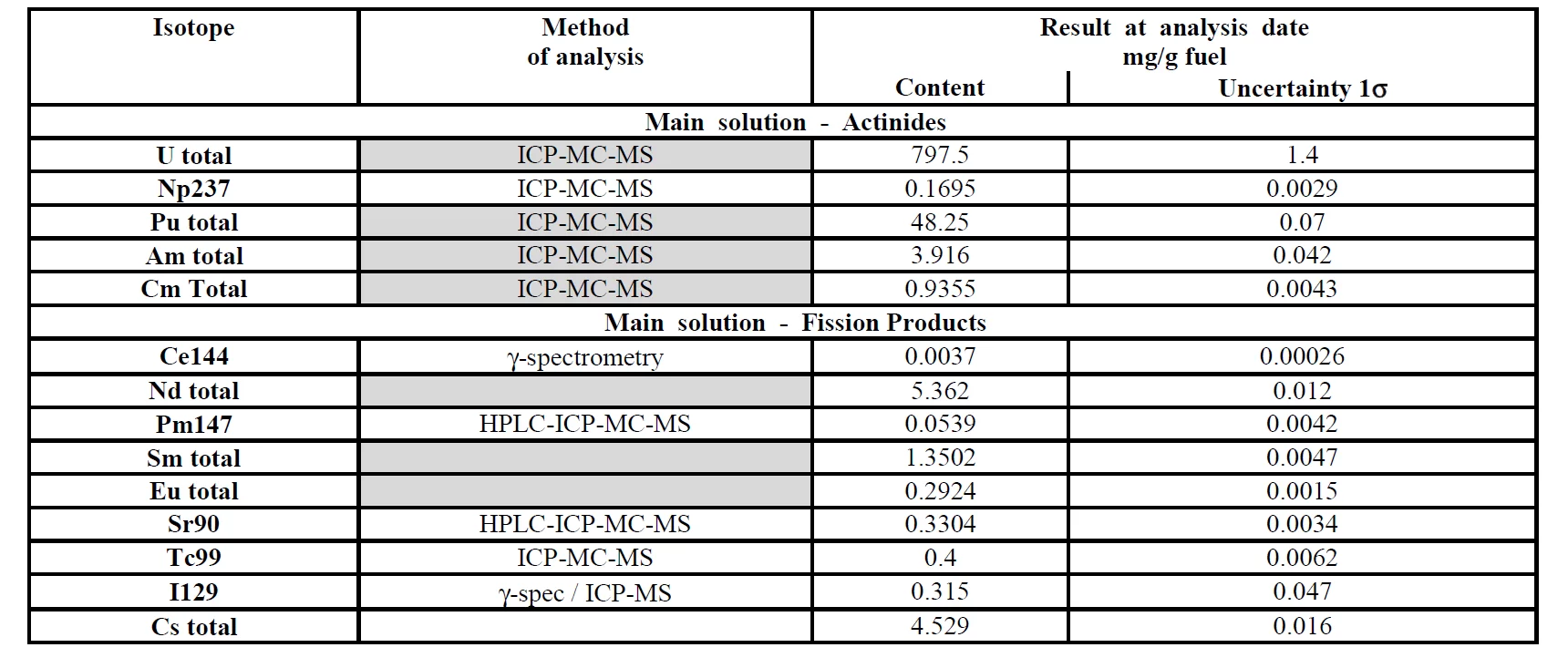
The PSI HOTLAB facility routinely performs examinations of spent nuclear fuel. This consequently leads to the accumulation of high level radioactive waste within the HOTLAB facility. Currently around 700 g of spent nuclear fuel dissolved in approx. 30 liters of 8 M nitric acid are stored within the facility. A representative composition of such fuel waste is presented in Table 1.
For the disposal of this waste extensive radiochemical separations are needed. These can be divided into three steps producing separate waste fractions that will be suitable for repository purposes. The first step is the separation of Uranium and Plutonium as the main α-radiation emitting radionuclides from other nuclides. Separations are performed by the solvent extraction technique with use of TBP (tributyl-phosphate) as extracting agent, offering a high selectivity for tetra- and hexavalent actinides over the other oxidation states during the extraction process. Secondly, a group extraction of lanthanides and minor actinides (mainly Americium and Curium) using HDEHP (Di-(2ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid) as extracting agent is performed. Americium and Curium are then separated from the Lanthanides in the selective stripping with DTPA (diethylenetriamine-pentaacetic acid) also known as Talspeak process (1). The stripping solution is further purified with respect to Americium and Curium by the means of extraction chromatography utilizing the DTPA/Ln-resin system. Fission and activation products that are still left in the waste solution after the previous two steps can be further concentrated on a suitable ion exchanger with sufficiently high radiation stability. The procedure for the sorption of nuclides and eventually selective desorption of valuable or rare radionuclides is under development.
- Weaver B., Kappelmann F.A., Talspeak: A new method of separating Americium and Curium from an aqueous solution of an aminopolyacetic acid complex with a monoacidic organophosphate or phosphonate. August 1964, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, ORNL-3559