Background
High uncertainties in future climate predictions arise from insufficient knowledge of the interaction of clouds with visible (solar) and infrared (terrestrial) radiation. The optical properties and lifetime of clouds are strongly influenced by the ability of atmospheric aerosol particles to act as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) or ice nuclei (IN). This so-called indirect aerosol effect has been recognized as one of the greatest source of uncertainty in assessing human impact on climate.
Up to now, the climate relevant properties of clouds and their formation processes are still poorly understood, particularly those of mixed-phase clouds where supercooled cloud droplets and ice crystals coexist. Previous research has found that the cloud radiative properties strongly depend on the cloud ice mass fraction, which is influenced by the abundance of IN. Increased IN concentrations are also thought to enhance precipitation, thus causing a decrease in cloud lifetime and cloud cover, resulting in a warming of the atmosphere.
Scope of project
Burning questions that we will address in this project are:
- Which aerosol particles act as IN in our atmosphere ?
- By which detailed mechanisms do atmospheric aerosols contribute to the formation of ice ?
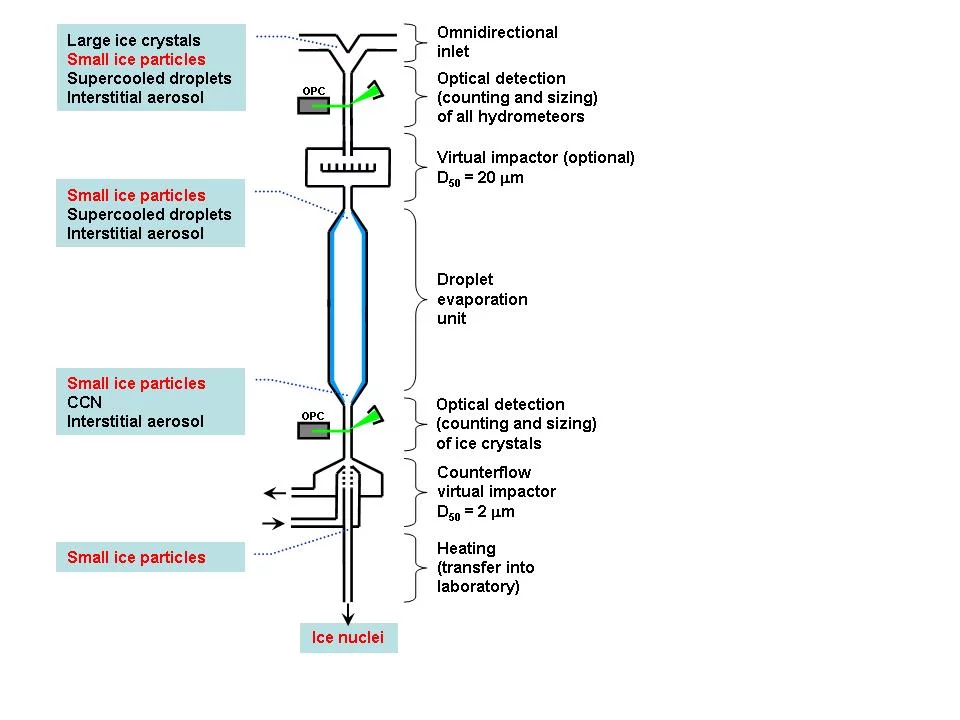
Field campaigns
A prototype inlet is currently being developed at PSI and it will be tested in Summer 2012 at the AIDA cloud chamber facility of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT).
In a next step, measurements will be performed in Winter 2012/2013 at the Jungfraujoch, located at 3580 m altitude in the middle of Switzerland. This unique location offers the possibility to perform these studies in mixed-phase clouds that are representative for the current European background.
Funding
This project is funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation and the German Research Foundation. Partners at the Institute for Meteorology and Climate Research at KIT will employ novel instrumentation for in-situ investigations of the size and shape of single ice crystals and their angular light scattering properties. More information of this project part is found here.