Conventional attenuation-based imaging
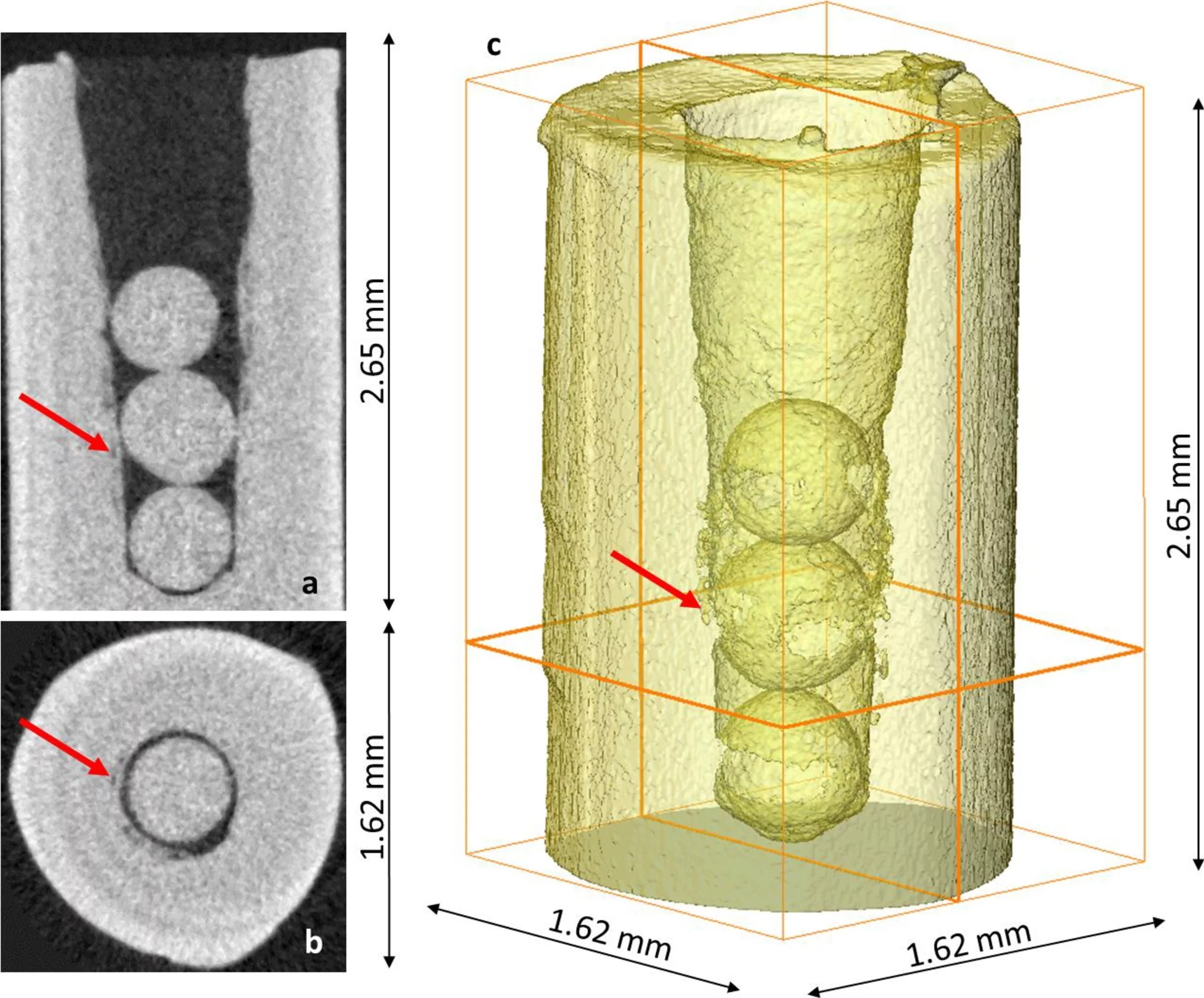
Conventional attenuation-based neutron radiography and tomography of the material can be carried out measuring the transmission of the incident neutron beam through the sample. Depending on the desired field of view and nominal pixel size, either a micro or midi camera box can be mounted. For high spatial resolution the neutron microscope (see below) or a fiber optics taper can be used.
High spatial resolution imaging with neutron microscope
More information available at https://www.psi.ch/en/niag/neutron-microscope
Bragg edge imaging
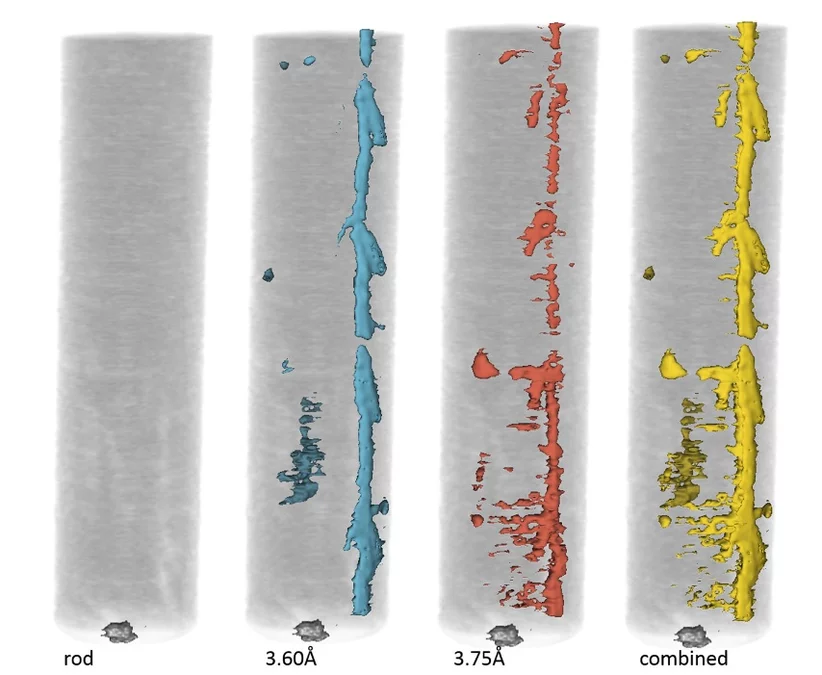
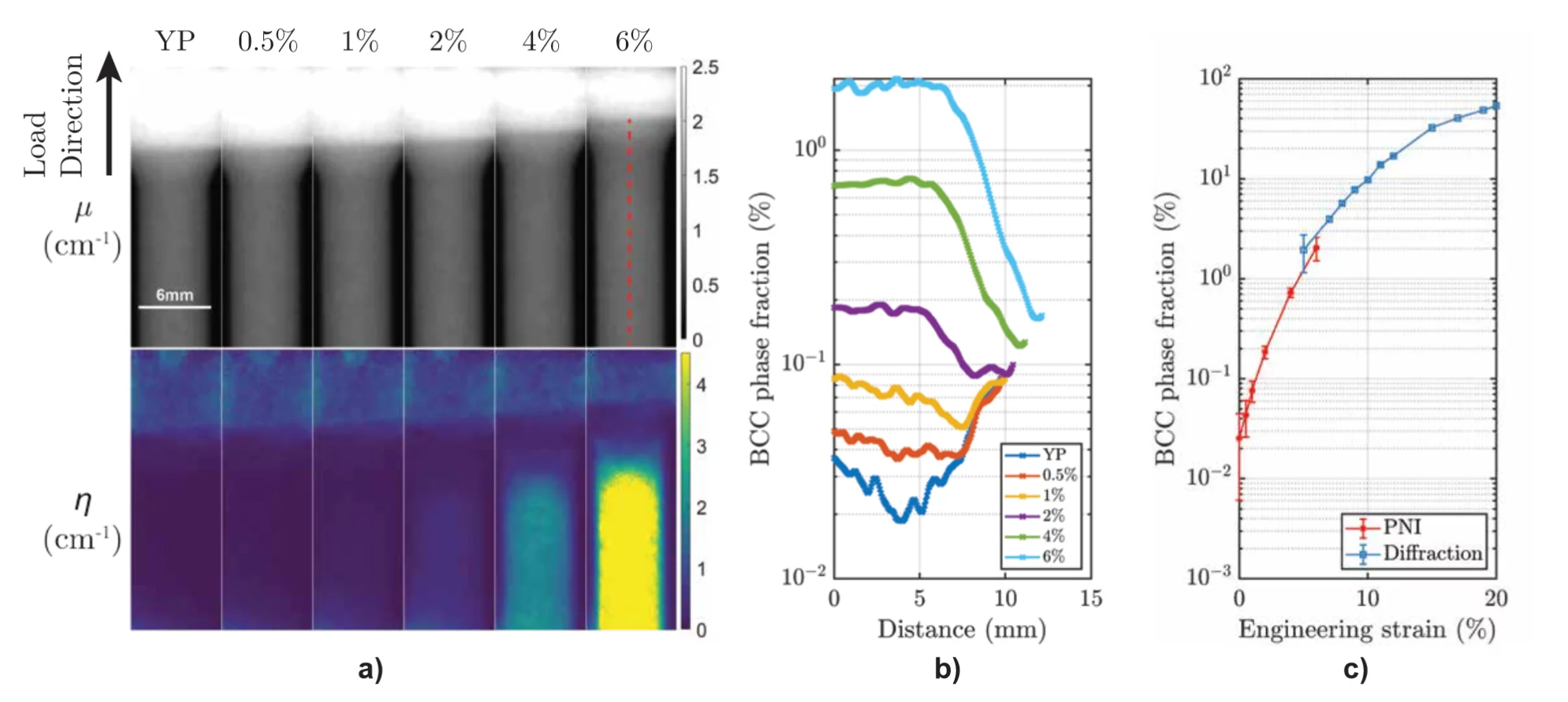
Neutron Bragg-edge imaging measures at each pixel of the neutron detector the wavelength dependence of the attenuation spectrum. This enables further characterization of the crystallographic properties of the material such as elastic lattice strain, residual stresses, crystalline phase transformations, crystallite grain size and crystallographic texture.
- Wavelength selective scan: Individual wavelengths are scanned via monochromatization of the neutron beam through the double crystal monochromator (DCM)
- Time-of-flight imaging: Using a chopper and a time-of-flight detector, the attenuation wavelength spectrum is acquired simultaneously with a single shot exposure
Polarization contrast neutron imaging (PNI)
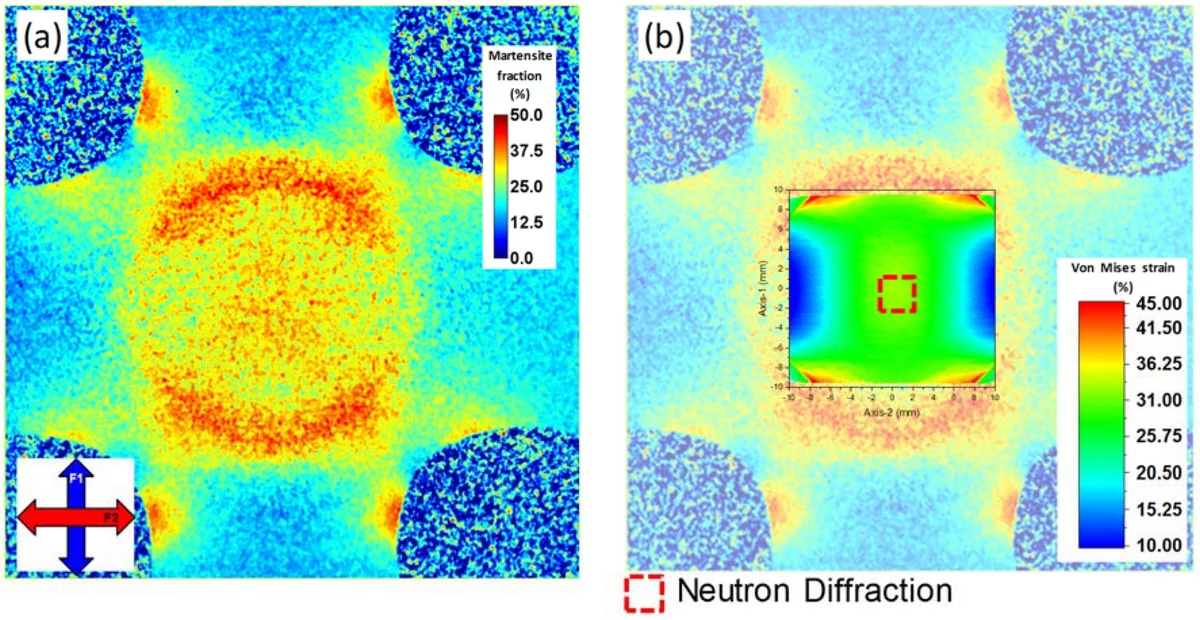
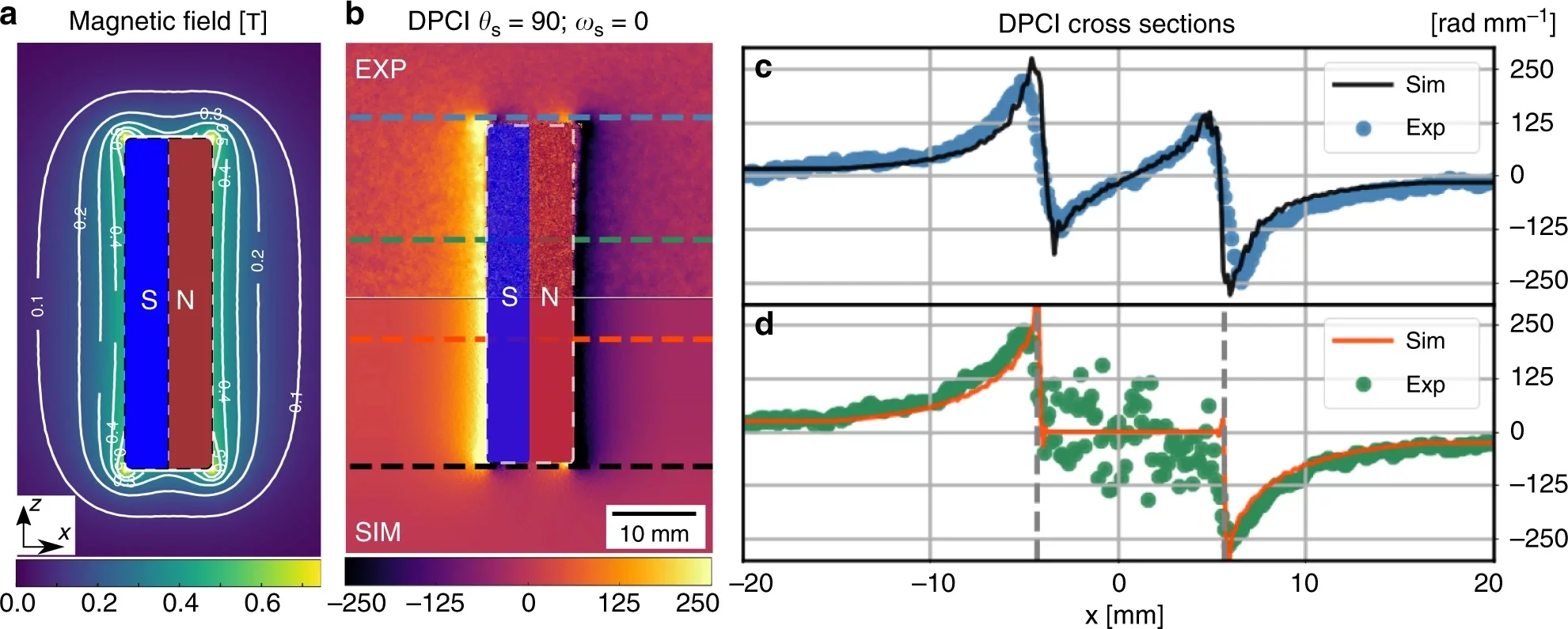
Imaging with a polarized neutron beam can be used to visualize various magnetic structures, fields and phenomena, and consists of characterizing them by measuring the local variations in the polarization of the transmitted beam with a spatial resolution using standard imaging neutron cameras.
Neutron grating interferometry imaging
With the neutron grating interferometry imaging setup, the transmission, dark field and differential phase contrast images of the sample exhamined can be acquired simultaneously.
- Symmetric Talbot-Lau setup: Conventional setup with a set of three gratings, and a micro-stepping motor for one of the gratings
- Single shot setup: Single shot dark field imaging is achieved by resolving directly the gratings pattern with the neutron detector
- 1-Directional: Directional dark field intensity, using line gratings
- Adirectional: Returns global dark field intensity, with no information on its direction
- Omnidirectional: Returns dark field intensity for all the direction enable by the grating's design
Depending on the setup, different autocorrelation length ranges are enabled. For more details contact matteo.busi@psi.ch.
SINQ Quicklinks
User Contacts
Office hours
Monday through Friday from 8:00-11:30 and 12:30-17:00
otherwise please contact us per email
User Office
Provides all information about user access to the PSI Large Research Facilities
DUO Login
Direct link to the Digital User Office