Show filters
Dreidimensionaler Blick in aktive Katalysatoren
Die operando-Röntgenspektroskopie erlaubt einen Blick ins Innere laufender Chemiereaktoren. Forschende des Karlsruher Instituts für Technologie (KIT), am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI und an der European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Frankreich setzen die Methode erfolgreich ein.
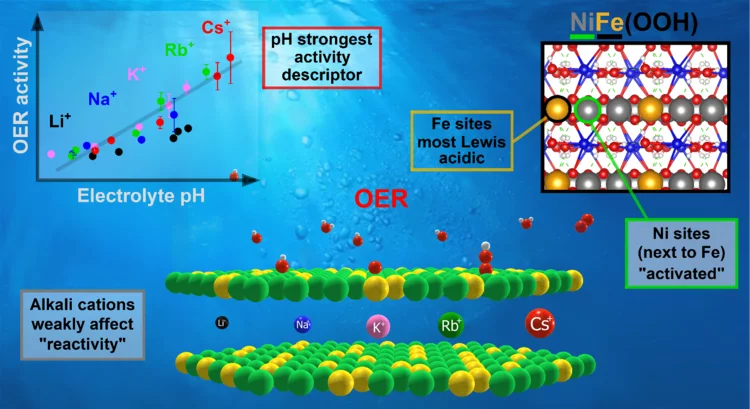
Key activity descriptors of nickel-iron oxygen evolution electrocatalysts in the presence of alkali metal cations
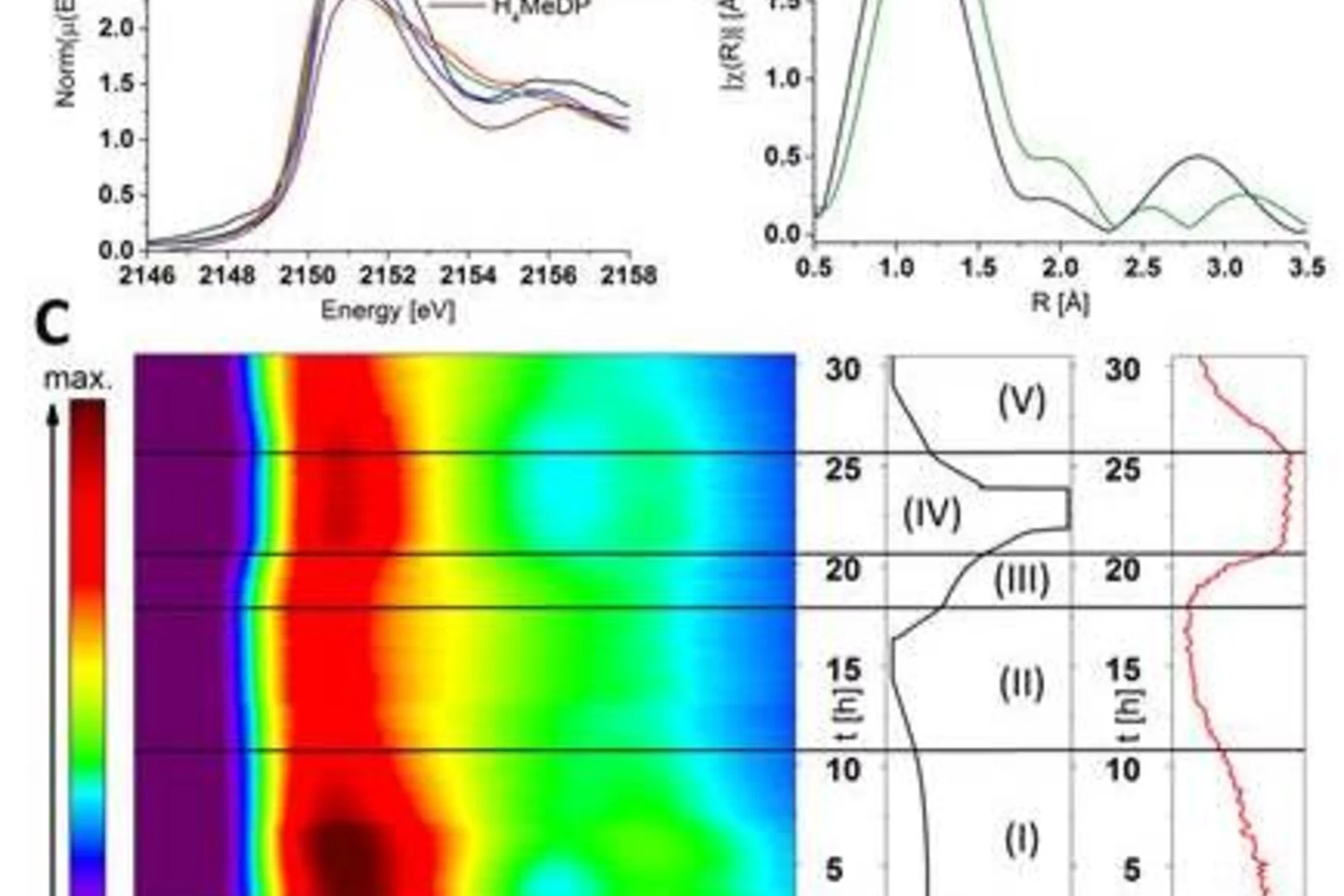
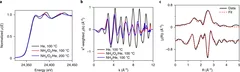
Ni-Fe oxyhydroxide is among the most active oxygen evolution electrocatalysts. Electrolyte alkali metal cations modify the activity and reaction intermediates, however, the exact mechanism is at question due to unexplained deviations from the cation size trend. Our X-ray absorption spectroelectrochemical results show that the OER activity follows the variations in .electrolyte pH rather than a specific cation. Our DFT-based reactivity descriptors confirm the conclusions of an indirect pH effect.
Ruzicka Prize
The Ružička Prize 2020 goes to Dr. Patrick Hemberger (PSI) for his research on understanding the mechanisms of catalytic fast pyrolysis by unveiling reactive intermediates in heterogeneous catalysts.
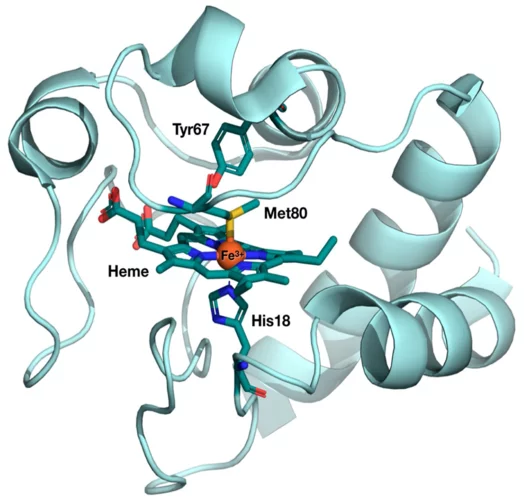
Spin cascade and doming in ferric hemes
In biology, structure and function are closely interwoven. A case in point is oxygen transport in the lungs, which relies on ferrous heme proteins adopting dome-like shapes.
First light in the SwissFEL Maloja endstation
The first endstation at the SwissFEL Athos soft X-ray branch is rapidly developing and on track for first experiments in 2021.
Unraveling the structural dynamics of Heme proteins at SwissFEL
The results from the very first user experiment at SwissFEL have just been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The measurements probed the electron transport properties of the cytochrome c protein, which is found in cellular mitochondria. The measurements show that when the Fe atom at the centre of the protein undergoes electronic excitation, for example when it gains or loses and electron, the active centre of the protein undergoes a doming structural rearrangement. This result raises interesting questions about how this structural change is involved in the electron transfer properties of cytochrome c.
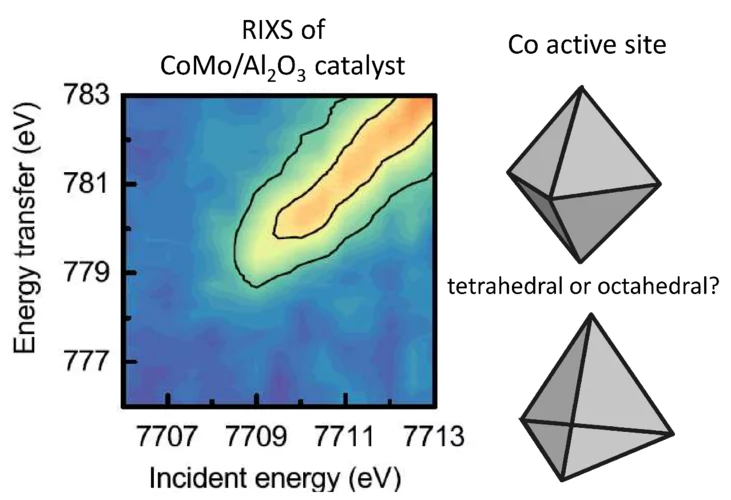
The structure of active sites of CoMo/Al2O3 catalysts determined by RIXS spectroscopy.
A fundamental understanding of the active sites in technical CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts is crucial to improve the production of clean transportation fuels by hydrodesulfurization (HDS), which removes sulfur from fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide, resulting from fossil fuel combustion, is one of the main causes for acid rain. In situ X-ray spectroscopic experiments at the SuperXAS beamline of the SLS provided insight in the structure and number of active sites (“Co−Mo−S”) in sulfided CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts. When the Co to Mo ratio is less than 0.1, cobalt forms isolated sites on the MoS2 phase, where the cobalt promoter atoms are in centrosymmetric octahedral coordination with six-sulfur ligands.
Methylbismuth: First observation of an organometallic biradical reactive intermediate
Open shell organometallic bismuth are promising agents for catalytic applications, but difficult to characterize due to their high reactivity. The simplest methylbismuth (Bi-CH3), a biradical species, was in-situ synthesized and spectroscopically characterized for the first time. Electronic and thermochemical properties could be obtained, which will guide future synthetic applications.
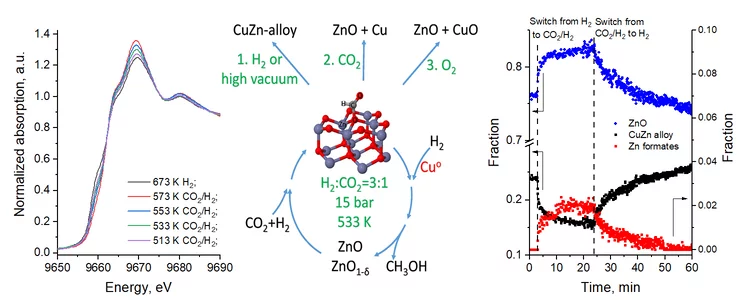
The unique interplay between copper and zinc during catalytic carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methanol
The nature of high activity of Cu/ZnO catalyst in methanol synthesis remains the subject of intensive debate. Here, the authors are revisiting carbon dioxide hydrogenation mechanism using high-pressure operando techniques.
Operando X-ray diffraction during laser 3D printing
Ultra-fast operando X-ray diffraction experiments reveal the temporal evolution of low and high temperature phases and the formation of residual stresses during laser 3D printing of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The profound influence of the length of the laser-scanning vector on the evolving microstructure is revealed and elucidated.
Auf der Suche nach dem Leuchtmaterial der Zukunft
Am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI haben Forschende Einblicke in ein vielversprechendes Material für organische Leuchtdioden (OLEDs) erhalten. Das neue Verständnis wird helfen, Leuchtmaterialien mit hoher Lichtausbeute zu entwickeln, die kostengünstig herzustellen sind.
Taking a snapshot of the triplet excited state of an OLED organometallic luminophore using X-rays
In this work, the complementarity of pump-probe experiments at SwissFEL (ALVRA endstation) and at synchrotrons (SuperXAS beamline of SLS and ID09 of ESRF) is used to investigate the triplet excited state of Cu OLED materials. Details about the charge transfer and structural rearrangements in the excited state of this material are revealed and obtained data can be used to verify computational methods for rational development of new OLED materials.
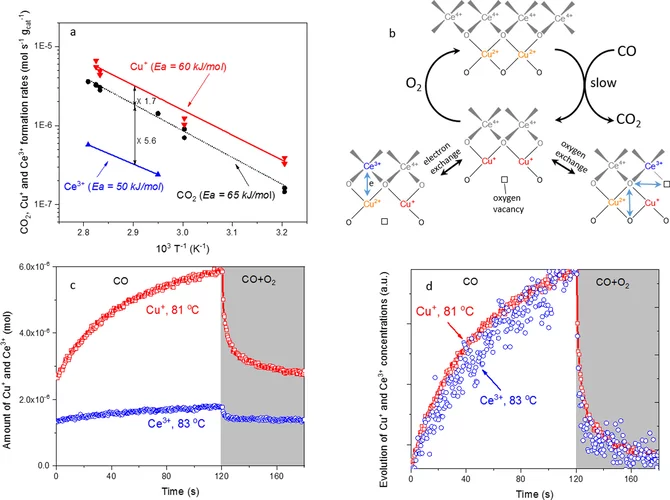
Elucidating the Oxygen Activation Mechanism on Ceria-Supported Copper-Oxo Species Using Time-Resolved X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
We monitored the dynamic structure of the active sites in a catalyst containing highly dispersed copper-oxo species on ceria during low-temperature CO oxidation using time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy. We quantitatively demonstrate that the CO oxidation mechanism below 90 °C involves an oxygen intermediate strongly bound to the active sites as well as the redox activity of Cu2+/Cu+ and Ce4+/Ce3+ couples.
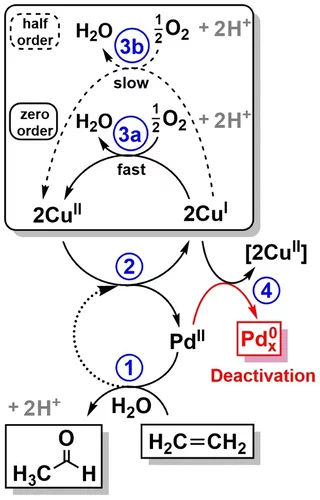
Elucidating the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y by transient XAS
Unlike the homogeneous Wacker process, the understanding of the mechanism of the heterogeneous system has long remained to be superficial. Here the authors investigated the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y through transient XAS coupled with kinetic studies and chemometric analysis.
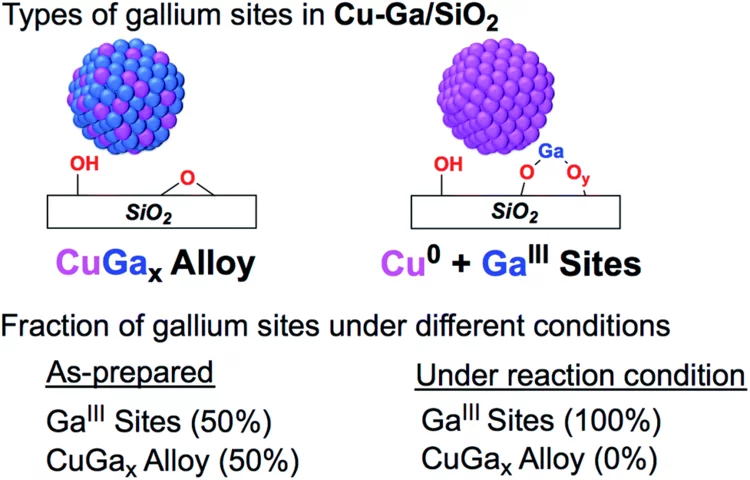
Enhanced CH3OH selectivity in CO2 hydrogenation using Cu-based catalysts generated via SOMC from GaIII single-sites
Small and narrowly distributed nanoparticles of copper alloyed with gallium supported on silica containing residual GaIII sites can be obtained via surface organometallic chemistry. This material is highly active and selective for CO2 hydrogenation to CH3OH. In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy shows that gallium is oxidized under reaction conditions while copper remains as Cu0.
Spectroscopic disentanglement of the quantum states of highly excited dicopper molecules
Transition metals, characterized by their partially filled d-orbitals, provide the basis for many of the most relevant processes in chemistry, biology, and physics. Embedded as single atoms or in small clusters, they give rise to exceptional optical, chemical, and magnetic properties. So far, it has proven impossible to disentangle the complex network of excited quantum states, which greatly hinders predicting and controlling of material properties. We employed double-resonant four-wave mixing spectroscopy to quantitatively resolve the bright and perturbing dark quantum states of the neutral copper dimer.
Christoph Bostedt named APS Fellow
Christoph Bostedt, Head of the Laboratory for Femtochemistry, was named APS Felllow. He received his fellowship certificate at at the 50th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics (DAMOP) APS Meeting in Milwaukee.
HERCULES school 2019 at SLS
In the week of April 1-5 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the European HERCULES 2019 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
Inside Batteries
Lithium ion batteries (LIB) are essential in modern everyday life, with increasing interest in enhancing their performance and lifetime. Secondary particles of Li-rich cathode material were examined with correlated ptychographic X-ray tomography and diffraction microscopy at different stages of cycling to probe the aging mechanism.
Selective Alkane Functionalization to Olefins
Light alkanes are abundantly available and cheap resources that are often burned at oil wells because of the missing infrastructure for valorization. Novel technologies are needed for their selective functionalization to use natural gas as an energy vector in the transition between the oil and the renewables era. Catalytic oxyhalogenation may unlock the transformation of cheap and abundant alkanes into commodities. When chlorine-based reactions are compared with bromine, improved selectivities above an iron catalyst arise from surface-confinement of the reaction mechanism in the case of chlorine as halogen.
Investigation of anionic redox activities in organic-based electrode for Li-ion batteries
To date the electrochemical activity of battery materials was always relying in the oxidation/reduction of cationic redox (change of oxidation state of transition metals generally). However, recently, it was established in new cathode materials (so call Li-rich cathode) that the oxygen from the crystal lattice might also play the role of anionic redox center leading to enhance then the specific charge of battery materials.
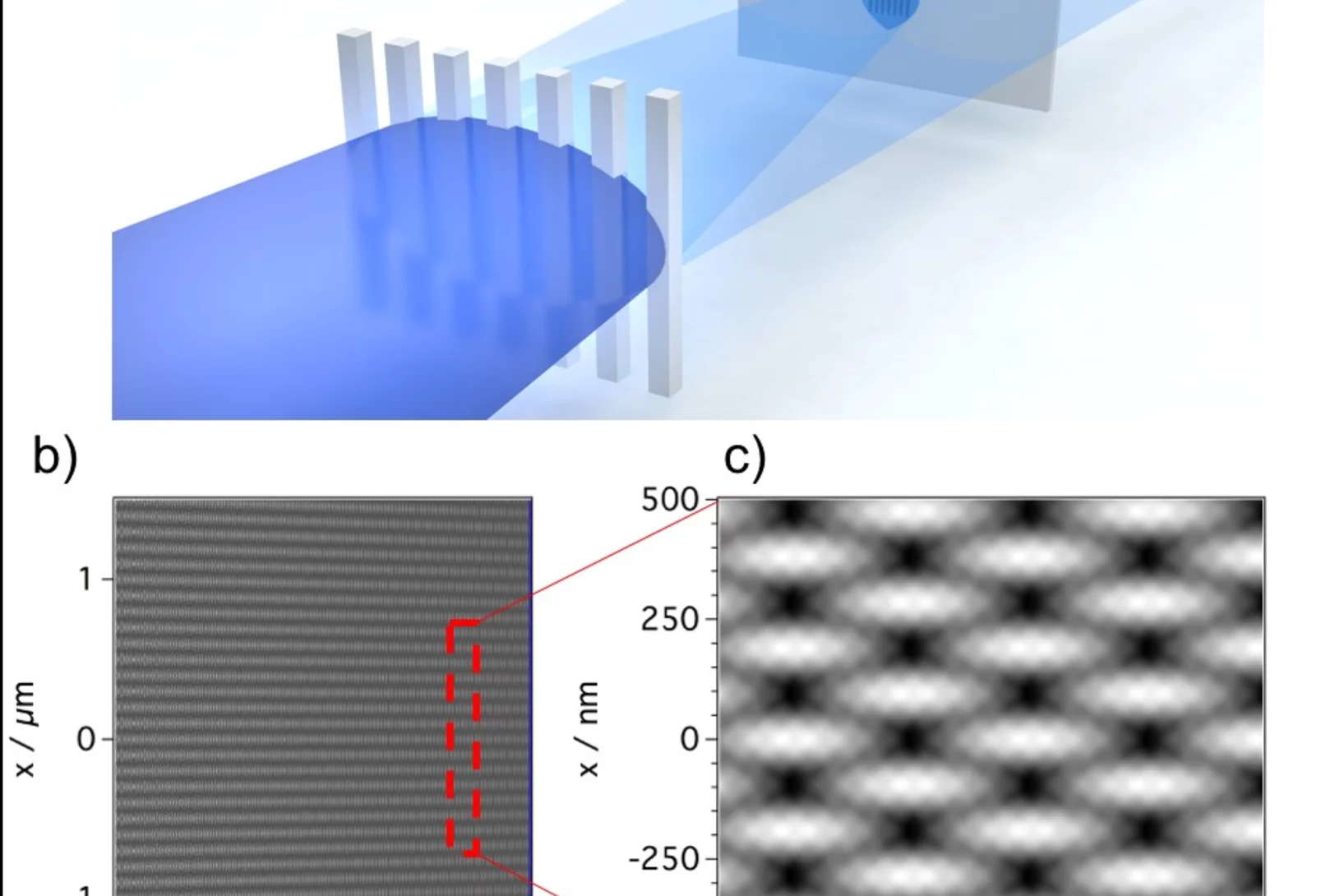
Towards X-ray Transient Grating Spectroscopy at SwissFEL
The high brilliance of new X-ray sources such as X-ray Free Electron Laser opens the way to non-linear spectroscopies. These techniques can probe ultrafast matter dynamics that would otherwise be inaccessible. One of these techniques, Transient Grating, involves the creation of a transient excitation grating by crossing X-ray beams on the sample. Scientists at PSI have realized a demonstration of such crossing by using an innovative approach well suited for the hard X-ray regime.
Structural selectivity of supported Pd nanoparticles for catalytic NH3 oxidation resolved using combined operando spectroscopy
The link between Pd nanoparticle structure and surface reactivity for NH3 abatement was found using operando X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy, diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier-transformed spectroscopy and on-line mass spectrometry.
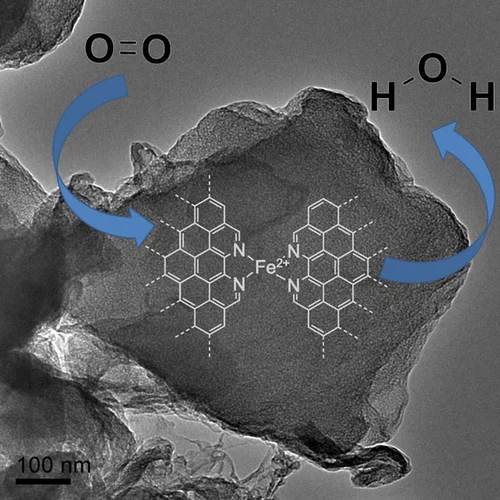
Fe-Based O2-Reduction Catalysts Synthesized Using Na2CO3 as a Pore-Inducing Agent
This work presents a new approach for synthesizing Fe-based oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalysts using sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) as an inexpensive but effective pore-inducing agent offering microporosity control.
First femtosecond protein pump-probe measurements at SwissFEL
A major milestone in the commissioning of SwissFEL has been reached: the first pump-probe experiments on proteins have been successfully carried out. Crystals of several retinal-binding proteins were delivered in a viscous jet system and a femtosecond laser was used to start the isomerization reaction. Microsecond to sub-picosecond snapshots were then collected, catching the retinal proteins shortly after isomerization of the chromophore.
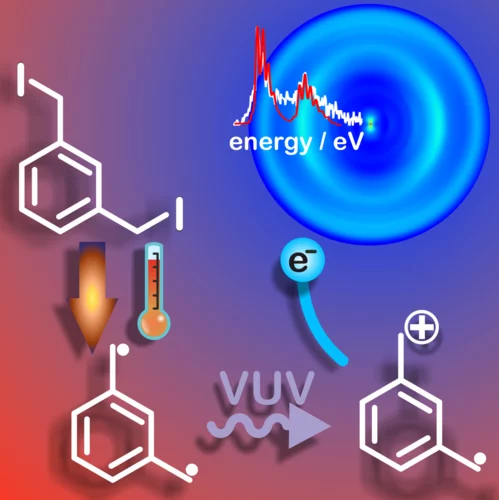
Taming Reactive Molecular Magnets
Studying organic molecular magnets is a challenge, because the high-spin diradical character of these compounds dramatically increases the reactivity and reduces the lifetime. Researchers from PSI, ETH Zurich, Wollongong and Melbourne, Australia succeeded in taming the meta-xylylene diradical and were able to study its electronic and thermochemical properties.
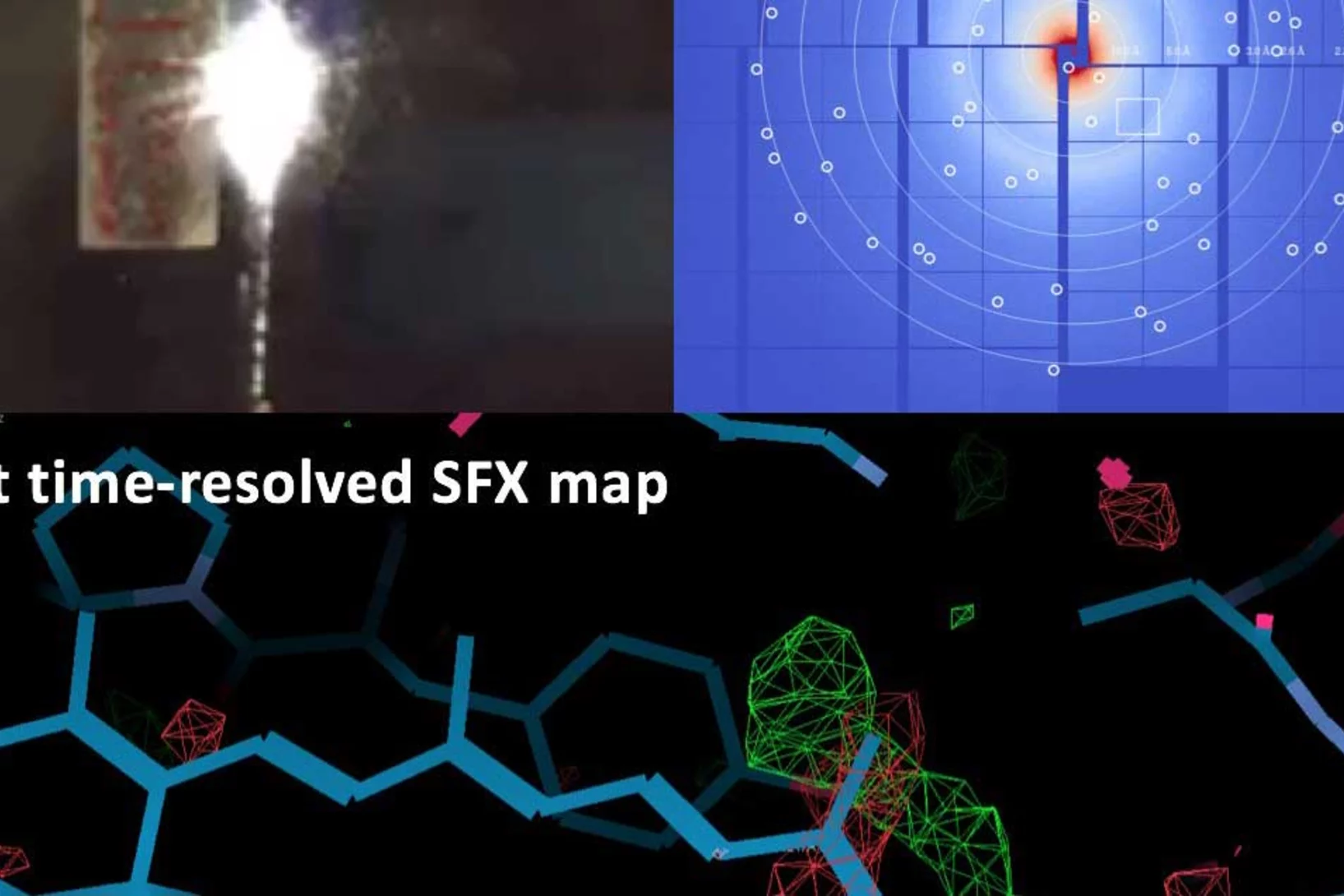
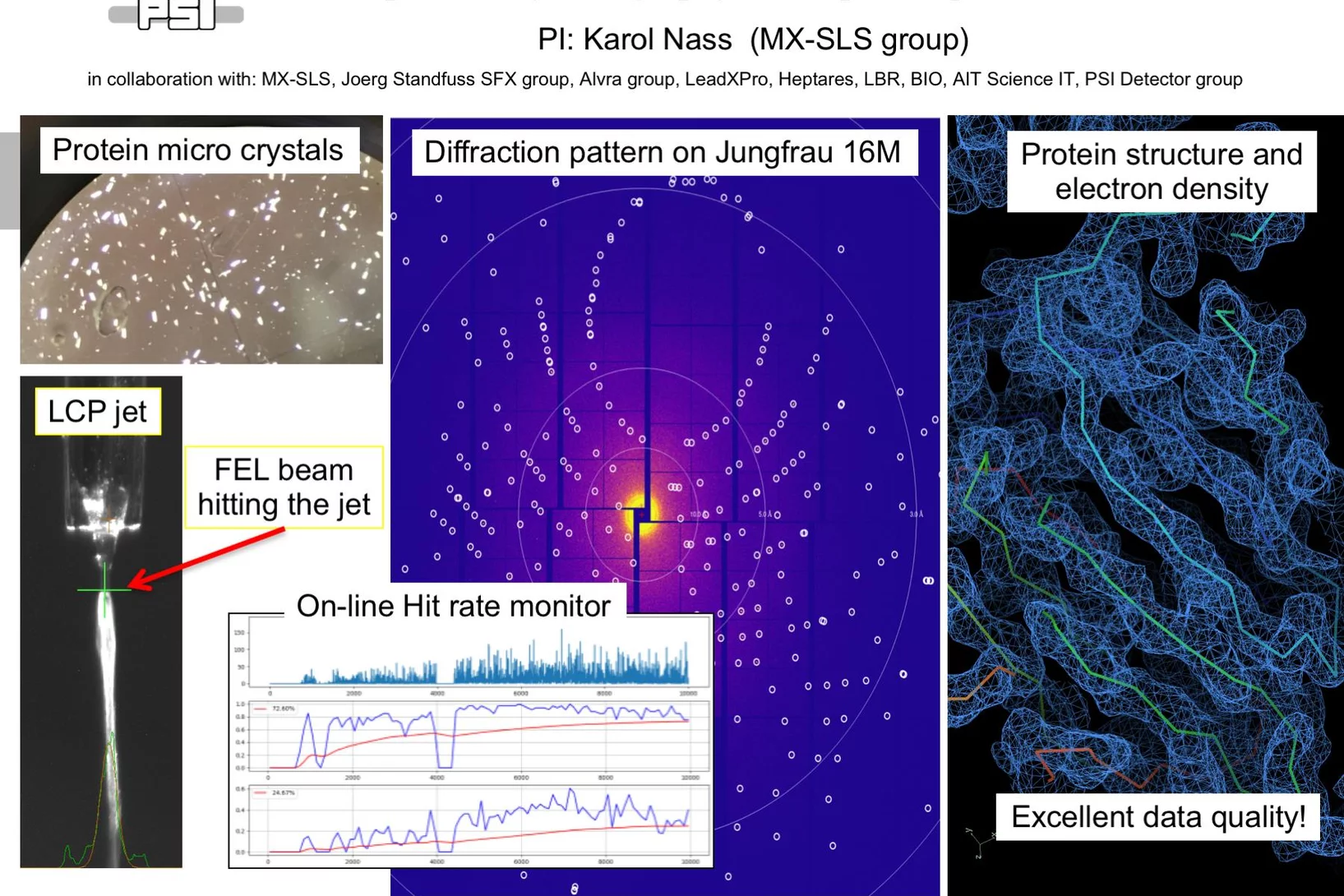
First serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) pilot user experiment at SwissFEL
On the 7th to 12th of August 2018, a collaborative group of scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute and members of the LeadXpro and Heptares pharmaceutical companies led by Karol Nass (PSI macromolecular crystallography MX-SLS group) performed the first serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) pilot user experiment at the SwissFEL X-ray free electron laser (XFEL).
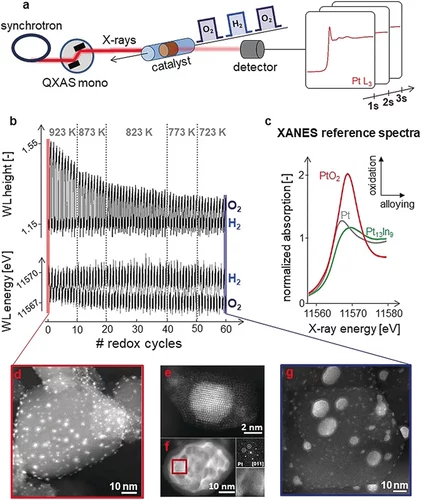
Kinetics of Lifetime Changes in Bimetallic Nanocatalysts Revealed by Quick X‐ray Absorption Spectroscopy
The different reaction steps involved in repeated Pt13In9 segregation‐alloying are identified by XAS and kinetically characterized at the single‐cycle level.
The SLS congratulates Ronald Frahm for receiving the IXAS outstanding achievement Award 2018
The highest award of the international X-ray absorption spectroscopy (IXAS) society, the Edward Stern Outstanding Achievement Award, was presented to Prof. Ronald Frahm during the tri-annual IXAS meeting in Kraków, Poland in July 2018.
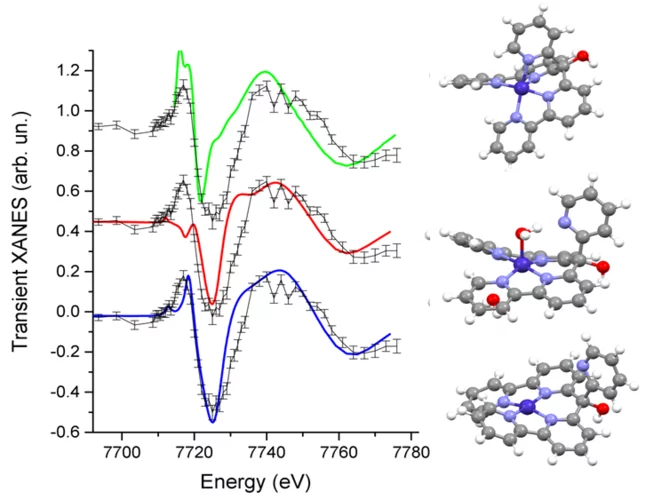
Structure of the Co(I) Intermediate of a Cobalt Pentapyridyl Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Revealed by Time‐Resolved X‐ray Spectroscopy
The mechanism of hydrogen evolution by cobalt polypyridyls catalysts is investigated. Pump-probe X‐ray absorption spectra measured at SuperXAS in the microsecond time range indicate that the pendant pyridine dissociates from the cobalt in the intermediate Co(I) state. This opens the possibility for pyridinium to act as an intramolecular proton donor, which can be used for the development of efficient catalysts.