Show filters
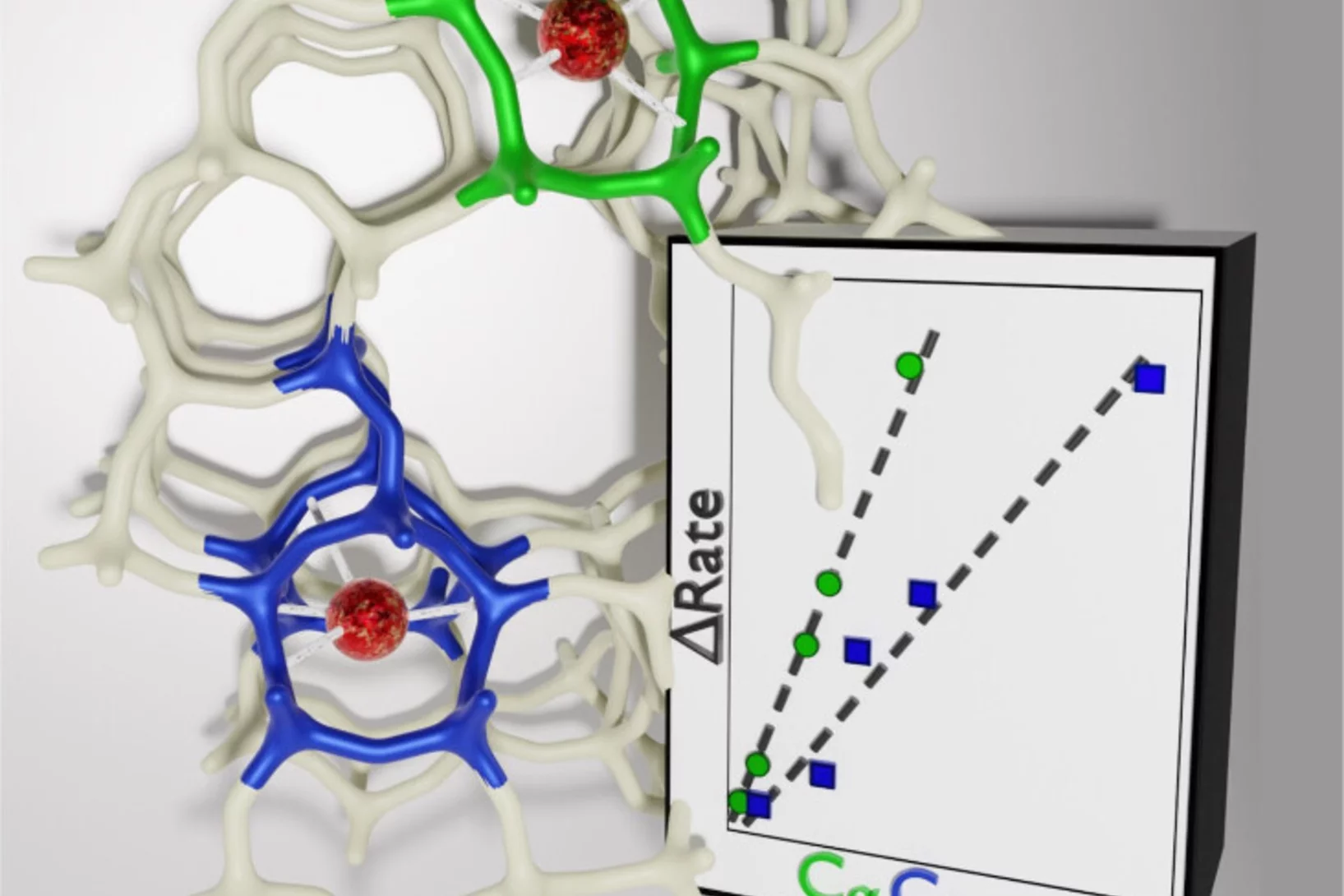
Acidity scale of carbenium ions in ZSM-5
A combination of Fourier transformed IR spectroscopy and density functional theory elucidates the higher reactivity of benzenium ions over cyclopentenyl cations in ZSM-5.
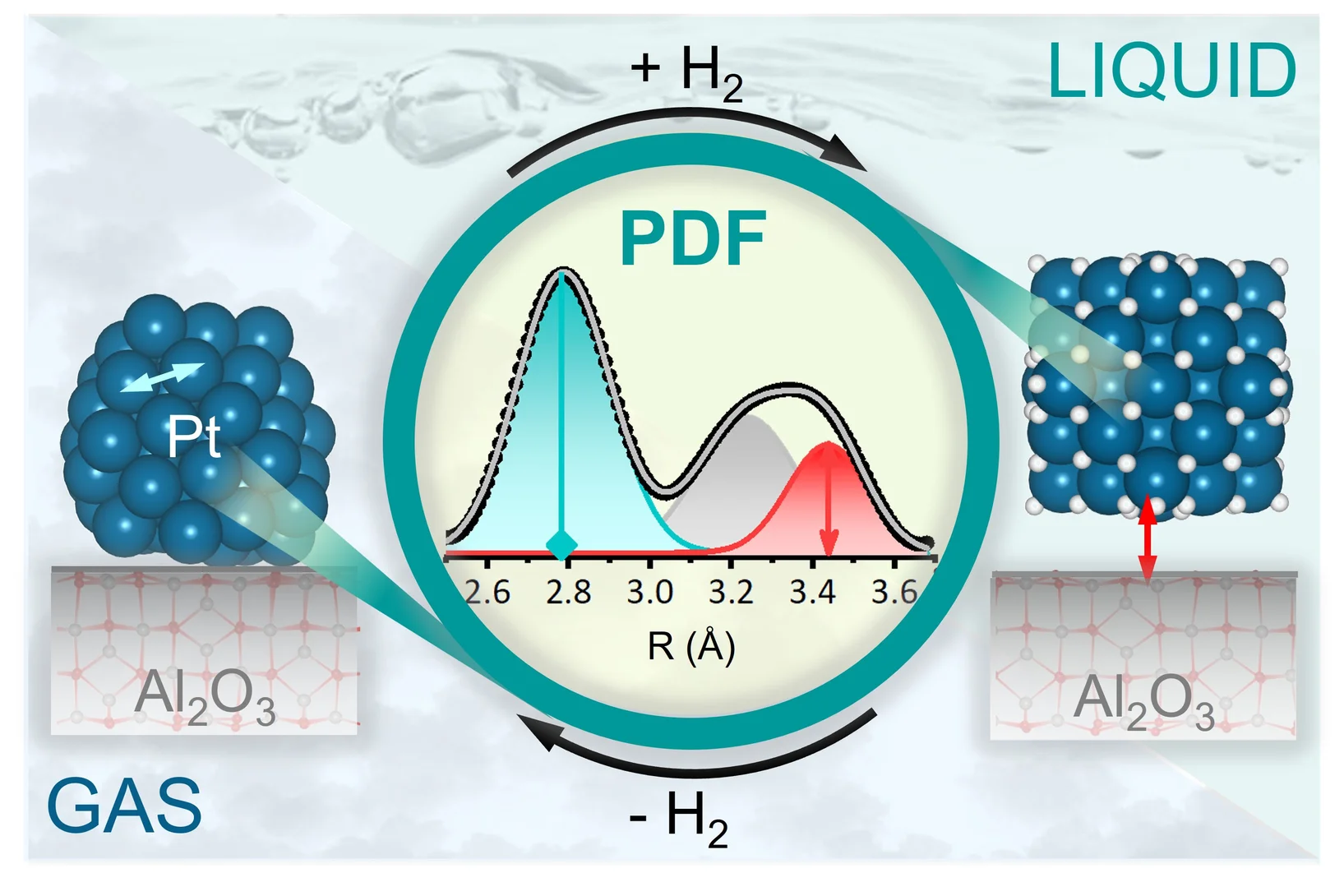
Seeing the subtle structural changes of Pt nanoparticles induced by hydrogen
We show that Pt nanoparticles reversibly expand and detach from Al2O3 in the presence of gas phase H2 and H2 dissolved in solvent.
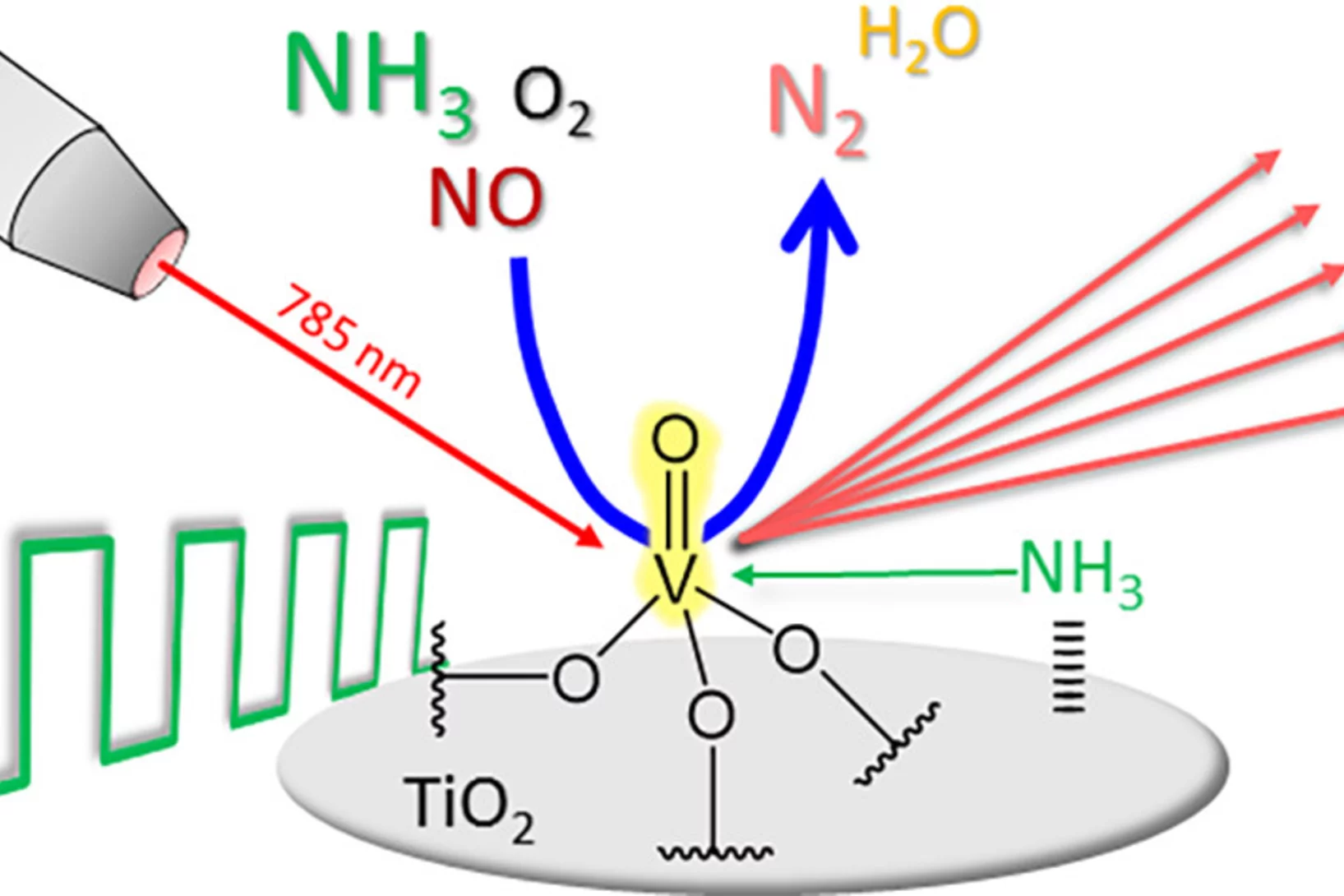
Key reaction steps in the simultaneous conversion of nitrous and nitric oxides on Fe-ZSM-5
After proposing the reaction mechanism of the N2O-NO-SCR reaction on Fe-FER, here we attempted at controlling the Fe speciation on ZSM-5 and at generalizing the result obtained on FER.
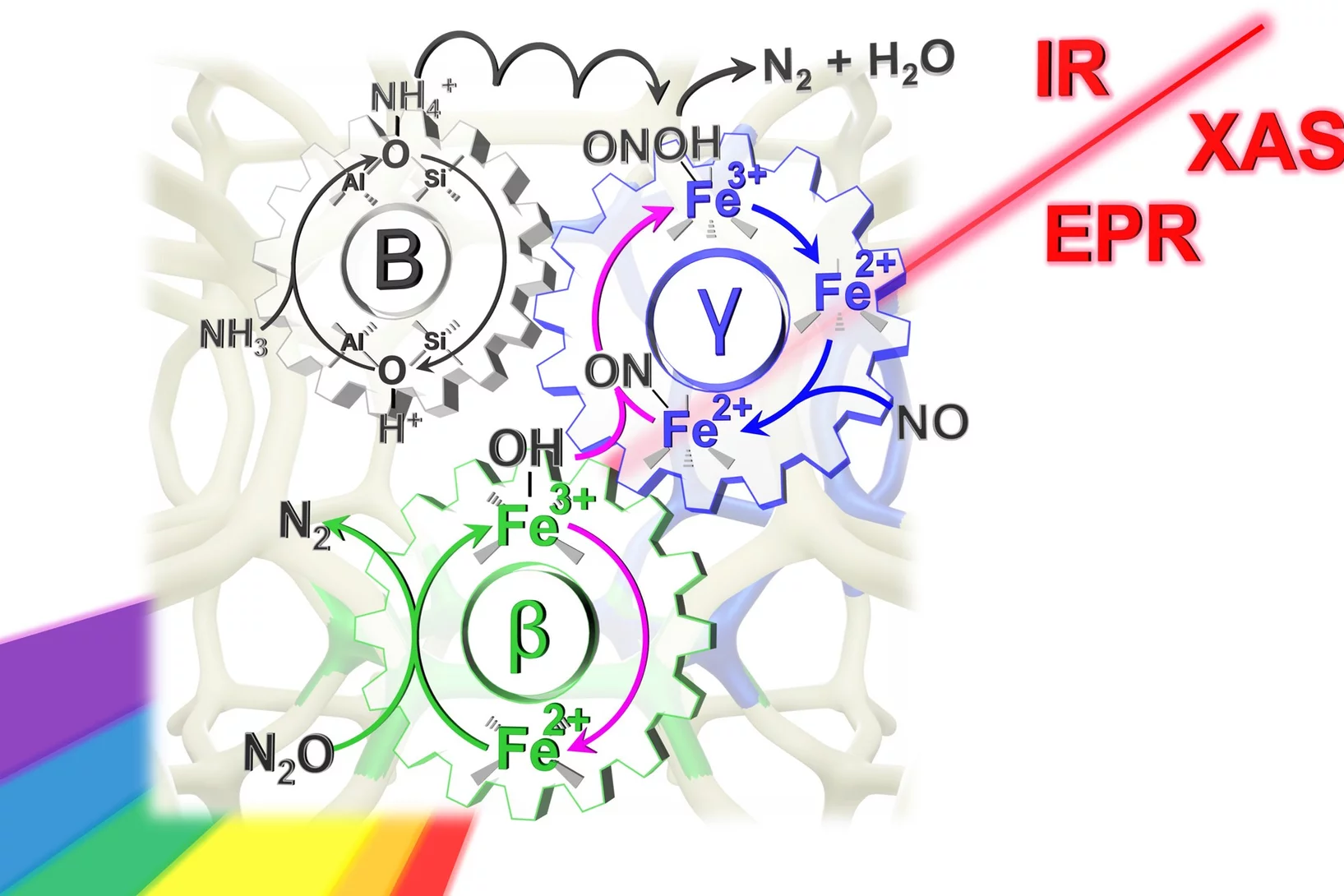
Dual-site reaction mechanism for the simultaneous reduction of nitrous and nitric oxides
We have applied three spectroscopic techniques (XAS, EPR and DRIFTS) in combination withe modulated excitation and catalytic data to decipher and propose the complete reaction mechanism of the simultaneous reduction of N2O and NO
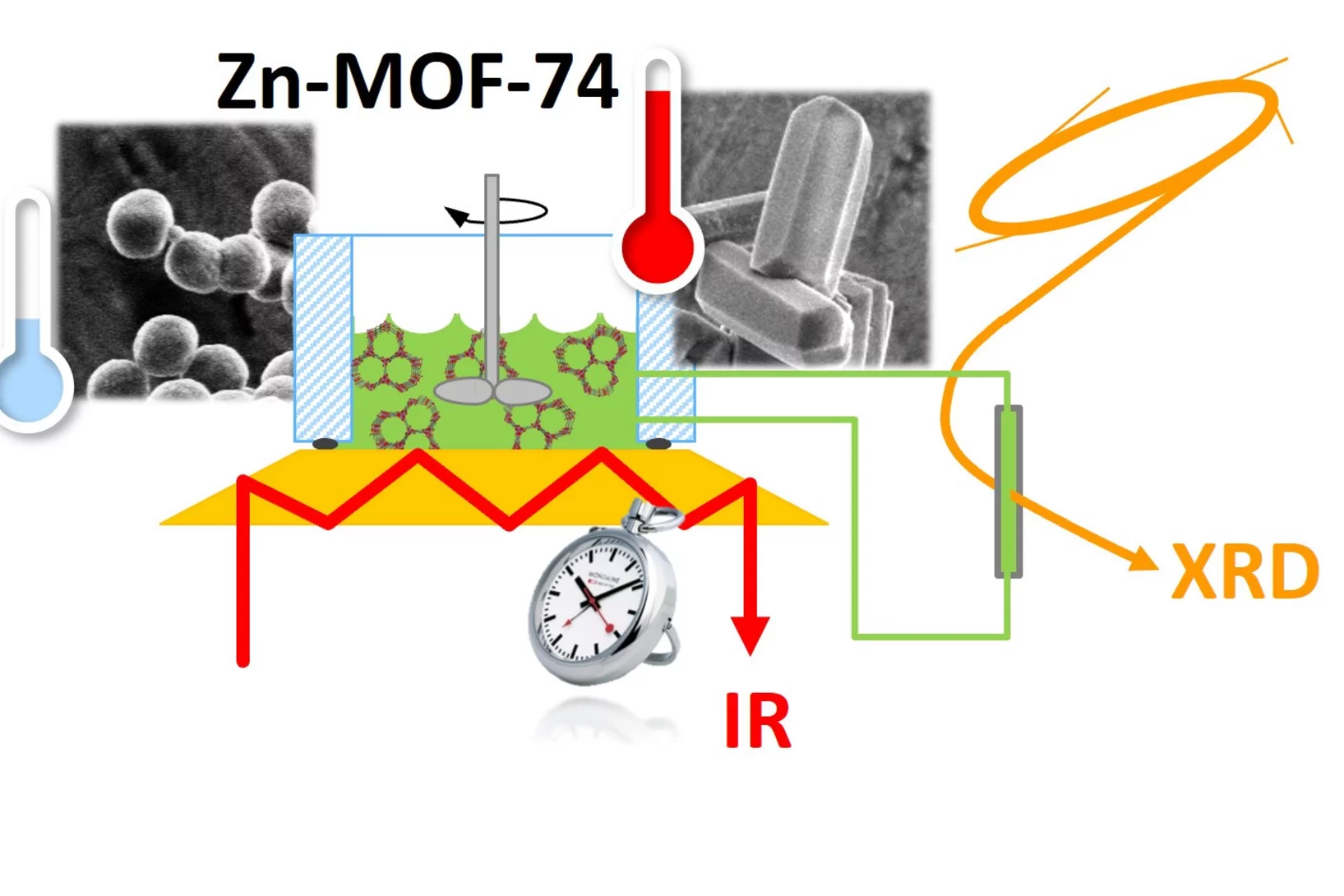
Uncovering the secrets of rapid and green metal-organic framework synthesis
Using ATR-IR spectroscopy and high-energy XRD, we have studied the mechanism of ambient temperature aqueous synthesis of Zn-MOF-74. Starting from the need to change Zn precursor to disentangle signals in ATR-IR spectroscopy, we also developed a rapid synthesis of Zn-MOF-74 with Zn perchlorate.
Carbenium ions in the methanol-to-olefins process
The methanol-to-olefins process converts methanol into hydrocarbons over zeolite-based catalysts following a dual-cycle reaction mechanism within the paradigm of an hydrocarbon pool chemistry. In this work, we use operando DRIFTS/GC to correlate the nature of species residing within the porosity of zeolites (DRIFTS) and the products distribution (GC).
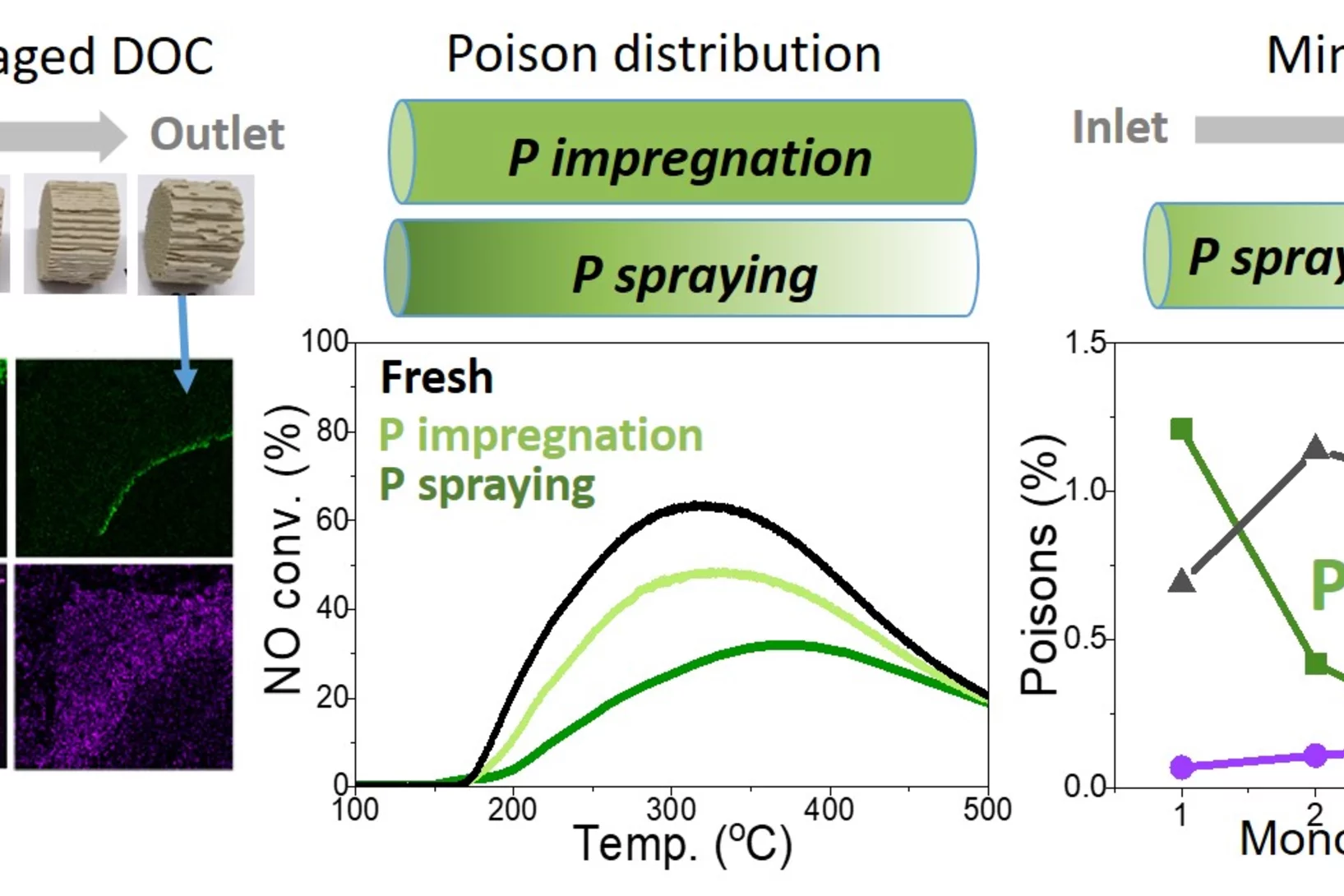
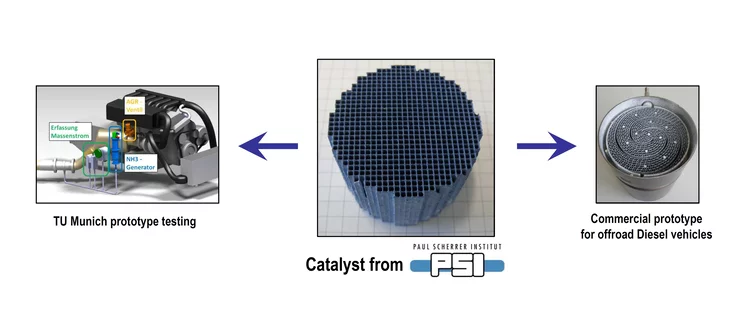
Aging of Diesel oxidation catalysts
Diesel oxidation catalysts mitigate toxic emissions in heavy duty vehicles but they age during operation due to deposition of chemical elements and structural changes in the active Platinum group metals. Here, vehicle aged catalysts have been characterised in detail to better understand the catalyst deterioration. Such understanding have been applied in the attempts to replicate the aging in the lab.
Modulated excitation Raman spectroscopy of vanadia-based catalysts
By combining modulated excitation and Raman spectroscopy, we obtained mechanistic insights that go beyond what is currently achievable with Raman experiments under steady-state conditions.
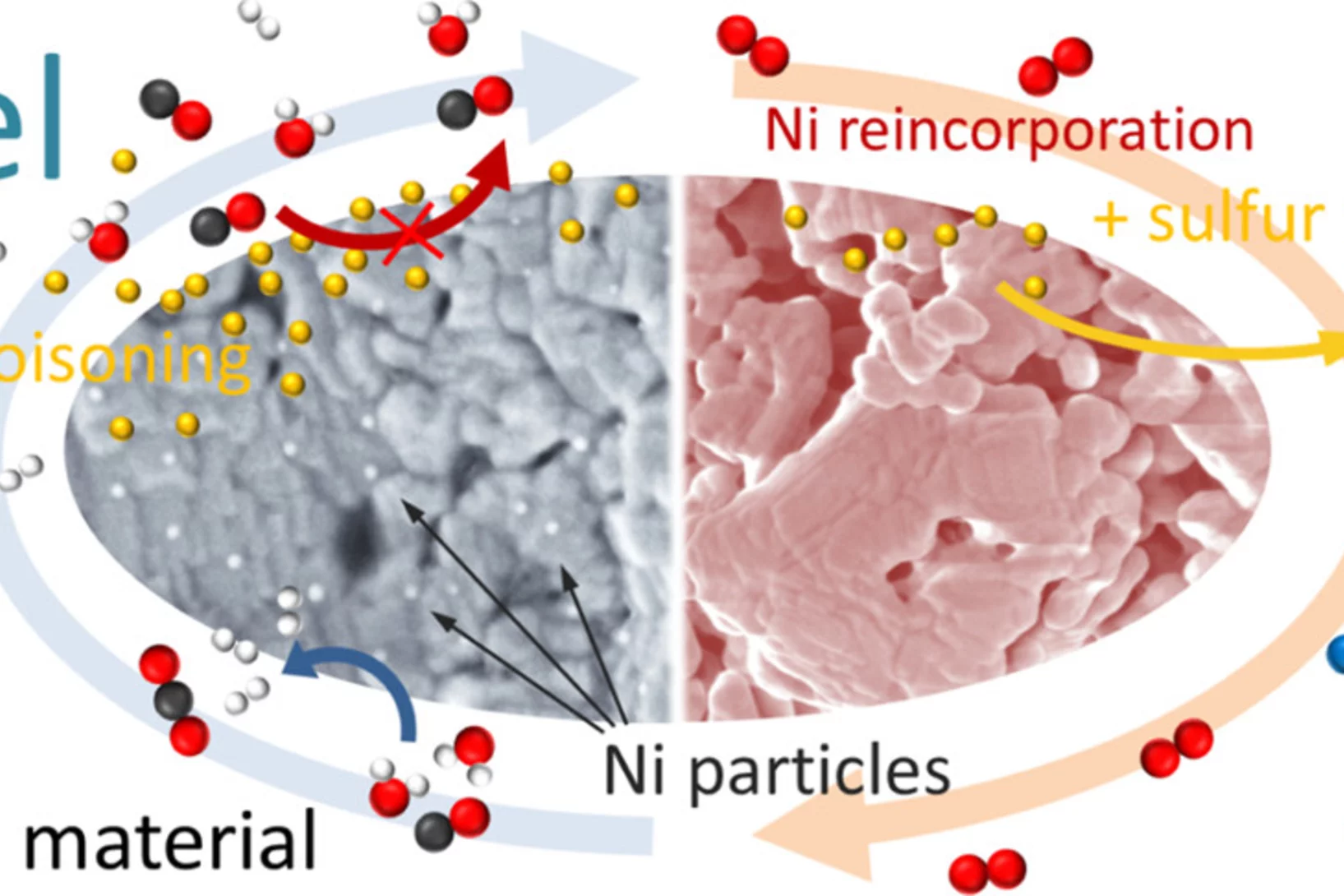
Sulfur poisoning recovery on a SOFC anode material through reversible segregation of Nickel
Exploitation of the self-regenerative property of perovskite-type oxides allowed to demonstrate recovery of La0.3Sr0.55Ti0.95Ni0.05O3 from sulfur poisoning by reversible segregation-incorporation of Ni at SOFC temperatures.
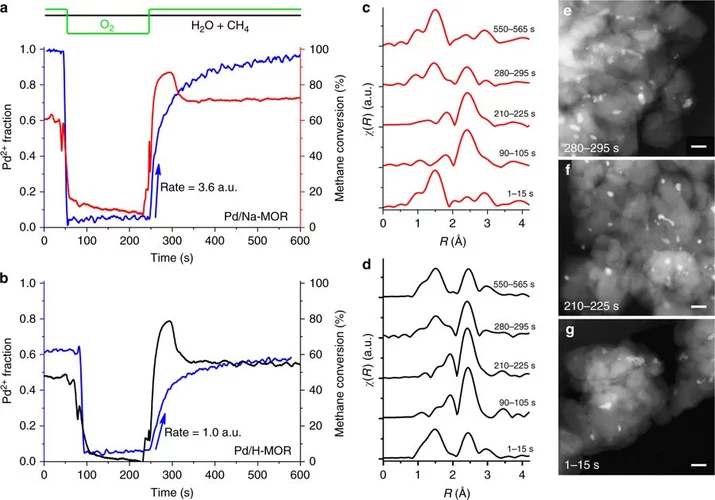
Stable complete methane oxidation over palladium based zeolite catalysts
Using targeted synthesis and in situ characterization a palladium catalyst with improved stability against sintering during methane oxidation was prepared.
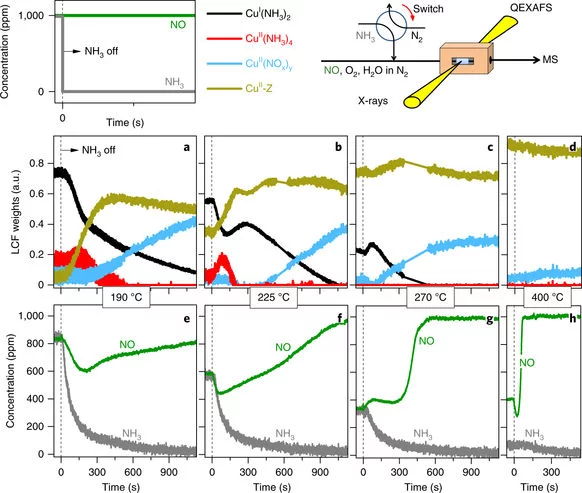
Time-resolved copper speciation during selective catalytic reduction of NO on Cu-SSZ-13
Through the combination of time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy and transient experimentation, we were able to capture an ammonia inhibition effect on the rate-limiting copper re-oxidation at low temperature.
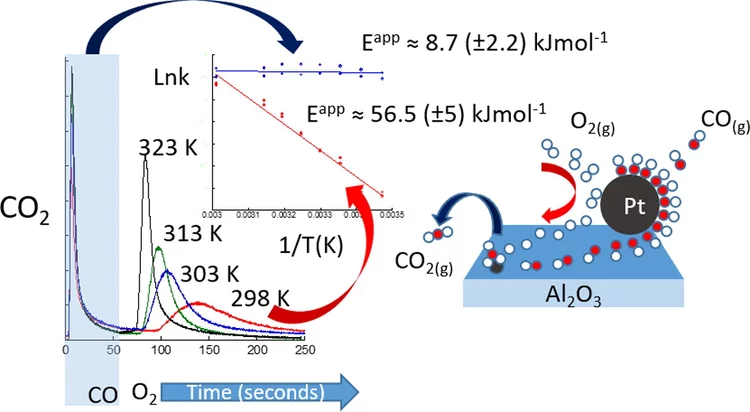
Kinetic studies of the Pt carbonate-mediated, room-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide by oxygen
The kinetics involved in ambient-temperature catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide by oxygen over a Pt/Al2O3 catalyst is evaluated under periodic redox operation using combined mass spectrometry, diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy and time-resolved Pt L3-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
Supported gold as catalyst for the decomposition of ammonia precursors in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx
Titanium dioxide-supported gold was found to catalyze the hydrolysis of formate-based ammonia precursor compounds which are proposed for the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides (NOx) in combustion exhaust gas. In contrast to other noble metals, the supported gold does not oxidize the released NH3, while it maintains decomposition of intermediate formic acid.
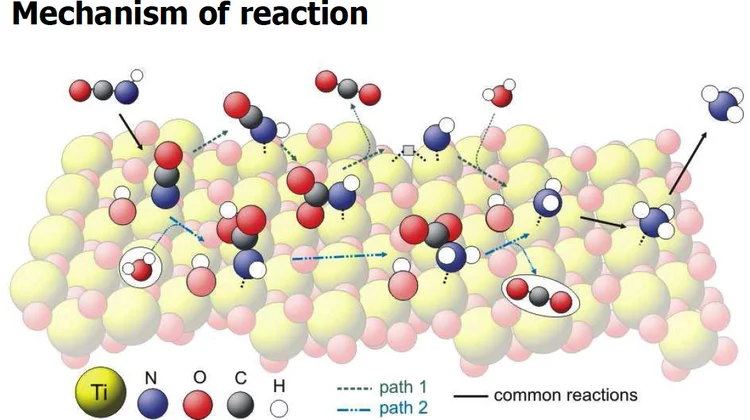
Vibrational spectra of adsorbates from DFT
The hydrolysis of isocyanic acid was studied experimentally and theoretically and a reaction mechanism on different catalysts was established. The decreasing NOx emission limits for diesel vehicles impel the further development of the existing NOx deactivation technologies, particularly the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of nitrogen oxides with urea. In the urea-SCR process, urea is injected into the hot exhaust gas, where it thermally decomposes into isocyanic acid (HNCO) and ammonia.