Show filters
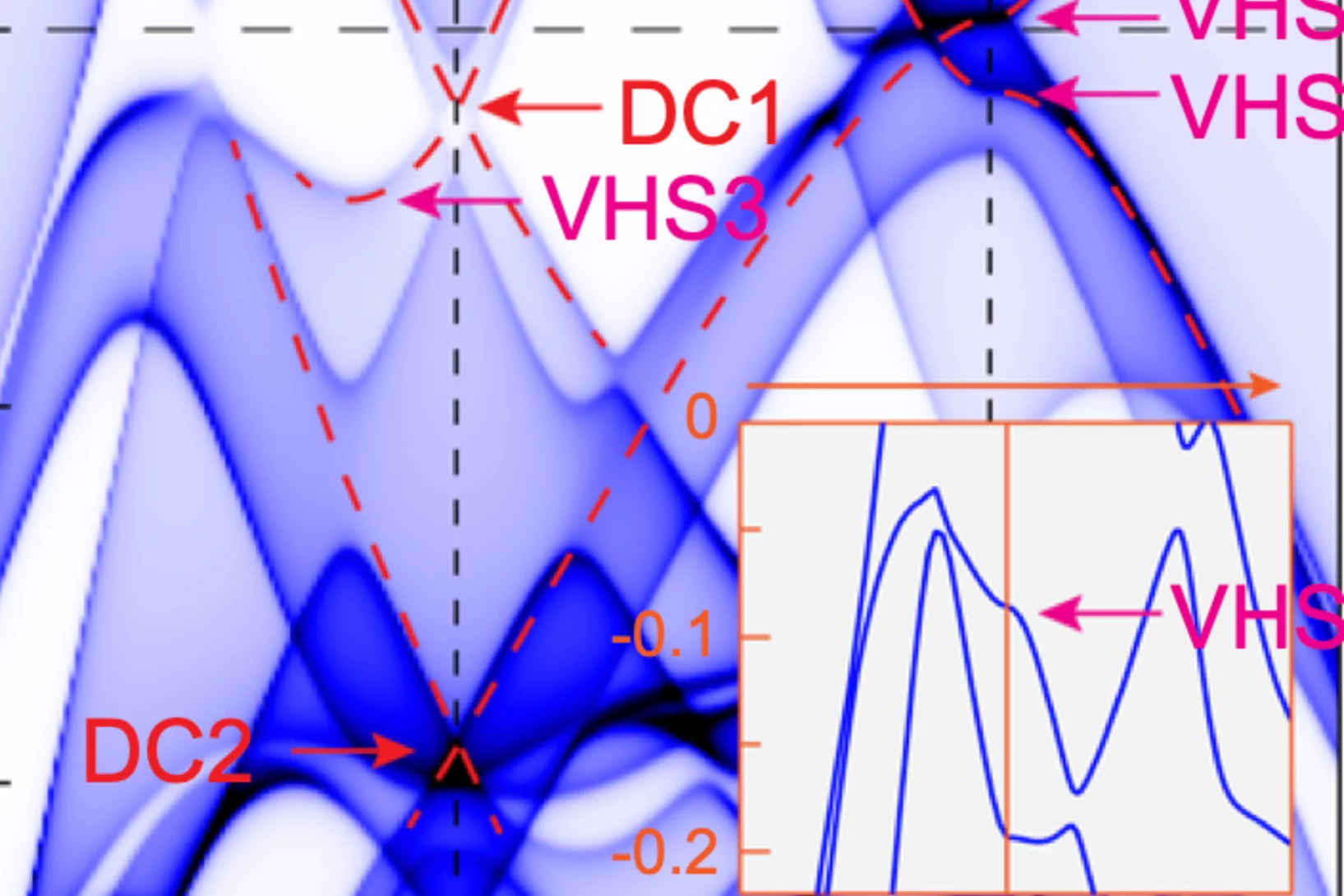
Phonon promoted charge density wave in topological kagome metal ScV6Sn6
Charge density wave (CDW) orders in vanadium-based kagome metals have recently received tremendous attention, yet their origin remains a topic of debate. The discovery of ScV6Sn6, a bilayer kagome metal featuring an intriguing √3 × √3 × √3 CDW order, offers a novel platform to explore the underlying mechanism behind the unconventional CDW. Here we combine ...
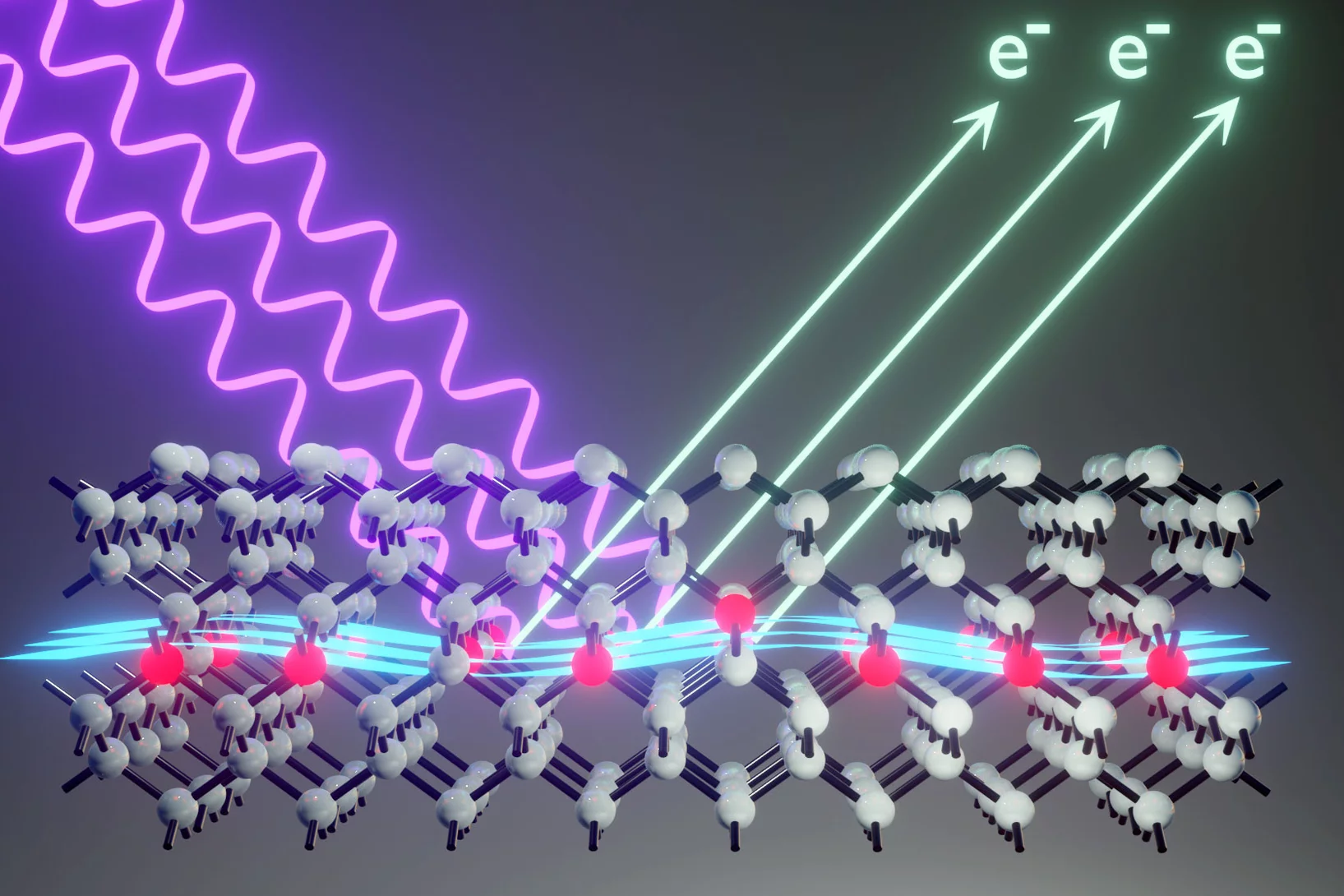
Extreme ultraviolet for scalable silicon quantum devices
Experiments at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) show the potential of extreme ultraviolet light (EUV) to make the building blocks of scalable quantum computers.
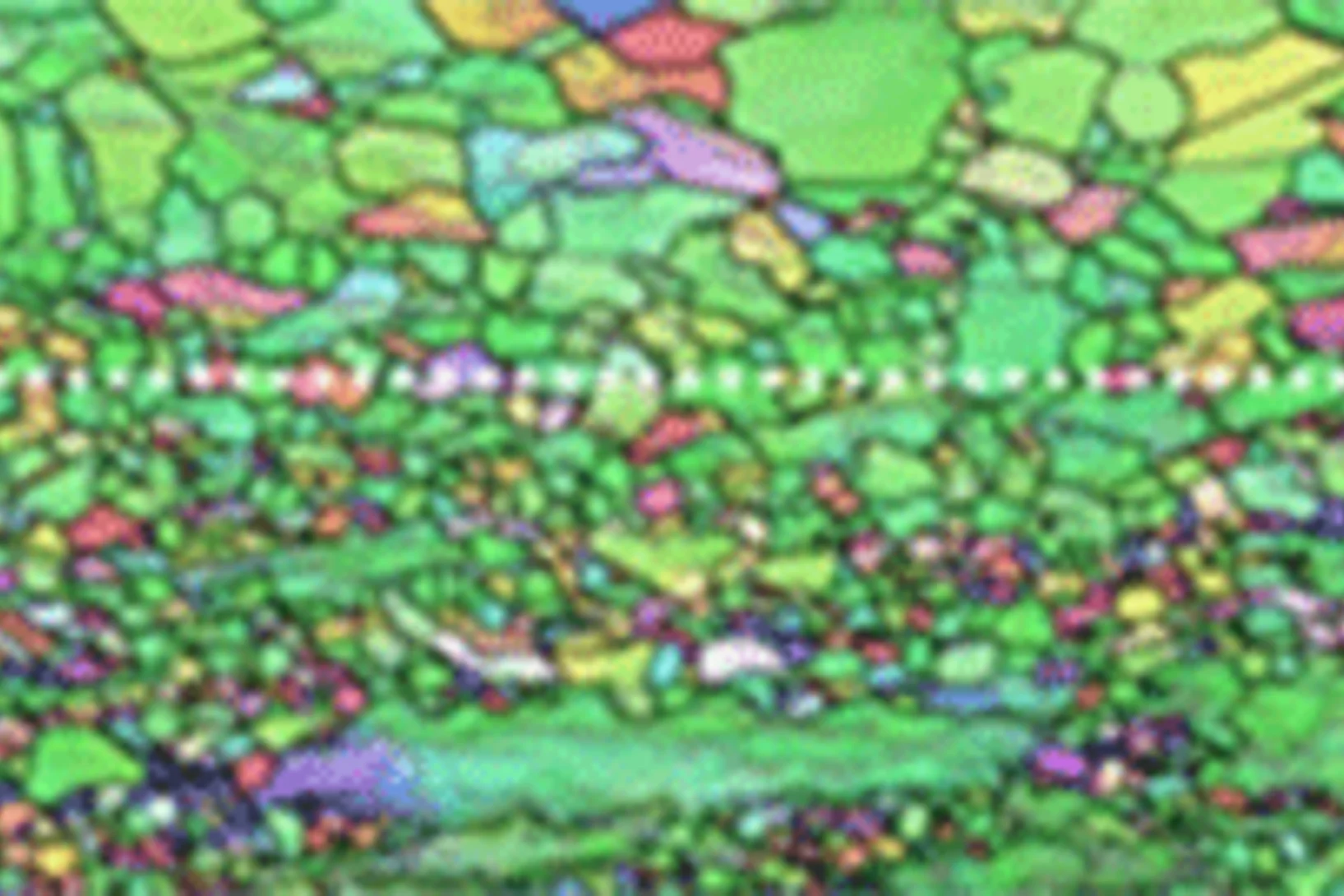
Observing laser-induced recrystallization
Synchrotron X-ray diffraction sheds light on laser-induced local recrystallization .
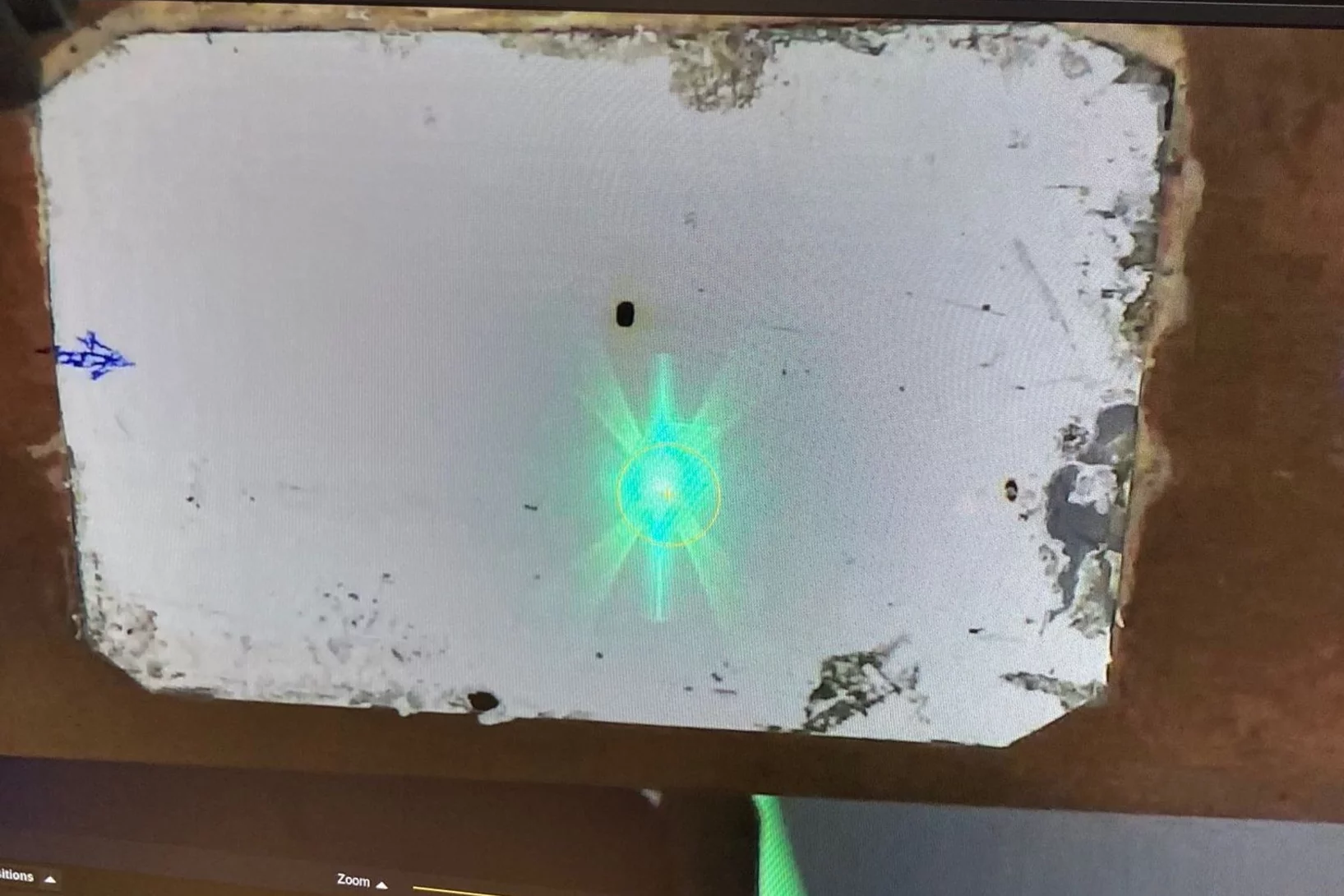
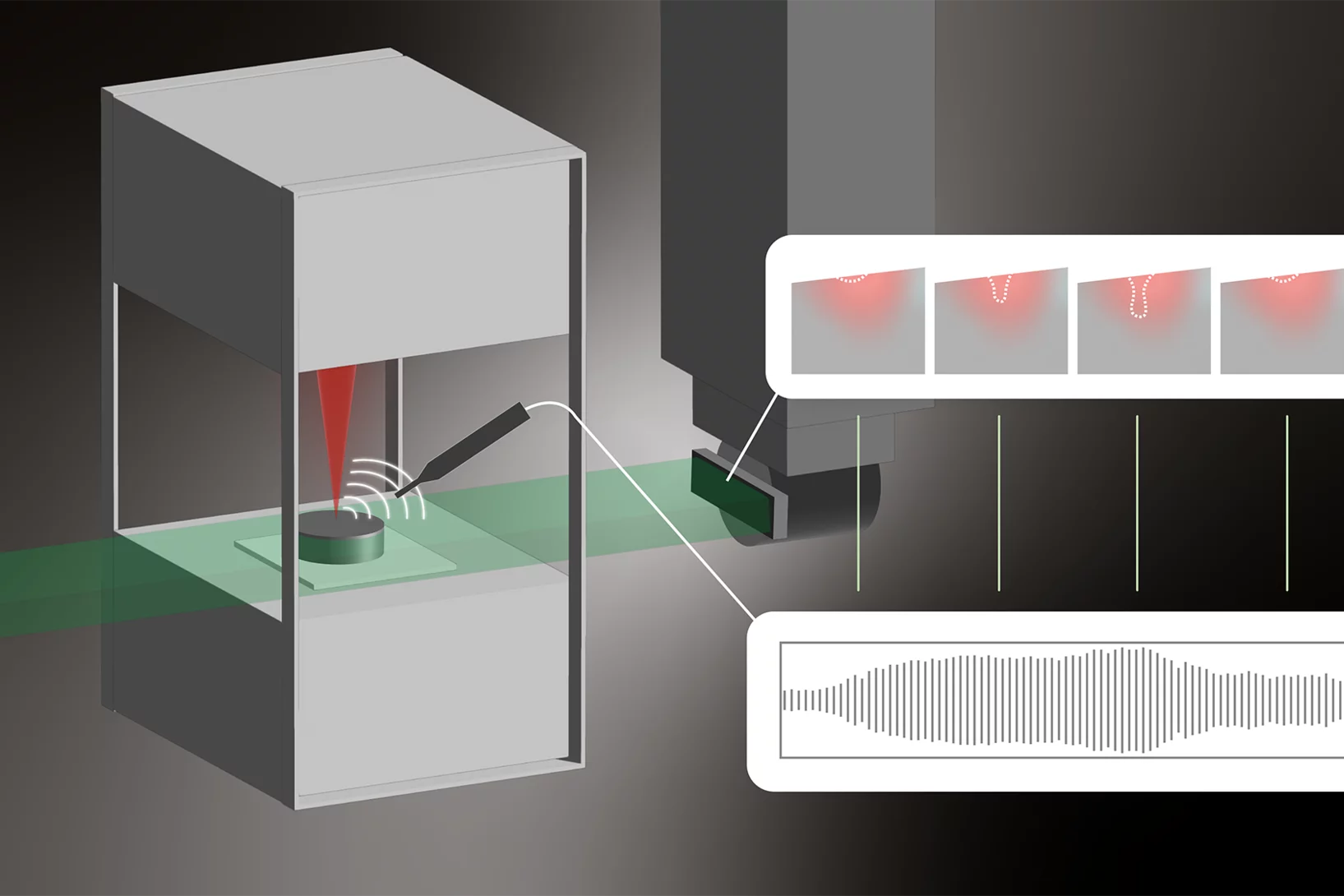
Listening for Defects as They Happen
Experiments at the Swiss Light Source SLS help resolve a long-standing debate surrounding metal 3D laser printing.
Smart glass and music from SLS
Every year the PSI Founder Fellowship Programme supports new ideas for innovative applications with up to 150,000 Swiss francs.
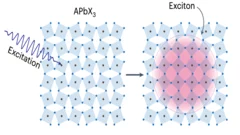
Excitons coupling to octahedral tilts in Pb nano-perovskites
Excitons coupling to octahedral tilts in Pb nano-perovskites
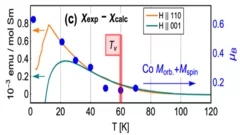
Crystal field rules heavy fermion delocalization in SmCoIn5
Crystal field rules heavy fermion delocalization
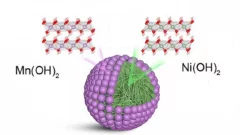
"Core-shell" cathodes for high performance Li-ion batteries
“Li-rich Ni-rich” core-shell particles are engineered as layered cathode materials for high energy Li-Ion batteries, including a controllable outer "Li-rich Mn-rich" shell improving cyclability.
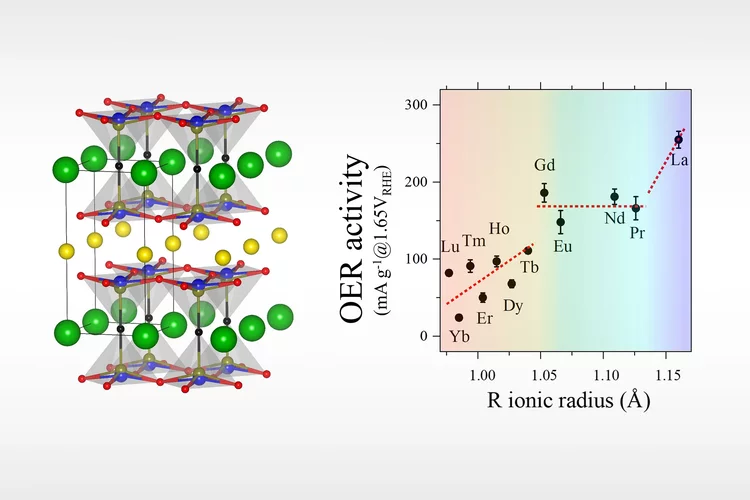
Cobalt-free layered perovskites RBaCuFeO5+d (R = 4f lanthanide) as electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
Co oxides with perovskite-related structure are particularly promising, cost-effective OER catalysts. However, the increasing Co demand by the battery industry is pushing the search for Co-free alternatives. Here we investigate the potential of the Co-free layered perovskite family RBaCuFeO5+δ (R = 4f lanthanide), where we identify the critical structural and electronic variables leading to high OER catalytical performance. The employed methodology, based in the use of advanced neutron and X-ray synchrotron techniques combined with ab initio DFT calculations allowed to reveal LaBaCuFeO5+δ as new, promising Co-free electroctalyst. Moreover, we could show that this material can be industrially produced in nanocrystalline form. We believe that the reported results and methodology may contribute to the implementation of new technologies aimed to generate energy with lower carbon emissions, and can also inspire the scientific community in their search of other Co-free materials with good OER electrocatalytical properties.
Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
Using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology, we devise special processing strategies to ‘program’ the thermal stability of the as-printed alloy, such that it is possible to decide, a priori, how the material’s microstructure will evolve upon heat treatment
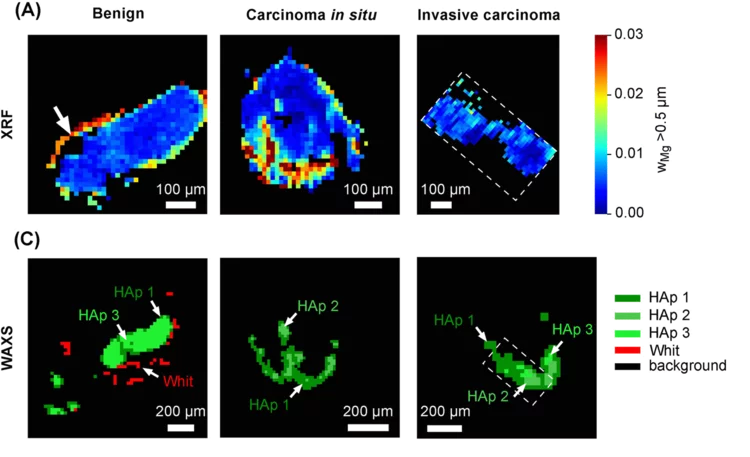
Whitlockite in mammary microcalcifications is not associated with breast cancer
Microcalcifications, small deposits of calcium-containing minerals that form in breast tissue, are often, but not always, a warning sign of breast cancer. The relationship between microcalcifications and cancer has not been fully understood thus far. Researchers discovered now that the relationship between microcalcifications and tumors seems to be linked to the presence of a particular mineral called whitlockite, which is rich in magnesium and is found in microcalcifications only in the absence of tumors.
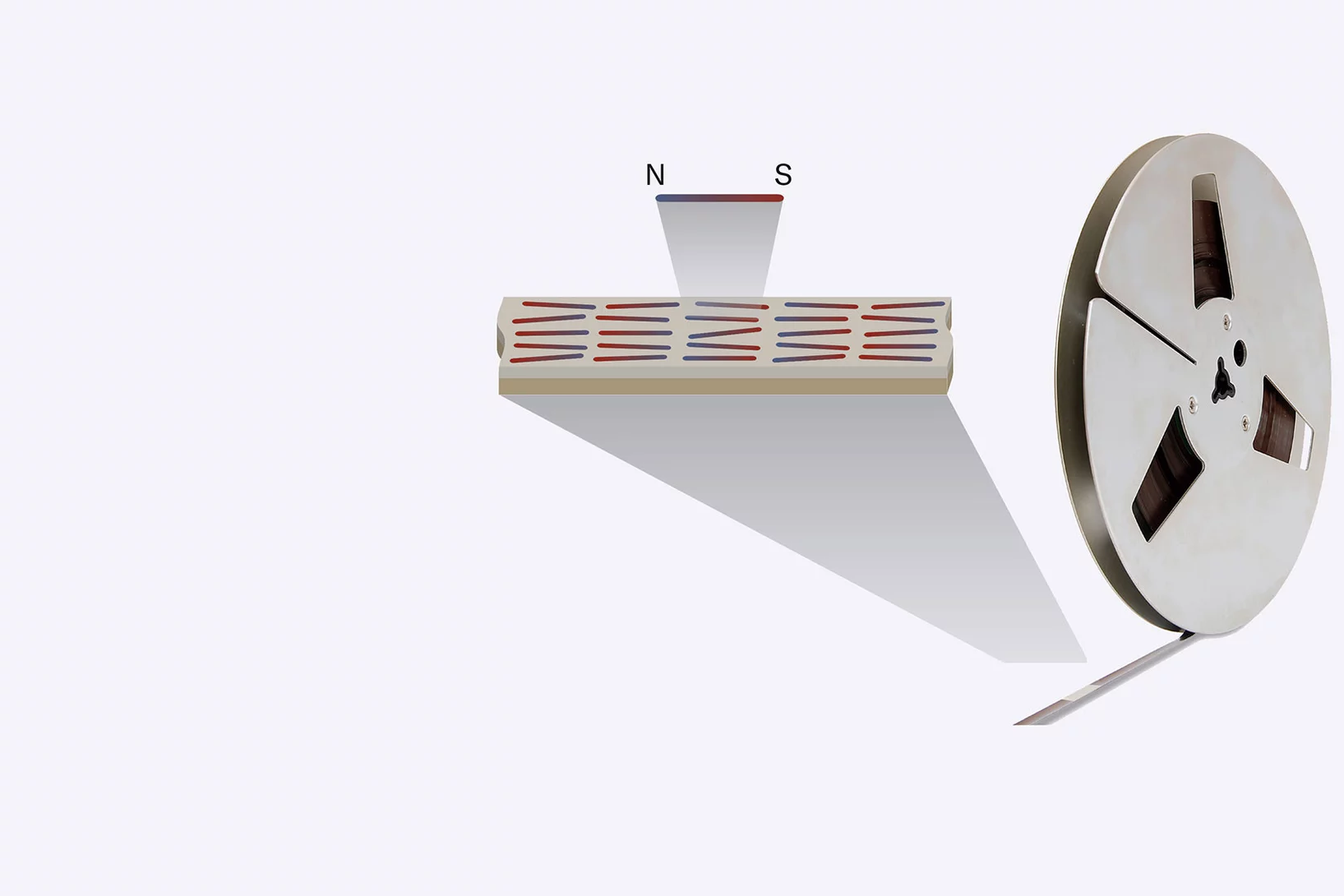
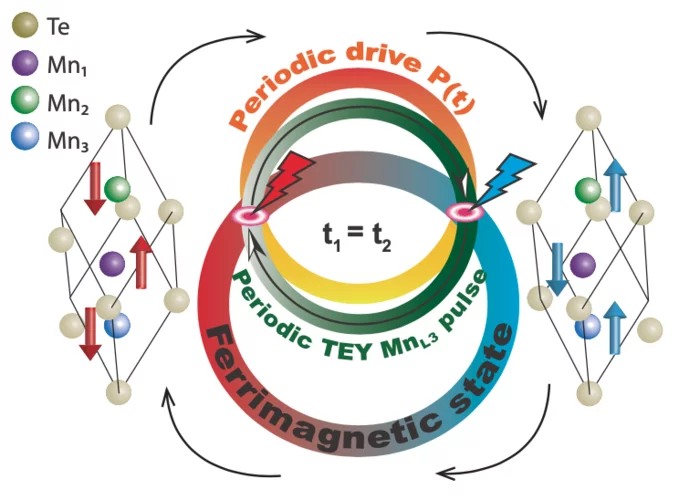
Efficient magnetic switching in a correlated spin glass
The interplay between spin-orbit interaction and magnetic order is one of the most active research fields in condensed matter physics and drives the search for materials with novel, and tunable, magnetic and spin properties. Here we report on a variety of unique and unexpected observations in thin multiferroic Ge1−xMnxTe films.
SLS 2.0: “Dark time” during the upgrade
The SLS is shutting down temporarily as it undergoes a major upgrade.
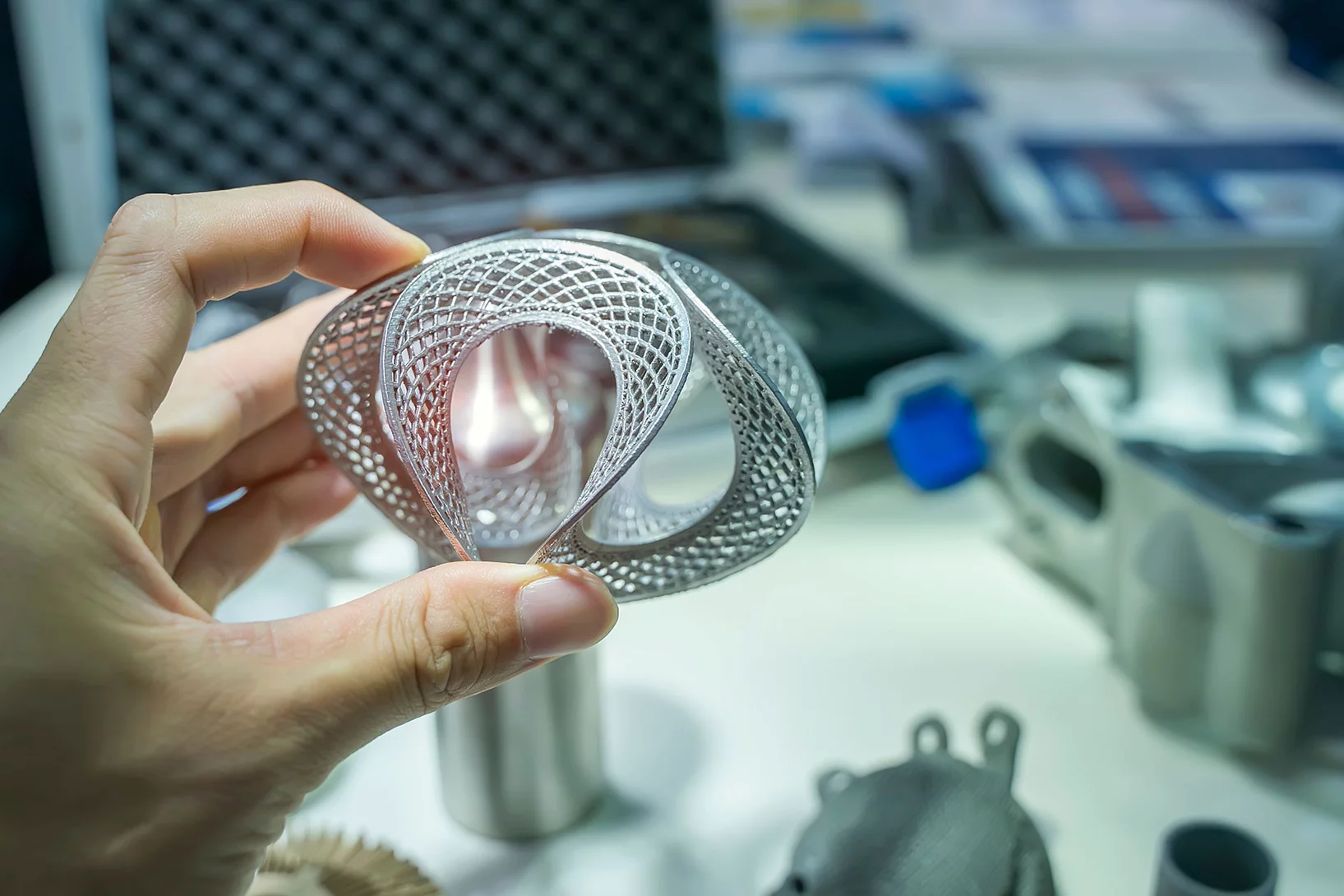
3D insights into an innovative manufacturing process
3D printing for creating complex shapes
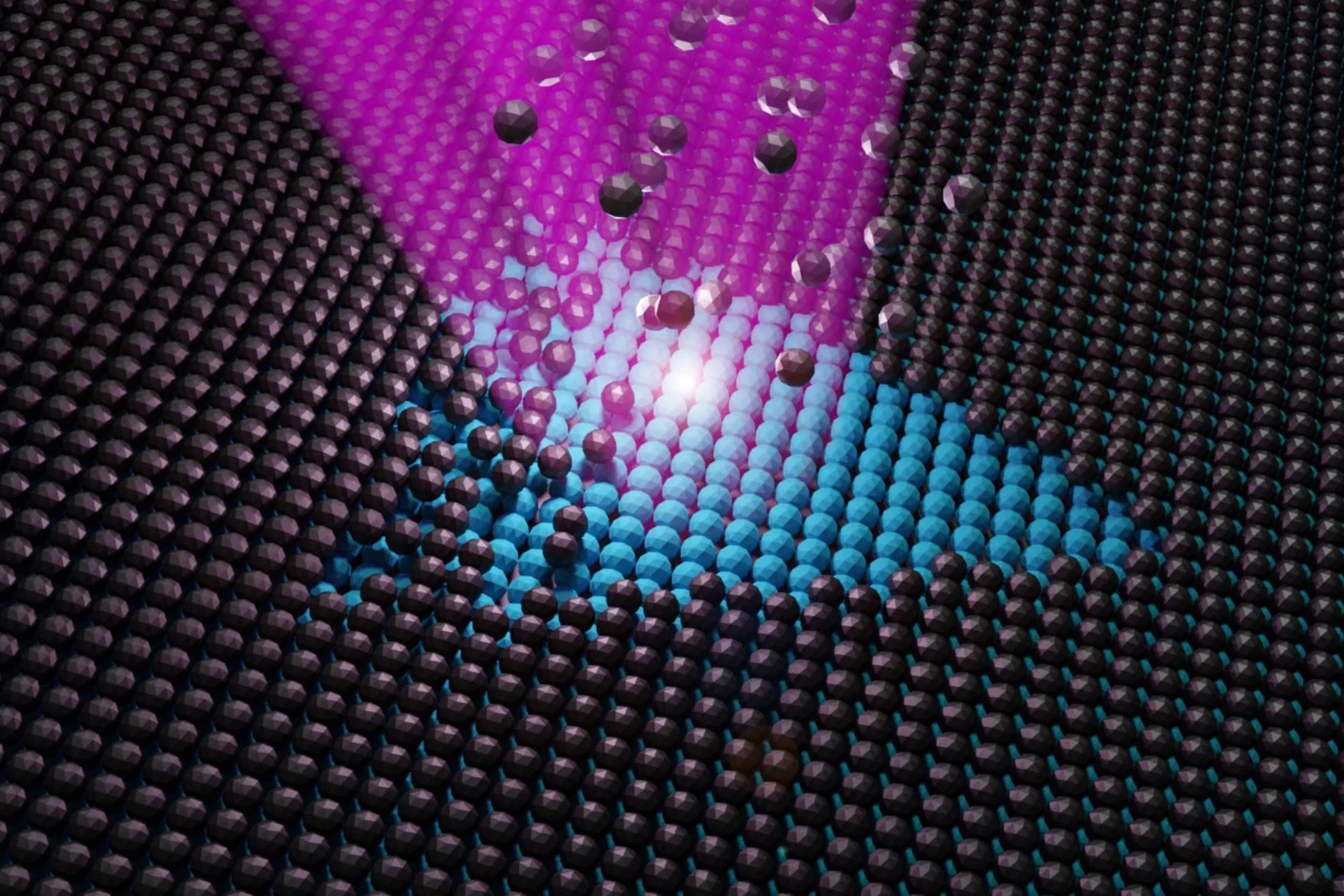
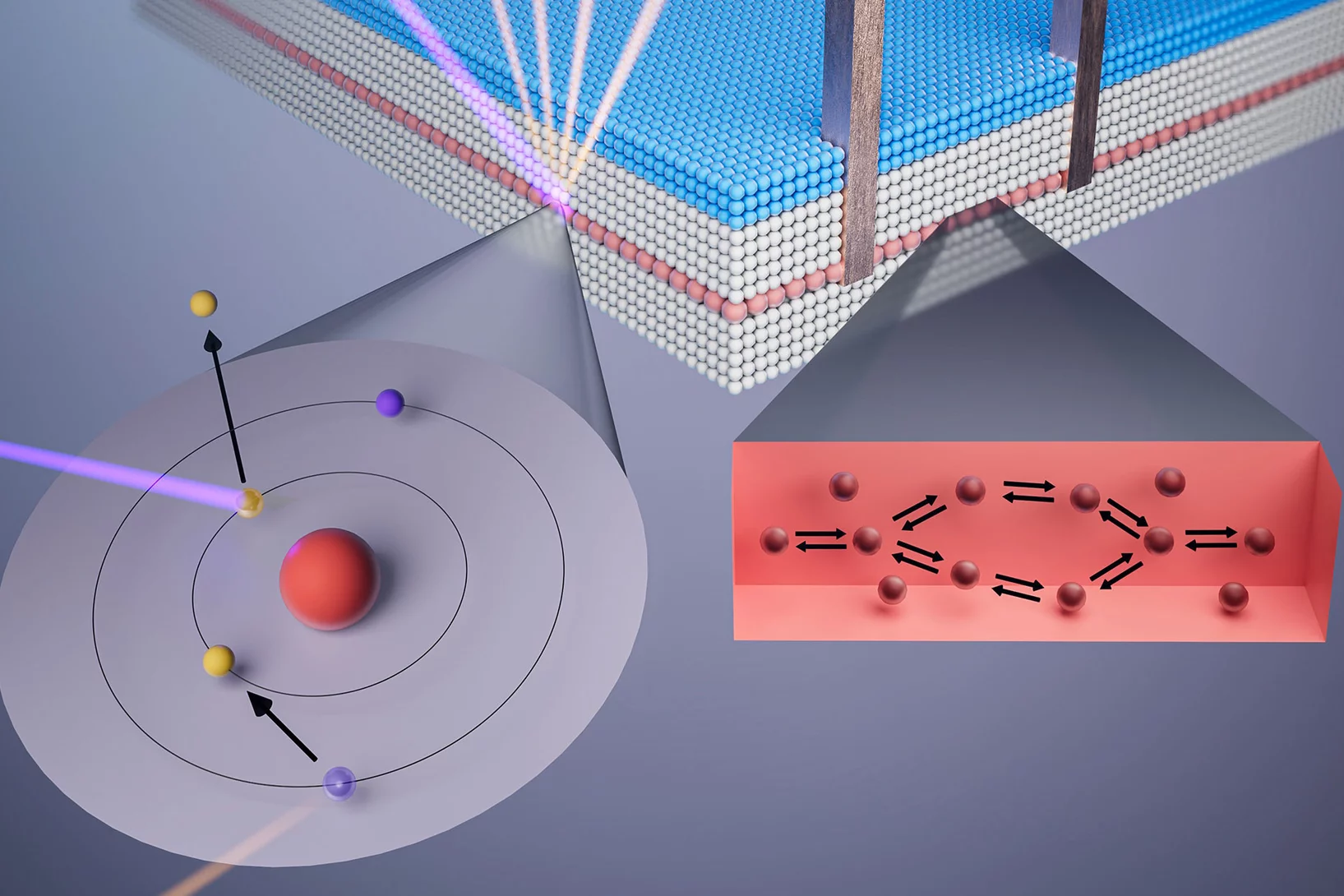
Unveiling ultra-thin electron liquids in silicon
Soft X-rays enable scientists to visualise non-invasively the electronic properties of ultra-thin dopant layers buried within semiconductor wafers.
A metal alloy like a sponge
Once the vacuum chambers for the SLS 2.0 upgrade are the right shape, they still need a special surface coating.
A six-metre high oven
The most complicated vacuum chambers for the SLS 2.0 upgrade are being built in the PSI workshop.
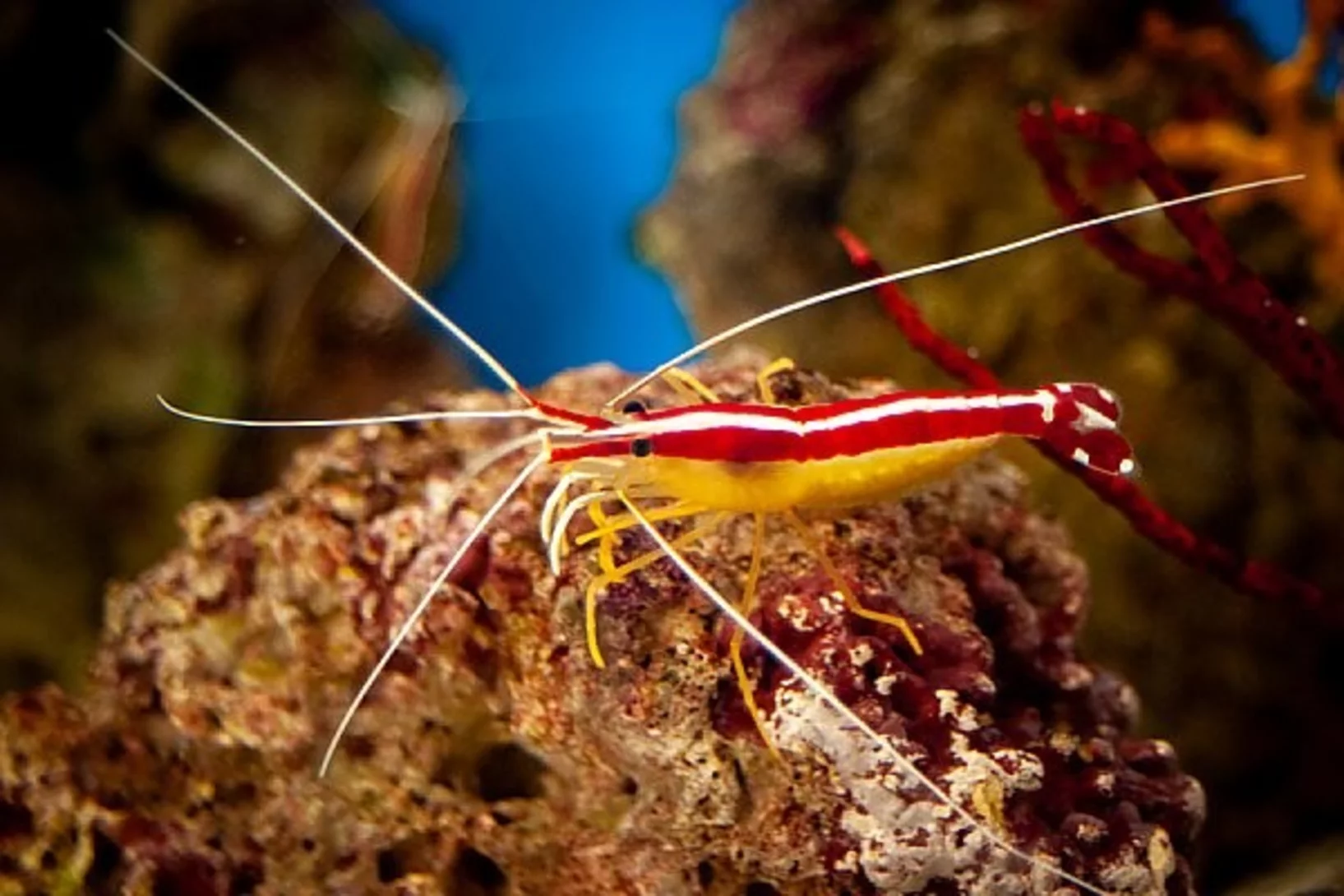
Bright white coloring of Pacific cleaner shrimp revelead
In a study published in Nature Photonics, researchers at the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel, explain the bright, white-colored stripes from Pacific cleaner shrimps, one of the most efficient white reflectors found in nature.
Progress of the X06DA-PXIII beamline upgrade: First light in the optics hutch
On June 7, 2023, the PXIII project team successfully shone the first light into the optics hutch at the upgraded X06DA-PXIII beamline. It is an essential first step for testing new hardware and software solutions that will be implemented at SLS2.0.
Tender X-rays show how one of nature’s strongest bonds breaks
Short flashes of an unusual kind of X-ray light at SwissFEL and SLS bring scientists closer to developing better catalysts to transform the greenhouse gas methane into a less harmful chemical.
500 vacuum chambers for the new ring
Making the tube through which the electrons will race after the SLS 2.0 upgrade.
PSI researchers use extreme UV light to produce tiny structures for information technology.
Synchrotron light can be used in follow-up after a heart transplant to determine whether the body may be rejecting the new organ.
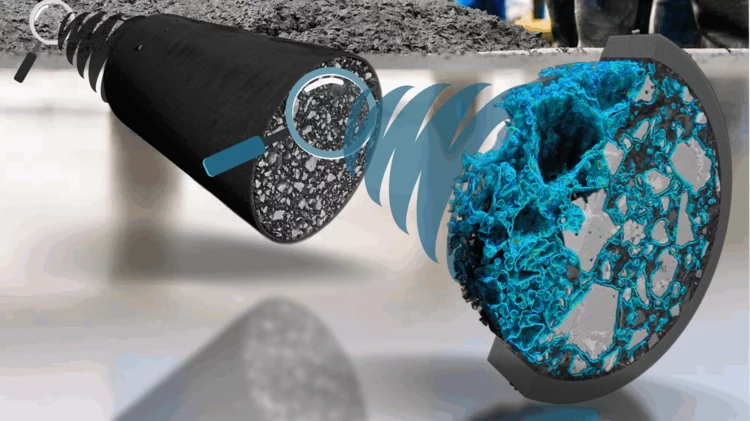
A deep look into hydration of cement
Researchers led by the University of Málaga show the Portland cement early age hydration with microscopic detail and high contrast between the components. This knowledge may contribute to more environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
Quality control of future transistors: Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
X-rays make 3D metal printing more predictable
Insights into the microscopic details of 3D printing from the Swiss Light Source SLS could propel the technology toward wider application
X-ray imaging after heart transplantations
Synchrotron light can be used in follow-up after a heart transplant to determine whether the body may be rejecting the new organ.
The Hercules School visits PSI
20 international students visited PSI as part of the renowned Hercules School to learn about our state-of-the-art techniques and methodologies at our large scale facilities.
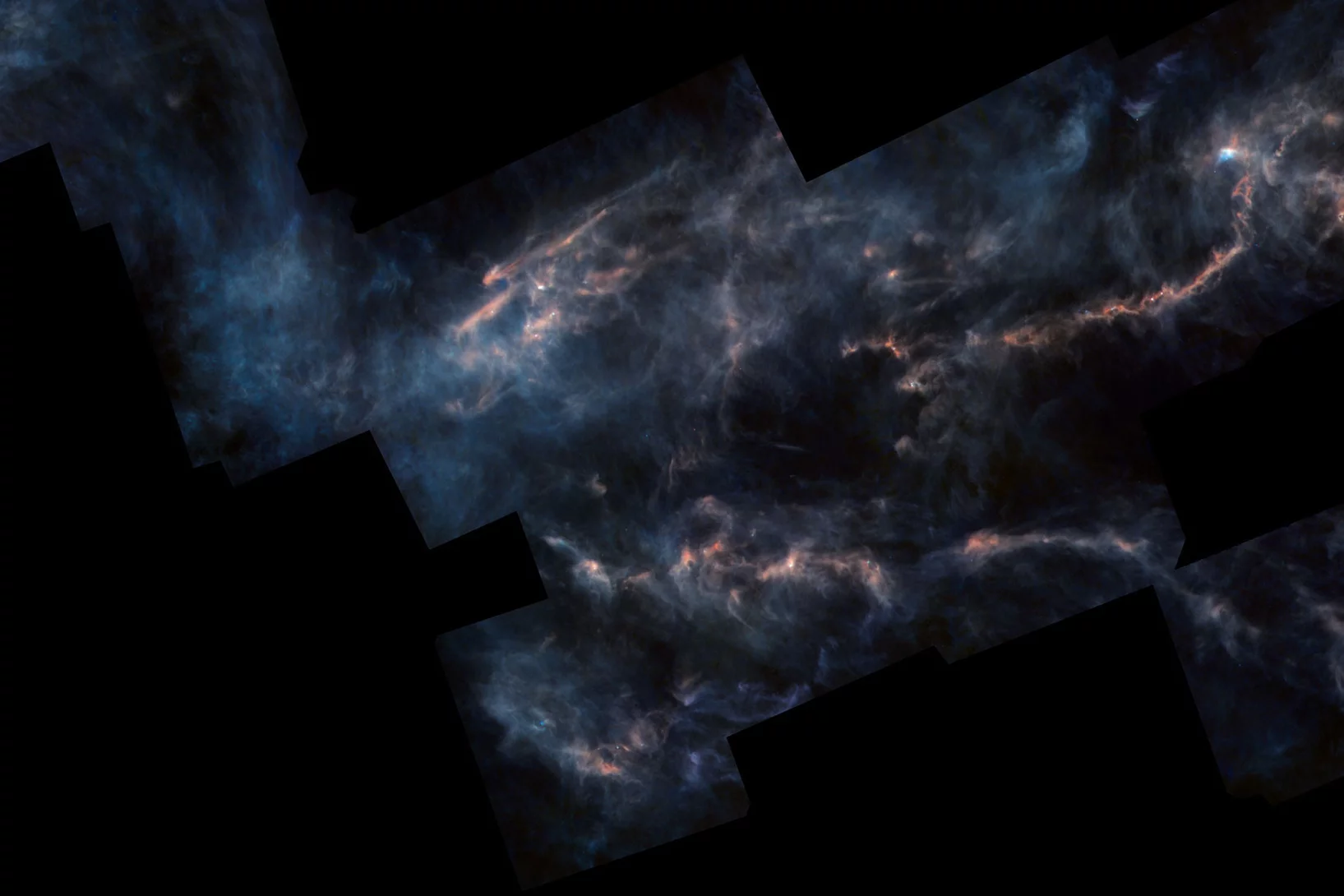
How football-shaped molecules occur in the universe
An international research team reveals how fullerene is formed in the universe.
A star is born
Swiss Light Source SLS reveals complex chemistry inside ‘stellar nurseries’
High-tech company VDL ETG: PSI’s new neighbour
The Dutch company VDL ETG has signed a rental agreement with Park Innovaare.
PSI Scientific Reports
Archive 2006-2012. The Scientific Reports – containing accounts of research topics from all the different areas – provide an impression of the variety of subjects researched at PSI.