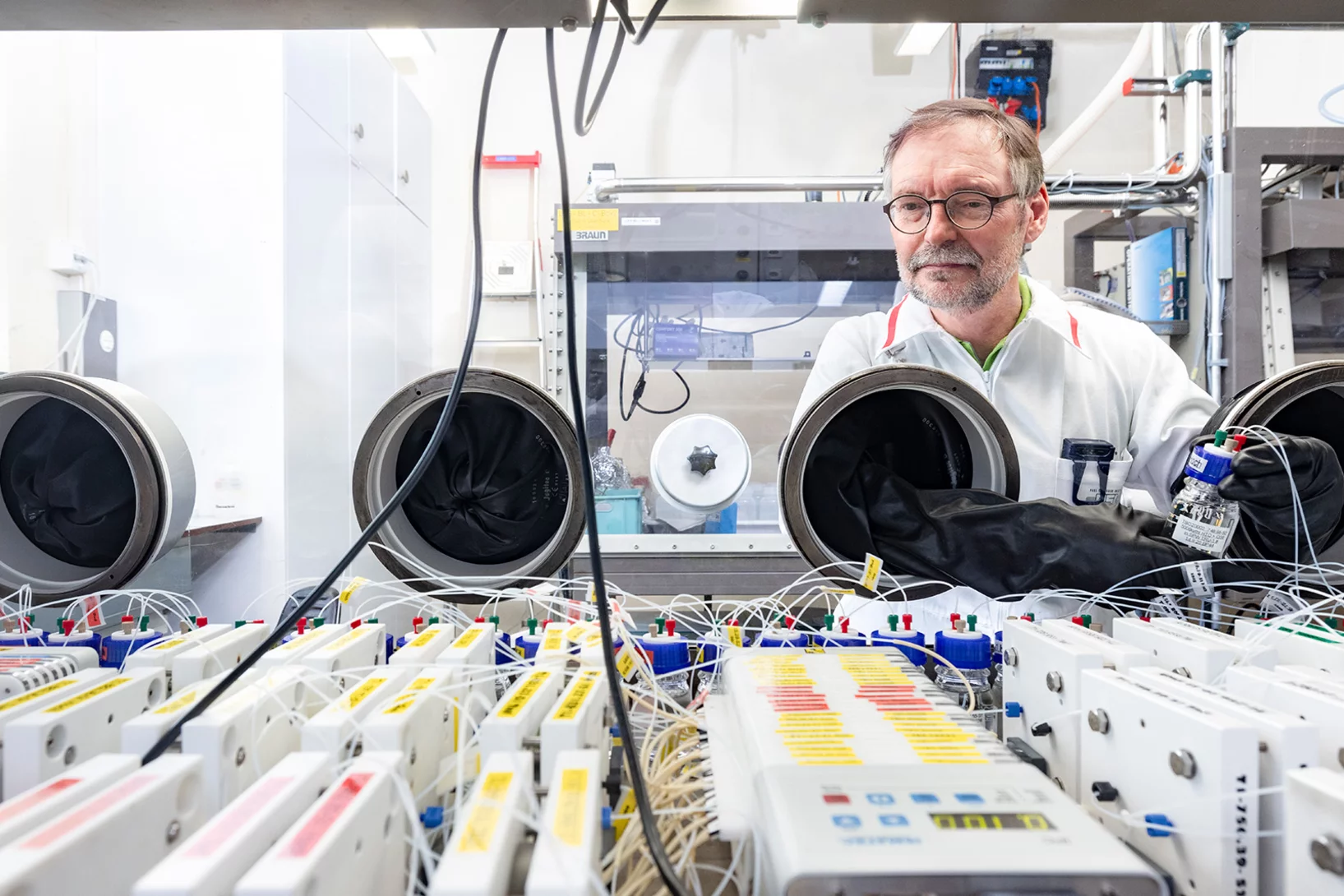
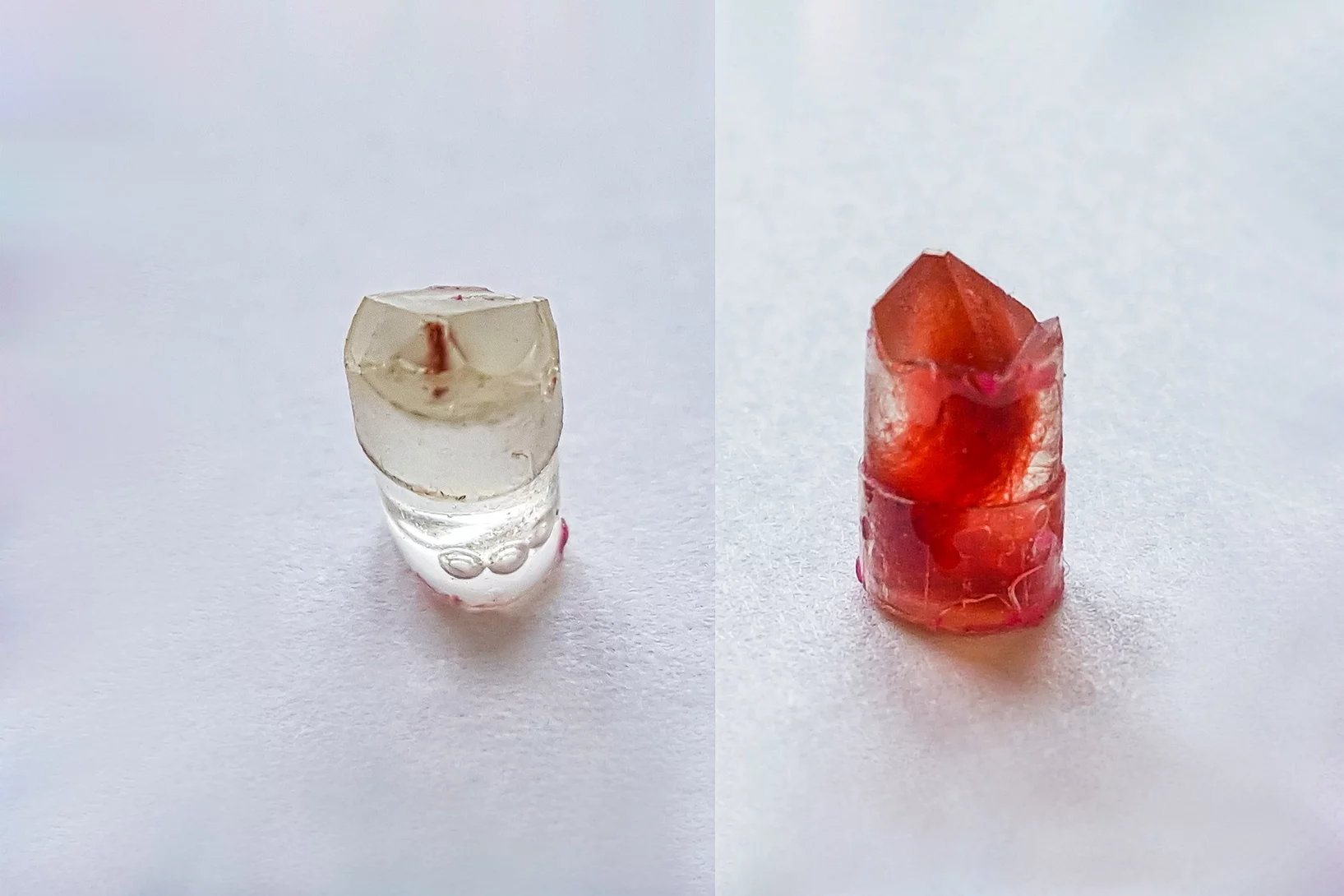
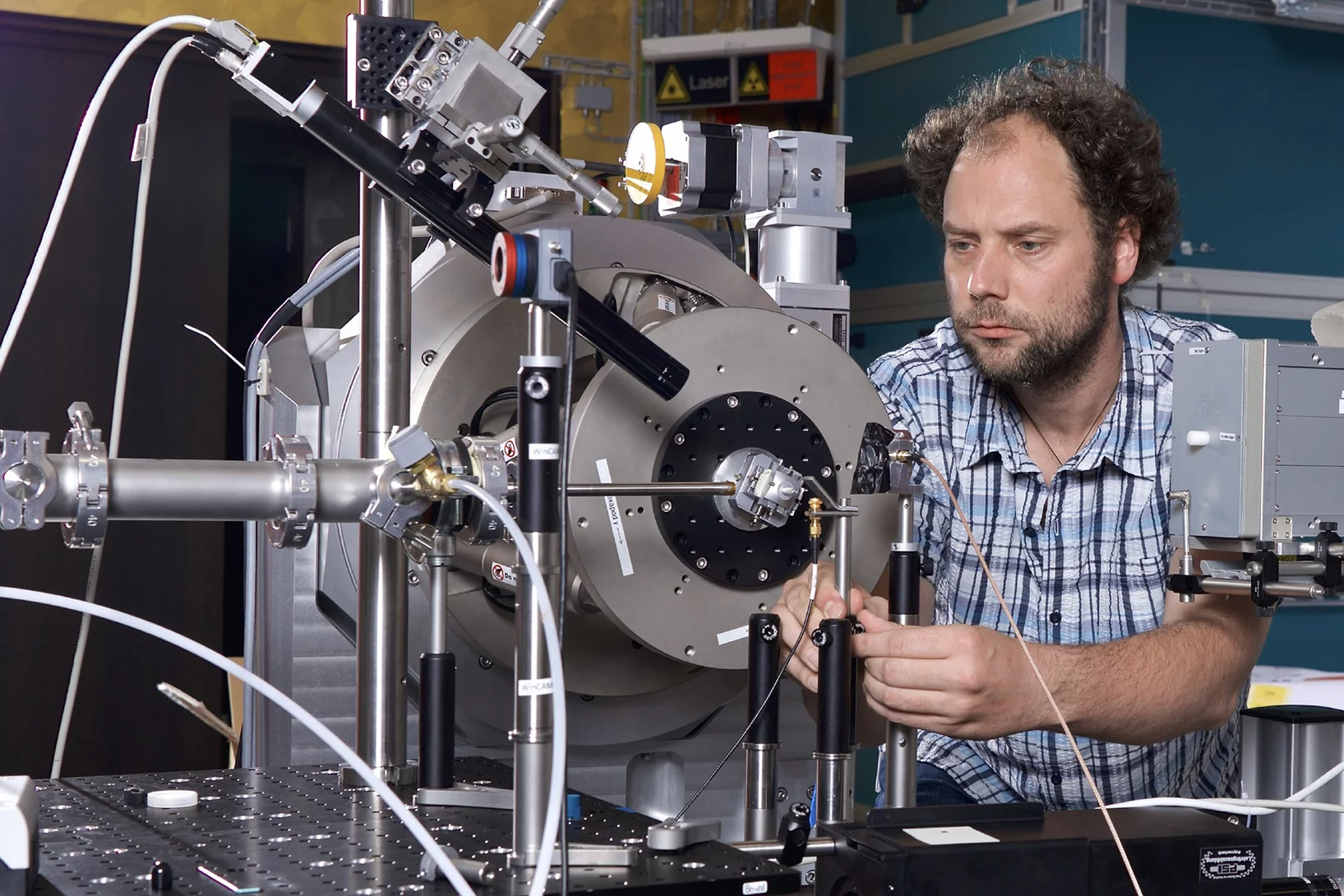
Creating novel quantum phases via the heterostructure engineering
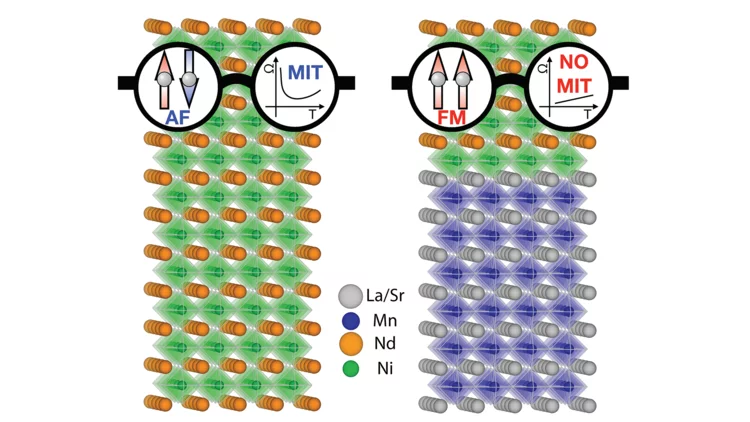
Within this synergetic collaboration, PSI scientists have investigated the correlation between magnetic and electronic ordering in NdNiO3 by tuning its properties through proximity to a ferromagnetic manganite layer. The main outcome is that the stray magnetic field from the manganite layer causes a novel ferromagnetic-metallic (FM-M) phase in NNO. This work demonstrates the utilization of heterostructure engineering for creating novel quantum phases.
Erstes Licht an Furka: Die Experimente können beginnen
Der Weg zu weltweit einzigartigen Experimenten ist frei.
Geheimnis der Stradivari-Geigen enthüllt
Wie ein internationales Team von Forschenden herausfand, griffen die alten italienischen Meister Stradivari und Guarneri beim Geigenbau zu unerwarteten chemischen Hilfsmitteln.
Die Physik in neuen Metallen verstehen
Forschende des PSI könnten gemeinsam mit internationalen Kollegen nun korrelierte Metalle für die Anwendung in der Supraleitung, Datenverarbeitung oder in Quantencomputern nutzbar gemacht haben.
Synchrotron movies
Prof Philip Willmott, the author of the book 'Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: techniques and applications' (second edition, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 2019. ISBN: 9781119280392), makes the scripts for the simulations and animations available to the public.
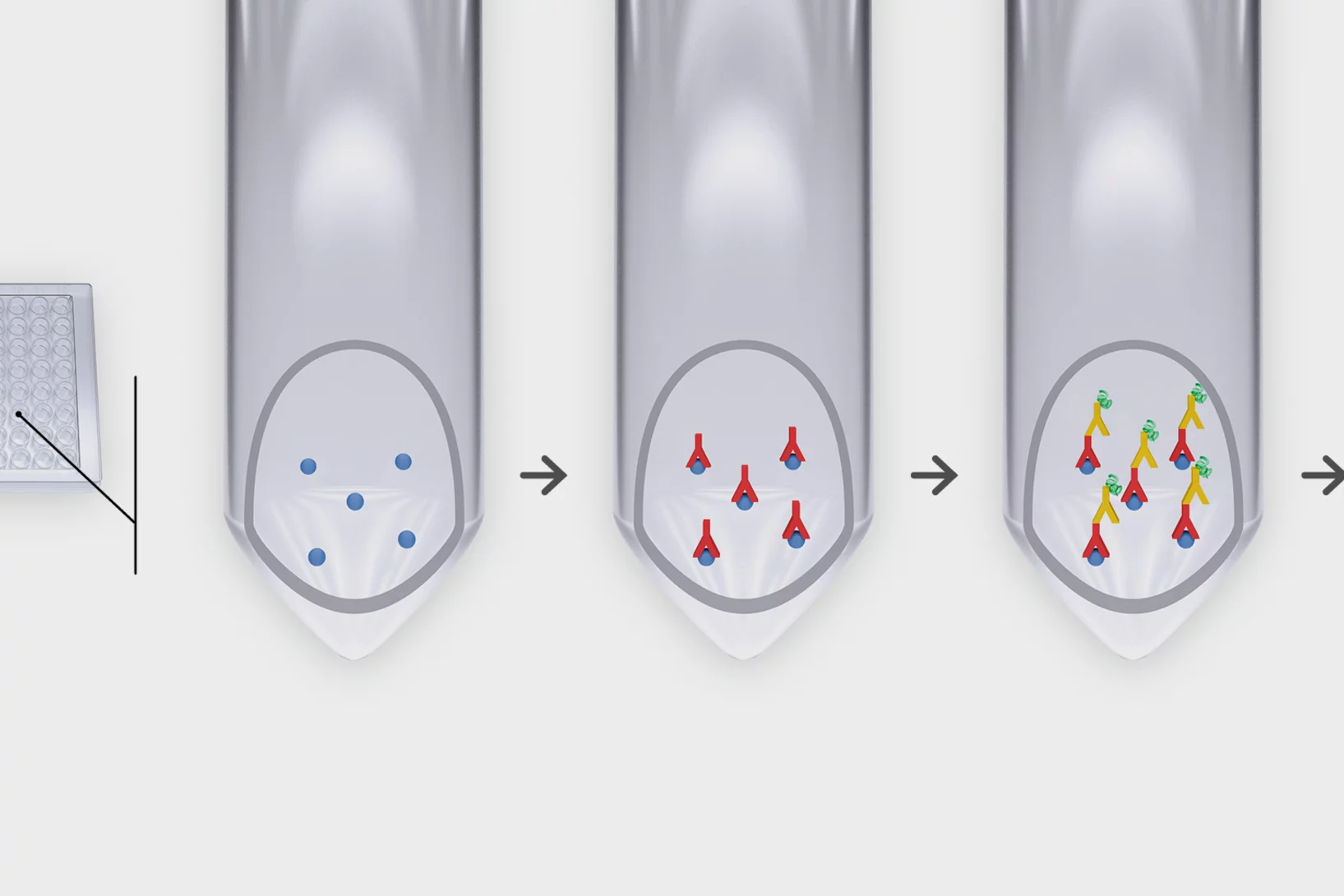
Der Corona-Dunkelziffer auf der Spur
Das Universitätsspital Zürich nutzt vom PSI hergestellte Proteine für seine breit angelegte Antikörperstudie, um herauszufinden, wie viele Menschen sich mit dem Coronavirus infiziert haben.
How ethane-consuming archaea pick up their favorite dish
Scientists decode the structure of the enzyme responsible for the ethane fixation by – beside others – using the SLS.
PSI: stetig voran im Kampf gegen Corona
Kristallstrukturanalyse, Computermodelle, Zellkulturen – um Sars-CoV-2 zu erforschen, beschreitet das PSI viele Wege. Ein Überblick.
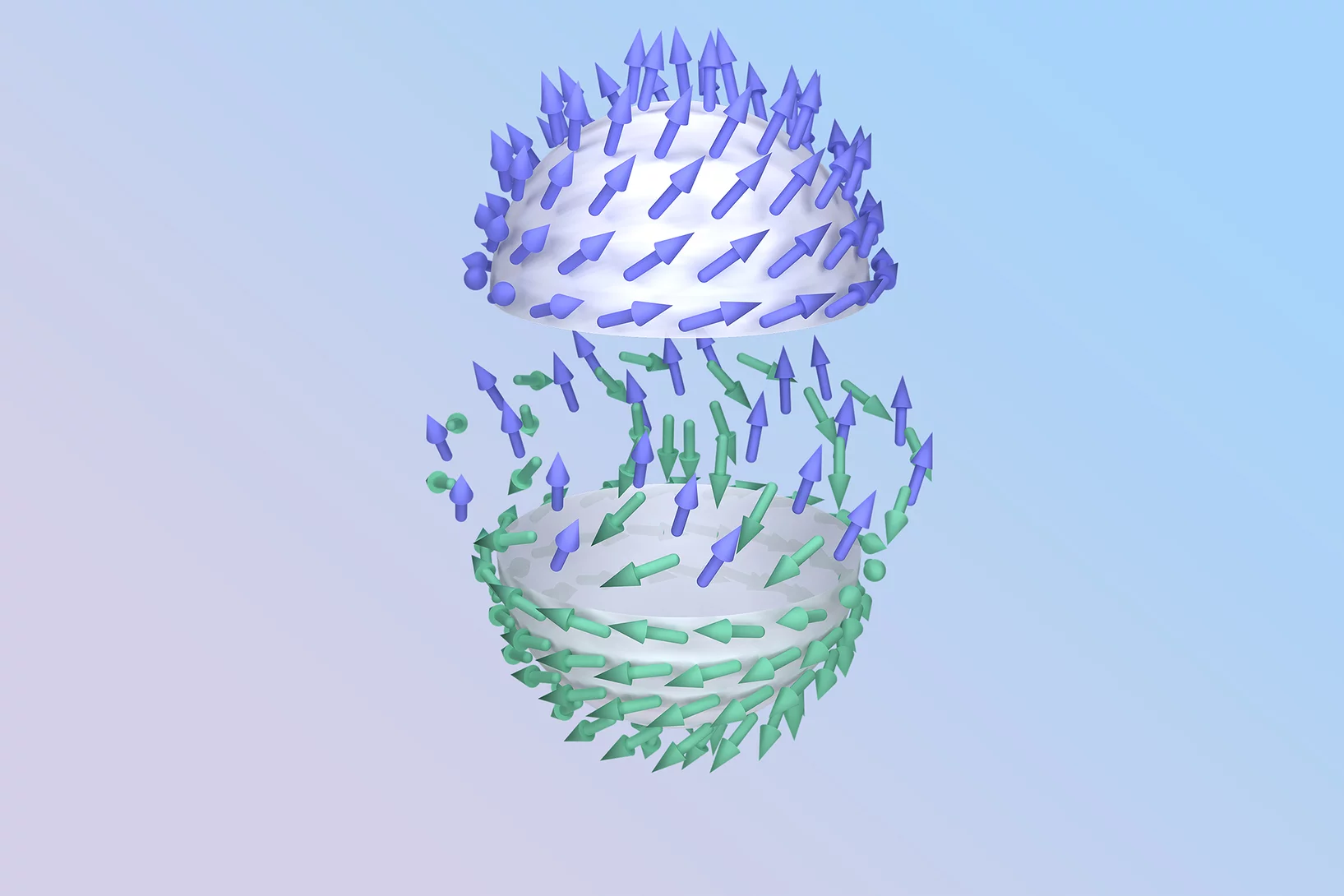
Magnetische Nanowelt
Am PSI stossen Forschende auf exotische Phänomene wie frustrierte Magnete und Nanowirbel, mit denen vielleicht dereinst Daten besser gespeichert werden können.
Wie Katalysatoren altern
Katalysatoren, die in der Industrie eingesetzt werden, verändern über die Jahre ihre Materialstruktur. Mit einer neuen Methode haben PSI-Forschende dies nun auf der Nano-Skala untersucht.
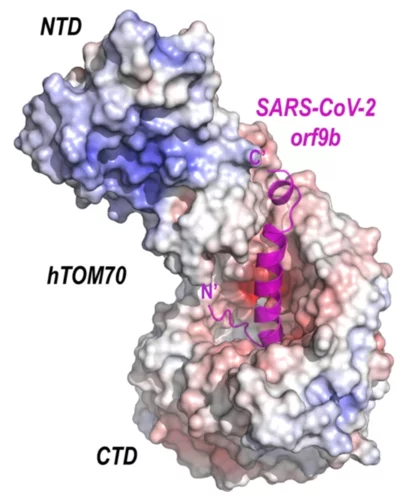
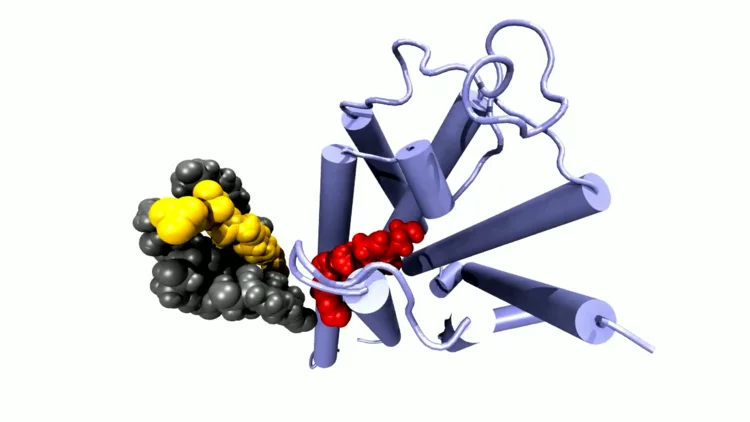
Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b in complex with human TOM70 suggests unusual virus-host interactions
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers at the NHC Key Laboratory of Systems Biology of Pathogens in Beijing, China, in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institut characterize the interactions of SARS-CoV-2 orf9b and human TOM70 biochemically, and they determine the 2.2 Å crystal structure of the TOM70 cytosolic domain with a bound SARS-CoV-2 orf9b peptide.
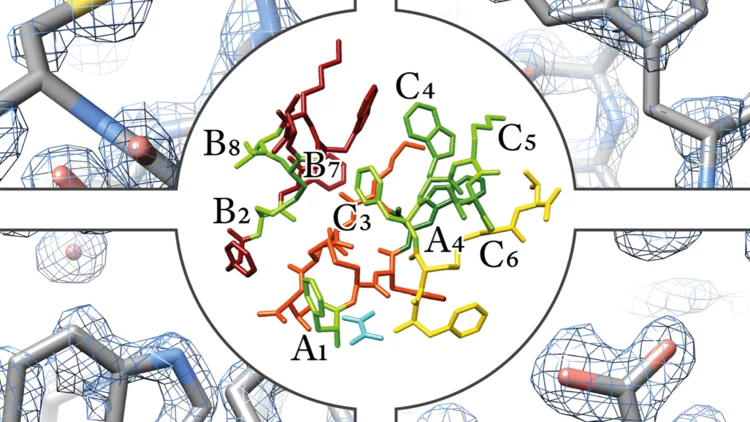
Application of synchrotron-XRPD to protein powders
Breakthrough applications of high-resolution and high-counting statistics synchrotron X-Ray Powder Diffraction to protein powders leading to the determination of a 1.8 structural model of the pharmaceutical peptide "octreotide" - the highest resolution ever achieved for a peptide of this complexity using X-ray powder diffraction and crystallographic methods.
Magische Kraft mit grosser Wirkung
Mikroroboter, Materialien mit Formgedächtnis oder bessere Teilchenbeschleuniger werden möglich durch die Erforschung des Magnetismus am PSI.
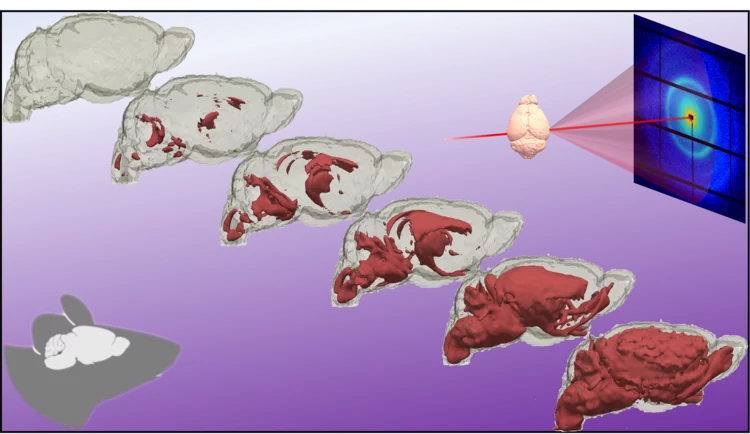
Quantifying oriented myelin in mouse and human brain
Myelin 'insulates' our neurons enabling fast signal transduction in our brain. Myelin levels, integrity, and neuron orientations are important determinants of brain development and disease. Small-angle X-ray scattering tensor tomography (SAXS-TT) is a promising technique for non-destructive, stain-free imaging of brain samples, enabling quantitative studies of myelination and neuron orientations, i.e. of nano-scale properties imaged over centimeter-sized samples.
Nicht auf der rosa Wolke
Licht ist lebenswichtig und für Forschende ein wunderbares Werkzeug, um zum Beispiel den Aufbau von Materialien besser zu verstehen.
Wie Remdesivir gegen das Coronavirus wirkt
Forschende der Goethe-Universität Frankfurt haben in Kooperation mit dem PSI vermutlich einen weiteren, bislang unbekannten Wirkmechanismus des Virostatikums Remdesivir entdeckt.
Das Zellskelett als Ziel für neue Wirkstoffe
Mit einer Kombination aus Computersimulation und Laborexperiment haben PSI-Forschende neue Bindungsstellen für Medikamente an dem lebenswichtigen Protein Tubulin identifiziert.
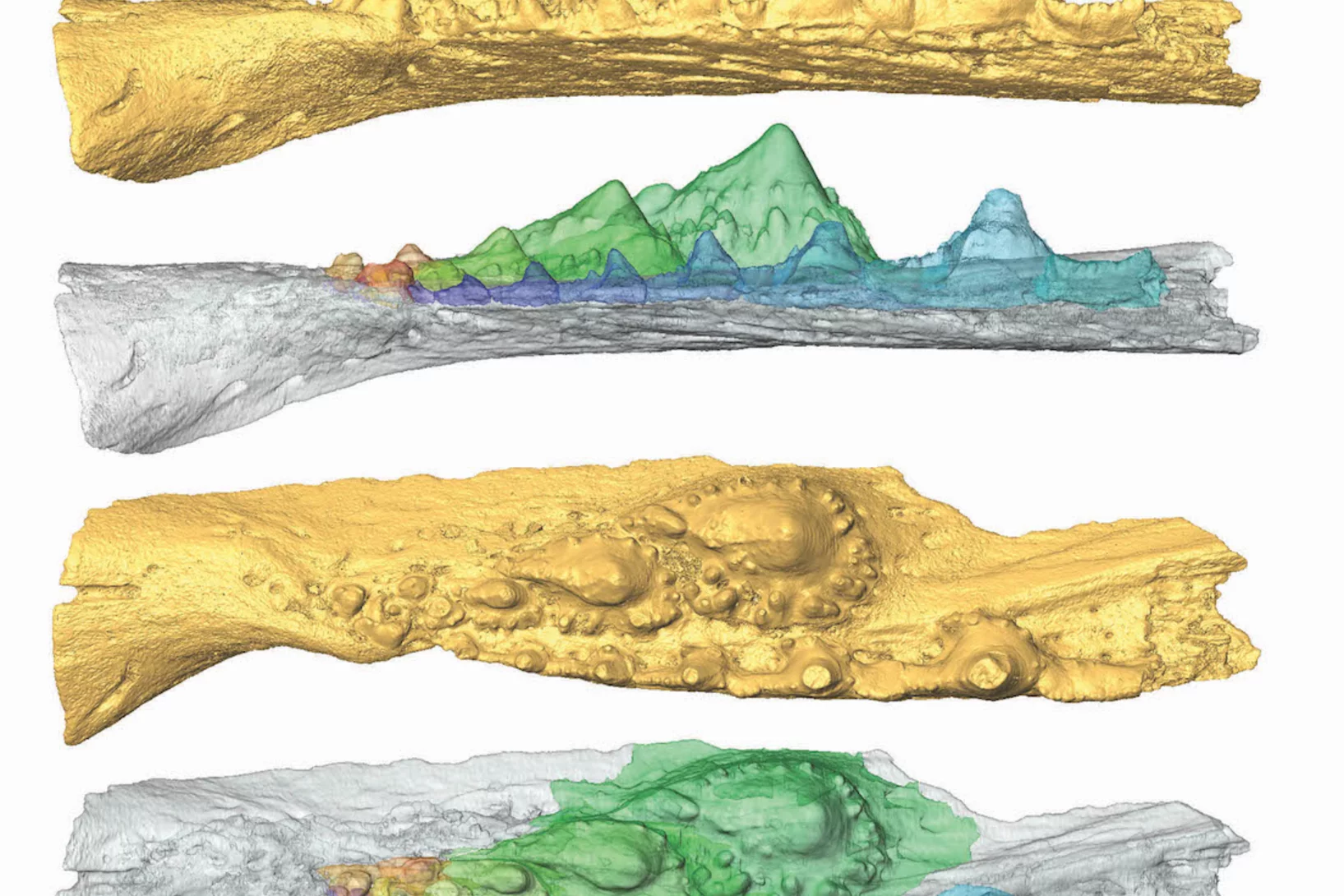
Deep evolutionary origins of the human smile
Detailed characterization of the tooth and jaw structure and development among shark ancestors by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden and the University of Bristol to the discovery that while teeth evolved once, complex dentitions have been gained and lost many times in evolutionary history.
«Ziel ist ein experimenteller Quantencomputer im Kanton Aargau»
Die ETH Zürich und das PSI eröffnen gemeinsam einen «Quantum Computing Hub». Ein Interview mit Gabriel Aeppli und Christian Rüegg über das neue Forschungszentrum.
ETH Zürich und PSI gründen Quantum Computing Hub
Die ETH Zürich und das Paul Scherrer Institut PSI eröffnen ein gemeinsames Zentrum zur Entwicklung von Quantencomputern. Ziel ist es, die Realisierung von Quantencomputern sowohl auf Basis von Ionenfallen als auch von supraleitenden Bauteilen voranzutreiben.
Einmalig scharfer Röntgenblick
Ein neues Verfahren des PSI erlaubt die quantenphysikalische Erforschung von Materialien mithilfe von Röntgenlasern.
Kompakt und leistungsstark wie ein Schweizer Taschenmesser
Der Freie-Elektronen-Röntgenlaser SwissFEL ist tatsächlich so kompakt, stark und vielseitig, wie er geplant war.
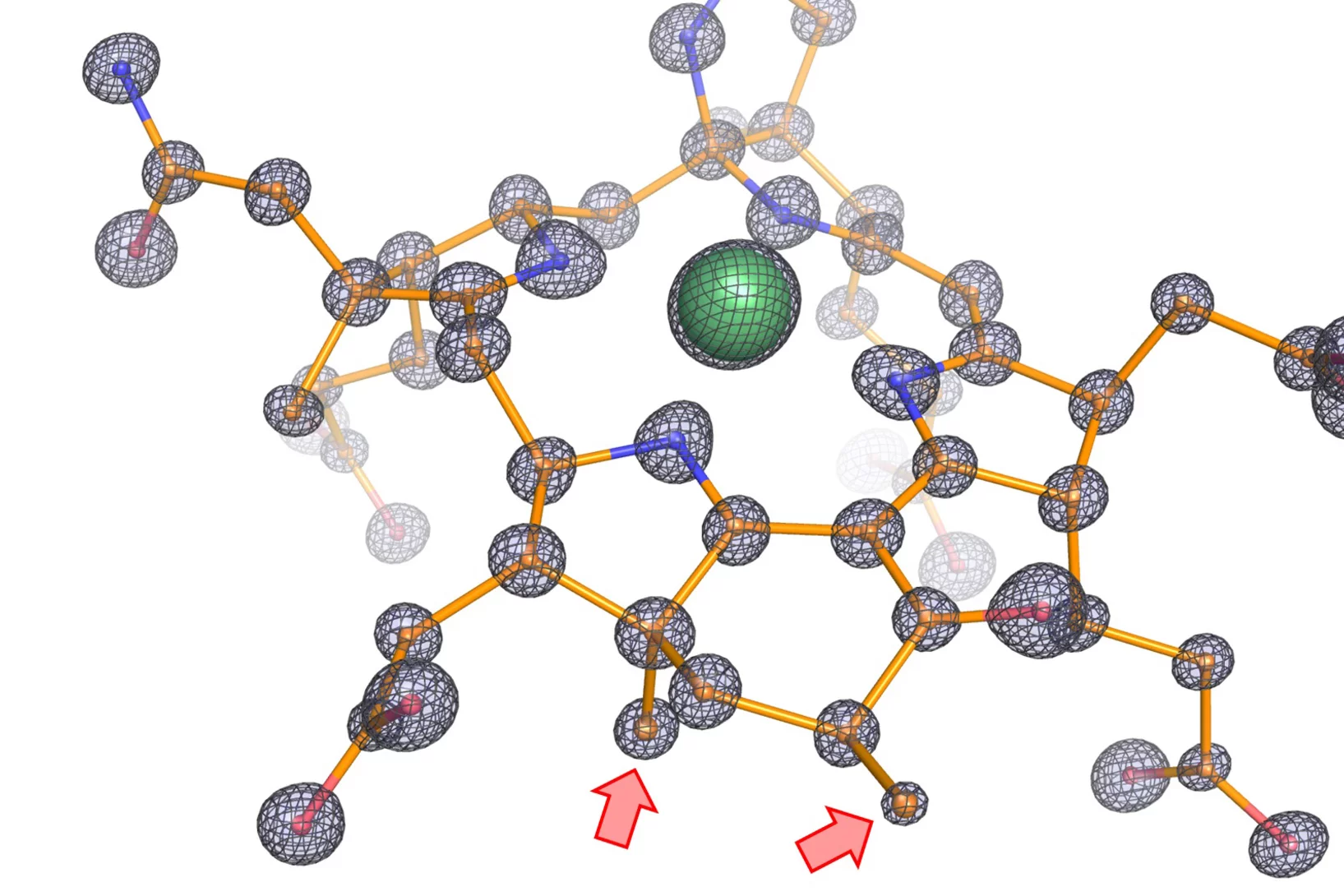
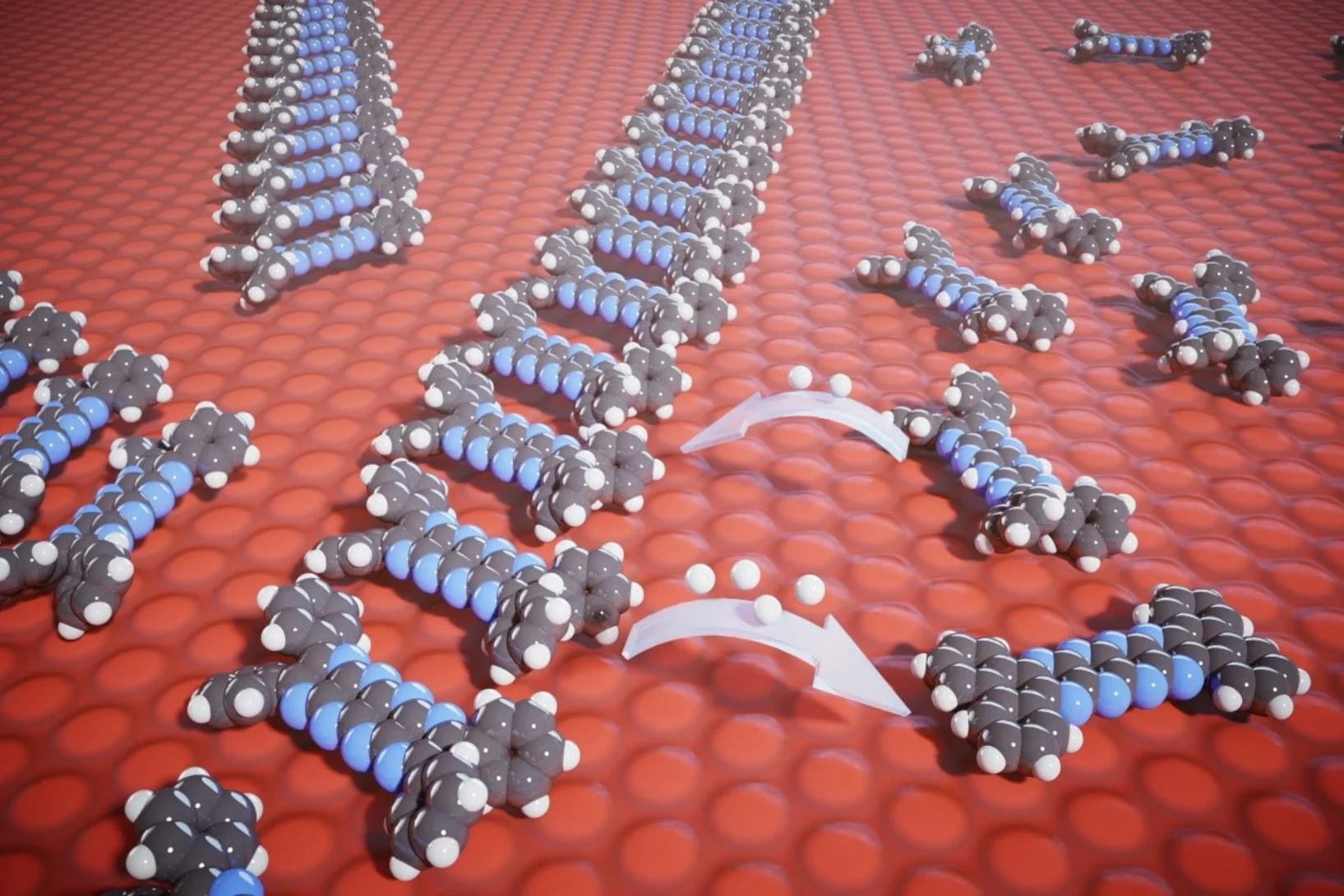
New class of substances for REDOX chemistry
The compounds known as ‘pyrazinacenes’ are simple, stable compounds that consist of a series of connected nitrogen-containing carbon rings. They are suitable for applications in electrochemistry or synthesis, as the researchers describe in the science journal Communications Chemistry. They were first designed, synthesized and chemically characterized in solution by the Hill team and carefully investigated by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy and Surface Chemical Analysis. The compounds have been shown to reversibly release and accept electrons and arrange themselves differently depending on the oxidation state. Interestingly, the oxidation and reduction reactions of the pyrazinacenes are not only affected by a chemical impulse, but can also be stimulated by light so they can be considered photo-redox active.
Für eine Million Jahre sicher verwahrt
Die Schweiz plant, bis zum Jahr 2050 ein Tiefenlager für ihre radioaktiven Abfälle zu errichten. Forschende am PSI helfen dabei herauszufinden, welcher Standort am geeignetsten ist.
HERCULES SCHOOL 2021 AT PSI
During the week of March 15 – 19, we had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and assistant professors at PSI, taking part in the first virtual HERCULES SCHOOL on Neutrons & Synchrotron Radiation.
Insights into the world’s oldest pile carpet
High-resolution XRF imaging of the specific metal distribution within wool fibers at the PHOENIX beamline gives insights into traditional oriental dyeing procedures.
Forschung zu Covid-19 am Paul Scherrer Institut
Während viele Bereiche des Lebens eingeschränkt sind, bleiben wichtige Forschungsanlagen am PSI in Betrieb.
Rezeptorproteinen beim Verbiegen zuschauen
G-Protein-gekoppelte Rezeptoren vermitteln unzählige Prozesse im Körper. Im Interview erzählt PSI-Forscher Ramon Guixà, wie er die Rezeptormoleküle auf dem Bildschirm lebendig werden lässt.
Neuer Bauplan für stabilere Quantencomputer
PSI-Forscher haben gezeigt, wie sich schnellere und genauere Quantenbits erschaffen liessen. Die zentralen Elemente sind dabei magnetische Atome aus der Klasse der sogenannten Seltenen Erden, die gezielt in das Kristallgitter eines Materials eingebracht würden.
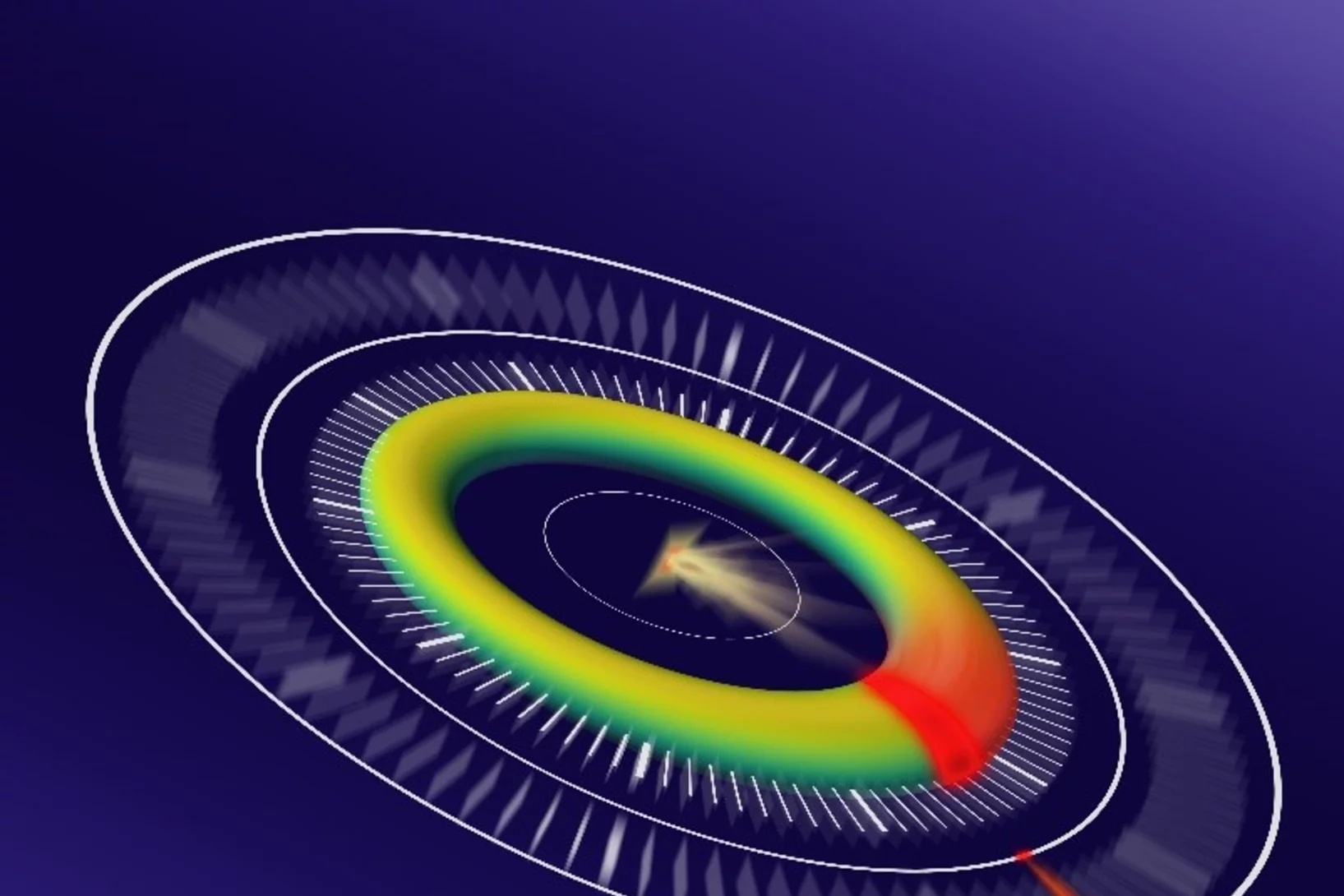
Clocking the movement of electrons inside an atom
Scientists pioneer an approach called self-referenced streaking, clocking Auger electrons with sub-femtosecond resolution. The breakthrough will unlock the broader potential for attosecond time resolution at X-ray free-electron lasers