Our research on multifocus off-axis zone plates was accepted in “Optica”, the highest impact journal of the Optical Society of America. In the paper we report on different ways to combine focusing and beam-splitting functionalities in one single optical element.
Our research on multifocus off-axis zone plates was accepted in “Optica”, the highest impact journal of the Optical Society of America. In the paper we report on different ways to combine focusing and beam-splitting functionalities in one single optical element.
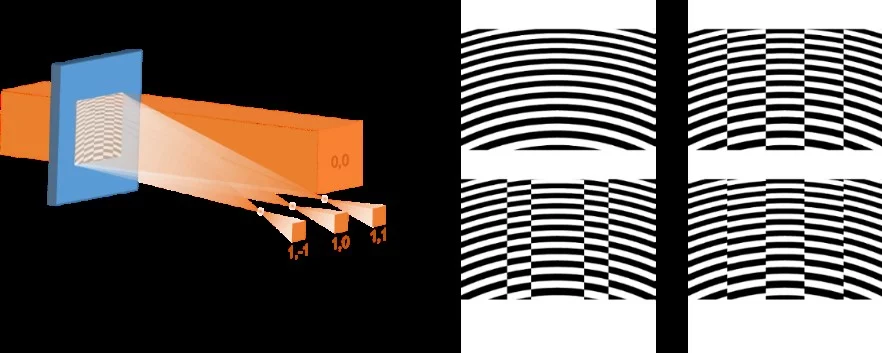
X-ray free electron lasers (XFELs) are currently among the most advanced light sources in the world and they are paving the way towards new experiments in many scientific fields. However, they suffer from strong intensity fluctuations inherent to the lasing process, which often leads to problems in signal normalization. In order to address this challenge, we designed, fabricated and characterized diffractive X-ray optics that combine the focusing properties of a Fresnel zone plate with the beam splitting capability of a grating in a single diffractive optical element. The possibility to split the incident beam into identical copies allows for direct shot-to-shot normalization of the sample signal, thereby greatly enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio in experiments with XFEL radiation.
These optics were fabricated at the Laboratory for Micro and Nanotechnology at PSI using state-of-the-art electron-beam nanolithography and plasma etching technology and characterized in detail using synchrotron light at the SIM beamline at the Swiss Light Source. Such optics enabled advanced experiments at the X-ray Free Electron Laser FERMI as well as at the European XFEL.
For future applications these devices become accessible via PSI’s recently founded high-tech startup XRnanotech (www.xrnanotech.ch).
Original Publication:
Florian Döring, Benedikt Rösner, Manuel Langer, Adam Kubec, Armin Kleibert, Jörg Raabe, Carlos A. F. Vaz, Maxime Lebugle, and Christian David, Multifocus off-axis zone plates for x-ray free-electron laser experiments, Optica Vol. 7, Issue 8, pp. 1007-1014 (2020) (https://doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.398022)