Suchen
Improved Interfacial Stability of Ni-rich Oxide Full-Cells
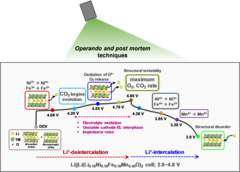
PSI researchers have identified a novel electrolyte additive, allowing extended voltage range of Ni-rich oxide full-cells, while keeping excellent performance. The instability of cathode–electrolyte interface causes the structural degradation of cathode active material and the electrolyte consumption, resulting in a rapid capacity fading and shortening battery life-time. The PSI-identified additive help to alleviate these problems and extend battery life-time.
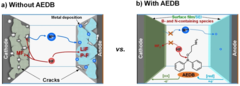
Cross-Talk–Suppressing Electrolyte Additive for Li-ion Batteries
Control of interfacial reactivity at high-voltage is a key to high-energy-density Li-ion batteries. 2-aminoethyldiphenyl borate was investigated as an electrolyte additive to stabilize surface and bulk of both NCM851005 and graphite in the cell with upper cut-off voltage of 4.4 V vs Li+/Li. AEDB almost completely eliminated the “cross-talk” in the cell, by significantly reducing metal leaching from the cathode, preventing their deposition at the anode, and further electrolyte decomposition.
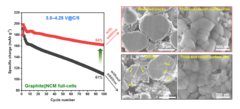
Stable Performance of High Capacity Cobalt-Free Li-ion Battery
Lithium-rich layered oxides, containing cobalt, despite being promising high-capacity cathode materials, need alternatives to eliminate toxic and geopolitically restricted cobalt. An ongoing search for low-cost, Co-free Li-rich cathode materials with a better structural stability lead to investigation of Li1.16Ni0.19Fe0.18Mn0.46O2 (LNFM), where cobalt is replaced by abundant iron. Our LNFM not only delivered a high capacity of 229 mAh/g but also has a stable average discharge voltage when cycled to upper cutoff potential of 4.8 V in additive-free electrolyte.
LEC Seminar Archive
Die Seminare finden im Raum ODRA/111 jeweils am Mittwoch um 11:00 Uhr statt. Externe Gäste (ausserhalb des PSI) sind willkommen, werden aber gebeten, sich im Labor-Sekretariat bei Frau Cordelia Gloor unter Tel.: +41 56 310 2919 oder per e-mail anzumelden. Lectures take place in room ODRA/111 on every Wednesday at 11:00 am. External guests (from outside PSI) are welcome, but are requested to register with our secretary Cordelia Gloor at phone: +41 56 310 2919 or via e-mail.
Battery Electrodes and Cells
The primary goal is the development of a safe, environmentally benign, and cost effective electrochemical energy storage system with significantly improved specific energy. The research work focuses equally on the scientific background essential for the development of new technologies and on the analysis of ageing and safety relevant aspects of current industrial batteries. The investigated systems include both lithium-ion and post-lithium-ion batteries.