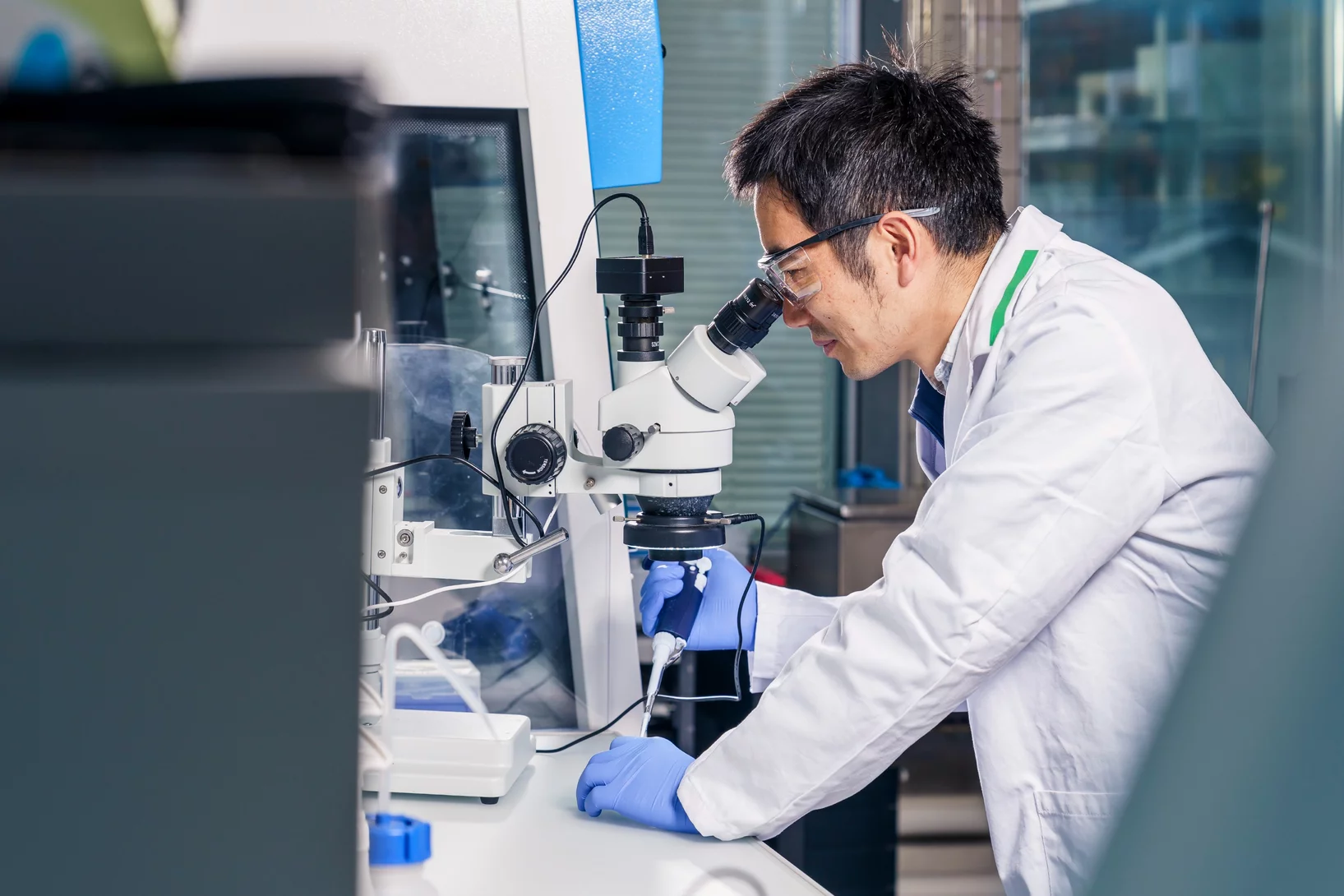
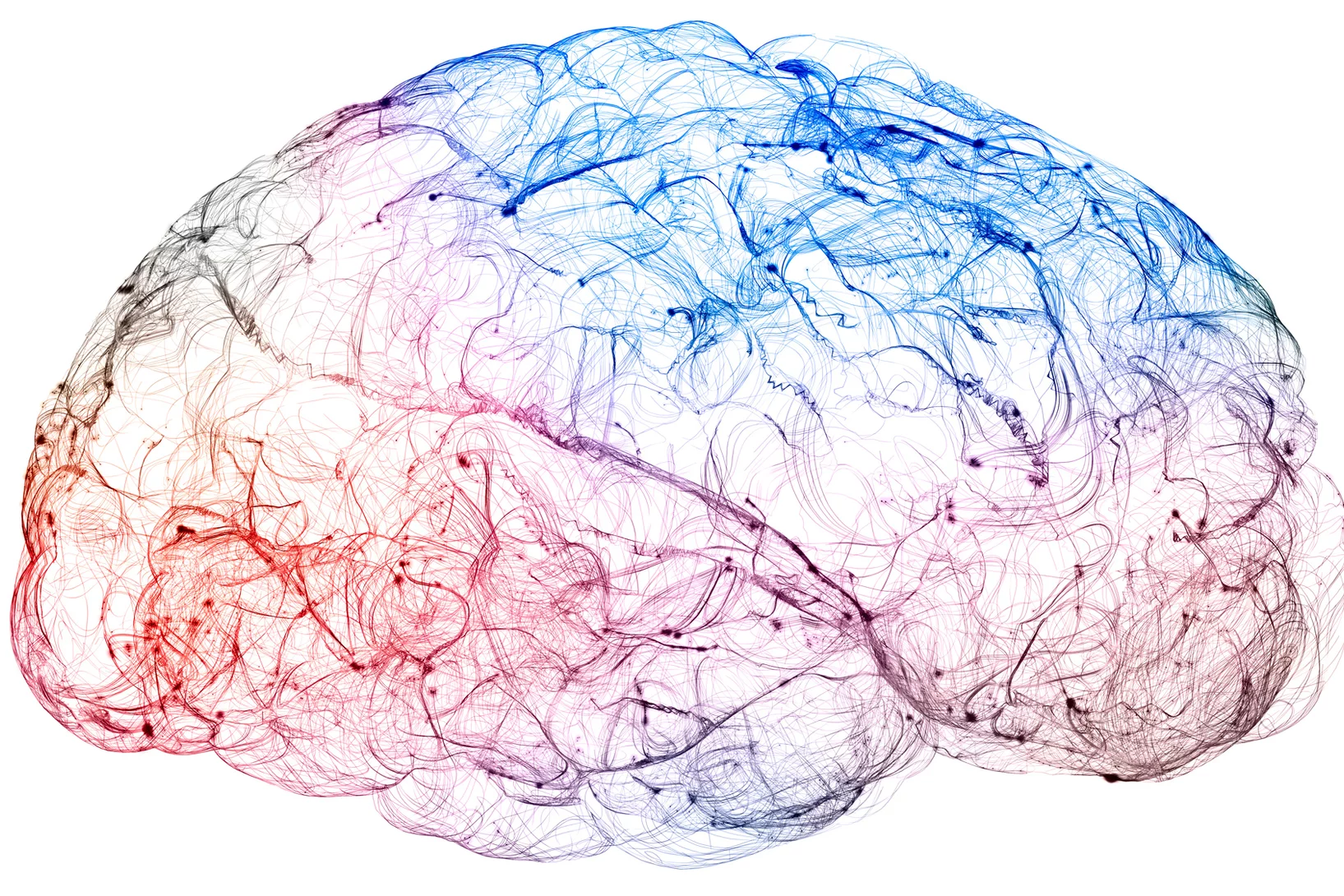
X-rays bring high-resolution brain mapping within reach
A new imaging breakthrough could reveal brain connectivity in 3D detail never before accessible.
How the cheese-pasta principle could help counter Alzheimer's
PSI researchers have discovered cellular mechanisms that could help to mitigate diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
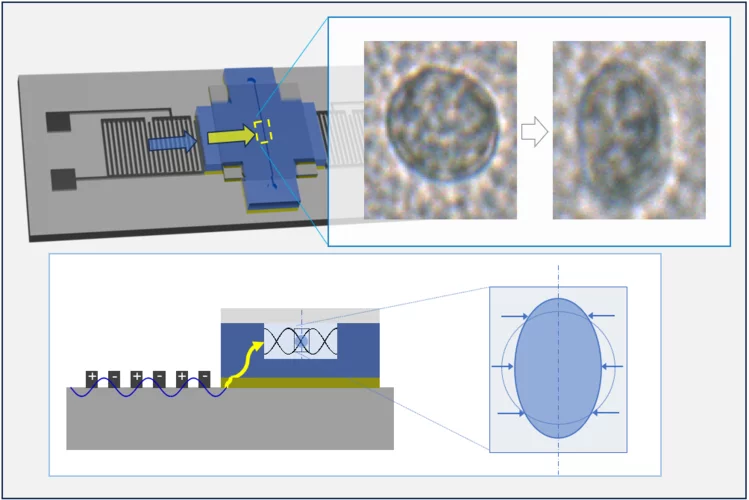
Manipulating microscopic object with sound
Manipulating microscopic objects with sound: hybrid acoustic tweezers with strong acoustic field were developed and successfully applied for transient mechanical deformation and capturing of biological cells.
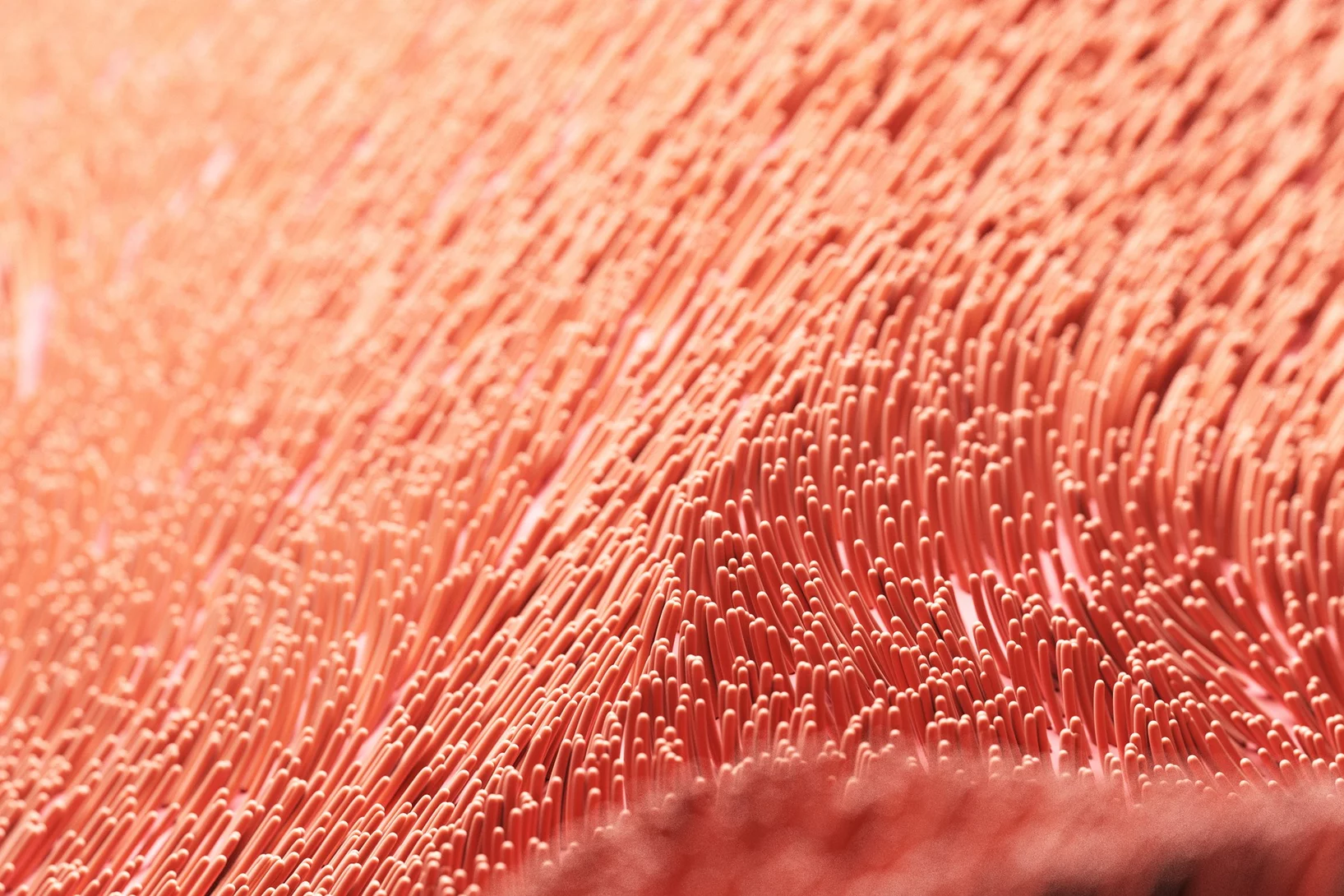
New insights into a rare disease
Researchers at PSI have uncovered how genetic defects damage human cilia in different ways – a step towards improving the diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia, a disease that has until now been poorly understood.
Demystifying electron ptychography with the PtychoScopy tool
The open-source PtychoScopy tool guides users towards higher quality and faster electron ptychographic reconstructions.
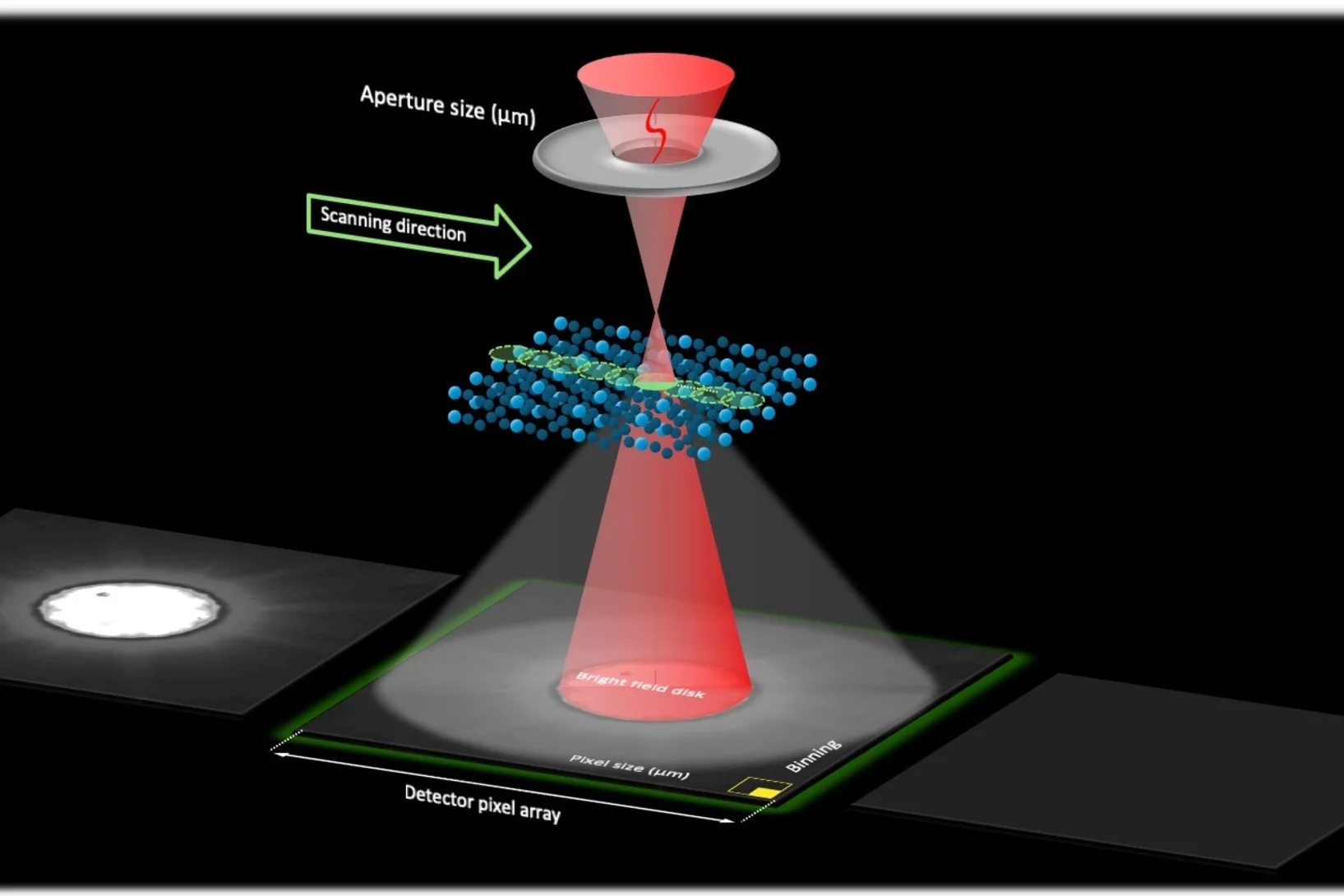
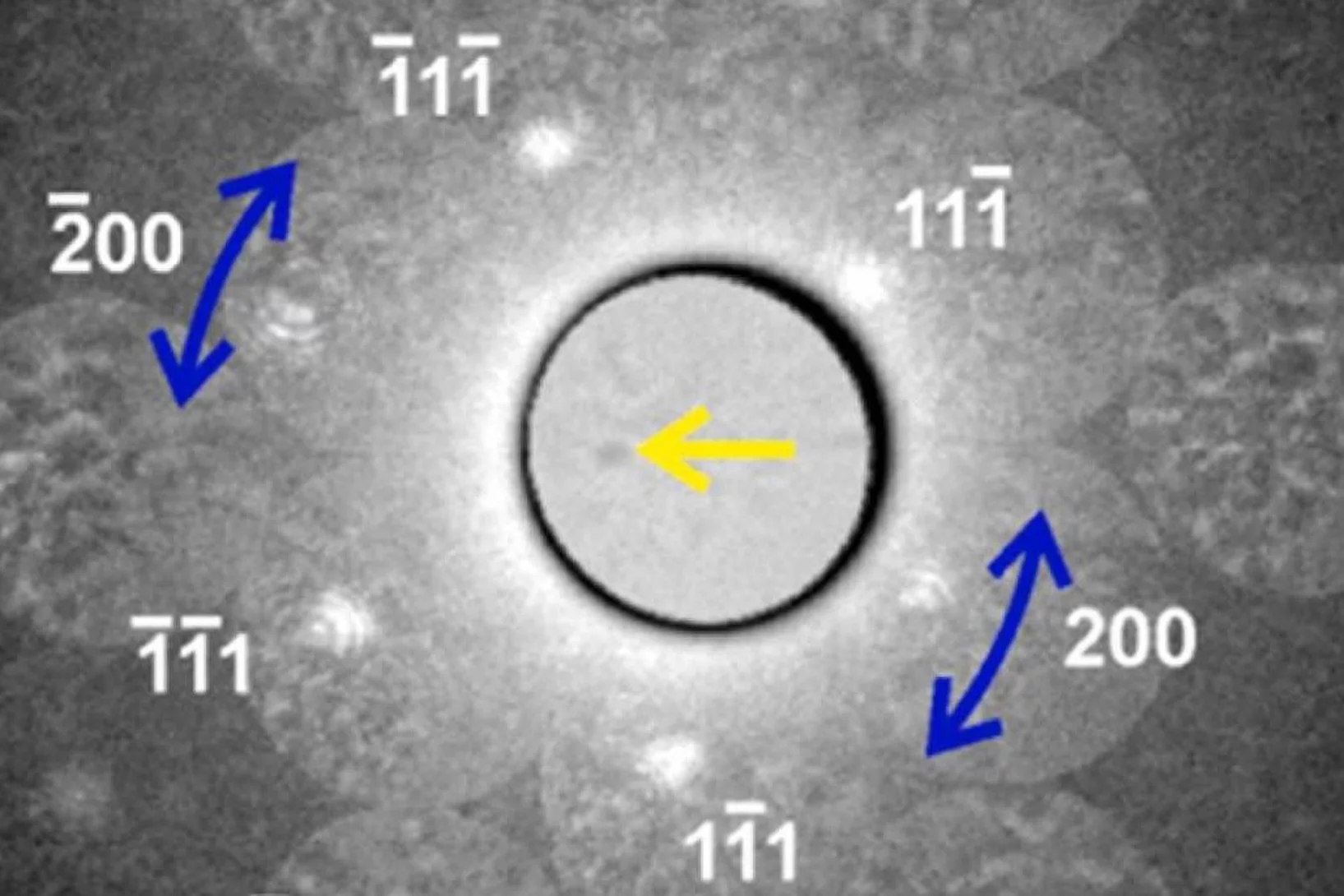
Gold nanoparticle dynamics on graphene probed by convergent beam electron diffraction.
Dynamics of single Au nanoparticles on graphene were probed simultaneously in real- and diffraction space by time-series convergent beam electron diffraction.
Using AI to identify genetic perturbations from cell images
New AI identifies genetic perturbations in chromatin – a potential approach in diagnostics and drug development.
Dynamical transitions in dense packings
Biophysical modeling points to changes in collective dynamics under confinement as a key aspect of cell state transitions.
Breast cancer classification using AI
Researchers at PSI and MIT are developing a new approach, which combines imaging and artificial intelligence to improve the staging of breast cancer.