Show filters
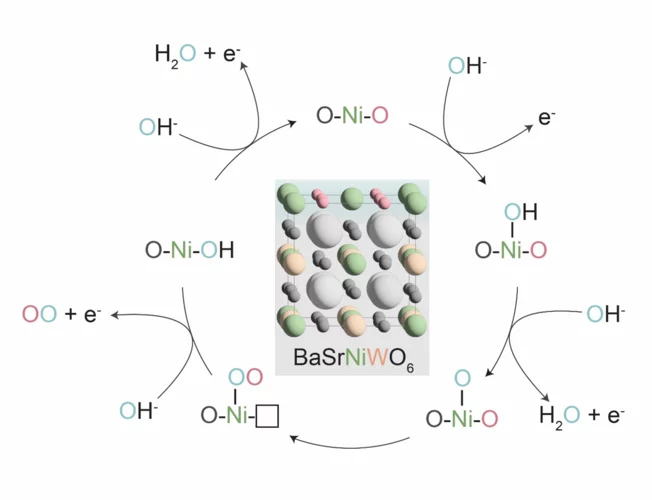
Confining surface oxygen redox in double perovskites for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction activity
Nickel-based double perovskites AA’BB’O6 are an underexplored class of oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts. In particular, BaSrNiWO6 exhibits high oxygen evolution activity, attributed to the evolution of a highly OER active surface phase. The redox transformation of Ni2+(3d8) to Ni3+(3d7) combined with partial W dissolution into the electrolyte drives an in-situ reconstruction of the surface to an amorphized, NiO-like layer, promoting oxygen redox in the OER mechanism.
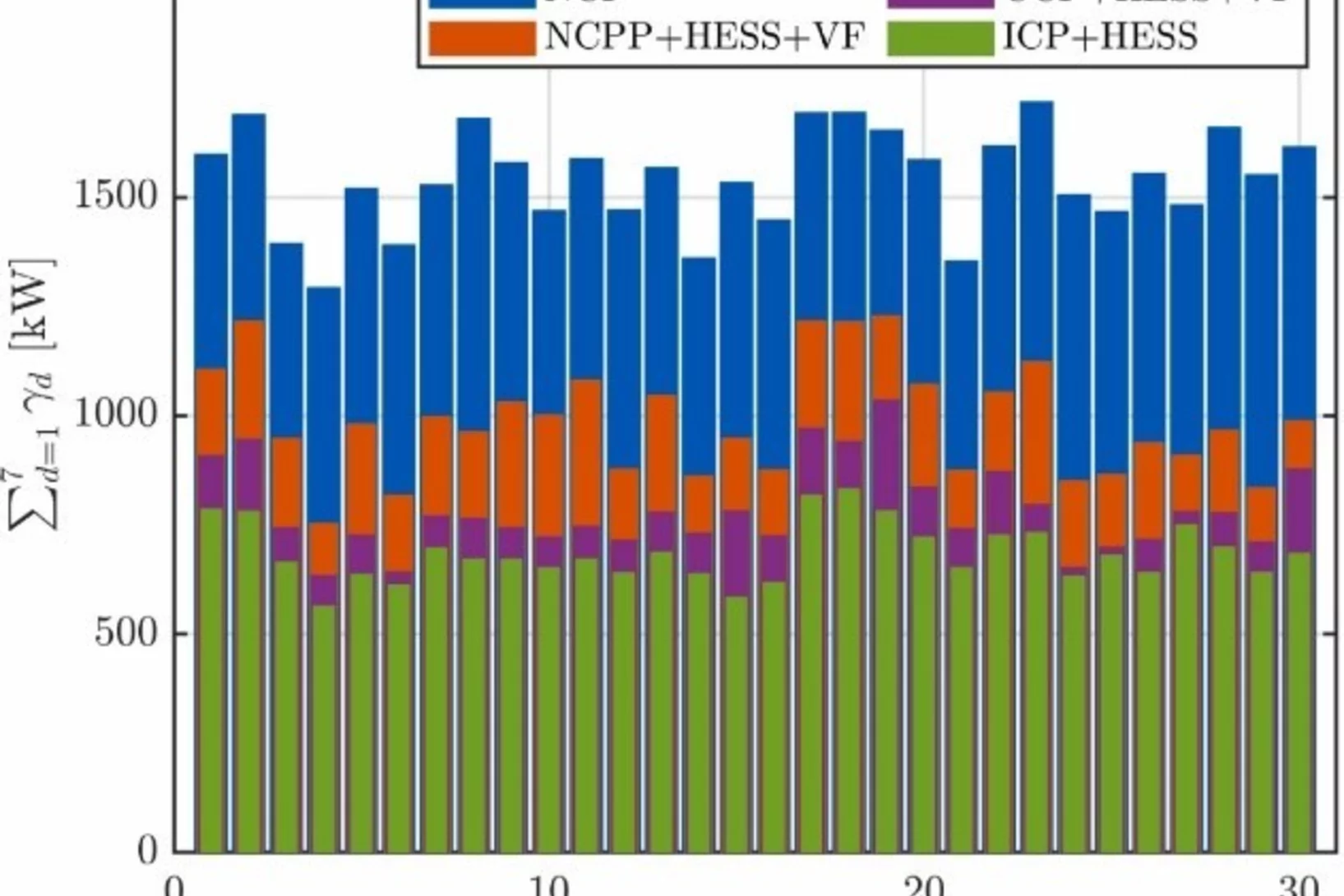
Decentralized hydrogen-based stationary energy storage systems complemented by smart control can provide increased operational flexibility in the energy system
While the electrification of the energy system implies a reduction of greenhouse gas emissions greatly beneficial to society, it can also pose technical challenges. The most notable among these are that the capacity of the local electric grid may be exceeded, along with the occurrence of imbalances between decentralized renewable energy production and final consumption. Hydrogen-based energy storage systems (HESS) are regarded as promising solutions to address these challenges. However, the feasibility has not been demonstrated and the involved processes are not well characterized on a technical relevant power level, so far.
Understanding the Interplay between Artificial SEI and Electrolyte Additives in Enhancing Silicon Electrode Performance for Li-Ion Batteries
Maintaining a stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) is crucial for Li-ion battery safety, especially with high-capacity anode containing silicon. Therefore, our study explored long-term cycling of Si electrodes with artificial alucone-based SEI, deposited by molecular layer deposition (MLD) in combination with a fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) electrolyte additive. MLD of flexible Li-ion permeable artificial SEI coatings onto electrode resulted in improved capacity, enhanced Si electrode cycle life and capacity retention.
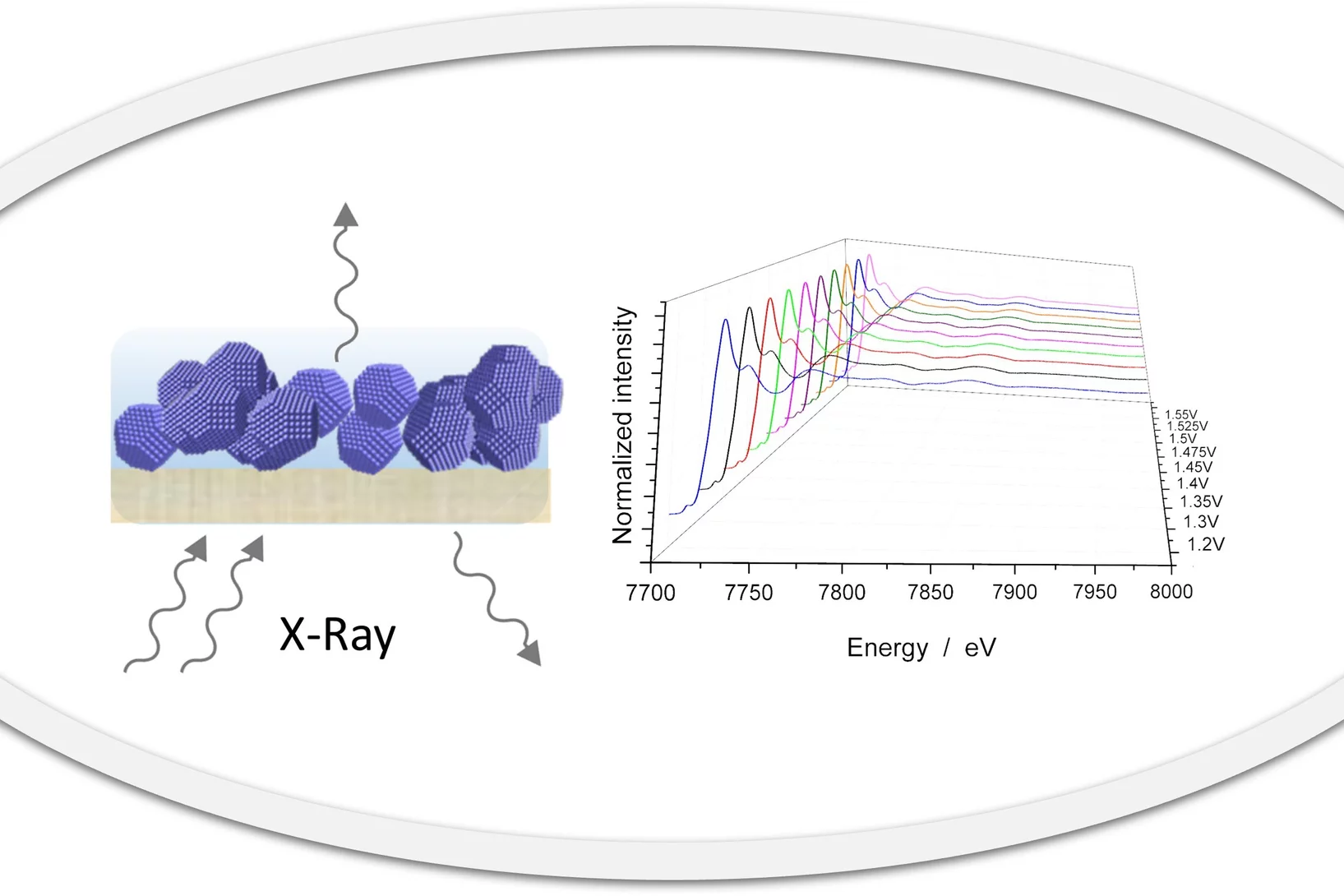
Best practices for harnessing operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy in electrocatalytic water splitting studies
X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) has found applications in a range of fields including materials, physics, chemistry, biology and earth science. XAS can probe the local electronic and geometric structure, such as the average oxidation state, coordination environment and interatomic distances, surrounding an element of interest. Thus, XAS is a valuable tool to inform catalyst design by tracking catalyst evolution under operating conditions, for example, via providing dynamic snapshots of the essential information.
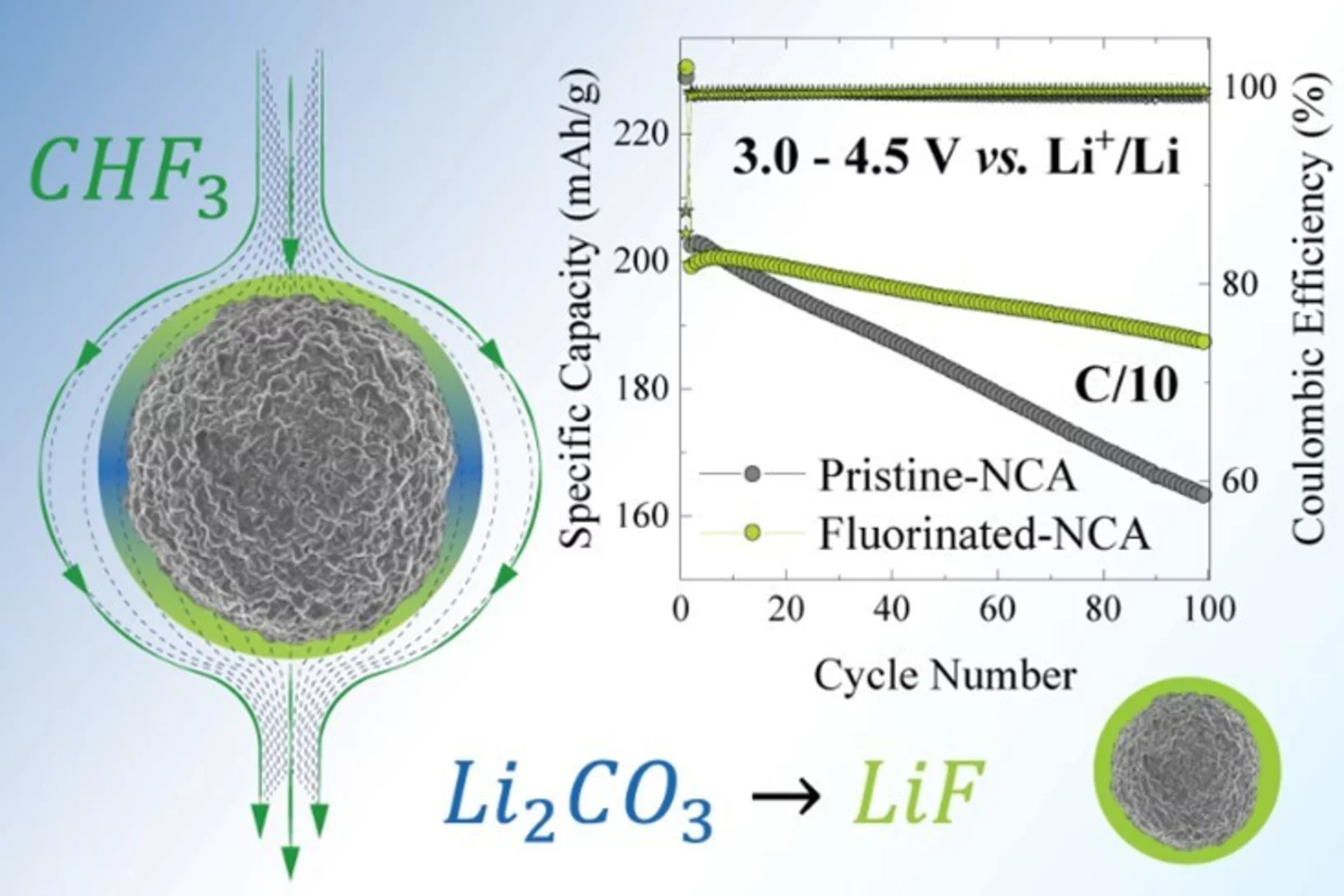
Converting the CHF3 greenhouse gas into LiF coating for high-voltage cathode materials toward high-energy density Li-ion batteries
The instability and the fading of high voltage cathode materials above 4.3 V remains a major challenge for the next generation of high energy density Li-ion batteries. Here, we present a facile, environmentally friendly, cost effective and scalable method to address this problem by uniformly fluorinating the surface of cathode materials with CHF3, a mild fluorinating agent but a potent greenhouse gas. CHF3 is successfully transformed into ~2 nm LiF homogenous layer covering the surface of layered-oxide cathode materials.
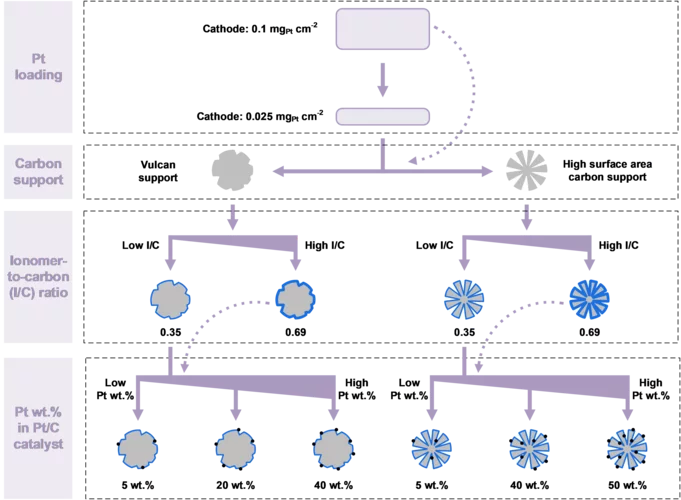
Hydrogen Electrode for Membrane Water Electrolyzers with Low Gas Crossover
Proton exchange membrane (PEM) water electrolyzer are considered a for the Energy Transition to produce green hydrogen for fuel cell-based mobility, industrial processes, and seasonal storage. Platinum group metals (PGMs) are conventionally used as catalysts for electrode reactions due to their outstanding catalytic activity and chemical stability in the harsh acidic environment of the cell. Commercial carbon-supported platinum (Pt/C) electrocatalysts remains a state-of-the-art choice for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) on the cathode side of the cell. While a high Pt loading between 0.5 and 1.0 mgPt/cm2 is commonly used today, a reduction of the Pt loading to below 0.05 mgPt/cm2 is desired to reduce the cost of PGM usage in megawatt-scale PEM water electrolysis systems. In addition, in connection with the trend towards the use of thinner membranes (<0.1 mm), gas crossover through the membrane from the cathode to the anode side can lead to the formation of an explosive gas mixture in the anode product stream. In this study, we varied the design parameters for the cathode catalyst layer to reduce the Pt loading to 0.025 mg/cm2 while at the same time minimizing the rate of hydrogen crossover to the anode.
Real-Time Insights into Sodium-Ion Battery Chemistry
Identification of gaseous decomposition products from irreversible side-reactions enables understanding of inner working of rechargeable batteries. Unlike for Li-ion batteries, the knowledge of the gas-evolution processes in Na-ion batteries is limited. Our study revealed that Na-ion cells develop a less stable solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) compared to Li-ion cells due to higher solubility of SEI constituents in Na-electrolytes.
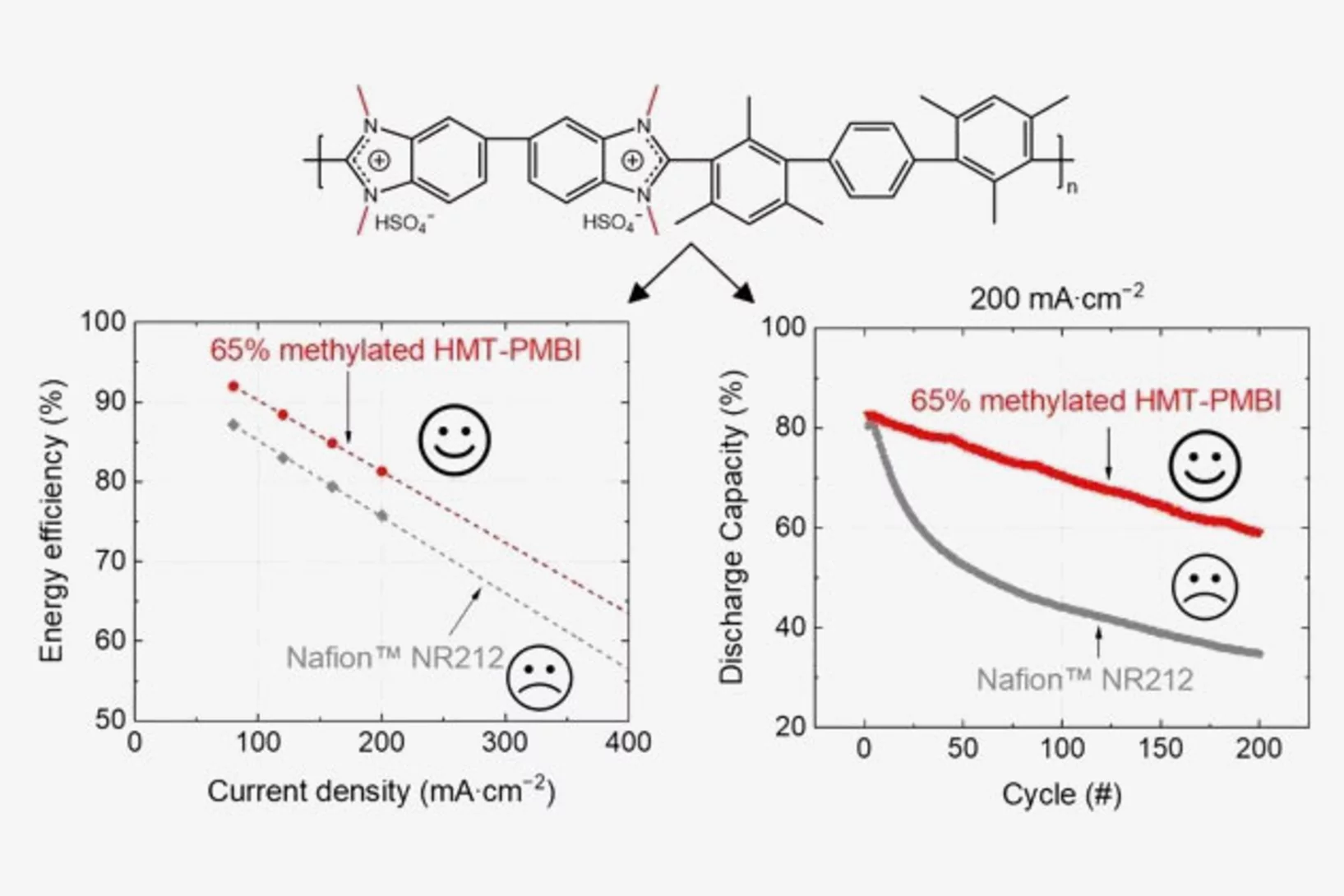
Polybenzimidazole Membrane Design Principles for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
Energy storage technologies with long storage duration are essential to stabilize electricity grids with a high share of intermittent renewable power. In a redox flow battery, the electrochemical conversion unit, where the charging and discharging reaction takes place, is spatially separated from the energy storage medium. In the all-vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), a sulfuric acid aqueous electrolyte with dissolved vanadium ions is used as the storage medium. Vanadium is present in 4 different oxidation states, the redox couple vanadium(II) and (III) on the negative side of the cell, and vanadium(IV) and (V) on the positive side. This allows the battery to be repeatedly charged and discharged. A separator or membrane is used between the negative and positive electrode, which should selectively conduct the ions of the supporting electrolyte and minimize the passage of vanadium ions. Fluorinated membranes, such as Nafion™, are often used for this key component, but these ionomers were not originally developed for this application and therefore have functional shortcomings. Furthermore, the production and use of fluorinated materials is to be severely restricted or even banned in Europe. Therefore, the development of hydrocarbon-based membranes for the VRFB is of great importance. The study reported here focuses on polybenzimidazole polymers and membranes, which could be a promising materials class for next generation flow batteries.
Unraveling degradation processes in a bipolar membrane CO2 electrolyzer by time-resolved X-ray tomographic microscopy
Employing a bipolar ion conducting membrane (BPM) in forward bias is a convenient solution for the biggest issues in the more common anion exchange membrane (AEM) CO2 co-electrolysis: the degradation of the performance caused by carbonate salt precipitation at the cathode and the decrease of net CO2 conversion caused by the crossover of this molecule from cathode to anode also requiring energy for downstream gas separation. However, the performance and stability of this device remain largely insufficient when using such a BPM configuration. To understand the reasons for this, we performed time-resolved X-ray tomographic microscopy of an operating BPM CO2 electrolyzer. The imaging method reveals partly unexpected degradation processes that result in design recommendations for improvement.
Insights into the superior oxygen evolution reaction activity of CoOx/CeO2 composite electrocatalyst
CeO2 significantly enhances the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity of CoOx, although the mechanism behind this synergy is still unclear. Here, operando hard X-ray absorption spectroscopy (hXAS) is applied to monitor the Co-K edge and Ce L3 edge in CoOx/CeO2 to shed light on the evolution of Co and Ce oxidation states during OER. In addition, ex situ soft XAS (sXAS) characterizations provide information on the irreversible surface-specific transformations of the Co L3 edge as well as the O K edge.
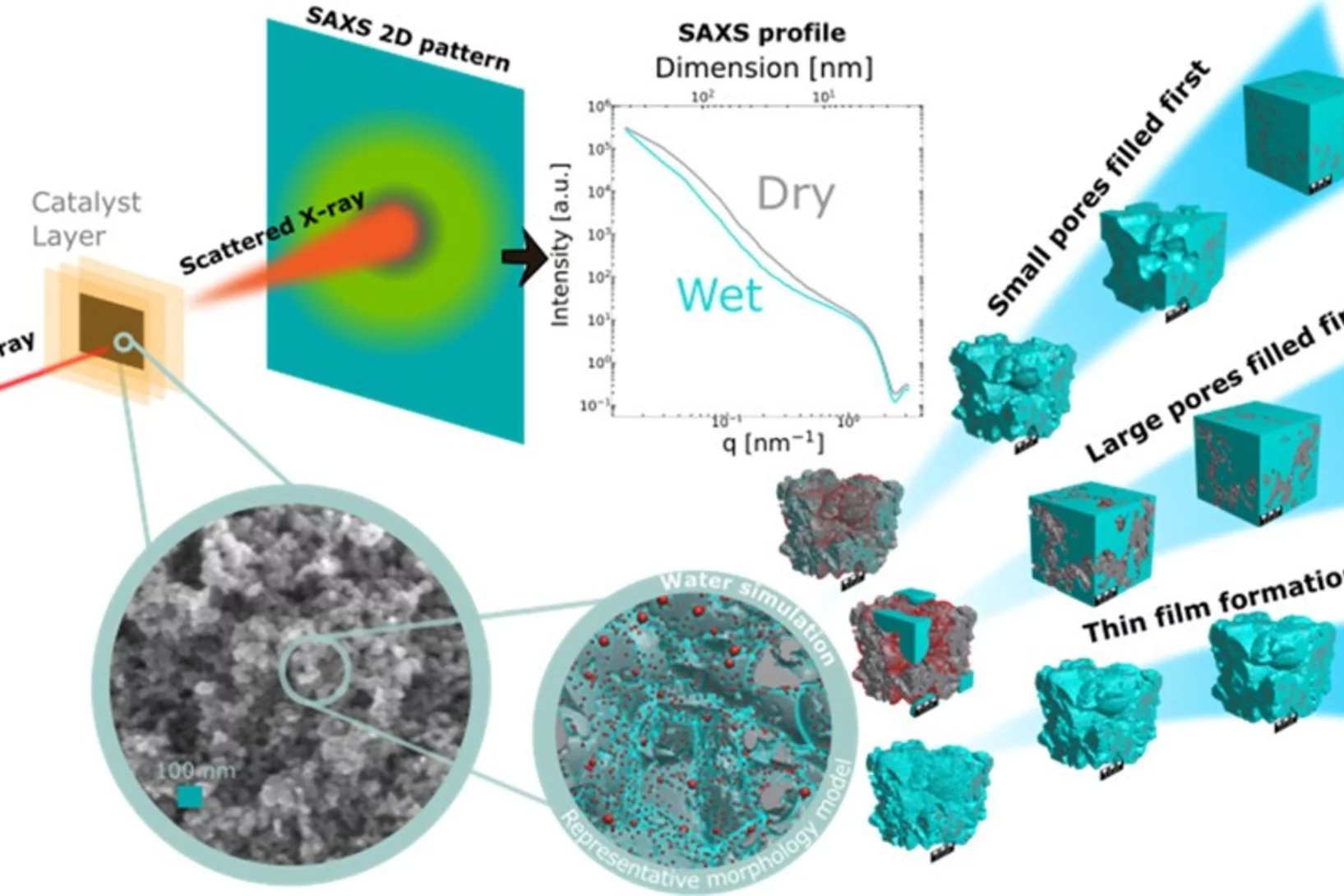
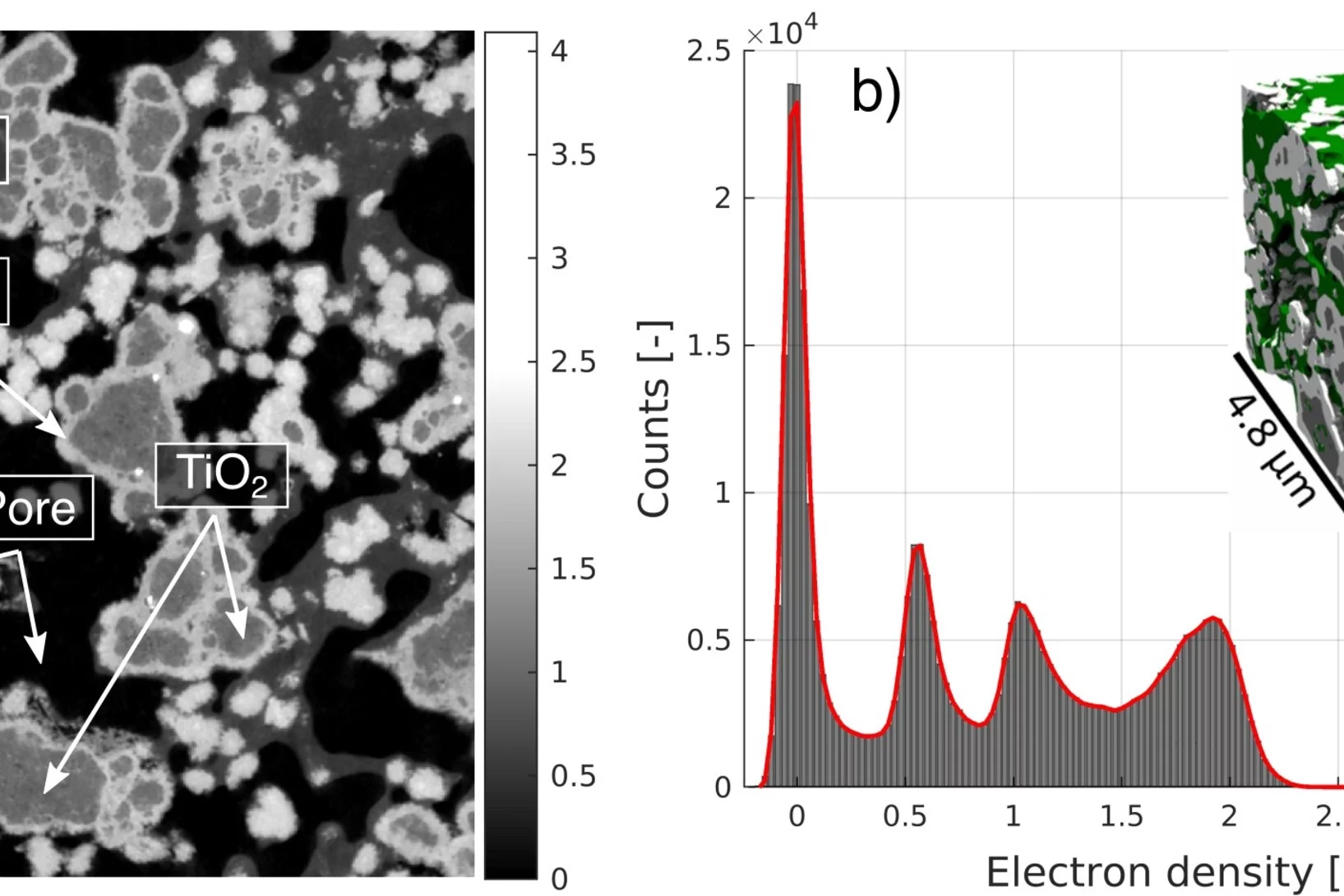
Quantification of PEFC Catalyst Layer Saturation via Small-Angle X‑ray Scattering
The complex nature of liquid water saturation in polymer electrolyte fuel cell (PEFC) catalyst layers (CLs) greatly affects the device performance. To investigate this problem, a method to quantify the presence of liquid water in a PEFC CL using small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) was developed in a collaboration of researchers of the Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM, Berlin, Germany), the Photon Science Division and the Electrochemistry Laboratory of PSI. The method leverages the differences in electron densities between the solid catalyst matrix and the CL-pores filled with liquid water under dry and wet conditions, respectively.
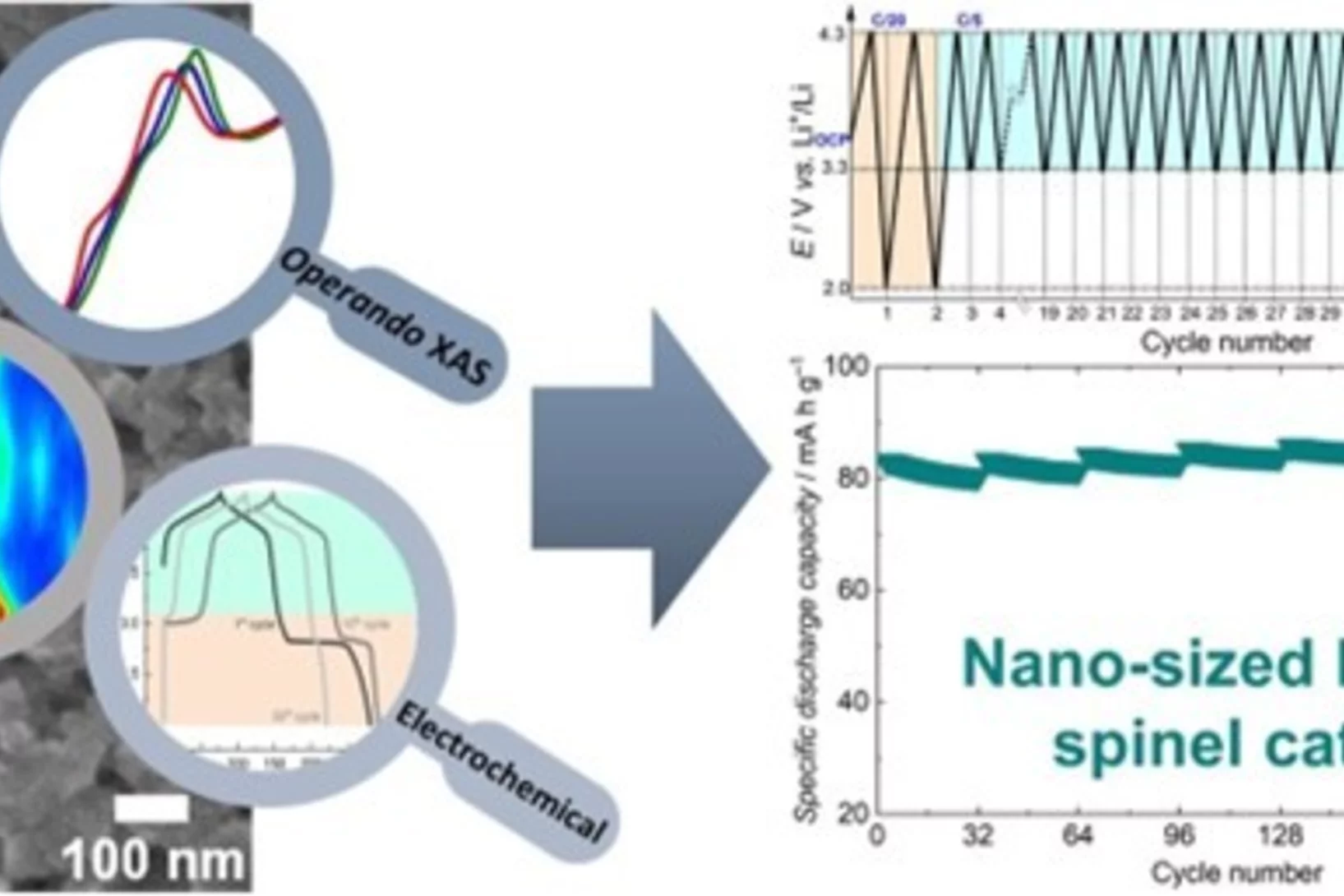
Understanding the (de-)lithiation mechanism of nano-sized LiMn2O4 allows achieving long-term cycling stability
We report an in-depth investigation of the local atomic geometry, electronic and crystallographic structure evolution of nano-sized LiMn2O4 using operando XAS and XRD to shed light on (de-)lithiation mechanism when cycled in wide voltage range of 2.0 to 4.3 V vs Li+/Li. Leveraging on these findings, a novel electrochemical cycling protocol, with periodic deep discharge, yields superior electrochemical performance cycled in the range of 3.3 to 4.3 V exhibiting an excellent structure cyclability and an unprecedented increase in the specific capacity upon long cycling.
Bessere Batterien für E-Autos
PSI-Forschende machen physikalische und chemische Veränderungen in Batterie-Elektrolyten sichtbar.
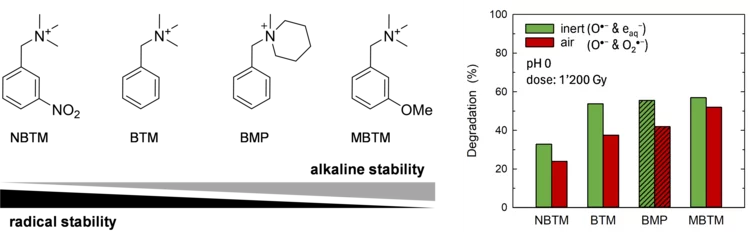
Insights into radical induced degradation of anion exchange membrane constituents
Electrochemical energy conversion devices, such as fuel cells and electrolyzers, using an anion exchange membrane (AEM) operating in the alkaline regime offer the prospect of the use of non-noble metal electrocatalysts and lower-cost cell construction materials. The wide-spread application of electrochemical cells with AEMs has been largely limited by the low chemical stability of the material. AEM degradation is triggered by i) nucleophilic attack by OH−, and ii) by reaction with free radicals formed during cell operation. Whereas the alkaline stability of AEMs has been greatly increased over the last 10 years, the understanding of mechanisms of radical induced degradation is limited. In this study, we have addressed this topic for the first time.
Wie lässt sich Kobalt in E-Auto-Batterien reduzieren?
Die Elektrifizierung des Verkehrs nimmt zu. Dafür braucht es mehr Batterien. Einige dieser Batterien enthalten jedoch einen äusserst problematischen Rohstoff: Kobalt. Das PSI forscht an Alternativen.
Improving the oxygen evolution reaction activity of Co-based oxides by phosphate functionalization
Our findings disclose that P-functionalization successfully enhances the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity of different cobalt-based catalysts (namely, La0.2Sr0.8CoO3–δ, La0.2Sr0.8Co0.8Fe0.2O3–δ, and CoOx) at near-neutral pHs and that both phosphate ion assistance in the OER mechanism and catalyst Co oxidation state can play a role in the enhanced OER activity.
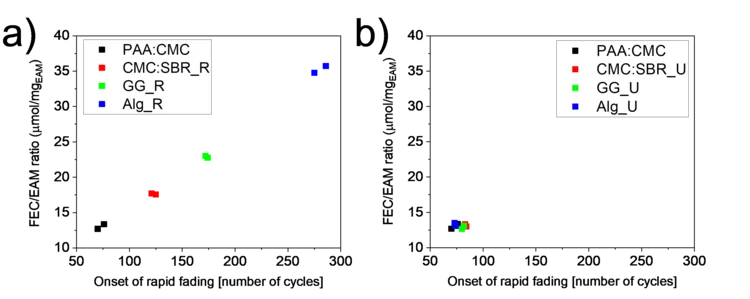
Importance of Identifying Key Experimental Parameters for the Li-ion Battery Performance Testing
The mass loading of Si-graphite electrodes is often considered as a parameter of secondary importance when testing their performance. However, if a sacrificial additive is present in the electrolyte, the electrode loading becomes the battery cycle-life-determining factor. A lower loading was obtained by keeping slurry preparation steps unchanged from binder to binder and resulted in a longer lifetime for some of the binders. When the final loading was kept constant instead, the performance became independent of the binder used.
Wie lässt sich erneuerbarer Strom ganzjährig nutzen?
Die Energiestrategie 2050 des Bundes sieht einen starken Ausbau von Photovoltaikanlagen vor. Doch woher nehmen wir unseren Strom, wenn die Sonne nicht scheint? Wasserstoff könnte eine Lösung sein.
Polymer electrolyte water electrolysis: Understanding the microstructure of a core-shell based anode catalyst layer
Reducing precious metal loading in the anodic catalyst layer (CL) is indispensable for lowering capital costs and enabling the widespread adoption of polymer electrolyte water electrolysis (PEWE). This work presents the first three-dimensional reconstruction of a TiO2-supported IrO2 based core shell catalyst layer, using high-resolution X-ray ptychographic tomography at cryogenic temperature of 90 K. The high data quality and phase sensitivity of the technique have allowed the reconstruction of all four phases namely pore space, IrO2, TiO2 support matrix and the ionomer network, the latter of which has proven to be a challenge in the past.
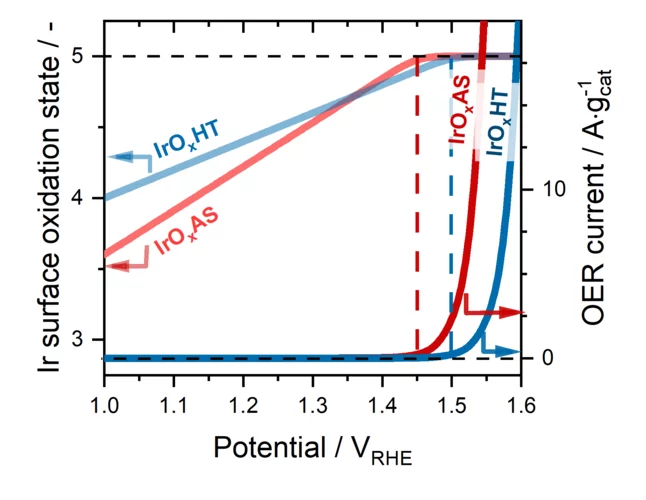
The evolution of O2 on Ir-based catalysts requires the complete oxidation of their surface to Ir+5
The evolution of O2 occurring in polymer electrolyte water electrolyzer anodes is a very slow reaction that must be catalyzed using iridium (Ir-) based materials. However, Ir is an extremely scarce metal, and thus the extended commercialization of these electrolyzers will only be possible if the amount of Ir implemented in their anodes is drastically reduced. This requires an improved understanding of the individual steps through which these Ir-based materials catalyze the evolution of O2. To shed light on this matter, in this work we studied four different Ir-based catalysts under operative conditions using time resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Our results show for the first time that, despite the differences between these materials, their surfaces must systematically be completely oxidized to a +5 state in order for the evolution of O2 to proceed on them.
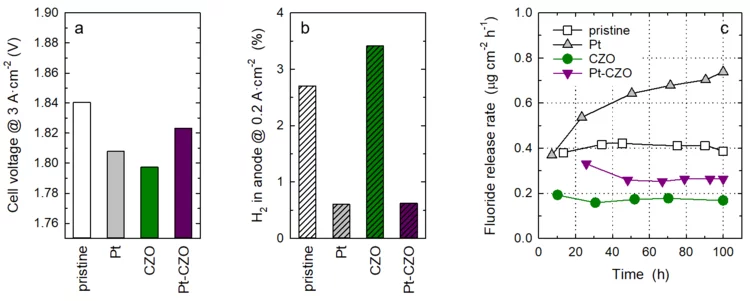
Towards Next Generation Membranes for Polymer Electrolyte Water Electrolysis
The conversion efficiency for green hydrogen production in a polymer electrolyte water electrolyzer (PEWE) is strongly influenced by the ohmic cell resistance and therefore the thickness of the membrane. The use of thin membranes (~50 micron or below) is limited by gas crossover of H2 and O2, which can lead to the formation of an explosive gas mixture. The incorporation of a Pt recombination catalyst provides remedy and allows a more dynamic operating mode (cf. Highlight 03/2022). However, the presence of Pt nanoparticles leads to an increase in the rate of membrane degradation. Therefore, we have additionally doped the membrane with cerium-zirconium-oxide (CZO) nanoparticles, which act as radical scavenger. The rate of membrane degradation can thus be reduced.
Integration of Li4Ti5O12 crystalline films on silicon towards high-rate performance lithionic devices
The growth of crystalline Li-based oxide thin films on silicon substrates is essential for the integration of next-generation solid-state lithionic and electronic devices. In this work, we employ a 2 nm γ-Al2O3 buffer layer on Si substrates in order to grow high quality crystalline thin films Li4Ti5O12 (LTO). Long-term galvanostatic cycling of 50 nm LTO demonstrates exceptional electrochemical performance, specific capacity of 175 mAh g-1 and 56 mAh g-1 at 100C and 5000C respectively, with a capacity retention of 91% after 5000 cycles.
Updated electrochemical impedance model for understanding the interface of metallic lithium
Lithium metal negative electrodes are often used as counter electrodes while testing other electrochemically active materials, and are considered to be equivalent, independently of their thickness, supplier and production processes used. Here, we clearly demonstrate, using Electrochemical Impedance spectroscopy (EIS) that it is not the case, as well as the often-used symmetric cells are actually not so symmetric, when EIS spectra are disentangled using Thee-electrode cells.
Prevention of freezing propagation in fuel cells using segmentation
The ability to start-up in extreme environmental conditions, including sub-freezing temperatures, is essential to the deployment of the fuel cell technology. Water produced in fuel cells at these temperatures can be in the super-cooled state, and freezing can lead to a rapid shutdown, as water cannot be removed anymore as a liquid. By segmenting a fuel cell, it is possible to prevent the propagation of freezing, which enables the cell operation even after the first freezing event occurred.
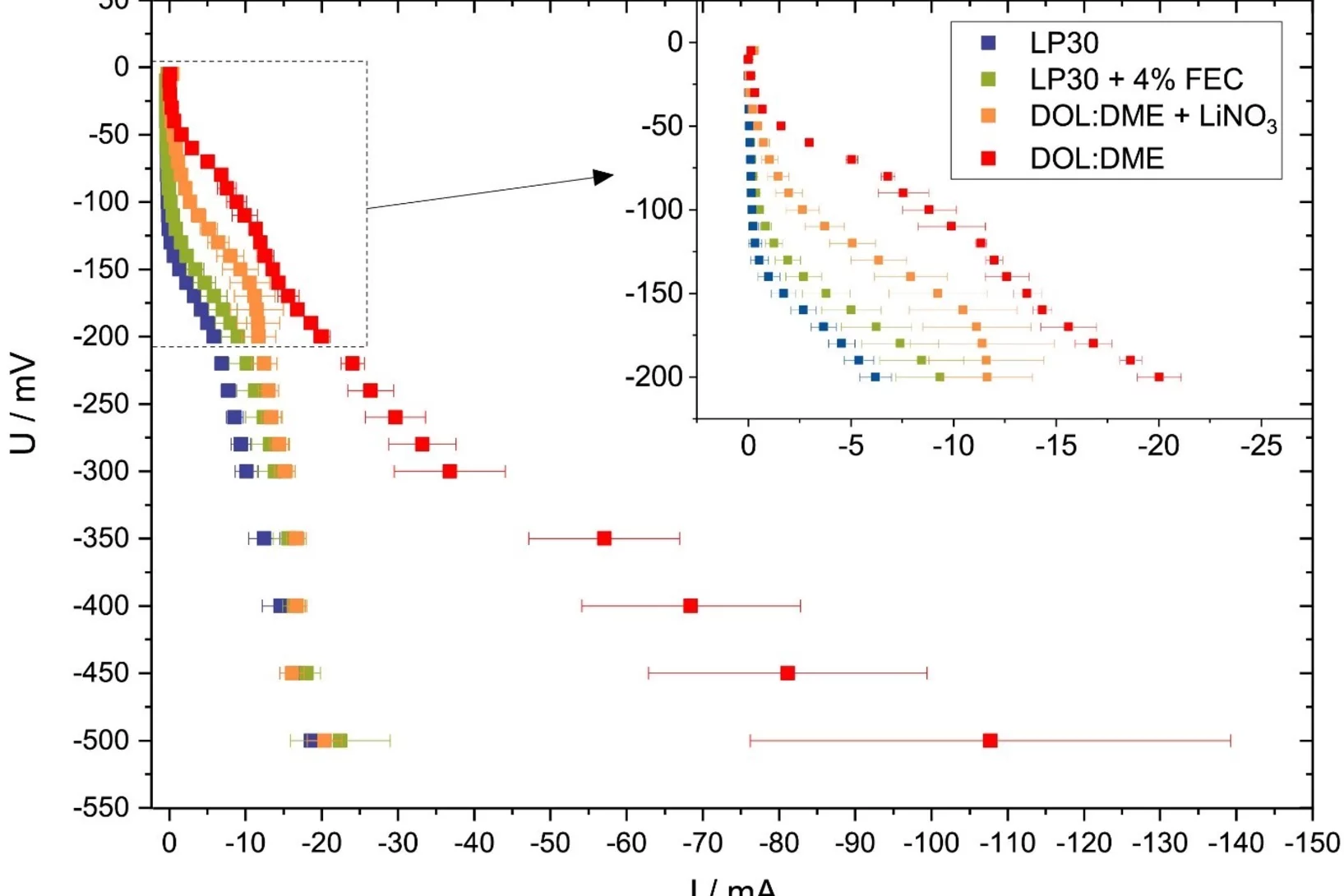
Versatile and Fast Methodology for Evaluation of Metallic Lithium Negative Battery Electrodes
Evaluating potential electrolyte candidates is typically a lengthy procedure requiring long-term cycling experiments. To speed this process up, we have investigated potentiostatic lithium plating as a potential method for fast electrolyte suitability investigation. The applications of this methodology is not limited to liquid electrolytes, - effects of solid-state electrolytes, coatings, and other modifications can be readily assessed.
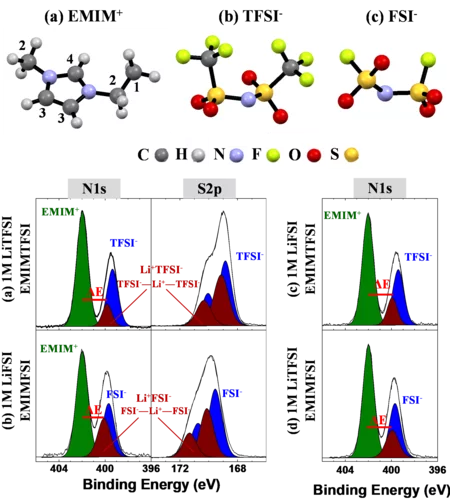
Li-ion solvation in TFSI and FSI - based ionic liquid electrolytes probed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
We demonstrate the capability of conventional laboratory XPS to determine the anions solvation shell of Li+ cation within 1M of LiTFSI and 1M of LiFSI salts dissolved in (EMIM+-FSI-) and (EMIM+-TFSI-) ionic liquids. The binding energy difference between the N1s components originating from the EMIM+ cation and from TFSI- or FSI- anions, solvating the Li+, confirms that both TFSI- and FSI- contribute simultaneously to the Li+ solvation. Additionally, the degradation of the TFSI and FSI -based electrolytes under X-ray exposure is proved.
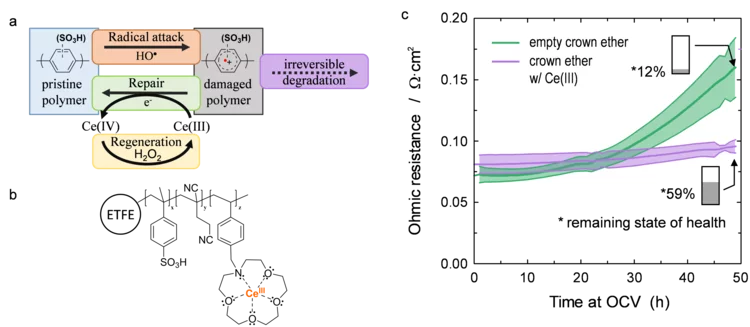
Damage-Repair Cycle in Hydrocarbon Based Membranes for Fuel Cells
The development of next generation fuel cell membranes based on aromatic hydrocarbon chemistry calls for a new antioxidant strategy to tackle radical induced membrane degradation. Although damage by radicals cannot be prevented, the formed aromatic intermediates can be repaired by a suitable additive. Fuel cell experiments demonstrate that the approach is viable on the device level and that repair is a catalytic mechanism.
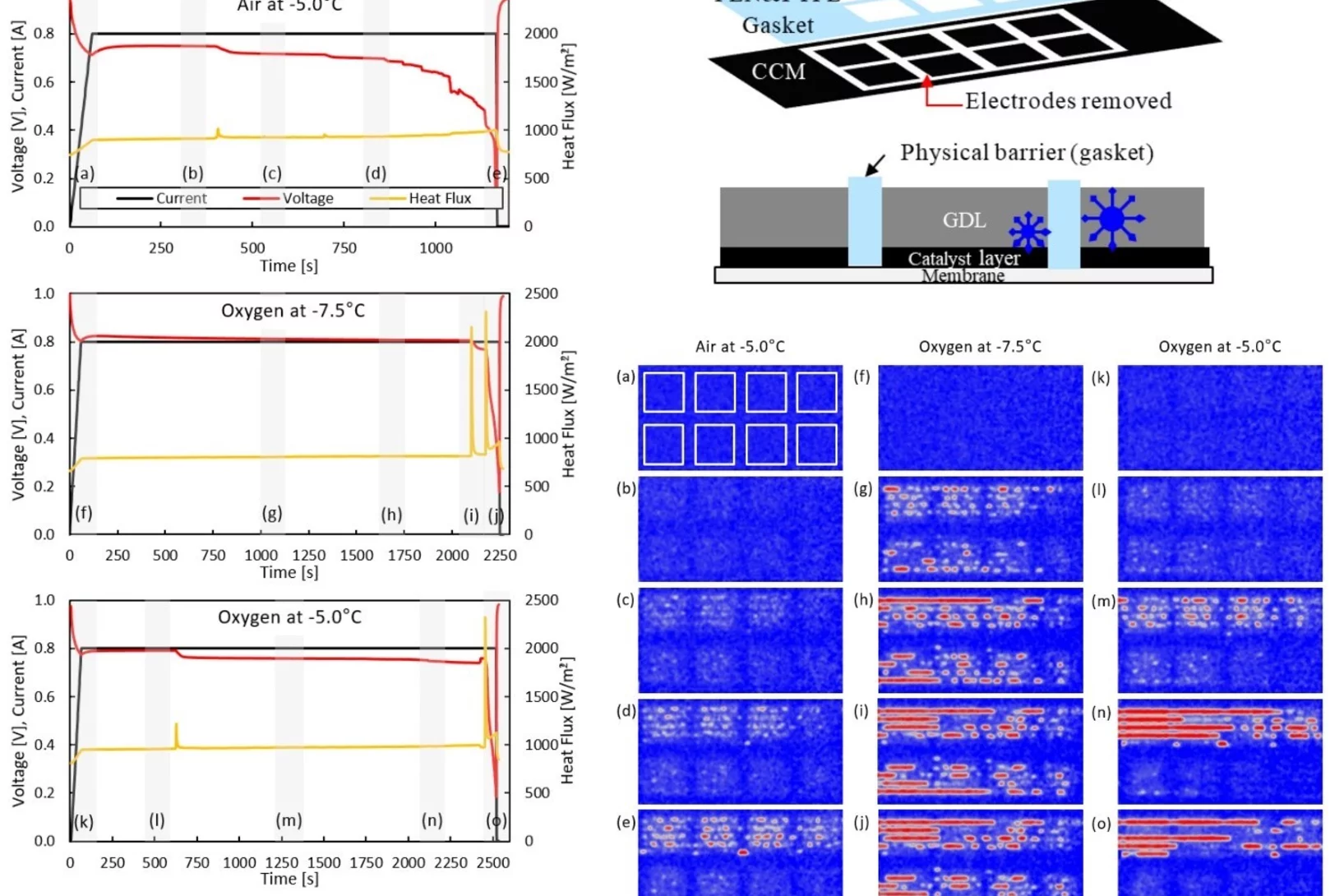
The Effects of Hydrophobicity Treatment of Gas Diffusion Layer on Ice Crystallization in PEFCs
Water management is crucial to the successful cold-start in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs). The sudden freeze of supercooled water blocks the reactant gas in the cathode and causes rapid voltage failure. In this work, we statistically evaluated the effects of the gas diffusion layer (GDL) substrate, size, saturation, and the coating loads and methods of hydrophobic polymer on the freezing probability of supercooled water by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC).
High performance gas diffusion layers with added deterministic structures
Hydrogen will play an important role in a future energy system based on renewable sources, providing energy storage, being a base material for industry and an energy carrier in transport applications. For the efficient electrification of hydrogen, polymer electrolyte fuel cell technology is developed and applied today in trucks, passenger cars and stationary applications. It is envisaged that even more demanding applications such as airplanes may follow. For road transport applications an increase in power density is required to further reduce cost and future applications may need these advances to be technically competitive. In this work we describe a novel concept for gas diffusion layers, highly important for achieving high fuel cell power densities.
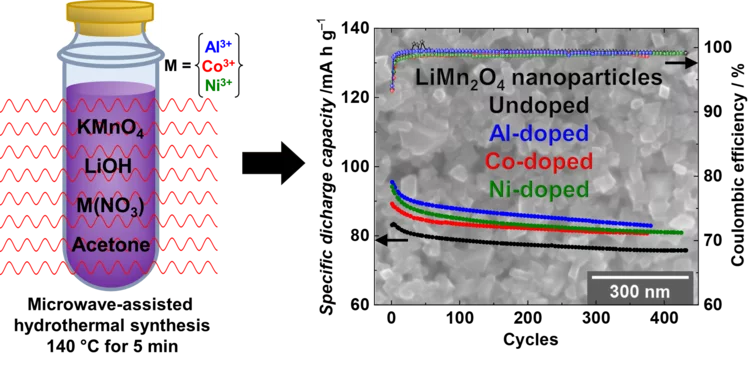
High performance doped Li-rich Li1+xMn2-xO4 cathodes nanoparticles synthesized by facile, fast and efficient microwave-assisted hydrothermal route
Li-rich nanoparticles of Li1+xMn2-xO4 doped with Al, Co or Ni are successfully synthesized using a facile, fast and efficient microwave-assisted hydrothermal route. In this study, we demonstrate that nanocrystallinity and cationic doping play an important role in improving the electrochemical performance with respect to LiMn2O4 microparticles. They significantly reduce the charge-transfer resistance, lower the 1st cycle irreversible capacity to 6%, and achieve a capacity retention between 85 and 90% after 380 cycles, with excellent columbic efficiency close to 99%.