An international collaboration consisting of metrology and photon diagnostics groups Germany, the U.S.A., Switzerland, and Japan performed a set of cross-calibration measurements of optical properties on the Bernina branch of the Aramis beamline [1]. The collaboration saw the DESY-developed gas detector, a novel diamond detector from Brookhaven, and a room temperature radiometer from AIST in Japan placed at the Bernina end station and measure the absolute intensity of the FEL light as it passed through the optical elements. The cross-calibrated measurements used in conjuction with the photon beam intensity-gas (PBIG) monitor at the front end of the Aramis beamline to characterize the performance of the optical components on the Bernina branch and then compare them to the expected theoretical values. The measurements were performed at photon energies of 6.08 and about 7.22 keV.
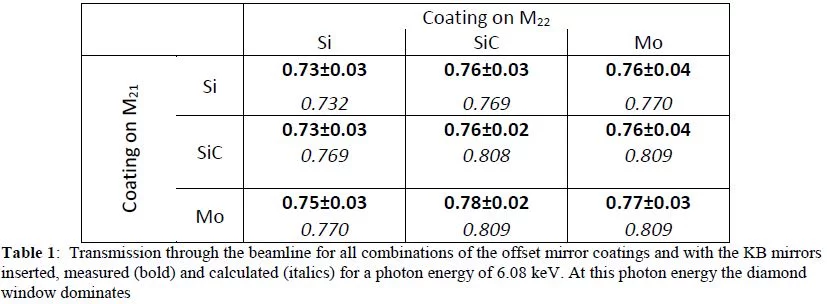
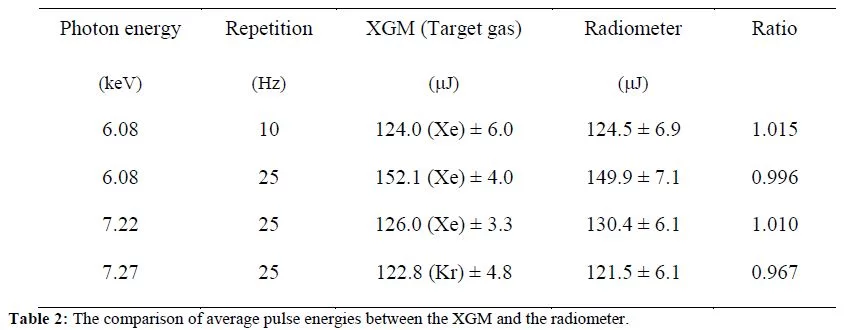
The measurements characterized the beamline offset mirrors with the Si, SiC, and Mo coatings, the performance of the grating used for the photon single shot spectrometer (PSSS), and the solid-state attenuators used for experiments. A good example of the type of measurement done is shown in Table 1. The measurement between the DESY gas detector and the PBIG shows that the transmission of the combination of coatings for the two offset mirrors on the Bernina branch match the theory very closely. Measurements like the ones shown in Table 2 show great agreement between the DESY XGM and the AIST radiometer, reinforcing the reliability of the transmission measurements.
Contact
Dr. Pavle Juranic
SwissFEL Photon Diagnostics
Paul Scherrer Institut
Telephone: +41 56 310 56 95
E-mail: pavle.juranic@psi.ch
References
[1] 1. Juranić, P., Tiedtke, K., Owada, S., Tanaka, T., Jastrow, U., Sorokin, A., Patthey, L., Mankowsky, R., Degenhardt, M., Arbelo, Y., Arrell, C., Smedley, J., Bohon, J. & Follath, R., Transmission measurement at the Bernina branch of the Aramis Beamline of SwissFEL, J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, (2019), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600577519013237