Recherche
Hierarchically Structured Porous Transport Layers for Polymer Electrolyte Water Electrolysis
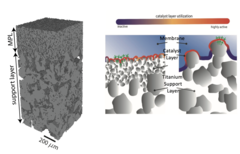
The high operational and capital costs of polymer electrolyte water electrolysis technology originate from limited catalyst utilization and the use of thick membrane electrolytes. PSI researchers have developed novel multi-layer porous transport materials, which provide superior electrochemical performance in comparison to conventional single-layer structures.
Understanding of the Oxygen Evolution Reaction Kinetics in Acidic Environment
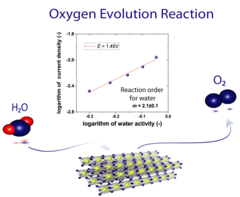
The high operational expenditure of polymer electrolyte water electrolysis (PEWE) technology, dominated by kinetic losses from the sluggish oxygen evolution reaction (OER), inhibits large-scale market penetration. PSI researchers have developed a novel methodology to access underlying reaction mechanism of the OER. For the first time the reaction order for water has been determined. Advanced benchmarking of catalysts in technical environment also supports the development of novel, highly efficient catalyst materials.
Using X-ray emission spectroscopy to study the electronic properties of single atom catalysts
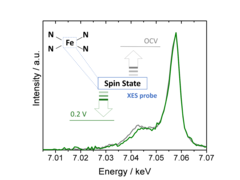
Single atom catalysts hold great promise as O2- or CO2-reduction electrocatalysts, but a deeper understanding of their active sites’ structure and electronic properties is needed in order to render them sufficiently active and stable. To this end, we have used X-ray emission spectroscopy to determine these catalysts’ electronic configuration, and performed in situ measurements that unveil the effect of potential on this key feature.
ESI-Plattform
Themenübersicht
Erneuerbare Energien: Versuchsplattform ESI startet
Diesen Herbst ist es so weit: Die Energy-System-Integration-Plattform am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI nimmt ihren Betrieb auf. Im Rahmen der Doppeltagung „Vernetzte Energieforschung Schweiz“ wurde sie heute den Medien und rund 150 Vertretern aus Politik, Industrie und Wissenschaft vorgestellt.
Efficient Water Electrolysis at Elevated Temperature using Commercial Cell Components
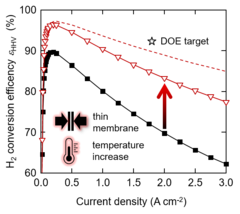
Decarbonization of the energy system across different sectors using power-to-X concepts relies heavily on the availability of low-cost hydrogen produced from renewable power by water electrolysis. Polymer electrolyte water electrolysis (PEWE) is a promising technology for hydrogen (and oxygen) production for distributed as a well as centralized operation. The total cost of hydrogen is dominated by the electricity cost. Therefore, increase of conversion efficiency is pivotal in improving the commercial viability of electrolytically produced hydrogen. In this study, we investigate the prospects of improving conversion efficiency by reducing the membrane thickness from 200 to 50 micron and increasing the cell temperature from 60 to 120°C.
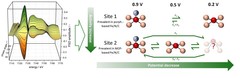
In situ spectroscopy unveils the structural changes of the sites in single atom catalysts
To improve the performance of single atom catalysts (SACs), the structure of their active sites under operative conditions needs to be better understood. For this, we have performed in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements using a modulation excitation approach selectively sensitive to the species involved in the electrochemical reactions. This has allowed us to study the structural changes undergone by two types of SACs, and to tie the observed differences to their catalytic activities.
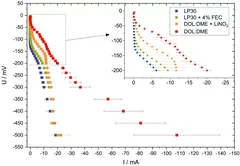
Versatile and Fast Methodology for Evaluation of Metallic Lithium Negative Battery Electrodes
Evaluating potential electrolyte candidates is typically a lengthy procedure requiring long-term cycling experiments. To speed this process up, we have investigated potentiostatic lithium plating as a potential method for fast electrolyte suitability investigation. The applications of this methodology is not limited to liquid electrolytes, - effects of solid-state electrolytes, coatings, and other modifications can be readily assessed.
Des rayons X pour améliorer les propulsions des véhicules
Relever les défis de l’avenir, pour le trafic routier suisse, va surtout demander des efforts de recherche. Aux grandes installations du PSI, des chimistes et des ingénieurs étudient comment rendre les propulsions des véhicules plus efficaces et moins polluantes.