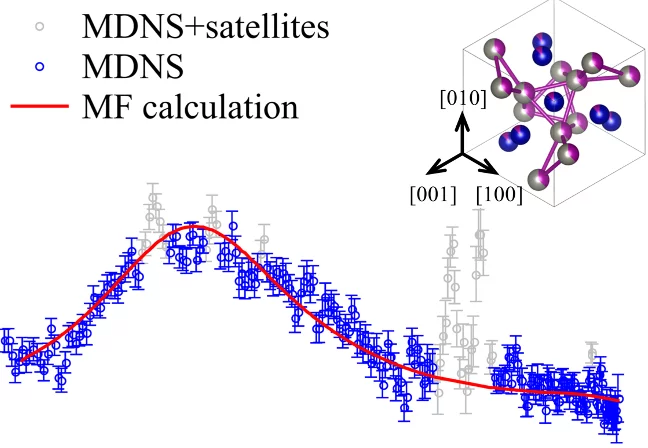
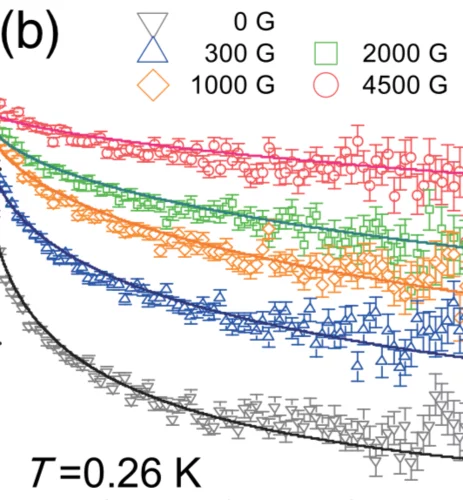
Frustration-driven magnetic fluctuations as the origin of the low-temperature skyrmion phase in Co7Zn7Mn6
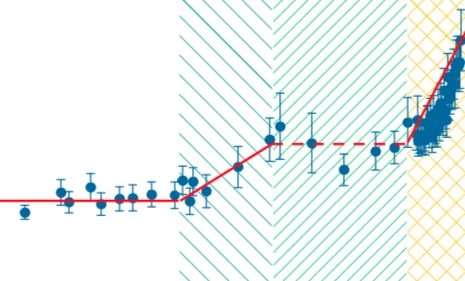
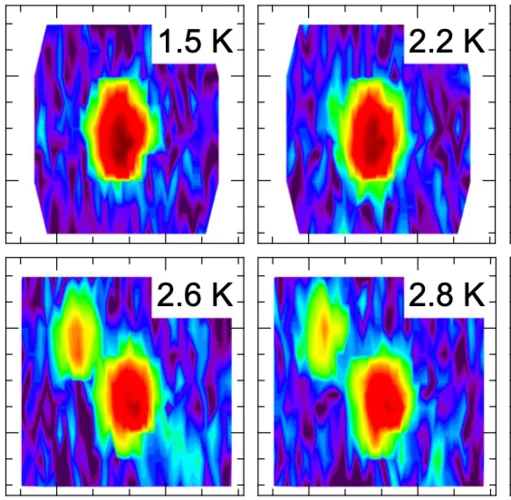
Magnetic skyrmions in chiral cubic helimagnets, are stabilized by thermal fluctuations over a narrow region directly below the magnetic ordering temperature. Due to often being touted for use in applications, there is high demand to identify new mechanism that can expand the equilibrium skyrmion phases where these topological vortices may display an enhanced robustness against external perturbations, such as magnetic fields, due to a larger magnetic order parameter.
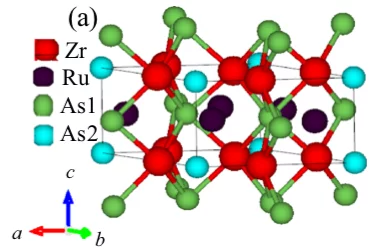
Probing the superconducting gap structure in the noncentrosymmetric topological superconductor ZrRuAs
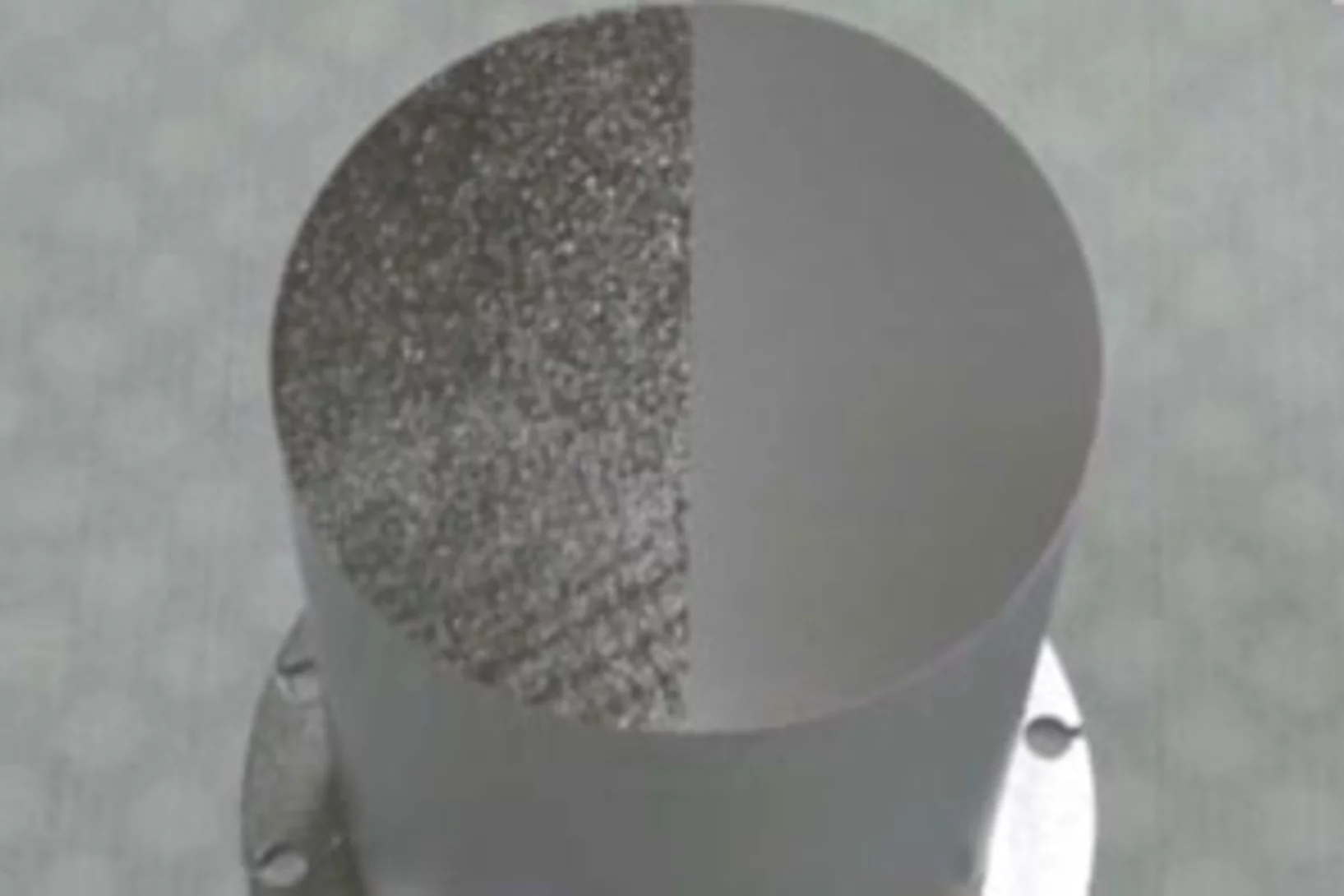
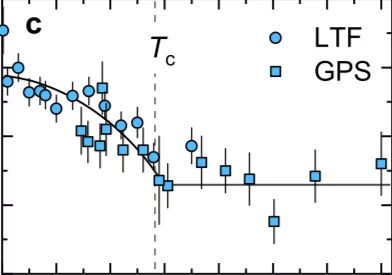
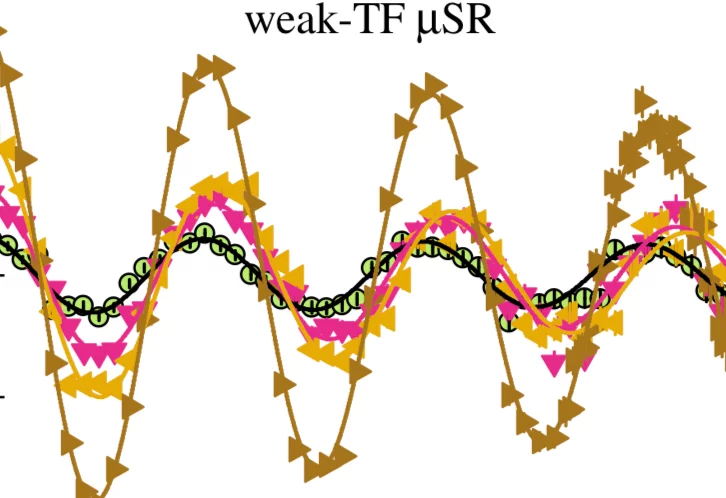
The superconducting gap structure of the topological superconductor candidate ZrRuAs with a noncen- trosymmetric crystal structure has been investigated using muon-spin rotation/relaxation (μSR) measurements in transverse-field (TF) and zero-field (ZF) geometries. Magnetization, electrical resistivity, and heat capacity measurements reveal bulk superconductivity below a superconducting transition temperature Tc = 7.9(1) K.
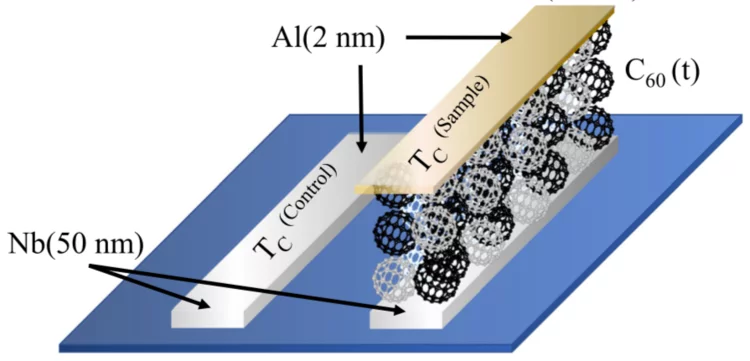
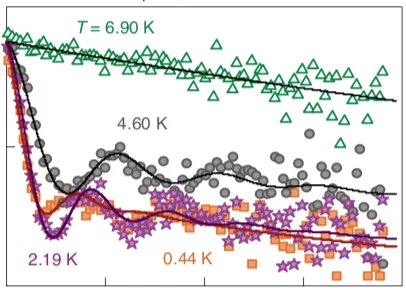
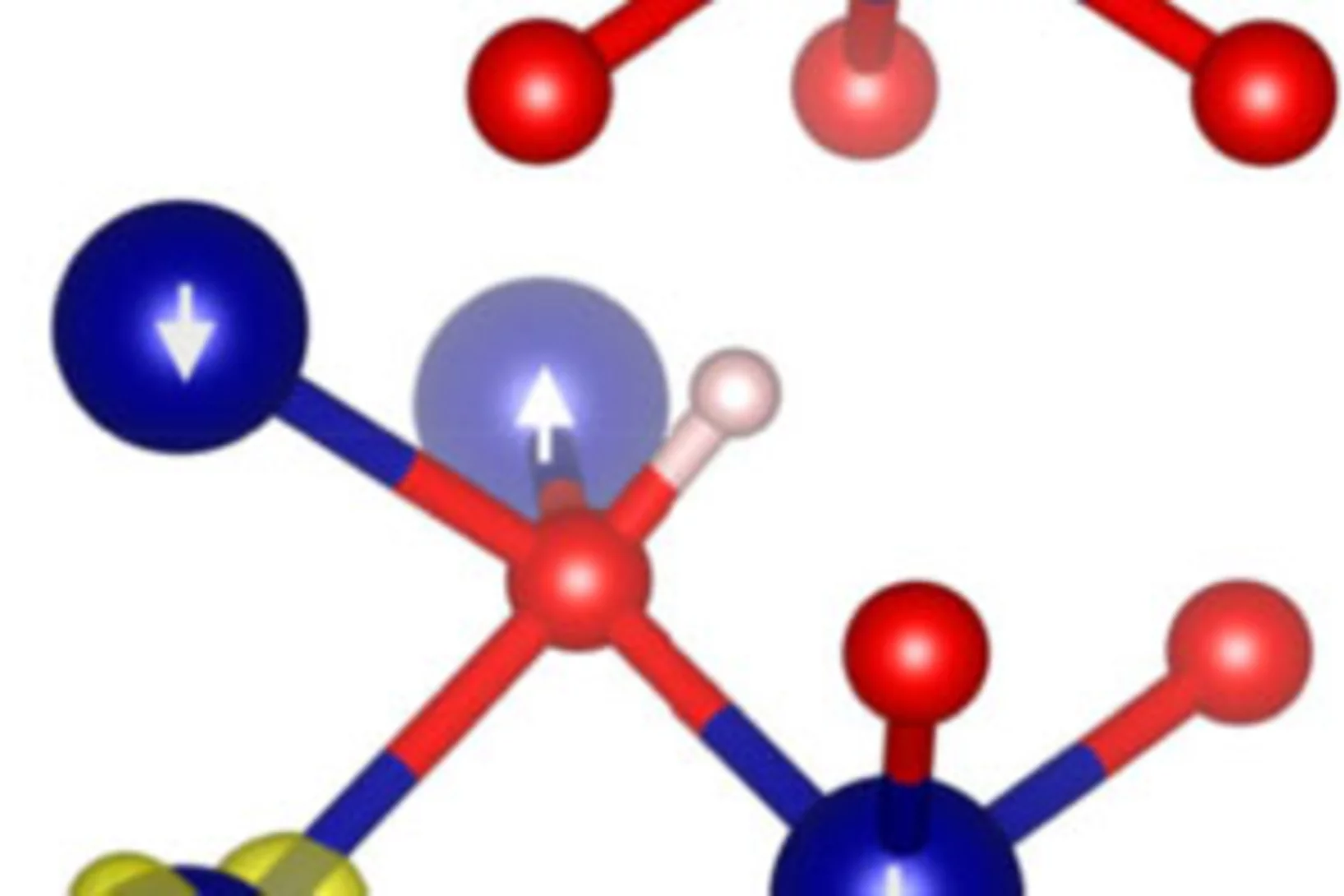
Spin-singlet to triplet Cooper pair converter interface
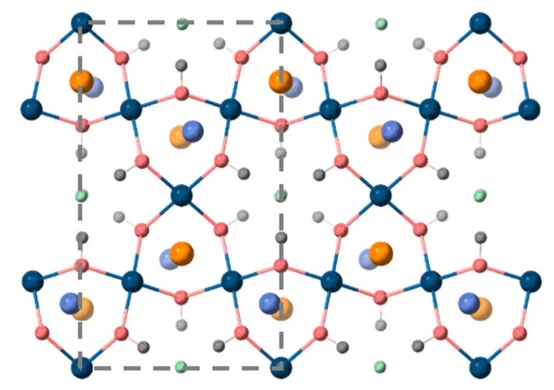
Combining magnetic and superconducting functionalities enables lower energy spin transfer and magnetic switching in quantum computing and information storage, owing to the dissipationless nature of quasi-particle mediated supercurrents. Here, we put forward a system where emergent spin-ordering and diffusion of Cooper pairs are achieved at a non-intrinsically magnetic nor superconducting metallo-molecular interface.
Split superconducting and time-reversal symmetry-breaking transitions in Sr2RuO4 under stress
Strontium ruthenate (Sr2RuO4) continues to present an important test of our understanding of unconventional superconductivity, because while its normal-state electronic structure is known with precision, its superconductivity remains unexplained. There is evidence that its order parameter is chiral, but reconciling this with recent observations of the spin part of the pairing requires an order parameter that is either finely tuned or implies a new form of pairing. Therefore, a definitive resolution of whether the superconductivity of Sr2RuO4 is chiral is important for the study of superconductivity.
Quantum spin-liquid states in an organic magnetic layer and molecular rotor hybrid
A better understanding of quantum spin liquids (QSLs), where spin dimer configurations are fluctuating even at the low- est temperatures, could be of use in quantum information, in superconducting or other technologies. This macroscopic collective state typically arises from geometrical frustration or low dimensionality. In the layered EDT-BCO, we report a QSL state, which is generated, on different bases, with the intrinsic disorder.
Re(1−x)Mox as an ideal test case of time-reversal symmetry breaking in unconventional superconductors
Non-centrosymmetric superconductors (NCSCs) are promising candidates in the search for unconventional and topological superconductivity. The α-Mn-type rhenium-based alloys represent excellent examples of NCSCs, where spontaneous magneticfields, peculiar to time-reversal symmetry (TRS) breaking, have been shown to develop in the superconducting phase. By converse, TRS is preserved in many other isostructural NCSCs, thus leaving the key question about its origin fully open. Here, we consider ...
From magnetic order to quantum disorder in the Zn-barlowite series of S = 1/2 kagomé antiferromagnets
We report a comprehensive muon spectroscopy study of the Zn-barlowite series of S=1/2 kagomé antiferromagnets, ZnxCu4−x(OH)6FBr, for x = 0.00 to 0.99(1). By combining muon spin relaxation and rotation measurements with state-of-the-art density-functional theory muon-site calculations, we observe the formation of both μ–F and μ–OH complexes in Zn-barlowite. From these stopping sites, implanted muon spins reveal the suppression of long-range magnetic order into a possible quantum spin liquid state upon the increasing concentration of Zn-substitution.
Front passivation of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells using Al2O3: Culprits and benefits
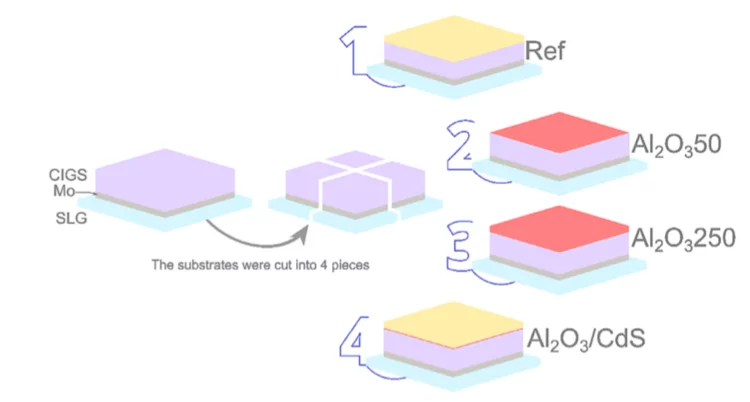
In the past years, the strategies used to break the Cu(In,Ga)Se2 (CIGS) light to power conversion effi- ciency world record value were based on improvements of the absorber optoelectronic and crystalline properties, mainly using complex post-deposition treatments. To reach even higher efficiency values, fur- ther advances in the solar cell architecture are needed, in particular, with respect to the CIGS interfaces. In this study, we evaluate the structural, morphological and optoelectronic impact of an Al2O3 layer as a potential front passivation layer on the CIGS properties, as well as an Al2O3 tunneling layer between CIGS and CdS.
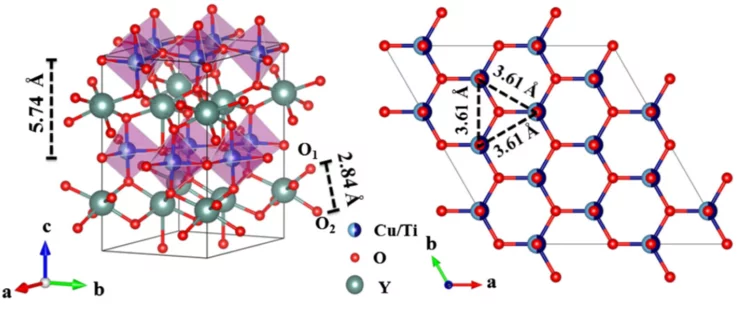
Signatures of a Spin-1/2 Cooperative Paramagnet in the Diluted Triangular Lattice of Y2CuTiO6
We present a combination of thermodynamic and dynamic experimental signatures of a disorder driven dynamic cooperative paramagnet in a 50% site diluted triangular lattice spin-1/2 system: Y2CuTiO6. Magnetic ordering and spin freezing are absent down to 50 mK, far below the Curie-Weiss scale (-θCW) of ∼134 K.
Spin-orbit quantum impurity in a topological magnet
Quantum states induced by single-atomic impurities are at the frontier of physics and material science. While such states have been reported in high-temperature superconductors and dilute magnetic semiconductors, they are unexplored in topological magnets which can feature spin-orbit tunability. Here we use spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy/ spectroscopy (STM/S) to study the engineered quantum impurity in a topological magnet Co3Sn2S2. We find that each substituted In impurity introduces a striking localized bound state.
Using Uniaxial Stress to Probe the Relationship between Competing Superconducting States in a Cuprate with Spin-stripe Order
We report muon spin rotation and magnetic susceptibility experiments on in-plane stress effects on the static spin-stripe order and superconductivity in the cuprate system La2−xBaxCuO4 with x = 0.115. An extremely low uniaxial stress of ∼0.1 GPa induces a substantial decrease in the magnetic volume fraction and a dramatic rise in the onset of 3D superconductivity, from ∼10 to 32 K.
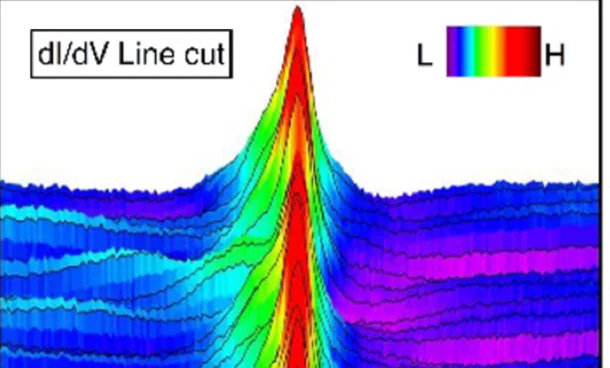
Many-Body Resonance in a Correlated Topological Kagome Antiferromagnet
We use scanning tunneling microscopy to elucidate the atomically resolved electronic structure in the strongly correlated kagome Weyl antiferromagnet Mn3Sn. In stark contrast to its broad single-particle electronic structure, we observe a pronounced resonance with a Fano line shape at the Fermi level resembling the many-body Kondo resonance. We find that this resonance does not arise from the step edges or atomic impurities but the intrinsic kagome lattice.
Handedness-dependent quasiparticle interference in the two enantiomers of the topological chiral semimetal PdGa
It has recently been proposed that combining chirality with topological band theory results in a totally new class of fermions. Understanding how these unconventional quasiparticles propagate and interact remains largely unexplored so far. Here, we use scanning tunneling microscopy to visualize the electronic properties of the prototypical chiral topological semimetal PdGa.
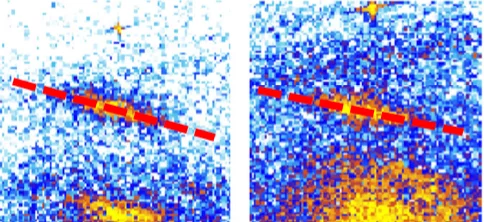
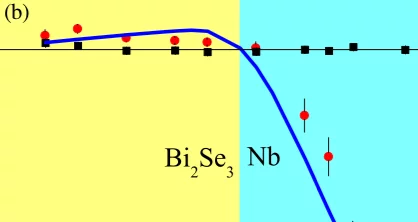
Proximity-Induced Odd-Frequency Superconductivity in a Topological Insulator
At an interface between a topological insulator (TI) and a conventional superconductor (SC), superconductivity has been predicted to change dramatically and exhibit novel correlations. In particular, the induced superconductivity by an s-wave SC in a TI can develop an order parameter with a p-wave component. Here we present experimental evidence for an unexpected proximity-induced novel super- conducting state in a thin layer of the prototypical TI, Bi2Se3 proximity coupled to Nb.
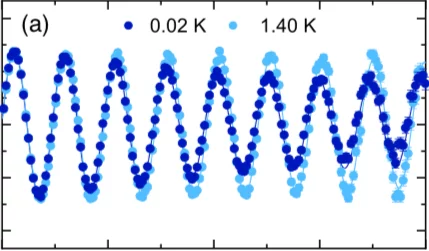
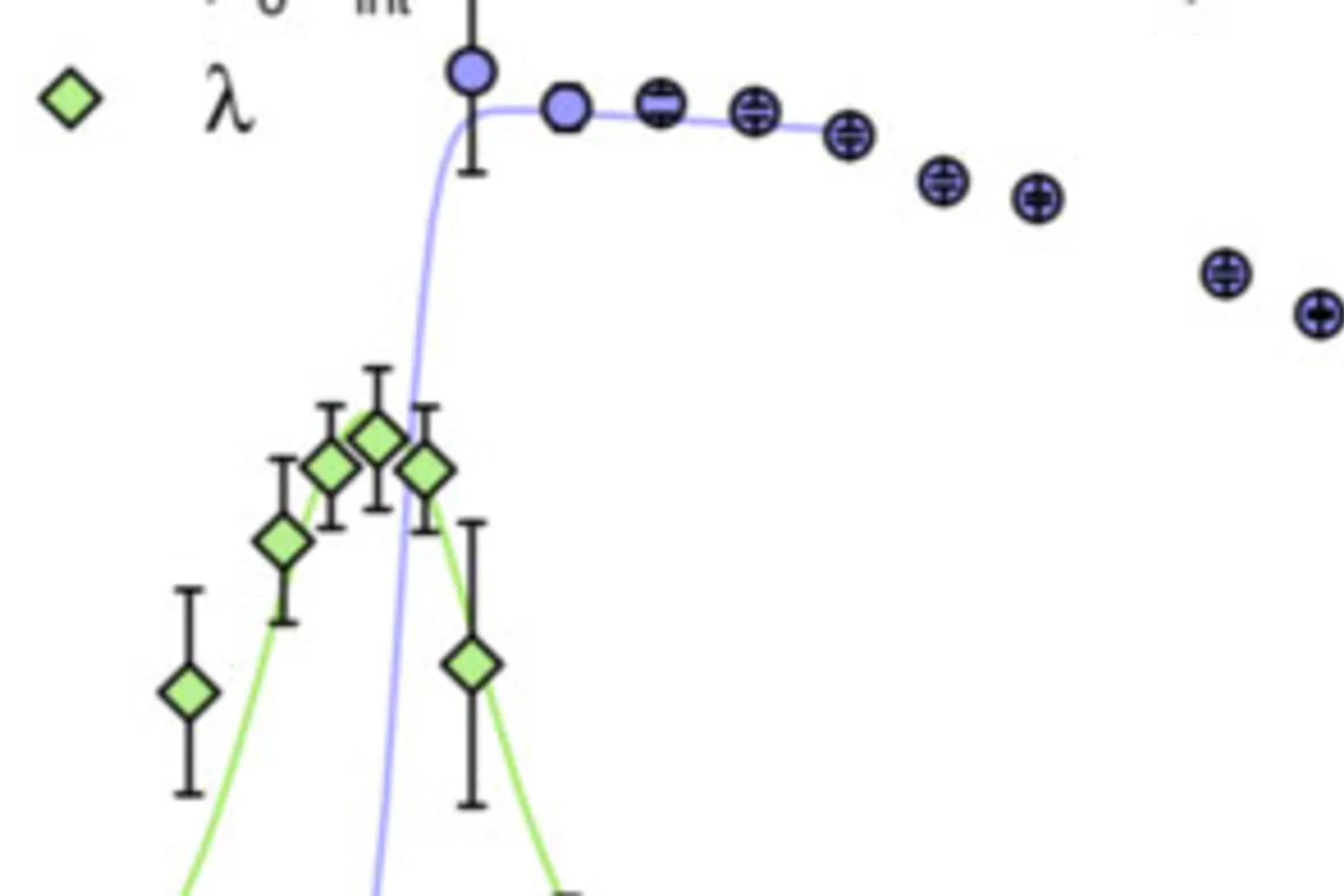
Simultaneous Nodal Superconductivity and Time-Reversal Symmetry Breaking in the Noncentrosymmetric Superconductor CaPtAs
By employing a series of experimental techniques, we provide clear evidence that CaPtAs represents a rare example of a noncentrosymmetric superconductor which simultaneously exhibits nodes in the superconducting gap and broken time-reversal symmetry (TRS) in its superconducting state (belowTc ≈ 1.5 K). Unlike in fully gapped superconductors, the magnetic penetration depth λ(T) does not saturate at low temperatures, but instead it shows a T2 dependence, characteristic of gap nodes.
Superconductivity with broken time-reversal symmetry inside a superconducting s-wave state
In general, magnetism and superconductivity are antagonistic to each other. However, there are several families of superconductors in which superconductivity coexists with magnetism, and a few examples are known where the superconductivity itself induces spontaneous magnetism. The best known of these compounds are Sr2RuO4 and some non-centrosymmetric superconductors. Here, we report the finding of ...
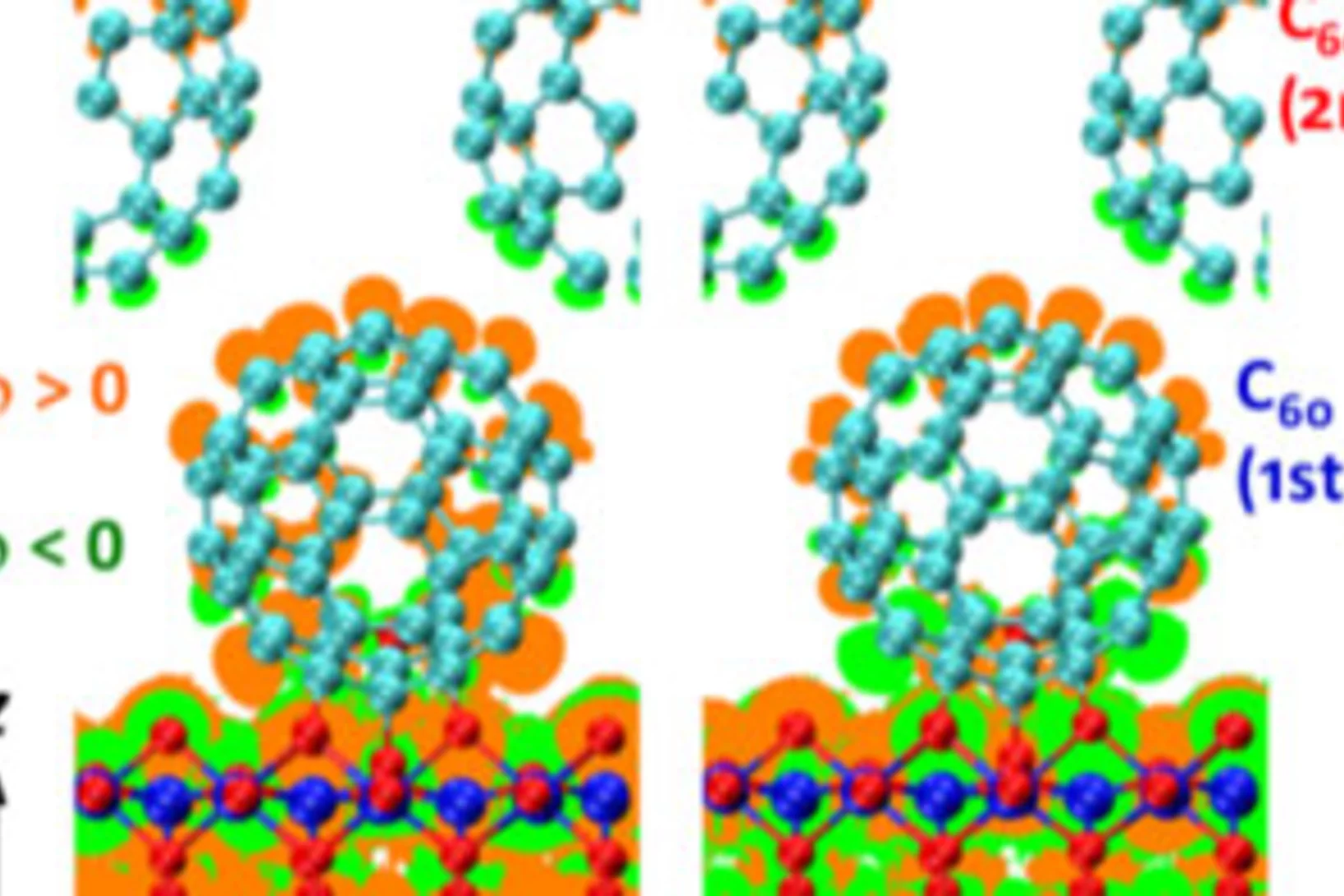
Reversible spin storage in metal oxide - fullerene heterojunctions
We show that hybrid MnOx/C60 heterojunctions can be used to design a storage device for spin-polarized charge: a spin capacitor. Hybridization at the carbon-metal oxide interface leads to spin-polarized charge trapping after an applied voltage or photocurrent. Strong electronic structure changes, including a 1-eV energy shift and spin polarization in the C60 lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, are then revealed by x-ray absorption spectroscopy, in agreement with density functional theory simulations.
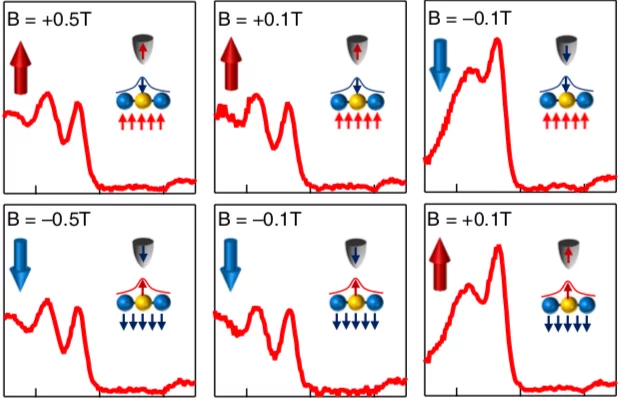
Observation of a Charge-Neutral Muon-Polaron Complex in Antiferromagnetic Cr2O3
We report a comprehensive muon spin rotation (μSR) study of the prototypical magnetoelectric antiferromagnet Cr2O3. We find the positively charged muon (μ+) occupies several distinct interstitial sites and displays a rich dynamic behavior involving local hopping, thermally activated site transitions, and the formation of a charge-neutral complex composed of a muon and an electron polaron.
Tunable anomalous Hall conductivity through volume-wise magnetic competition in a topological kagome magnet
Magnetic topological phases of quantum matter are an emerging frontier in physics and material science. Along these lines, several kagome magnets have appeared as the most promising platforms. Here, we explore magnetic correlations in the kagome magnet Co3Sn2S2. Using muon spin-rotation, we present evidence for competing magnetic orders in the kagome lattice of this compound.
Magnetic-Field Control of Topological Electronic Response near Room Temperature in Correlated Kagome Magnets
Strongly correlated kagome magnets are promising candidates for achieving controllable topological devices owing to the rich interplay between inherent Dirac fermions and correlation-driven magnetism. Here we report tunable local magnetism and its intriguing control of topological electronic response near room temperature in the kagome magnet Fe3Sn2 using small angle neutron scattering, muon spin rotation, and magnetoresistivity measurement techniques.
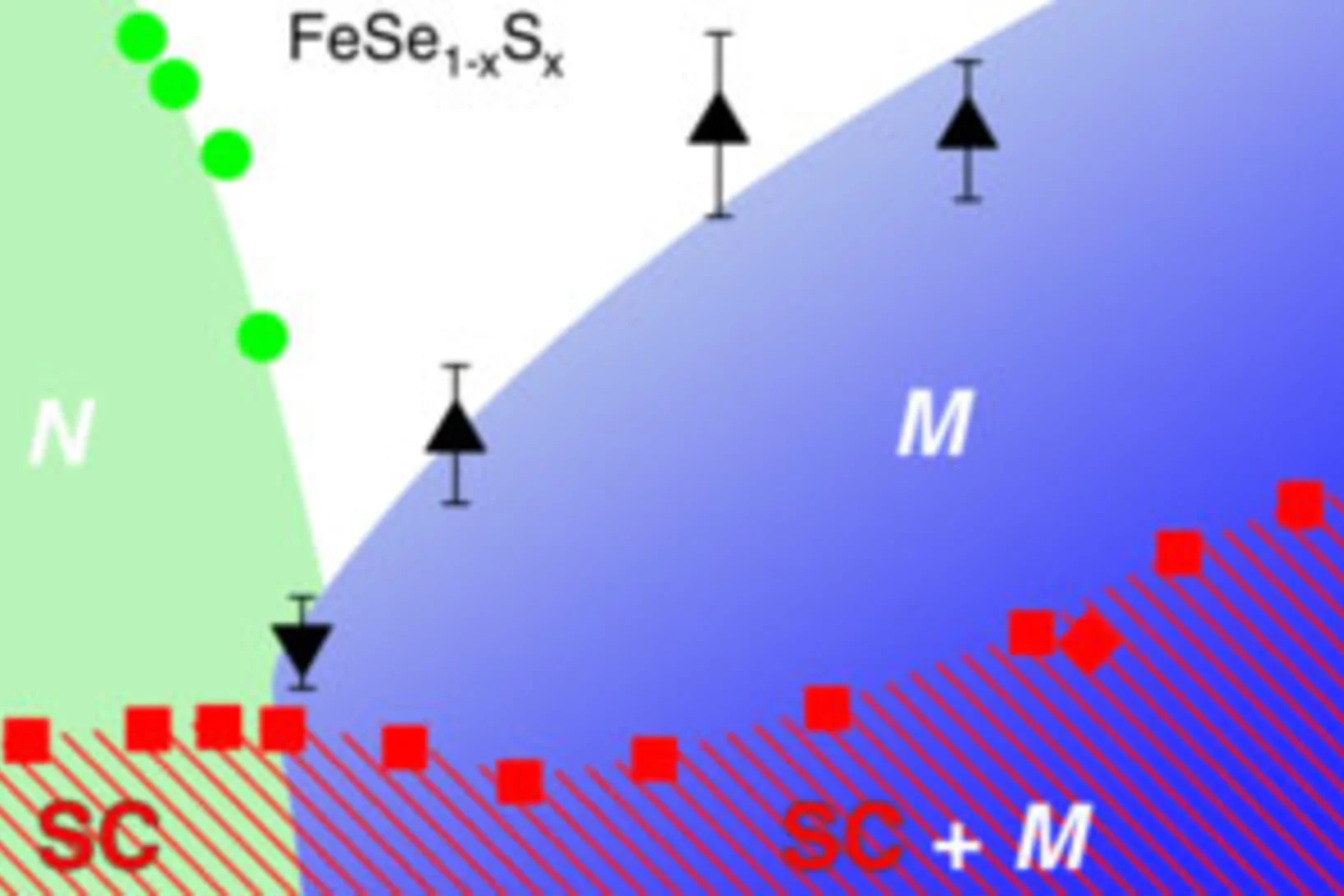
Extended Magnetic Dome Induced by Low Pressures in Superconducting FeSe(1 − x)Sx
We report muon spin rotation and magnetization measurements under pressure on Fe1+δSe1−xSx with x ≈ 0.11. Above p ≈ 0.6 GPa we find a microscopic coexistence of superconductivity with an extended dome of long range magnetic order that spans a pressure range between previously reported separated magnetic phases.
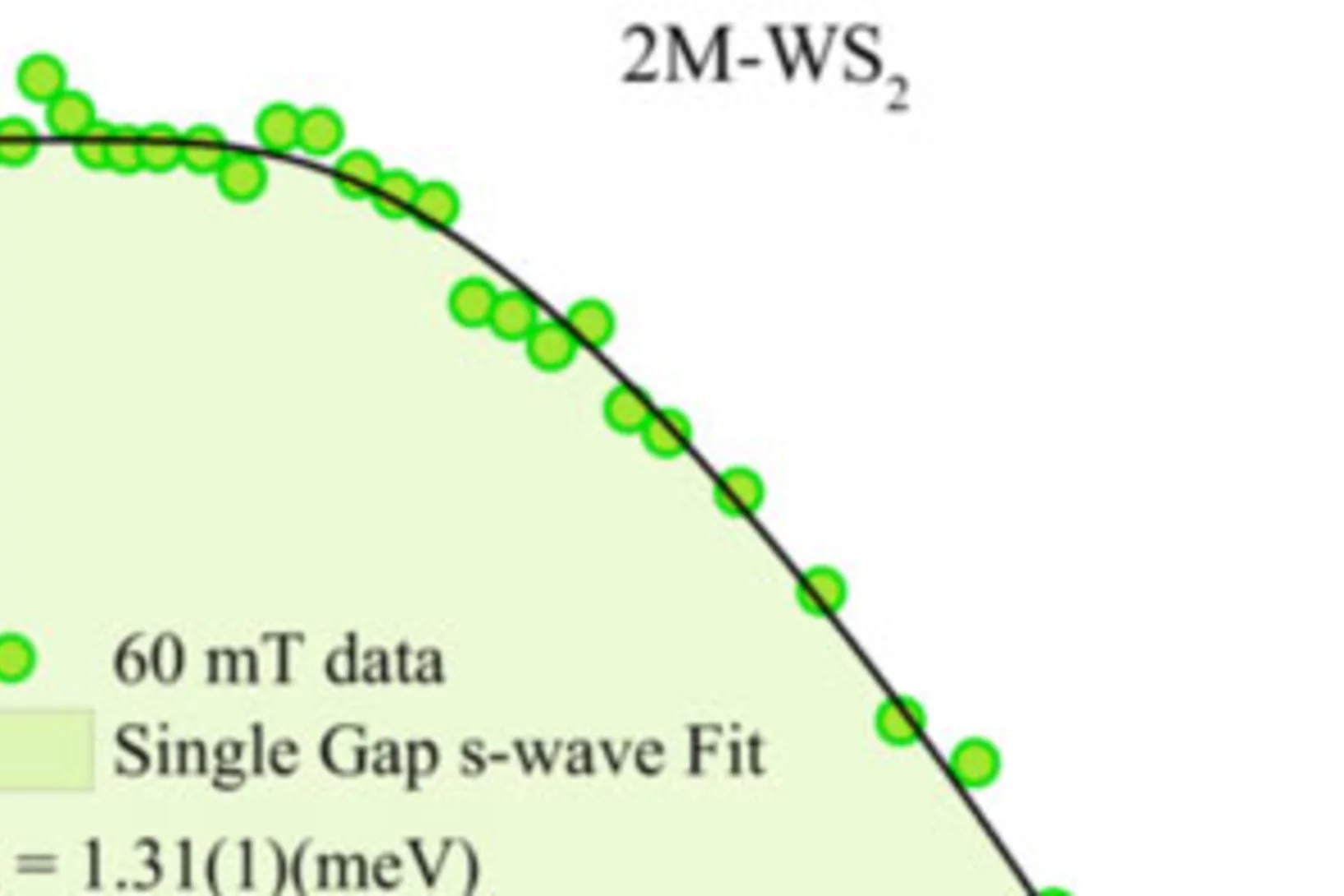
Nodeless superconductivity and its evolution with pressure in the layered dirac semimetal 2M-WS2
Recently, the transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) system 2M-WS2 has been identified as a Dirac semimetal exhibiting both superconductivity with the highest Tc ~ 8.5 K among all the TMD materials and topological surface states. Here we report on muon spin rotation (μSR) and density functional theory studies of microscopic SC properties and the electronic structure in 2M-WS2 at ambient and under hydrostatic pressures (pmax = 1.9 GPa).
Experimental signatures of a three-dimensional quantum spin liquid in effective spin-1/2 Ce2Zr2O7 pyrochlore
A quantum spin liquid is a state of matter where unpaired electrons’ spins, although entangled, do not show magnetic order even at the zero temperature. The realization of a quantum spin liquid is a long-sought goal in condensed-matter physics.
Critical fields of Nb3Sn prepared for superconducting cavities
Nb3Sn is currently the most promising material other than niobium for future superconducting radiofrequency cavities. Critical fields above 120 mT in pulsed operation and about 80 mT in CW have been achieved in cavity tests. This is large compared to the lower critical field as derived from the London penetration depth, extracted from low field surface impedance measurements.
Phase transition in the cuprates from a magnetic-field-free stiffness meter viewpoint
A method to measure the superconducting (SC) stiffness tensor ρs, without subjecting the sample to external magnetic field, is applied to La1.875Sr0.125CuO4. The method is based on the London equation J=-ρsA, where J is the current density and A is the vector potential which is applied in the SC state.
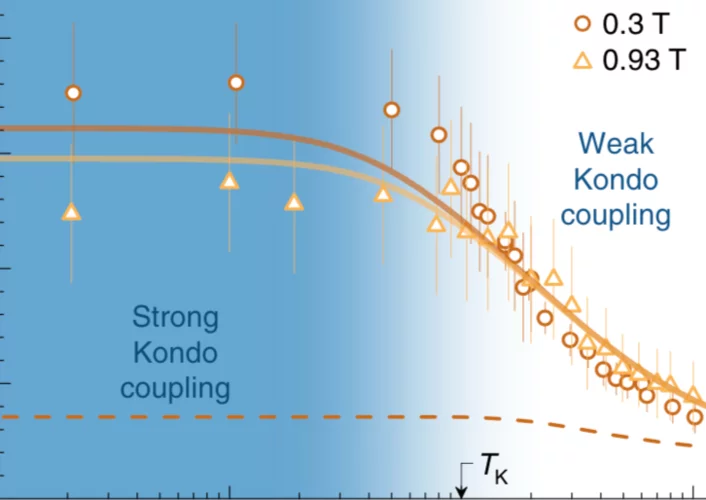
Kondo screening in a charge-insulating spinon metal
The Kondo effect, an eminent manifestation of many-body physics in condensed matter, is traditionally explained as exchange scattering of conduction electrons on a spinful impurity in a metal. The resulting screening of the impurity's local moment by the electron Fermi sea is characterized by a Kondo temperature TK, below which the system enters a strongly coupled regime.
Elementary excitation in the spin-stripe phase in quantum chains
Elementary excitations in condensed matter capture the complex many-body dynamics of interacting basic entities in a simple quasiparticle picture. In magnetic systems the most established quasiparticles are magnons, collective excitations that reside in ordered spin structures, and spinons, their fractional counterparts that emerge in disordered, yet correlated spin states.
Exotic Low-Energy Excitations Emergent in the Random Kitaev Magnet Cu2IrO3
We report on magnetization M(H), dc and ac magnetic susceptibility Χ(T), specific heat Cm(T) and muon spin relaxation (μSR) measurements of the Kitaev honeycomb iridate Cu2IrO3 with quenched disorder. In spite of the chemical disorders, we find no indication of spin glass down to 260 mK from the Cm(T) and μSR data.
Negative flat band magnetism in a spin–orbit-coupled correlated kagome magnet
Electronic systems with flat bands are predicted to be a fertile ground for hosting emergent phenomena including unconven- tional magnetism and superconductivity, but materials that manifest this feature are rare. Here, we use scanning tunnelling microscopy to elucidate the atomically resolved electronic states and their magnetic response in the kagome magnet Co3Sn2S2.
Search for the Magnetic Monopole at a Magnetoelectric Surface
We show, by solving Maxwell’s equations, that an electric charge on the surface of a slab of a linear magnetoelectric material generates an image magnetic monopole below the surface provided that the magnetoelectric has a diagonal component in its magnetoelectric response. The image monopole, in turn, generates an ideal monopolar magnetic field outside of the slab.