Scientific Highlights
Imaging the inside of injection needles with neutrons
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, the University of Basel and Roche have used neutron imaging to investigate why cool storage is crucial for syringes pre-filled with a liquid medication.
Fresnel Zone Plates with Zone Widths below 10 nm
The spot size of a Fresnel Zone Plate lens is mainly determined by the zone widths of its outermost zone. It is therefore essential to fabricate zone plates with structures as small as possible for high-resolution X-ray microscopy. Researchers at the Laboratory for Micro- and Nanotechnology at the PSI have now developed Fresnel zone plates with zone widths well below 10 nm, down to 6.4 nm. These lenses are capable of pushing resolution in X-ray microscopy to the single-digit regime.
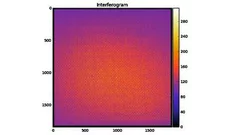
A first glance at the SwissFEL x-rays wave-front
X-ray Free Electron Lasers (XFELs) combine the properties of synchrotron radiation (short wavelengths) and laser radiation (high lateral coherence, ultrashort pulse durations). These outstanding machines allow to study ultra-fast phenomena at an atomic level with unprecedented temporal resolution for answering the most intriguing open questions in biology, chemistry and physics.
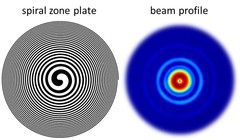
Extreme Ultraviolet Vortices at Free Electron Lasers
PSI scientists have developed tailored diffractive X-ray optics for a free electron laser that induces an optical vortex in extreme ultraviolet radiation. The experiment facilitates the first demonstration of orbital angular momentum in radiation created by a free electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet regime, with an extraordinary clean and defined wavefront. In a collaborative effort with researchers from the FERMI free electron laser in Trieste, Italy and from the University of Nova Gorica in Slovenia, the wavefront of the intense beams carrying an orbtial angular momentum was characterized. Furthermore, a method to characterize the footprint of a focused beam from a free electron laser was refined based on ablation imprints in polymers and subsequent treatment with organic solvents. In this way, the sensitivity of the imprint method could be enhanced to a dynamic range of three orders of magnitude in a single shot.
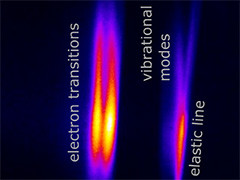
A new RIXS analyzer scheme based on transmission zone plates
PSI scientists have developed a new type of X-ray optics that allows for analyzing the emission in resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) experiments. The new approach combines the energy dispersion with imaging capabilities. In a collaborative effort with research groups from Göttingen and Hamburg, two new classes of RIXS experiments, energy mapping and RIXS imaging, have been demonstrated.
Scientists get first direct look at how electrons ‘dance’ with vibrating atoms
Research experience from California's X-ray free-electron laser benefits SwissFEL. It's the camera that allows researchers to make extremely rapid processes visible: the X-ray free-electron laser. Currently, however, only three sites worldwide—in the US, Japan and South Korea—have facilities capable of carrying out such measurements. Two current articles in Science and Nature Communications co-authored by researchers now at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI exemplify the kind of outstanding scientific work that can be carried out at such facilities, enabling new insights into the mechanisms of superconductors and magnetic switching in molecules. The measurements were conducted at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) free-electron laser in California. Press release PSI / Press release SLAC
Poster Prize for Marcin Gorzny at the Swiss Nanoconvention 2017
Dr. Marcin Gorzny, Post-Doc at LMN in the PSI career return program recieved a poster prize at the Swiss Nanoconvention 2017 for his contribution entitled: "Silicon chip as lipid membrane holder for serial crystallography experiments".
Wafer-thin Magnetic Materials Developed for Future Quantum Technologies
For the first time, researchers have produced a wafer-thin ferrimagnet, in which molecules with different magnetic centers arrange themselves on a gold surface to form a checkerboard pattern. Scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute, in collaboration with their research partners, published the findings in the journal Nature Communications.
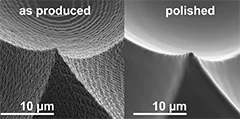
Contact-less micro-polishing
A new method of material modification using 172 nm UV photons enables to fabricate ultra-smooth and self-optimized polymer surfaces. The method, published in Advanced Materials Technologies, was used in the production of high quality micro-optics to remove typical process flaws after a 2-photon-lithography process.