Show filters
First magnetic image at PolLux with SLS 2.0
First magnetic image acquired at the PolLux beamline of the SLS 2.0 DLSR source
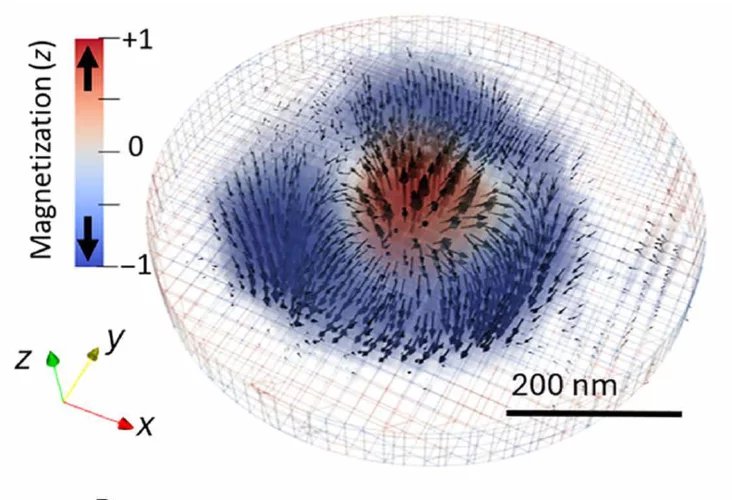
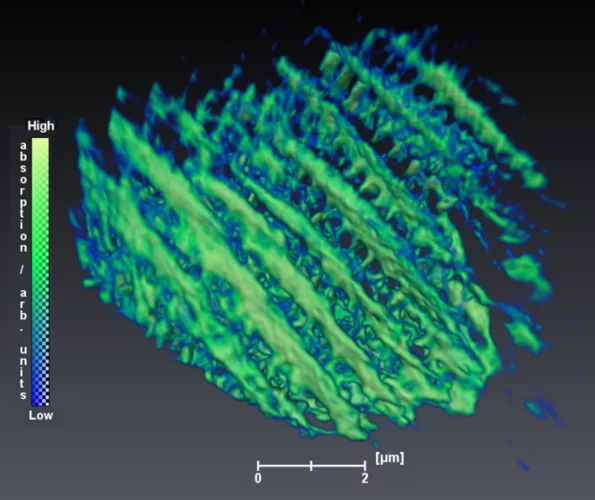
Skyrmion topology quantified in 3D
Researchers from an international collaboration between the United States of America and Switzerland have performed three-dimensional magnetic imaging of a magnetic skyrmion using soft X-ray laminography. This allowed for the investigation, in three dimensions, of the topological profile of the magnetic skyrmions.
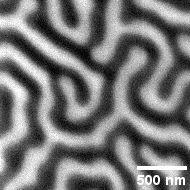
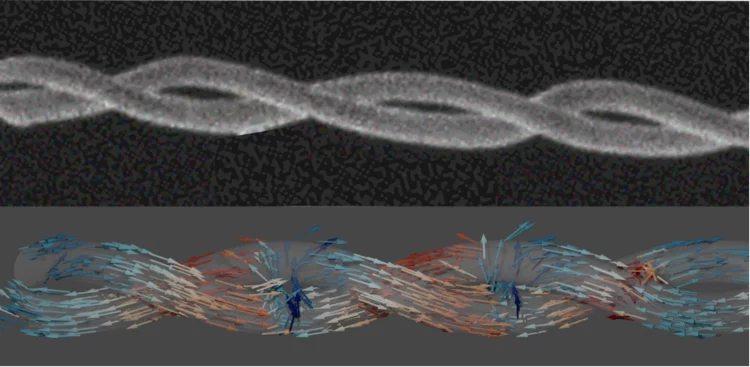
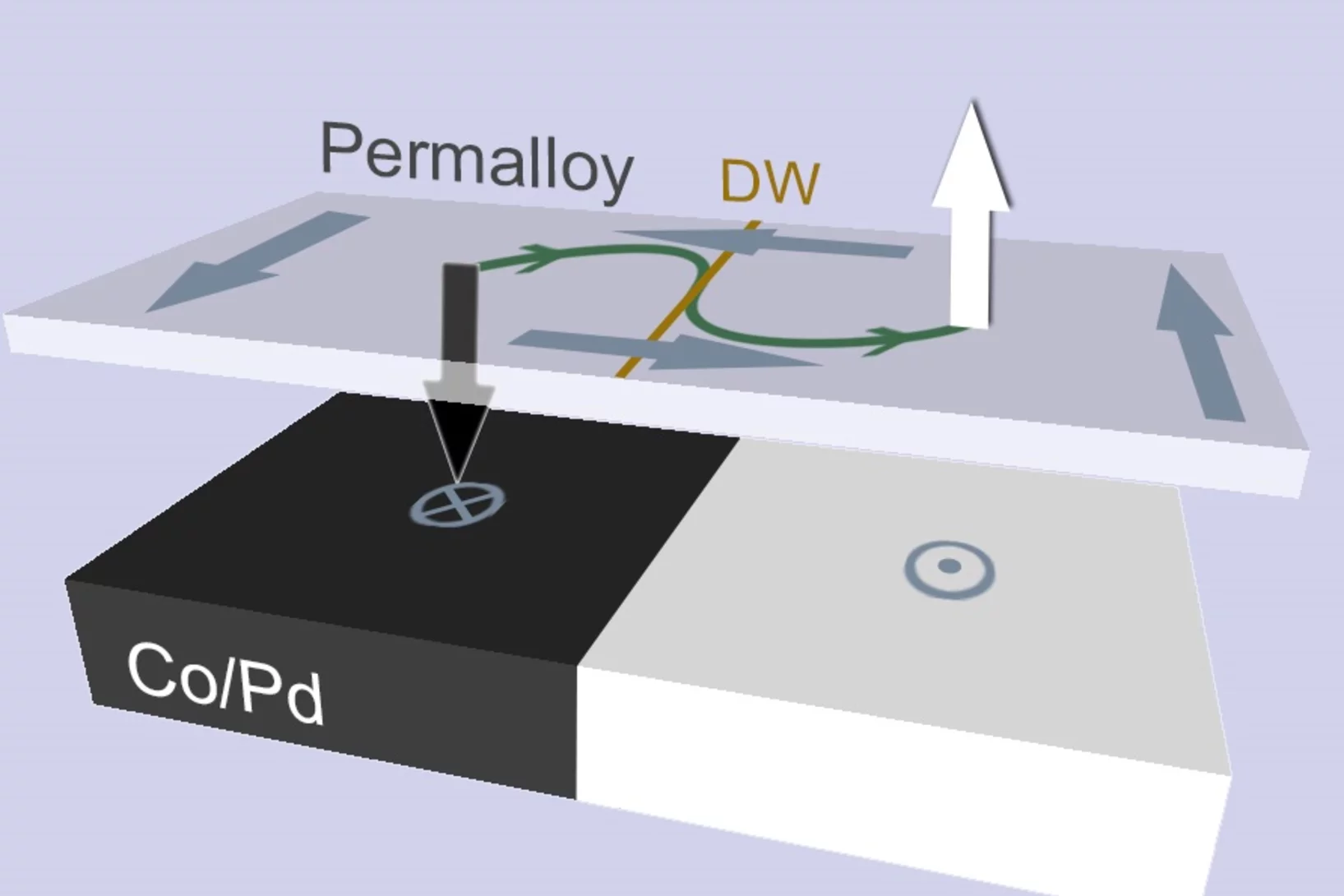
Spatially reconfigurable topological textures in freestanding antiferromagnetic nanomembranes
Researchers from the University of Oxford have imaged, through the use of the soft X-ray microscopy capabilities at the Swiss Light Source, spatially reconfigurable antiferromagnetic states in topologically rich free-standing nanomembranes
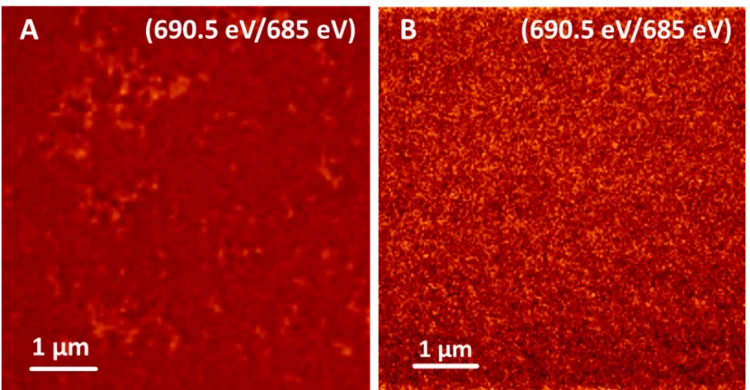
TEY-STXM confirms homogeneous doping of nanoparticles for non-fullerene organic solar cells
One of the challenges in modern research on the fabrication of non-fullerene acceptor based organic solar cells is the availability of very efficient hole transport layers (HTLs). A new approach that avoids mutual solubility issues is to deposit the HTL from a suspension of doped organic nanoparticles. Surface-sensitive TEY-STXM measurements at the PolLux beamline characterised the homogeneity of the dopant in the nanoparticles and develop efficient nanoparticle HTL materials for organic solar cells.
Biffo the fish: BiFeO3 nanoplate wins the Magnetism Art Competition at JEMS 2023 in Madrid
Dr. Tim A. Butcher from the Microspectroscopy group was awarded the first prize in the "Art in Magnetism" competition of the JEMS 2023 conference with his contribution "Biffo", obtained from a ptychography image of a BiFeO3 nanoplate.
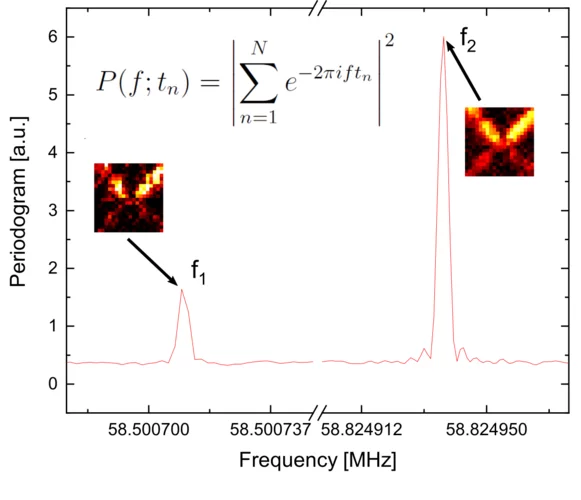
From light-years to nanometers: reconstruction of unknown oscillations in STXM
From light-years to nanometers: by repurposing an algorithm originally developed for the investigation of oscillatory dynamics in astronomical objects, scientists have been able to image non-locked dynamical processes at the nanosecond and nanometer scale.
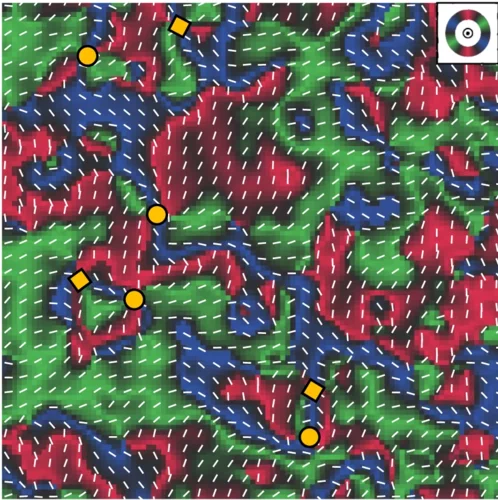
Nucleation of synthetic antiferromagnetic skyrmions
Magnetic skyrmions stabilized in synthetic antiferromagnets hold promise as nanoscale information carriers in novel non-volatile magnetic memory designs. In this work, scientists in a worldwide collaborative effort have demonstrated the electrically-induced nucleation of magnetic skyrmions in synthetic antiferromagnets, which is a vital stepping stone towards the applicability of these magnetic textures in devices.
Ferrimagnetic Skyrmions: fast and straight
Scientists have demonstrated, through magnetic X-ray microscopy, that magnetic skyrmions stabilized in ferrimagnetic heterostructures can be displaced by electrical currents at high velocities, and exhibit low deflection angles, proving that ferrimagnetic skyrmions are good candidates for fast skyrmionic devices.
Light amplification accelerates chemical reactions in aerosols
Aerosols in the atmosphere react to incident sunlight. This light is amplified in the interior of the aerosol droplets and particles, accelerating reactions. ETH and PSI researchers have now been able to demonstrate and quantify this effect and recommend factoring it into future climate models.
Into the fourth dimension: time-resolved soft X-ray laminography
Combining time-resolved soft X-ray STXM imaging with magnetic laminography, researchers were able to investigate magnetization dynamics in a ferromagnetic microstructure resolved in all three spatial dimensions and in time. Thanks to the possibility of freely selecting the frequency of the excitation applied to the magnetic element, this technique opens the possibility to investigate resonant magneto-dynamical processes, such as e.g. magnetic vortex core gyration and switching, and spinwave emission.
3D printed nanomagnets unveil a world of patterns in the magnetic field
Scientists have used state-of-the-art 3D printing and microscopy to provide a new glimpse of what happens when taking magnets to three-dimensions on the nanoscale – 1000 times smaller than a human hair.
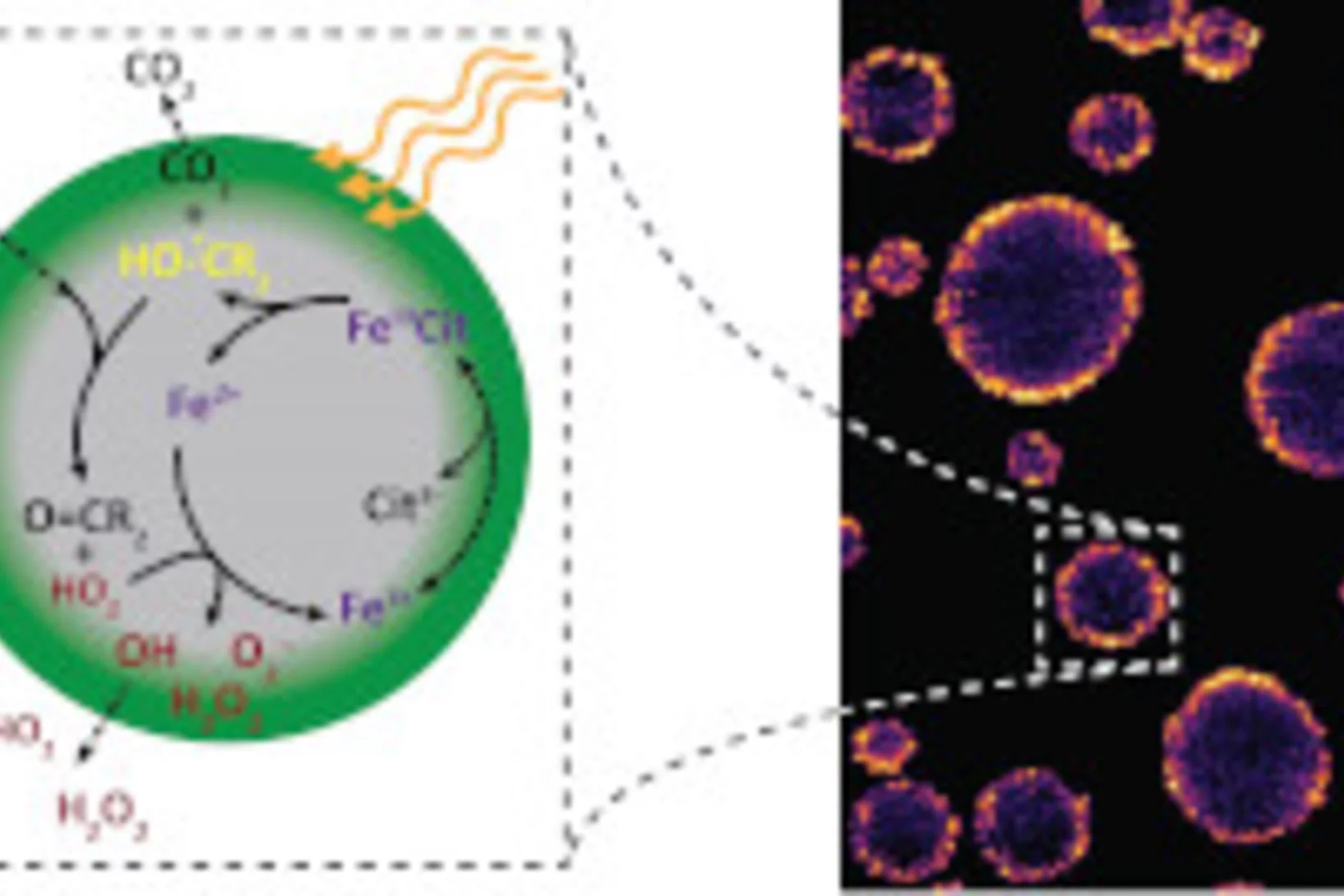
Looking inside airborne particles for the chemistry responsible for their adverse health effects.
Chemical changes inside of breathable airborne particles can cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) and carbon centered radicals (CCRs) to form, which are harmful to our bodies and induce oxidative stress in lungs. Using X-ray spectromicroscopy at the PolLux beamline and mimicking the environmental and sunlit conditions aerosol particles experience in the atmosphere near the Earth Surface, it was recently found that highly viscous organic particles with low water content can attain high concentrations of ROS and CCRs that persist over long times. Natural particles like these will occur in ambient humidity below 60% and effectively trap ROS and CCRs inside that react when exposed to light.
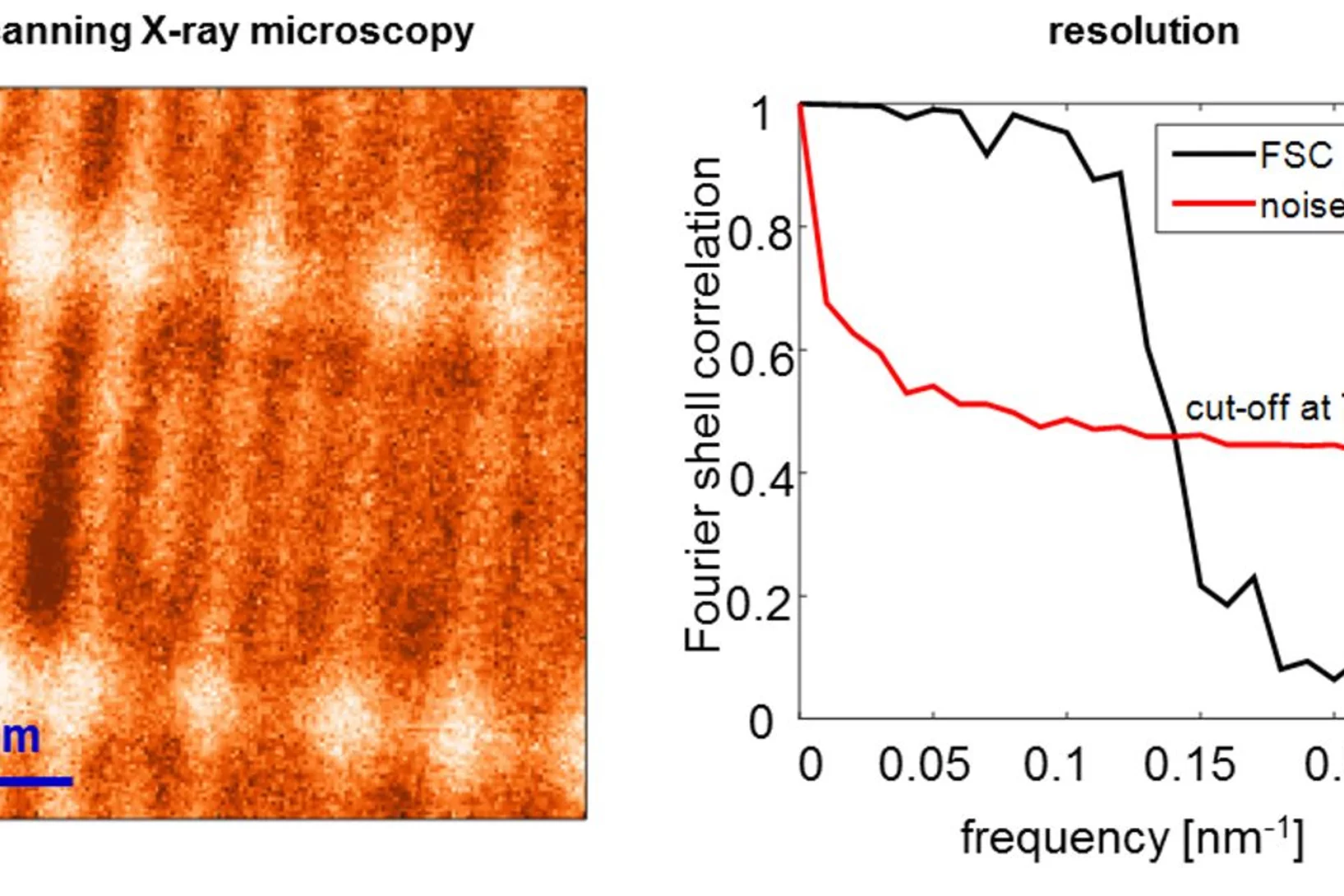
World Record: 7 nm Resolution in Scanning Soft X-ray Microscopy
During the past decade, scientists have put high effort to achieve sub-10 nm resolution in X-ray microscopy. Recent developments in high-resolution lithography-based diffractive optics, combined with the extreme stability and precision of the PolLux and HERMES scanning X-ray microscopes, resulted now in a so far unreached resolution of seven nanometers in scanning soft X-ray microscopy. Utilizing this highly precise microscopy technique with the X-ray magnetic circular dichroism effect, dimensionality effects in an ensemble of interacting magnetic nanoparticles can be revealed.
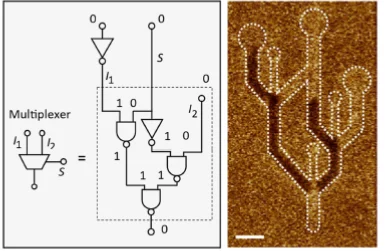
Logic operations with domain walls
A collaboration of scientists from the ETH Zürich and the Paul Scherrer Institute successfully demonstrated the all-electric operation of a magnetic domain-wall based NAND logic gate, paving the way towards the development of logic applications beyond the conventional metal-oxide semiconductor technology. The work has been published in the journal Nature.
Optics for spins
In this work, published on the front cover page of Advanced Materials, an international collaboration of Italian, American, and Swiss scientists demonstrated a novel concept for the generation and manipulation of spin waves, paving the way towards the development of magnonic nano-processors.
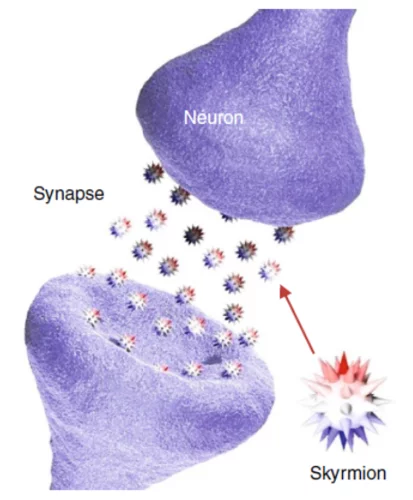
Can skyrmions read?
Can a skyrmion-based device be used to read a handwritten text? In this work, an international scientist collaboration led by the Korea Institute of Technology and the IBM Watson research center could provide a first answer to this question by fabricating a proof-of-principle single-neuron artificial neural network, using X-ray magnetic microscopy at the Swiss Light Source to investigate its performances.
Many skyrmions, one angle
Employing a tailored multilayered magnetic film, optimized for the zero-field stabilization of magnetic skyrmions, researchers have investigated the influence of the skyrmion diameter on its current-induced sideways motion, uncovering mechanisms that allow for this topological property to be controlled.
Soft X-ray Laminography: 3D imaging with powerful contrast mechanisms
3D imaging using synchrotron radiation is a widely used tool that allows access to the inner structure of complex objects. An international and interdisciplinary consortium of scientists from the Swiss Light Source (PolLux and cSAXs), the Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, and the University of Cambridge developed the new 3D imaging technique of Soft X-ray Laminography (SoXL). SoXL allows for the investigation of thin and extended samples while taking advantage of the characteristic absorption contrast mechanisms in the soft X-ray range, providing 3D information with nm spatial resolution.
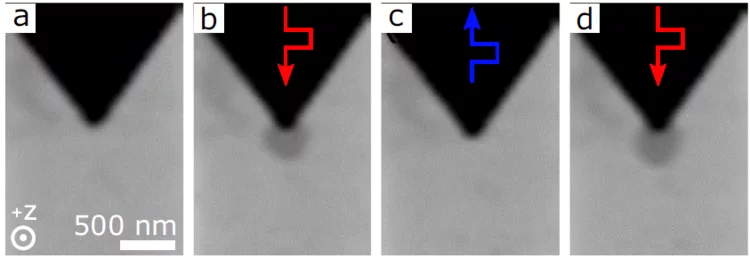
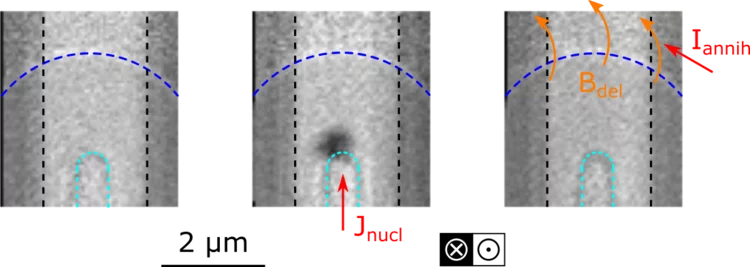
Nano-engineered contact for the zero-field nucleation of magnetic skyrmions
Researchers in a joint collaboration between the PolLux endstation of the Swiss Light Source and the University of Leeds have achieved the reliable and reproducible electrical nucleation of magnetic skyrmions from a nano-engineered point contact structure, investigating the physical mechanisms driving the nucleation process.
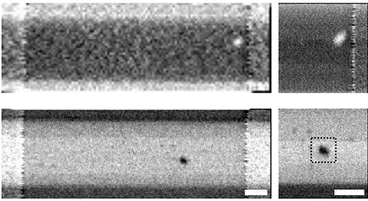
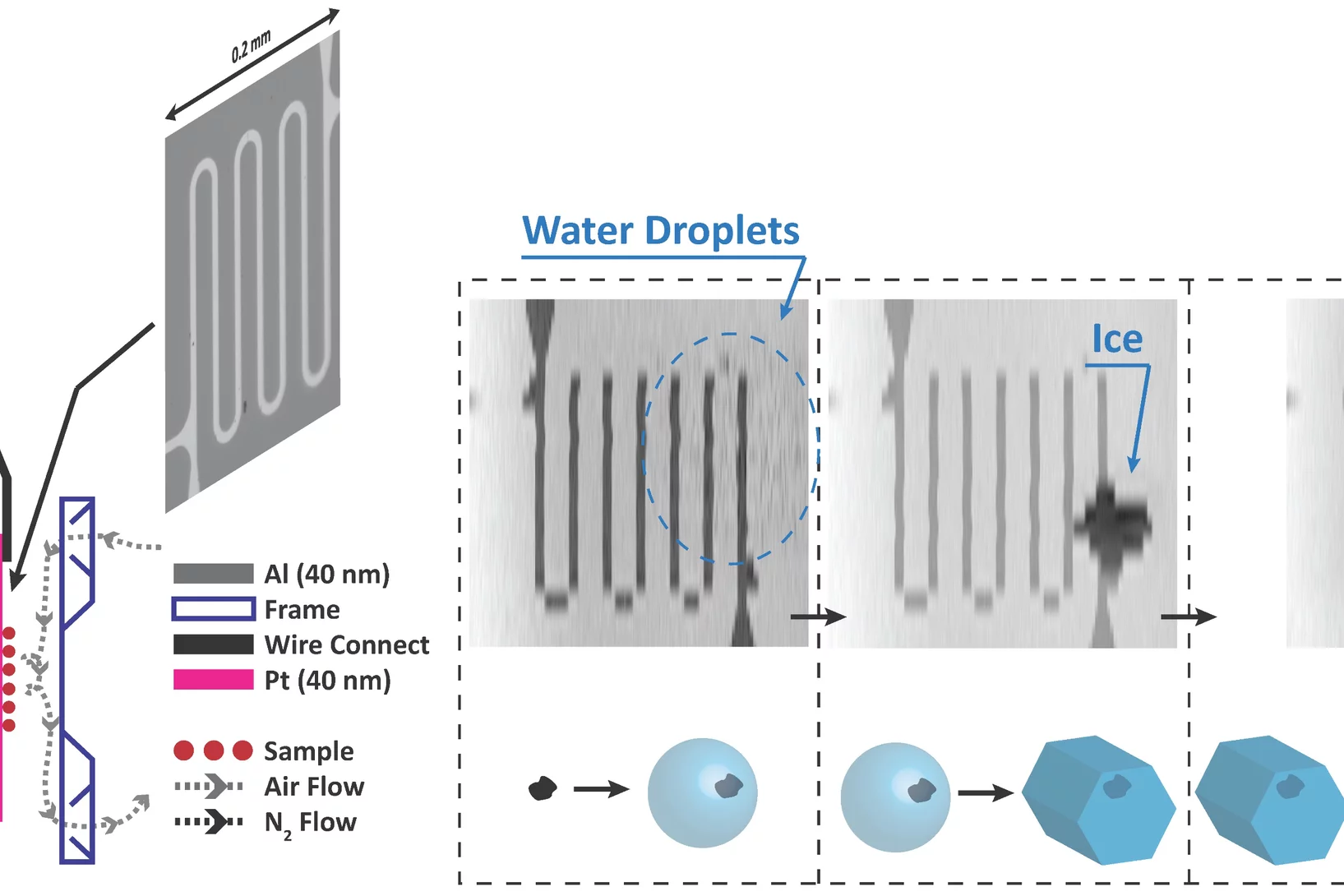
Chemically mapping ice forming particles
Scientists have just nucleated ice in an X-ray microscope for the first time and they created chemical maps of those responsible.
HERCULES school 2019 at SLS
In the week of April 1-5 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the European HERCULES 2019 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
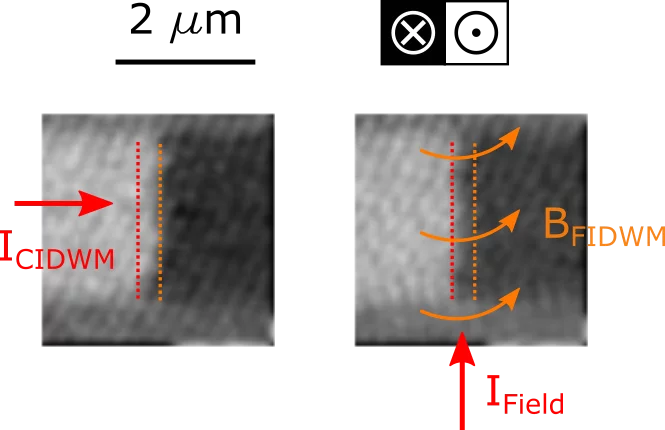
Sub-ns magnetic domain wall motion dynamics
Magnetic domain walls can be reliably displaced by electrical currents, allowing for the fabrication of retentive magnetic memory elements without mechanically moving parts, such as e.g. the magnetic racetrack memory. Researchers in a joint collaboration between the PolLux endstation of the Swiss Light Source and the University of Leeds were able to investigate the dynamics of magnetic domain wall motion with a sub-ns time step, providing a substantial step forward towards the unraveling of the physical processes behind the current- and magnetic field-induced motion of magnetic domains.
Discrete Hall contribution of magnetic skyrmions
The reliable electrical detection of magnetic skyrmions is of fundamental importance for the application of such topological magnetic quasi-particles for data storage devices. Researchers in a joint collaboration between the University of Leeds and the PolLux endstation have investigated the electrical detection of isolated magnetic skyrmions in applications-relevant nanostructured devices, observing the presence of a strong skyrmion-dependent contribution to the Hall resistivity.
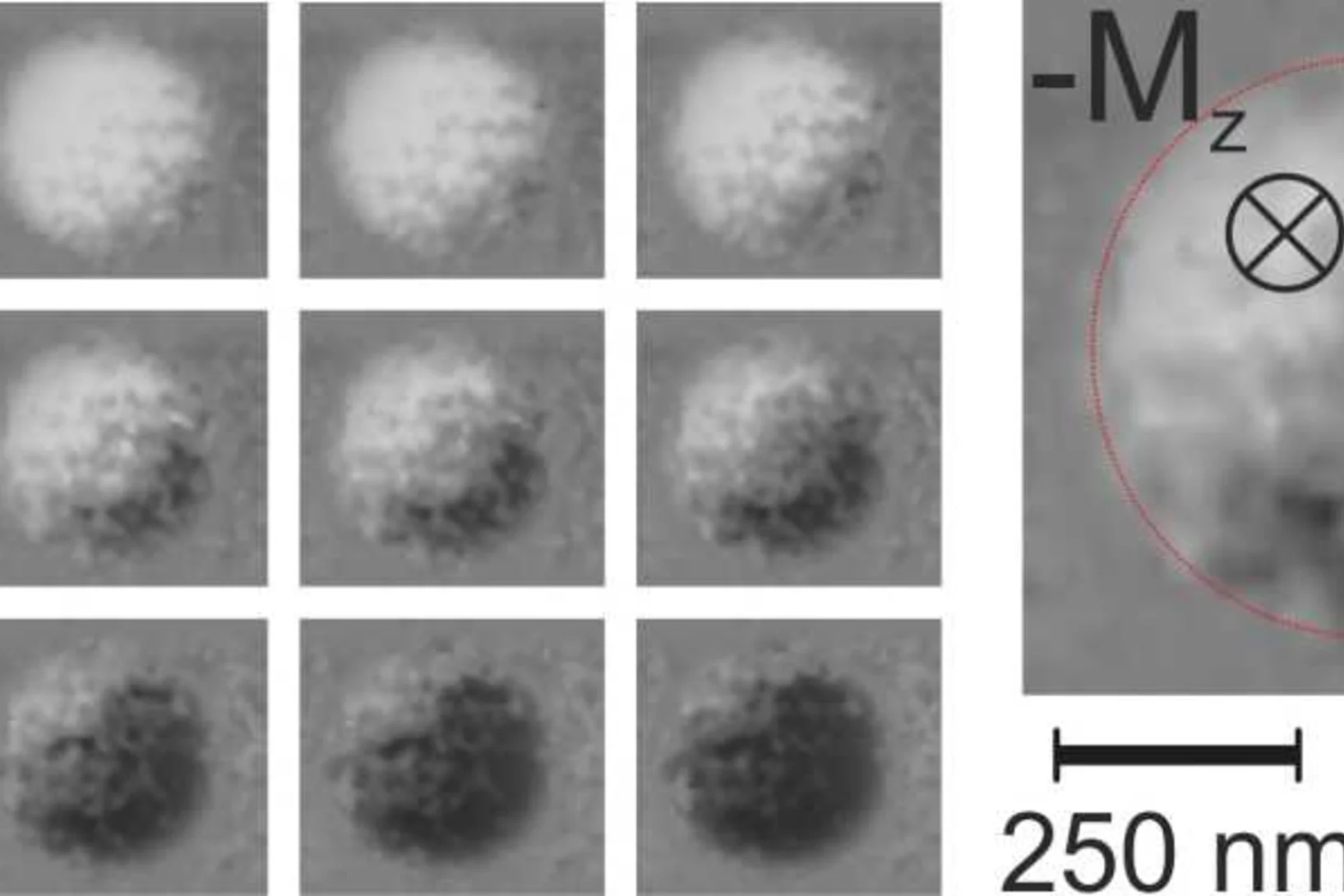
Creation and deletion of isolated magnetic skyrmions via electrical currents
The writing and deletion of magnetic Skyrmions is a fundamental step towards the fabrication of memory devices based on this promising spin configuration. Researchers at the Korea Institute of Technology have demonstrated the writing and deleting of isolated magnetic Skyrmions at room temperature in ferrimagnetic multilayer superlattice stacks using electrical currents.
Fresnel Zone Plates with Zone Widths below 10 nm
The spot size of a Fresnel Zone Plate lens is mainly determined by the zone widths of its outermost zone. It is therefore essential to fabricate zone plates with structures as small as possible for high-resolution X-ray microscopy. Researchers at the Laboratory for Micro- and Nanotechnology at the PSI have now developed Fresnel zone plates with zone widths well below 10 nm, down to 6.4 nm. These lenses are capable of pushing resolution in X-ray microscopy to the single-digit regime.
HERCULES at the Swiss Light Source
In the week of March 18-23 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the HERCULES 2018 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
Time- and spatially-resolved magnetization dynamics driven by spin-orbit torques
Current-induced spin-orbit torques hold a great potential for manipulation of magnetization at ultrafast timescales. Researchers at ETH Zürich have demonstrated, using time-resolved STXM imaging at the Swiss Light Source, the influence of spin-orbit torques on the switching behaviour of Pt/Co/AlOx nanostructured elements.
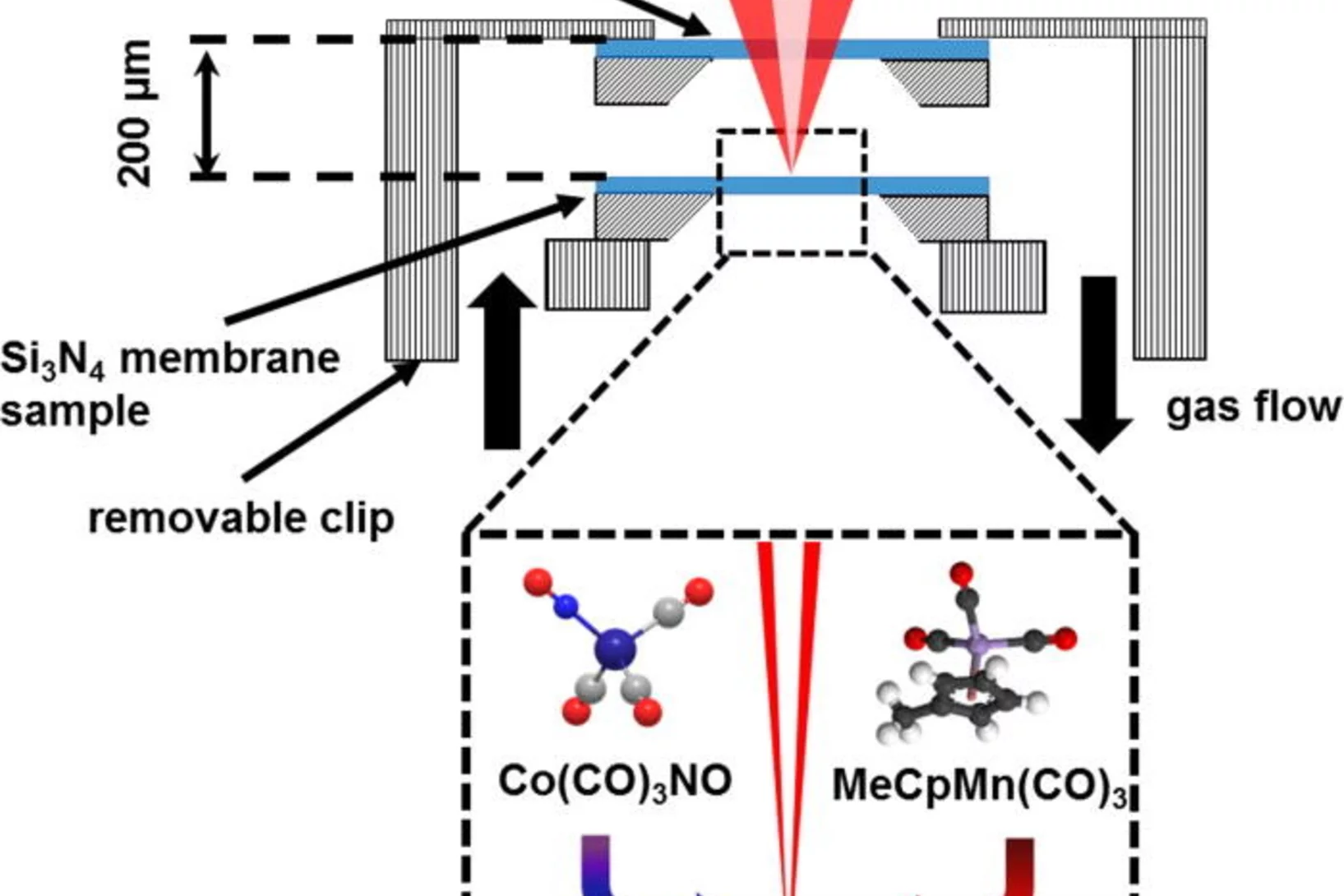
Additive Nanofabrication with Focused X-rays
Metal nanostructures can be fabricated by irradiation of suitable metal organic precursor molecules with a focused X-ray beam. This novel techniques offer the advantage of energy-selective deposition by switching of the incident photon energy due to the non-linear photon absorption cross-section of the precursor molecules for resonant excitation.
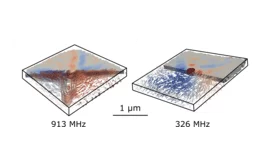
A Mini-Antenna for the Data Processing of Tomorrow
The use of spin-wave signals in future information processing devices can substantially reduce power consumption over present charge current based technologies. As part of an international research venture, scientists at PSI now introduced a concept to generate spin waves with nanoscale wavelengths exploiting the driven dynamics of magnetic vortex cores in magnetic heterostructures.
Nanoscale switch for vortex polarization mediated by Bloch core formation in magnetic hybrid systems
Vortices are fundamental magnetic topological structures characterized by a curling magnetization around a highly stable nanometric core.