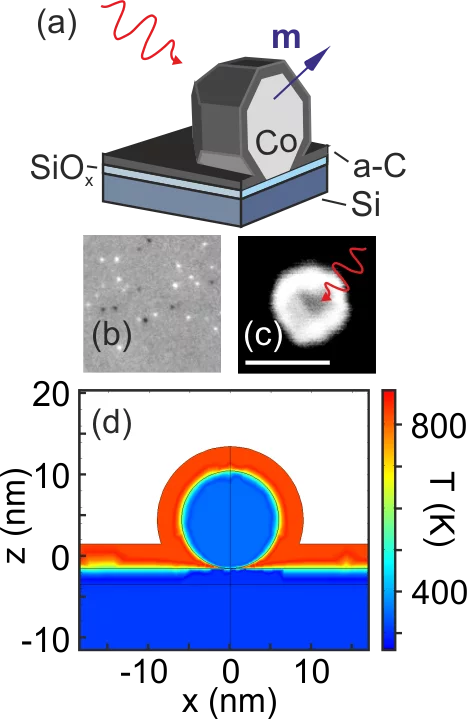
Laser-induced manipulation of magnetism at the nanoscale is a rapidly growing research topic with potential for applications in spintronics. In this work, we address the role of the scattering cross section, thermal effects, and laser fluence on the magnetic, structural, and chemical stability of individual magnetic nanoparticles excited by single femtosecond laser pulses. We find that the energy transfer from the fs laser pulse to the nanoparticles is limited by the Rayleigh scattering cross section, which in combination with the light absorption of the supporting substrate and protective layers determines the increase in the nanoparticle temperature. We investigate individual Co nanoparticles (8 to 20 nm in size) as a prototypical model system, using x-ray photoemission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy upon excitation with single femtosecond laser pulses of varying intensity and polarization. In agreement with calculations, we find no deterministic or stochastic reversal of the magnetization in the nanoparticles up to intensities where ultrafast demagnetization or all-optical switching is typically reported in thin films. Instead, at higher fluences, the laser pulse excitation leads to photochemical reactions of the nanoparticles with the protective layer, which results in an irreversible change in the magnetic properties. Based on our findings, we discuss the conditions required for achieving laser-induced switching in isolated nanomagnets.
This work has been highlighted as Editors' Suggestion in Physical Review B.
Contact
Dr. Armin Kleibert
Staff Scientist
PSI, Photon Science Division
Forschungsstrasse 111, 5232 Villigen PSI, Switzerland
Telephone: +41 56 310 5527
E-mail: armin.kleibert@psi.ch
Original Publication
Single Femtosecond Laser Pulse Excitation of Individual Cobalt Nanoparticles
T. M. Savchenko, M. Buzzi, L. Howald, S. Ruta, J. Vijayakumar, M. Timm, D. Bracher, S. Saha, P. M. Derlet, A. Béché, J. Verbeeck, R. W. Chantrell, C. A. F. Vaz , F. Nolting, and A. Kleibert
Physical Review B 102, 205418 (2020)
DOI: 10.1003/PhysRevB.102.205418 (link is external)