Scope of project
At Roveredo in the Mesolcina Valley in Switzerland, we studied the air-quality focusing on particulate matter and some gasphase parameters. Wood burning emissions were in general found to be very important in this region because 80% of the houses in Roveredo and the neighbouring villages are heated with wood.
Field campaigns
- Roveredo Dec 2004 - Jan 2005, Mar 2005, Jun 2005, Nov-Dec 2005
Key findings
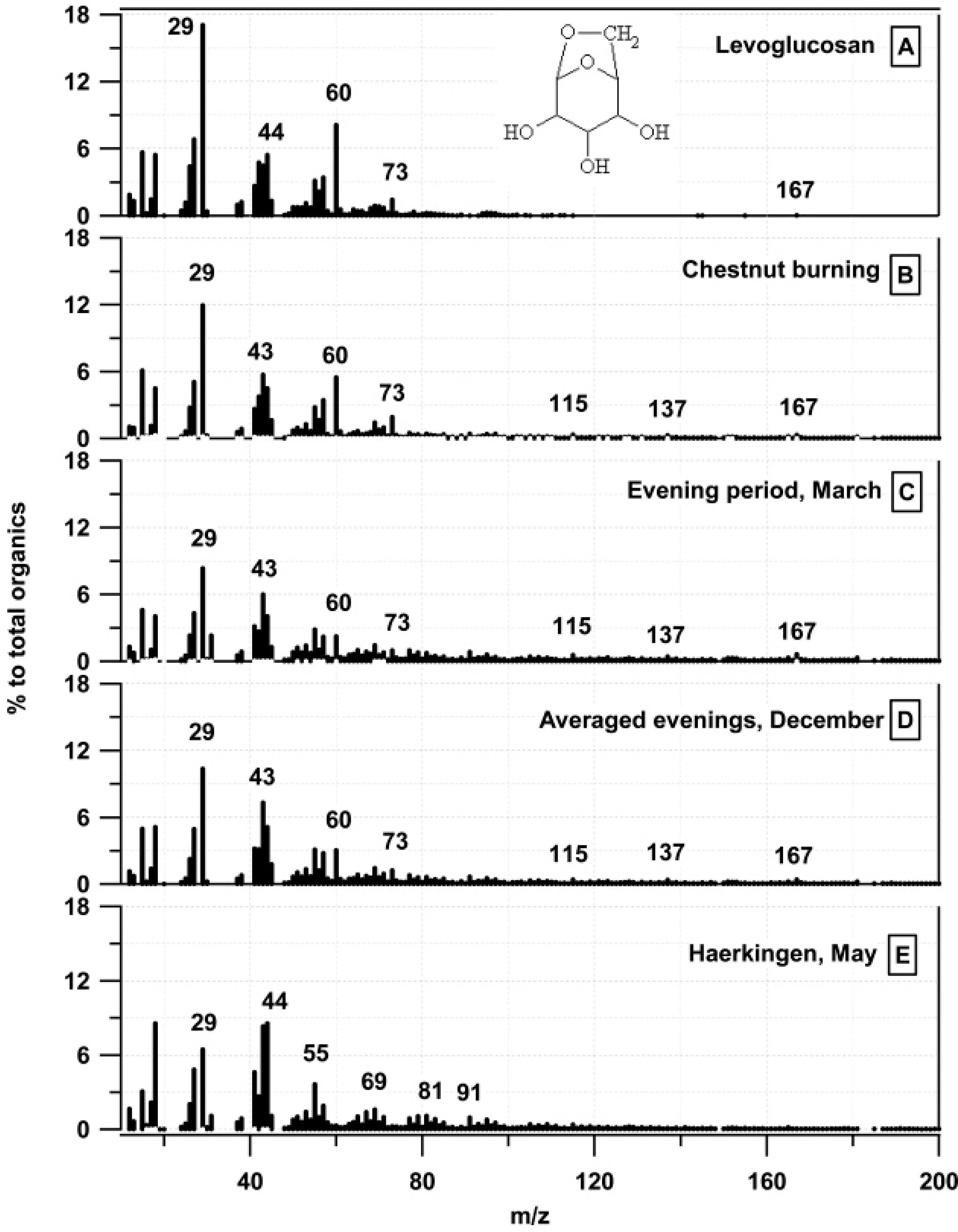
- First comparison of wood burning emission spectra with ambient measurements revealing high importance of wood burning in Roveredo (Alfarra et al., 2007)
- Identification of m/z60, 73, 137 as markers of wood burning (Alfarra et al., 2007)
- OC nearly completely due to non-fossil carbon (Szidat et al., 2007)
- Even EC is sometimes more than 50% non-fossil which is very unusual (Szidat et al., 2007)
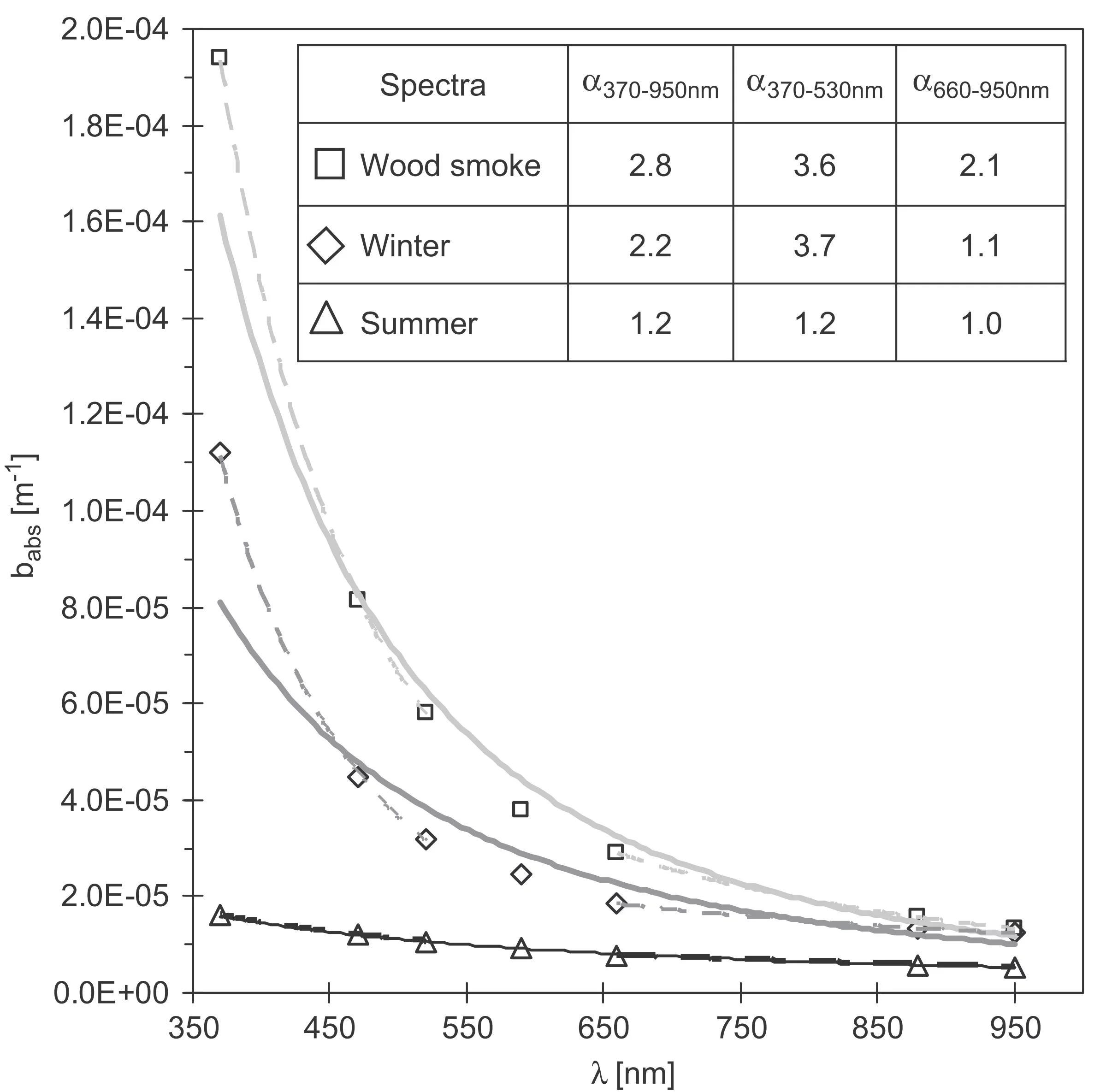
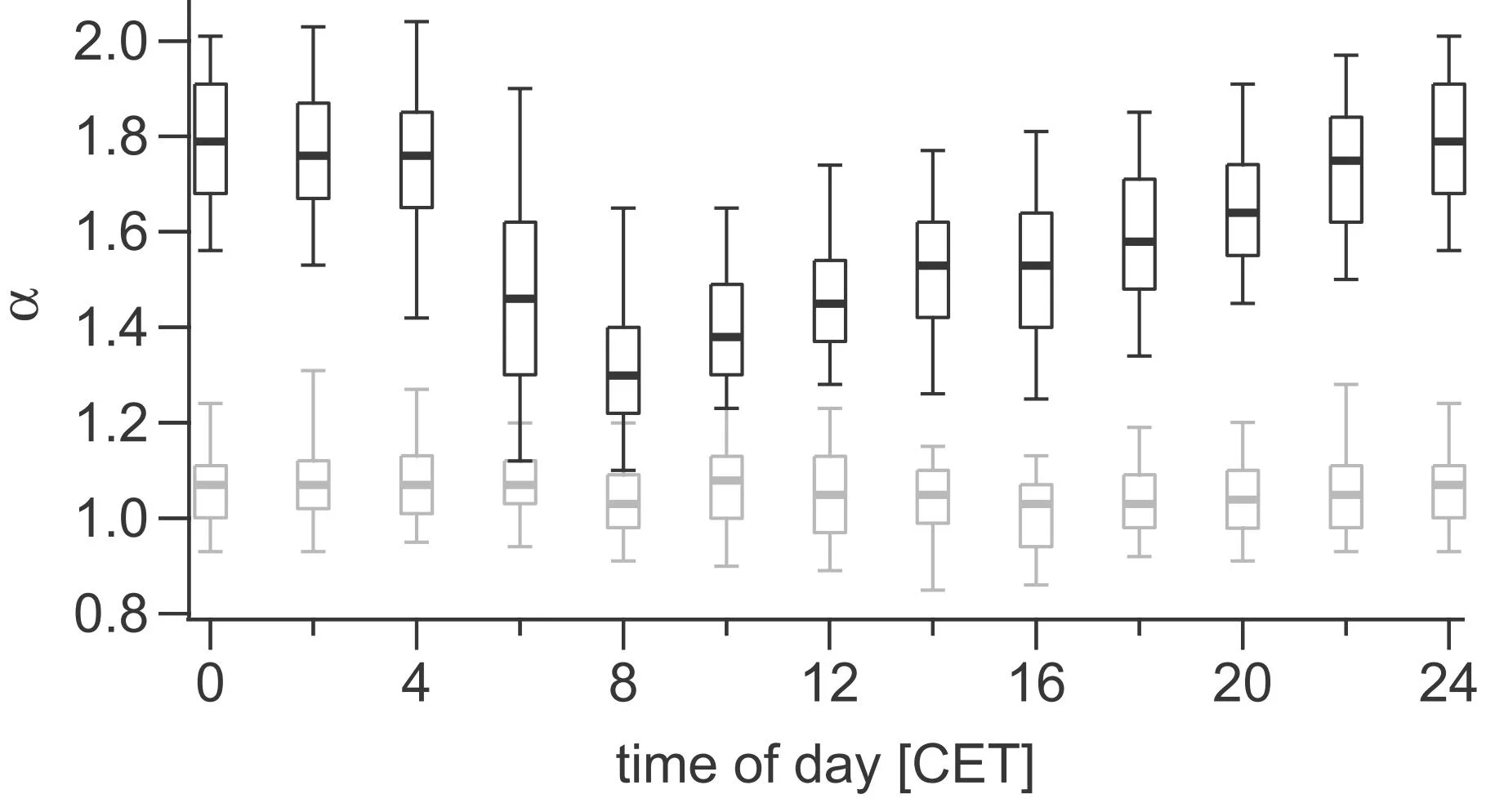
- The average power law exponents alpha of the light absorption coefficients (between lambda 370 and 950 nm were 1.6 in winter and 1.1 in summer on average (Sandradewi et al., 2008a)
- In the evening with high wood burning contributions the absorption exponents alpha were 2.7 (370-520nm) and 1.3 (660-950 nm) (Sandradewi et al., 2008a)
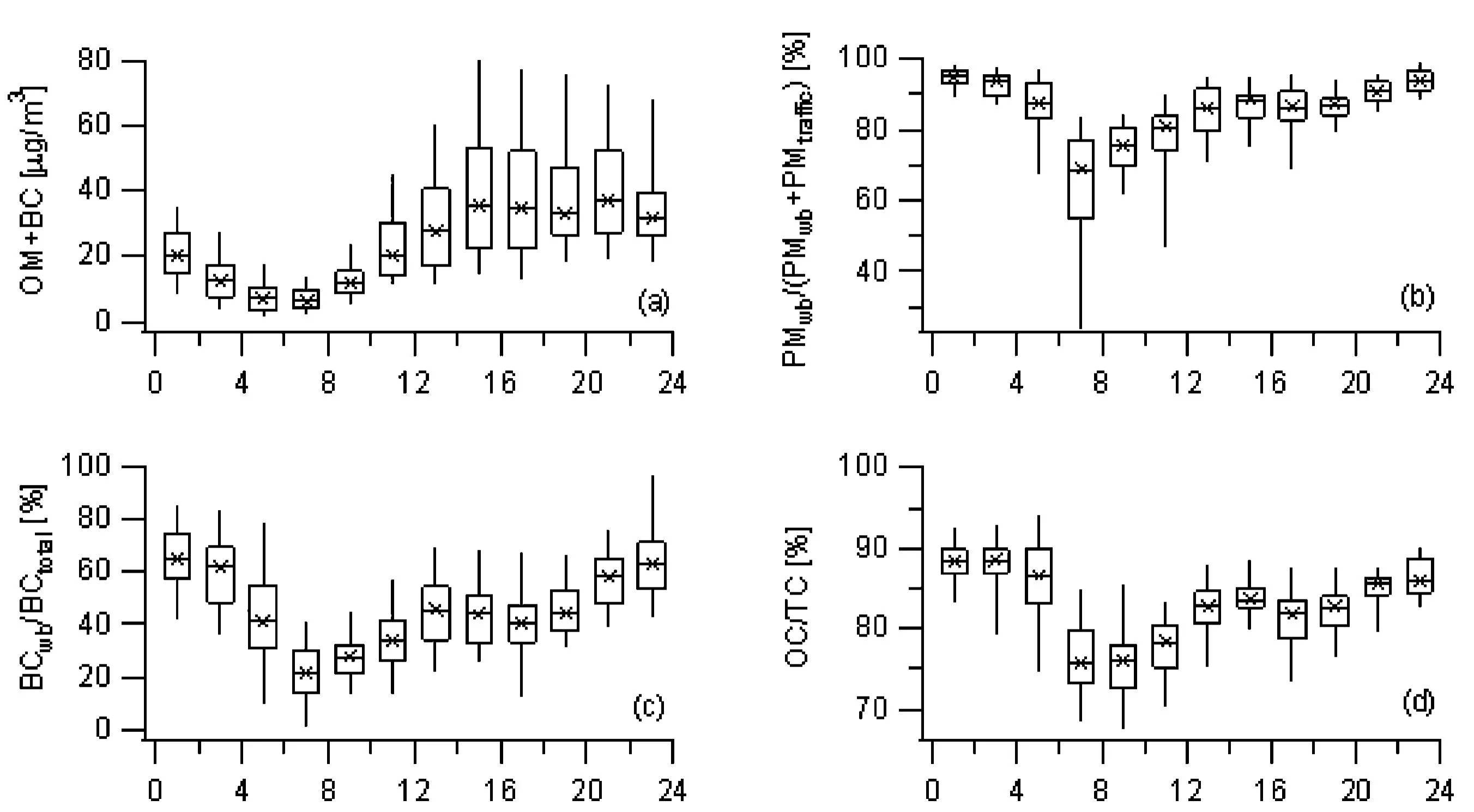
- The first quantitative method was developed to quantify the contributions of wood burning and traffic to black carbon and to carbonaceous matter. The method was calibrated by using 14C and AMS data (Sandradewi et al., 2008b).
- On average, 51% of black carbon was assigned to wood burning and 49% to traffic. 88% of the total carbonaceous material was assigned to wood burning and 12% to traffic (Sandradewi et al., 2008b) Lanz et al. (2010) suggest that a large fraction of the organics is secondary.
- Strong diurnal cycles of the organics and the wood burning contributions were found with maxima in the evening to the early night (Sandradewi et al., 2008a; 2008b)
- Of the NMHCs and OVOCs analyzed most were assessed to be very strongly influenced by wood burning exept trimethylbenzene, methylbutenol and isopropanol dominated by traffic. Especially dominated by wood burning were methanol, 1,3-butadiene, acrolein, methacrolein, methylacetate, and methyl vinyl ketone (Gaeggeler et al., 2008)
- Using stable isotope measurements, 70% of the night time carbon monoxide was assessed to come from wood burning in Roveredo (Saurer et al., 2009)
Further Information
- 14-C Analysis
- Aerosol Mass Spectrometer
- Aethalometer
- Stable Isotopes
Publications
Journal Articles
Identification of the mass spectral signature of organic aerosols from wood burning emissions.Alfarra, M. R., A. S. H. Prevot, S. Szidat, J. Sandradewi, S. Weimer, D. Schreiber, M. Mohr, and U. Baltensperger, 2007
Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 5770-5777.
Residential wood burning in an Alpine valley as a source for oxygenated volatile organic compounds, hydrocarbons and organic acids.
Gaeggeler, K., A. S. H. Prevot, J. Dommen, G. Legreid, S. Reimann, and U. Baltensperger, 2008
Atmospheric Environment, 42, 8278-8287.
Characterization of aerosol chemical composition with aerosol mass spectrometry in Central Europe: an overview.
Lanz, V. A., A. S. H. Prévôt, M. R. Alfarra, S. Weimer, C. Mohr, P. F. DeCarlo, M. F. D. Gianini, C. Hueglin, J. Schneider, O. Favez, B. D'Anna, C. George, and U. Baltensperger, 2010
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 10, 10453-10471.
Using aerosol light absorption measurements for the quantitative determination of wood burning and traffic emission contributions to particulate matter.
Sandradewi, J., A. S. H. Prevot, S. Szidat, N. Perron, M. R. Alfarra, V. A. Lanz, E. Weingartner, and U. Baltensperger, 2008
Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 3316-3323.
A study of wood burning and traffic aerosols in an Alpine valley using a multi-wavelength aethalometer.
Sandradewi, J., A. S. H. Prevot, E. Weingartner, R. Schmidhauser, M. Gysel, and U. Baltensperger, 2008
Atmos. Environ., 42, 101-112.
The influence of traffic and wood combustion on the stable isotopic composition of carbon monoxide.
Saurer, M., A. S. H. Prevot, J. Dommen, J. Sandradewi, U. Baltensperger, and R. T. W. Siegwolf, 2009
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 3147-3161.
Dominant impact of residential wood burning on particulate matter in Alpine valleys during winter.
Szidat, S., A. S. H. Prevot, J. Sandradewi, M. R. Alfarra, H.-A. Synal, L. Wacker, and U. Baltensperger, 2007
Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L05820, doi:10.1029/2006GL028325.
Funding
Canton Graubünden and the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN).
The GC-MS data were provided by the Laboratory for Air Pollution/Environmental Technology at Empa (Materials Science and Technology), Switzerland.