Show filters
Zinc detected in clogged syringes
With the help of researchers at PSI, ANAXAM has been investigating, on behalf of the pharmaceutical company MSD, whether zinc may contribute to clogging of pre-filled syringes.
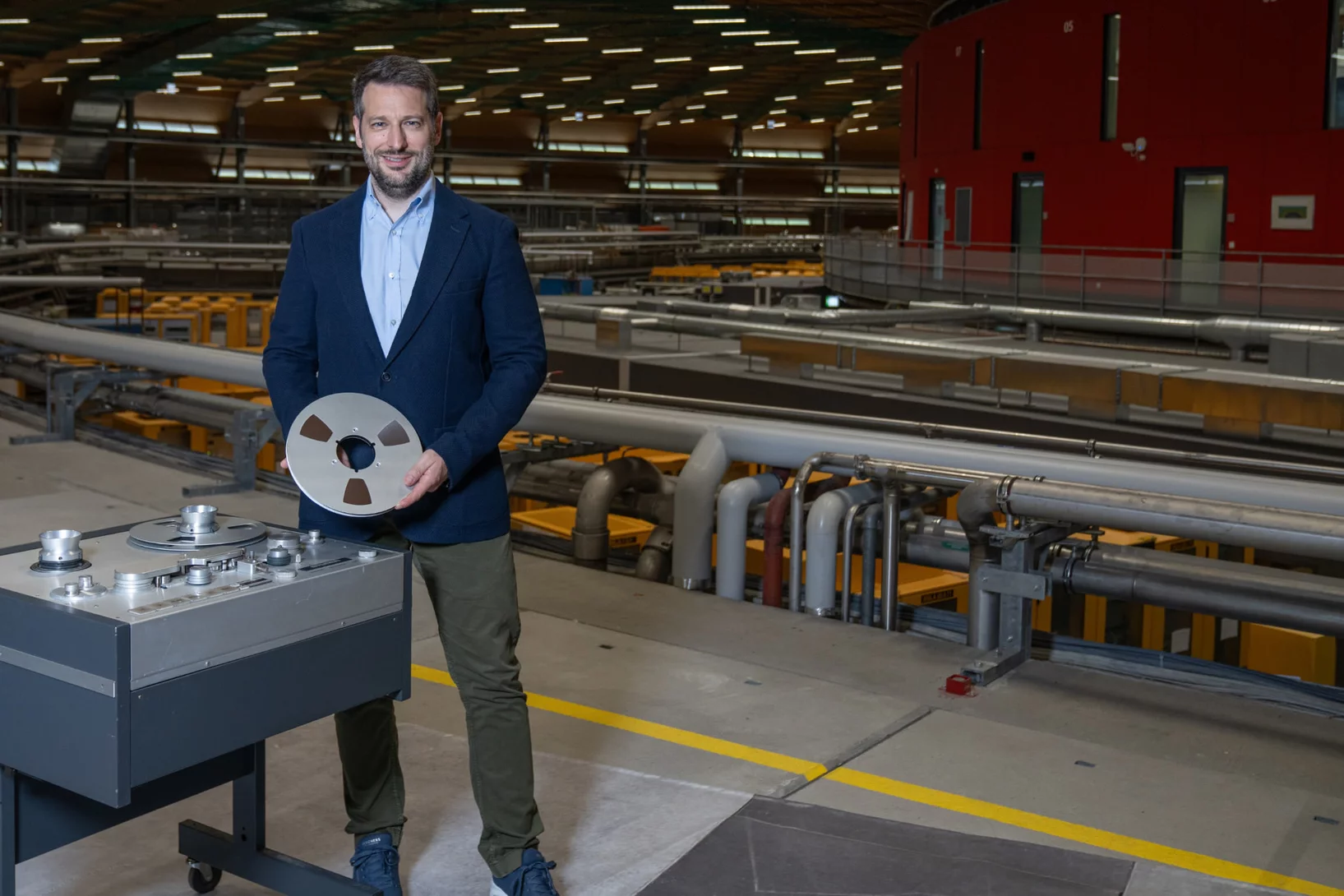
Rescuing music with X-rays
SLS plays the King of the Blues – B.B. King! In collaboration with the Montreux Jazz Digital Project, historic audio tapes are being digitised at PSI.
Making powerful lithium-air batteries suitable for everyday use
Chemical processes in lithium-air batteries revealed using neutron beams and synchrotron light.
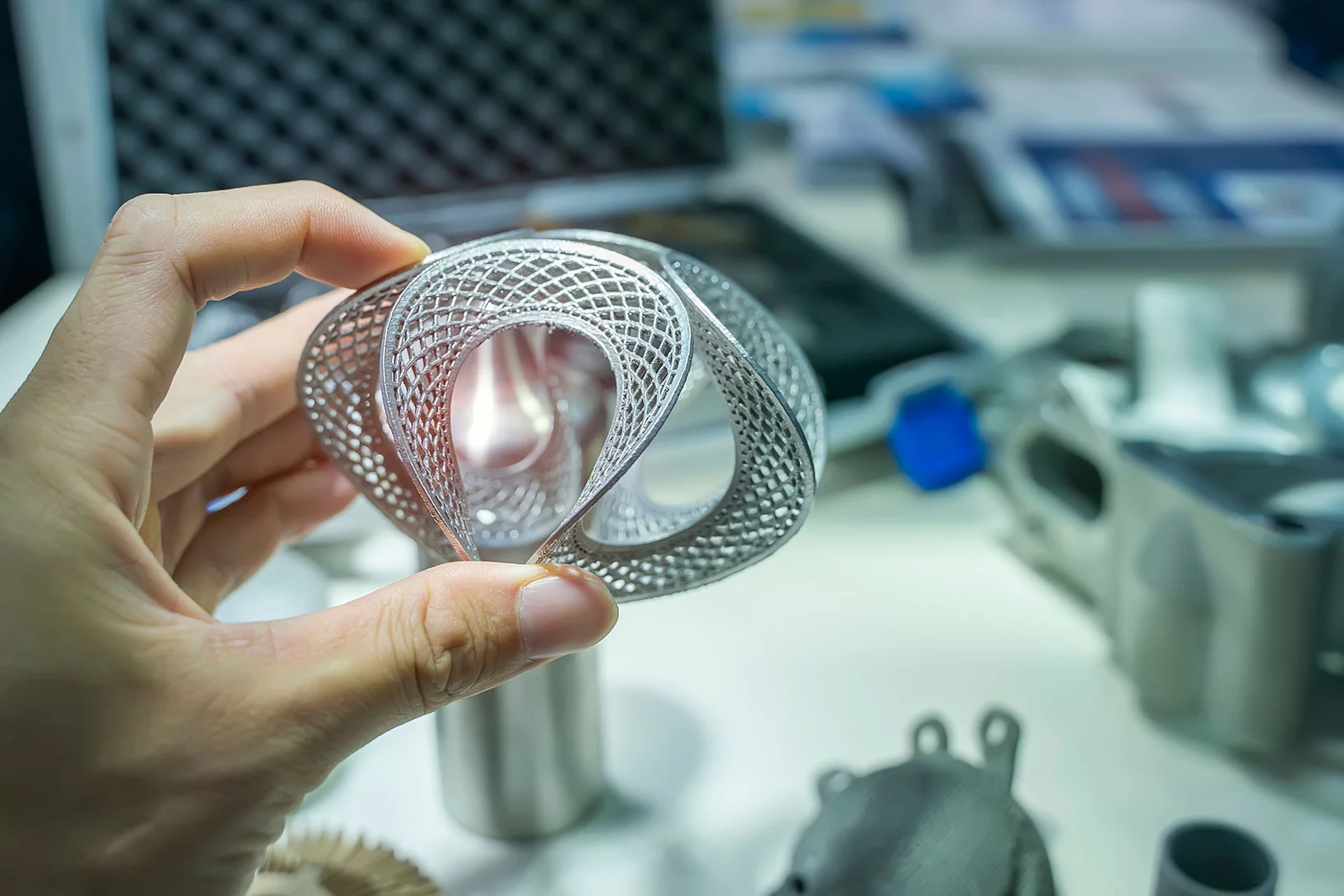
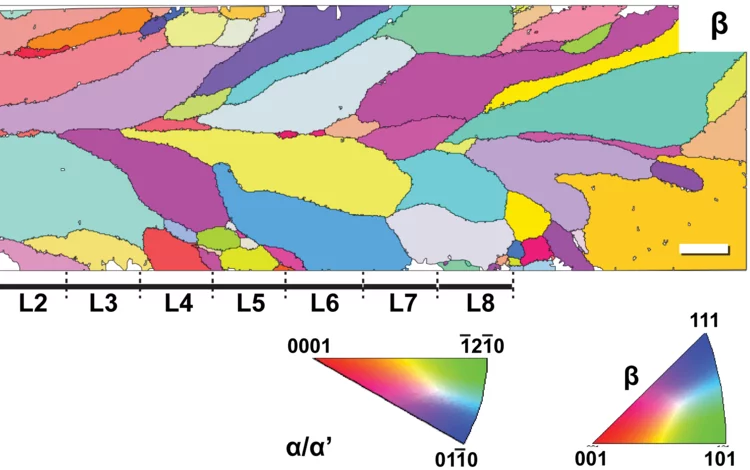
Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
Using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology, we devise special processing strategies to ‘program’ the thermal stability of the as-printed alloy, such that it is possible to decide, a priori, how the material’s microstructure will evolve upon heat treatment
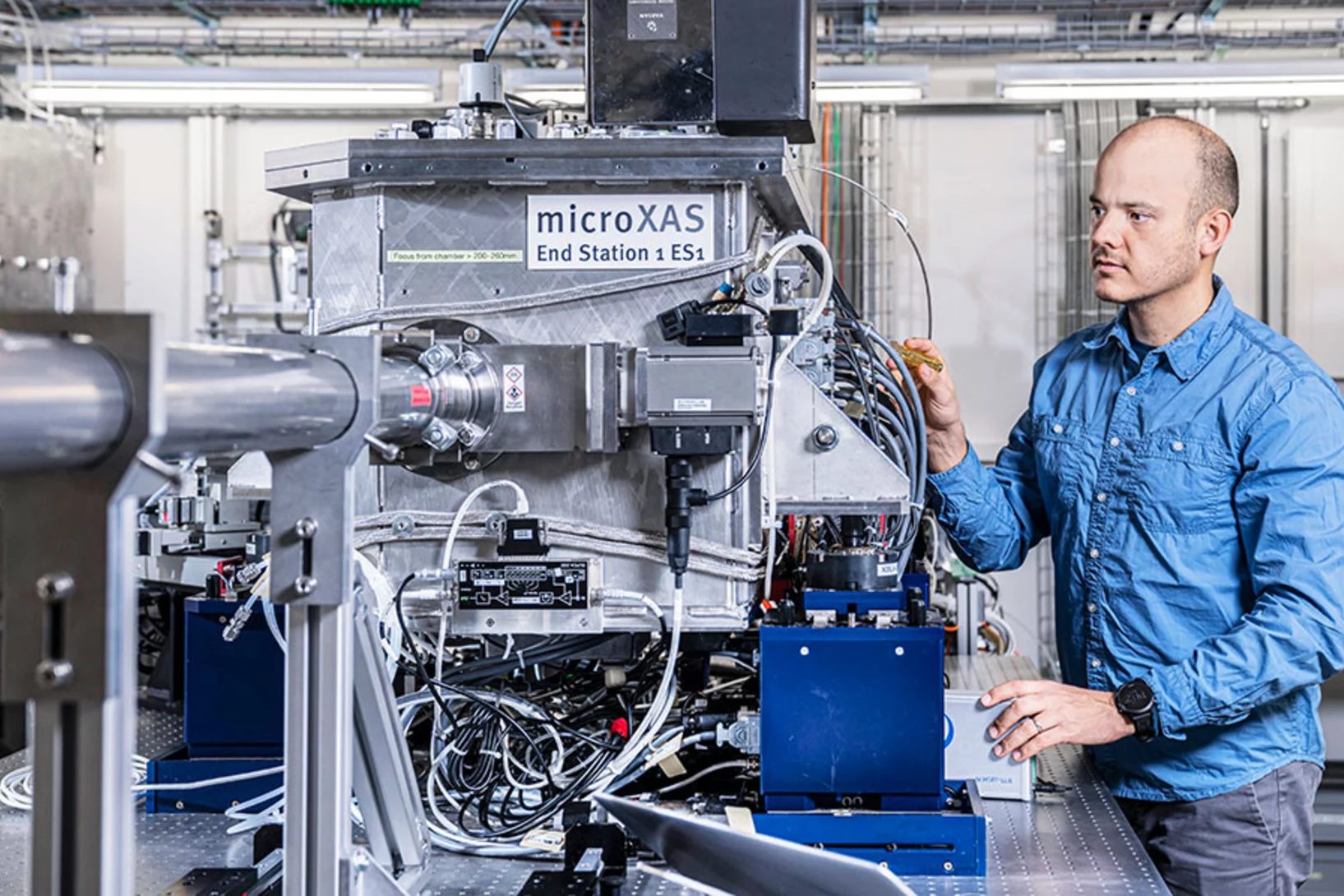
Quality control of future transistors: Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
X-rays make 3D metal printing more predictable
Insights into the microscopic details of 3D printing from the Swiss Light Source SLS could propel the technology toward wider application
Thermal cycling during 3D laser printing
High-speed in situ X-ray diffraction is used to measure temperature profiles and cooling rates during 3D printing of a a Ti-6Al-4V single-track wall.
Thermal and phase evolution during laser powder bed fusion of Al-Sc-Zr elemental powder blends
The reaction of elemental scandium and zirconium powders with liquid aluminum is observed directly via operando X-ray diffraction during laser 3D printing. This work demonstrates that elemental blends can be used to create fine-grained crack-free Al-alloys and highlights the importance of feature size.
Simulant material could aid in Fukushima cleanup
A new simulation of the most dangerous radioactive debris from the Fukushima nuclear power plant will help with clean-up efforts.
Direct observation of crack formation mechanisms with operando Laser Powder Bed Fusion X-ray radiography
Operando high-speed X-ray radiography experiments reveal the cracking mechanism during 3D laser printing of a Ni superalloy.
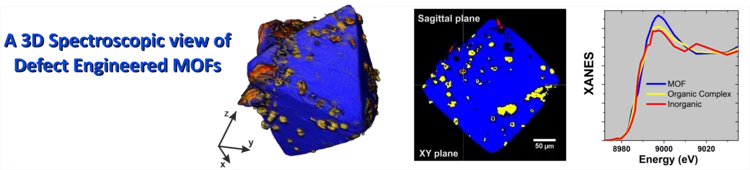
Full-field X-ray absorption tomography reveals the chemical structure of defects in metal-organic frameworks
Cryo-full-field XANES computed tomography was used to visualize the presence and distribution of a second coordination polymer of reduced copper coordination within defect-engineered HKUST-1 MOF crystals. Observations encourage a revisitation of the structure-property relationships of defect-engineered MOFs.
How catalysts age
Catalysts used in industry change their material structure over the years. Using a new method, PSI researchers have now studied this on the nanoscale.
Look Inside a Chemical Reactor
Operando X-ray spectrotomography allows scientists to look inside of functioning chemical reactors. A research team at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), at Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in France have employed this method successfully.
Operando X-ray diffraction during laser 3D printing
Ultra-fast operando X-ray diffraction experiments reveal the temporal evolution of low and high temperature phases and the formation of residual stresses during laser 3D printing of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The profound influence of the length of the laser-scanning vector on the evolving microstructure is revealed and elucidated.
Inside Batteries
Lithium ion batteries (LIB) are essential in modern everyday life, with increasing interest in enhancing their performance and lifetime. Secondary particles of Li-rich cathode material were examined with correlated ptychographic X-ray tomography and diffraction microscopy at different stages of cycling to probe the aging mechanism.
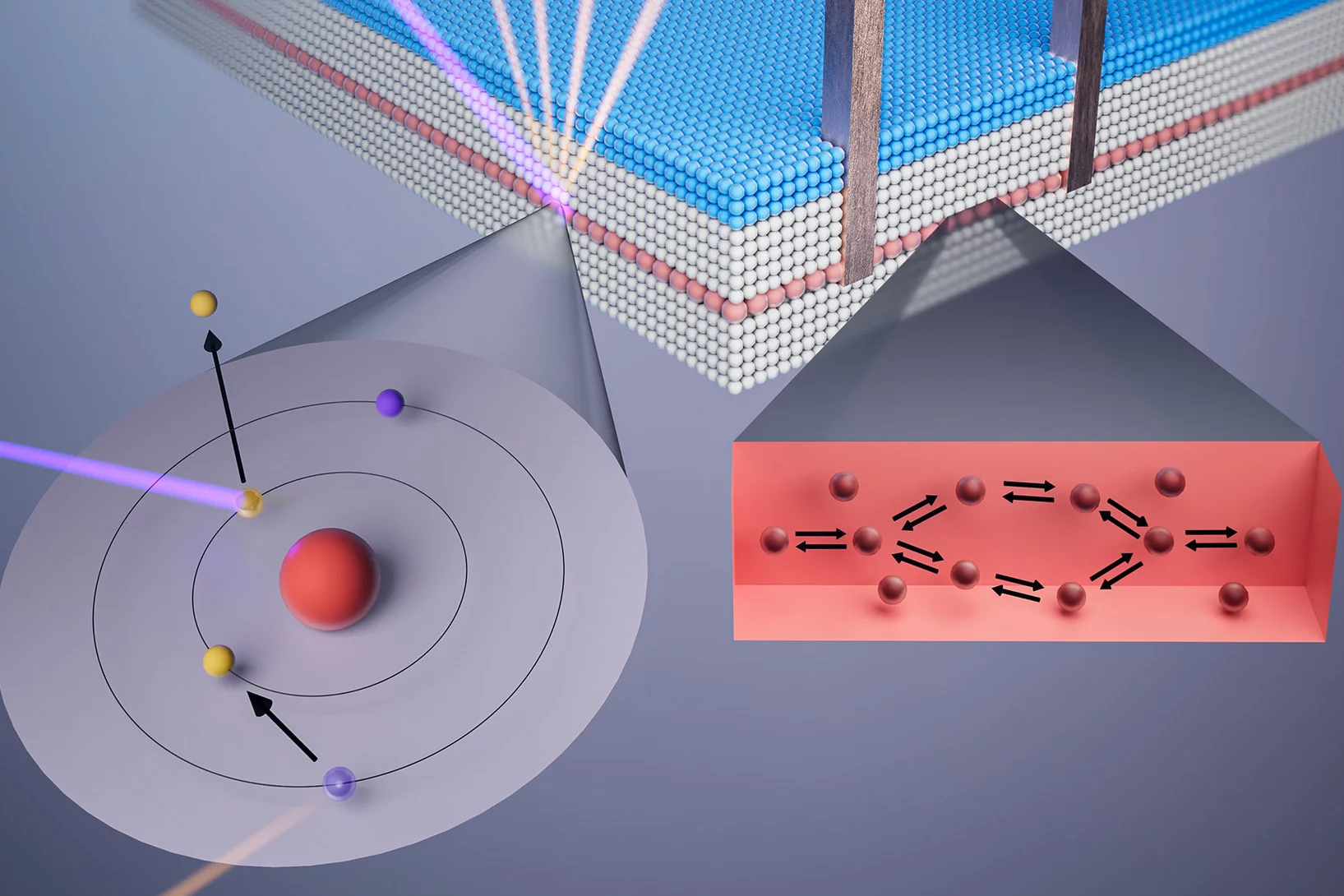
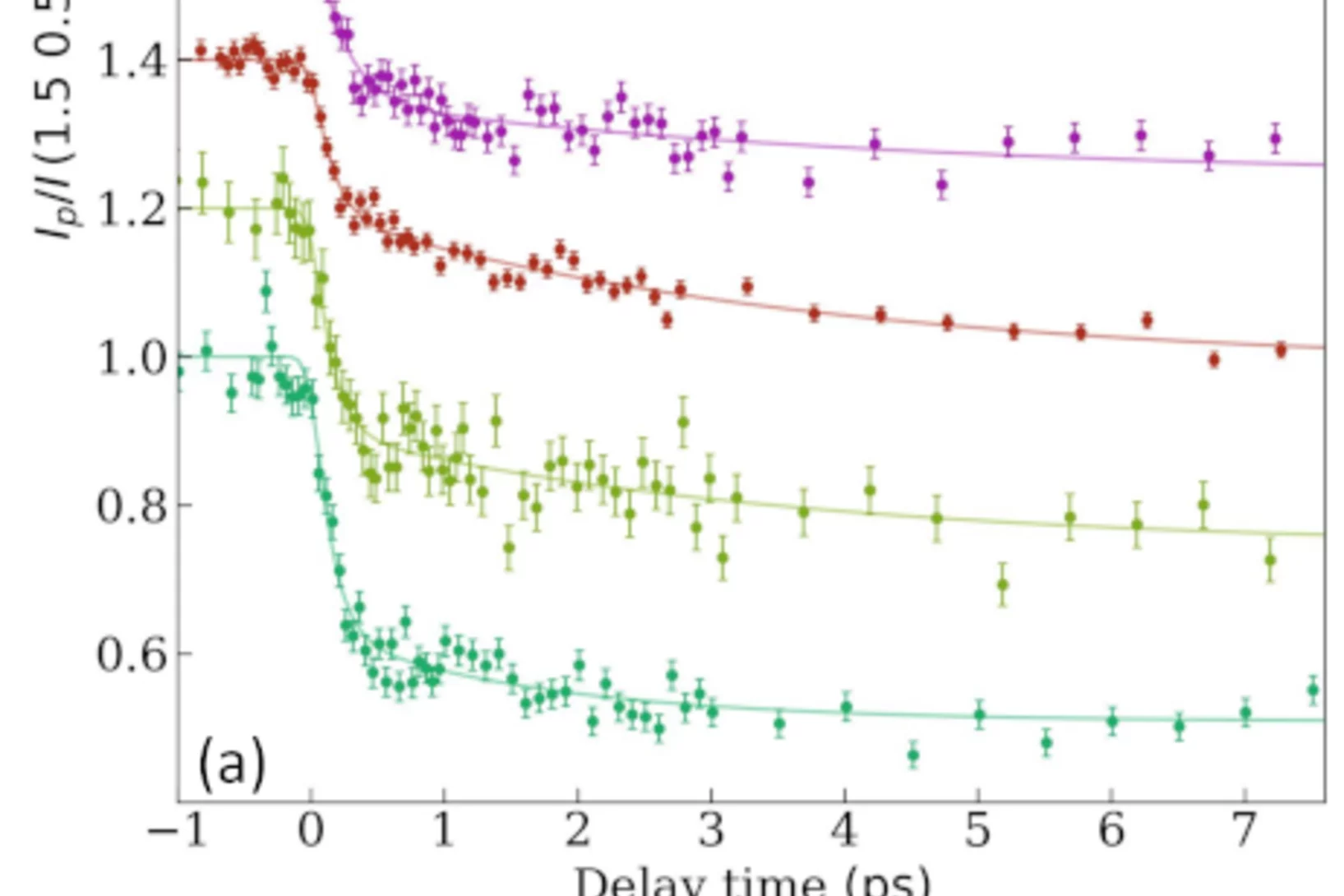
Moving Atoms by Photodoping
Understanding how and how fast we can drive atoms to create a structural phase transition is of fundamental interest as it directly relates to many processes in nature. Here we show that a photoexcitation can drive a purely structural phase transition before the energy is relaxed in the material that corresponds to a “warmer” equilibrated state.
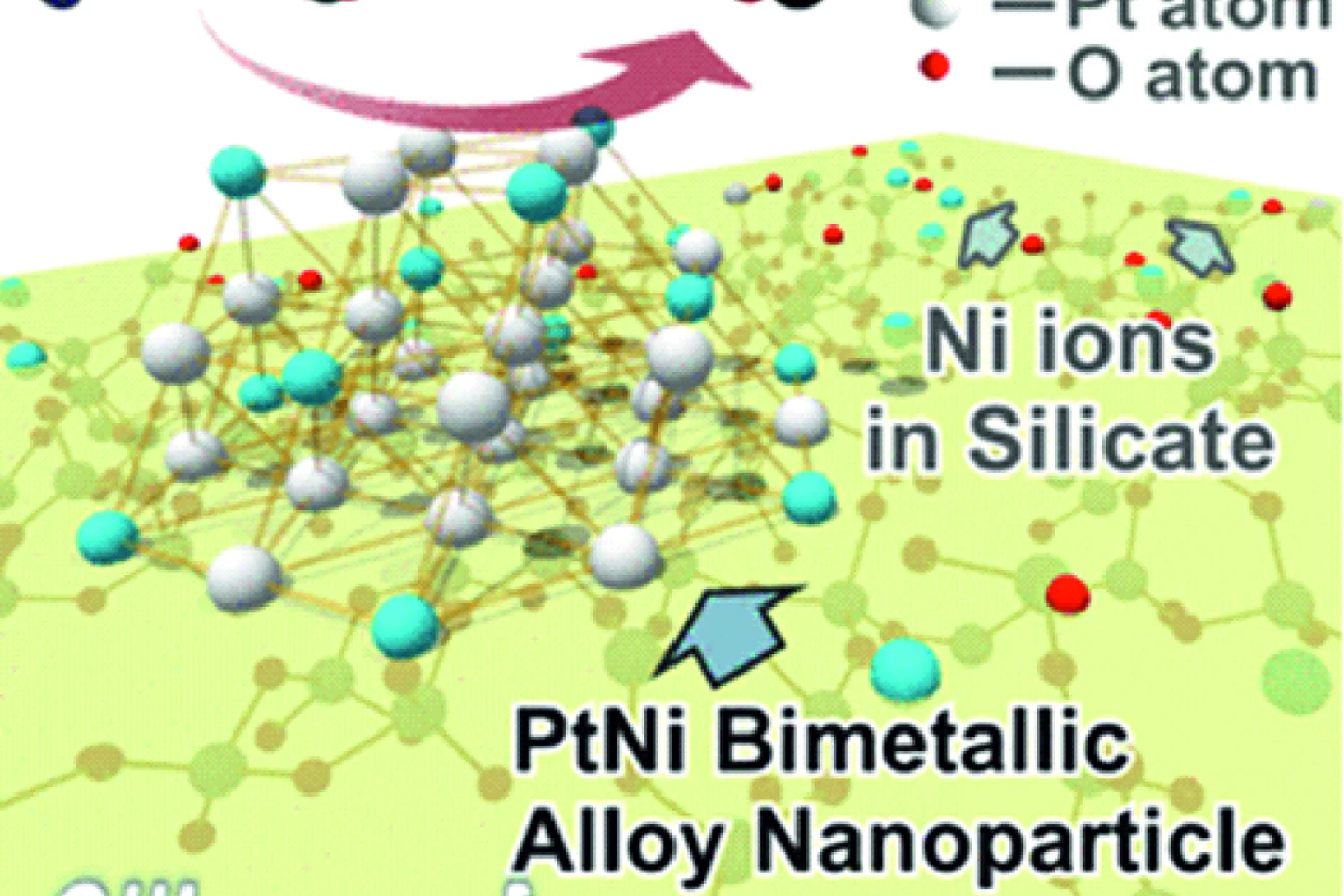
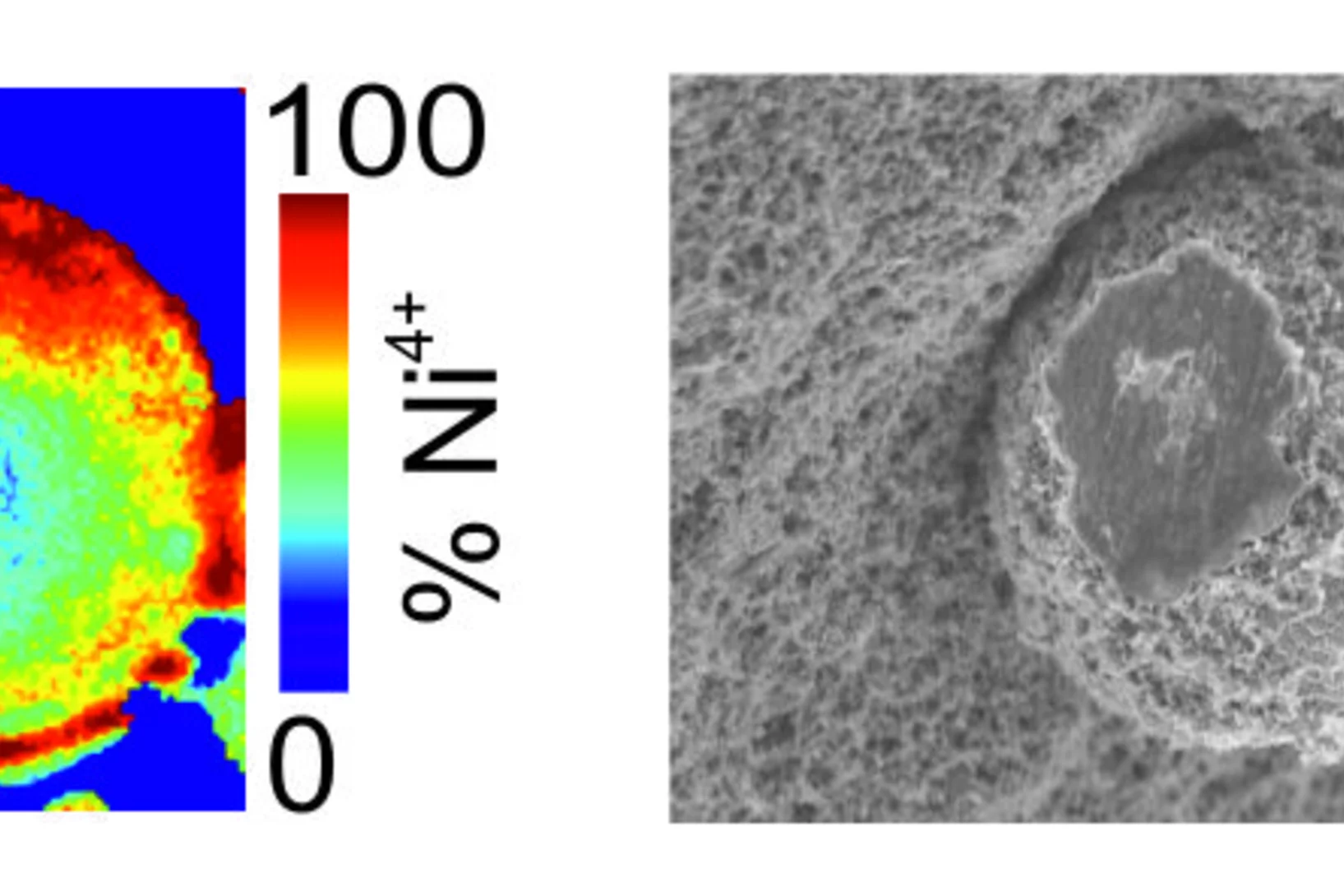
Active Sites of supported bimetallic nano-Catalysts
Dynamic Structural Changes of Active Sites in Pt–Ni Bimetallic Catalysts Revealed by a Multimodal Approach
Making the world go round - a look into the structure of a prominent heterogeneous catalyst
Fluid catalytic cracking catalysts, which are composite particles of hierarchical porosity, were examined using ptychographic X-ray tomography. These particles are essential to the conversion of crude oil into gasoline. Examination of catalysts at decreasing levels of catalytic conversion efficacy allowed the detection of possible deactivation causes.
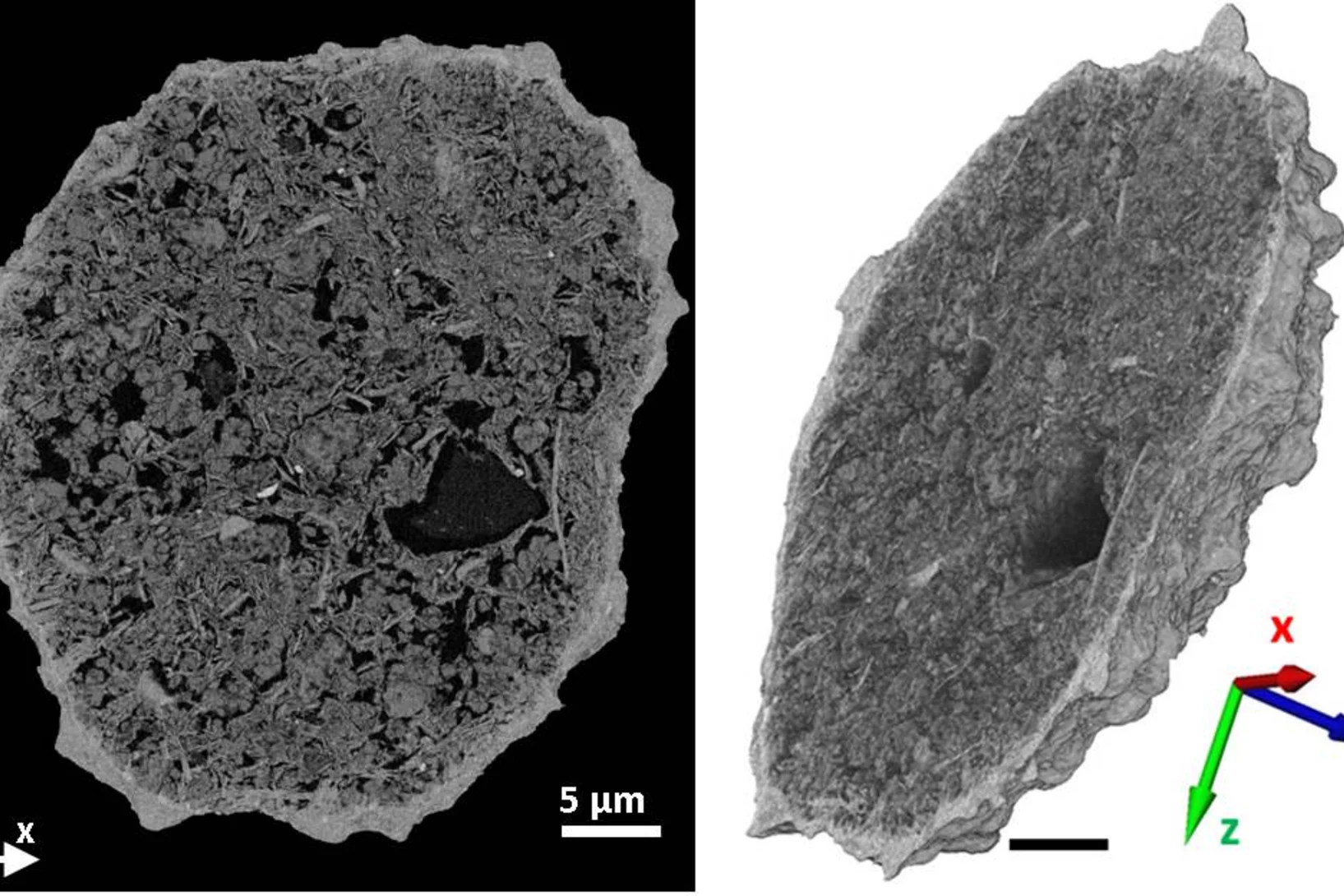
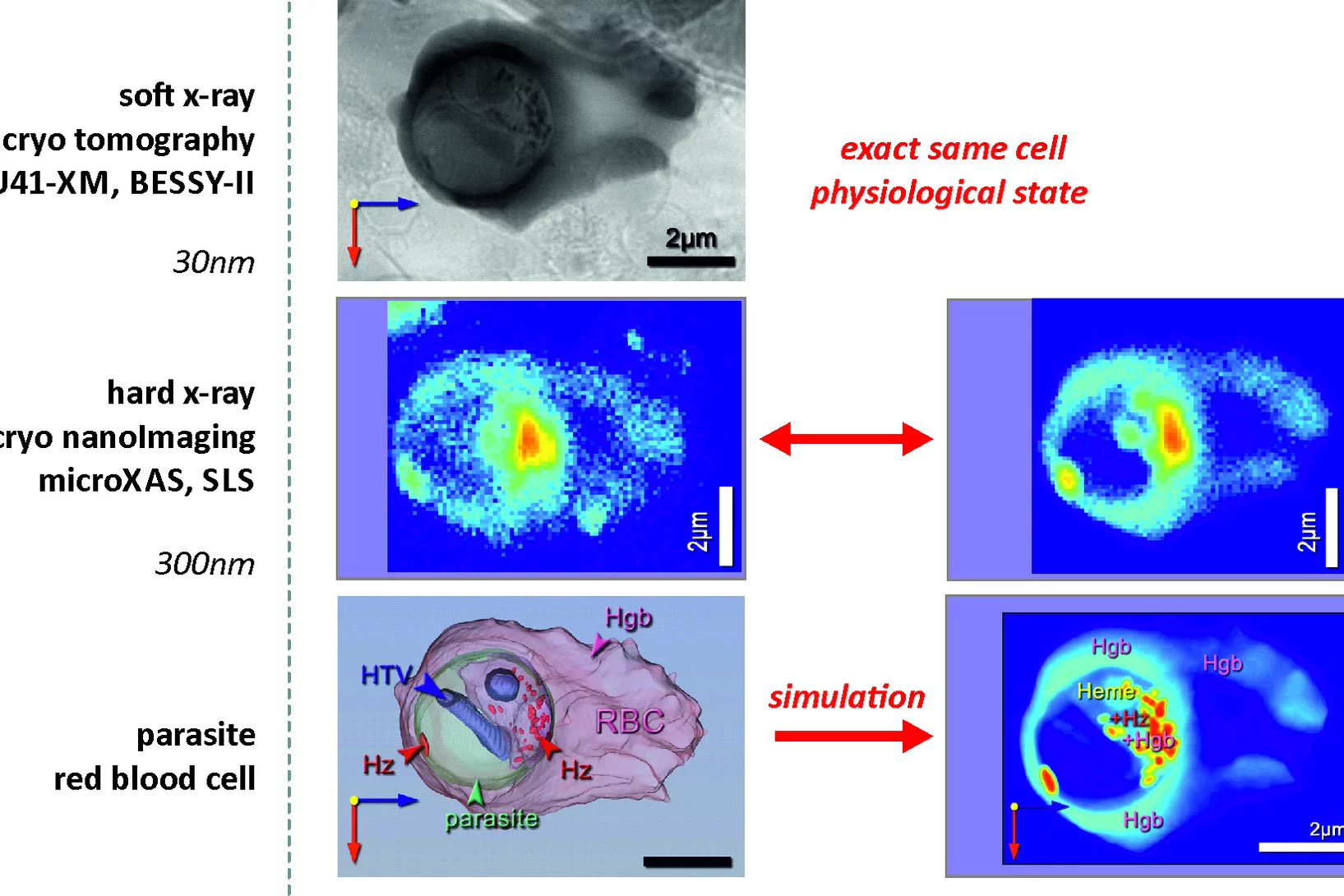
Chemical Imaging to Spy on Malaria Parasites
Unique insights into the adolescence and metabolism of a Malaria parasite in a human red blood cell are obtained by a new chemical imaging methodology – in situ correlative X-ray fluorescence microscopy and soft X-ray tomography.
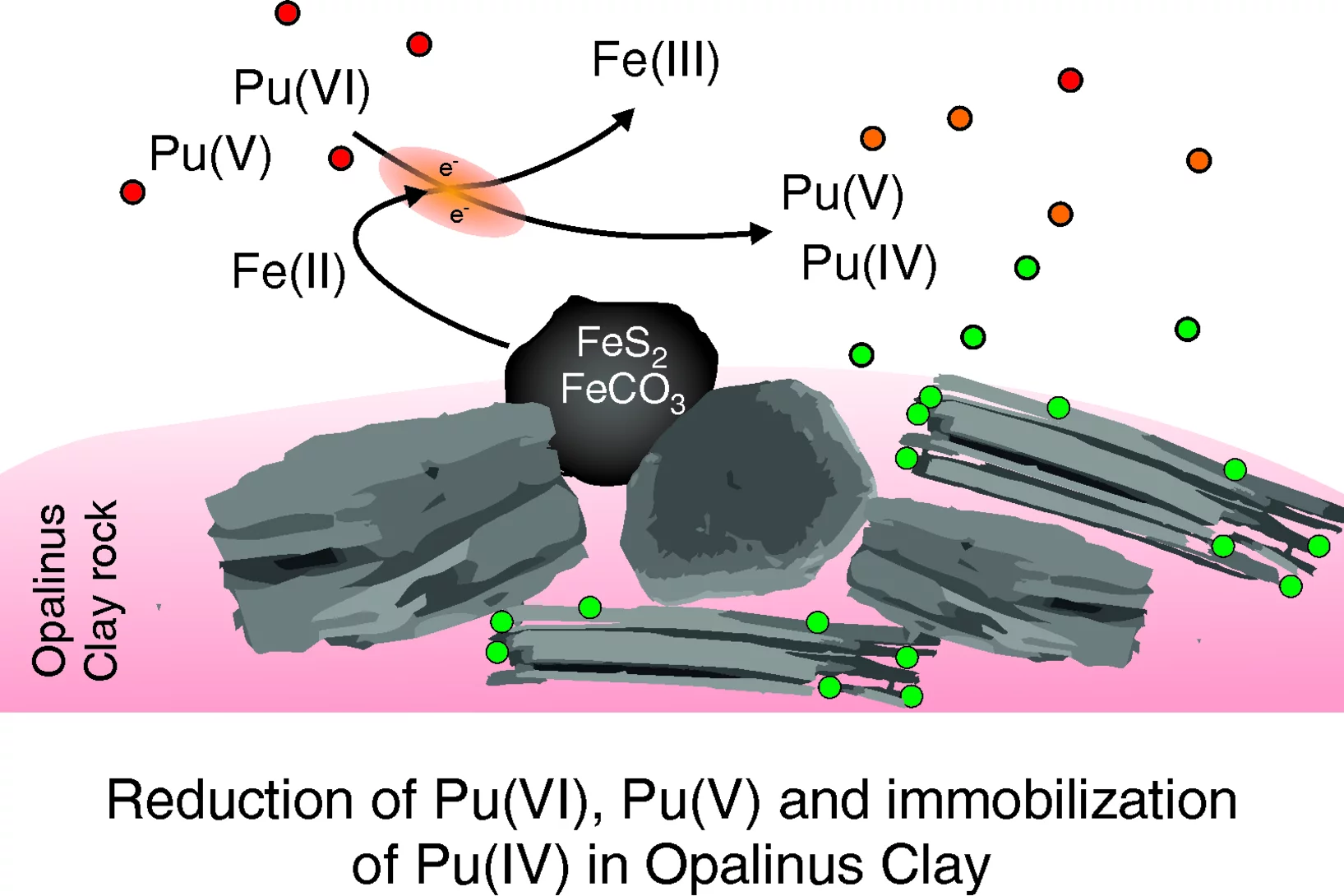
Fate of Plutonium through a Geological Reactive Barrier
Natural geological and engineered barriers play a key role in protecting the environment and the anthroposphere from the hazardous impact of deposited waste or spreading contaminants. Such natural geological and engineered barrier materials are commonly complex and heterogeneous. In-situ multimodal microscopic studies under conditions relevant to deep geological formations are crucial to identify the reactive components and reaction pathways or to validate proposed immobilization mechanisms. The present study demonstrated that a simplistic description by a sole reactive component is not an adequate representation of the geochemical reactivity responsible for the immobilization of plutonium within a natural Clay Rock barrier. Multimodal chemical imaging studies on intact, undisturbed systems are absolutely essential to ascertain the geochemical reactivity for relevant geochemical conditions and settings.
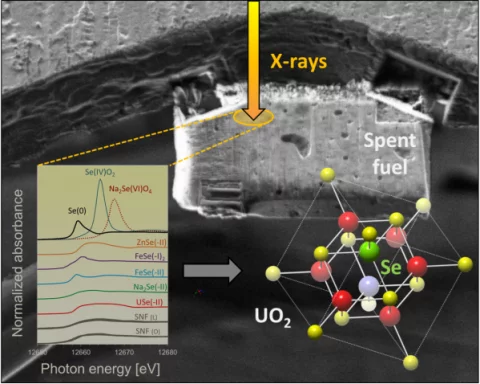
The chemical state of 79Se in spent nuclear fuel
An interdisciplinary study conducted at different PSI laboratories (LES,AHL, LRS, SYN) in collaboration with Studsvik AB (Sweden) demonstrates that selenium originating from fission in light water reactors is tightly bound in the crystal lattice of UO2. This finding has positive consequences for the safety assessment of high-level radioactive waste repository planned in Switzerland, as it implies (contrary to previous assumptions) that the safety-relevant radionuclide 79Se will be released at extremely low rates during aqueous corrosion of the waste in a deep-seated repository.By Enzo Curti (PSI-LES)
Researchers find key to zinc rich plants to combat malnutrition
The diet in many developing countries is lacking zinc, but researchers have just solved the riddle of how to get more zinc into crop seeds. The discovery has been published in Nature Plants, and the research was led by University of Copenhagen.By Johanne Uhrenholt Kusnitzoff
Watching lithium move in battery materials
In order to understand limitations in current battery materials and systematically engineer better ones, it is helpful to be able to directly visualize the lithium dynamics in materials during battery charge and discharge. Researchers at ETH Zurich and Paul Scherrer Institute have demonstrated a way to do this.
Structure of concrete disease
solved
When bridges, dam walls and other structures made of concrete are streaked with dark cracks after a few decades, the culprit is the so-called the concrete disease. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and Empa have now solved the structure of the material produced in these cracks at atomic level - and have thereby discovered a previously unknown crystalline arrangement of the atoms.