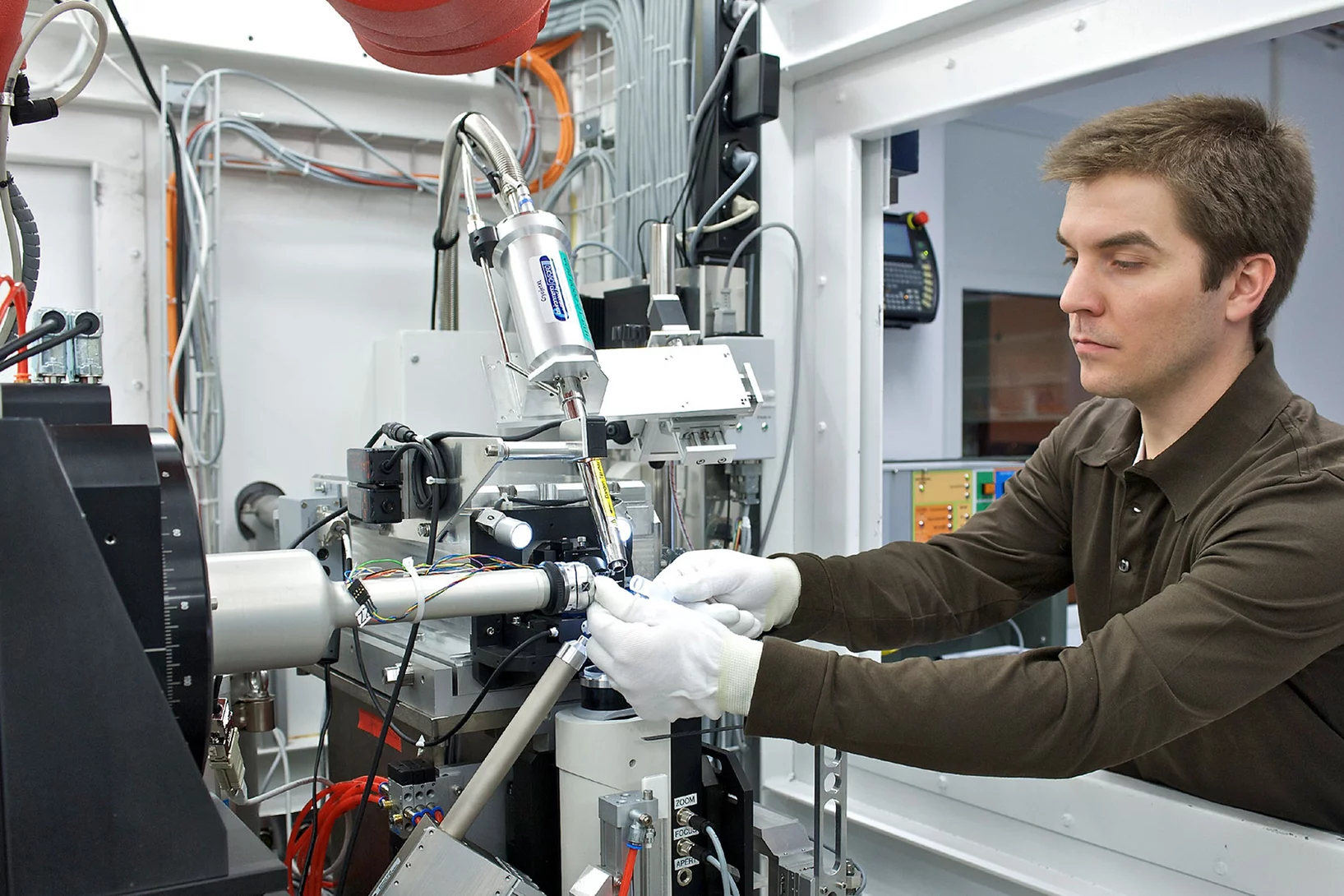
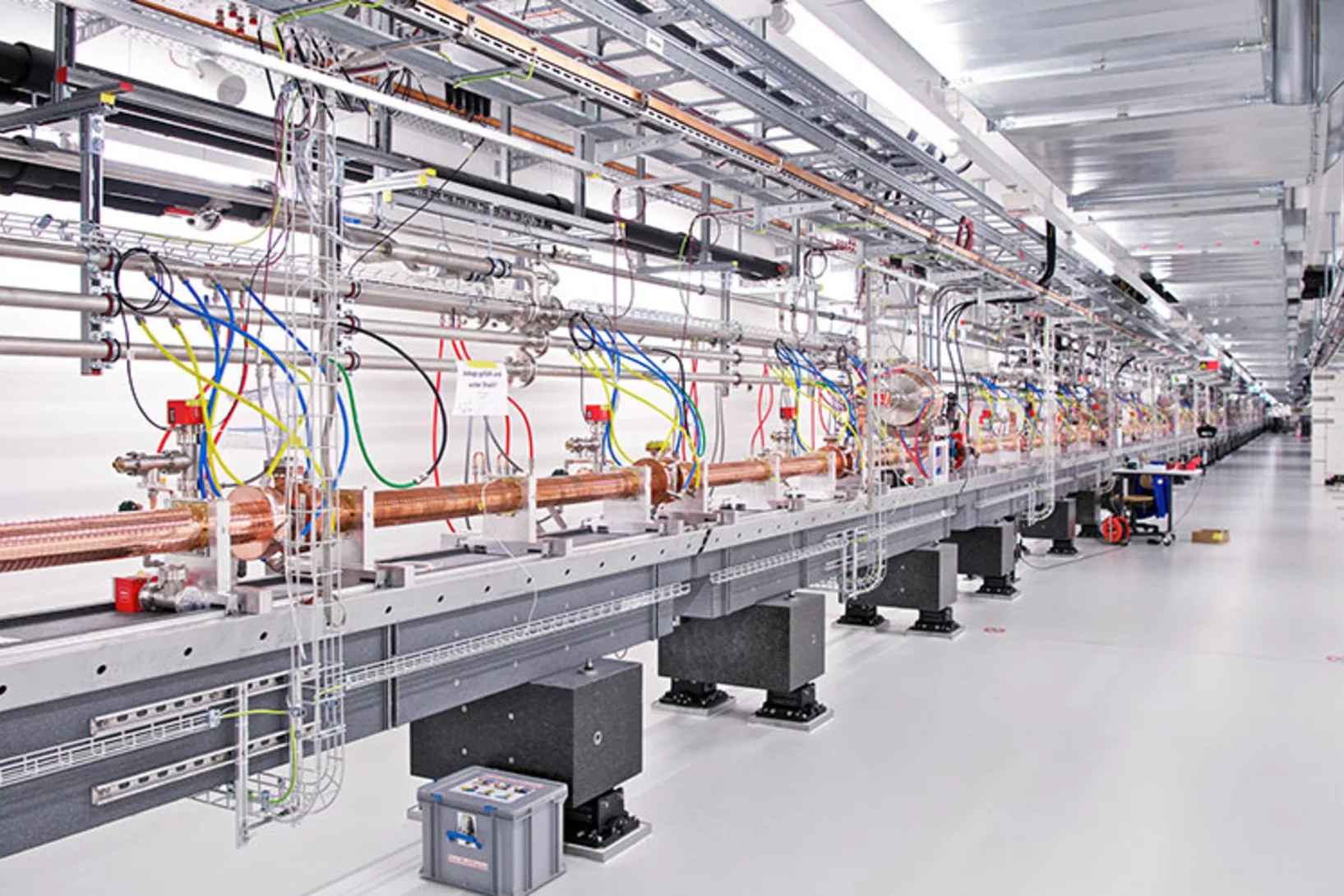
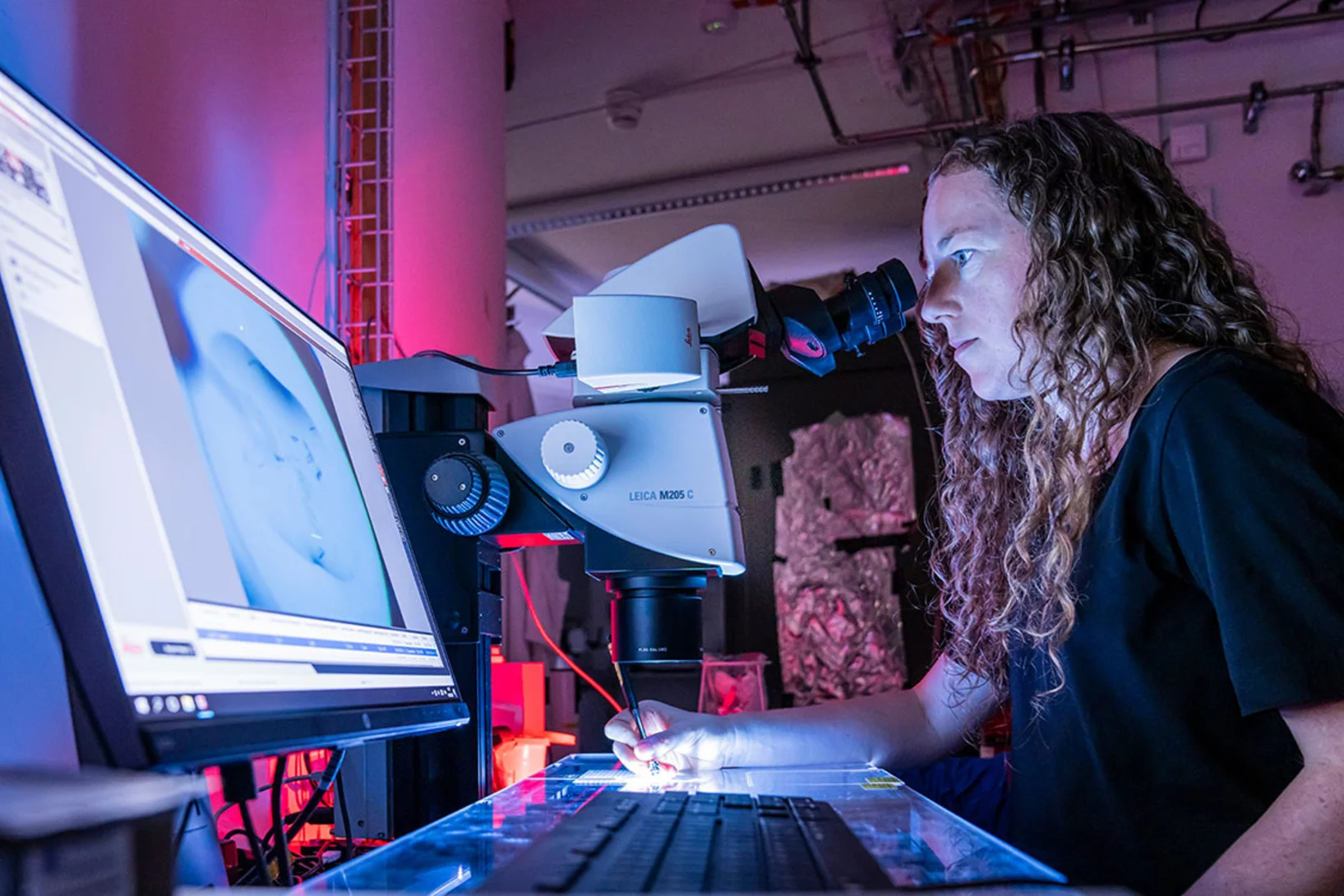
Forschung zu Covid-19 am Paul Scherrer Institut
Während viele Bereiche des Lebens eingeschränkt sind, bleiben wichtige Forschungsanlagen am PSI in Betrieb.
Watching receptor proteins changing shape
In our bodies, G protein-coupled receptors mediate countless processes. PSI researcher Ramon Guixà talks about how he brings those receptor molecules to life on the computer screen.
New blueprint for more stable quantum computers
PSI researchers have shown how faster and better defined quantum bits can be created. The central elements are magnetic atoms from the class of so-called rare-earth metals, selectively implanted into the crystal lattice of a material.
Clocking the movement of electrons inside an atom
Scientists pioneer an approach called self-referenced streaking, clocking Auger electrons with sub-femtosecond resolution. The breakthrough will unlock the broader potential for attosecond time resolution at X-ray free-electron lasers
SLS 2.0 approved - TOMCAT 2.0 cleared for takeoff!
In December 2020 the Swiss parliament approved the Swiss Dispatch on Promotion of Education, Research and Innovation (ERI) for 2021 to 2024 which includes funding for the planned SLS 2.0 upgrade. The new machine will lead to significantly increased brightness, thus providing a firm basis for keeping the SLS and its beamlines state-of-the-art for the decades to come. The TOMCAT crew is very excited that the TOMCAT 2.0 plans (deployment of the S- and I-TOMCAT branches, see SLS 2.0 CDR, p. 353ff) have been included in the Phase-I beamline upgrade portfolio. These beamlines will receive first light right after the commissioning of the SLS 2.0 machine around mid 2025. A first milestone towards this goal has just been achieved, with the successful installation of the S-TOMCAT optics hutch during W1 of 2021. The TOMCAT scientific and technical staff would like to thank Mr. Nolte and his Innospec crew for delivering perfectly on schedule.
PSI equips the Swiss Light Source SLS for the future
Green light for SLS 2.0: The planned upgrade of the Swiss Light Source SLS can proceed; the funding is provided for within the framework of the ERI Dispatch for 2021-2024, which has been approved.
Look Inside a Chemical Reactor
Operando X-ray spectrotomography allows scientists to look inside of functioning chemical reactors. A research team at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), at Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in France have employed this method successfully.
The librarian of the petabytes
It is necessary to prepare now for the planned upgrade of the Swiss Light Source SLS. In order to do justice to future research, Alun Ashton is estimating the amount of data that future experiments will produce.
Milestone for the second beamline of SwissFEL
At the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, the second beamline is currently being put into operation. With Athos, researchers want to understand how catalysts work or how biomolecules cause hereditary diseases.
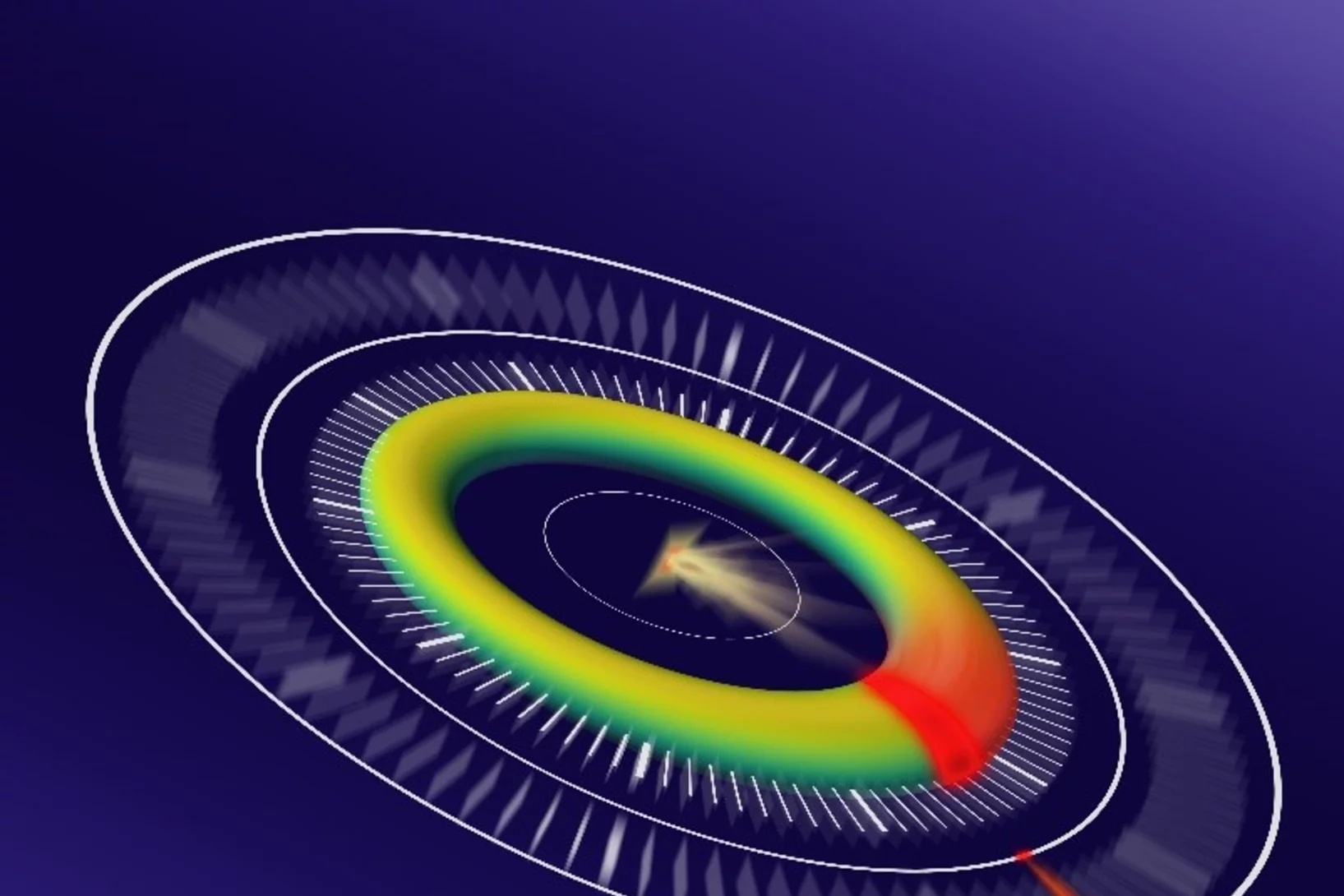
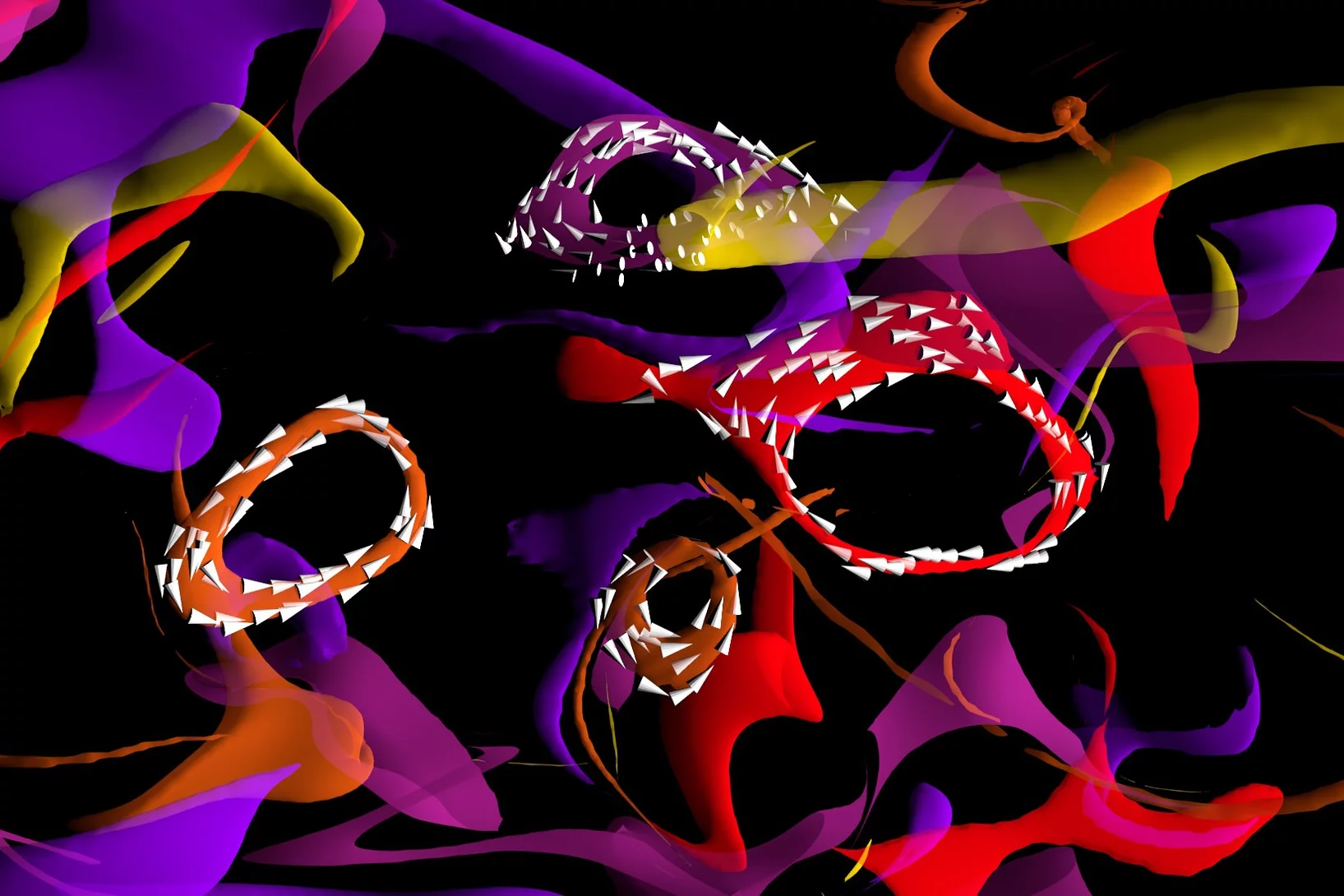
Magnetic vortices come full circle
The first experimental observation of three-dimensional magnetic ‘vortex rings’ provides fundamental insight into intricate nanoscale structures inside bulk magnets, and offers fresh perspectives for magnetic devices.
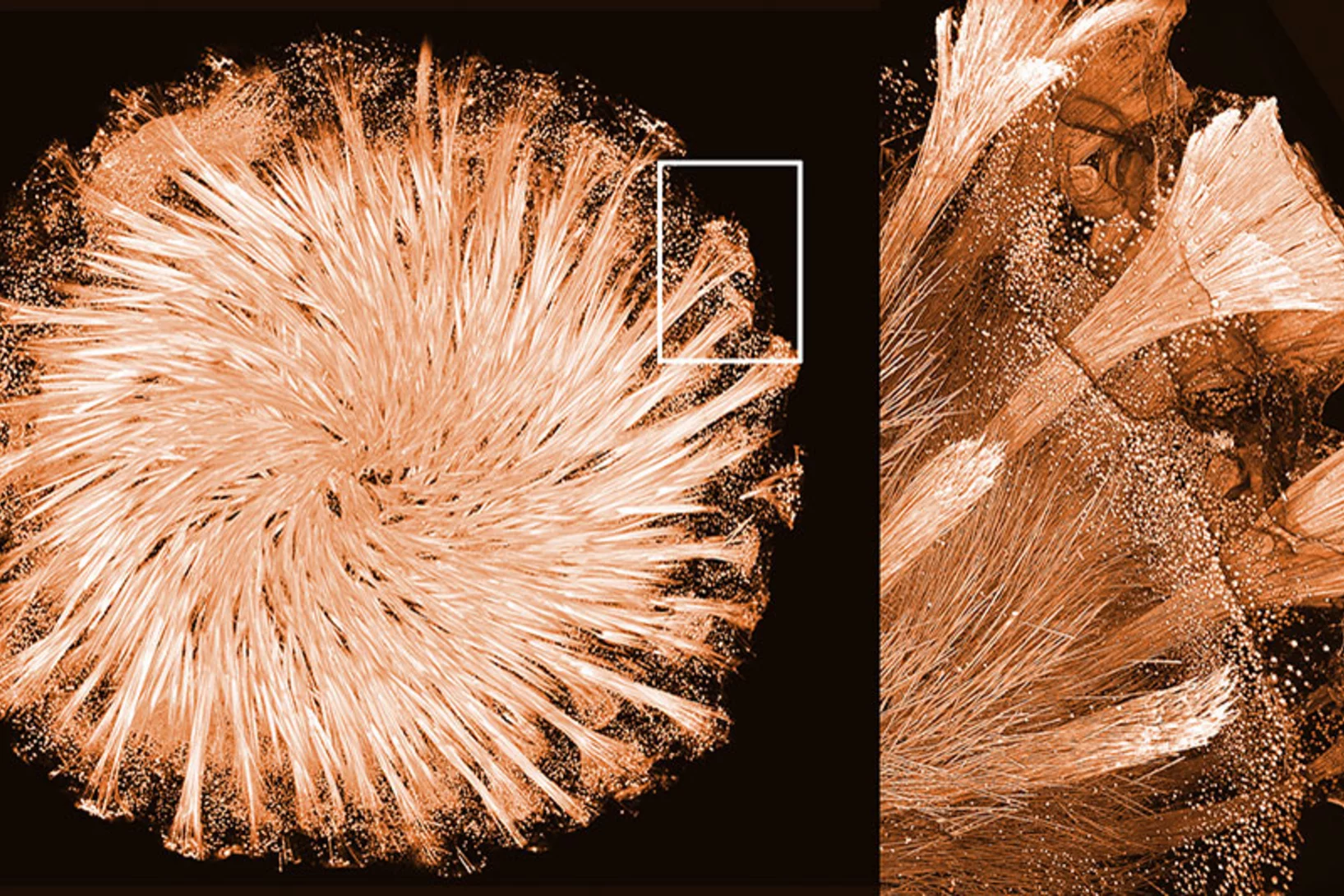
Scientists determine the structure of glass-shaping protein in sponges
Measurements at the Swiss Light Source SLS have helped to understand how the only known natural protein-mineral crystal is formed. It is part of the fascinating glass skeleton of sponges.
Ruzicka Prize
The Ružička Prize 2020 goes to Dr. Patrick Hemberger (PSI) for his research on understanding the mechanisms of catalytic fast pyrolysis by unveiling reactive intermediates in heterogeneous catalysts.
BEATS beamline scientist from SESAME synchrotron trains at TOMCAT
TOMCAT welcomes Gianluca Iori, beamline scientist from BEATS - the new beamline for tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan, to a 3-month training on beamline operations. Gianluca’s visit is part of the Staff Training (BEATS Work Package 2) organized for BEATS scientific staff and SESAME control engineers. BEATS is a European project, funded under the EU’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and coordinated by the ESRF.
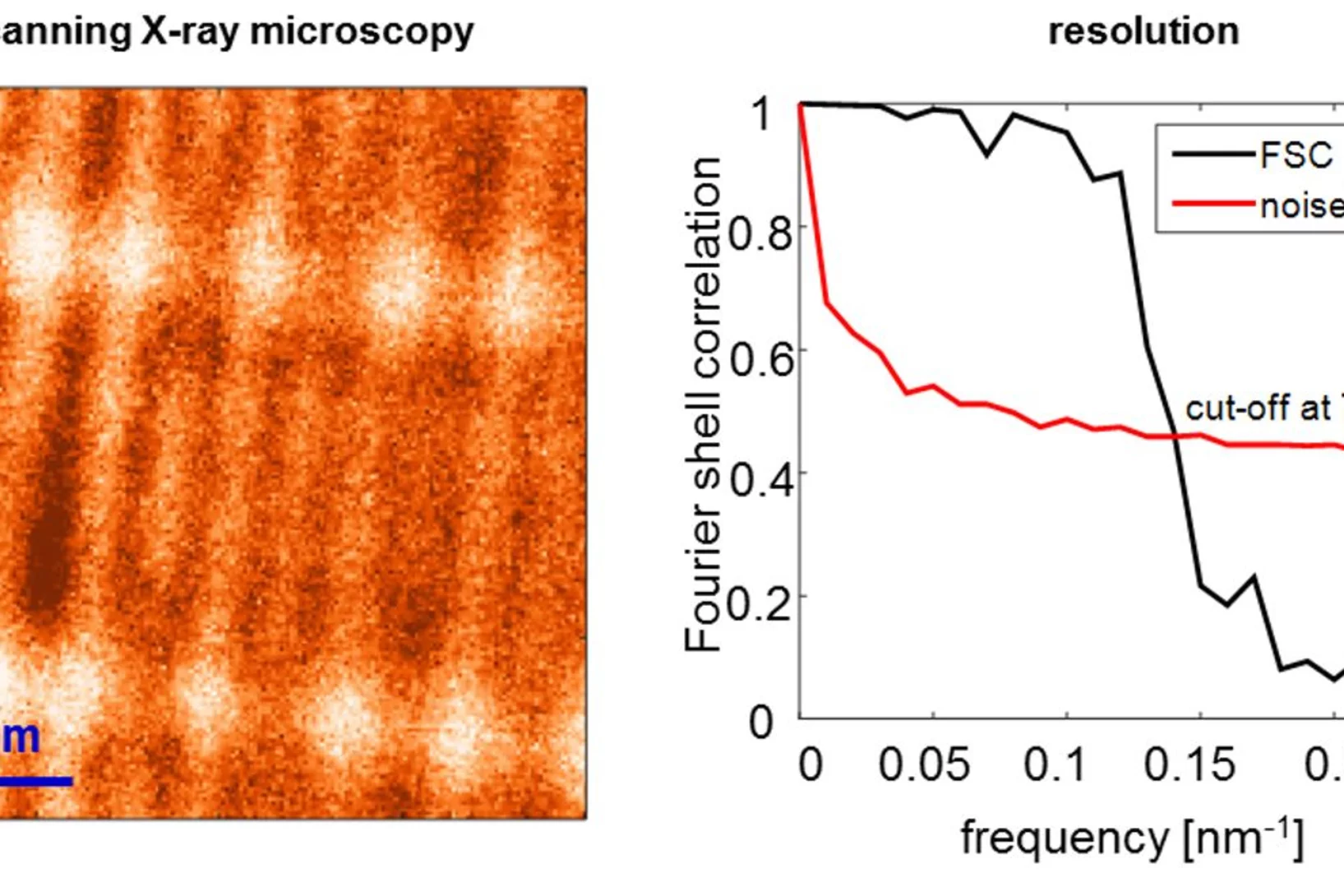
World Record: 7 nm Resolution in Scanning Soft X-ray Microscopy
During the past decade, scientists have put high effort to achieve sub-10 nm resolution in X-ray microscopy. Recent developments in high-resolution lithography-based diffractive optics, combined with the extreme stability and precision of the PolLux and HERMES scanning X-ray microscopes, resulted now in a so far unreached resolution of seven nanometers in scanning soft X-ray microscopy. Utilizing this highly precise microscopy technique with the X-ray magnetic circular dichroism effect, dimensionality effects in an ensemble of interacting magnetic nanoparticles can be revealed.
BEATS Project
Mirjam van Daalen, chair of the BEATS Steering Committee
COVID-19 - travel assistance websites launched
The Bio Nano spinout of Prof. Aeppli has launched new travel assistance websites that provide continually updated information on restrictions such as multi-day quarantines imposed on travel between countries, together with the latest pandemic predictions so that travellers can make informed decisions.
SwissFEL: a perfect habitat for the black mortar bee
For the construction of the SwissFEL facility in 2013, around five hectares of forest were cleared and transformed into a new habitat for flora and fauna. Biologists and forest engineers have now assessed the results of the renaturization project and are excited about the progress to date.
Wait and see, and grow crystals
At PSI, researchers decipher the structure of the proteins in bacteria and viruses. This knowledge can aid, for example, in the development of drugs against infectious diseases. But before the investigation can begin, an extremely tricky problem has to be solved: the crystallisation of the molecules.
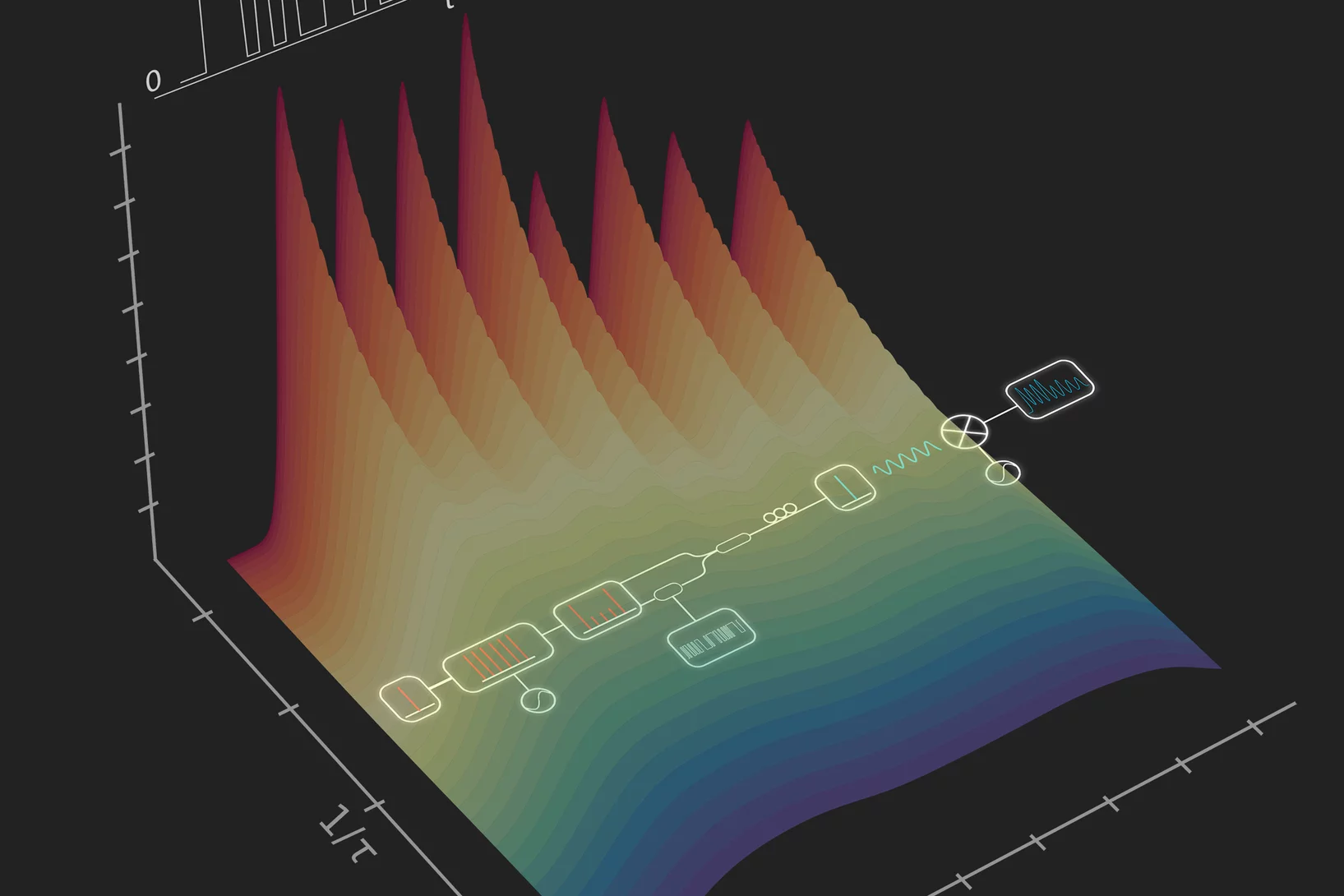
Harnessing components from the optical internet for programmable spectroscopy
A novel concept for extracting information from spectra where traditional post-processing procedures fail, dubbed ‘software-defined spectroscopy’, offers a fresh approach to high-resolution terahertz spectroscopy. The new method implements an ‘optical comb’ and combines it with a programmable modulator, all using components from the optical internet.
Measurements at PSI enabled detailed understanding of genetic scissors
PSI congratulates Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna on winning this year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Experiments at the Swiss Light Source SLS in 2013 made it possible to elucidate the structure of the protein complex CRISPR-Cas9.
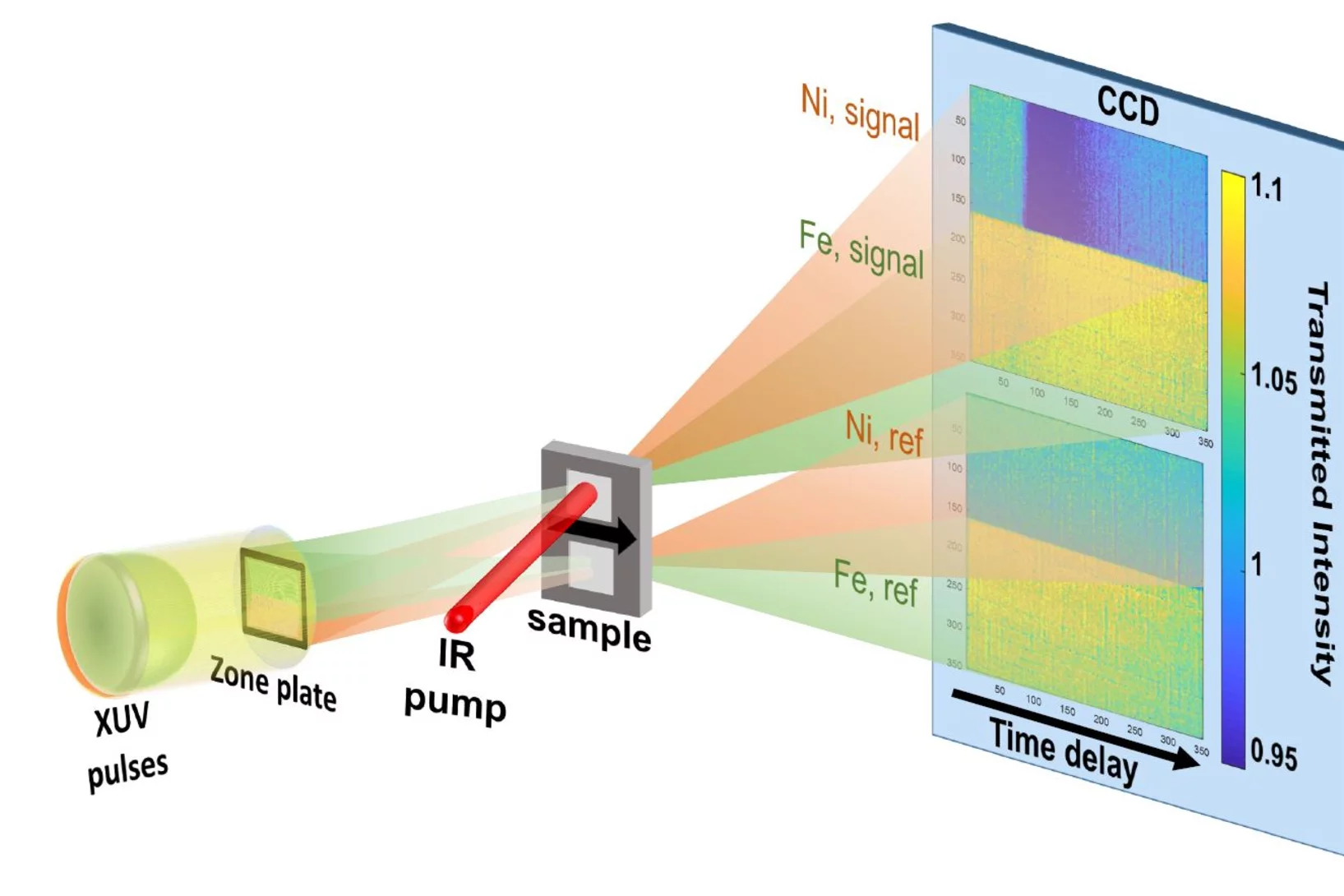
Two-color snapshots of ultrafast charge and spin dynamics
In a joint research effort, an international team of scientists lead by Emmanuelle Jal (Sorbonne Université) performed a time-resolved experiment at the FERMI free-electron laser to disclose the dynamic behavior of two magnetic element of a compount material in only one snapshot. The X-ray Optics and Applications group developed a dedicated optical element for this experiment that is usable with two different photon energies (colors) simultaneously.
PSI - member of the Microsoft Quantum Network
The PSD is a research partner in the Microsoft Quantum Network, which is a broad community of individuals and organizations collaborating with Microsoft to advance a comprehensive quantum ecosystem, develop practical solutions, and build a robust quantum workforce.
The institutions of scientific excellence are partnering collaboratively with Microsoft to pursue the advancement of quantum computing research, development, and education. The large scale facilities at PSI, in particular the Swiss Light Source, offers unique characterizations techniques to shed light on the secrets of functional materials.
First light in the SwissFEL Maloja endstation
The first endstation at the SwissFEL Athos soft X-ray branch is rapidly developing and on track for first experiments in 2021.
Customising an electronic material
PSI scientists have investigated a material that could be suitable for future data storage applications. They have manipulated the crystalline structure of their sample while measuring how this affects the material’s magnetic and electronic properties.
Analytical Research Infrastructures of Europe (ARIE) join forces to face COVID-19 and other viral and microbial threats
After the joint position paper published as a pre-release in July, in which the Analytical Research Infrastructures of Europe (ARIE) presented their plan to tackle HE Missions, the ARIE enhanced its cross-border, multidisciplinary collaboration to offer Europe a strong and valid weapon against the present COVID-19 challenge and other potential viral and microbial threats.
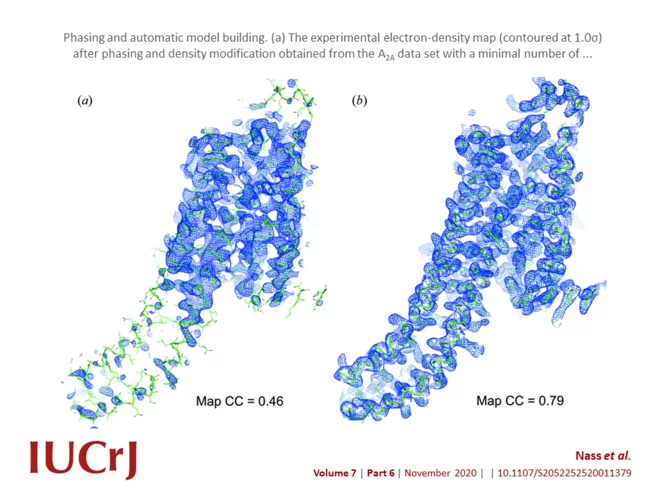
Advances in long-wavelength native phasing at X-ray free-electron lasers
Long-wavelength pulses from the Swiss X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) have been used for de novo protein structure determination by native single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (native-SAD) phasing of serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) data.
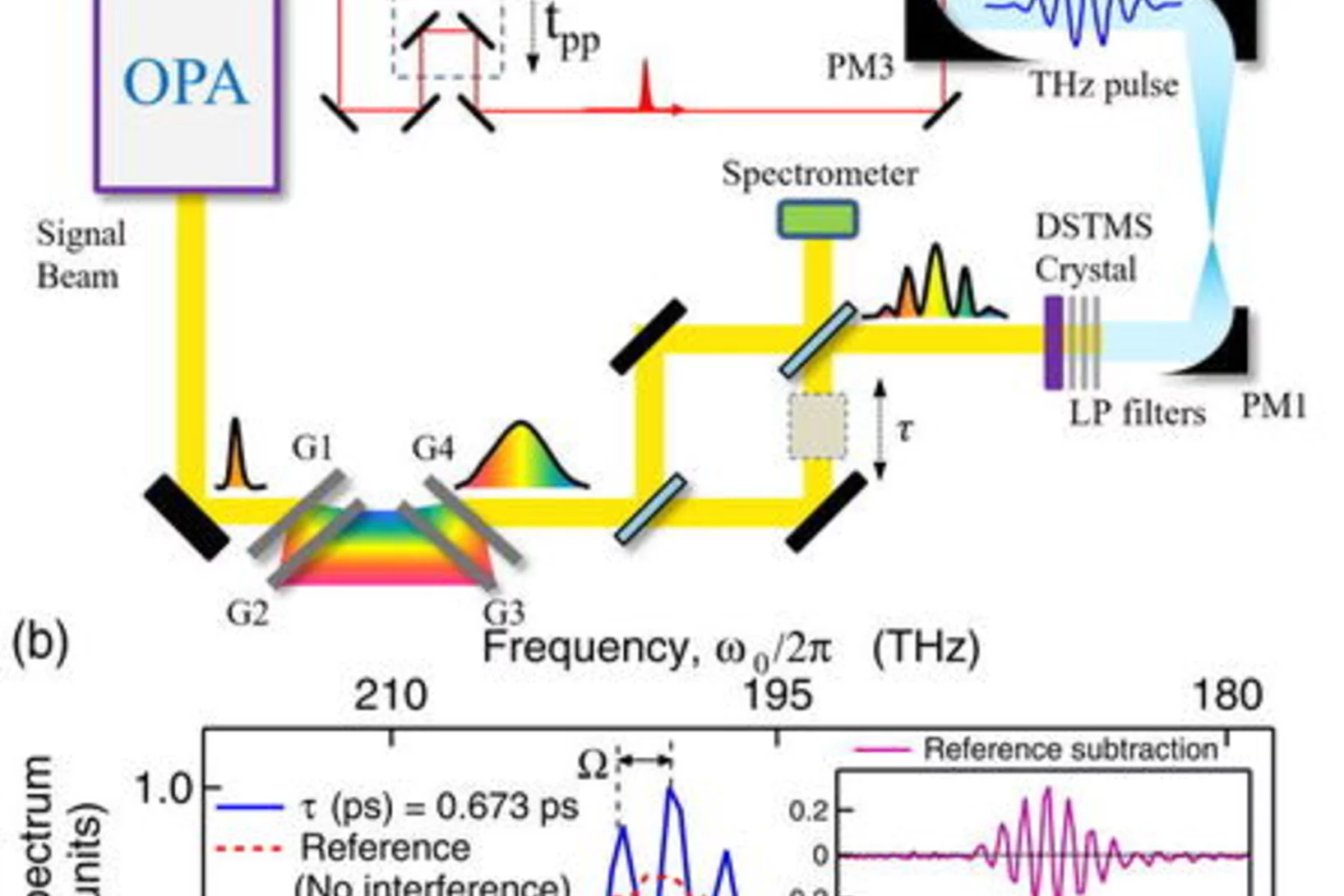
Narrow-band and tunable intense terahertz pulses for mode-selective coherent phonon excitation
We generate frequency-tunable narrow-band intense fields in the terahertz (THz) range by optical rectification of a temporally modulated near-infrared laser pumping a nonlinear organic crystal.
«Forschung online erleben»: Mittendrin statt nur dabei
Erstmals Live-Rundgang durch eine Grossforschungsanlage per Video-Stream. Am 9. September haben Interessierte exklusiv die Möglichkeit, sich von Experten des PSI durch den neuen Freie-Elektronen-Röntgenlaser SwissFEL führen zu lassen und zu erfahren, welche Rätsel der Materie und der Natur sich damit lösen lassen.
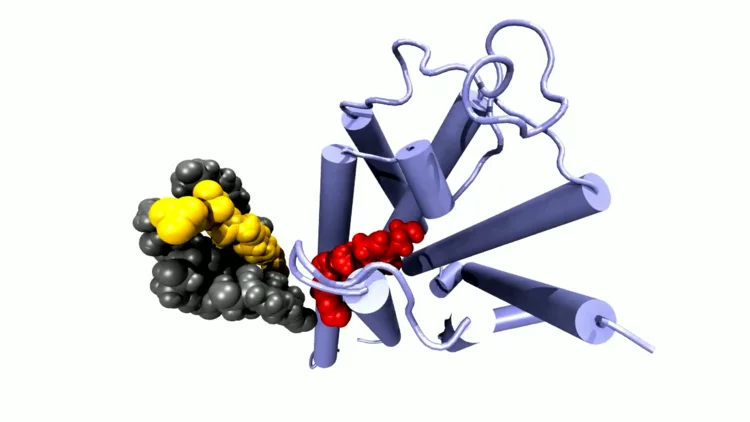
A question of binding
At PSI, researchers are screening molecule fragments to see if these bind to important proteins of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and thus have the potential to disable it. They are hoping the many individual pieces of information will yield an answer as to what an effective drug might look like.
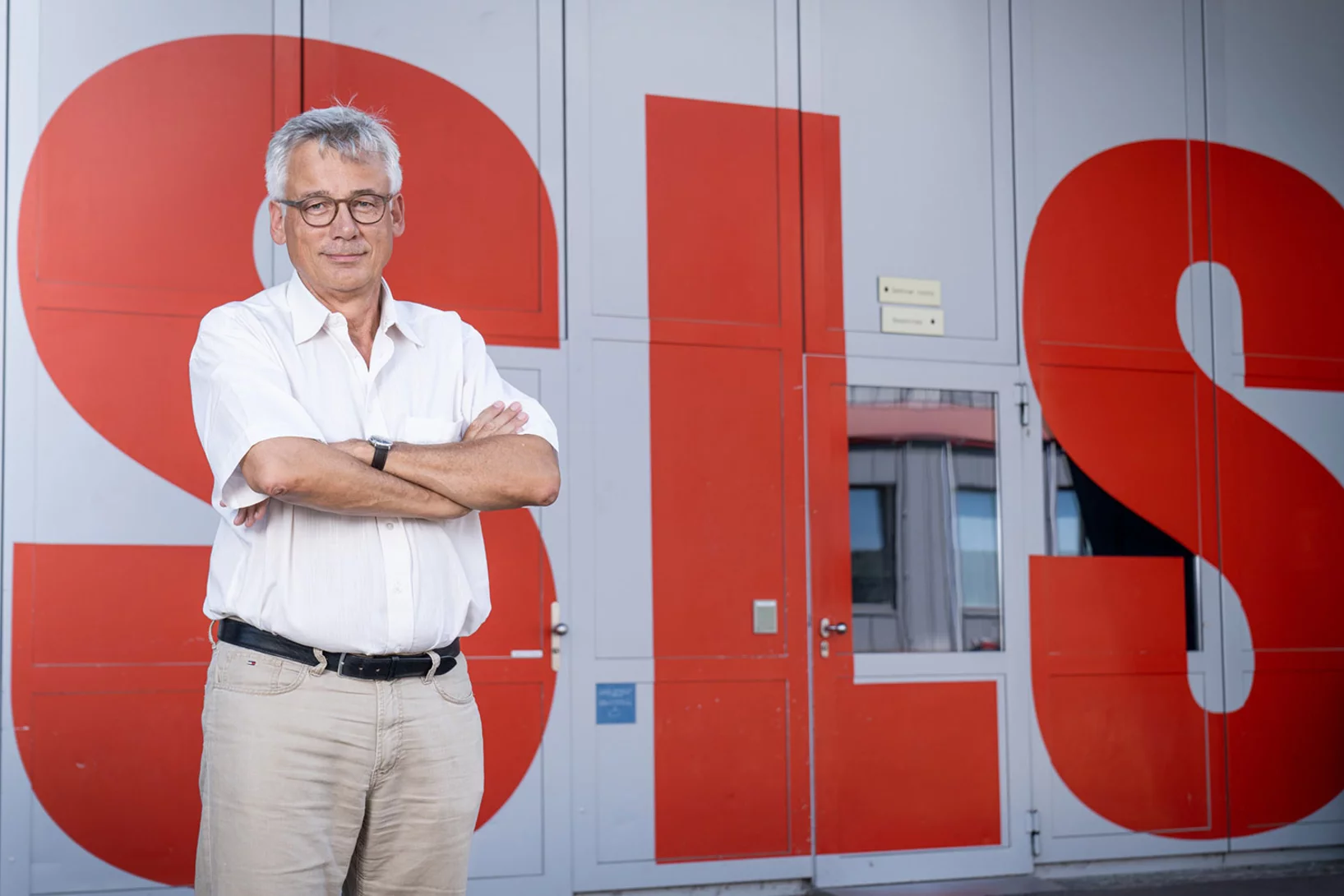
«We're making SLS fit for the future»
The Swiss Light Source SLS is set to get an upgrade to make excellent research possible in the coming decades as well. Hans Braun, SLS 2.0 project leader, talks about this undertaking in an interview.