Expertise
We use unique tools to study the interaction of membrane constituents with radicals to improve our understanding of the chemical degradation of membranes, both proton exchange membranes (PEMs) and alkaline anion exchange membranes (AEMs), and develop novel antioxidant strategies. The image shows the 60Co gamma source at PSI, which is used for continuous water radiolysis studies. The ionizing radiation of the gamma-photons yields to water radiolysis and the formation of defined amounts of radicals, which then react with model compounds, representative of the membrane chemistry, dissolved in the aqueous solution.
We synthesize and engineer new membranes and membrane additives for next generation H2 fuel cells and water electrolyzers. One focus topic is the use of non-fluorinated hydrocarbon membranes for fuel cells, where we collaborate with other world-renowned academic partners and aim to characterize the most-promising chemistries. In the area of water electrolyzers, we focus on currently established perfluorinated membranes and seek to engineer them for improved functionality in terms of conversion efficiency and durability. The image shows a transmission electron microscopy image of a cerium-zirconium oxide (CZO) supported Pt-nanoparticles, which are added to the membrane for the dual functionality of gas recombination (Pt) and radical scavenging (CZO).
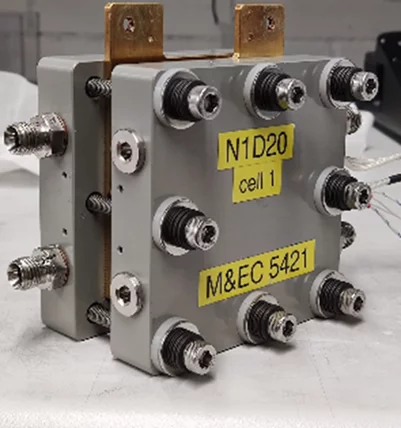
A key focus of the group is the in-situ characterization of membranes in single cells to understand performance characteristics and obtain durability metrics. The laboratory operates a number of commercial and in-house built testbenches for characterization of fuel cells, water and CO2 electrolyzers. The customized cell teststands allow us to adapt their functionalities to the particular research topics under investigation. We typically use custom-built single cell hardware. The image shows a fuel cell with an active area of 16 cm2 with a parallel flow field, which is suited for component degradation studies.
Research Team
Current group members:
- Lorenz Gubler, Head
- Torben Saatkamp, Tenure-Track Scientist
- Zarina Turtayeva, Postdoctoral Researcher
- Ivan Zelocualtecatl Montiel, Postdoctoral Researcher
- Zongyi Han, PhD Student
- Eliot Petitdemange, PhD Student
- Lara Cuda, Master thesis student
- Samiro Meyer, Apprentice
Team member profile: Zongyi Han
PhD student funded by Johnson Matthey (UK) on the topic of 'Hydrocarbon fuel cell proton exchange membranes (PEMs): chemical durability and testing protocols'
Open Positions
There are no open positions at the moment.
Furthermore, we have regular openings for student's projects in different areas: fuel cells, electrolyzers, redox flow cells on topics ranging from materials synthesis and characterization to test system design and implementation.
Projects
| Project | Description | Duration | Contact |
|---|---|---|---|
| AntioxAEM | Deciphering and Mitigation of Radical Induced Damage in Alkaline Anion Conducting Ionomers for Fuel Cells and Electrolyzers Swiss National Science Foundation | 2023-2027 | Lorenz Gubler |
| HCmem | Hydrocarbon Fuel Cell Proton Exchange Membranes (PEMs): Chemical Durability and Testing Protocols Johnson Matthey (UK) | 2023-2027 | Lorenz Gubler |
| ELYMEM | New materials for electrolysis cells and next generation electrochemical water splitting devices (collaboration with the group Chemical Processes and Materials - CPM at PSI) Swiss Federal Office of Energy | 2025-2028 | Lorenz Gubler |
| Industry | Projects funded by industrial partners, subject to confidentiality | Lorenz Gubler |
Recent Publications
A complete publication list can be found on Scopus.
-
Aliyah K, Appel C, Lazaridis T, Prehal C, Ammann M, Xu L, et al.
Operando scanning small-/wide-angle X-ray scattering for polymer electrolyte fuel cells: investigation of catalyst layer saturation and membrane hydration- capabilities and challenges
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces. 2024; 16: 25938-25952. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c11173
DORA PSI -
Barros Á, Aranzabe E, Artetxe B, Duburg JC, Gubler L, Gutiérrez-Zorrilla JM, et al.
Polyoxometalate-based symmetric redox flow batteries: performance in mild aqueous media
ACS Applied Energy Materials. 2024; 7(9): 3729-3739. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.4c00085
DORA PSI -
Carreón Ruiz ER, Malamud F, Lee J, Burca G, Trabesinger S, Gubler L, et al.
Operando lateral state-of-charge inhomogeneity mapping via wavelength-resolved neutron imaging
Materials Today Energy. 2024; 46: 101710 (10 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2024.101710
DORA PSI -
Duburg JC, Chen B, Holdcroft S, Schmidt TJ, Gubler L
Design of polybenzimidazolium membranes for use in vanadium redox flow batteries
Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 2024; 12(11): 6387-6398. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ta07212f
DORA PSI -
Hampson E, Duburg JC, Casella J, Schmidt TJ, Gubler L
A simple approach to balancing conductivity and capacity fade in vanadium redox flow batteries by the tunable pretreatment of polybenzimidazole membranes
Chemical Engineering Journal. 2024; 485: 149930 (11 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.149930
DORA PSI -
Muroyama AP, Abu-Arja D, Rogerio BK, Masiello D, Winzely M, Gubler L
Performance enhancement of a membrane electrochemical cell for CO2 capture
Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 2024; 171(1): 013504 (7 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ad1acf
DORA PSI -
Nemeth T, Han Z, Gubler L
High-performance fluorine-lean thin aromatic hydrocarbon membranes based on polyvinylidene fluoride for hydrogen fuel cells
Membranes. 2024; 14(12): 263 (12 pp.). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120263
DORA PSI -
Schuler T, Weber CC, Wrubel JA, Gubler L, Pivovar B, Büchi FN, et al.
Ultrathin microporous transport layers: implications for low catalyst loadings, thin membranes, and high current density operation for proton exchange membrane electrolysis
Advanced Energy Materials. 2024; 14(7): 2302786 (12 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202302786
DORA PSI -
Weber CC, De Angelis S, Meinert R, Appel C, Holler M, Guizar-Sicairos M, et al.
Microporous transport layers facilitating low iridium loadings in polymer electrolyte water electrolysis
EES Catalysis. 2024; 2(2): 585-602. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ey00279a
DORA PSI -
Zhang Z, Baudy A, Testino A, Gubler L
Cathode catalyst layer design in PEM water electrolysis toward reduced Pt loading and hydrogen crossover
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces. 2024; 16(18): 23265-23277. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c01827
DORA PSI -
Aliyah K, Prehal C, Diercks JS, Diklić N, Xu L, Ünsal S, et al.
Quantification of PEFC catalyst layer saturation via in silico, ex situ, and in situ small-angle X-ray scattering
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces. 2023; 15(22): 26538-26553. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c00420
DORA PSI -
Carreon Ruiz ER, Lee J, Strobl M, Stalder N, Burca G, Gubler L, et al.
Revealing the impact of temperature in battery electrolytes via wavelength-resolved neutron imaging
Science Advances. 2023; 9(39): eadi0586 (12 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adi0586
DORA PSI -
Carreón Ruiz ER, Stalder N, Lee J, Gubler L, Boillat P
Prospects of spectroscopic neutron imaging: optimizing experimental setups in battery electrolyte research
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2023; 25(36): 24993-25007. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3cp03434h
DORA PSI -
Carreón Ruiz ER, Lee J, Márquez Damián JI, Strobl M, Burca G, Woracek R, et al.
Spectroscopic neutron imaging for resolving hydrogen dynamics changes in battery electrolytes
Materials Today Advances. 2023; 19: 100405 (6 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtadv.2023.100405
DORA PSI -
Gubler L, de Wild T, Nemeth T, Nauser T
Radical attack and damage mitigation in hydrocarbon-based ionomers
In: Polymer electrolyte fuel cells and electrolyzers 23 (PEFC&E23). Vol. 112. ECS transactions. IOP Publishing; 2023:305-313. https://doi.org/10.1149/11204.0305ecst
DORA PSI -
Soon WL, Peydayesh M, de Wild T, Donat F, Saran R, Müller CR, et al.
Renewable energy from livestock waste valorization: amyloid-based feather keratin fuel cells
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces. 2023; 15(40): 47049-47057. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c10218
DORA PSI -
Weber CC, Wrubel JA, Gubler L, Bender G, De Angelis S, Büchi FN
How the porous transport layer interface affects catalyst utilization and performance in polymer electrolyte water electrolysis
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces. 2023; 15(29): 34750-34763. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c04151
DORA PSI -
Yazili D, Marini E, Saatkamp T, Münchinger A, de Wild T, Gubler L, et al.
Sulfonated poly(phenylene sulfone) blend membranes finding their way into proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Journal of Power Sources. 2023; 563: 232791 (10 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2023.232791
DORA PSI -
de Wild T, Wurm J, Becker P, Günther D, Nauser T, Schmidt TJ, et al.
A nature-inspired antioxidant strategy based on porphyrin for aromatic hydrocarbon containing fuel cell membranes**
ChemSusChem. 2023; 16(21): e202300775 (13 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202300775
DORA PSI -
de Wild T, Nemeth T, Becker P, Günther D, Nauser T, Schmidt TJ, et al.
Repair of aromatic hydrocarbon-based membranes tested under accelerated fuel cell conditions
Journal of Power Sources. 2023; 560: 232525 (13 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.232525
DORA PSI