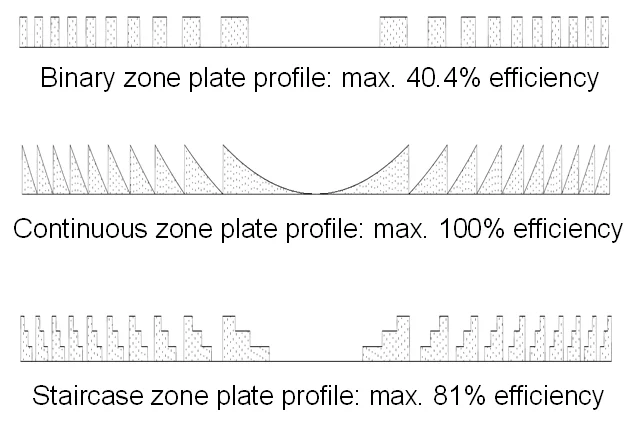
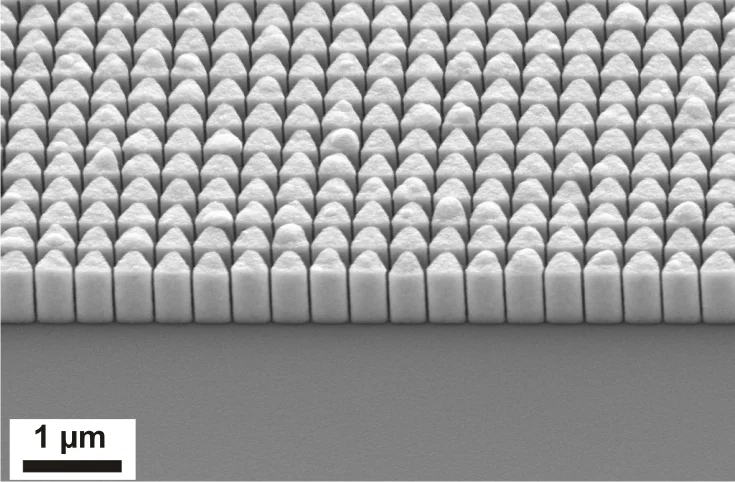
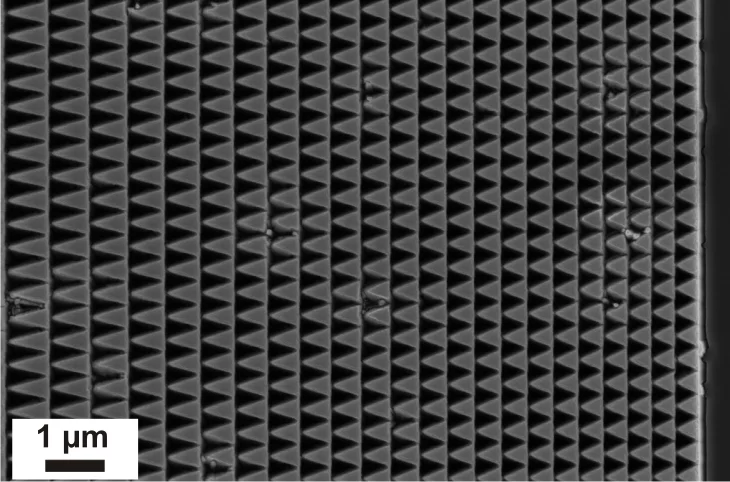
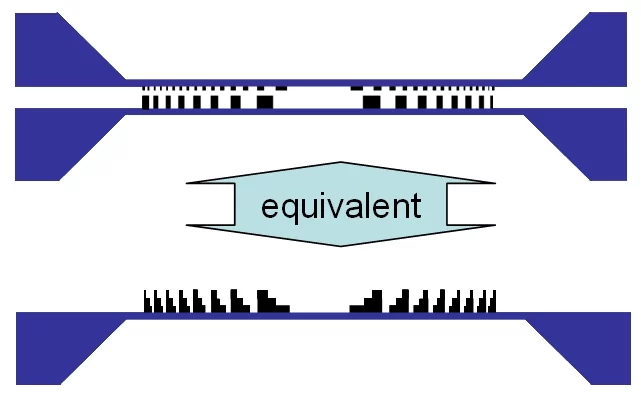
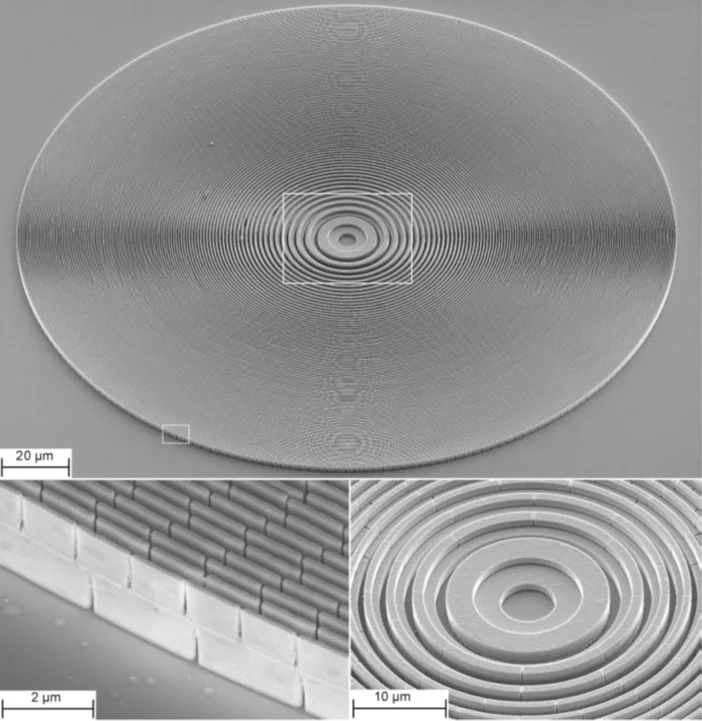
The diffractive optics developed and fabricated at the LMN enable ultra-high resolution for X-ray microscopy applications. However, the efficiency of conventional (binary) Fresnel zone plates is limited. Therefore the development and application of so called blazed diffractive X-ray optics is one of the research topics of the X-ray optics group. These special optics are designed to induce a continuous or a multi-level phase change, thus overcoming the fundamental limitations of conventional designs. Two main approaches under development are a tilted geometry of two specially designed 1D-lenses and the stacking of two Fresnel zone plates on top of each other.
Tilted X-ray Optics
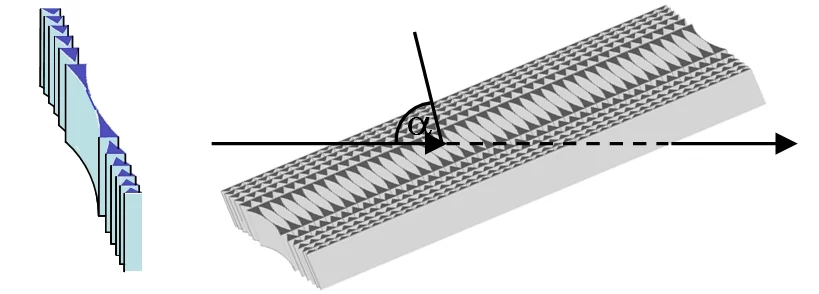
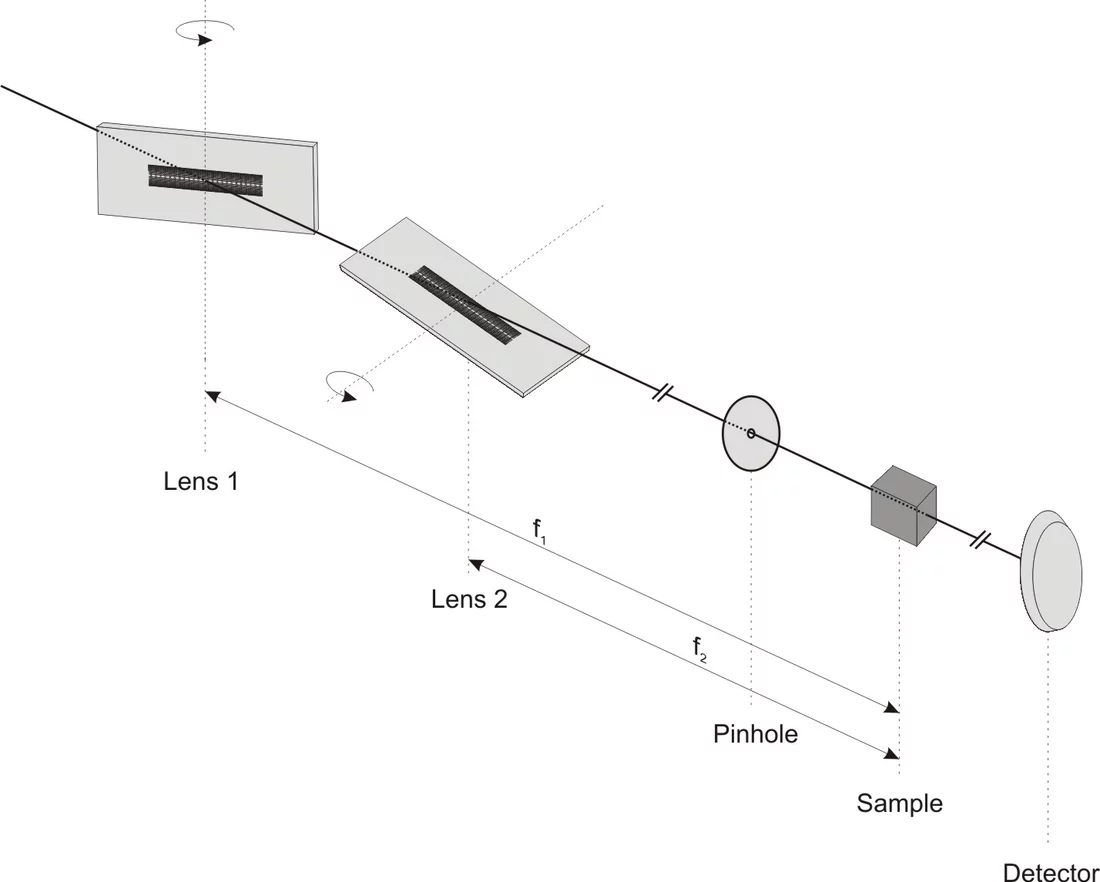
One implementation of blazed X-ray optics is a nano-focusing module based on two linear Fresnel zone plates in tilted geometry. Adjustment of the tilt angle enables tuning of the setup for optimal efficiency over a wide range of photon energies. The zone plates are specially designed to generate a blazed phase profile in tilted geometry, thus overcoming the efficiency limitations of binary diffractive structures. The tilted arrangement has the important advantage, that the acceptance of the lenses is not limited to the height of the individual lenslets. We achieved diffraction efficiencies of >50% for two Nickel lenses in series (>70% for a single lens) at 8 keV photon energy. The lenses have an acceptance of 400 µm × 440 µm and provide spot sizes of ~100 nm FWHM [1].
Publications
-
Karvinen P, Grolimund D, Willimann M, Meyer B, Birri M, Borca C, et al.
Kinoform diffractive lenses for efficient nanofocusing of hard X-rays
Optics Express. 2014; 22(14): 16676-16685. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.22.016676
DORA PSI -
Lebugle M, Dworkowski F, Pauluhn A, Guzenko VA, Romano L, Meier N, et al.
High-intensity x-ray microbeam for macromolecular crystallography using silicon kinoform diffractive lenses
Applied Optics. 2018; 57(30): 9032-9039. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.009032
DORA PSI
Stacked Fresnel Zone Plates
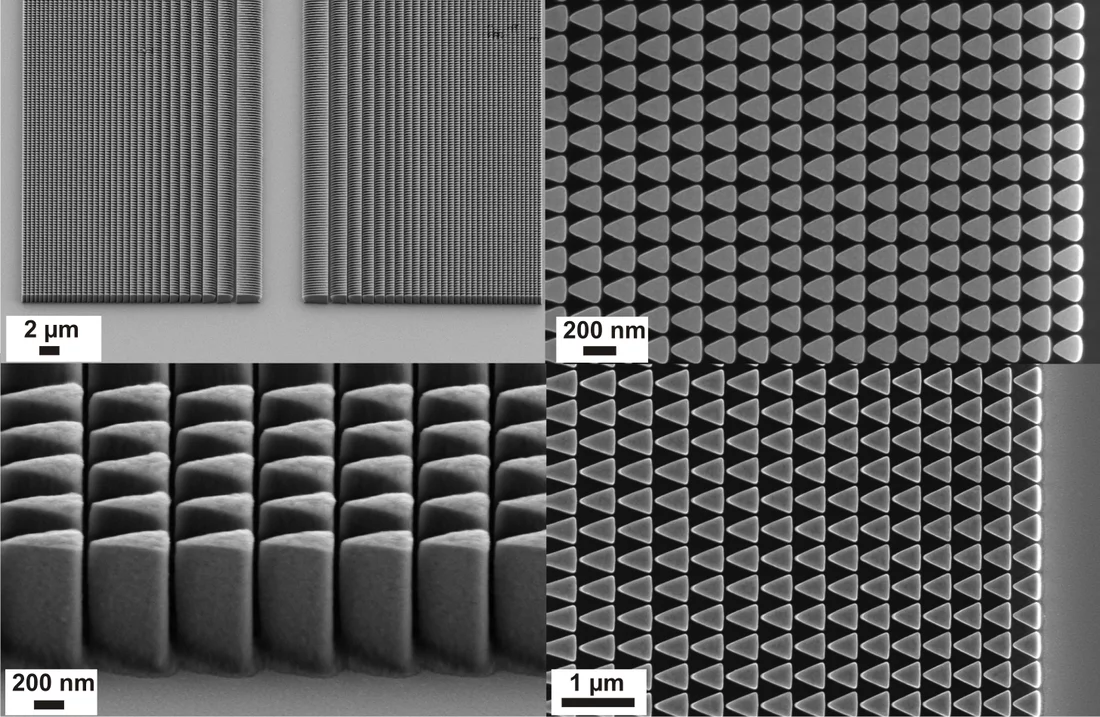
The second approach discussed is stacking two FZPs. Previously stacking of two identical FZPs has been used to double the height of the structures and thus the induced phase shift. Our approach is to design the individual FZPs to form a multilevel phase profile when stacked, effectively approximating the optimal continuous blazed profile.
In a collaboration funded by the Nanoscopium beam line of Synchrotron SOLEIL, we have developed schemes for the blazed stacking of zone plates with 3, 4, and 6 height levels by aligned electron-beam exposures and electroplating of Nickel. The measured efficiencies reached 54% at 6.5 keV photon energy [1,2].
Publications
- I. Mohacsi, P. Karvinen, I. Vartiainen, V.A. Guzenko, A. Somogyi, C. Kewish, P. Mercere, and C. David, High efficiency X-ray nanofocusing by multilevel zone plates Journal of Synchrotron Radiation 21 (2014) p. 497
- I. Mohacsi, I. Vartiainen, M. Guizar-Sicairos, P. Karvinen, V.A. Guzenko, E. Müller, C.M. Kewish, A. Somogyi and C. David Fabrication and characterization of high efficiency double-sided blazed X-ray optics Optics Letters 41 (2016) p. 281