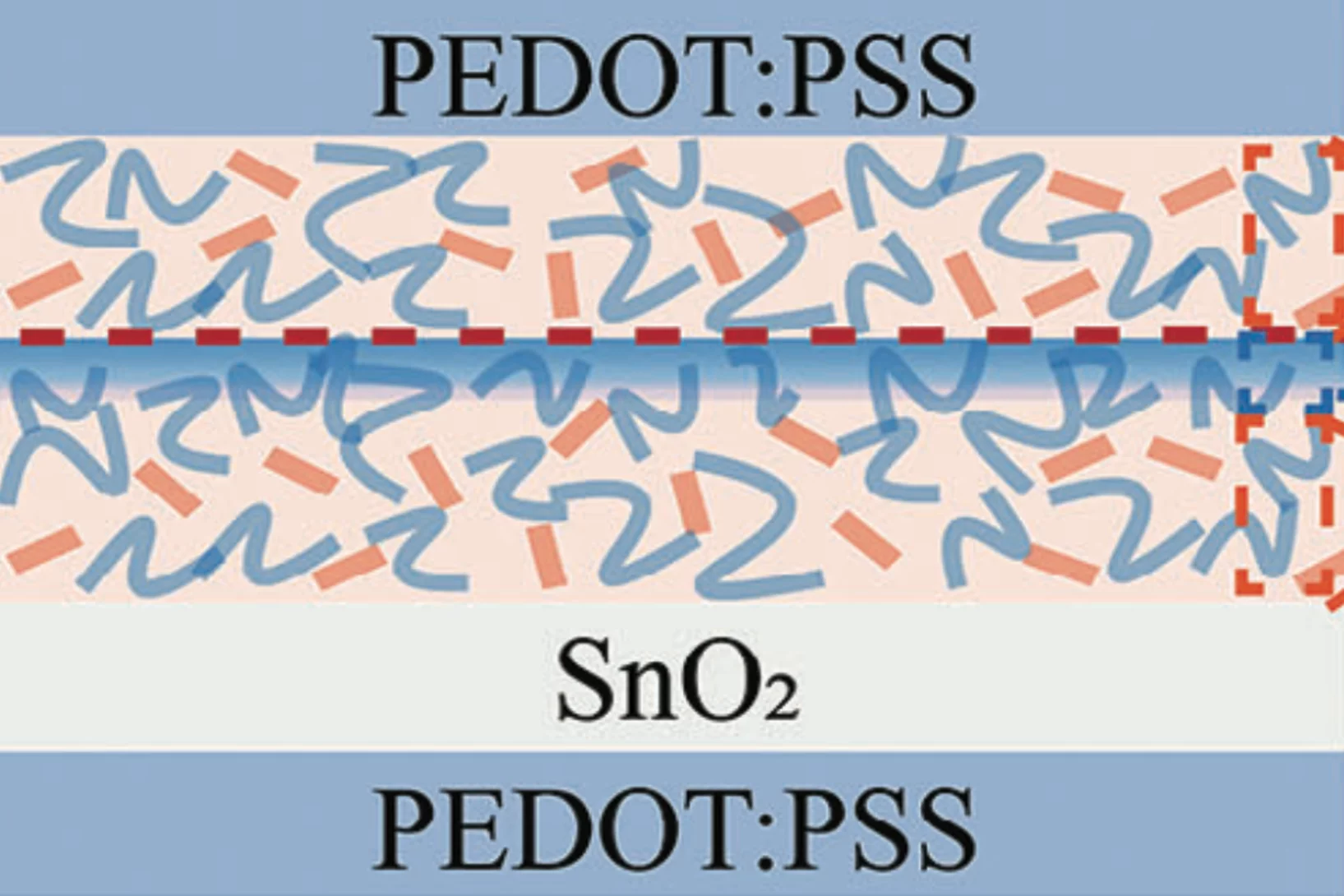
Understanding and Addressing the Performance Asymmetry Issue in Semitransparent Laminated Organic Photovoltaic Devices
Organic photovoltaics (OPVs) offer a promising solution for indoor energy harvesting. However, fundamental investigations to understand and optimize industrial processes such as roll-to-roll lamination for upscaling remain limited. This study investigates a critical failure mode in the upscaling of OPVs.
One major challenge ...
Absence of Altermagnetic Magnon Band Splitting in MnF2
Altermagnets are collinear compensated magnets in which the magnetic sublattices are related by rotation rather than translation or inversion. One of the quintessential properties of altermagnets is the presence of split chiral magnon modes. Recently, such modes have been predicted in MnF2.
Here, we report inelastic neutron scattering results ...
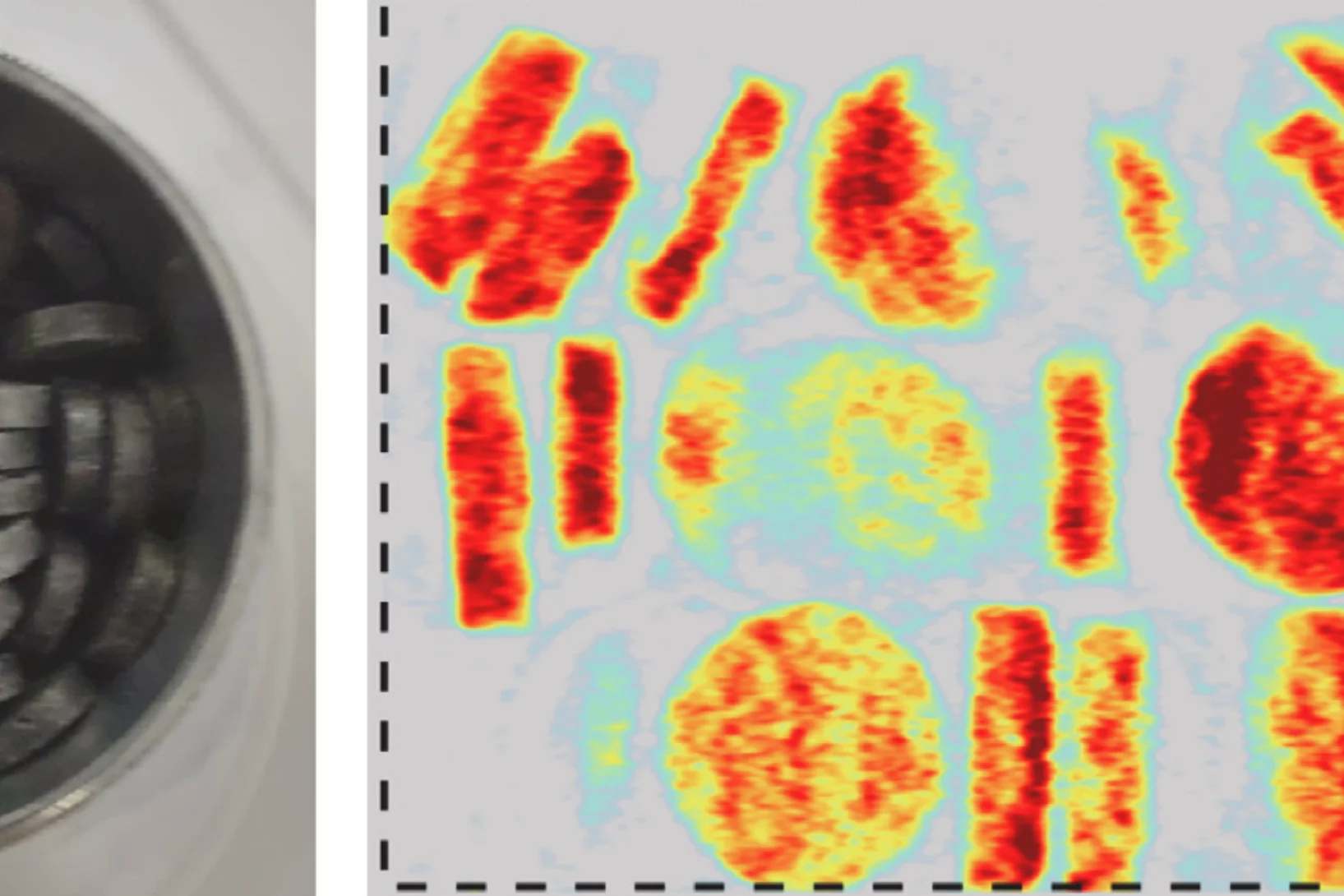
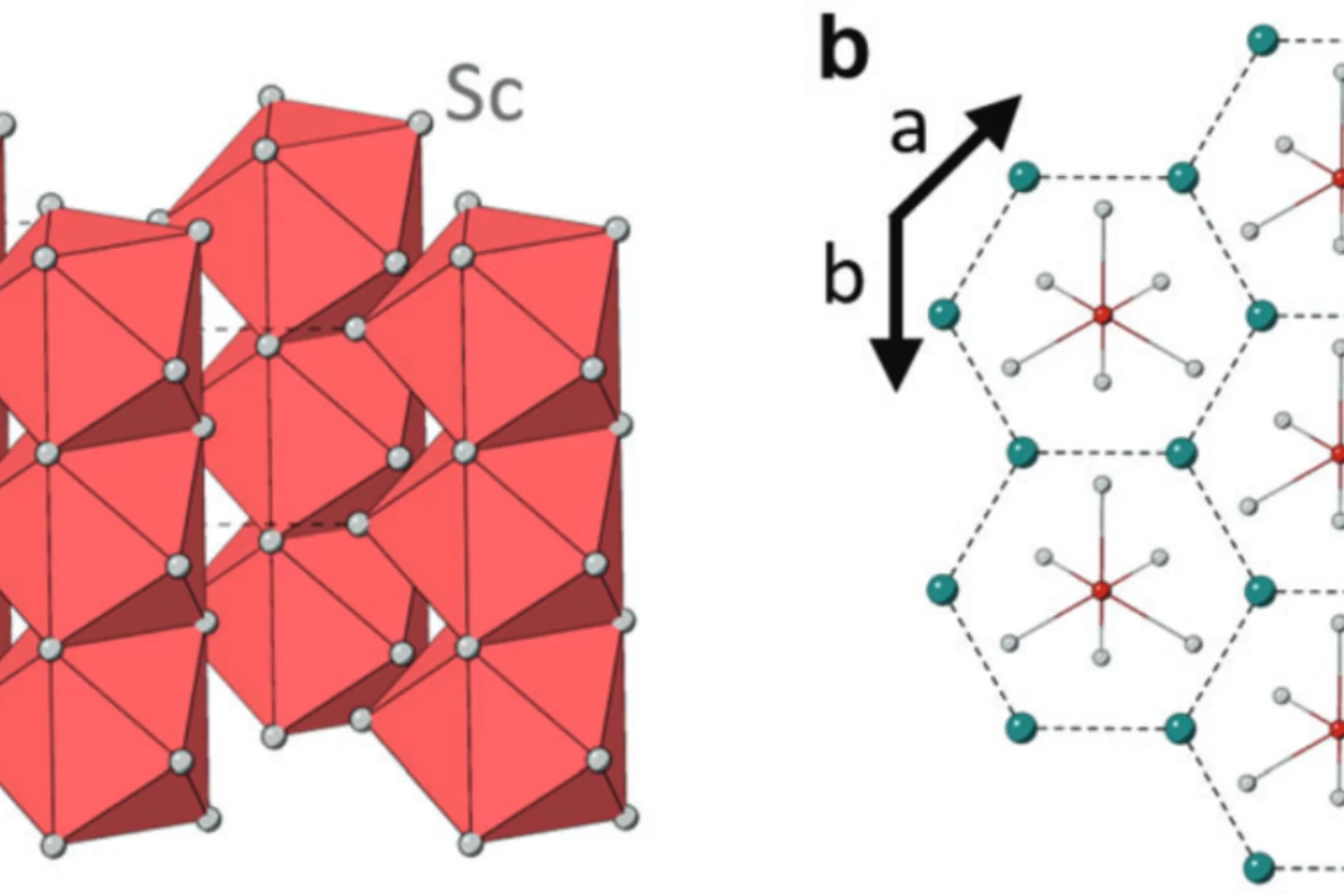
Tailoring the Normal and Superconducting State Properties of Ternary Scandium Tellurides, Sc6MTe2 (M = Fe, Ru, and Ir) Through Chemical Substitution
The pursuit of a unifying theory for non-BCS superconductivity has faced significant challenges. One approach to overcome such challenges is to perform systematic investigations into superconductors containing d-electron metals in order to elucidate their underlying mechanisms. Recently, the Sc6MTe2 (M = d-electron metal) family has emerged as a unique series of isostructural compounds exhibiting superconductivity across a range of 3d, 4d, and 5d electron systems.
In this study, muon spin rotation, neutron diffraction, and magnetization techniques are employed to probe ...
Achieving Uniform Phase Structure for Layer-by-Layer Processed Binary Organic Solar Cells with 20.2% Efficiency
Layer-by-layer (LBL) deposition has become a facile and promising method to fabricate highly efficient organic solar cells (OSCs). However, characterization and optimization of 3D morphology remain a grand challenge for LBL- processed active layers, and their correlation with photovoltaic properties of OSC devices is not clear to date.
Here, to address this issue, ...
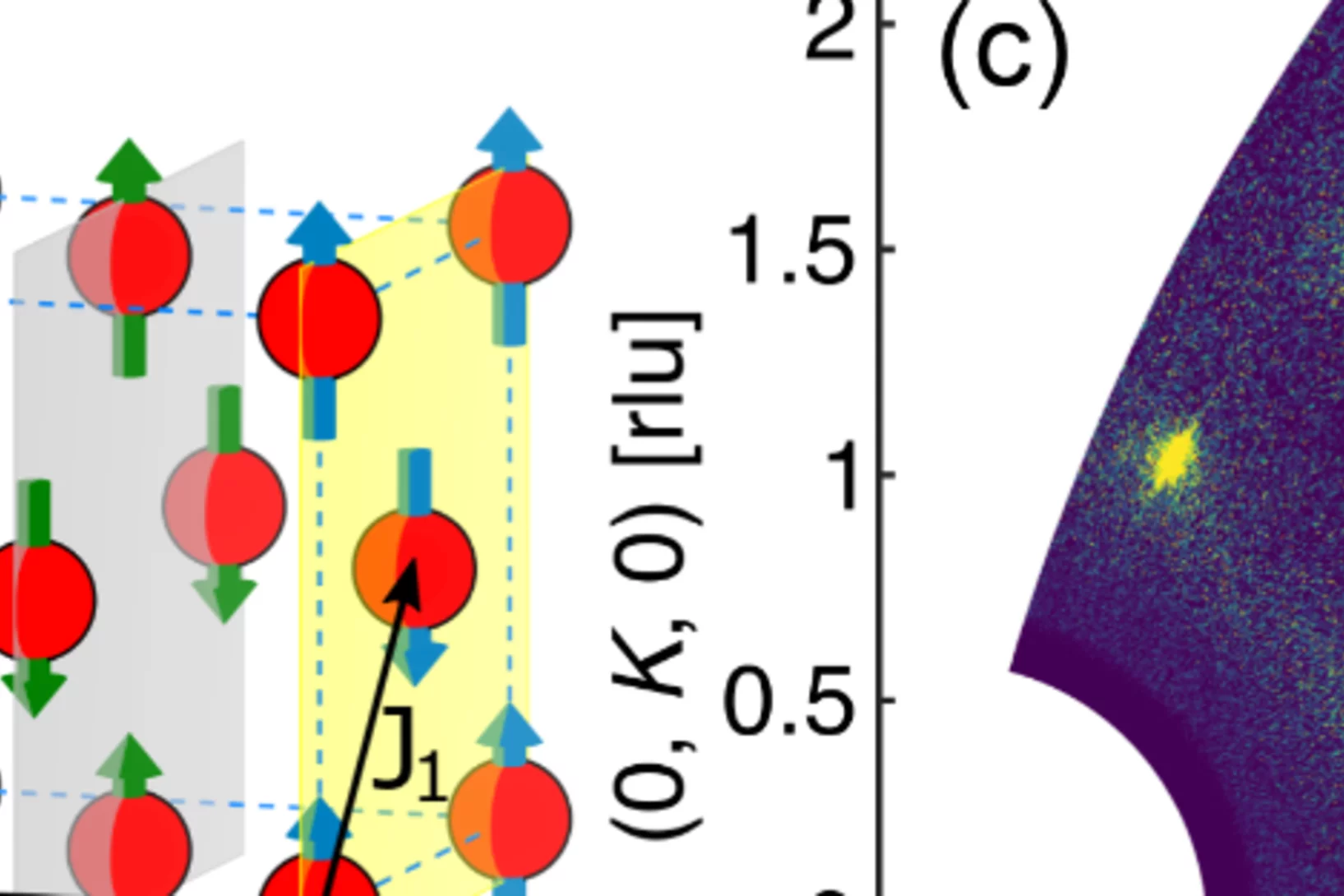
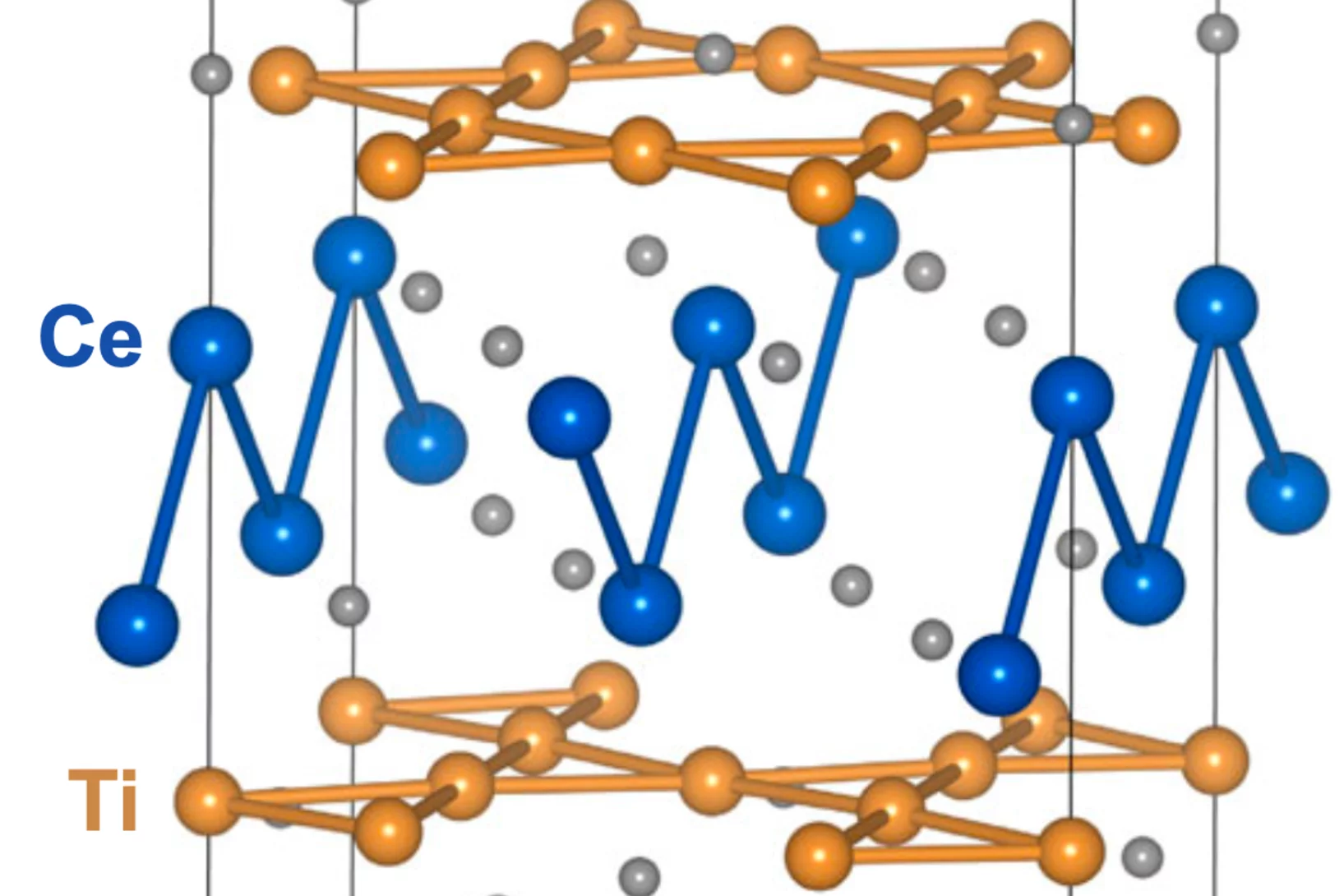
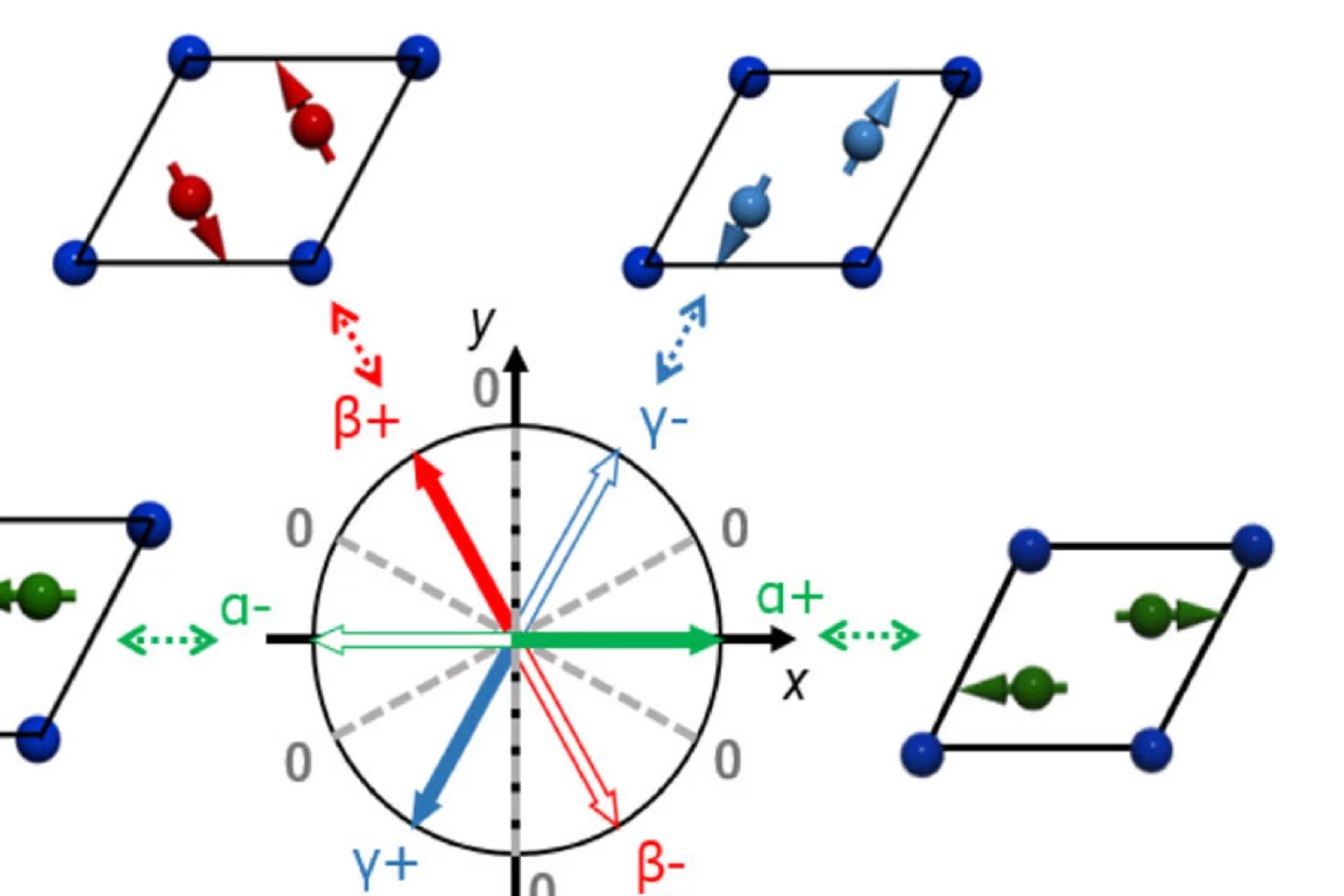
Spin density wave and van Hove singularity in the kagome metal CeTi3Bi4
Kagome metals with van Hove singularities near the Fermi level can host intriguing quantum phenomena such as chiral loop currents, electronic nematicity, and unconventional superconductivity. However, to our best knowledge, unconventional magnetic states driven by van Hove singularities–like spin-density waves–have not been observed experimentally in kagome metals. Here, we report ...
4D imaging of frost heave and ice lens growth in silt using neutron and x-ray computed tomography
There are substantial changes in soil structure in regions where the soil is freezing. Water movements in the freezing soil introduce level changes beyond what can be expected by the expansion of water when it freezes. The impact of frost heave is seasonal damage to our built environment ...
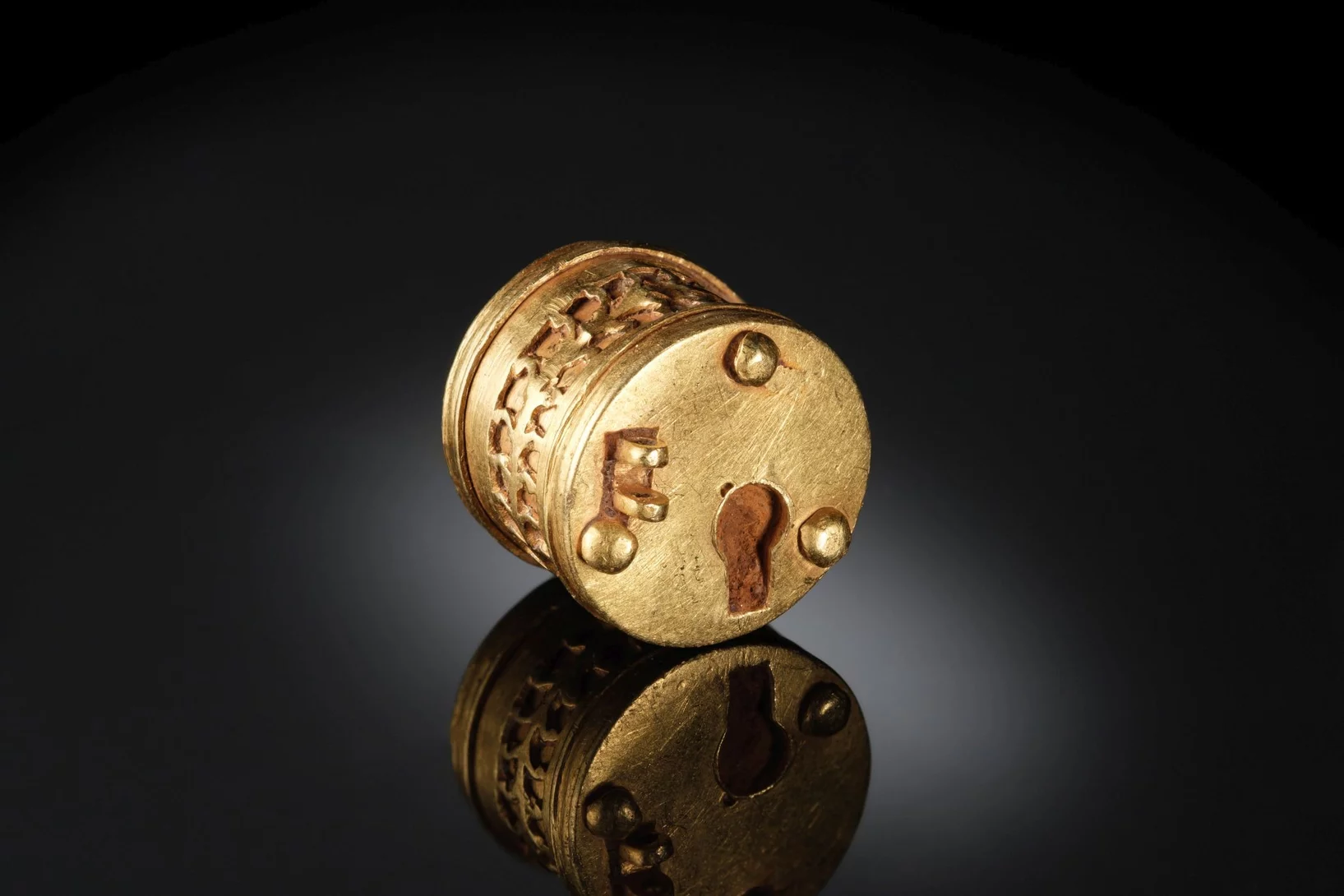
A tiny golden object from Roman times
PSI’s David Mannes has used neutrons to unravel the mystery of a fascinating archaeological artefact.
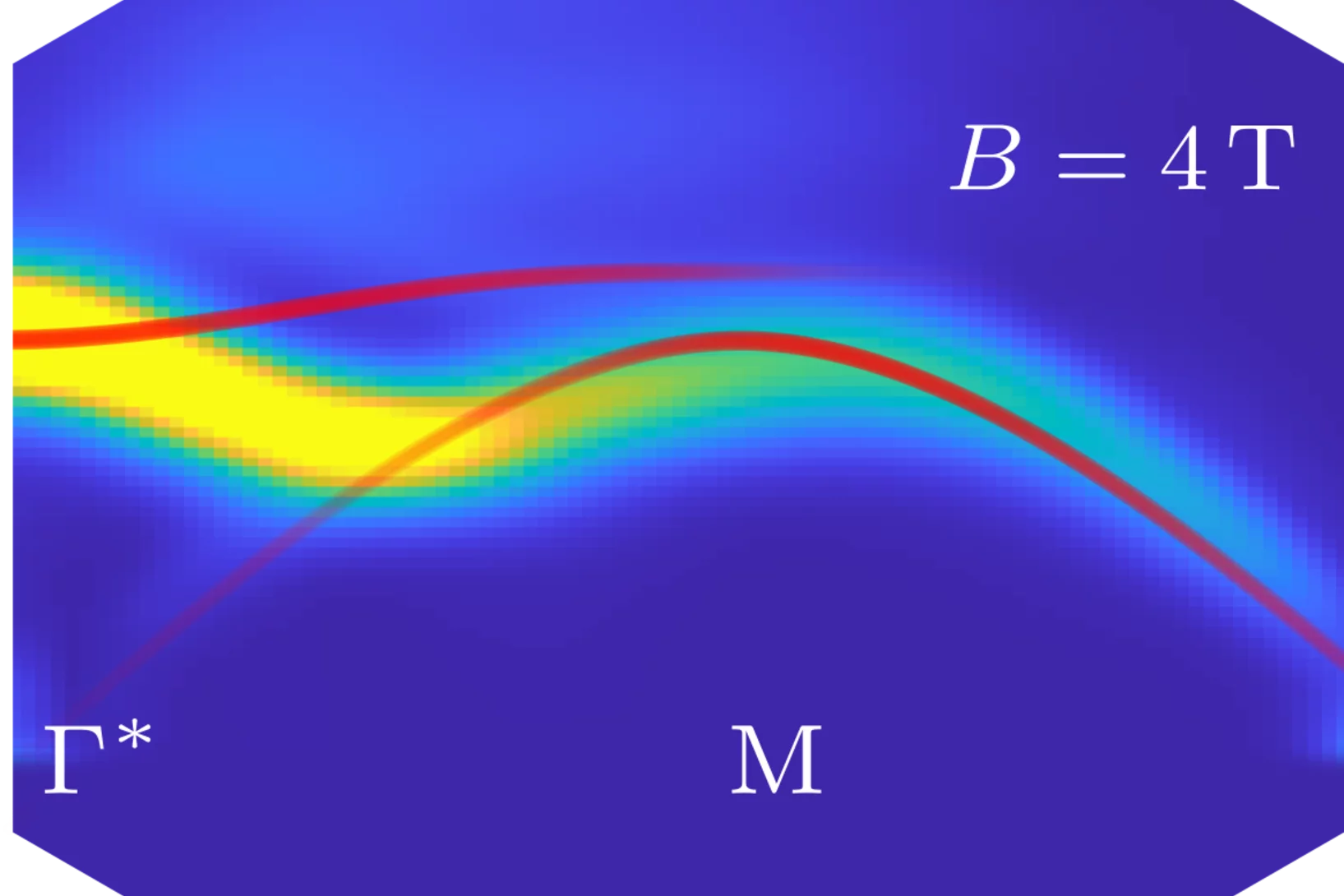
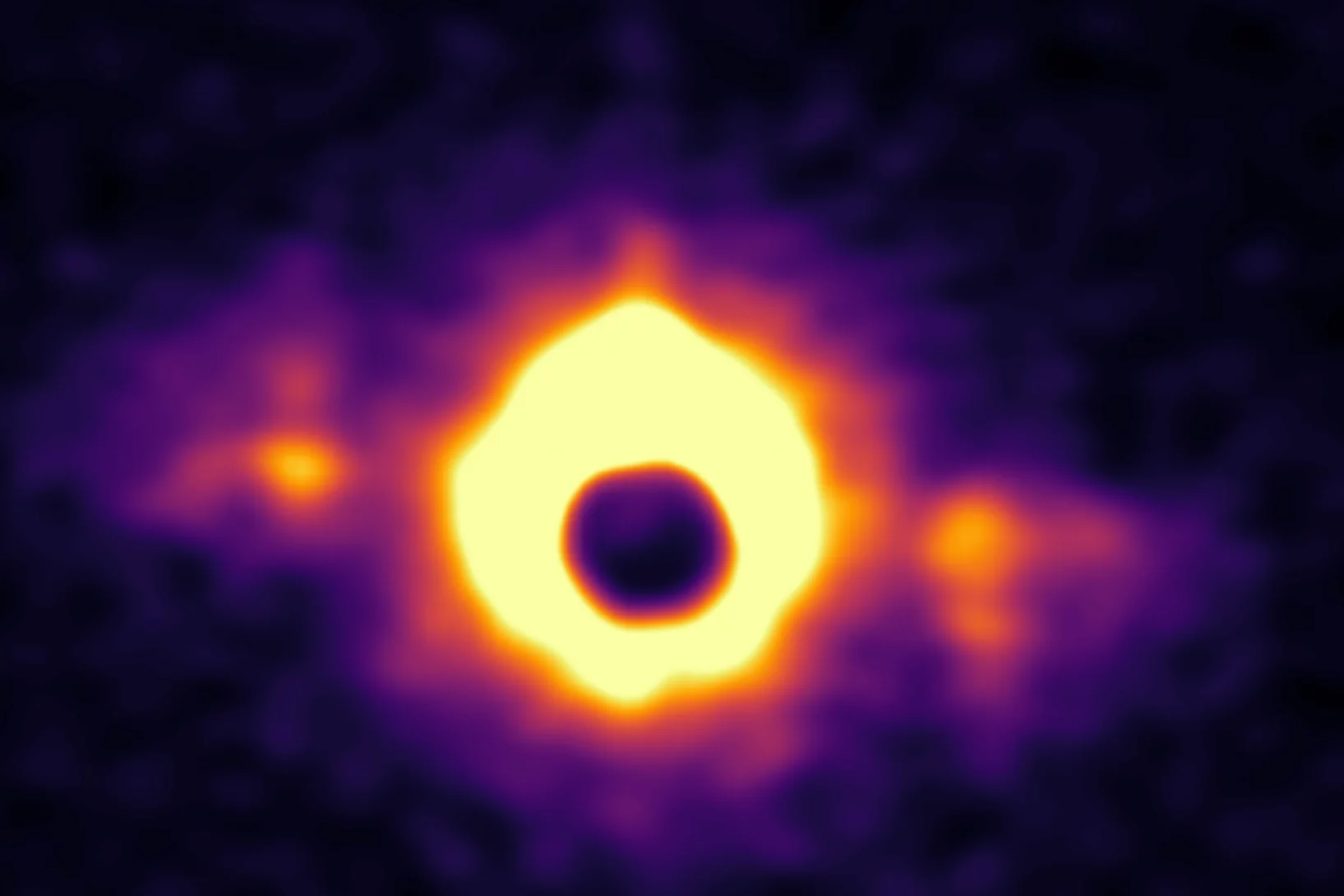
Emergence of topological Hall effect from a fluctuation-based dynamic origin
The topological nature of the electronic bands or spin structure has direct manifestation in experimentally measured Hall conductivity. The extra topological (or geometrical) component to the Hall effect (THE) usually emerges due to multi-k structures, which inherently possess a finite static scalar spin chirality (SSC). Generating a THE in a single-k structure necessitates the consideration of the dynamical origin of SSC, the real material examples of such cases remain scarce to date.
Zero-field Hall effect emerging from a non-Fermi liquid in a collinear antiferromagnet V1/3NbS2
Magnetically intercalated transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) provide a versatile three-dimensional (3D) material platform to explore quantum phenomena and functionalities that emerge from an intricate interplay among magnetism, band structure, and electronic correlations.
Generation of Neutron Airy Beams
The Airy wave packet is a solution to the potential-free Schrödinger equation that exhibits remarkable properties such as self-acceleration, nondiffraction, and self-healing. Although Airy beams are now routinely realized ....
Anomalous Hall Effect due to Magnetic Fluctuations in a Ferromagnetic Weyl Semimetal
The anomalous Hall effect (AHE) has emerged as a key indicator of time-reversal symmetry breaking (TRSB) and topological features in electronic band structures. Absent of a magnetic field, the AHE requires spontaneous TRSB but has proven hard to probe due to averaging over domains. The anomalous component of the Hall effect is thus frequently derived from extrapolating the magnetic field dependence of the Hall response. We show ....