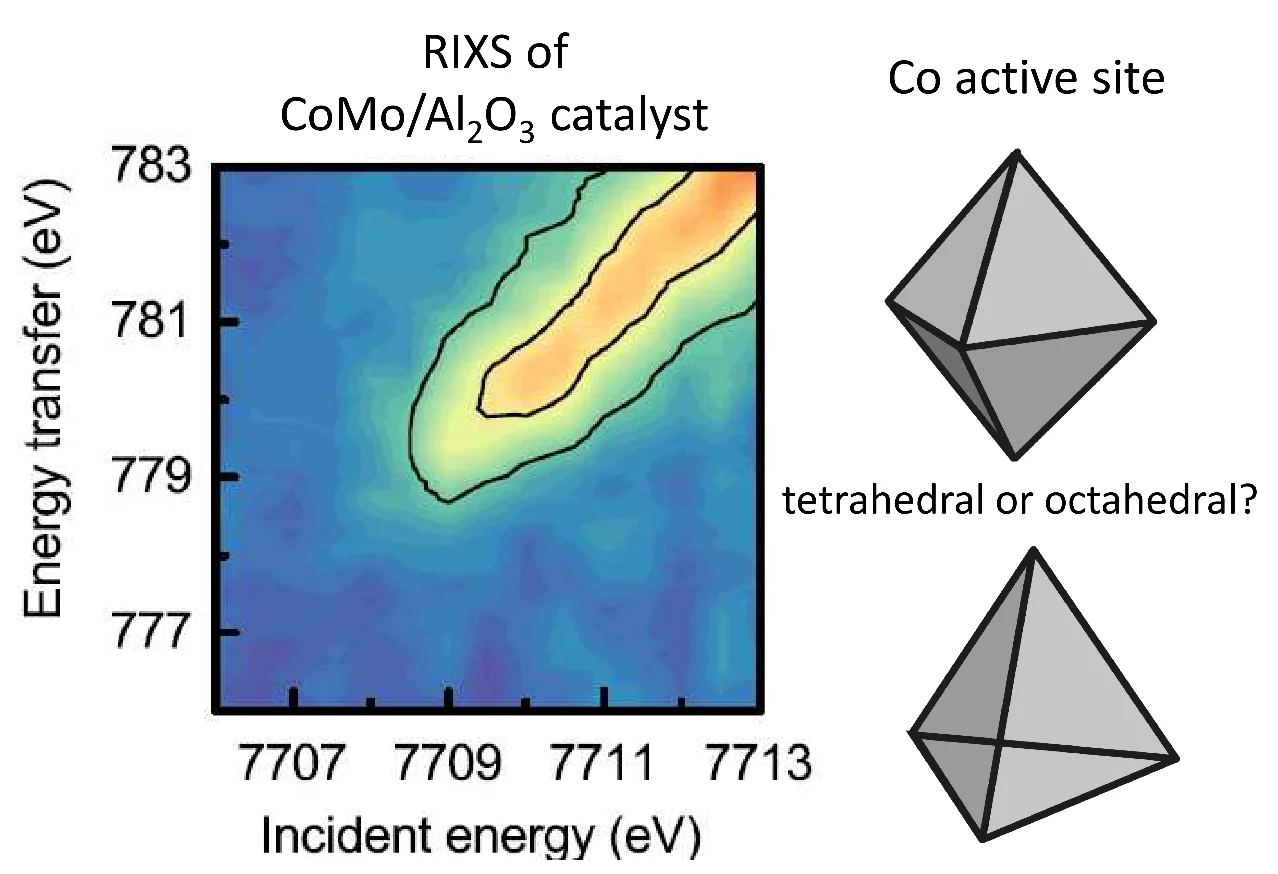
A fundamental understanding of the active sites in technical CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts is crucial to improve the production of clean transportation fuels by hydrodesulfurization (HDS), which removes sulfur from fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide, resulting from fossil fuel combustion, is one of the main causes for acid rain. In situ X-ray spectroscopic experiments at the SuperXAS beamline of the SLS provided insight in the structure and number of active sites (“Co−Mo−S”) in sulfided CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts. When the Co to Mo ratio is less than 0.1, cobalt forms isolated sites on the MoS2 phase, where the cobalt promoter atoms are in centrosymmetric octahedral coordination with six-sulfur ligands.
A fundamental understanding of the number and structure of active sites in alumina supported CoMo catalysts is crucial to improve the production of clean transportation fuels by hydrodesulfurization (HDS). In situ 1s2p resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), collected at the SuperXAS beamline of the SLS, provided insight in the coordination state and number of active sites (“Co−Mo−S”) of the sulfided CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts prepared with and without chelating additives. Based on the evaluation of thiophene HDS activity as a function of the Co/Mo ratio, it was determined that only for Co/ Mo < 0.1, cobalt is exclusively in interaction with the MoS2 phase, making this the ideal catalyst for identifying the nature of the active cobalt sites for hydrogenolysis. These cobalt promoter atoms were identified to be in centrosymmetric coordination with the MoS2 phase, with six sulfur ligands coordinated to each cobalt center. The octahedral coordination of cobalt in Co−Mo−S in alumina-supported HDS catalysts contrasts the tetrahedral cobalt coordination found in co-promoted MoS2 model systems supported on gold or carbon. We attribute the difference to the more disordered MoS2 structures in technical alumina-supported HDS catalysts. The number of Co−Mo−S sites depended strongly on the catalyst preparation method. Chelating additives, such as citric acid and nitrilotriacetic acid, increased the number of Co−Mo−S sites without significantly altering their intrinsic activity. These results demonstrate that state-of-the-art structural characterization tools, such as RIXS, identify the structure of active sites in actual technical catalysts and that these structures may be different from model systems. Combining such characterization tools with guided catalyst design can provide an insight into the structure of amorphous, nanostructured materials, which aid in the development of improved heterogeneous catalysts for widely used catalytic processes.
Contact
Dr. Grigory Smolentsev
SuperXAS beamline
Operando spectroscopy group & Laboratory for Synchrotron Radiation and Femtochemistry (LSF)
Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Intitute
5232 Villigen-PSI, Switzerland
+41 56 310 58 05
grigory.smolentsev@psi.ch
Original Publication
Evidence of Octahedral Co–Mo–S Sites in Hydrodesulfurization Catalysts as Determined by Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering and X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
Lennart van Haandel, Grigory Smolentsev, Jeroen A. van Bokhoven, Emiel J.M. Hensen, Thomas Weber
ACS Catalysis , 31 August 2020
DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.0c03062