Recherche
Electrocatalysis and Interfaces
The Electrocatalysis and Interfaces Group was established in 2012 combining the electrocatalysis activites of the former Fuel Cell Group and the Interface analytical activities of the former Interface and Capacitor Group. Electrocatalysis is the key topic for electrochemical energy conversion.
Energiewende
Themenübersicht
Energie und Klima
Themenübersicht
Damage-Repair Cycle in Hydrocarbon Based Membranes for Fuel Cells
The development of next generation fuel cell membranes based on aromatic hydrocarbon chemistry calls for a new antioxidant strategy to tackle radical induced membrane degradation. Although damage by radicals cannot be prevented, the formed aromatic intermediates can be repaired by a suitable additive. Fuel cell experiments demonstrate that the approach is viable on the device level and that repair is a catalytic mechanism.
Publications 2015
Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC)
Publications 2018
Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC)
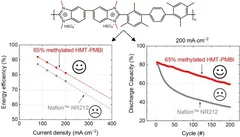
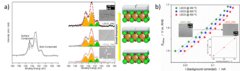
Polybenzimidazole Membrane Design Principles for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
Energy storage technologies with long storage duration are essential to stabilize electricity grids with a high share of intermittent renewable power. In a redox flow battery, the electrochemical conversion unit, where the charging and discharging reaction takes place, is spatially separated from the energy storage medium. In the all-vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), a sulfuric acid aqueous electrolyte with dissolved vanadium ions is used as the storage medium. Vanadium is present in 4 different oxidation states, the redox couple vanadium(II) and (III) on the negative side of the cell, and vanadium(IV) and (V) on the positive side. This allows the battery to be repeatedly charged and discharged. A separator or membrane is used between the negative and positive electrode, which should selectively conduct the ions of the supporting electrolyte and minimize the passage of vanadium ions. Fluorinated membranes, such as Nafion™, are often used for this key component, but these ionomers were not originally developed for this application and therefore have functional shortcomings. Furthermore, the production and use of fluorinated materials is to be severely restricted or even banned in Europe. Therefore, the development of hydrocarbon-based membranes for the VRFB is of great importance. The study reported here focuses on polybenzimidazole polymers and membranes, which could be a promising materials class for next generation flow batteries.
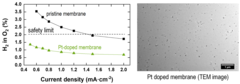
Enabling the use of Thin Membranes in Water Electrolyzers using a Recombination Catalyst
The conversion efficiency for green hydrogen production in a polymer electrolyte water electrolyzer (PEWE) is strongly influenced by the ohmic cell resistance and therefore the thickness of the membrane used. The use of thin membranes (~50 micron or below) is limited by gas crossover of H2 and O2, which can lead to the formation of explosive gas mixtures. The incorporation of a recombination catalyst provides remedy and allows a more dynamic operating mode.
Publications
Thin Films and Interfaces
List of papers describing details of the beamline
Please cite the corresponding beamline paper in your publications. Contact the beamline scientist if you are not sure which paper you should cite.
Collaborations
We are working together in our actual (and past ) projects with various national and international collaboration partners.
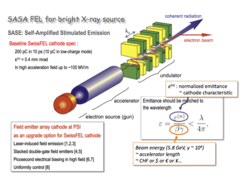
Vacuum Nanoelectronics
We have been studying all-metal field emitter array (FEA) cathode [1-14] as a potential high current and high brilliance electron source for advanced accelerator applications e.g. X-ray free electron lasers such as SwissFEL [15], requiring stringent cathode specs: high current (200 pC in 10 ps), low normalized transverse emittance (0.4 mm-mrad), and compatibility with the high acceleration electric field in the order of 100 MV/m.
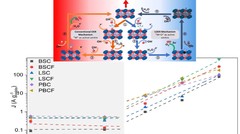
Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity and Underlying Mechanism of Perovskite Electrocatalysts at Different pH
PSI researchers have studied the how the electrolyte pH values influence the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity and stability of different promising perovskite oxide catalysts for application as anodic electrodes in alkaline water electrolyzers. The OER activity and stability decreased decreasing the electrolyte pH values. By combining electrochemical studies and operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements, it has been suggested that different reaction mechanisms dominate in alkaline and near-neutral electrolyte pH region.
Surface segregation acts as surface engineering for the oxygen evolution reaction on perovskite oxides in alkaline media
PSI researchers have studied the influence of surface segregation on the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity for the, La0.2Sr0.8CoO3-d (LSCO) perovskite, one of the most active perovskite towards the OER in alkaline electrolyte. It has been found that the higher the perovskite synthesis temperature the more strontium segregation occurs on the surface. However, the segregated strontium compounds are soluble in water and they are easily removed when the surface of the electrode is in contact with the electrolyte, leading to the exposure of cobalt enriched layers very active for the OER.
Publications 2009
Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC)